A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Transoral Endoscopic Thyroidectomy Vestibular Approach for Thyroid Lobectomy
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a protocol to describe the methodology for the transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach in detail.
Abstract
The manuscript describes the transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach (TOETVA) for thyroid lobectomy. The patient is placed in the supine position with extension and fixation of the neck. One 20 mm transverse incision and two 5 mm incisions are made through the mucosa of the oral vestibule for camera and instrument placement after disinfection of the skin and oral cavity. The workspace is established and maintained by the skin suspension device, which is made of unabsorbable string (3-0) and rubber bands, and the CO2 insufflation pressure. Lobectomy using a medial-to-lateral technique and prophylactic ipsilateral central neck dissection is performed simultaneously on patients with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). The specimen is extracted through the 20 mm incision. The parathyroid gland is immediately searched for in the specimen and auto-transplanted to the left brachioradialis. A drainage tube is inserted through the retractor hole into the bed of the thyroid gland, and absorbable sutures are used to close the mucosal incisions in the oral vestibule and the linea alba cervicalis. Prophylactics administered intravenously are recommended for the first 24 h after surgery, and oral antibiotics are used for 7 days postoperatively.
Introduction
Conventional open thyroidectomy has been safely performed using a cervical incision for more than 100 years1. Although most patients have efficient scar healing and the cosmetic effect is generally acceptable, a permanent scar on the neck always draws immediate attention from common observers2. Nearly 20% of post-thyroidectomy patients experience self-awareness, and more than 10% consider further treatments to remove the scar3. Moreover, a negative impact of the cervical incision on health-related quality of life (HRQOL) has also been reported4. Varied remote-access approaches for thyroid surgery, such as axillobreast, transaxillary, retroauricular, and subclavian approaches, have been developed to avoid a visible neck scar5,6,7,8 by moving the cutaneous incision to less conspicuous locations.9 However, these approaches require wide-flap dissection to access the thyroid gland and still leave cutaneous scars at the incision sites10.
Since 2008, techniques for natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for transoral thyroid surgery have been developed. These can be performed via the oral vestibular approach or the sublingual approach. The former is more popular because it is associated with fewer complications. In 2016, Anuwong published the first case series of 60 patients undergoing the transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach (TOETVA) and identified an excellent prognosis11. In comparison with the remote-access methods, TOETVA is considered truly minimally invasive because the area of the flap dissection is similar to conventional open thyroidectomy, and it does not leave any scars on the body10.
TOETVA, a revolutionary endoscopic method, meets women's cosmetic needs and allows easy access to the bilateral thyroid and central compartment12. It is distinguished by the complete exposure and dissection of the central lymph nodes, which is beneficial in treating differentiated thyroid cancer with cN1a10,13,14,15. However, because of the limited operating space, dealing with large tumors in the upper pole of the thyroid gland is relatively challenging. The current study describes the step-by-step procedures of TOETVA.
Protocol
The study was approved by the medical ethics committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University (2018[457]), and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
1. Preoperative preparation
- Patient eligibility
- Select patients who have stringent cosmetic requirements and meet the following criteria: (1) a benign nodule <4 cm in diameter; (2) a differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) <2 cm in diameter without clinical lateral lymph node metastasis or distance metastasis; and (3) no imaging indication of central lymph node metastasis or a metastatic lymph node <2 cm in diameter without fusion and fixation.
- Exclude patients who meet the following criteria: (1) medullary carcinoma or undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma; (2) oral or neck infections; (3) severe thyroiditis that has an acute impact on thyroid function; (4) suspicious invasion of the primary tumor or metastatic lymph node to adjacent organs, such as the esophagus, trachea, or recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN); (5) location of the primary tumor in the upper pole; (6) previous history of neck surgery, ablation, or neck radiation; (7) biochemical evidence of uncontrolled hyperthyroidism; (8) substernal goiter; and (9) intolerance to surgery.
- Patient preparation
- Evaluate the patients preoperatively with fine-needle aspiration cytologic testing, parathyroid gland tests, thyroid function tests, laryngoscopy, and thyroid ultrasonography16.
- Ask the patient to prepare the oral cavity by using mouthwash (such as tinidazole) before and after meals at least 2 days before the TOETVA and keeping the mouthwash in the mouth for at least 15 s every time.
- Equipment
- Ensure the availability of the absorbable sutures (5-0) for oral wounds.
- Ensure the availability of all the instruments and materials required for the protocol (see Table of Materials).
2. Surgical preparation
- Pre-operative preparation
- Assess the anesthesia risk of surgery according to the American Society of Anesthesiologists' classification17.
- Induce general anesthesia with orotracheal intubation using intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM).
- Tape the eyes and nose, and pad the head to avoid inadvertent trauma.
- Perform catheterization.
- Operation field
NOTE: Figure 1 shows the schematic of the operating room layout.- Let the operator stand in front of the patient's head. Let the first assistant stand on the left side of the patient's head.
NOTE: The first assistant will be responsible for holding the endoscope. - Let the second assistant stand beside the patient's body according to the location of the lesion to hold the hook. Let the scrub nurse stand beside the patient's leg.
- Place the endoscopic equipment and monitor beyond the patient's feet.
- Place the patient in the supine position with the neck extended. Fix the patient's head with the top cuff during the operation to avoid neck rotation.
- Let the operator stand in front of the patient's head. Let the first assistant stand on the left side of the patient's head.
- Disinfection
- Skin disinfection: Prepare the upper chest, neck, and lower face with iodine solution three times according to the principle of top-down and in-out.
- Oral disinfection: Put the diluted iodine gauze into the mouth, disinfect the oral cavity with it three times, and rinse it with normal saline.

Figure 1: A schematic of the operating room layout. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Designing the incisions and establishing the working space (Figure 2)
- Make the camera port incision with an electrotome; this should be a 20 mm transverse incision 5 mm above the frenulum through the alveolar mucosa of the central lower lip vestibule.
- Advance the camera port incision to the chin with an electrotome. Take care to avoid the penetration of the mentum skin. Use hemostatic forceps and a subcutaneous stripping rod to make a tunnel in the midline of the neck, and further extend to the lower neck.
- Place a 10 mm camera through the central port. Insufflate the working space with carbon dioxide gas to establish a pressure of 4 mmHg.
NOTE: The pressure of the carbon dioxide gas should be <8 mmHg to avoid complications caused by high pressure. - Make two 5 mm vertical incisions laterally from the first premolars for instrument placement.
- Use an ultrasonic scalpel to make the working space, and widen it to both sternocleidomastoid muscles laterally and along the subplatysmal plane to the sternal notch inferiorly. Use the traction of the skin suspension device, which is made of unabsorbable sutures (3-0) and rubber bands, to help expand the working space (Figure 3).
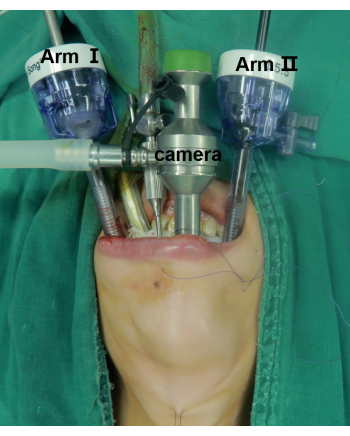
Figure 2: Positioning of the patient and the laparoscopic ports. The center one is the camera port. Arm I and Arm II are for instrument placement. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
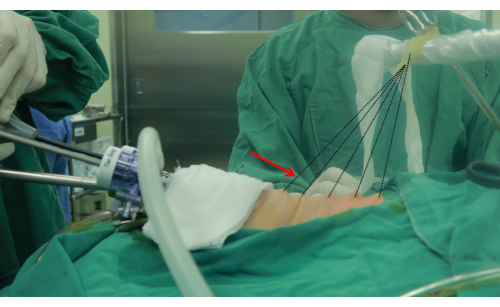
Figure 3: The traction suspension device. The arrow points at the traction suspension device. The suspension device is made of unabsorbable string (3-0) and rubber bands. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Thyroid lobectomy
- Divide the linea alba coli with an ultrasonic scalpel. Separate part of strap muscle from the thyroid gland.
- Use a 20 mL needle to pierce the skin at the level of the inferior corner of the thyroid cartilage, and place a pull hook through the hole. Use the pull hook to grab the separated part of the strap muscle.
- Use the ultrasonic scalpel to separate the remaining part of the strap muscle and expose the common carotid artery. Find the vagus nerve, and use the IONM to record the signal.
NOTE: The IONM technology helps to quickly locate, identify, and protect the recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) and the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN). The use of IONM is encouraged; it is an excellent auxiliary tool, but not a mandatory tool. - Use nontraumatic forceps to hold the inferior margin of the isthmus. Use the ultrasonic scalpel to cut the isthmus from the inferior portion of the cricoid cartilage and expose the trachea. For the lobectomy of the TOETVA, first locate the trachea, and take it as a sign.
- Use the nontraumatic forceps to hold the upper pole of the thyroid, and divide the cricothyroid space with the ultrasonic scalpel. Transect part of the sternothyroid muscle. Expose the upper pole of the thyroid.
- Sever the superior thyroid artery and vein. Free the lateral glands from the top down. Lift up the upper pole of the gland, find the RLN under direct visualization, and use the IONM to record the signal.
- Use the ultrasonic scalpel to separate the thyroid capsule from the trachea. Divide the inferior thyroid vessels, and cut the Berry's ligament with the ultrasonic scalpel.
- Remove the unilateral lobe of the thyroid gland from the trachea. Use the IONM to record the signal of the vagus nerve and RLN again.
5. Central lymph node dissection
- Locate the inferior parathyroid gland first, and try to retain it in situ.
NOTE: The thymus should be carefully identified and protected to ensure the functionality of the inferior parathyroid gland from the source of the thymus blood supply and to prevent accidental resection of the parathyroid gland. Carbon nanoparticles can be chosen to help facilitate the identification of the parathyroid glands and the dissection of the lymph nodes. Autotransplantation is feasible for parathyroid glands that cannot be retained in situ. - Stretch the strap muscles to the outside as much as possible to fully expose the operative field.
- Identify the central lymph node compartment by the hyoid bone (superior), suprasternal fossa (inferior), carotid artery (lateral), superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia (anterior), and esophagus (posterior).
- Use the ultrasonic scalpel to dissect the pretracheal and prelaryngeal lymph nodes. Cut the connective tissue in front of the carotid artery to determine the lateral boundary of the central lymph nodes and the connective tissue in front of the trachea to determine the medial boundary of the central lymph nodes. Sweep the anterior side of the left RLN or the anterior and posterior side of the right RLN to complete the central lymph node dissection.
NOTE: The lateral margin should not be swept too deep in order to prevent damage to the vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk. When cleaning the inferior margin, injury to the innominate vessels and pleura should be avoided.
6. Removal of the specimen and closure
- Use endoscopic pouches to remove the specimens.
NOTE: To avoid ectopic implantation, the specimens should be completely removed by the endoscopic pouches. - Wash the surgical wound repeatedly with a large amount of warm sterile distilled water.
- Place a surgical drain (4#) through a small skin puncture in the anterior neck.
- Re-approximate the strap muscles. Close the oral wounds with 5-0 absorbable sutures.
7. Parathyroid gland autotransplantation
- Preserve the parathyroid glands with normal saline, and examine them by frozen section biopsy.
- Cut the isolated parathyroid gland into tiny fragments of 1 mm x 1 mm x 1 mm with ophthalmic scissors. Mix the fragments with normal saline. Inject the mixture into the brachioradialis muscle of the forearm.
Results
We set up a routine clinical pathway for patients with TOETVA at the center. Laryngoscopy and a thyroid ultrasound are carried out on each patient before the operation. Parathyroid hormone (PTH), thyroid function, 25-dihydroxy vitamin D (25-OH-VD), and serum calcium are routinely measured before the operation, and all of them except for thyroid function are remeasured 1 day after the surgery. In our hospital, Foley catheters are routinely used for patients who will have a TOETVA surgery of more than 3 h. The Foley cathet...
Discussion
TOETVA is characterized by the full exposure and dissection of the central lymph nodes, which is significantly advantageous in the treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinoma with cN1a10,13,14,15. However, it should be noted that due to the limited operating space, it is relatively difficult to deal with the big tumors located in the upper pole of the thyroid gland. The surgical indications a...
Disclosures
The authors declare no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients who participated in this study for their cooperation. This research was supported by the project fund of the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province. (Grant No. 2021YFS0103).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Allis Grasping Forceps,310 mm x 5 mm | AESCULAP | PO111R | |
| Button Electrode Tip | AESCULAP | GK385R | |
| Ceramic Electrode | AESCULAP | GK384R | |
| Complete Trocar | AESCULAP | EJ751R | |
| Endoscope | Olympus | WA53005A | |
| IONM | Medtronic | NIM-3.0 | |
| Light Transmitting Bundle | Olympus | WA03310A | |
| Maryland Dissecting Forceps, 310 mm x 5 mm | AESCULAP | PO102R | |
| Monopolar Handle (5 mm diameter, 33 cm working length) | AESCULAP | GK372R | |
| Pneumoperitoneum tube,4 m | STRYKE | 620-240-223 | |
| Pyramidal Tip Obturator | AESCULAP | EJ755R | |
| Reusable Monopolar Cable | AESCULAP | GK245 | |
| Scissors | AESCULAP | P0004R | |
| Suction irrigation tube | AESCULAP | PG027R | |
| Super Righting Needle Holder, 5 mm | AESCULAP | PL414R | |
| Veress | TianSong | E2014.6 |
References
- Latifi, R., et al. Outcomes of 1,327 patients operated on through twelve multispecialty surgical volunteerism missions: A retrospective cohort study. International Journal of Surgery. 60, 15-21 (2018).
- Liao, D., et al. Transoral neck surgery prevents attentional bias towards the neck compared to open neck surgery. Laryngoscope. 130 (6), 1603-1608 (2020).
- Best, A. R., Shipchandler, T. Z., Cordes, S. R. Midcervical scar satisfaction in thyroidectomy patients. Laryngoscope. 127 (5), 1247-1252 (2017).
- Choi, Y., et al. Impact of postthyroidectomy scar on the quality of life of thyroid cancer patients. Annals of Dermatology. 26 (6), 693-699 (2014).
- Kang, S. W., et al. Robotic thyroid surgery using a gasless, transaxillary approach and the da Vinci S system: The operative outcomes of 338 consecutive patients. Surgery. 146 (6), 1048-1055 (2009).
- Choe, J. H., et al. Endoscopic thyroidectomy using a new bilateral axillo-breast approach. World Journal of Surgery. 31 (3), 601-606 (2007).
- Inukai, M., Usui, Y. Clinical evaluation of gasless endoscopic thyroid surgery. Surgery Today. 35 (3), 199-204 (2005).
- Terris, D. J., Singer, M. C., Seybt, M. W. Robotic facelift thyroidectomy: II. Clinical feasibility and safety. Laryngoscope. 121 (8), 1636-1641 (2011).
- Russell, J. O., et al. Transoral thyroid and parathyroid surgery via the vestibular approach-a 2020 update. Gland Surgery. 9 (2), 409-416 (2020).
- Chai, Y. J., et al. Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: Initial experience of a single surgeon. Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research. 93 (2), 70-75 (2017).
- Anuwong, A. Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach: A series of the first 60 human cases. World Journal of Surgery. 40 (3), 491-497 (2016).
- Arora, A., et al. The perception of scar cosmesis following thyroid and parathyroid surgery: A prospective cohort study. International Journal of Surgery. 25, 38-43 (2016).
- Dionigi, G., Chai, Y. J., Tufano, R. P., Anuwong, A., Kim, H. Y. Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy via a vestibular approach: Why and how. Endocrine. 59 (2), 275-279 (2018).
- Wang, Y., et al. Implementation of intraoperative neuromonitoring for transoral endoscopic thyroid surgery: A preliminary report. Journal of Laparoendoscopic and Advanced Surgical Techniques. Part A. 26 (12), 965-971 (2016).
- Wu, G. Y., et al. Endoscopic central lymph node dissection via breast combined with oral approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma: A preliminary study. World Journal of Surgery. 41 (9), 2280-2282 (2017).
- Yang, J., et al. Complete endoscopic thyroidectomy via oral vestibular approach versus areola approach for treatment of thyroid diseases. Journal of Laparoendoscopic and Advanced Surgical Techniques. Part A. 25 (6), 470-476 (2015).
- Su, A., et al. Does the number of parathyroid glands autotransplanted affect the incidence of hypoparathyroidism and recovery of parathyroid function. Surgery. 164 (1), 124-129 (2018).
- Doyle, D. J., Hendrix, J. M., Garmon, E. H. American Society of Anesthesiologists Classification. StatPearls. , (2022).
- Park, J. O., Kim, M. R., Kim, D. H., Lee, D. K. Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy via the trivestibular route. Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research. 91 (5), 269-272 (2016).
- Dionigi, G., et al. Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy: Preliminary experience in Italy. Updates in Surgery. 69 (2), 225-234 (2017).
- Udelsman, R., et al. Trans-oral vestibular endocrine surgery: A new technique in the United States. Annals of Surgery. 264 (6), 13-16 (2016).
- Choe, J. -. H., et al. Endoscopic thyroidectomy using a new bilateral axillo-breast approach. World Journal of Surgery. 31 (3), 601-606 (2007).
- Son, S. K., Kim, J. H., Bae, J. S., Lee, S. H. Surgical safety and oncologic effectiveness in robotic versus conventional open thyroidectomy in thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 22 (9), 3022-3032 (2015).
- Lee, K. E., et al. Robotic thyroidectomy by bilateral axillo-breast approach: Review of 1,026 cases and surgical completeness. Surgical Endoscopy. 27 (8), 2955-2962 (2013).
- Kim, M. J., et al. Yonsei experience of 5000 gasless transaxillary robotic thyroidectomies. World Journal of Surgery. 42 (2), 393-401 (2018).
- Jitpratoom, P., Ketwong, K., Sasanakietkul, T., Anuwong, A. Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach (TOETVA) for Graves' disease: A comparison of surgical results with open thyroidectomy. Gland Surgery. 5 (6), 546-552 (2016).
- Yi, J. W., et al. Transoral endoscopic surgery for papillary thyroid carcinoma: Initial experiences of a single surgeon in South Korea. Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research. 95 (2), 73-79 (2018).
- Wang, D., et al. Transoral thyroidectomy vestibular approach versus non-transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgical Endoscopy. 36 (3), 1739-1749 (2022).
- Wang, T., et al. Safety of central compartment neck dissection for transoral endoscopic thyroid surgery in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Japanese journal of clinical oncology. 50 (4), 387-391 (2020).
- Sun, H., et al. Comparison of transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach, total endoscopic thyroidectomy via areola approach, and conventional open thyroidectomy: A retrospective analysis of safety, trauma, and feasibility of central neck dissection in the treatment of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Surgical Endoscopy. 34 (1), 268-274 (2020).
- Tanaka, K. Comparative study on bacterial flora of oral cavity and upper pharynx in healthy elderly. The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. 54, 19-21 (2001).
- Guo, F., Wang, W., Zhu, X., Xiang, C., Wang, Y. Comparative study between endoscopic thyroid surgery via the oral vestibular approach and the areola approach. Journal of Laparoendoscopic and Advanced Surgical Techniques. 30 (2), 170-174 (2019).
- Chae, S., Min, S. Y., Park, W. S. Comparison study of robotic thyroidectomies through a bilateral axillo-breast approach and a transoral approach. Journal of Laparoendoscopic and Advanced Surgical Techniques. 30 (2), 175-182 (2020).
- Kim, W. W., et al. A comparison study of the transoral and bilateral axillo-breast approaches in robotic thyroidectomy. Journal of Surgical Oncology. 118 (3), 381-387 (2018).
- Nguyen, H. X., Long, T. N., Nguyen, H. V., Nguyen, H. X., Le, Q. V. Comparison of transoral thyroidectomy vestibular approach and unilateral axillobreast approach for endoscopic thyroidectomy: A prospective cohort study. Journal of Laparoendoscopic and Advanced Surgical Techniques. 31 (1), 11-17 (2020).
- Bhattacharyya, N. Surgical treatment of cervical nodal metastases in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery. 129 (10), 1101-1104 (2003).
- Lundgren, C. I., Hall, P., Dickman, P. W., Zedenius, J. Clinically significant prognostic factors for differentiated thyroid carcinoma: A population-based, nested case-control study. Cancer. 106 (3), 524-531 (2006).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved