Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Method Article
Métodos basados en imágenes para estudiar los eventos de tráfico de membrana en células de linaje estomática
En este artículo
Resumen
Aquí se introducen varios métodos de uso común para estudiar los eventos de tráfico de membrana de una quinasa receptora de membrana plasmática. Este manuscrito describe protocolos detallados que incluyen la preparación del material vegetal, el tratamiento farmacológico y la configuración de imágenes confocales.
Resumen
En las células eucariotas, los componentes de la membrana, incluidas las proteínas y los lípidos, se transportan espacio-temporalmente a su destino dentro del sistema de endomembranas. Esto incluye el transporte secretor de proteínas recién sintetizadas a la superficie celular o al exterior de la célula, el transporte endocítico de cargas extracelulares o componentes de la membrana plasmática dentro de la célula, y el transporte de reciclaje o transporte de cargas entre los orgánulos subcelulares, etc. Los eventos de tráfico de membrana son cruciales para el desarrollo, el crecimiento y la adaptación ambiental de todas las células eucariotas y, por lo tanto, están sujetos a una estricta regulación. Las quinasas receptoras de la superficie celular, que perciben las señales de ligandos del espacio extracelular, experimentan tanto el transporte secretor como el endocítico. Aquí se describen los enfoques comúnmente utilizados para estudiar los eventos de tráfico de membrana utilizando una quinasa receptora de repetición rica en leucina localizada en la membrana plasmática, ERL1. Los enfoques incluyen la preparación del material vegetal, el tratamiento farmacológico y la configuración de imágenes confocal. Para monitorizar la regulación espacio-temporal de ERL1, en este estudio se describe el análisis de colocalización entre ERL1 y una proteína marcador corporal multivesicular, RFP-Ara7, el análisis de series temporales de estas dos proteínas y el análisis de la pila z de ERL1-YFP tratada con los inhibidores del tráfico de membrana brefeldina A y wortmannina.
Introducción
El tráfico de membrana es un proceso celular conservado que distribuye los componentes de la membrana (también conocidos como cargas), incluidas proteínas, lípidos y otros productos biológicos, entre diferentes orgánulos dentro de una célula eucariota o a través de la membrana plasmática hacia y desdeel espacio extracelular. Este proceso es facilitado por una colección de membranas y orgánulos denominada sistema de endomembranas, que consiste en la membrana nuclear, el retículo endoplásmico, el aparato de Golgi, las vacuolas/lisosomas, la membrana plasmática y múltiples endosomas1. El sistema de endomembranas permite la modificación, el empaquetado y el transporte de los componentes de la membrana mediante vesículas dinámicas que se desplazan entre estos orgánulos. Los eventos de tráfico de membranas son cruciales para el desarrollo, el crecimiento y la adaptación ambiental de las células y, por lo tanto, están sujetos a una regulación estricta y compleja2. En la actualidad, se han desarrollado y aplicado múltiples enfoques en biología molecular, biología química, microscopía y espectrometría de masas al campo del tráfico de membranas y han avanzado enormemente en la comprensión de la regulación espacio-temporal del sistema de endomembranas 3,4. La biología molecular se utiliza para las manipulaciones genéticas clásicas de los supuestos actores implicados en el tráfico de membranas, como la alteración de la expresión génica de la proteína de interés o el etiquetado de la proteína de interés con ciertas etiquetas. Las herramientas de la biología química incluyen el uso de moléculas que interfieren específicamente con el tráfico de ciertas rutas 4,5. La espectrometría de masas es potente para identificar los componentes de un orgánulo que ha sido aislado mecánicamente por aproximaciones bioquímicas 3,4. Sin embargo, el tráfico de membranas es un proceso biológico dinámico, diverso y complejo1. Para visualizar el proceso de tráfico de membranas en células vivas en diversas condiciones, la microscopía óptica es una herramienta esencial. Se ha avanzado continuamente en las técnicas avanzadas de microscopio para superar los desafíos en la medición de la eficiencia, cinética y diversidad de los eventos4. Aquí, este estudio se centra en las metodologías ampliamente adoptadas en biología química/farmacológica, biología molecular y microscopía para estudiar los eventos de tráfico de membrana en un sistema naturalmente simplificado y experimentalmente accesible, el proceso de desarrollo de estomas.
Los estomas son microporos en las superficies aéreas de las plantas que se abren y cierran para facilitar el intercambio de gases entre las células internas y el medio ambiente 6,7,8. Por lo tanto, los estomas son esenciales para la fotosíntesis y la transpiración, dos eventos que son cruciales para la supervivencia y el crecimiento de las plantas. El desarrollo de los estomas se ajusta dinámicamente mediante señales ambientales para optimizar la adaptación de la planta al entorno9. La identificación de la proteína receptora Too Many Mouths (TMM) abrió la puerta a una nueva era de investigación de los mecanismos moleculares del desarrollo estomatológico en la planta modelo Arabidopsis thaliana10. Después de unas pocas décadas, se ha identificado una vía de señalización clásica. De arriba a abajo, esta vía incluye un grupo de ligandos de péptidos secretores de la familia de los factores de patrón epidérmico (EFP), varias quinasas del receptor de repeticiones ricas en leucina (LRR) de la superficie celular de la familia EREECTA (ER), la proteína del receptor LRR TMM, una cascada de MAPK y varios factores de transcripción de bHLH, incluidos SPEECHLESS (SPCH), MUTE, FAMA y SCREAM (SCRM)11,12,13,14, 15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26. Trabajos previos indican que uno de los receptores quinasas, ER-LIKE 1 (ERL1), demuestra comportamientos subcelulares activos sobre la percepción de EPF20. ERL2 también transita dinámicamente entre la membrana plasmática y algunos orgánulos intracelulares27. El bloqueo de los pasos de tráfico de membrana causa un patrón estomático anormal, lo que resulta en grupos de estomas en la superficie de la hoja28. Estos resultados sugieren que el tráfico de membranas juega un papel esencial en el desarrollo de los estomas. En este estudio se describe un protocolo para investigar espacio-temporalmente la dinámica de ERL1 mediante el análisis de colocalización subcelular proteína-proteína combinado con el tratamiento farmacológico mediante algunos inhibidores del tráfico de membrana.
Protocolo
1. Preparación de las soluciones
- Prepare la solución de esterilización de semillas mezclando 15 ml de lejía con 35 ml de agua destilada y 50 μl de Triton X-100.
- Preparar la solución de brefeldina A (BFA) disolviendo el polvo de BFA en etanol hasta una concentración final de 10 mM (stock). Prepare la solución de wortmannina (Wm) disolviendo el polvo de Wm en DMSO hasta una concentración final de 10 mM (stock).
2. Sembrando las semillas
- Alícuota 10-50 semillas de cada una de las plantas transgénicas requeridas en tubos de microcentrífuga de 1,5 mL. Agregue 1 ml de solución de esterilización de semillas en cada tubo y mezcle bien invirtiendo el tubo suavemente durante 10 minutos en un agitador.
- Deseche la solución de esterilización de semillas y lave las semillas con 1 ml de agua destilada esterilizada en autoclave cinco veces.
- Agregue 300 μL de agua destilada esterilizada en autoclave en cada tubo y siembre las semillas en medios MS de concentración media que contengan 1% (p/v) de sacarosa y 0,75% (p/v) de agar. Complemente el medio con los antibióticos correspondientes según sea necesario.
- Mantener la placa boca abajo a 4 °C en la oscuridad durante 2 días para sincronizar la germinación.
- Después de 2 días, transfiera la placa a una sala de crecimiento con un ciclo de 16 h de luz/8 h de oscuridad (80 μmol/m2/s1) a 22 °C. Esto se considera el primer día después de la germinación (1 dpg).
- Trasplante las plántulas al suelo a 10 dpg para un mayor crecimiento.
3. Preparación de plantas transgénicas F1 de dos colores
- Cultive plantas transgénicas homocigóticas portadoras de ERL1-YFP (planta A) y plantas transgénicas homocigóticas portadoras de una proteína marcadora marcada con RFP RFP-Ara7 (planta B)20 una al lado de la otra hasta que florezcan en una sala de crecimiento con un ciclo de 16 h de luz/8 h de oscuridad (80 μmol/m2/s1) a 22 °C.
- Elija una inflorescencia joven de la planta A. Mantenga una flor que esté a punto de abrirse en la inflorescencia para los cruces genéticos. Retira todas las flores y siluas más viejas. Además, retire con cuidado las flores más jóvenes y los meristemos florales para evitar confusiones futuras.
- Disecciona suavemente la flor sin abrir quitando los sépalos, los pétalos y el estambre con un par de pinzas afiladas. Solo deje el pistilo en la inflorescencia.
- Tome un estambre maduro de una flor abierta en la planta B y deposite los granos de polen en el estigma del pistilo disecado en la planta A.
- Etiquete esta flor cruzada manualmente indicando su padre, madre y la fecha del cruce genético. Deje que la flor madure y coseche las semillas F1 cuando la sílice se vuelva amarilla / marrón (~ 20 días después del cruce). Compruebe si hay una planta de F1 exitosa que tenga señales YFP y RFP.
4. Tratamiento farmacológico
- Para el tratamiento con BFA, retire los cotiledones de las plántulas de 7 días de edad, sumerja el resto de las plántulas en una solución simulada (etanol al 0,3%) o en una solución de BFA de 30 μM, aplique vacío durante 1 minuto y mantenga la muestra sumergida durante 30 minutos antes de obtener imágenes.
- Para el tratamiento con wortmannin, retire los cotiledones de las plántulas de 7 días de edad, sumerja el resto de las plántulas en una solución de DMSO al 0,25% o en 25 mM de wortmannina, aplique vacío durante 1 minuto y mantenga la muestra sumergida durante 30 minutos antes de obtener imágenes.
- Para el tratamiento al vacío de muestras, en un tubo de microcentrífuga de 1,5 ml, agregue 500 μl de la solución de fármaco correspondiente y sumerja las plántulas disecadas en la solución. Conecte firmemente una jeringa de 10 ml al tubo de microcentrífuga y aplique vacío durante 1 minuto (Figura 1). Retire la jeringa y mantenga la muestra en la solución durante el tiempo requerido. Saque con cuidado las plántulas para prepararlas para la obtención de imágenes.

Figura 1: Dispositivo de vacío simple. Se conecta una jeringa de 10 ml a un tubo de microcentrífuga de 1,5 ml para el tratamiento al vacío. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
5. Preparación de la muestra para la obtención de imágenes
- Diseccione la hoja verdadera de la muestra tratada con una cuchilla de afeitar afilada. Coloque suavemente la hoja verdadera en una gota de agua en un portaobjetos de vidrio y mantenga el lado abaxial hacia arriba. Cubra lentamente la hoja verdadera con un cubreobjetos mientras evita atrapar burbujas.
6. Imágenes confocales
NOTA: Se utilizó un microscopio confocal de barrido invertido Leica SP8 para obtener imágenes de la señal de fluorescencia de las muestras de este trabajo.
- Configuración de la trayectoria del haz
- Seleccione un láser de 514 nm para la excitación YFP. Utilice una alta potencia láser para aumentar la intensidad de la señal y, así, obtener una alta calidad de imagen. Sin embargo, las potencias del láser superiores al 5% corren el riesgo de fotoblanqueo y la salud de la muestra puede verse afectada. Si la señal de muestra no es demasiado tenue, comience con una intensidad láser baja.
- Active PMT/HyD para la detección y defina los umbrales de la banda de emisión superior e inferior en función del espectro del fluoróforo YFP. Establezca una ventana de detección de 530-570 nm para recoger la señal YFP.
- Imágenes secuenciales para el segundo color: Haga clic en el botón Seq y agregue un nuevo canal. De forma predeterminada, la trayectoria del haz YFP diseñada anteriormente será Seq 1. En la Secuencia 2, seleccione un láser de 561 nm para la excitación RFP y establezca una ventana de detección de 570-630 nm para recopilar la señal RFP.
- Configuración de las condiciones de escaneo (Figura 2)
- Para obtener imágenes de la actividad de tráfico de la membrana subcelular dentro de las células precursoras estomáticas, elija una lente Corr de 63x/1,2 W en el sistema para obtener imágenes.
- El formato se refiere al tamaño de la imagen en píxeles. Comience con 1.024 píxeles x 1.024 píxeles y, a continuación, optimícelo en función del factor de zoom y la configuración del objetivo para obtener una buena resolución de calidad de publicación.
- La velocidad se refiere a la velocidad del cabezal de escaneo a medida que el láser pasa sobre cada píxel. Aunque las velocidades de escaneo lentas a menudo dan como resultado una mejor relación señal-ruido, es posible que no capturen de manera eficiente los eventos de tráfico de membrana que cambian rápidamente. Comience con una velocidad de 400 Hz y optimícela en función de la situación específica de las muestras.
- El factor de zoom se utiliza para acercar una región de interés sin cambiar la lente del objetivo. Comience con un factor de zoom de 1 y optimícelo en función de las necesidades específicas del experimento.
- El promedio de línea se refiere al número de veces que se escaneará cada línea X para obtener un resultado promedio . Un promedio de línea mayor reduce el ruido en la imagen resultante, pero también aumenta el tiempo de escaneo y el tiempo de exposición a la luz láser. Para obtener imágenes de eventos de tráfico de membranas, no utilice un promedio de línea alto. Comience con un promedio de línea de 2x y optimice según sea necesario.
- Recopilación de una serie temporal
NOTA: Cuando se estudian los eventos de tráfico de membranas, a menudo se necesita una serie temporal para registrar el rápido movimiento de los endosomas subcelulares.- En el modo de adquisición, seleccione el modo de escaneo xyt para habilitar la utilidad de serie temporal.
- Decida un período de espera entre los puntos de tiempo en Intervalo de tiempo. Alternativamente, haga clic en Minimizar para tomar las imágenes inmediatamente una tras otra. Se utilizó un intervalo de tiempo de 7 s en el siguiente experimento de series temporales.
- Seleccione Duración e introduzca el tiempo total que tarda en ejecutarse el experimento. Como alternativa, defina el número de fotogramas que se van a recopilar seleccionando Fotogramas (Figura 3).
- Para recopilar la información tridimensional sobre el evento de tráfico de membrana dentro de toda la célula, utilice el modo de escaneo Z-stack. La proyección de máxima intensidad de las imágenes de la pila Z se utiliza a menudo para el análisis.
- Seleccione el modo de escaneo xyz en el modo de adquisición y, a continuación, se podrá acceder a la utilidad Z-Stack.
- Seleccione la opción Z-wide . En el modo de escaneo, defina la imagen superior y la imagen inferior de la pila Z con los botones Iniciar y Fin .
- Defina el grosor del paso z haciendo clic en el tamaño del paso z. Alternativamente, defina cuántas imágenes tomar para cubrir todo el rango de la pila Z. Para garantizar la coherencia entre las muestras, defina el tamaño del paso z (Figura 4).
- Tratamiento de imágenes
- La proyección de máxima intensidad de las imágenes de la pila z es generada por el software confocal (http://www.leica-microsystems.com). En la pestaña Proceso principal, primero elija el archivo z-stack interesado en la pestaña Abrir proyectos en el extremo izquierdo. Luego, cambie a la pestaña central llamada Herramientas de proceso, seleccione la función Proyección , elija Máximo en el panel desplegable de Método y haga clic en el botón Aplicar . Se generará una imagen de proyección de pila z en la pestaña Proyectos abiertos.
- El vídeo de las imágenes de la serie temporal ha sido generado por Fiji (https://imagej.net/Fiji). En la pestaña Archivo , utilice la función Abrir para abrir todas las imágenes de series temporales en el orden correcto. En la pestaña Imagen , busque la función Apilar y elija Imágenes para apilar para generar un vídeo. Guarde el archivo en formato .avi con la velocidad de fotogramas deseada (5 fotogramas / s para Video 1).
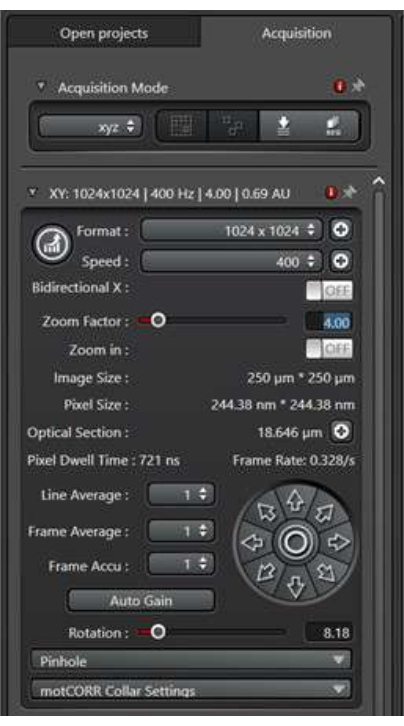
Figura 2: El panel de modo de escaneo de la dimensión XY. El panel de modo de escaneo se utiliza para configurar las condiciones de escaneo de la imagen. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
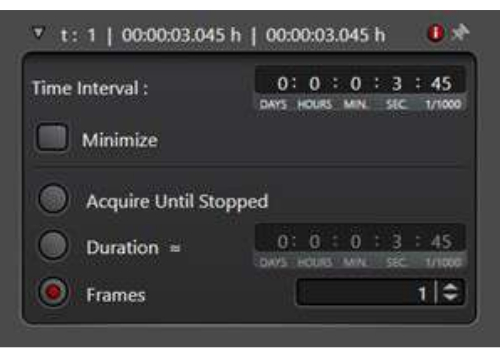
Figura 3: La utilidad de serie temporal en el modo de escaneo xyt. La utilidad de serie temporal se utiliza para configurar las condiciones de imagen para recopilar consecutivamente una serie de imágenes. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
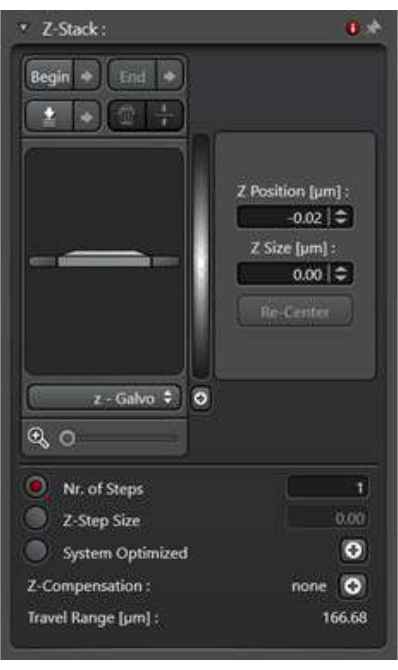
Figura 4: La utilidad z-stack en el modo de escaneo xyz. La utilidad z-stack se utiliza para configurar las condiciones de imagen para recopilar una serie de imágenes en el eje z. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
Resultados
Un estudio previo indicó que ERL1 es un receptor quinasa activo que experimenta eventos dinámicos de tráfico de membrana20. ERL1 es una quinasa transmembrana del receptor LRR en la membrana plasmática. La ERL1 recién sintetizada en el retículo endoplásmico se procesa en los cuerpos de Golgi y se transporta posteriormente a la membrana plasmática. Las moléculas ERL1 de la membrana plasmática pueden percibir ligandos EPF utilizando su dominio18 LRR extracelular. Tra...
Discusión
El sistema de endomembranas separa el citoplasma de una célula eucariota en diferentes compartimentos, lo que permite la función biológica especializada de estos orgánulos. Para llevar las proteínas de carga y las macromoléculas a su destino final en el momento adecuado, se guían numerosas vesículas para que se transporten entre estos orgánulos. Los eventos de tráfico de membranas altamente regulados juegan un papel fundamental en la viabilidad, el desarrollo y el crecimiento de las células. El mecanismo que r...
Divulgaciones
Los autores declaran no tener conflictos de intereses.
Agradecimientos
Este trabajo fue apoyado por la Fundación Nacional de Ciencias (IOS-2217757) (X.Q.) y el Premio de la Fundación Bronson de la Universidad de Arkansas para Ciencias Médicas (UAMS) (H.Z.).
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 10 mL syringes | VWR | BD309695 | Vacuum samples |
| Brefeldin A (BFA) | Sigma | B7651 | membrane trafficking drug |
| Confocal Microscope | Leica | Lecia SP8 TCS with LAS-X software package | Imaging |
| Dissecting Forceps | VWR | 82027-402 | Genetic cross |
| Fiji | NIH | https://imagej.net/Fiji | Image processing |
| Leica LAS AF software | Leica | http://www.leica-microsystems.com | Image processing |
| transgenic seeds of ERL1-YFP | Qi, X. et al. The manifold actions of signaling peptides on subcellular dynamics of a receptor specify stomatal cell fate. Elife. 9, doi:10.7554/eLife.58097, (2020). | ||
| transgenic seeds of RFP-Ara7 | Ebine, K. et al. A membrane trafficking pathway regulated by the plant-specific RAB GTPase ARA6. Nat Cell Biol. 13 (7), 853-859, doi:10.1038/ncb2270, (2011). | ||
| Wortmannin (Wm) | Sigma | W1628 | membrane trafficking drug |
Referencias
- Aniento, F., Sanchez de Medina Hernandez, V., Dagdas, Y., Rojas-Pierce, M., Russinova, E. Molecular mechanisms of endomembrane trafficking in plants. Plant Cell. 34 (1), 146-173 (2022).
- Sigismund, S., et al. Endocytosis and signaling: Cell logistics shape the eukaryotic cell plan. Physiological Reviews. 92 (1), 273-366 (2012).
- Lyu, Z., Genereux, J. C. Methodologies for measuring protein trafficking across cellular membranes. ChemPlusChem. 86 (10), 1397-1415 (2021).
- Rodriguez-Furlan, C., Raikhel, N. V., Hicks, G. R. Merging roads: Chemical tools and cell biology to study unconventional protein secretion. Journal of Experimental Botany. 69 (1), 39-46 (2017).
- Foissner, I., Sommer, A., Hoeftberger, M., Hoepflinger, M. C., Absolonova, M. Is wortmannin-induced reorganization of the trans-Golgi network the key to explain charasome formation. Frontiers in Plant Science. 7, 756 (2016).
- Qi, X., Torii, K. U. Hormonal and environmental signals guiding stomatal development. BMC Biology. 16 (1), 21 (2018).
- Han, S. K., Kwak, J. M., Qi, X. Stomatal lineage control by developmental program and environmental cues. Frontiers in Plant Science. 12, 751852 (2021).
- Bharath, P., Gahir, S., Raghavendra, A. S. Abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure: An important component of plant defense against abiotic and biotic stress. Frontiers in Plant Science. 12, 615114 (2021).
- Becklin, K. M., Ward, J. K., Way, D. A. . Photosynthesis, Respiration, and Climate Change., 1st edition. , (2021).
- Yang, M., Sack, F. D. The too many mouths and four lips mutations affect stomatal production in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 7 (12), 2227-2239 (1995).
- Hara, K., Kajita, R., Torii, K. U., Bergmann, D. C., Kakimoto, T. The secretory peptide gene EPF1 enforces the stomatal one-cell-spacing rule. Genes & Development. 21 (14), 1720-1725 (2007).
- Hara, K., et al. Epidermal cell density is autoregulated via a secretory peptide, EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTOR 2 in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant & Cell Physiology. 50 (6), 1019-1031 (2009).
- Hunt, L., Gray, J. E. The signaling peptide EPF2 controls asymmetric cell divisions during stomatal development. Current Biology. 19 (10), 864-869 (2009).
- Sugano, S. S., et al. Stomagen positively regulates stomatal density in Arabidopsis. Nature. 463 (7278), 241-244 (2010).
- Kondo, T., et al. Stomatal density is controlled by a mesophyll-derived signaling molecule. Plant & Cell Physiology. 51 (1), 1-8 (2010).
- Hunt, L., Bailey, K. J., Gray, J. E. The signalling peptide EPFL9 is a positive regulator of stomatal development. New Phytologist. 186 (3), 609-614 (2010).
- Shpak, E. D., McAbee, J. M., Pillitteri, L. J., Torii, K. U. Stomatal patterning and differentiation by synergistic interactions of receptor kinases. Science. 309 (5732), 290-293 (2005).
- Lin, G., et al. A receptor-like protein acts as a specificity switch for the regulation of stomatal development. Genes & Development. 31 (9), 927-938 (2017).
- Lee, J. S., et al. Direct interaction of ligand-receptor pairs specifying stomatal patterning. Genes & Development. 26 (2), 126-136 (2012).
- Qi, X., et al. The manifold actions of signaling peptides on subcellular dynamics of a receptor specify stomatal cell fate. Elife. 9, e58097 (2020).
- MacAlister, C. A., Ohashi-Ito, K., Bergmann, D. C. Transcription factor control of asymmetric cell divisions that establish the stomatal lineage. Nature. 445 (7127), 537-540 (2007).
- Pillitteri, L. J., Sloan, D. B., Bogenschutz, N. L., Torii, K. U. Termination of asymmetric cell division and differentiation of stomata. Nature. 445 (7127), 501-505 (2007).
- Ohashi-Ito, K., Bergmann, D. C. Arabidopsis FAMA controls the final proliferation/differentiation switch during stomatal development. Plant Cell. 18 (10), 2493-2505 (2006).
- Kanaoka, M. M., et al. SCREAM/ICE1 and SCREAM2 specify three cell-state transitional steps leading to Arabidopsis stomatal differentiation. Plant Cell. 20 (7), 1775-1785 (2008).
- Bergmann, D. C., Lukowitz, W., Somerville, C. R. Stomatal development and pattern controlled by a MAPKK kinase. Science. 304 (5676), 1494-1497 (2004).
- Wang, H., Ngwenyama, N., Liu, Y., Walker, J. C., Zhang, S. Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 19 (1), 63-73 (2007).
- Ho, C. M., Paciorek, T., Abrash, E., Bergmann, D. C. Modulators of stomatal lineage signal transduction alter membrane contact sites and reveal specialization among ERECTA kinases. Developmental Cell. 38 (4), 345-357 (2016).
- Le, J., et al. Auxin transport and activity regulate stomatal patterning and development. Nature Communications. 5, 3090 (2014).
- Geldner, N., et al. The Arabidopsis GNOM ARF-GEF mediates endosomal recycling, auxin transport, and auxin-dependent plant growth. Cell. 112 (2), 219-230 (2003).
- Qi, X., et al. Autocrine regulation of stomatal differentiation potential by EPF1 and ERECTA-LIKE1 ligand-receptor signaling. Elife. 6, 24102 (2017).
- Heilemann, M., et al. Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging with conventional fluorescent probes. Angewandte Chemie. 47 (33), 6172-6176 (2008).
- Leighton, R. E., Alperstein, A. M., Frontiera, R. R. Label-free super-resolution imaging techniques. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry. 15 (1), 37-55 (2022).
- Oreopoulos, J., Berman, R., Browne, M. Spinning-disk confocal microscopy: Present technology and future trends. Methods in Cell Biology. 123, 153-175 (2014).
- Gao, R., et al. Cortical column and whole-brain imaging with molecular contrast and nanoscale resolution. Science. 363 (6424), (2019).
- Nwaneshiudu, A., et al. Introduction to confocal microscopy. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 132 (12), (2012).
- Sanderson, J. Multi-photon microscopy. Current Protocols. 3 (1), 634 (2023).
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoExplorar más artículos
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados