A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing of Rat Embryos using Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) and 2-Cell Embryo Electroporation
In This Article
Summary
This protocol presents an optimized approach for producing genetically modified rat models. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is used to deliver a DNA repair template, and electroporation is used to deliver CRISPR-Cas9 reagents to complete the genome editing process in 2-cell embryo.
Abstract
Genome editing technology is widely used to produce genetically modified animals, including rats. Cytoplasmic or pronuclear injection of DNA repair templates and CRISPR-Cas reagents is the most common delivery method into embryos. However, this type of micromanipulation necessitates access to specialized equipment, is laborious, and requires a certain level of technical skill. Moreover, microinjection techniques often result in lower embryo survival due to the mechanical stress on the embryo. In this protocol, we developed an optimized method to deliver large DNA repair templates to work in conjunction with CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing without the need for microinjection. This protocol combines AAV-mediated DNA delivery of single-stranded DNA donor templates along with the delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) by electroporation to modify 2-cell embryos. Using this novel strategy, we have successfully produced targeted knock-in rat models carrying insertion of DNA sequences from 1.2 to 3.0 kb in size with efficiencies between 42% and 90%.
Introduction
The development of CRISPR-based genome editing tools has accelerated our ability to efficiently generate new and more sophisticated genetically engineered rat models. Single-guide RNA, along with Cas9 nuclease, is combined to form Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes that target DNA sequences of interest within the genome and result in double-stranded DNA breaks. Because cellular DNA repair mechanisms are error-prone, insertions and deletions (INDELs) are introduced during the repair process that can disrupt a target gene's function. When there is co-delivery of a desired engineered DNA sequence (repair template) along with genome editing reagents, insertion of the repair template in the region containing the double-stranded DNA break occurs through a process called homology-directed repair (HDR). This is an effective strategy for generating animal models with targeted DNA insertions/substitutions (knock-ins). One limitation is that knock-in sequences are often large in size, which has been shown to reduce gene editing efficiency, thus making generating the desired model more difficult1. Strategies to increase knock-in efficiencies have included linearization of both double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) repair templates and chemical modification of DNA repair templates2,3,4. In addition, pronuclear microinjection along with HDR stimulating compounds, application of electrical pulses in conjunction with microinjection, and timed microinjection into 2-cell embryos have all been attempted5,6,7. Despite the success of some of these approaches, the incorporation of DNA sequences larger than 1.0 kb remains technically challenging.
Electroporation, which is a common method for introducing reagents into cultured cell lines, offers an alternative to microinjection for delivering CRISPR-Cas9 components into embryos. Embryo electroporation, first demonstrated in rat embryos8, has since been successfully used as a delivery method in mice9,10,11,12,13, pigs14,15, and other animal model organisms16,17,18. Embryos, suspended in the medium containing CRISPR-Cas9 reagents, are placed into a cuvette or onto a glass slide between two electrodes and subjected to direct pulses of electrical currents. This creates transient openings in the zona pellucida and embryo plasma membrane through which the CRISPR-Cas9 components enter the embryos. Typically, mid-level electrical "poring" pulses are used to create the temporary openings followed by lower level electrical "transfer pulses" that facilitate movement of the negatively charged genome editing components. Embryo electroporation is efficient, has a high throughput, and is easy to perform. However, while embryo electroporation has been shown to be highly successful for the introduction of small (<200 bp) ssDNA repair templates, there are few reports of successful electroporation of larger (>1.0 kb) repair templates13,19. This size restriction represents a major limitation of embryo electroporation for generating knock-in animal models requiring large insertions.
In the context of gene therapy, adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) have long been used as vehicles to deliver genetic material due to their efficient in vivo infectivity of both dividing and non-dividing cells, lack of pathogenicity, and rare genomic integration20,21. Recently, more studies have combined AAVs with CRISPR-Cas9 technology to introduce DNA repair templates and CRISPR reagents22,23,24. This approach allows delivery of larger DNA repair templates without the need for microinjection techniques.
The HDR pathway is more active in the late S and G2 phases of the cell cycle25,26. In studies performed in vitro, significant increases in knock-in efficiency were achieved by delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 RNPs and DNA repair templates into G2-synchronized cells or by restriction of the presence of Cas9 protein to late S and G2 phases using a Cas9-Geminin fusion protein2. Moreover, there is a major zygotic genome activation (ZGA) event which occurs during the extended G2 phase of the 2-cell stage embryo, and this is associated with an open chromatin state. It is speculated that this provides the CRISPR-Cas9 RNPs and repair templates with greater accessibility to the genomic DNA.
Our goal was to build on all these observations, by combining the AAV approach with embryo electroporation to introduce CRISPR-Cas9 RNPs at the 2-cell stage of embryo development. This strategy takes advantage of the larger DNA repair template delivery capacity of AAV, the technical ease of electroporation and the more optimal 2-cell time point for genomic accessibility during embryo development to create an efficient method for targeted genetic engineering of DNA insertions. As highlighted in this protocol, our optimized method allows for the production of targeted knock-in rat models carrying insertions of DNA sequences from 1.2 to 3.0 kb in size without the need for microinjection techniques.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All experimental procedures were approved by the University of Missouri's Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (ACUC protocol #25580) and were performed according to the guidelines set forth in the Guide for the Use and Care of Laboratory Animals.
1. AAV-mediated DNA repair template delivery
- Design the DNA construct to contain the desired knock-in sequence in between two homology arms. Typical homology arm lengths are 300-500 bp in length. Ensure that the entire DNA repair template (homology arms + desired knock-in sequence) is flanked by inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) by cloning into an appropriate plasmid backbone and packaging into recombinant ssAAV1 or ssAAV6 (serotypes 1 or 6).
NOTE: If the sgRNA target sequence is present in the DNA repair template, it is important to engineer silent mutations to disrupt this sequence thus preventing CRISPR-Cas9 mediated editing of the correctly targeted allele.
CAUTION: Recombinant AAV viral vectors are non-integrating and classified as BSL-1. Standard aseptic techniques are used for pipetting and handling embryos that have been exposed to virus. - Add engineered ssAAV1 or ssAAV6 (packaged with DNA repair template) to 30 µL of KSOM-R media27,28 to a final concentration of 3 × 107 genome copies (GC)/µL under mineral oil in 35 mm Petri dish.
- Place zygotes with visible pronuclei into the KSOM-R media containing engineered ssAAV.
NOTE: Using this protocol there is no need to thin the zona pellucida as AAV serotypes 1 and 6 are able to readily pass through for efficient DNA repair template delivery. - Incubate at 37 °C with 5% CO2 and maximal humidity for 18-20 h to allow for sufficient viral transduction.
2. Electroporation preparation
- On the following day, make an electroporation mixture containing 100 ng/µL of sgRNA and 100 ng/µL of Cas9 protein diluted in Opti-MEM media in a sterile RNase-free tube. Gently mix.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 min to allow for RNP formation.
- During the incubation time, turn on the electroporator and connect leads to a 1.5 mm gap glass slide electrode.
- Set electroporation parameters as described in Table 1.
3. 2-cell embryo electroporation
- Gently pipette 5 µL of the CRISPR electroporation mixture between the two electrodes on the glass slide taking care not to introduce air bubbles to the solution.
- Remove the 2-cell stage embryo from the AAV solution. Line up 2-cell stage embryos in the mixture without allowing them to touch the sides of the electrodes. This is done to avoid lysis.
- Press the Ohm button to measure the impedance. Check to ensure impedance is between 0.100 and 0.300 kΩ. The reaction volume will alter the impedance (add volume to decrease impedance and subtract volume to increase impedance).
- Press Start. The process takes few seconds to complete.
- Remove embryos immediately following the electroporation and wash 3 times in fresh 30 µL drops of KSOM-R media.
- Place embryos back in 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2 and maximal humidity for in vitro culture in 500 µL drops of KSOM-R media under mineral oil. Alternatively, surgically transfer embryos to a 1.5-day post coitum (dpc) pseudopregnant female rat to produce live offspring.
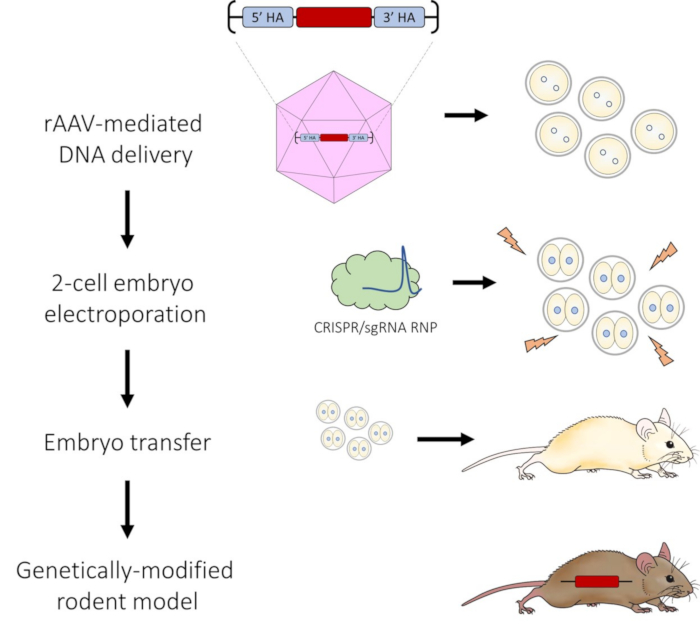
Figure 1: Schematic of AAV-mediated DNA delivery and 2-cell embryo electroporation pipeline for CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Following the protocol, there is effective AAV-mediated delivery of the DNA repair template allowing for highly efficient HDR after 2-cell embryos are electroporated with CRISPR-Cas9 RNPs. As shown in the video, a successful electroporation process results in bubbles forming on each electrode (Figure 2C) and the impedance remaining within the range of 0.100 and 0.300 kΩ. After electroporation it is not uncommon for embryos to swell filling the perivitelline...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The CRISPR-Cas genome editing system has revolutionized the field of genetic engineering by allowing the efficient production of both straightforward and complex, customized genetic modifications in a variety of animal species. Frequent refinements and improvements in techniques associated with genome editing further its versatility. Here we have described a new approach using ssAAV-mediated DNA delivery along with 2-cell embryo electroporation of CRISPR-Cas9 reagents into 2-cell rodent embryos. We have demonstrated that...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Nolan Davis for assistance with videography and video editing.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Leads with alligator clips for electrodes | NepaGene | C117 | |
| Mineral oil | MilliporeSigma | M5310 | |
| NepaGene21 Super Electroporator | NepaGene | NEPA21 | |
| Platinum plate electrodes on slide glass | NepaGene | CUY501P1-1.5 | |
| PURedit Cas9 Protein | MilliporeSigma | PECAS9 | |
| sgRNA (chemically-modified) | Synthego | N/A | |
| ssAAV1 or ssAAV6 packaged DNA repair template | Vectorbuilder | N/A |
References
- Lau, C. H., Tin, C., Suh, Y. CRISPR-based strategies for targeted transgene knock-in and gene correction. Fac Rev. 9, 20(2020).
- Gutschner, T., Haemmerle, M., Genovese, G., Draetta, G. F., Chin, L. Post-translational Regulation of Cas9 during G1 Enhances Homology-Directed Repair. Cell Rep. 14 (6), 1555-1566 (2016).
- Zhang, J. P., et al. Efficient precise knockin with a double cut HDR donor after CRISPR/Cas9-mediated double-stranded DNA cleavage. Genome Biol. 18 (1), 35(2017).
- Miura, H., Quadros, R. M., Gurumurthy, C. B., Ohtsuka, M. Easi-CRISPR for creating knock-in and conditional knockout mouse models using long ssDNA donors. Nat Protoc. 13 (1), 195-215 (2018).
- Gu, B., Posfai, E., Gertsenstein, M., Rossant, J. Efficient generation of large-fragment knock-in mouse models using 2-cell (2C)-homologous recombination (HR)-CRISPR. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 10 (1), e67(2020).
- Gu, B., Posfai, E., Rossant, J. Efficient generation of targeted large insertions by microinjection into two-cell-stage mouse embryos. Nat Biotechnol. 36 (7), 632-637 (2018).
- Kurihara, T., et al. DNA repair protein RAD51 enhances the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knock-in efficiency in brain neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 524 (3), 621-628 (2020).
- Kaneko, T., Sakuma, T., Yamamoto, T., Mashimo, T. Simple knockout by electroporation of engineered endonucleases into intact rat embryos. Sci Rep. 4, 6382(2014).
- Chen, S., Lee, B., Lee, A. Y., Modzelewski, A. J., He, L. Highly efficient mouse genome editing by CRISPR ribonucleoprotein electroporation of zygotes. J Biol Chem. 291 (28), 14457-14467 (2016).
- Hashimoto, M., Yamashita, Y., Takemoto, T. Electroporation of Cas9 protein/sgRNA into early pronuclear zygotes generates non-mosaic mutants in the mouse. Dev Biol. 418 (1), 1-9 (2016).
- Wang, W., et al. Delivery of Cas9 protein into mouse zygotes through a series of electroporation dramatically increases the efficiency of model creation. J Genet Genomics. 43 (5), 319-327 (2016).
- Troder, S. E., et al. An optimized electroporation approach for efficient CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in murine zygotes. PLoS One. 13 (5), e0196891(2018).
- Teixeira, M., et al. Electroporation of mice zygotes with dual guide RNA/Cas9 complexes for simple and efficient cloning-free genome editing. Sci Rep. 8 (1), 474(2018).
- Tanihara, F., et al. Efficient generation of GGTA1-deficient pigs by electroporation of the CRISPR/Cas9 system into in vitro-fertilized zygotes. BMC Biotechnol. 20 (1), 40(2020).
- Tanihara, F., et al. Generation of CD163-edited pig via electroporation of the CRISPR/Cas9 system into porcine in vitro-fertilized zygotes. Anim Biotechnol. 32 (2), 147-154 (2021).
- Camargo, L. S. A., Owen, J. R., Van Eenennaam, A. L., Ross, P. J. Efficient one-step knockout by electroporation of ribonucleoproteins into zona-intact bovine embryos. Front Genet. 11, 570069(2020).
- Lin, J. C., Van Eenennaam, A. L. Electroporation-mediated genome editing of livestock zygotes. Front Genet. 12, 648482(2021).
- Betters, E., Charney, R. M., Garcia-Castro, M. I. Electroporation and in vitro culture of early rabbit embryos. Data Brief. 21, 316-320 (2018).
- Miyasaka, Y., et al. CLICK: one-step generation of conditional knockout mice. BMC Genomics. 19 (1), 318(2018).
- Epstein, B. E., Schaffer, D. V. Combining engineered nucleases with adeno-associated viral vectors for therapeutic gene editing. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1016, 29-42 (2017).
- Gaj, T., Epstein, B. E., Schaffer, D. V. Genome engineering using adeno-associated virus: basic and clinical research applications. Mol Ther. 24 (3), 458-464 (2016).
- Chen, S., et al. CRISPR-READI: Efficient generation of knockin mice by CRISPR RNP electroporation and AAV donor infection. Cell Rep. 27 (13), 3780-3789 (2019).
- Mizuno, N., et al. Intra-embryo gene cassette knockin by CRISPR/CAS9-mediated genome editing with adeno-associated viral vector. iScience. 9, 286-297 (2018).
- Davis, D. J., et al. Efficient DNA knock-in using AAV-mediated delivery with 2-cell embryo CRISPR-Cas9 electroporation. Front Genome Ed. 5, 1256451(2023).
- Smirnikhina, S. A., Zaynitdinova, M. I., Sergeeva, V. A., Lavrov, A. V. Improving homology-directed repair in genome editing experiments by influencing the cell cycle. Int J Mol Sci. 23 (11), (2022).
- Takata, M., et al. Homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining pathways of DNA double-strand break repair have overlapping roles in the maintenance of chromosomal integrity in vertebrate cells. EMBO J. 17 (18), 5497-5508 (1998).
- Men, H., Stone, B. J., Bryda, E. C. Media optimization to promote rat embryonic development to the blastocyst stage in vitro. Theriogenology. 151, 81-85 (2020).
- Men, H., Amos-Landgraf, J. M., Bryda, E. C., Franklin, C. L. KSOM-R supports both mouse and rat preimplantation embryo development in vitro. Theriogenology. 198, 69-74 (2023).
- Romeo, C., et al. AAV diffuses across zona pellucida for effortless gene delivery to fertilized eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 526 (1), 85-90 (2020).
- Fulka, J., Moor, R. M., Fulka, J. Electrofusion of mammalian oocytes and embryonic cells. Methods Mol Biol. 48, 309-316 (1995).
- Rems, L., et al. Cell electrofusion using nanosecond electric pulses. Sci Rep. 3, 3382(2013).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved