Method Article
An Adapted Optical Density-Based Microplate Assay for Characterizing Actinobacteriophage Infection
In This Article
Summary
An optical density-based microplate method is described to quantify long-term bacterial growth in the presence of bacteriophages, suitable for actinomycetes and other slow-growing bacteria. This method includes modifications to reduce evaporation and lid condensation and R code to calculate virus infection metrics, including the area under the curve, growth maximum, and relative virulence.
Abstract
Bacteriophages are a key part of natural environments, and they have a powerful ability to shape bacterial populations. To understand how individual phages interact with slow-growing bacterial hosts such as actinomycetes, an easy and reliable method for quantifying long-term bacterial growth in the presence of phages is needed. Spectrophotometric microplate readers allow for high-throughput repeated measurements, but incubating a small volume for an extended time can present technical challenges. This procedure adapts a standard 96-well microplate to allow for the co-culturing of phages and bacteria without sub-sampling for 96 h, with the bacterial growth recorded every 8 h using spectrophotometric absorbance values. These optical density values are analyzed using R to yield infection metrics, including the percent growth inhibition, relative virulence, and the Stacy-Ceballos index. The methods outlined here provide an effective way to conduct and analyze extended-duration microplate growth curve experiments and includes modifications to reduce evaporation and lid condensation. These protocols facilitate microplate-based assays of interactions between slow-growing bacterial hosts and their bacteriophages.
Introduction
Bacteriophages or phages are viruses that infect bacteria. They are the most numerous biological entities on the planet1, and it is generally accepted that bacteriophages influence bacterial evolution and ecosystem processes2,3,4. Several methods exist to describe, measure, and analyze bacteriophage host range8 and infection dynamics5,6, including agar-based methods such as the double-layer agar method7 and optical density-based microplate methods8,9,10,11,12. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Due to their efficiency, plating tests using the double-layer agar method are the "gold standard" for host range assays, but this method is time- and labor-intensive9. Rapid microplate methods, which return results in 24 h or less, give excellent results for fast-growing bacterial hosts such as Escherichia coli9,10,11,12 but are too brief to showcase bacteriophage infection progression in slower-growing bacterial hosts such as actinomycetes7,13,14,15.
An optical density-based microplate assay designed for fast-growing bacteria cannot be run for the multiple days required to characterize infection dynamics in a slow-growing host bacterium without evaporation occurring and giving artificially high bacterial densities. Thus, obtaining comparable high-throughput data on bacteriophage infection dynamics for slow-growing bacterial species requires specialized techniques adapted for these bacteria.
The microplate method presented here reduces evaporation, thus allowing slow-growing bacteria to be co-cultured with a phage for an extended 96 h period and enabling investigations into phage infection dynamics and host range. This method also showcases the Stacy-Ceballos index16, an optical density-based metric that allows for virulence comparisons among disparate host-virus systems.
Protocol
While this protocol is written for Gordonia terrae, it has also been successfully used for Gordonia lacunae, Gordonia rubripertincta, and Gordonia westfalica.
1. Bacteria preparation
- In a biosafety cabinet, use good microbiological practice17 to inoculate a single colony of Gordonia terrae CAG3 into a 1 L sterile baffled flask with 200 mL of peptone yeast calcium broth18(PYCa) containing 0.01 mg/mL cycloheximide (see the Table of Materials).
- Incubate the flask at 30 °C with shaking at 250 rpm until the culture is saturated or for 3 days7.
- Serially dilute the saturated G. terrae culture in PYCa broth, and spread-plate 100 µL each of the 10−4, 10−5, and 10−6 dilutions on PYCa plates19,20. Refrigerate the undiluted saturated culture at 4 °C.
- Incubate the spread plates inverted for 3 days at 30 °C.
- Following incubation, identify a "countable plate", a plate with 20-200 colonies. Count the number of colonies on that plate, and calculate the colony-forming units per milliliter (cfu/mL)19,20.
- Dilute the saturated culture with PYCa broth to 4.0 x 106 cfu/mL bacteria.
2. Phage preparation
NOTE: The representative results reported were obtained with the Gordonia phage DelRio21, a temperate bacteriophage isolated on G. terrae. These methods have also been successfully used with other Gordonia phages.
- Beginning with an isolated bacteriophage, serially dilute the phage sample in phage buffer7 to a 1 x 10−8 dilution. Perform a double-layer agar phage titer assay7 by infecting 0.3 mL of the saturated G. terrae culture with 10 µL of each phage dilution. Following a 5-10 min room temperature incubation, combine the bacteria-phage mixture with 3 mL of PYCa top agar, and pour onto PYCa agar plates.
- Incubate the plates inverted at 30 °C for 3 days or until plaques form7.
- Following incubation, identify a "countable plate", a plate with 20-200 plaques. Count the number of plaques on that plate, and calculate plaque-forming units per milliliter (pfu/mL)7.
3. Microplate preparation
NOTE: Flat-bottomed 96-well microplates (see the Table of Materials) should be used for this method. All the plate preparation and loading must be completed in a biosafety cabinet, and good microbiological practice17should be used.
- Prepare the anti-fog lid coating solution by combining 100 µL of Triton-X 100, 40 mL of 100% isopropanol, and 160 mL of deionized water22. Stir to mix, and store at room temperature.
- In a biosafety cabinet, add 6 mL of lid coating solution to the inside surface of a sterile 96-well microplate lid, holding the lid by the edges and rotating it to ensure that it is covered by the solution. Let the solution sit on the lid for 20 s, then pour the solution off, and invert the lid on an autoclaved paper towel at an angle until the lid is completely dry, which typically takes 35-45 min. Be careful to hold the lid by the edges.
- Prepare 20 mL of 0.1% agarose in water for each 96-well microplate, microwaving to melt the agarose.
- Once the agarose has cooled to 50-60 °C, pipet 100 µL of the 0.1% agarose into all of the spaces between the wells of the plate and 200 µL of agarose into the wells in row A and row H and column 1, column 2, column 11, and column 1223 (Figure 1).
4. Loading the plate with bacteria and phage
NOTE: All the plate preparation and loading must be completed in a biosafety cabinet, and good microbiological practice17 should be used.
- The 96-well plate will contain 75 µL of 2.0 x 106 cfu/mL bacteria in each well9. Dilute the 4.0 x 106 cfu/mL bacterial culture 1:1 with 2x PYCa broth to 2.0 x 106 cfu/mL. Prepare 5 mL per 96-well plate.
- Dilute the phage lysate using phage buffer7 to make 1 mL each of 2.0 x 106 pfu/mL, 2.0 x 105 pfu/mL, and 2.0 x 104 pfu/mL concentrations. This will allow for a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1, 0.1, and 0.01 within the microplate9.
- To load the microplate, take a plate that was prepared with anti-fog solution and agarose, and pipet 75 µL of the 2.0 x 106 cfu/mL bacteria into columns 3-10, following Figure 1.
- To column 3 and column 4, add 75 µL of sterile phage buffer to each well to serve as a no-phage positive control, following Figure 1, and pipette up and down to mix after each addition. Add 75 µL of the 2.0 x 106 pfu/mL phage to column 5 and column 6, 75 µL of the 2.0 x 105 pfu/mL phage to column 7 and column 8, and 75 µL of the 2.0 x 104 pfu/mL phage to column 9 and column 10, pipetting up and down to mix after each addition.
- Tape both short sides of the plate with 0.5 in labeling tape to partially seal the plate while allowing gas exchange.
5. Incubation and absorbance measurement
- Once the plates are loaded with bacteria and phage, place them on a microplate shaker at 250 rpm, and incubate at 30 °C.
- Incubate the plates for 96 h, taking an optical density measurement at 600 nm on a microplate reader every 8 h starting at hour 16. Return the plates to the shaker between measurements.
NOTE: Measurement periods of 4, h 6 h, 8 h, and 12 h were assessed, beginning at hour 0, and it was determined that an 8 h sampling period beginning at 16 h post-infection best captured the Gordonia-phage interactions. - Monitor the lid for condensation throughout the experiment. If condensation is observed, replace the lid with another lid coated according to step 3.2.
- Generate control and infected growth curves following protocol section 6.
6. Data analysis
- Use a spreadsheet program to calculate the average and standard deviation for each phage dilution, following the spreadsheet layout in the Stacy-Ceballos-Index GitHub repository (https://github.com/eichristenson/Stacy-Ceballos-Index).
- Create control and infected growth curves, and calculate infection metrics using R (see the Table of Materials) with the DescTools24, dplyr25, ggplot226, and readxl27 packages and following the R script in the Stacy-Ceballos-Index GitHub repository (https://github.com/eichristenson/Stacy-Ceballos-Index).
- AUCcon is the area under the uninfected control curve, while AUCinf is the area under the infected curve16. Calculate the AUC, and then calculate percent growth inhibition based on the area under the curve values, PIAUC16, using the following equation:
(1 - [AUCinf/AUCcon]) × 100 - The dashed horizontal lines on each curve show the peak growth, with the uninfected growth peak labeled Nasymptote(con) and the infected growth peak labeled Nasymptote(inf). Identify the Nasymptote values, and then calculate percent growth inhibition based on these peak growth values, PImax16, using the following equation:
(1 - [Nasymptote(inf)/ Nasymptote(con)]) × 100 - Calculate the Stacy-Ceballos index, ISC16, from the PIAUC and PImax values, as follows:
(PIAUC × PImax)0.5
Calculate relative virulence by integrating the Stacy-Ceballos index over time16.
- AUCcon is the area under the uninfected control curve, while AUCinf is the area under the infected curve16. Calculate the AUC, and then calculate percent growth inhibition based on the area under the curve values, PIAUC16, using the following equation:
Results
An experiment is successful if the resulting growth curve shows an increase in the positive control bacterial population over time with no sudden fluctuation in absorbance. Examples of a successful experiment at an MOI of 1 with and without a productive phage infection are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively. A productive infection at an MOI of 0.01 is represented in Figure 4. The positive control growth pattern (green curve) seen in all three figures indicates that the bacteria are growing, they are not clumping during growth, and no contaminants are present. Clumping and contamination are indicated by unusually high absorbance at a single time point. Standard deviations typically increase over the time course of an experiment; however, a drastic increase or standard deviations overlapping between the control and infected curves may indicate contamination or clumping in one or more wells.
The growth curve depicting a productive phage infection, represented by Figure 2, shows reduced bacterial absorbance over time in wells with the phage added. This reduction in bacterial density will not be seen if the bacterium is outside of the phage's host range, as shown in Figure 3.
Infection metrics are shown for all the representative experiments, with a relatively large ISC for the productive infections in Figure 2 and Figure 4 and a very small ISC in Figure 3 for the phage that did not efficiently infect the host bacterium.
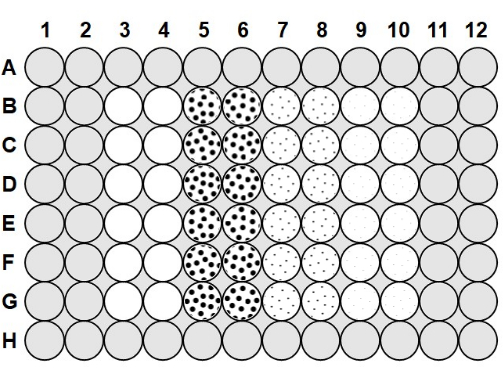
Figure 1: Microplate layout. The gray areas are filled with 0.1% agarose. The blank wells in column 3 and column 4 are no-phage positive control wells containing only phage buffer and 2.0 x 106 cfu/mL bacteria. The dotted wells contain phage and 2.0 x 106 cfu/mL bacteria; the large dots in column 5 and column 6 indicate an MOI of 1 with 2.0 x 106 pfu/mL phage; the medium dots in column 7 and column 8 indicate an MOI of 0.1 with 2.0 x 105 pfu/mL phage; and the small dots in column 9 and column 10 indicate an MOI of 0.01 with 2.0 x 104 pfu/mL phage. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
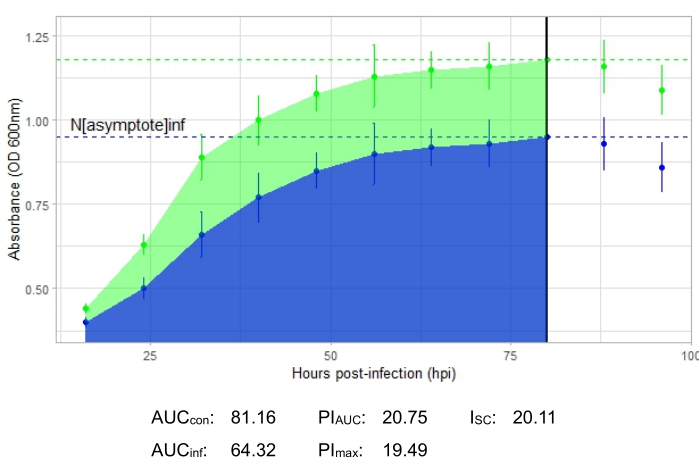
Figure 2: A successful growth curve experiment with a phage at an MOI of 1 that productively infects the host bacterium. The average absorbance values (± standard deviation) are shown for uninfected bacteria (green) and bacteria with the phage added (blue). Abbreviations: AUC = area under the curve; PIAUC = percent growth inhibition calculated from the area under the curve; Nasymptote = peak growth value; PImax = percent growth inhibition calculated from the peak growth values; ISC = Stacy-Ceballos index. This graph represents the temperate Gordonia phage DelRio infecting G. terrae, the bacterium it was isolated on. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
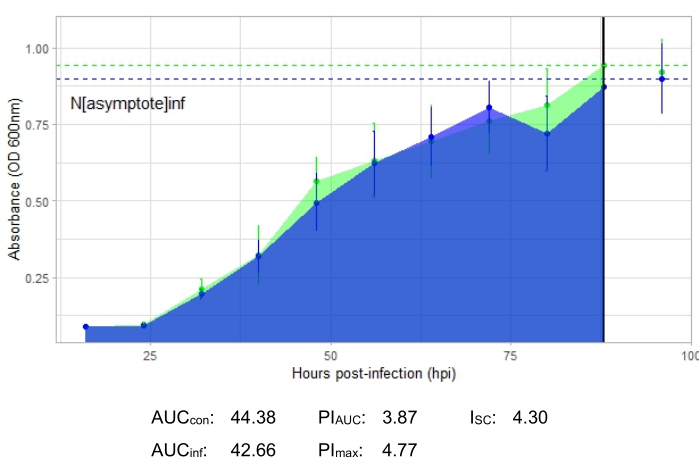
Figure 3: A successful growth curve experiment with a phage at an MOI of 1 that does not efficiently infect the host bacterium. The average absorbance values (± standard deviation) are shown for uninfected bacteria (green) and bacteria with the phage added (blue). Abbreviations: AUC = area under the curve; PIAUC = percent growth inhibition calculated from the area under the curve; Nasymptote = peak growth value; PImax = percent growth inhibition calculated from the peak growth values; ISC = Stacy-Ceballos index. This graph represents G. rubripertincta infection by DelRio. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
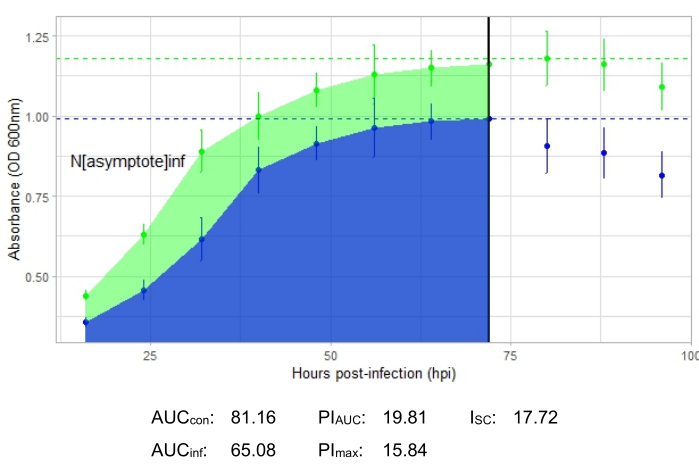
Figure 4: A successful growth curve experiment with a phage at an MOI of 0.01. The average absorbance values (± standard deviation) are shown for uninfected bacteria (green) and bacteria with the phage added (blue). Abbreviations: AUC = area under the curve; PIAUC = percent growth inhibition calculated from the area under the curve; Nasymptote = peak growth value; PImax = percent growth inhibition calculated from the peak growth values; ISC = Stacy-Ceballos index. This graph represents G. terrae infection by DelRio. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
This optical density-based microplate method permits investigation into bacteriophage host range and infection dynamics11 and shows the utility of the Stacy-Ceballos index16 as a measure of bacteriophage virulence. While this method could be utilized with any bacteriophage-host system, it was designed specifically to adapt rapid microplate growth assays9,10,11 for use with slower-growing bacteria such as actinomycetes. Rapid microplate assays cannot be used for slow-growing bacteria without modifications to address evaporation and lid condensation. This method describes these necessary modifications and demonstrates, for the first time, the use of the Stacy-Ceballos index and related metrics16 to describe bacteriophage infection.
Evaporation can be a substantial challenge in multi-day 96-well plate growth curve assays; this method resolves that problem by adding agarose to the border wells and the spaces between the wells. The agarose margin, combined with the anti-fog lid treatment22, provides the necessary humidity within the microplate and allows for reliable optical density measurements. Without the added humidity, substantial edge effect evaporation occurs23 during the lengthy incubation period required, leading to artificially high optical density readings. The anti-fog lid treatment is a necessary modification because lid condensation can also artificially elevate the optical density values. Shaking the plates during the incubation period is a recommended modification, as actinomycete bacteria may clump during growth, giving artificially high optical density values and effectively decreasing the multiplicity of infection.
The ratio of bacteria to phage in experiments characterizing infection dynamics is critical, as there must be enough phage to show an infection effect but not so many that the host bacterial population immediately crashes9 or the frequency of lysogeny is dramatically increased28. In this method, the ratio found to be most effective for obtaining consistent results was an MOI of 1, but usable results were also obtained with MOIs of 0.1 and 0.01. When implementing this method, it is recommended to choose one concentration of bacteria and test multiple phage concentrations in the MOI range of 0.01-19,10,11.
This technique described here allows bacteriophage-host interactions to be assessed for slow-growing bacteria in high-throughput microplate assays rather than with sub-sampling from a larger culture flask at each measurement interval29. Further, by demonstrating how microplate growth assays9,10,11 may be adapted, this technique increases the utility of other microplate-based bacteriophage assays for slower-growing bacteria, including phage characterization5,6,12 and evolution studies30,31. Finally, this method demonstrates the use of the Stacy-Ceballos index16 to describe bacteriophage infection. This metric was initially developed with data from an archaeal virus model system and is calculated from optical density values, thus giving it widespread utility across disparate virus systems.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an NSF DBI Biology Integration Institute (BII) grant (award no. 2119968; PI-Ceballos) and by the Arkansas INBRE program, with a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, (NIGMS), P20 GM103429 from the National Institutes of Health. The authors also appreciate the support of the Patterson Summer Undergraduate Research Program at Ouachita Baptist University.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Agarose | Omni-Pur | 2090 | for filling border wells of microplate |
| Costar 96 Well Lid Low Evaporation Corner Notch | Corning | 3931 | replacement microplate lid |
| Isopropanol | Fisher Chemical | A461-4 | for lid coating |
| Microplate reader | Tecan Spark 20M | ||
| Microplate Shaker with 4-Place Platform | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 88-861-023 | to shake plates during incubation |
| Non-Tissue Culture-Treated Plate 96 well | Falcon (a Corning Brand) | 351172 | microplate for growth curve assay |
| Peptone yeast calcium (PYCa) agar | Homemade | 1 g peptone 15 g yeast extract 15 g agar 990 mL dd H2O 4.5 mL 1 M CaCl2 2.5 mL 40% dextrose 1 mL 10 mg/mL cycloheximide | |
| Peptone yeast calcium (PYCa) broth | Homemade, from Reference 16 | 1 g peptone 15 g yeast extract 990 mL dd H2O 4.5 ml 1 M CaCl2 2.5 mL 40% dextrose 1 mL 10 mg/mL cycloheximide | |
| Peptone yeast calcium (PYCa) top agar | Homemade | 1 g peptone 15 g yeast extract 4 g agar 990 mL dd H2O 4.5 mL 1M CaCl2 2.5 mL 40% dextrose | |
| Petri plates | Thermo Fisher Scientific | FB0875713 | for determination of bacterial concentration and phage titer assay |
| Phage Buffer | Homemade, from Reference 7 | 10 mL 1 M Tris, pH 7.5 10 mL 1 M MgSO4 4 g NaCl 980 ml dd H2O | |
| R software | https://www.r-project.org/ | version 4.3.0 | |
| Sterile Disposable PETG Flask Baffled Bottom w/Vented Closure | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 4116-1000 | for bacterial culture |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma Aldrich | 9036-19-5 | for lid coating |
References
- Mushegian, A. R. Are there 1031 virus particles on Earth, or more, or fewer. Journal of Bacteriology. 202 (9), e00052-e00020 (2020).
- Chevallereau, A., Pons, B. J., van Houte, S., Westra, E. R. Interactions between bacterial and phage communities in natural environments. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 20 (1), 49-62 (2022).
- Olszak, T., Latka, A., Roszniowski, B., Valvano, M. A., Drulis-Kawa, Z. Phage life cycles behind bacterial biodiversity. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 24 (36), 3987-4001 (2017).
- Weitz, J. S., et al. Phage-bacteria infection networks. Trends in Microbiology. 21 (2), 82-91 (2013).
- Turner, P. E., Draghi, J. A., Wilpiszeski, R. High-throughput analysis of growth differences among phage strains. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 88 (1), 117-121 (2012).
- Storms, Z. J., Teel, M. R., Mercurio, K., Sauvageau, D. The virulence index: A metric for quantitative analysis of phage virulence. PHAGE. 1 (1), 27-36 (2020).
- . Phage Discovery Guide Available from: https://seaphagesphagediscoveryguide.helpdocsonline.com/home (2012)
- Martinez-Soto, C. E., et al. PHIDA: A high throughput turbidimetric data analytic tool to compare host range profiles of bacteriophages isolated using different enrichment methods. Viruses. 13 (11), 2120-2137 (2021).
- Rajnovic, D., Muñoz-Berbel, X., Mas, J. Fast phage detection and quantification: An optical density-based approach. PLoS One. 14 (5), e0216292 (2019).
- Xie, Y., Wahab, L., Gill, J. J. Development and validation of a microtiter plate-based assay for determination of bacteriophage host range and virulence. Viruses. 10 (4), 189-204 (2018).
- Sørensen, P. E., et al. Classification of in vitro phage-host population growth dynamics. Microorganisms. 9 (12), 2470-2486 (2021).
- Konopacki, M., Grygorcewicz, B., Dołęgowska, B., Kordas, M., Rakoczy, R. PhageScore: A simple method for comparative evaluation of bacteriophages lytic activity. Biochemical Engineering Journal. 161, 107652 (2020).
- Holt, J. G., Krieg, N. R., Sneath, P. H. A., Staley, J. T., Williams, S. T. . Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology., 9th edition. , (1994).
- Fusconi, R., Godinho, M. J. L., Bossolan, N. R. S. Culture and exopolysaccharide production from sugarcane molasses by Gordonia polyisoprenivorans CCT 7137, isolated from contaminated groundwater in Brazil. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 24 (7), 937-943 (2007).
- Bujold, A. R., Lani, N. R., Sanz, M. G. Strain-to-strain variation of Rhodococcus equi growth and biofilm formation in vitro. BMC Research Notes. 12 (1), 519 (2019).
- Ceballos, R. M., Stacy, C. L. Quantifying relative virulence: When µmax fails and AUC alone just is not enough. Journal of General Virology. 102 (1), 001515 (2021).
- Siddiquee, S. The basic concept of microbiology. Practical Handbook of the Biology and Molecular Diversity of Trichoderma Species from Tropical Regions. , 1-15 (2017).
- Petrovski, S., Seviour, R. J., Tillett, D. Genome sequence and characterization of the Tsukamurella bacteriophage TPA2. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 77 (4), 1389-1398 (2011).
- Growth curves: Generating growth curves using colony forming units and optical density measurements. JoVE Science Education Database. Microbiology Available from: https://www.jove.com/v/10511/growth-curvesgenerating-growth-curves-using-colony-forming-units (2023)
- Preparing spread plates protocols. American Society for Microbiology Available from: https://asm.org/ASM/media/Protocol-Images/Preparing-Spread-Plates-Protocols.pdf (2006)
- Mathes, H. N., et al. Complete genome sequences of Chop, DelRio, and GrandSlam, three Gordonia phages isolated from soil in Central Arkansas. Microbiology Resource Announcements. 12 (5), e0002323 (2023).
- Krishnamurthi, V. R., Niyonshuti, I. I., Chen, J., Wang, Y. A new analysis method for evaluating bacterial growth with microplate readers. PLoS One. 16 (1), 0245205 (2021).
- DescTools: Tools for descriptive statistics, R package version 0.99.49. DescTools Available from: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=DescTools (2023)
- . dplyr: A grammar of data manipulation, R package version 1.1.2 Available from: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (2023)
- . ggplot2: Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics, R package version 3.4.2 Available from: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggplot2 (2023)
- . readxl: Read excel files, R package version 1.4.2 Available from: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=readxl (2023)
- Yao, T., Coleman, S., Nguyen, T. V. P., Golding, I., Igoshin, O. A. Bacteriophage self-counting in the presence of viral replication. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 118 (51), 2104163118 (2021).
- Fang, Q., Feng, Y., McNally, A., Zong, Z. Characterization of phage resistance and phages capable of intestinal decolonization of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in mice. Communications Biology. 5, 48 (2022).
- Burrowes, B. H., Molineux, I. J., Fralick, J. A. Directed in vitro evolution of therapeutic bacteriophages: The Appelmans protocol. Viruses. 11 (3), 241 (2019).
- Shapiro, J. W., Williams, E. S. C. P., Turner, P. E. Evolution of parasitism and mutualism between filamentous phage M13 and Escherichia coli. PeerJ. 4, e2060 (2013).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved