腹部考试四: 急性腹痛评估
Overview
来源:约瑟夫 Donroe,MD,内科和儿科,耶鲁大学医学院临床医学专业,纽黑文,康涅狄格
腹痛是在急诊科和办公室设置一个频繁呈现问题。急性腹痛被指疼痛持续少于 7 天,虽然急腹症被指严重腹痛起病与建议手术 intervenable 过程的特点。急性腹痛的鉴别诊断是宽;因此,临床医师必须有一个系统方法的检查指导下仔细询问病史,记住在腹腔外的病理也会引起腹痛,包括肺、 心脏、 直肠和生殖器疾病。
术语用于描述的腹部压痛位置包括右边和左边的上部和下部象限和上腹部,脐,和下腹部区域 (数字 1,2)。彻底检查需要有组织的方式,涉及检查、 听诊、 打击乐,触诊,有目的地执行每个机动与解剖明确心理表征。而不是整个腹部触诊随机,开始从温柔,系统地朝着招标区域,并思考下面手指在每个位置是什么样的网站远程触诊。有用的技巧是想象与剑突的钟面在 12:00 和耻骨联合在 6:00 (图 3)。触诊在 8:00,还有皮肤、 肌肉、 盲肠、 阑尾,输尿管。以这种方式执行考试协助临床推理和缺少病理学的机会减到最小。
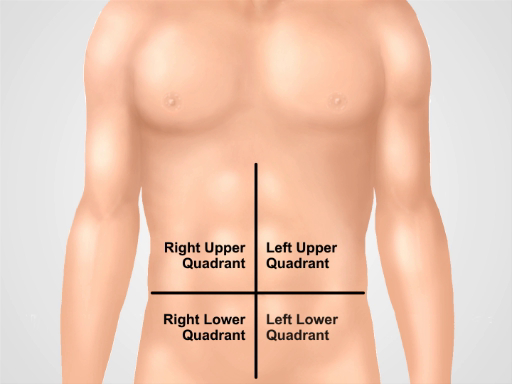
图 1。四个腹部象限。腹部可以分为四个区域由两个假想线相交,脐。右上象限 (通常指定为 RUQ),在离开上象限 (呵呵),右下腹 (RLQ) 和左的下腹 (时延) 显示。
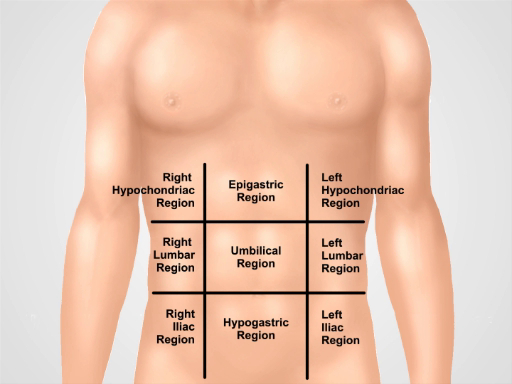
图 2。九的腹部地区。锁骨线和肋和结节间面分成九个区域的腹部: 上腹部的区域、 右胁、 左胁区域、 脐区、 腰椎右侧区域、 左的腰部,下腹、 右腹股沟和左腹股沟区。
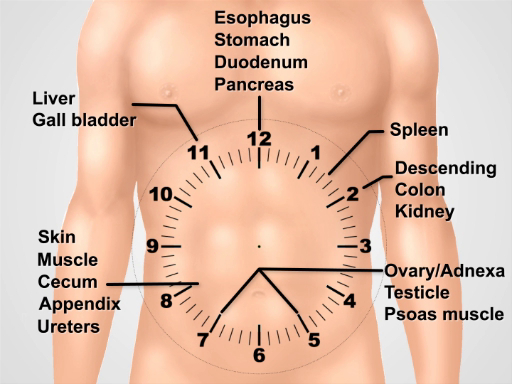
图 3。在下腹部为执行考试时的基本解剖思考可视化钟面。
Procedure
1.编制
- 洗你的手,温暖他们在检查病人之前。
- 有病人穿上一件长袍。额外的悬垂有必要遮住下身。
- 开头在病人仰卧在床或考试表上。
2.急性腹痛的探讨
- 拥有一套完整的生命体征开始测试。
- 进了房间,立即开始仔细检查。腹膜炎患者可能会更喜欢静静地躺着弯曲的臀部和膝盖。
- 置于病人的下半身至耻骨联合的悬垂性和提高外衣刚好乳房。请注意腹胀、 皮肤颜色、 标志灌流不足,如斑块,可见脉动或蠕动,凸出,和疤痕。
- 如果病人是警报,要求患者用一根手指指向痛苦的区域。要求患者咳嗽 (咳嗽测试) 或者轻轻地撞床,可以本地化腹膜炎的痛苦。
- 听诊左的下腹横膈膜用光压。无肠声音可能表明肠梗阻,虽然高音调的声音表明即将发生机械性肠梗阻。听诊有腹部疼痛的诊断演习的最低产量。
- 在任何鼓鼓的地区,以评估为肠管听诊。
- 继续使用听诊器团长同时继续听诊触诊毕业压力下,四个象限。观察
Application and Summary
Tags
跳至...
此集合中的视频:

Now Playing
腹部考试四: 急性腹痛评估
Physical Examinations II
67.3K Views

眼科检查
Physical Examinations II
77.3K Views

眼底检查
Physical Examinations II
68.1K Views

耳朵考试
Physical Examinations II
55.3K Views

鼻子、 鼻窦、 口腔和咽部考试
Physical Examinations II
65.9K Views

甲状腺考试
Physical Examinations II
105.2K Views

淋巴结考试
Physical Examinations II
387.9K Views

腹部考试 i: 检查和听诊
Physical Examinations II
202.8K Views

腹部考试 II: 打击乐
Physical Examinations II
248.4K Views

腹部考试 III: 触诊
Physical Examinations II
138.6K Views

男性直肠检查
Physical Examinations II
114.7K Views

全面的乳房检查
Physical Examinations II
87.8K Views

外生殖器的盆腔检查 i: 评估
Physical Examinations II
307.9K Views

骨盆 II: 窥镜考试成绩
Physical Examinations II
150.6K Views

盆腔检查三: 双手和直肠阴道考试
Physical Examinations II
147.9K Views
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。