A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
BrainBeats as an Open-Source EEGLAB Plugin to Jointly Analyze EEG and Cardiovascular Signals
In This Article
Summary
The BrainBeats toolbox is an open-source EEGLAB plugin designed to jointly analyze EEG and cardiovascular (ECG/PPG) signals. It includes heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP) assessment, feature-based analysis, and heart artifact extraction from EEG signals. The protocol will aid in studying brain-heart interplay through two lenses (HEP and features), enhancing reproducibility and accessibility.
Abstract
The interplay between the brain and the cardiovascular systems is garnering increased attention for its potential to advance our understanding of human physiology and improve health outcomes. However, the multimodal analysis of these signals is challenging due to the lack of guidelines, standardized signal processing and statistical tools, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), and automation for processing large datasets or increasing reproducibility. A further void exists in standardized EEG and heart-rate variability (HRV) feature extraction methods, undermining clinical diagnostics or the robustness of machine learning (ML) models. In response to these limitations, we introduce the BrainBeats toolbox. Implemented as an open-source EEGLAB plugin, BrainBeats integrates three main protocols: 1) Heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP) and oscillations (HEO) for assessing time-locked brain-heart interplay at the millisecond accuracy; 2) EEG and HRV feature extraction for examining associations/differences between various brain and heart metrics or for building robust feature-based ML models; 3) Automated extraction of heart artifacts from EEG signals to remove any potential cardiovascular contamination while conducting EEG analysis. We provide a step-by-step tutorial for applying these three methods to an open-source dataset containing simultaneous 64-channel EEG, ECG, and PPG signals. Users can easily fine-tune parameters to tailor their unique research needs using the graphical user interface (GUI) or the command line. BrainBeats should make brain-heart interplay research more accessible and reproducible.
Introduction
For a long time, the reductionist approach has dominated scientific inquiry in human physiology and cognition. This approach involved dissecting complex bodily and mental processes into smaller, more manageable components, allowing researchers to focus on individual systems in isolation. This strategy arose due to the challenges in studying the intricate and interconnected nature of the human body and mind1. Reductionism has been instrumental in understanding individual subsystems in isolation, such as elucidating the role of ion channels and action potentials for neural2 or cardiac3 communication. However, a significant gap remains in our understanding of how these isolated systems interact on a larger spatial and temporal scale. The multimodal (integrative or ecological) framework considers the human body a complex multidimensional system, where the mind is seen not as a product of the brain but as an activity of the living being, an activity that integrates the brain within the everyday functions of the human body4. The multimodal and reductionist approaches are not exclusive, just like we cannot study one neuron without the whole brain or the whole brain without understanding individual neuron properties. Together, they pave the way for a more comprehensive, synergetic understanding of human health, pathology, cognition, psychology, and consciousness. The present method aims to ease the multimodal investigation of the interplay between the brain and the heart by providing joint analysis of electroencephalography (EEG) and cardiovascular signals, namely electrocardiography (ECG) and photoplethysmography (PPG). This toolbox, implemented as an EEGLAB plugin in MATLAB, addresses existing methodological limitations and is made open source to facilitate accessibility and reproducibility in the scientific area. It implements the latest guidelines and recommendations into its design and default parameters to encourage users to follow known best practices. The proposed toolbox should be a valuable resource for researchers and clinicians interested in 1) studying heartbeat-evoked potentials , 2) extracting features from EEG and ECG/PPG signals, or 3) removing heart artifacts from EEG signals.
Heart-brain research
The relationship between the heart and the brain has been historically studied via neuroimaging methods such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). Using these tools, researchers highlighted some brain regions associated with cardiovascular control (e.g., manipulation of heart rate and blood pressure5), showed the influence of heart rate on the BOLD signal6, or identified potential brain-body pathways contributing to coronary heart disease (i.e., stress-evoked blood pressure7). While these studies have significantly advanced our understanding of the complex interplay between the central nervous system (CNS) and cardiovascular function, these neuroimaging techniques are expensive, have limited availability, and are confined to controlled laboratory settings, which restricts their practicality for real-world and large-scale applications.
In contrast, EEG and ECG/PPG are more affordable and portable tools that offer the potential for studying brain-heart interactions in more diverse settings and populations or over longer periods, providing new opportunities. ECG measures the electrical signals generated by each heartbeat when the heart contracts and relaxes via electrodes placed on the skin (usually on the chest or arms)8. PPG measures blood volume changes in the microvascular tissues (i.e., blood flow and pulse rate) using a light source (e.g., LED) and a photodetector (commonly placed on a fingertip, wrist, or forehead), relying on how blood absorbs more light than the surrounding tissue9. Both methods provide valuable information about cardiovascular function but serve different purposes and offer distinct data types. Like ECG, EEG records the electrical fields generated by the synchronized activity of thousands of cortical neurons that propagate through the extracellular matrix, tissues, skull, and scalp until they reach the electrodes placed on the scalp's surface10. As such, the use of EEG and ECG/PPG holds great promise for advancing our understanding of the physiological, cognitive, and emotional processes underlying brain-heart interactions and their implications for human health and well-being. Therefore, capturing heart-brain interplay from EEG, ECG/PPG signals with the BrainBeats toolbox may be particularly useful for the following scientific areas: clinical diagnostic and forecasting, big data machine learning (ML), real-world self-monitoring11, and mobile brain/body imaging (MoBI)12,13.
Two approaches for jointly analyzing EEG and ECG signals
There are two main approaches to studying interactions between EEG and cardiovascular signals:
The heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP) in the time domain: event-related potentials (ERP), and the heartbeat-evoked oscillations (HEO) in the time-frequency domain: event-related spectral perturbations (ERSP) and inter-trial coherence (ITC). This approach examines how the brain processes each heartbeat. With millisecond (ms) accuracy, this method requires that both time series are perfectly synchronized and the heartbeats to be marked in the EEG signals. This approach has gained interest in recent years14,15,16,17,18,19.
Feature-based approach: this approach extracts EEG and heart-rate variability (HRV) features from continuous signals and examines associations between them. This has been done independently for EEG (often termed quantitative EEG or qEEG20), ECG21,22,23, and PPG24,25,26. This approach presents promising applications by capturing both state- and trait-related variables. Note that, for both EEG and cardiovascular signals, the longer the recording, the more dominant the trait variable27,28,29. Thus, the applications depend on the recording parameters. Feature-based analyses are gaining growing interest, providing new quantitative metrics for forecasting the development of mental and neurological disorders, treatment-response, or relapse30,31,32,33,34,35. This approach is especially compelling with large and real-world datasets (e.g., clinic, remote monitoring), which can be more easily obtained thanks to the recent innovations in wearable neurotechnology11. A less explored application is the identification of associations between specific brain and heart features, highlighting potential underlying central nervous system dynamics. Heart rate variability (HRV) can be calculated from both ECG and PPG signals. It provides information about the autonomous nervous system (ANS) by measuring the variations in time intervals between heartbeats (i.e., the normal-to-normal intervals)27. Increased sympathetic (SNS) activity (e.g., during stress or exercise) typically reduces HRV, while parasympathetic (PNS) activity (e.g., during relaxation) increases it. A slower breathing rate generally increases HRV due to enhanced PNS activity, especially for short recordings (<10 min)27. Higher HRV scores generally suggest a more resilient and adaptable ANS, while a lower HRV can indicate stress, fatigue, or underlying health issues. Long HRV recordings (i.e., at least 24 h) provide a predictive prognosis for various health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, stress, anxiety, and some neurological conditions27. Measures like blood pressure, heart rate, or cholesterol levels give information about the cardiovascular system's status. In contrast, HRV adds a dynamic aspect, showing how the heart responds to and recovers from stress.
BrainBeats' advantages over existing methods
While tools exist, as reviewed below, to process cardiovascular and EEG signals independently from each other, they cannot be jointly analyzed. Furthermore, most available means to process cardiovascular signals involve costly licensing, do not allow automated processing (especially beneficial for large datasets), have proprietary algorithms that prevent transparency and reproducibility, or require advanced programming skills by not providing a graphical user interface (GUI)36. To our knowledge, four open-source MATLAB toolboxes support HEP/HEO analysis with a GUI: the ecg-kit toolbox37, the BeMoBIL pipeline38, the HEPLAB EEGLAB plugin39, and the CARE-rCortex toolbox40. While HEPLAB, BeMoBIL, and ecg-kit facilitate HEP analysis by detecting heartbeats and marking them in the EEG signals, they do not provide statistical analysis or are limited to the time domain (i.e., HEP). The CARE-rCortex plugin addressed these issues by supporting ECG and respiratory signals, time-frequency domain analysis, statistics, and advanced baseline normalization and correction methods adapted to HEP/HEO analysis. However, it uses the Bonferroni method for statistical correction of the type 1 error (i.e., false positives), which is too conservative and not physiologically sound for EEG applications, leading to an increase in type II errors (i.e., false negatives)41. Furthermore, the toolbox does not offer command-line access for automation. Finally, recent studies recommend against baseline correction methods42,43,44, as they reduce the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and are statistically unnecessary and undesirable.
To address these limitations, we introduce the BrainBeats toolbox, currently implemented as an open-source EEGLAB plugin in the MATLAB environment. It incorporates the following advantages over previous methods:
1) An easy-to-use GUI and command-line capabilities (for programmers aiming to perform automated processing). 2) Validated algorithms, parameters, and guidelines for processing cardiovascular signals, such as detecting R peaks, interpolating RR artifacts, and computing HRV metrics (e.g., implanting guidelines for windowing, resampling, normalization, etc.27,45,46). This is important because Vest et al. demonstrated how modest differences in these processing steps can lead to divergent results, contributing to the lack of reproducibility and clinical applicability of HRV metrics46. 3) Validated algorithms, default parameters, and guidelines for processing EEG signals, including filtering and windowing44,47, re-referencing48,49, removal of abnormal channels and artifacts50,51,52, optimized ICA decomposition and classification of independent components53,54,55,56. The users can fine-tune all preprocessing parameters or even preprocess their EEG data with their preferred method before using the toolbox to match their needs (e.g., with EEGLAB clean_rawdata plugin50,52, the BeMoBIL pipeline38, the PREP pipeline57, etc.). 4) Heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP, i.e., time domain) and oscillations (HEO; event-related spectral perturbations with wavelet or FFT methods, and inter-trial coherence are available through the standard EEGLAB software) from ECG signals. Parametric and nonparametric statistics with corrections for type 1 errors are available via EEGLAB's standard software. Nonparametric statistics include permutation statistics and spatiotemporal corrections for multiple comparisons (e.g., spatiotemporal clustering or threshold-free cluster enhancement)58,59. Users can use the LIMO-EEG plugin to implement hierarchical linear modeling, which accounts well for within and between-subjects variance and implements an assumption-free mass-univariate approach with robust control for type I and II errors60,61. The HEP/HEO data statistical analyses can be performed in the channel and independent component domains. 5) HEP/HEO and HRV analysis from PPG signals (for the first time for HEP/HEO). 6) Supports the joint extraction of EEG and HRV features for the first time. 7) The toolbox provides various data visualizations to inspect signals at various necessary processing steps and outputs at the subject level.
| Method | Detect R-peaks from ECG | Detect R-waves from PPG | HEP/HEO | EEG & HRV features | Remove heart artifacts from EEG | GUI | Command line |
| ecg-kit | X | X | X | X | |||
| BeMoBIL | X | X | X | ||||
| HEPLAB | X | X | X | X | |||
| CARE-rCortex | X | X | X | X | |||
| BrainBeats | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
TABLE 1: Novelties brought by BrainBeats relative to pre-existing, similar methods.
Information to help readers decide whether the method is appropriate for them
This toolbox is appropriate for any researcher or clinician with EEG and ECG/PPG data. The plugin does not yet support importing EEG and ECG/PPG signals from separate files (although this feature will be available soon). The toolbox is appropriate for anyone aiming to perform HEP/HEO analysis, extract EEG and/or HRV features with standardized methods, or simply remove heart artifacts from EEG signals. See Figure 1 for a block diagram summarizing BrainBeats' overall flow and methods.
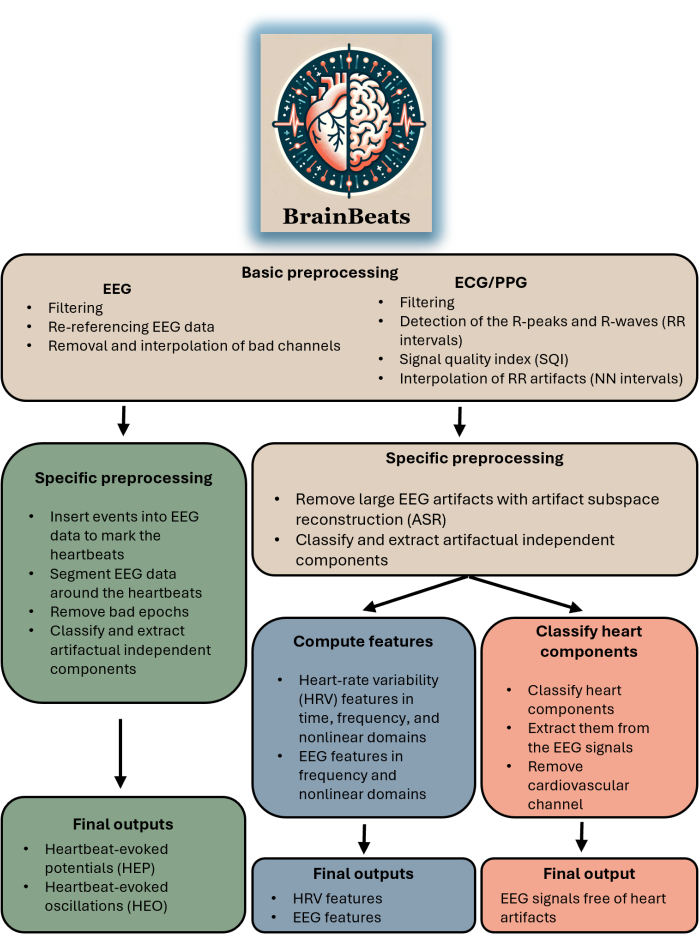
FIGURE 1. Block diagram summarizing BrainBeats' overall architecture and flow. The operations that are common across the three methods are brown. Operations specific to heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP) and oscillations (HEO) are green. Operations specific to the extraction of EEG and HRV features are blue. Operations specific to removing heart artifacts from the EEG signals are red. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
Informed consent was obtained from each participant, and the Ural Federal University ethics committee approved the experimental protocol.
1. BrainBeats requirements
- Install MATLAB and EEGLAB on the computer. EEGLAB can be downloaded at https://github.com/sccn/eeglab and unzipped (or cloned for Git users) anywhere on the computer. See the GitHub page for more details on installation.
- Add the path to the EEGLAB folder in MATLAB's home panel by clicking Set Path button. Select the eeglab folder with the unzipped file and click Save > Close.
- Launch EEGLAB by typing eeglab in MATLAB's command window.
- Install the BrainBeats plugin by clicking File > Manage EEGLAB extensions. Type brainbeats in the search bar, select the BrainBeats plugin in the list and click Install/Update.
- Load the sample dataset into EEGLAB. Click File > Load existing data. Navigate to the EEGLAB folder, go to the plugins folder, go to the BrainBeats folder and open to the sample_data folder. Select the file dataset.set.
NOTE: This dataset corresponds to sub-032 (resting state with eyes opened) from an open-source multi-subject dataset62,63. This was selected because it contains simultaneous EEG (64 channels), ECG (one channel), and PPG (one channel), at a 1000 Hz sampling rate. ECG and PPG signals were collected using the auxiliary inputs of the actiCHamp system. EEG data were recorded with active electrodes placed according to the 10-20 system, with FCz as the online reference and Fpz as the ground electrode, and with the impedance maintained below 25 kOm. ECG was recorded using one active electrode placed on the right wrist, the reference electrode on the left wrist, and the ground on the left inner forearm at 3 cm distally from the elbow. PPG was recorded from the left index finger. EEG, ECG, and PPG data are time-synchronized since they were recorded simultaneously with the same amplifier. See references62,63 for more details. - Check the Save Outputs checkbox to save everything in the corresponding .set file at the same location as the original file that was loaded into EEGLAB.
NOTE: For this tutorial, we merged the EEG, ECG, and PPG data into one EEGLAB dataset, loaded the 3D boundary element method (BEM) electrode coordinates, and downsampled the signal to 250 Hz to reduce the file weight (for user download) and accelerate computing time. Because this dataset had no abnormal EEG channel, we artificially modified channel TP9 to illustrate BrainBeats' bad channel detection and removal algorithm. Similarly, we artificially simulate a large EEG artifact at the beginning of the file and a high-frequency muscle-like artifact in the temporal channels from 3-6 s to illustrate BrainBeats' artifact removal feature.
2. Heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP) and oscillations (HEO)
- Open BrainBeats' first general user interface (GUI) to select the main parameters. In EEGLAB, click Tools > BrainBeats > 1st level (subject level). Select Heartbeat-evoked potentials HEP as the analysis to run, ECG as the heart data type, and click on the button to display the list of channels to select the ECG channel labeled ECG (or type it directly in the text box). Keep the options Visualize outputs (recommended) and Save outputs selected and click Ok.
- A second GUI window pops up based on the previous choices (i.e., HEP analysis with ECG data). Select preprocessing parameters for both EEG and ECG signals. Turn off preprocessing by unchecking the boxes Preprocess ECG and Preprocess EEG to see if the data has already been preprocessed prior to launching BrainBeats. Change Power line noise to 50 Hz in the Preprocess EEG section since these EEG data were recorded in Russia. Click OK to launch.
- A warning message will appear, asking for confirmation to remove the PPG channel that has been detected. This is because the toolbox is not designed to analyze both ECG and PPG simultaneously (or other auxiliary channels) and keeping it in the dataset will lead to severe errors (e.g., artifact removal, poor ICA decomposition, etc.). Click Yes. BrainBeats starts performing some checks, setting some default parameters, and separates the ECG from the EEG data to preprocess the ECG signal and compute the RR intervals.
- ECG and RR time series are preprocessed using validated algorithms from the Physionet Cardiovascular Signal toolbox46,64 adapted to fit BrainBeats' data formatting, increase clarity, parameter tuning, and computing time (see references for validation of the algorithms). The plugin outputs the RR intervals, timestamps, filtered ECG signal, R-peaks indices, and heart rate (HR). Tune these parameters via the GUI or command line.
NOTE: The ECG signal is bandpass-filtered using a customized, validated filter (1-30 Hz) and scans the signal to identify the QRS complex and R-peaks using the Pan-Tompkins (P&T) method65, implementing some signal processing operations including differentiation, squaring, integration, and smoothing for best performance. The P&T energy threshold is estimated based on the sample rate and the smoothed ECG values to avoid disruption from large bumps. If the RR interval variability exceeds 1.5 times the median, it searches for missed peaks. The mean R-peak sign is calculated over 30 s segments, and peak points are refined through a refractory period check, managing flatline conditions and ensuring consistent detection. - Next, BrainBeats identifies abnormal RR intervals or spikes within RR intervals using a forward-backward search and physiological thresholds. The signal quality index (SQI) is calculated46; check this if the system displays warnings where more than 20% of the RR times series contains RR artifacts (outside of physiological limits or with an SQI below 0.9). A plot displays the filtered ECG signal, identified R-peaks, NN intervals, and interpolated artifacts (see Figure 2).
NOTE: The RR artifacts are interpolated by default using the shape-preserving piecewise cubic method to obtain the normal-to-normal (NN) intervals but remove them (not recommended) or use another interpolation method (linear, cubic, nearest neighbor, previous/next neighbor, spline, cubic convolution, or modified Akima cubic) if needed. When several ECG channels are present, the RR intervals are estimated for each, and the channel with the least number of RR artifacts is selected for the following steps. - Scroll through zoomed-in 30 s windows of the R-peaks for closer inspection by pressing the Right/left Arrows. If the data contains several ECG/PPG channels, use the channel with the best signal quality index for the RR intervals. BrainBeats does not support both ECG and PPG signals simultaneously at the moment. For tutorial purposes, we chose a sample dataset that contains both datatypes.
- Once done with the ECG signal, BrainBeats bandpass filters the EEG data at 1-40 Hz using a nonlinear causal minimum-phase FIR filter by default to reduce smearing activity between pre- and post-heartbeat periods, preserve causality, and avoid undesired group delays44. This is particularly important for users examining the pre-heartbeat period. If the lowpass filter is set to a value above the power line frequency (e.g., 80 Hz lowpass with power line frequency at 50 Hz), use a sharp notch filter to remove the line noise artifact. The EEG data are then re-referenced to infinity using the REST algorithm (best suited for HEP analysis49) unless less than 30 channels are detected (in which case they cannot be reliably re-referenced, and a warning is generated to let users know).
- BrainBeats then detects, removes, and interpolates abnormal EEG channels (Figure 3). Check that the default parameters are flat lines greater than 5 s (clean_flatlines algorithm), a maximum high-frequency noise standard deviation of 10, a window length of 5 s (to better capture slow-frequency artifacts52), a minimum correlation between neighboring channels of .65, and a maximum tolerated portion of 33% (clean_channels algorithm).
NOTE: The number of RANSAC samples is set to 500 by default to increase convergence and replicability of bad channel rejection (although it increases the computation time). - Next, insert R-peaks as event markers into the EEG data to mark each heartbeat and segment the data around these markers without baseline removal (per guidelines43,66; Figure 4). Since NN intervals have different lengths and EEG must be segmented at a constant length, estimate the minimum epoch size cutoff following R-peak events using the 5th percentile of the interbeat-interval (IBI) data (i.e., the value below which 5% of the shortest IBIs fall, displayed as a dashed red line on a histogram; see Figure 5).
NOTE: This 5th percentile value is a good compromise to preserve as many epochs as possible while ensuring they are not too short since the period of interest for HEP/HEO analysis is 200-600 ms post heartbeat49,67. - Segment EEG data from -300 ms before the R-peaks to the 5th percentile value post-R-peak, with the R-peak at time 0. Reject epochs shorter than 550 ms or containing more than one R-peak (which would bias the ERP/ERSP), per guidelines49,67. Epochs containing large EEG artifacts are detected using root-mean-square (RMS) and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) metrics and MATLAB's isoutlier function (Figure 6). Artifactual epochs are removed.
- Perform blind source separation using the default Infomax algorithm, accounting for data rank for best performance53. If desired, choose the preconditioned independent component analysis (PICARD) algorithm for fast computation54,54 by choosing the option Picard (fast) or the modified Infomax algorithm by choosing the option Modified Infomax (long but replicable) for the field ICA method (although this involves much longer computation times). Use the ICLabel plugin56 to automatically classify ICs to extract non-brain artifacts (ocular components are removed with 90% confidence, whereas muscular, line noise and channel noise are removed with 99% confidence; Figure 7).
- Keep the option Visualize outputs selected in the first GUI window to visualize the final EEG time series, the grand average HEP (Figure 8 top), HEP for each heartbeat (Figure 8 bottom), and the grand average heartbeat-evoked oscillations (HEO; Figure 9). Examine HEOs in terms of event-related spectral perturbation (ERSP, i.e., changes in EEG power across heartbeats; Figure 9 top) and inter-trial phase coherence (ITC, i.e., consistency of the phase angle across heartbeats; Figure 9 bottom).
NOTE: ERSP is computed using a default 3-cycle wavelet (with a Hanning-tapered window applied, pad ratio of 2) and with the number of cycles in the wavelets used for higher frequencies expanding slowly up to 20% of the number of cycles in the equivalent FFT window at its highest frequency (1 minus 0.8). This controls the shapes of the individual windows measured by the function and their shapes in the resulting time/frequency panes. An arbitrary baseline is removed for illustration purposes, and ERSP is computed for frequencies 7-25 Hz to capture the typical HEO effect described in the literature, namely 300-450 ms post heartbeat in the alpha band (8-13 Hz) over frontocentral electrodes17,67. Lower frequencies cannot be estimated due to the short epoch size defined by the interbeat intervals. Nonparametric (permutation) statistics are applied to visualize the HEO for a p-value of 0.05, corrected for false discovery rate (FDR, i.e., type 1 error or family-wise error). These plots are generated for tutorial purposes or single-trials analysis. - Preprocessing plots are generated to visualize the different steps. To turn it off, uncheck the box Visualize preprocessings. The final EEG data (cleaned and segmented around the R-peaks) do not include the ECG data since it would bias the ERP/ERSP analysis. To preserve the heart channel in the final output, check the box Keep heart channel.
NOTE: Pause here if needed before processing the next file (next condition or participant). - BrainBeats supports EEGLAB's history function. At the end of all operations, type eegh in MATLAB's command window to print the command line to repeat all the above steps via a single command line, with the parameters that were selected manually in the GUI, allowing easy automation. Find preprocessing outputs (e.g., signal quality index of the cardiovascular time series, NN intervals, removed EEG channels, segments, and components, etc.) in the EEGLAB structure: EEG.brainbeats.preprocessings. All parameters are also exported in EEG.brainbeats.parameters.
- For advanced users, perform all the above steps with default parameters with the following command lines (see the tutorial script in the BrainBeats repository for more options):
eeglab; close; % Launch EEGLAB without the GUI
main_path = fileparts(which('eegplugin_BrainBeats.m')); cd(main_path);
EEG = pop_loadset('filename','dataset.set',
'filepath',fullfile(main_path, 'sample_data')); %Load the sample dataset
EEG = brainbeats_process(EEG,'analysis',
'hep','heart_signal','ECG', 'heart_channels',
{'ECG'},'clean_eeg',true); % Launch BrainBeats 1st level to process the file for HEP analysis with default parameters - The steps above performed HEP/HEO from the ECG signal. Use the following steps for the PPG signal.
- In the following steps, perform the same operations but using a PPG signal. Load the same dataset again (see step 1.5) since the previous operations overwrote it, and open BrainBeats' first GUI again to select the main parameters. Click Tools > BrainBeats > 1st level (subject level). Select Heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP) as the analysis to run, PPG as the heart data type, and click on the button to display the list of channels to select the PPG channel. Keep the options Visualize outputs (recommended) and Save outputs selected and click OK.
- The second GUI window pops up in a manner similar to step 2.2 . The only difference is that we can now fine-tune the parameter to process the PPG signal instead of the ECG signal. Click OK to run with the default parameters.
- A warning message appears, asking for confirmation to remove the extra ECG channel that has been detected. Again, this is expected. Click Yes. By default, the toolbox will preprocess the PPG signal, detect the pulse waves to obtain the RR intervals, identify RR artifacts, if any, and interpolate them (Figure 10). Steps 2.7. to 2.12. are performed, and the same plots and outputs are generated but based on the R waves detected from the PPG signal (see Figure 11 and Figure 12).
NOTE: R waves are detected using the slope of the signal within a specified window. Potential pulses are then flagged when the slope exceeds a dynamic threshold, which is adjusted based on the detection history and signal characteristics. The algorithm then searches within an eye-closing period to pinpoint the maximum slope, and subsequently, the onset of the pulse wave is determined through thresholding. The R-wave peaks are identified as the valleys near the onset, and their locations are recorded. The algorithm iterates through the entire signal, continuously adjusting detection thresholds and identifying R-wave peaks, which are then used to calculate the RR intervals. - For advanced users, perform all the above steps with default parameters with the following command lines (see the tutorial script in the BrainBeats repository for more options):
eeglab; close; % Launch EEGLAB without the GUI
main_path = fileparts(which('eegplugin_
BrainBeats.m')); cd(main_path);
EEG = pop_loadset('filename','dataset.set',
'filepath',fullfile(main_path, 'sample_data')); %Load the sample dataset
EEG = brainbeats_process(EEG,'analysis',
'hep','heart_signal','PPG', 'heart_channels',
{'PPG'},'clean_eeg',true); % Launch BrainBeats 1st level to process the file for HEP analysis with default parameters
3. Extracting EEG and HRV features
- Load the same dataset again (see step 1.5; Click File > Load existing dataset > Select dataset.set) since it was overwritten by the previous operations and open the main GUI again to select the main parameters (step 2.1; Click Tools > BrainBeats > 1st level). Select Extract EEG & HRV features for the analysis type, ECG for the heart signal type, and select ECG in the list of electrode labels. Click OK.
- The second GUI window pops up like in step 2.2 but with different parameters for EEG preprocessing and extracting HRV and EEG features. Set these parameters as described below. Click OK to launch with default parameters.
- In the HRV section, click on the button freq. options to select the method to compute HRV power (default set to normalized Lomb-Scargle periodogram), the window overlap (default set to 25%), and for performing a second-level normalization (unset by default; see note below for more detail).
- In the EEG features section, click on the button freq. options to fine-tune some parameters, such as the overall frequency range on which to compute the power spectral density (PSD; default = 1-40 Hz), the units (decibels, µV2/Hz, or normalized by total power), the window type (default = hamming), the window overlap (default = 50%), the window length (default = 2 s), and the types of frequency bounds for each band.
NOTE: HRV power is computed by default using the normalized Lomb-Scargle periodogram, which does not require resampling (therefore better preserving original information) and best deals with non-uniformly sampled data, missing data, and noise (typical with NN intervals)68. The normalized version scales the power by the variance of the signal, providing results that are less sensitive to varying noise levels, more focused on the relative strength of periodic components, and more comparable across different recordings or subjects. Other methods available include the non-normalized Lomb-Scargle periodogram, the Welch method, and the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). Resampling is automatically performed for the Welch and FFT methods to create the necessary regularly sampled time series. A second-level normalization can be applied by dividing the power of each frequency band by the total power, providing a more intuitive measure of the relative contribution of each frequency component to the overall power. It is disabled by default since it is only meaningful when all four bands are available, requiring at least 24 h of signal. These algorithms are adapted from the Physionet Cardiovascular signal processing toolbox46.
- The same warning message appears, asking for confirmation to remove the extra PPG channel that has been detected. Again, this is expected. Click Yes. BrainBeats will start preprocessing the ECG data and extracting the NN intervals identically, as in step 2.4. Then, it extracts heart-rate variability (HRV) features from the NN intervals in the time (SDNN, RMSSD, pNN50), frequency (ULF, VLF, LF, HF, LF:HF ratio, total power), and nonlinear (Poincare, phase-rectified signal averaging, fuzzy entropy, and fractal dimension) domains.
NOTE: BrainBeats automatically checks the file length to ensure that minimum requirements are met (e.g., ULF-HRV power requires 24 h of data), sends warning messages if not, and does not export these features to prevent unreliable estimations. BrainBeats follows guidelines and recommendations for estimating HRV metrics27,45. - BrainBeats preprocesses the EEG data as in step 2.7 . (see Figure 3). Large artifacts are detected automatically in the continuous data using the artifact subspace reconstruction (ASR) algorithm50,52 (default SD criterion set to 30 and using 80% of available RAM to increase speed). These large artifacts are removed from the EEG data (see Figure 13). To adjust these parameters in the GUI, select the fields Threshold to reject bad segments with ASR and Available RAM to use for ASR.
NOTE: The EEG and cardiovascular time series do not need to be time synchronized for the features mode since the features are estimated on each signal separately. Thus, EEG artifacts can be removed directly from the EEG data (in red, Figure 13), unlike for the HEP mode, where epochs containing artifacts were rejected for both time series because time synchronization with ms accuracy is essential for that method. - Perform ICA using the same algorithms and parameters as for HEP (see step 2.11.), except that this time the heart components are removed if detected with 99% confidence (they were preserved for HEP/HEO since we do not want to remove relevant cardiac-related signals).
- The box Frequency domain is checked in step 3.2., so BrainBeats extracts the following frequency domain features: the average power spectral density (PSD) for the delta (1-3 Hz), theta (3-7 Hz), alpha (8-13 Hz), beta (13-30 Hz), and gamma (30+ Hz) frequency bands, the individual alpha frequency (IAF), and alpha asymmetry on all available (symmetric) electrode pairs. Check these features.
NOTE: PSD converted to decibels (dB) facilitates the comparison of results across recordings and subjects. The frequency bounds can be set to the conventional bounds (e.g., predefined 8-13 Hz for the alpha band) or to the individualized bounds, which are detected from the distribution of the power spectral density to account for inter-individual differences69 (e.g., 7.3-12.6 Hz for the alpha band). The algorithm was designed for the alpha band and does not perform as well for other bands, especially when peaks are not present in the power spectral distribution. The individual alpha frequency (IAF) is estimated using the alpha center of gravity to better deal with split peaks or ambiguous peaks69. Alpha asymmetry is computed following guidelines (2-s hamming window with 50% overlap, the logarithm of alpha power from the left channel minus logarithm of alpha power from the right channel)47. Hence, positive values indicate greater left-than-right alpha power and vice versa. Alpha asymmetry can be normalized by dividing alpha power from each electrode by the alpha power summed across all electrodes47. The symmetric pairs are obtained using theta distances, requiring the EEG data to contain electrode coordinates. - The box Nonlinear domain is checked in step 3.2., BrainBeats extracts the fuzzy entropy and the fractal dimension for each EEG channel.
NOTE: Nonlinear-domain features are thought to capture nonlinear, complex dynamics of the brain that are missed by spectral measures and show particular promise for investigating interactions between various body systems70,71,72. Fuzzy entropy is more reliable and robust than its alternatives (sample and approximate entropy) but requires longer computation times (especially with long EEG time series with high sampling rates). To address this issue, when EEG signals are longer than 2 minutes long with a sampling rate greater than 100 Hz, they are automatically downsampled (or decimated when the factor is not an integer) to 90 Hz (i.e., corresponding to a Nyquist frequency of 45 Hz, to match the default lowpass filter and avoid line noise artifacts as much as possible). Furthermore, parallel computing is activated by default when estimating EEG features, which reduces computing time, especially when many EEG channels are available. - Select Visualize outputs in the first GUI (see step 3.1.), to generate a plot displaying the power spectral density (PSD) for HRV and EEG data (Figure 14) along with scalp topographies displaying some EEG features (Figure 15).
NOTE: You can also find some preprocessing outputs in EEG.brainbeats.preprocessing and all the parameters used in EEG.brainbeats.parameters. We encourage users to report these outputs in scientific publications to increase the replicability of findings. - Keep the Save outputs box checked in the first GUI window to save all features exported into the EEGLAB .set file in EEG.brainbeats.features and save them in a .mat file in the same folder where the dataset was loaded.
- BrainBeats supports EEGLAB's history function. At the end of all operations, type eegh in MATLAB's command window to print the command linethat will allow you to repeat all the above steps via a single command line, with the parameters that were selected manually in the GUI, allowing easy automation and replication of the operations.
- For advanced users, perform all the steps above with the following command:
eeglab; close; % Launch EEGLAB without the GUI
main_path = fileparts(which('eegplugin_BrainBeats.m')); cd(main_path);
EEG = pop_loadset('filename','dataset.set',
'filepath',fullfile(main_path, 'sample_data')); % Load the sample dataset
EEG = brainbeats_process(EEG,' analysis',
'features','heart_signal','ECG', 'heart_channels',{'ECG'},'clean_eeg',true); - The previous steps extracted HRV features from ECG signal. Use the following steps to extract HRV features from PPG signal (EEG features are the same).
- Load the same dataset again (step 1.5.) since it was overwritten by the operations and open the main GUI again (step 2.5.). Select Extract EEG & HRV features for the analysis and select PPG for the heart signal type and PPG for the channel name. Click OK.
- The 2nd GUI window now shows the parameters for preprocessing PPG and for extracting the HRV and EEG features. Click OK to run with the default parameters. Parameters are described in step 2.17.
- A warning message will appear, asking for confirmation to remove the detected ECG channel. This is to be expected since the toolbox is not designed to analyze both ECG and PPG simultaneously (or other auxiliary channels) and keeping it in the dataset will lead to serious errors (e.g., artifact removal, poor ICA decomposition, etc.). Click Yes.
- BrainBeats preprocesses the PPG signal and estimates the NN intervals as in step 2.5. Check the extracted HRV features from the NN intervals, the same as in step 3.2 . except that the NN intervals have now been obtained from the PPG signal. The EEG signals are preprocessed as in step 3.2. BrainBeats plots the PSD (Figure 16). The only difference here is the PSD estimated from the NN intervals obtained from the PPG as opposed to ECG.
- For advanced users, perform all the steps above with the following command:
eeglab; close; % Launch EEGLAB without the GUI
main_path = fileparts(which('eegplugin_BrainBeats.m')); cd(main_path);
EEG = pop_loadset('filename','dataset.set','filepath',
fullfile(main_path, 'sample_data')); %Load the sample dataset
EEG = brainbeats_process(EEG,'analysis',
'features','heart_signal', 'PPG','heart_channels',{'PPG'},'clean_eeg',true);
4. Extract heart artifacts from EEG signals.
- Load the sample dataset (see step 1.5.).
- Open the main GUI window by clicking Tools > BrainBeats > 1st level (subject level) and select Extract heart artifacts from EEG signals for the analysis type, ECG for heart signal type and select ECG in the list of electrode labels. Click OK.
- The 2nd GUI window shows the preprocessing parameters. Set the Power line noise to 50 Hz (Europe), edit the confidence level if needed, check the box Boost mode (beta), and click OK to run with the default parameters since the EEG signals from the sample dataset are not preprocessed.
NOTE: the confidence level to detect heart components is set to 80% by default, which may be too low or too high for some datasets. Increasing this value will increase the chances of detecting heart components but decrease the reliability of that detection. The Boost mode (beta) is optional and aims to improve classification performance by smearing the heart signal into the EEG signals. - A warning message will appear, asking for confirmation to remove the extra PPG channel that has been detected. This is to be expected since the toolbox is not designed to analyze both ECG and PPG simultaneously (or other auxiliary channels) and keeping it in the dataset will lead to serious errors (e.g., artifact removal, poor ICA decomposition, etc.). Click Yes.
- The ECG signal is bandpass-filtered to remove slow frequency drifts below 1 Hz and high-frequency noise above 20 Hz (with a noncausal zero-phase FIR filter). Preprocess the EEG signals as in step 3.4.
- Perform independent component analysis (ICA) using the preconditioned ICA for real data algorithm (PICARD). To change this option, choose the standard Infomax algorithm or modified Infomax algorithm for replication from the GUI in step 4.3 . Then, classify the independent components automatically with ICLabel. If a component is classified as a heart component with 80% confidence, it is, by default, detected and extracted automatically from the EEG data.
- Keep the box Visualize outputs in the first main GUI (step 4.2.) to visualize the scalp topography of the removed component (Figure 17 Left) and the final EEG time series (in blue, Figure 17 Right) after extracting the heart component (in red, Figure 17 Right).
NOTE: the ECG channel is preserved for visualization to confirm the extraction of ECG-related components, but it is removed after this step since it no longer contains any relevant information. - For advanced users, perform these steps using the following command lines:
eeglab; close; % Launch EEGLAB without the GUI
main_path = fileparts(which('eegplugin_BrainBeats.m')); cd(main_path);
EEG = pop_loadset('filename','dataset.set','filepath',
fullfile(main_path, 'sample_data'));
EEG = brainbeats_process(EEG,'analysis','rm_heart',
'heart_signal','ECG', ...
'heart_channels',{'ECG'},'clean_eeg',true,'vis_cleaning',false,...
'conf_thresh',.8,'boost',true);
Results
First, the BrainBeats plugin was used to preprocess EEG and ECG data, identify and remove artifacts, and analyze heartbeat-evoked potentials (HEP) and oscillations (HEO). BrainBeats successfully detected the RR intervals from the ECG signal and some RR artifacts (Figure 2). BrainBeats also reported in the command window that 11/305 (3.61%) of the heartbeats were flagged as artifacts and interpolated. The average signal quality index (SQI) of the RR intervals (before interpolation) has a valu...
Discussion
Critical steps in the protocol
Critical steps are described in steps 1.1-1.4. Warnings and error messages are implemented at various places in the toolbox to help users understand why they may encounter issues (e.g., electrode locations not loaded in the EEG data, file length being too short for calculating a reliable measure of ultra-low frequency HRV, signal quality being too low for any reliable analysis, etc.). Each function is documented for advanced users, and the parameters can be easily fin...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The Institute of Noetic Sciences supported this research. We thank the developers of the original open-source algorithms that were adapted to develop some of BrainBeats' algorithms.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| EEGLAB | Swartz Center for Computational Neuroscience (SCCN) | Free/Open-source | |
| MATLAB | The Mathworks, Inc. | Requires a license | |
| Windows PC | Lenovo, Inc. |
References
- von Bertalanffy, L. . General system theory Foundations, development, applications. , (1968).
- Hodgkin, A. L., Huxley, A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 117 (4), 500-544 (1952).
- Bean, B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U SA. 81 (20), 6388-6392 (1984).
- Fuchs, T. . Ecology of the brain: The phenomenology and biology of the embodied mind. , (2017).
- Napadow, V., et al. Brain correlates of autonomic modulation: Combining heart rate variability with fMRI. NeuroImage. 42 (1), 169-177 (2008).
- Chang, C., Cunningham, J. P., Glover, G. H. Influence of heart rate on the BOLD signal: The cardiac response function. NeuroImage. 44 (3), 857-869 (2009).
- Gianaros, P. J., Sheu, L. K. A review of neuroimaging studies of stressor-evoked blood pressure reactivity: Emerging evidence for a brain-body pathway to coronary heart disease risk. NeuroImage. 47 (3), 922-936 (2009).
- Burch, G. E., DePasquale, N. P. . A history of electrocardiography. No 1. , (1990).
- Allen, J. Photoplethysmography and its application in clinical physiological measurement. Physiol Meas. 28 (3), 1 (2007).
- Cohen, M. X. Where does EEG come from and what does it mean. Trends Neurosci. 40 (4), 208-218 (2017).
- Cannard, C., Brandmeyer, T., Wahbeh, H., Delorme, A. Self-health monitoring and wearable neurotechnologies. Handb Clin Neurol. 168, 207-232 (2020).
- Gramann, K., Ferris, D. P., Gwin, J., Makeig, S. Imaging natural cognition in action. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 91 (1), 22-29 (2014).
- Jungnickel, E., Gehrke, L., Klug, M., Gramann, K. Chapter 10 - MoBI-Mobile brain/body imaging. Neuroergonomics. , 59-63 (2019).
- Al, E., et al. Heart-brain interactions shape somatosensory perception and evoked potentials. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 117 (19), 10575-10584 (2020).
- Banellis, L., Cruse, D. Skipping a beat: Heartbeat-evoked potentials reflect predictions during interoceptive-exteroceptive integration. Cereb Cortex Commun. 1 (1), (2020).
- Baranauskas, M., Grabauskaitė, A., Griškova-Bulanova, I., Lataitytė-Šimkevičienė, B., Stanikūnas, R. Heartbeat evoked potentials (HEP) capture brain activity affecting subsequent heartbeat. Biomed Signal Process. Cont. 68, 102731 (2021).
- Candia-Rivera, D., et al. Neural responses to heartbeats detect residual signs of consciousness during resting state in postcomatose patients. J Neurosci. 41 (24), 5251-5262 (2021).
- Jiang, H., et al. Brain-heart interactions underlying traditional Tibetan buddhist meditation. Cereb cortex. 30 (2), 439-450 (2020).
- Kumral, D., et al. Attenuation of the heartbeat-evoked potential in patients with atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 8 (10), 1219-1230 (2022).
- Thakor, N. V., Tong, S. Advances in quantitative electroencephalogram analysis methods. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 6, 453-495 (2004).
- Thayer, J. F., Åhs, F., Fredrikson, M., Sollers, J. J., Wager, T. D. A meta-analysis of heart rate variability and neuroimaging studies: Implications for heart rate variability as a marker of stress and health. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 36 (2), 747-756 (2012).
- Mather, M., Thayer, J. F. How heart rate variability affects emotion regulation brain networks. Curr Opin Beha. Sci. 19, 98-104 (2018).
- Kemp, A. H., Quintana, D. S. The relationship between mental and physical health: Insights from the study of heart rate variability. Int J Psychophysiol. 89 (3), 288-296 (2013).
- Daneshi Kohan, M., Motie Nasrabadi, A., Shamsollahi, M. B., Sharifi, A. EEG/PPG effective connectivity fusion for analyzing deception in interview. Signal Image Video Process. 14 (5), 907-914 (2020).
- Übeyli, E. D., Cvetkovic, D., Cosic, I. Analysis of human PPG, ECG and EEG signals by eigenvector methods. Digit Signal Process. 20 (3), 956-963 (2010).
- Zambrana-Vinaroz, D., Vicente-Samper, J. M., Manrique-Cordoba, J., Sabater-Navarro, J. M. Wearable epileptic seizure prediction system based on machine learning techniques using ECG, PPG and EEG signals. Sensors. 22 (23), 9372 (2022).
- Shaffer, F., Ginsberg, J. P. An overview of heart rate variability metrics and norms. Front Public Health. 5, 258 (2017).
- Coan, J. A., Allen, J. J. B. The state and trait nature of frontal EEG asymmetry in emotion. The asymmetrical brain. , 565-615 (2003).
- Hagemann, D., Hewig, J., Seifert, J., Naumann, E., Bartussek, D. The latent state-trait structure of resting EEG asymmetry: replication and extension. Psychophysiology. 42 (6), 740-752 (2005).
- Widge, A. S., et al. Electroencephalographic biomarkers for treatment response prediction in major depressive illness: A meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 176 (1), 44-56 (2019).
- Olbrich, S., Arns, M. EEG biomarkers in major depressive disorder: Discriminative power and prediction of treatment response. Int Rev Psychiatry. 25 (5), 604-618 (2013).
- Kumar, Y., Dewal, M. L., Anand, R. S. Epileptic seizures detection in EEG using DWT-based ApEn and artificial neural network. Signal Image Video Process. 8, 1323-1334 (2014).
- Acharya, U. R., et al. Automated diagnosis of epileptic EEG using entropies. Biomed Signal Process Control. 7 (4), 401-408 (2012).
- de Aguiar Neto, F. S., Rosa, J. L. G. Depression biomarkers using non-invasive EEG: A review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 105, 83-93 (2019).
- Cannard, C., Wahbeh, H., Delorme, A. Electroencephalography correlates of well-being using a low-cost wearable system. Front Hum Neurosci. 15, 736 (2021).
- Tarvainen, M. P., Niskanen, J. P., Lipponen, J. A., Ranta-aho, P. O., Karjalainen, P. A. Kubios HRV - Heart rate variability analysis software. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 113 (1), 210-220 (2014).
- Demski, A. J., Soria, M. L. ECG-kit: a Matlab toolbox for cardiovascular signal processing. Journal of Open Research Software. 4 (1), e8 (2016).
- Klug, M., et al. The BeMoBIL pipeline for automated analyses of multimodal mobile brain and body imaging data. BioRxiv. , (2022).
- Perakakis, P. . HEPLAB. , (2023).
- Grosselin, F., Navarro-Sune, X., Raux, M., Similowski, T., Chavez, M. CARE-rCortex: A Matlab toolbox for the analysis of CArdio-REspiratory-related activity in the Cortex. J Neurosci Meth. 308, 309-316 (2018).
- Luck, S. J., Gaspelin, N. How to get statistically significant effects in any ERP experiment (and why you shouldn't). Psychophysiology. 54 (1), 146-157 (2017).
- Alday, P. M. How much baseline correction do we need in ERP research? Extended GLM model can replace baseline correction while lifting its limits. Psychophysiology. 56 (12), e13451 (2019).
- Delorme, A. EEG is better left alone. Sci Rep. 13 (1), 2372 (2023).
- Widmann, A., Schröger, E., Maess, B. Digital filter design for electrophysiological data - a practical approach. J Neurosci Methods. 250, 34-46 (2015).
- Pham, T., Lau, Z. J., Chen, S. H. A., Makowski, D. Heart Rate Variability in Psychology: A Review of HRV Indices and an Analysis Tutorial. Sensors. 21 (12), 3998 (2021).
- Vest, A. N., et al. An open source benchmarked toolbox for cardiovascular waveform and interval analysis. Physiol Meas. 39 (10), 105004 (2018).
- Smith, E. E., Reznik, S. J., Stewart, J. L., Allen, J. J. B. Assessing and conceptualizing frontal EEG asymmetry: An updated primer on recording, processing, analyzing, and interpreting frontal alpha asymmetry. Int J Psychophysiol Off J Int Organ Psychophysiol. 111, 98-114 (2017).
- Dong, L., et al. MATLAB toolboxes for reference electrode standardization technique (REST) of scalp EEG. Front Neurosci. 11, 601 (2017).
- Candia-Rivera, D., Catrambone, V., Valenza, G. The role of electroencephalography electrical reference in the assessment of functional brain-heart interplay: From methodology to user guidelines. J Neurosci Methods. 360, 109269 (2021).
- Mullen, T. R., et al. Real-time Neuroimaging and cognitive monitoring using wearable dry EEG. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng Spec Issue Wearable Technol. 62 (11), 2553-2567 (2015).
- Chang, C. Y., Hsu, S. H., Pion-Tonachini, L., Jung, T. P. Evaluation of artifact subspace reconstruction for automatic EEG artifact removal. 40th Ann Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. , 1242-1245 (2018).
- Miyakoshi, M. Artifact subspace reconstruction: a candidate for a dream solution for EEG studies, sleep or awake. Sleep. 46 (12), 241 (2023).
- Kim, H., et al. ICA's bug: How ghost ICs emerge from effective rank deficiency caused by EEG electrode interpolation and incorrect re-referencing. Front Signal Process. 3, 1064138 (2023).
- Frank, G., Makeig, S., Delorme, A. A Framework to evaluate independent component analysis applied to EEG signal: testing on the Picard algorithm. ArXiv. , (2022).
- Ablin, P., Cardoso, J. F., Gramfort, A. Faster independent component analysis by preconditioning with Hessian approximations. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 66 (15), 4040-4049 (2018).
- Pion-Tonachini, L., Kreutz-Delgado, K., Makeig, S. ICLabel: An automated electroencephalographic independent component classifier, dataset, and website. NeuroImage. 198, 181-197 (2019).
- Bigdely-Shamlo, N., Mullen, T., Kothe, C., Su, K. M., Robbins, K. A. The PREP pipeline: standardized preprocessing for large-scale EEG analysis. Front Neuroinformatics. 9, 12 (2015).
- Maris, E., Oostenveld, R. Nonparametric statistical testing of EEG- and MEG-data. J Neurosci Methods. 164 (1), 177-190 (2007).
- Pernet, C. R., Latinus, M., Nichols, T. E., Rousselet, G. A. Cluster-based computational methods for mass univariate analyses of event-related brain potentials/fields: A simulation study. J Neurosci Methods. 250, 85-93 (2015).
- Pernet, C. R., Chauveau, N., Gaspar, C., Rousselet, G. A. LIMO EEG: A toolbox for hierarchical LInear MOdeling of ElectroEncephaloGraphic data. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2011, 1-11 (2011).
- Pernet, C., et al. Electroencephalography robust statistical linear modelling using a single weight per trial. Aperture Neuro. 2022 (7), 51 (2022).
- Pavlov, Y. G., Kasanov, D., Kosachenko, A. I., Kotyusov, A. I., Busch, N. A. Pupillometry and electroencephalography in the digit span task. Sci. Data. 9 (1), 325 (2022).
- Pavlov, Y. G., Kasanov, D., Kosachenko, A. I., Kotyusov, A. I. EEG, pupillometry, ECG and photoplethysmography, and behavioral data in the digit span task and rest. OpenNeuro. , (2024).
- Clifford, G. . Signal processing methods for heart rate variability. , (2002).
- Pan, J., Tompkins, W. J. A real-time QRS detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 3, 230-236 (1985).
- Maess, B., Schröger, E., Widmann, A. Highpass filters and baseline correction in M/EEG analysis. Commentary on: "How inappropriate highpass filters can produce artefacts and incorrect conclusions in ERP studies of language and cognition. J. Neurosci. Methods. 266, 164-165 (2016).
- Park, H. D., Blanke, O. Heartbeat-evoked cortical responses: Underlying mechanisms, functional roles, and methodological considerations. NeuroImage. 197, 502-511 (2019).
- Lomb, N. R. Least-squares frequency analysis of unequally spaced data. Astrophys Space Sci. 39, 447-462 (1976).
- Corcoran, A. W., Alday, P. M., Schlesewsky, M., Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, I. Toward a reliable, automated method of individual alpha frequency (IAF) quantification. Psychophysiology. 55 (7), e13064 (2018).
- Chen, W., Zhuang, J., Yu, W., Wang, Z. Measuring complexity using FuzzyEn, ApEn, and SampEn. Med Eng Phys. 31 (1), 61-68 (2009).
- Cannard, C., Delorme, A. . An open-source EEGLAB plugin for computing entropy-based measures on MEEG signals. , (2022).
- Lau, Z. J., Pham, T., Chen, S. H. A., Makowski, D. Brain entropy, fractal dimensions and predictability: A review of complexity measures for EEG in healthy and neuropsychiatric populations. Eur J Neurosci. 56 (7), 5047-5069 (2022).
- Costa, M., Goldberger, A. L., Peng, C. -. K. Multiscale entropy analysis of biological signals. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 71 (2), 021906 (2005).
- Humeau-Heurtier, A. multiscale entropy approaches and their applications. Entropy. 22 (6), 644 (2020).
- Armañac-Julián, P., et al. Reliability of pulse photoplethysmography sensors: Coverage using different setups and body locations. Front Electron. 3, 906324 (2022).
- Catrambone, V., Greco, A., Vanello, N., Scilingo, E. P., Valenza, G. Time-resolved directional brain-heart interplay measurement through synthetic data generation models. Ann Biomed Eng. 47, 1479-1489 (2019).
- Georgieva-Tsaneva, G., Gospodinova, E., Gospodinov, M., Cheshmedzhiev, K. Portable sensor system for registration, processing and mathematical analysis of PPG signals. Appl Sci. 10 (3), 1051 (2020).
- Kim, J. H., Park, S. E., Jeung, G. W., Kim, K. S. Detection of R-peaks in ECG signal by adaptive linear neuron (ADALINE) artificial neural network. MATEC Web Conf. 54, 10001 (2016).
- Lei, R., Ling, B. W. K., Feng, P., Chen, J. Estimation of heart rate and respiratory rate from PPG signal using complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition with both independent component analysis and non-negative matrix factorization. Sensors. 20 (11), 3238 (2020).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved