A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Isolation and Identification of Waterborne Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Molecular Characterization of their Antibiotic Resistance Genes
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a detailed protocol for the isolation and identification of antibiotic-resistant bacteria from water and the molecular characterization of their antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). The use of culture-based and non-culture-based (metagenomic analysis) techniques provides complete information about the total bacterial diversity and the total pool of different ARGs present in freshwaters from Mumbai, India.
Abstract
The development and spread of antibiotic resistance (AR) through microbiota associated with freshwater bodies is a major global health concern. In the present study, freshwater samples were collected and analyzed with respect to the total bacterial diversity and AR genes (ARGs) using both conventional culture-based techniques and a high-throughput culture-independent metagenomic approach. This paper presents a systematic protocol for the enumeration of the total and antibiotic-resistant culturable bacteria from freshwater samples and the determination of phenotypic and genotypic resistance in the culturable isolates. Further, we report the use of whole metagenomic analysis of the total metagenomic DNA extracted from the freshwater sample for the identification of the overall bacterial diversity, including non-culturable bacteria, and the identification of the total pool of different ARGs (resistome) in the water body. Following these detailed protocols, we observed a high antibiotic-resistant bacteria load in the range of 9.6 × 105-1.2 × 109 CFU/mL. Most isolates were resistant to the multiple tested antibiotics, including cefotaxime, ampicillin, levofloxacin, chloramphenicol, ceftriaxone, gentamicin, neomycin, trimethoprim, and ciprofloxacin, with multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) indexes of ≥0.2, indicating high levels of resistance in the isolates. The 16S rRNA sequencing identified potential human pathogens, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae, and opportunistic bacteria, such as Comamonas spp., Micrococcus spp., Arthrobacter spp., and Aeromonas spp. The molecular characterization of the isolates showed the presence of various ARGs, such as blaTEM, blaCTX-M (β-lactams), aadA, aac (6')-Ib (aminoglycosides), and dfr1 (trimethoprims), which was also confirmed by the whole metagenomic DNA analysis. A high prevalence of other ARGs encoding for antibiotic efflux pumps-mtrA, macB, mdtA, acrD, β-lactamases-SMB-1, VIM-20, ccrA, ampC, blaZ, the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene catB10, and the rifampicin resistance gene rphB-was also detected in the metagenomic DNA. With the help of the protocols discussed in this study, we confirmed the presence of waterborne MAR bacteria with diverse AR phenotypic and genotypic traits. Thus, whole metagenomic DNA analysis can be used as a complementary technique to conventional culture-based techniques to determine the overall AR status of a water body.
Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been identified as one of the most pressing global problems. The rapid evolution of AMR and its worldwide spread are one of the greatest threats to human health and the global economy in terms of the health costs associated with it1. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to an increase in AR. This has been highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic, during which the treatment of associated secondary infections, in many cases, was hugely compromised due to AMR in the affected patients2. Besides the direct use/misuse of antibiotics by humans, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in agriculture and animal husbandry and their inappropriate discharge into the environment, including water bodies, are a major concern3. The rise of new resistance traits and multidrug resistance in bacteria urgently highlights the need for a better understanding of the factors leading to the development of AR and its dissemination. Multiple antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which often carry multiple AR genes (ARGs) on mobile genetic elements such as plasmids, can transfer these resistance genes to non-resistant microorganisms, including potential human pathogens, thus leading to the emergence of superbugs that are untreatable with even last-resort antibiotics4. These multiple antibiotic-resistant bacteria, if present in water ecosystems, can directly enter the human gut via the consumption of contaminated water-based foods such as fish, crabs, and mollusks. Previous studies have shown that the spread of AR bacteria in naturally occurring water systems can also reach other water supplies, including drinking water, and, thus, can enter the human food chain5,6,7.
The aim of the present study is to provide a comprehensive protocol using a combination of culture-based and non-culture-based (whole metagenomic analysis) techniques to obtain complete information about the total bacterial diversity and the total pool of different ARGs present in a water body in Mumbai, India. Conventionally, culture-based techniques have been used to study the bacterial diversity in water bodies. As culturable microorganisms constitute only a small percentage of the total microbiota in any niche, to have a better understanding of the overall status of bacterial diversity and the various resistant traits prevalent in any sample, various culture-based and culture-independent techniques must be used in tandem. One such robust and reliable culture-independent technique is whole metagenomic DNA analysis. This high-throughput method has been successfully utilized in various studies on bacterial diversity or the functional annotations of various ARGs8,9. This technique uses the metagenome (the total genetic material in a sample) as the starting material for various analyses and, hence, is culture-independent. The protocols in the present study can be used for whole metagenomic DNA analysis to obtain information about the total bacterial diversity and various ARGs (resistome) in water samples.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Sample collection and processing
- Sample collection
- Collect the appropriate volume of the water sample in sterile sample container(s), ensuring that not more than 3/4 of the container is filled.
- Transport the samples to the laboratory under aseptic conditions as soon as possible after collection and immediately process them.
- Sample processing
- Aseptically filter the water sample through a sterile muslin cloth to remove any particulate matter.
- Carry out appropriate serial dilutions of the filtered water for further analysis.
2. Estimation of the total bacterial load and the antibiotic-resistant bacteria count
- Determination of the total bacterial load
- Suspend 18.12 g of R2A Agar, Modified powder in 1,000 mL of double-distilled water, and dissolve the mixture by heating. Autoclave the dissolved mixture at 121 °C, 15 psi for 20 min. Prepare R2A Agar, Modified plates by pouring the appropriate quantity of the autoclaved mixture into sterile Petri plates (e.g., add approximately 20 mL of autoclaved sterile medium to a 90 mm sterile Petri plate).
- Evenly spread 100 µL of the appropriate dilutions of the filtered water sample on the R2A Agar, Modified plate once the medium solidifies. Perform the experiment in duplicate.
- Incubate all the above plates at 35-37 °C for 48 h (vary the temperature and incubation time depending upon the media used for isolation).
- Express the total bacterial load in terms of colony-forming units per milliliter (CFU/mL) using equation (1):
 (1)
(1)
- Determination of the AR bacterial count
- Follow steps 2.1.1-2.1.4. However, instead of R2A Agar, Modified plates, use R2A Agar, Modified plates supplemented individually with five different antibiotics, namely cefotaxime (3 µg/mL), ciprofloxacin (0.5 µg/mL), erythromycin (20 µg/mL), kanamycin (15 µg/mL), and vancomycin (3 µg/mL).
- Add the antibiotics separately into tubes containing 20 mL of sterile molten R2A Agar, Modified (with the temperature of the molten R2A Agar, Modified at ≤40 °C) to achieve the final antibiotic concentration as mentioned in step 2.2.1.
- Swirl for even mixing and pour onto sterile Petri plates before the agar solidifies. Perform the experiment in duplicate.
- Incubate all the above plates at 35-37 °C for 48 h (if using a different media, the temperature and incubation time may vary).
- For quality control and checking the efficacy of the antibiotics, spread 100 µL of bacterial suspensions of the Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 strains onto their respective antibiotic-containing R2A Agar, Modified plates (ensure that the density of the fresh culture used for the inoculation is OD = 0.5 at 600 nm).
- Determine the antibiotic-resistant bacterial count in terms of CFU/mL as described in step 2.1.4.
- Glycerol stocks of the isolates
- Select morphologically distinct AR colonies.
- Suspend a single isolated colony in 2 mL of sterile Luria-Bertani broth containing the respective antibiotic (e.g., if a colony was selected from a plate containing cefotaxime, inoculate the colony from step 2.3.1 in sterile Luria-Bertani broth containing cefotaxime at its respective concentration).
- Incubate the inoculated tubes at 37 °C at 80 rpm until the OD600 reaches 0.5.
- Prepare glycerol stocks of the isolates by mixing 750 µL of the culture suspension from step 2.3.3 into 250 µL of sterile 100% glycerol under aseptic conditions.
- Store the glycerol stocks at −80 °C until further analysis.
NOTE: For the revival of the cultures from the glycerol stocks, thaw the glycerol stocks at 4 °C. Inoculate a loopful of this stock into 2 mL of sterile Luria-Bertani broth containing the respective antibiotic and allow to grow.
3. Identification of culturable bacteria by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Preparation of DNA template from the isolates for PCR
NOTE: The protocol described for the preparation of DNA template for PCR for the isolation of crude DNA from the bacteria is given by Carlson et al.10.- Using a sterile toothpick, take a single, isolated, pure colony of the isolate growing on a Petri plate. Suspend the bacterial colony in 100 µL of sterile double-distilled water in a sterile microcentrifuge tube and boil for 10 min.
- Centrifuge the suspension at 10,000 × g for 2 min to pellet the debris, and transfer the supernatant to a fresh sterile microcentrifuge tube for use as the crude DNA template.
- Targeted PCR amplification of the V3 region of the 16S rRNA gene and sequencing
- Prepare 40 µL of the reaction mixture in a PCR tube for PCR amplification, as mentioned in Table 1.
NOTE: The DNA preparation should be carried out on an ice block while minimizing the chance of contamination (wear gloves while handling the reagents, and clean the work surface thoroughly with 70% ethanol). - Place the tube in the thermal block, and run the appropriate program in the PCR thermal cycler. See Table 2 for the standardized PCR cycling conditions and the primer information for the amplification of the V3 regions of the 16S rRNA genes.
- For resolving the amplicons and visualization, carry out agarose gel electrophoresis (AGE). Mix 10 µL of the amplified PCR product and 2 µL of 6x gel loading buffer (Table 3), and load this mixture into wells on 1.5% agarose gel (dissolve 1.5 g of agarose powder in 100 mL of 1x TAE buffer [Table 3]) containing 5 µL of 10 mg/mL ethidium bromide (EtBr) to a final concentration of 0.5 µg/mL EtBr in 100 mL of the agarose gel.
CAUTION: EtBr is a potent carcinogen. Gloves should be worn at all times while handling EtBr and gels containing EtBr. - Add DNA ladder for the estimation of the size of the amplicons.
- Carry out electrophoresis of the gel in a TAE tank buffer at 80-100 V.
- Once the tracking dye runs 3/4 of the gel, stop the electrophoresis, and visualize the amplicon bands under a UV transilluminator.
- Use the PCR product (amplicon) for 16S rRNA gene sequencing to identify the isolate.
- Quantify the amplicon by subjecting it to spectrophotometric analysis using equation (2).
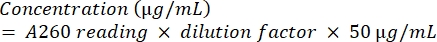 (2)
(2) - To check the purity of the DNA, calculate the ratio of A260/A280.
NOTE: Ideally, this number should be above 1.5 and, preferably, between 1.8 and 2.0. - To identify the isolates, compare the sequences that are obtained with sequence databases using an appropriate alignment search tool.
- Prepare 40 µL of the reaction mixture in a PCR tube for PCR amplification, as mentioned in Table 1.
4. Detection of antibiotic resistance in the isolates using antibiotic susceptibility testing
NOTE: This protocol describes the method for antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) by disc diffusion. The following antibiotic discs were used: cefotaxime (5 µg), ampicillin (10 µg), levofloxacin (5 µg), chloramphenicol (30 µg), tigecycline (15 µg), ceftriaxone (30 µg), imipenem (10 µg), gentamicin (10 µg), neomycin (10 µg), trimethoprim (5 µg), and ciprofloxacin (5 µg).
- Preparation of the inoculum for the AST
- Aseptically inoculate a single, isolated, purified AR colony using a sterile loop in 2 mL of a sterile non-selective medium, such as Luria-Bertani broth (without any antibiotic), and incubate at 37 °C at 80 rpm overnight.
- Resuspend by taking 100-150 µL of the overnight grown culture (approximately, OD600 = 1.8-2.0) in 2 mL of fresh non-selective Luria-Bertani broth medium and incubate for 2-4 h (until the OD600 reaches 0.4-0.5).
- Dilute this freshly grown culture suspension using sterile 0.85% saline solution such that the density of the culture is equal to 0.5 McFarland standard (approximately, OD600 = 0.1), which roughly corresponds to 1-2 × 108 cells/mL.
- Gently mix the bacterial suspension for an even cell distribution.
- Use the above suspension within 15 min of dilution.
- Inoculation of the agar plates
- Prepare Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA) plates for performing the AST by mixing 38 g of MHA in 1,000 mL of double-distilled water, and dissolve the mixture by heating. Autoclave the dissolved mixture at 121 °C, 15 psi for 15 min.
- Ensure that the depth of MHA in the plates is 4 mm (25 mL of medium per plate).
- Simultaneously, remove the antibiotic discs from the freezer and warm them to room temperature.
NOTE: The antibiotic discs should be gradually thawed by initially thawing the discs at 4 °C and later at room temperature to reduce any potential danger of condensation on the discs, which may subsequently affect the zone of inhibition (ZOI). - Under aseptic conditions, dip a sterile cotton swab into the inoculum prepared in step 4.1, and remove excess suspension to avoid over-inoculation of the plates.
- Spread the culture evenly on the plates, starting from the top of the MHA plate and going back and forth from edge to edge. Rotate the plate by 60° while swabbing.
- Application of the antibiotic discs
- With the help of flame-sterilized forceps, aseptically transfer the antibiotic discs onto the inoculated MHA plates, and press the discs gently to ensure complete level contact with the agar.
NOTE: This procedure has to be done within 15 min of the inoculation of the culture on the plates. - Place the appropriate number of antibiotic discs on the agar plate by taking into account the organism, the antibiotic used, and the size of the plate to avoid overlapping of the zones of inhibition.
NOTE: Four to five discs can be accommodated on a 90 mm circular plate.
- With the help of flame-sterilized forceps, aseptically transfer the antibiotic discs onto the inoculated MHA plates, and press the discs gently to ensure complete level contact with the agar.
- Incubation of the plates
- Within 15 min of the application of the antibiotic discs, invert the plates and incubate at 37 °C overnight.
- Interpretation of the results
- Measure the ZOI diameter in millimeters (mm), and interpret according to the breakpoint values given by EUCAST11. See the two examples given below.
- The zone diameter breakpoint (mm) for a ciprofloxacin antibiotic disc (5 µg) for Enterobacterales is S ≥ 25 and R < 22, which means that it is considered to be sensitive (S) if ZOI ≥ 25 mm, while it is resistant (R) if ZOI < 22 mm. If the ZOI diameter falls between 22 and 25, the isolate is considered to be intermediate (I).
- The zone diameter breakpoint (mm) for a chloramphenicol antibiotic disc (30 µg) for Staphylococcus spp. is S ≥ 18 and R < 18, which means that it is considered to be sensitive if ZOI ≥ 18 mm, while it is resistant if ZOI < 18 mm.
- Determine the multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index by finding the ratio of the number of antibiotics to which the isolate is resistant to the total number of antibiotics to which the isolate is exposed.
NOTE: For quality control, E. coli ATCC 25922 and S. aureus ATCC 29213 are used as reference strains following the protocol as in step 4.
- Measure the ZOI diameter in millimeters (mm), and interpret according to the breakpoint values given by EUCAST11. See the two examples given below.
5. PCR-based detection of antibiotic resistance genes in the isolates
- Use a standard PCR protocol for the identification of ARGs in the isolates. Prepare the DNA template using the protocol given in step 3.1.
NOTE: The PCR cycling conditions used in this study were 94 °C for 10 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, annealing for 30 s at the appropriate temperature (as standardized for each primer set), extension at 72 °C for 40 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. The reaction mixture is described in Table 4. The list of ARGs, primers, and annealing temperatures is given in Table 5. - To resolve, visualize, and check the purity of the amplicons, follow steps 3.2.3-3.2.10.
6. Whole metagenomic DNA analysis for the identification of the total bacterial diversity and the detection of ARGs in the metagenome
- Extraction of the total DNA (metagenome) from the water sample
- Extract the metagenomic DNA from the filtered water samples.
NOTE: In the current study, the metagenomic DNA (total DNA) was extracted from the filtered water samples using the referenced DNA isolation kit following the manufacturer's protocol (see the Table of Materials). - Check the quality of the DNA by loading 3 µL of the extracted metagenomic DNA onto a 0.8% agarose gel, and run the gel at 80-110 V for approximately 30 min.
- Check for the presence of a single intact band.
- Check the DNA concentration using a fluorometer.
- Extract the metagenomic DNA from the filtered water samples.
- Determination of bacterial diversity and detection of ARGs using whole metagenomic DNA sequencing
- Library preparation and PCR amplification:
- Prepare a paired-end sequencing library using the referenced DNA library prep kit (see the Table of Materials).
- Ready the DNA for adapter ligation by taking 200 ng of DNA and mechanically shearing it into smaller fragments, followed by a continuous step of end-repair in which an "A" is added to the 3' ends.
- Depending on the platform used for sequencing, ligate specific adapters to both ends of the DNA fragments.
NOTE: Sequences crucial for binding dual-barcoded libraries to a flow cell for sequencing are present in these adapters. This allows for PCR amplification of the adapter-ligated fragments and binding the standard sequencing primers. - To check the quality and quantity, analyze the amplified library using a high-sensitivity DNA chip as per the manufacturer's instructions.
- Cluster generation and sequencing:
- Load the amplified library onto the appropriate sequencing platform for cluster generation and subsequent sequencing.
NOTE: The library molecules bind to the complementary adapter oligos on the paired-end flow cell. During sequencing, the forward strands are selectively cleaved after the resynthesis of the reverse strand. This copied reverse strand is then sequenced from the opposite end of the fragment.
- Load the amplified library onto the appropriate sequencing platform for cluster generation and subsequent sequencing.
- Bioinformatic analysis:
- Generate scaffolds from the high-quality data using the appropriate platform.
- Subject these scaffolds to bioinformatics analysis for the taxonomic classification and identification of the ARGs.
NOTE: The workflow for the whole metagenomic DNA analysis for the identification of the total bacterial diversity and the detection of ARGs in the metagenome is given in Figure 1. A flowsheet of the complete methodology described in the manuscript is given in Figure 2.
- Library preparation and PCR amplification:
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Total bacterial load and antibiotic-resistant (AR) bacteria count
The enumeration of the total bacterial load was carried out by spreading 10−4 to 10−6 fold dilutions of the water samples on R2A Agar, Modified medium. For the enumeration of the AR bacteria count, 10−3 to 10−6 fold dilutions were spread on media plates containing antibiotics (Figure 3). The total and AR bacteria counts were calculated a...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The sample collection and processing play a significant role and might affect the results and interpretation of the study. Hence, to rule out variability in the samples, it is important to carry out sampling at multiple locations of the freshwater body being studied. Maintaining proper aseptic environmental conditions when handling such samples can prevent contamination. Moreover, to prevent changes in the bacterial composition that may influence the quality and quantity of extracted nucleic acids, the transit conditions...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicting interests to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by financial grants from the Department of Science and Technology-Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence (DST-PURSE) Scheme of the University of Mumbai. Devika Ghadigaonkar worked as a Project Fellow under the scheme. The technical help provided by Harshali Shinde, Senior Research Fellow under the Department of Science and Technology-Science and Engineering Research Board (DST-SERB) Project no: CRG/2018/003624, is acknowledged.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 100 bp DNA ladder | Himedia | MBT049-50LN | For estimation of size of the amplicons |
| 2x PCR Taq mastermix | HiMedia | MBT061-50R | For making PCR reaction mixture |
| 37 °C Incubator | GS-192, Gayatri Scientific | NA | For incubation of bacteria |
| 6x Gel Loading Buffer | HiMedia | ML015-1ML | Loading and Tracking dye which helps to weigh down the DNA sample and track the progress of electrophoresis |
| Agarose powder | Himedia | MB229-50G | For resolving amplicons during Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (AGE) |
| Ampicillin antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD002 | For performing AST |
| Autoclave | Equitron | NA | Required for sterilization of media, glass plates, test tubes, etc |
| Bioanalyzer 2100 | Agilent Technologies | NA | To check the quality and quantity of the amplified library |
| Bisafety B2 Cabinet | IMSET | IMSET BSC-Class II Type B2 | Used for microbiological work like bacterial culturing, AST etc. |
| Cefotaxime antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD295E-5VL | For performing AST |
| Cefotaxime antibiotic powder | HiMedia | TC352-5G | For preparation of antibiotic stock solution required during isolation of antibiotic resistant bacteria |
| Ceftriaxone antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD065 | For performing AST |
| Centrifuge Minispin | Eppendorf | Minispin Plus-5453 | Used to pellet the debris during crude DNA preparation |
| Chloramphenicol antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD006-5x50DS | For performing AST |
| Ciprofloxacin antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD060-5x50DS | For performing AST |
| Ciprofloxacin antibiotic powder | HiMedia | TC447-5G | For preparation of antibiotic stock solution required during isolation of antibiotic resistant bacteria |
| Colorimeter | Quest | NA | For checking the OD of culture suspensions |
| Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) database | functional annotation of ARGs; https://card.mcmaster.ca/ | ||
| Cooling Shaker Incubator | BTL41 Allied Scientific | NA | For incubation of media plates for culturing bacteria |
| Deep Freezer (-40 °C) | Haier | DW40L, Haier Biomedicals | For storage of glycerol stocks |
| DNA Library Prep Kit | NEB Next Ultra DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina | NA | Paired-end sequencing library preparation |
| EDTA | HiMedia | GRM1195-100G | For preparation of Gel running buffer for Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (AGE) |
| Electrophoresis Apparatus | TechResource | 15 cm gel casting tray | For making the agarose gel and carrying out electrophoresis |
| Electrophoresis Power pack with electrodes | Genei | NA | For running the AGE |
| Erythromycin antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD222-5VL | For performing AST |
| Erythromycin antibiotic powder | HiMedia | CMS528-1G | For preparation of antibiotic stock solution required during isolation of antibiotic resistant bacteria |
| Erythromycin antibiotic powder | HiMedia | TC024-5G | For preparation of antibiotic stock solution required during isolation of antibiotic resistant bacteria |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | HiMedia | 0335X-1 | Used as a control while performing AST |
| Ethidium Bromide | HiMedia | MB071-1G | Intercalating agent and visualizaion of DNA after electrophoresis under Gel Documentation System |
| Fluorometer | Qubit 2.0 | NA | For determining concentration of extracted metagenomic DNA |
| Gel Documentation System | BioRad | Used for visualizing PCR amplicons after electrophoresis | |
| Gentamicin antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD170-5x50DS | For performing AST |
| Glacial Acetic Acid | HiMedia | AS119-500ML | For preparation of Gel running buffer for Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (AGE) |
| Glycerol | HiMedia | GRM1027-500ML | For making glycerol stocks |
| Imipenem antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD073 | For performing AST |
| Kaiju Database | NA | NA | For taxonomical classification of reads; https://kaiju.binf.ku.dk/ |
| Kanamycin antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD017-5x50DS | For performing AST |
| Kanamycin antibiotic powder | HiMedia | MB105-5G | For preparation of antibiotic stock solution required during isolation of antibiotic resistant bacteria |
| Levofloxacin antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD216-5VL | For performing AST |
| Luria Bertani broth | Himedia | M1245-500G | For enrichment of cultures |
| McFarland Standards | Himedia | R092-1No | To compare density of culture suspension |
| Molecular Biology water | HiMedia | TCL018-500ML | For making PCR reaction mixture |
| Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA) | HiMedia | M173-500G | For performing Antibiotc Susceptibility Testing (AST) |
| Neomycin antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD731-5x50DS | For performing AST |
| PCR Gradient Thermal Cycler | Eppendorf | Mastercycler Nexus Gradient 230V/50-60 Hz | Used for performing PCR for amplification of 16S rRNA region and various Antibiotic Resistance genes |
| Primers | Xcelris | NA | For PCR amplication |
| R2A Agar, Modified | HiMedia | M1743 | For preparation of media plates for isolation of total and antibiotic resistant (AR) bacterial load |
| Scaffold generation | CLC Genomics Workbench 6.0 | NA | For generation of scaffolds |
| Sequencer | Illumina platform (2 x 150 bp chemistry) | NA | Sequencing of amplified library |
| Sodium Chloride | HiMedia | TC046-500G | For preparation of 0.85% saline for serially diluting the water sample |
| Soil DNA isolation Kit | Xcelgen | NA | For extraction of whole metagenomic DNA from the filtered water sample |
| Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus ATCC 29213 | HiMedia | 0365P | Used as a control while performing AST |
| Taxonomical Classification | Kaiju ioinformatics tool | NA | For classification of reads into different taxonomic groups from phylum to genus level |
| The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) | NA | NA | For functional annotation of ARGs |
| Tigecycline antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD278 | For performing AST |
| Trimethoprim antibiotic disc | HiMedia | SD039-5x50DS | For performing AST |
| Tris base | HiMedia | TC072-500G | For preparation of Gel running buffer for Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (AGE) |
| Vancomycin antibiotic powder | HiMedia | CMS217 | For preparation of antibiotic stock solution required during isolation of antibiotic resistant bacteria |
| Weighing Balance | Mettler Toledo | ME204 Mettler Toledo | Used for weighing media powders, reagent powders etc. |
| NA - Not Applicable |
References
- Prestinaci, F., Pezzotti, P., Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathogens and Global Health. 109 (7), 309-318 (2015).
- Knight, G., et al. Antimicrobial resistance and COVID-19: Intersections and implications. Elife. 10, 64139(2021).
- Ventola, C. L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 40 (4), 277-283 (2015).
- Naik, O. A., Shashidhar, R., Rath, D., Bandekar, J. R., Rath, A. Metagenomic analysis of total microbial diversity and antibiotic resistance of culturable microorganisms in raw chicken meat and mung sprouts (Phaseolus aureus) sold in retail markets of Mumbai. India. Current Science. 113 (1), 71-79 (2017).
- Naik, O. A., Shashidhar, R., Rath, D., Bandekar, J., Rath, A. Characterization of multiple antibiotic resistance of culturable microorganisms and metagenomic analysis of total microbial diversity of marine fish sold in retail shops in Mumbai, India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 25 (7), 6228-6239 (2018).
- Czekalski, N., GascónDíez, E., Bürgmann, H. Wastewater as a point source of antibiotic-resistance genes in the sediment of a freshwater lake. The ISME Journal. 8 (7), 1381-1390 (2014).
- Kraemer, S., Ramachandran, A., Perron, G. Antibiotic pollution in the environment: From microbial ecology to public policy. Microorganisms. 7 (6), 180(2019).
- Edmonds-Wilson, S., Nurinova, N., Zapka, C., Fierer, N., Wilson, M. Review of human hand microbiome research. Journal of Dermatological Science. 80 (1), 3-12 (2015).
- de Abreu, V., Perdigão, J., Almeida, S. Metagenomic approaches to analyze antimicrobial resistance: An overview. Frontiers in Genetics. 11, 575592(2021).
- Carlson, S., et al. Detection of multiresistant Salmonella typhimurium DT104 using multiplex and fluorogenic PCR. Molecular and Cellular Probes. 13 (3), 213-222 (1999).
- Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters, Version 12.0. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. , Available from: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_12.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (2022).
- Bharti, R., Grimm, D. Current challenges and best-practice protocols for microbiome analysis. Briefings in Bioinformatics. 22 (1), 178-193 (2019).
- Choo, J., Leong, L., Rogers, G. Sample storage conditions significantly influence faecal microbiome profiles. Scientific Reports. 5, 16350(2015).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 11th edition. , Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Wayne, PA. (2015).
- Bayot, M., Bragg, B. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. StatPearls. , StatPearls Publishing. Treasure Island, FL. (2021).
- Joseph, A. A., Odimayo, M. S., Olokoba, L. B., Olokoba, A. B., Popoola, G. O. Multiple antibiotic resistance index of Escherichia coli isolates in a tertiary hospital in South-West Nigeria. Medical Journal of Zambia. 44 (4), 225-232 (2017).
- Lorenz, T. Polymerase chain reaction: Basic protocol plus troubleshooting and optimization strategies. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (63), e3998(2012).
- Rolin, J. Food and human gut as reservoirs of transferable antibiotic resistance encoding genes. Frontiers in Microbiology. 4, 173(2013).
- Racewicz, P., et al. Prevalence and characterisation of antimicrobial resistance genes and class 1 and 2 integrons in multiresistant Escherichia coli isolated from poultry production. Scientific Reports. 12, 6062(2022).
- Gebreyes, W., Thakur, S. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Muenchen from pigs and humans and potential interserovar transfer of antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 49 (2), 503-511 (2005).
- Li, L., et al. Prevalence and characteristics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase and plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolated from chickens in Anhui Province, China. PLoS One. 9 (8), 104356(2014).
- Akers, K., et al. Aminoglycoside resistance and susceptibility testing errors in Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. Journal Of Clinical Microbiology. 48 (4), 1132-1138 (2010).
- Ciesielczuk, H. Extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli in the UK: The importance in bacteraemia versus urinary tract infection, colonisation of widespread clones and specific virulence factors. , Queen Mary University of London. PhD thesis (2015).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved