A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Mimicking Ding's Roll Method on Notexin-Induced Muscle Injury in Rats
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes a simple device that mimics Ding's roll method, establishes a rat model of skeletal muscle injury, and uses hematoxylin-eosin staining to observe the pathology of damaged tissue and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect changes in serum damage markers.
Abstract
Ding's roll method is one of the most commonly used manipulations in traditional Chinese massage (Tuina) clinics and one of the most influential contemporary Tuina manipulations in China. It is based on the traditional rolling method commonly used in the one finger Zen genre and named Ding's roll method. Due to its anti-inflammatory and blood circulation-promoting effects, Ding's rolling method has sound therapeutic effects on myopathy. Because of the large area of force applied to human skin, Ding's roll method is challenging to perform on experimental animals with small skin areas, such as rats and rabbits. Additionally, the strength of Tuina applied to the human body differs from that applied to experimental animals, so it may happen that the strength is too high or too low to achieve the therapeutic effect of Tuina during the experiment. This experiment aims to create a simple massager suitable for rats based on Ding's rolling manipulation parameters (strength, frequency, Tuina duration). The device can standardize manipulation in animal experiments and reduce the variation in Tuina force applied to different animals due to subjective factors. A rat model of notexin-induced skeletal muscle injury was established, and plasma injury markers creatine kinase (CK) and fatty acid binding protein 3 (FABP3) were used to assess the therapeutic effect of Tuina on skeletal muscle injury. The results showed that this Tuina massager could reduce the levels of CK and FABP3 expression and slow down the degree of skeletal muscle injury. Therefore, the Tuina massager described here, mimicking Ding's roll method, contributes to standardizing Tuina manipulation in experimental research and is of great help for subsequent research on the molecular mechanism of Tuina for myopathy.
Introduction
Muscle injuries are common traumatic injuries in clinical and daily life, caused by external blows (contusions) or chronic overstrain of muscle fibers (strains), etc., resulting in muscle dysfunction and pain, even seriously affecting the patient's quality of life1. Starting rehabilitation as early as possible after an acute strain injury is the key to reducing the time to return to sports2 and in reducing pain3,4. In modern Western medicine, clinical first aid for muscle injuries follows the principles of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to stop injurious bleeding into the muscle tissue5 and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain6. The discovery of novel therapies such as exosomes7 and tissue engineering8 became potential treatment strategies for skeletal muscle diseases, compensating for previous pharmacological treatments' shortcomings. However, it can also increase the cost of treatment for patients, putting them under tremendous financial pressure9. Therefore, alternative and complementary therapies are recommended for treating musculoskeletal problems10. Tuina is widely used clinically in China as a traditional medical method and is popular among patients for its efficacy and fewer side effects. Tuina therapy for musculoskeletal disorders can alleviate pain and improve function11,12,13. Mr. Ding Jifeng, a famous Shanghai Tuina practitioner, founded Ding's roll method14. It is a unique rolling and crushing technique with a large force area, uniform and gentle force, and intense penetration.
Different animal models are based on different etiologies. They have advantages and disadvantages, and the selection of correct and appropriate animal models is of great significance to basic experiments, which helps understand the cellular and molecular signaling pathways of regeneration and repair after skeletal muscle injury to develop new therapies for treating the treatment of skeletal muscle diseases. Chemically induced models of muscle injury are widely used, with injections of skeletal muscle causing myofiber necrosis and producing regenerated areas that can effectively regenerate within 2 weeks15. Both notexin and bupivacaine can cause muscle damage. However, notexin can cause more severe myotoxic damage to skeletal muscle than bupivacaine, and natural functional recovery is relatively slower16. Drug intramuscular injection molding not only takes less time but also has controlled effects and extent of skeletal muscle damage. This quantifiable control makes successful molding less difficult15,17.
Inflammatory response is an essential biological response that has been extensively studied in the context of myopathy18,19. In the early stages of skeletal muscle injury, myofiber necrosis disrupts local muscle homeostasis, and many inflammatory cells infiltrate the injury site, secreting many pro-inflammatory cytokines19. Creatine kinase (CK) is a traditional serum biomarker for assessing skeletal muscle injury. However, it lacks tissue specificity20 and sensitivity21, which limits its ability to assess the extent of drug-induced muscle damage and indirectly report the extent of muscle recovery after injury. Novel biomarkers, including fatty acid binding protein 3 (FABP3), have recently shown relatively high tissue specificity and sensitivity in rodent models of skeletal muscle injury. FABP3 is a family of binding proteins expressed primarily in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells and implicated in fatty acid metabolism, transport, and signaling22. Therefore, we chose a combination of two biomarkers, CK and FABP3, to assess the extent of notexin-induced skeletal muscle damage and recovery after treatment.
In rodents, the muscles are shallow, and the skin area is small, which also determines that the various parameters of massage in rodents will not be the same as in humans, such as in animal therapy, the massage therapist should treat them with less force using Ding's roll method, and may not be conducive to the operation of this technique due to the small size of the injured area, which can ultimately lead to a reduction in the effectiveness of the massage. Therefore, the experiment utilized the rolling massager made in-house, which conforms to the characteristics of Ding's roll method, to intervene and evaluate the therapeutic effect of the notexin-induced skeletal muscle injury model in rats, which helps to standardize the parameters of Tuina in experimental animal studies in order to profoundly investigate the molecular mechanism of action of Tuina, a traditional Chinese medicine treatment method, on musculoskeletal diseases.
Protocol
Procedures involving animals have been approved by the Institutional Care and Use Committee at Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.
1. Assembly of the rolling massager
- Select a massager that consists of a rubber roller, fork holder, spring, limit baffle, adjustment splint, screw, and acrylic handle (Figure 1). Ensure the rubber roller measures 3 cm long and 1.6 cm in diameter, the spring measures 3 cm long and 0.9 cm in diameter, the limit baffle is 3 cm long and 2 cm wide, and the handle measures 12 cm long and 0.9 cm in diameter.
- Force control: According to the literature results23, Ding's roll method downward pressure was found to be about 10% of the body weight, so the pressure applied during the design of forward rolling is about 10% of the rat's body weight (0.2-0.3 N). Test the maximum pressure of the massager on the weighing controller to be about 0.3 N by adjusting the angle of the limit baffle. This pressure requirement meets the needs of the rat.
- Ensure the minimum pressure is about 0.08 N when rolling back (Figure 2). Ensure the pressure is precisely in conformity with the requirement of Ding's roll method that the ratio of the forward and backward forces is 3:1.
- Before treatment, ask the operator to work with the metronome software to control the rolling frequency to 140 rolls/min and practice this more than 3x in the pre-experiment to ensure the operation is standardized.
2. Establishment of a rat model of skeletal muscle injury
- Randomly divide 24 male, Sprague-Dawley rats (weighing 200-250 g) into three groups of eight rats each, including control (C), notexin (NTX), and notexin with Tuina (NTX + Tuina), and feed on a standard diet. Maintain on a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle, house at 20-25 °C and 50%-70% humidity.
- Anesthetize with 1% pentobarbital sodium (40 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection and then remove hair from the right lower limb with hair removal cream. After removing the fur, wipe the residual cream using saline. Confirm adequate anesthesia by toe-pinch response. Apply ophthalmic ointment to moisturize the eyes while the animal is under anesthesia. Provide thermal support throughout the procedure.
- Alternate skin disinfection for the right lower limb with iodophor disinfecting solution and 75% alcohol before injection. Touch a cotton swab soaked in iodophor disinfecting solution to the center of the skin of the lower extremity and apply in a circular motion outward. Repeat with an ethanol-soaked cotton swab.
- Establish skeletal muscle injury models according to the reference method24. Inject notexin in only one leg (to prevent double notexin injection). Draw 200 µL of notexin solution (10 µg/mL notexin solution prepared by adding 100 µg of notexin to 10 mL of normal saline in a 15 mL centrifuge tube) into a 1 mL syringe with a 30G needle and inject the notexin solution intramuscularly into the gastrocnemius muscle to produce muscle injury.
- Inject the notexin slowly and wait for 3 s before pulling out the needle (to be fully injected).
CAUTION: Notexin is a toxic chemical that requires immediate flushing with plenty of water upon contact with an open wound and prompt medical attention if necessary. - Inject the rats in the control group with 200 µL of saline solution. Move anesthetized rats to empty cages with clean bedding. Take care to remove the padding around the rats' nose and mouth to keep their breathing clear. Visually observe the tissue color and respiratory rate at the end of the injection until the rats regain sufficient consciousness.
- Return rats to the home cage and typically rear them for 24 h.
3. Tuina therapy
- Place an SD rat in a prone position with its head covered with a black cloth on the experimental platform disinfected with 75% alcohol to expose the gastrocnemius muscle. Do not cover too tightly.
- Using the Tuina massager for the NTX+Tuina group: Hold the massager and place the roller on the gastrocnemius muscle of the rat and roll forward until the spring contacts the limit baffle. Then retract the force and return to its original position, thereby reciprocating movement (Figure 3).
- Roll the massager at a speed of 140 rolls per min, and perform each operation for 3 min. Perform the massages once in the morning and once in the afternoon for 3 consecutive days.
- Return rats to the home cage after each treatment and fast for 8 h after the last treatment.
4. Collecting blood and tissues from rats after the experiment
- According to the requirements of the relevant animal experiment ethics committee, anesthetize rats by intraperitoneal injection of 1% pentobarbital sodium (40 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection). Confirm adequate anesthesia by toe-pinch response. Euthanize rats by abdominal aorta bloodletting after blood collection.
- Alternate skin disinfection with iodophor disinfecting solution and 75% alcohol before injection. Touch a cotton swab soaked in povidone-iodine to the center of the abdominal skin and apply in a circular motion outward. Repeat with an ethanol-soaked cotton swab. Repeat disinfection 3x.
- Ask the assistant to use two hemostats to lift the skin in the middle of the abdomen. As the operator, use a scalpel to cut through the abdominal skin and muscles from the raphe to the pubic symphysis.
- After opening the abdominal cavity, separate the bowel with sterile cotton balls to expose the abdominal aorta in the posterior abdominal wall.
- Locate the abdominal aorta, take 5 mL of rat blood into blood collection tubes, and obtain the plasma into 1.5 microtubes by centrifuging at 3000 x g for 10 min after standing blood for 1 h. Store plasma at -80 °C.
- Cut open the skin with surgical scissors along the lower abdominal opening toward the lateral aspect of the right lower limb, exposing the lower limb muscles, and after carefully separating the fascia with forceps, cut the scalpel to remove the intact gastrocnemius muscle.
- Wash the gastrocnemius muscle in sterile saline to remove adhering hair and blood.
- Place the removed gastrocnemius muscle into a 15 mL centrifuge tube containing 4% paraformaldehyde.
5. Detection of plasma CK and FABP 3 levels by ELISA
- Calculate and determine the number of pre-wrapped plates required for one experiment. Remove the required plates, place them in the 96-well frame, put the remaining microplates back into the aluminum foil bag for sealing, and store them at 4 °C.
- Equilibrate the kits and samples at room temperature (25-28 °C) for 120 min, fully equilibrate to room temperature.
NOTE: Equilibration of the kit and the sample is critical and must be equilibrated to sufficient time. - Set standard, sample, and blank wells. Add 50 µL of CK or FABP3 standard at different concentrations (100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 0 ng/mL) to the standard wells. Repeat each standard once, occupying a total of 12 wells.
- Fill sample wells with 40 µL of sample diluent (0.8 g NaCl, 0.02 g KH2PO4, 0.29 g Na2HPO412H2O, 0.02 g KCl, 0.01 g NaN3in 100 mL of double distilled water, pH 7.4), followed by 10 µL of the sample to be tested. Repeat each sample once, occupying 48 wells in total.
- Except for the blank wells located two wells behind the last sample well, add 100 µL of HRP-labeled anti-human CK or FABP3 antibody (enzyme-labeled antibody) to each standard and sample well.
- Seal the wells with sealing film and incubate in a 37 °C water bath or thermostat for 60 min.
- Discard the liquid, pat dry on absorbent paper, fill each well with washing liquid, leave for 20 s, shake off the washing liquid, pat dry on blotting paper, and repeat washing the plate 5x (or use a plate washer).
- Add 50 µL of chromogen solution A (20 mg tetramethylbenzidine 10 mL ethanol in 100 mL of double distilled water) and 50 µL of chromogen solution B (0.1 M/L citric acid, 0.2 M/L sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer, pH 5.0-5.4) to each well. Keep away from light for 15 min at 37 °C.
- For standard wells, sample wells, and blank wells, add 50 µL of termination solution to each well, and measure the optical density value of each well at 450 nm within 15 min.
6. Histological analysis of notexin-induced gastrocnemius muscle injury in rats
- Prepare 5 µm thick paraffin sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin for light microscopic examination as described in25.
7. Image processing and data analysis
- Read and analyze the images captured by the imaging system with analysis software. Move the selected image field of view to the center of the screen with the mouse, click 40x, and then click Take Snapshot.
- Record the OD values from the ELISA in a spreadsheet and calculate the rat CK and FABP3 levels in the samples using the standard curve.
- Use statistical analysis software for the statistical analyses. Express measurements as mean ± standard deviation (
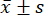 ), and analyze the comparisons between groups by one-way ANOVA, with the LSD test when the variance was uniform, and the Tamhane T2 method when the variance was not uniform. The difference was considered statistically significant at a p-value less than 0.05.
), and analyze the comparisons between groups by one-way ANOVA, with the LSD test when the variance was uniform, and the Tamhane T2 method when the variance was not uniform. The difference was considered statistically significant at a p-value less than 0.05.
Results
In order to observe the morphological properties of rat skeletal muscle after injury, the gastrocnemius muscle was stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and the stained images were read with an analysis software as described in the protocol for 8 rats per group. In rats with gastrocnemius muscle injury induced by notexin (NTX group), many muscle cells were ruptured, atrophic, necrotic, and irregularly arranged. There was also a high infiltration of neutrophils and lymphocytes around the affected area (...
Discussion
Here, we described a protocol for Tuina treatment of skeletal muscle injury in rats and then analyzed the degree of skeletal muscle injury after treatment to verify the effectiveness of the method. Notably, rat skeletal muscle injury models, including but not limited to drug induction (notexin, bupivacaine)16, blunt contusion26, crush27, and ischemia-reperfusion28, can be intervened with Tuina. Through HE staining to observe t...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.82174521), Innovation Project for Graduate Students of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine(2022CX109)
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1 mL syringe | JIANGXI FENGLIN | 20220521 | |
| 1.5 microtubes | Servicebio | EP-150X-J | |
| 15 mL centrifuge tube | Servicebio | EP-1501-J | |
| 30G needle | CONPUVON | 220318 | |
| 5 mL blood collection tube | Servicebio | QX0023 | |
| Acrylic handle | Guangdong Guangxingwang Plastic Materials Co., Ltd | 65643645 | |
| Adjustment splint | CREROMEM | 20220729 | |
| Cotton Swab | INOHV | 22080215 | |
| Enzyme-labeled Instrument | Rayto | RT-6100 | |
| Ethanol | INOHV | 211106 | |
| Fork holder | Yongkang Kangzhe Health Technology Co., Ltd | JL001 | |
| Hair removal cream | Veet, France | LOTC190922002 | |
| Hematoxylin dyeing solution set | Wuhan Google Biotech | G1005 | |
| Imaging system | Nikon, Japan | Nikon DS-U3 | |
| IODOPHOR disfecting solution | Hale&Hearty | 20221205 | |
| Light microscope | Nikon, Japan | Nikon Eclipse E100 | |
| Limit baffle | CREROMEM | 20220724 | |
| Notexin | Latoxan S.A.S. | L8104-100UG | |
| Pentobarbital sodium | Merck KGaA | P3761 | |
| Rat creatine kinase (CK) ELISA kit | LunChangShuoBiotech | YD-35237 | |
| Rat fatty acid-binding protein 3 (FABP3) ELISA kit | LunChangShuoBiotech | YD-35730 | |
| Rubber roller | Hebei Mgkui Chemical Technology Co.,Ltd | 202207 | |
| Screw | Weiyan Hardware | B05Z122 | |
| Sprague Dawley rats | Hunan Slake Kingda Laboratory Animal Co. | SYXK2019-0009 | |
| Spring | Bingzhang Hardware | TH001 | |
| Surgical blade | Covetrus | #23 | |
| Weigh controller | Iyoys | HY-XSQ |
References
- Lempainen, L., et al. Management of anterior thigh injuries in soccer players: practical guide. BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation. 14 (1), 41 (2022).
- Bayer, M. L., Mackey, A., Magnusson, S. P., Krogsgaard, M. R., Kjær, M. Treatment of acute muscle injuries (in Danish). Ugeskrift for Laeger. 181 (8), V11180753 (2019).
- Serner, A., et al. Progression of Strength, Flexibility, and Palpation Pain During Rehabilitation of Athletes with Acute Adductor Injuries: A Prospective Cohort Study. The Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy. 51 (3), 126-134 (2021).
- Gozubuyuk, O. B., Koksal, C., Tasdemir, E. N. Rehabilitation of a patient with bilateral rectus abdominis full thickness tear sustained in recreational strength training: a case report. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice. 38 (13), 3216-3225 (2022).
- Hotfiel, T., et al. Current Conservative Treatment and Management Strategies of Skeletal Muscle Injuries. Zeitschrift für Orthopädie und Unfallchirurgie. 154 (3), 245-253 (2016).
- de Sire, A., et al. Pharmacological Treatment for Acute Traumatic Musculoskeletal Pain in Athletes. Medicina. 57 (11), 1208 (2021).
- Connor, D. E., et al. Therapeutic potential of exosomes in rotator cuff tendon healing. Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism. 37 (5), 759-767 (2019).
- Martins, A. L. L., Giorno, L. P., Santos, A. R. Tissue Engineering Applied to Skeletal Muscle: Strategies and Perspectives. Bioengineering. 9 (12), 744 (2022).
- Horgan, D., et al. Clouds across the new dawn for clinical, diagnostic and biological data: accelerating the development, delivery and uptake of personalized medicine. Diagnosis. , (2023).
- Urits, I., et al. A Comprehensive Review of Alternative Therapies for the Management of Chronic Pain Patients: Acupuncture, Tai Chi, Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine, and Chiropractic Care. Advances in Therapy. 38 (1), 76-89 (2021).
- Lee, N. W., et al. Chuna (or Tuina) Manual Therapy for Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: eCAM. 2017, 8218139 (2017).
- Xie, J., Deng, D. X., Chen, Y., Peng, L. Progress in the intervention of massage techniques on skeletal muscle injury. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 34 (04), 199-201 (2018).
- Yuan, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, G. H., Xue, X. N. Research progress on microstructure changes and rehabilitation treatment of exercise-induced skeletal muscle injury. Massage and Rehabilitation Medicine. 14 (6), 29-33 (2023).
- Zhao, Y. The Establishment of Famous Tuina Master Ding Jifeng and Wei Fa - Commemorating the 100th Anniversary of Mr. Ding Jifeng's Birthday. Traditional Chinese Medicine Culture. 9 (6), 18-21 (2014).
- Hardy, D., et al. Comparative Study of Injury Models for Studying Muscle Regeneration in Mice. PloS one. 11 (1), e0147198 (2016).
- Plant, D. R., Colarossi, F. E., Lynch, G. S. Notexin causes greater myotoxic damage and slower functional repair in mouse skeletal muscles than bupivacaine. Muscle & Nerve. 34 (5), 577-585 (2006).
- Tierney, M. T., Sacco, A. Inducing and Evaluating Skeletal Muscle Injury by Notexin and Barium Chloride. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1460, 53-60 (2016).
- Torres-Ruiz, J., Alcalá-Carmona, B., Alejandre-Aguilar, R., Gómez-Martín, D. Inflammatory myopathies and beyond: The dual role of neutrophils in muscle damage and regeneration. Frontiers in Immunology. 14, 1113214 (2023).
- Tu, H., Li, Y. L. Inflammation balance in skeletal muscle damage and repair. Frontiers in Immunology. 14, 1133355 (2023).
- Castro, C., Gourley, M. Diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory myopathy: issues and management. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease. 4 (2), 111-120 (2012).
- Dabby, R., et al. Asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic hyperCKemia: histopathologic correlates. The Israel Medical Association Journal: IMAJ. 8 (2), 110-113 (2006).
- Khodabukus, A., et al. Tissue-Engineered Human Myobundle System as a Platform for Evaluation of Skeletal Muscle Injury Biomarkers. Toxicological Sciences. 176 (1), 124-136 (2020).
- Zhou, X. W., Jin, W. D., Zhu, L., Liu, X. H., Zhou, B. H. Experimental observation on the influence of different frequency, intensity and action time of Ding rolling manipulation on hemodynamics. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. (06), 42-44 (1998).
- Pablos, A., et al. Protective Effects of Foam Rolling against Inflammation and Notexin Induced Muscle Damage in Rats. International Journal of Medical Sciences. 17 (1), 71-81 (2017).
- Wisner, L., Larsen, B., Maguire, A. Enhancing Tumor Content through Tumor Macrodissection. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (180), e62961 (2022).
- Deng, P., et al. Contusion concomitant with ischemia injury aggravates skeletal muscle necrosis and hinders muscle functional recovery. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 247 (17), 1577-1590 (2022).
- Dobek, G. L., Fulkerson, N. D., Nicholas, J., Schneider, B. S. Mouse model of muscle crush injury of the legs. Comparative Medicine. 63 (3), 227-232 (2013).
- Armstrong, D. M., et al. Sildenafil citrate protects skeletal muscle of ischemia-reperfusion injury: immunohistochemical study in rat model. Acta Cirúrgica Brasileira. 28 (4), 282-287 (2013).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved