Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Method Article
Generación de líneas celulares knockout de proteína E CENP-E-/- asociadas al centrómero utilizando el sistema CRISPR/Cas9
En este artículo
Resumen
En este artículo se informa de la construcción de células knockout de proteína E asociada al centrómero (CENP-E) utilizando el sistema CRISPR/Cas9 y tres estrategias de cribado basadas en el fenotipo. Hemos utilizado la línea celular knockout CENP-E para establecer un enfoque novedoso para validar la especificidad y toxicidad de los inhibidores de CENP-E, que es útil para el desarrollo de fármacos y la investigación biológica.
Resumen
El sistema CRISPR (repeticiones palindrómicas cortas agrupadas regularmente interespaciadas)/Cas9 se ha convertido en una poderosa herramienta para la edición genética precisa y eficiente en una variedad de organismos. La proteína E ASOCIADA AL CENTRÓMERO (CENP-E) es una quinesina dirigida al extremo positivo necesaria para la captura del cinetocoro-microtúbulo, la alineación cromosómica y el punto de control de ensamblaje del huso. Aunque las funciones celulares de las proteínas CENP-E han sido bien estudiadas, ha sido difícil estudiar las funciones directas de las proteínas CENP-E utilizando protocolos tradicionales porque la ablación de CENP-E generalmente conduce a la activación del punto de control del ensamblaje del huso, la detención del ciclo celular y la muerte celular. En este estudio, hemos eliminado por completo el gen CENP-E en células HeLa humanas y hemos generado con éxito las células CENP-E-/- HeLa utilizando el sistema CRISPR/Cas9.
Se establecieron tres estrategias optimizadas de cribado basadas en el fenotipo, que incluyen el cribado de colonias celulares, los fenotipos de alineación cromosómica y las intensidades fluorescentes de las proteínas CENP-E, que mejoran eficazmente la eficacia del cribado y la tasa de éxito experimental de las células knockout CENP-E . Es importante destacar que la deleción de CENP-E da lugar a una desalineación cromosómica, a la localización anormal de las proteínas serina/treonina quinasa B (BubR1) del punto de control mitótico BUB1 y a defectos mitóticos. Además, hemos utilizado el modelo de células HeLa knockout de CENP-E para desarrollar un método de identificación de inhibidores específicos de CENP-E.
En este estudio, se ha establecido un enfoque útil para validar la especificidad y toxicidad de los inhibidores de CENP-E. Además, en este trabajo se presentan los protocolos de edición génica de CENP-E utilizando el sistema CRISPR/Cas9, que podría ser una poderosa herramienta para investigar los mecanismos de CENP-E en la división celular. Además, la línea celular knockout de CENP-E contribuiría al descubrimiento y validación de inhibidores de CENP-E, que tienen importantes implicaciones para el desarrollo de fármacos antitumorales, estudios de mecanismos de división celular en biología celular y aplicaciones clínicas.
Introducción
La edición genómica modificada media las modificaciones específicas de los genes en una variedad de células y organismos. En eucariotas, la mutagénesis específica del sitio puede introducirse mediante la aplicación de nucleasas específicas de secuencia que estimulan la recombinación homóloga del ADN diana1. En los últimos años, se han diseñado varias tecnologías de edición del genoma, incluidas las nucleasas de dedos de zinc (ZFN)2,3, las nucleasas efectoras similares a activadores de transcripción (TALEN)4,5 y las meganucleasas homing 6,7, para escindir genomas en sitios específicos, pero estos enfoques requieren ingeniería de proteínas compleja y procedimientos experimentales redundantes. Los estudios han demostrado que el sistema de repeticiones palindrómicas cortas (CRISPR)/Cas agrupadas regularmente interespaciadas de tipo II es una tecnología eficiente de edición de genes, que media específicamente la escisión del ADN guiada por ARN y específica del sitio en una amplia variedad de células y especies 8,9,10,11. La tecnología de knockout del gen CRISPR/Cas9 ha revolucionado los campos de la biología básica, la biotecnología y la medicina12.
Las bacterias y la mayoría de las arqueas han desarrollado un sistema inmunitario adaptativo basado en ARN que utiliza proteínas CRISPR y Cas para identificar y destruir virus y plásmidos. Streptococcus pyogenes La endonucleasa Cas9 (SpCas9) contiene la resolvasa de la unión Holliday similar a RuvC (RuvC) y el dominio His-Asn-His (HNH), que puede mediar de manera eficiente las roturas de doble cadena (DSB) específicas de la secuencia al proporcionar un ARN sintético de guía única (sgRNA) que contiene ARN CRISPR (crRNA) y crRNA transactivador (tracrRNA)14,15,16. Los DSB pueden ser reparados a través de la vía de unión de extremos no homólogos (NHEJ) o de reparación dirigida por homología (HDR) que forma indel, que introduce múltiples mutaciones, incluyendo inserciones, deleciones o sustituciones de un solo nucleótido sin cicatrices, en células de mamíferos 1,8. Tanto la vía NHEJ, propensa a errores, como la vía HDR de alta fidelidad se pueden utilizar para mediar en la eliminación de genes a través de inserciones o deleciones, lo que puede causar mutaciones de cambio de marco y codones de parada prematuros10.
La kinesina-7 CENP-E es necesaria para la unión cinetocoro-microtúbulos y la alineación cromosómica durante la división celular 17,18,19. La microinyección de anticuerpos20,21, la depleción de siRNA22,23, la inhibición química 24,25,26 y la deleción genética 27,28,29 de CENP-E conducen a la desalineación cromosómica, la activación del punto de control del ensamblaje del huso y defectos mitóticos, lo que resulta en aneuploidía e inestabilidad cromosómica 19,30. En ratones, la deleción de CENP-E resulta en un desarrollo anormal y letalidad embrionaria en las primeras etapas del desarrollo 27,29,31. La deleción genética de CENP-E generalmente conduce a la desalineación cromosómica y a la muerte celular 26,27,29, lo que constituye un obstáculo para el estudio de las funciones y mecanismos de las proteínas CENP-E.
Un estudio reciente ha establecido una línea celular knockout condicional de CENP-E utilizando un método de edición génica CRISPR/Cas9 inducible por auxinas32, que permite una rápida degradación de las proteínas CENP-E en un tiempo relativamente corto33. Sin embargo, hasta la fecha, no se han establecido líneas celulares estables de CENP-E knockout, lo cual es un desafío técnico no resuelto en la biología de CENP-E. Teniendo en cuenta la robustez genética34, las respuestas de compensación genética 35,36,37 y los entornos intracelulares complejos, ya que las consecuencias directas de la deleción completa de CENP-E pueden ser complejas e impredecibles, es importante establecer líneas celulares knockout de CENP-E para la investigación de los mecanismos de alineación cromosómica, el punto de control del ensamblaje del huso y las vías de señalización posteriores.
El descubrimiento y las aplicaciones de los inhibidores de CENP-E son importantes para el tratamiento del cáncer. Hasta la fecha, se han encontrado y sintetizado siete tipos de inhibidores de CENP-E, incluyendo GSK923295 y sus derivados24,25, PF-2771 38,39, imidazo[1,2-a]piridina derivados de andamios 40,41, compuestoA 42,43, sintelina44,45, UA6278446 y derivados de benzo[d]pirrolo[2,1-b]tiazol47. Entre estos inhibidores, GSK923295 es un inhibidor alostérico y eficiente de CENP-E que se une al dominio motor de CENP-E e inhibe la actividad de la ATPasa estimulada por microtúbulos de CENP-E con una Ki de 3,2 ± 0,2 nM24,25. Sin embargo, en comparación con los efectos inhibidores de la GSK923295 en células cancerosas cultivadas, los efectos terapéuticos de la GSK923295 en pacientes clínicos con cáncer no son ideales48,49, lo que también planteó preocupaciones sobre la especificidad de la GSK923295 para CENP-E. Además, la especificidad y los efectos secundarios de otros inhibidores de CENP-E sobre las proteínas CENP-E son cuestiones clave en la investigación del cáncer.
En este estudio, hemos eliminado por completo el gen CENP-E en células HeLa utilizando el sistema CRISPR/Cas9. Se han establecido tres estrategias optimizadas de cribado basadas en el fenotipo, que incluyen el cribado de colonias celulares, los fenotipos de alineación cromosómica y las intensidades fluorescentes de las proteínas CENP-E, para mejorar la eficacia del cribado y la tasa de éxito de la edición génica CENP-E. Además, las líneas celulares knockout de CENP-E se pueden utilizar para probar la especificidad de los compuestos candidatos para CENP-E.
Protocolo
1. Construcción de los vectores knockout del gen CRISPR/Cas9
- Seleccione la secuencia de ADN genómico diana en el gen CENP-E humano (Acceso GenBank No. NM_001286734.2) y diseñar el sgRNA utilizando una herramienta de diseño CRISPR en línea (http://crispor.tefor.net/).
- Introduzca una sola secuencia genómica, seleccione el genoma de "Homo sapiens-human-UCSC Dec 2013 (conjunto de análisis hg38) + polimorfismos de un solo nucleótido (SNPs): dbSNP148", y seleccione el motivo adyacente del protoespaciador "20 bp-NGG-spCas9". Elija dos secuencias guía, que incluyen sgRNA-1, 5'-CGGCCGCACTCGCACGCAGA-3' y sgRNA-2 5'-TTCTTTAGAGACGCGGGCTC-3', de acuerdo con las puntuaciones de especificidad50, la eficiencia predicha10 y los objetivos mínimos.
- Ordenar y sintetizar los oligonucleótidos de ADN monocatenario (ssODN). Diluir los ssODN en ddH2O hasta una concentración final de 100 μM. Para fosforilar y recocer los oligonucleótidos de ARNsg, añadir 1 μL de oligonucleótido directo, 1 μL de oligonucleótido inverso, 0,5 μL de polinucleótido quinasa T4, 1 μL de tampón de polinucleótido quinasa T4 y 6,5 μL de agua libre de ARNasa en un tubo de reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (PCR), e incubar el tubo a 37 °C durante 30 min, 95 °C durante 5 min; luego, baje a 25 °C a 5 °C min-1.
- Digiera el plásmido pX458 utilizando la enzima de restricción Bbs
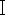 . Agregue 1 μg del plásmido pX458, 2 μL de 10x tampón G, 1 μL de Bbs
. Agregue 1 μg del plásmido pX458, 2 μL de 10x tampón G, 1 μL de Bbs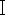 y agregue ddH2O sin RNasa a 20 μL en un tubo de centrífuga de 1,5 mL. Incubar el tubo a 37 °C durante 2 h. A continuación, purifique el plásmido lineal utilizando el kit de extracción de gel de ADN en columna de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante.
y agregue ddH2O sin RNasa a 20 μL en un tubo de centrífuga de 1,5 mL. Incubar el tubo a 37 °C durante 2 h. A continuación, purifique el plásmido lineal utilizando el kit de extracción de gel de ADN en columna de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante. - Ligue los oligonucleótidos de sgRNA en el plásmido pX458 (plásmido de proteína fluorescente verde (GFP) pSpCas9(BB)-2A, Addgene ID. 48138). Añadir 1 μL de los oligonucleótidos recocidos, 25 ng del plásmido lineal, 1 μL de tampón de ligadura de ADN T4 10x, 0,5 μL de ADN ligasa T4 (350 U/μL) y hacer hasta 10 μL conddH2O en un tubo de centrífuga de 1,5 mL. Incubar la solución de ligadura a 16 °C durante 2 h.
- Incubar 10 μL del plásmido construido con las células DH5α competentes en hielo durante 30 min, choque térmico a 42 °C durante 45 s y colocarlas inmediatamente en hielo durante 5 min. Añadir 500 μL de medio Luria-Bertani (LB) y sembrar las células en una placa LB que contenga ampicilina (100 μg/mL). Incubar a 37 °C durante 16 h y cribar los clones resistentes.
- Seleccione de 5 a 10 colonias individuales con una punta de pipeta esterilizada y transfiéralas a un cultivo de 1 ml de medio LB con ampicilina (100 μg/ml). Incubar el cultivo a 37 °C y agitarlo a 180 rpm durante 12-16 h.
- Aísle el ADN del plásmido utilizando un kit de extracción de plásmidos de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante. Validar el ADN plasmídico de cada colonia mediante secuenciación Sanger desde el sitio promotor U6 utilizando el cebador U6-Fwd 5'-GAGGGCCTATTTCCCATGATTCC-3'.
- Extraiga y purifique los plásmidos utilizando el kit de ADN de plásmidos endo-libres de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante.
2. Transfección, aislamiento y cribado de las células HeLa knockout de CENP-E
- Cultivo de células HeLa en medio de águila modificado con Dulbecco (DMEM) suplementado con suero fetal bovino al 10% y penicilina/estreptomicina al 1% en incubadora humidificada a 37 °C con 5% de CO2.
- Incubar las células HeLa utilizando tripsina/ácido etilendiamino tetraacético (EDTA) al 0,25% a 37 °C durante 2-3 min, disociar las células pipeteando suavemente y, a continuación, sembrar las células en nuevas placas a una proporción de dilución de 1:4 para el paso celular.
- Siembre las células en una placa de 12 pocillos y cultive hasta una confluencia del 60-70% antes de la transfección. Transfectar los plásmidos pX458-sgRNA en células HeLa utilizando los reactivos de referencia de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante (consulte la Tabla de materiales).
- Mezclar suavemente 1 μg de plásmido pX458-sgRNA validado y 50 μL de medio sérico reducido en el tubo A. A continuación, mezcle suavemente 2 μl del reactivo de transfección y 50 μl de medio sérico reducido en el tubo B. Incubar los tubos A y B por separado a temperatura ambiente durante 5 min.
- Mezcle el tubo A y el tubo B suavemente e incube a temperatura ambiente durante 5 minutos. Agregue la mezcla a una placa de 12 pocillos, incube las células durante 6 h y reemplace el medio con un medio DMEM nuevo.
- Examine las células HeLa después de 24 h o 48 h utilizando un microscopio de fluorescencia para determinar la eficacia de la transfección. Después de la transfección durante 48 h, disociar completamente las células HeLa transfectadas utilizando tripsina/EDTA al 0,25% a 37 °C durante 3-5 min, contar el número de células utilizando una cámara de Neubauer o un contador celular automatizado, y colocar las células en tres placas separadas de 96 pocillos para cada población transfectada de acuerdo con los métodos de dilución en serie10.
- Regrese las células a una incubadora humidificada y luego cultívelas durante otras 1-2 semanas. Cambie el medio de cultivo una vez cada 3 días. Para el cribado basado en el fenotipo y la validación del knockout de CENP-E , disocie y expanda las células en placas de 24 o 12 pocillos durante 5-7 días.
- Examinar las células mutantes con diámetros de colonia celular más pequeños utilizando un microscopio invertido equipado con lentes de objetivo de 10x y 20x.
NOTA: Las mutaciones en CENP-E suelen dar lugar a un aumento significativo en el número de células que se dividen en las colonias celulares, lo que puede ser uno de los indicadores clave para el cribado de las células mutantes de CENP-E . - Recolectar las células para la extracción de ADN utilizando el kit de extracción de ADN genómico animal de columna de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante. Configure las reacciones de PCR de la siguiente manera: 0,25 μL de Taq polimerasa, 5 μL de tampón 10x (Mg2+ plus), 4 μL de mezclas de dNTP, 500 ng de plantilla de ADN, 1 μL de oligonucleótido directo, 1 μL de oligonucleótido inverso y ajuste ddH2O a 50 μL. Utilice la siguiente configuración del programa de PCR para la amplificación de genes: 98 °C, 10 s; 98 °C, 10 s, 55 °C, 30 s, 72 °C, 60 s durante 33 ciclos; 72 °C, 10 min, y luego mantener a 4 °C.
NOTA: Los cebadores específicos para la clonación del locus diana se enumeran a continuación: CENP-E diana F1, 5'-GAGGGTCCTGGCCATTTTCCTG-3'; Objetivo R1 del CENP-E , 5'-AGATCTCCGATCCTCCCCTGTC-3'; Objetivo CENP-E F2, 5'-TGGTAACTGCATTTTGGTGTTCTAC-3'; Objetivo CENP-E R2, 5'-CCTGTTGCAACGTGAGGGAAG-3'. - Libar el ADN objetivo en el vector pMD18-T de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante. Transfectar el plásmido ligado en células DH5α competentes y cultivarlo para la selección de clones.
- Realice la secuenciación de Sanger para determinar los tipos de knockout de CENP-E . Aísle el ADN del plásmido utilizando un kit de extracción de plásmidos de acuerdo con los protocolos del fabricante. Llevar a cabo la secuenciación Sanger del ADN plasmídico de cada colonia utilizando los cebadores M13 hacia adelante y hacia atrás. Imprimación M13F, 5'-TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGT-3'; Imprimación M13R, 5'-CAGGAAACAGCTATGACC-3'.
- Siembre las células HeLa de tipo salvaje y mutantes CENP-E en cubreobjetos de vidrio de 12 mm en una placa de 24 pocillos, respectivamente. Retire el medio DMEM completo y fije las células en una solución fijadora de solución salina tamponada con paraformaldehído/fosfato (PBS) al 4% a temperatura ambiente durante 10 min.
- Tiñir los núcleos con la solución de 4',6-diamidino-2-fenilindol (DAPI) a temperatura ambiente durante 5 min. Cribar y validar las células mutantes de CENP-E en función del fenotipo de alineación cromosómica utilizando un microscopio de fluorescencia equipado con un objetivo Plan Fluor 40x/ Apertura numérica (NA) 0,75.
- Cribar y validar las células knockout de CENP-E mediante tinción y análisis de inmunofluorescencia (ver sección 3) de proteínas CENP-E.
3. Tinción de inmunofluorescencia y microscopía confocal de alta resolución
- Fijar las células con una solución fijadora de paraformaldehído/PBS al 4% a temperatura ambiente durante 10 min y sumergir durante 2 x 5 min en 1x PBS.
NOTA: Asegúrese de que las células estén en buenas condiciones y de que las células se recojan y fijen suavemente para evitar el desprendimiento de células en metafase. - Permeabilizar las células con Triton X-100/PBS al 0,25% a temperatura ambiente durante 10 min y sumergirlas en 1x PBS durante 2 x 5 min.
- Bloquee las celdas con 1% BSA/PBST (0,1% Tween 20 en PBS) a temperatura ambiente durante 1 h. Diluir los anticuerpos primarios con BSA/PBST al 1% e incubar las muestras a 4 °C durante 12 h.
- Deseche las soluciones de anticuerpos primarios, enjuague las células 3 x 5 min con 1x PBS e incube las células con anticuerpos secundarios diluidos a temperatura ambiente durante 2 h.
- Deseche los anticuerpos secundarios y enjuague las células en 1x PBS durante 3 x 5 min.
- Tiñir los núcleos con DAPI a temperatura ambiente durante 5 min. Monte las guías con el medio de montaje. Sella los portaobjetos con esmalte de uñas.
- Observe y registre las imágenes de fluorescencia utilizando un microscopio confocal de barrido equipado con un objetivo 63x/NA 1.40.
4. Preparación cromosómica y análisis del cariotipo
- Cultivar las células de tipo salvaje y CENP-E-/- HeLa en medio DMEM completo suplementado con suero fetal bovino al 10% y penicilina/estreptomicina al 1% durante 24 h y, a continuación, incubar las células de tipo salvaje y CENP-E-/- HeLa con 300 nM de colchicina durante 5 h.
- Incubar las células con tripsina/EDTA al 0,25% a 37 °C durante 3 min y recoger las células en tubos de centrífuga de 1,5 mL.
- Centrifugar las células a 1.000 × g durante 5 min a temperatura ambiente, desechar los sobrenadantes, añadir 1,2 mL de solución de KCl 0,075 mol/L e incubar a 37 °C durante 20 min.
- Centrifugar las células a 1.000 × g durante 5 min a temperatura ambiente, desechar los sobrenadantes, añadir 0,2 mL de la solución fijadora (metanol: ácido acético glacial = 3:1) para la prefijación y mezclar suavemente durante 1 min.
- Centrifugar las células a 1.000 × g durante 5 min a temperatura ambiente, recoger los gránulos, añadir 1,5 mL de la solución fijadora a temperatura ambiente durante 10 min, y luego centrifugar a 1.000 × g durante 5 min a temperatura ambiente.
- Deseche los sobrenadantes, agregue 0,6 ml de las soluciones fijadoras y prepare una suspensión celular. Añadir 3-5 gotas de las suspensiones celulares desde una altura de 35-40 cm en los toboganes de hielo.
NOTA: Mantenga la altura para liberar las suspensiones de la celda en los toboganes en 35-40 cm; De lo contrario, los cromosomas pueden estar demasiado dispersos o no estar separados entre sí. - Seque los portaobjetos inmediatamente con una lámpara de alcohol, tiña las muestras con solución de tinción Giemsa al 10% durante 7 min, enjuague los portaobjetos con agua corriente durante 2 min y observe las muestras con un microscopio óptico equipado con un objetivo Plan Fluor 40x/NA 0,75.
5. Ensayo de formación de colonias celulares
- Prepare las suspensiones celulares en las placas de 6 pocillos a una densidad celular de 1,000-2,000 celdas/pocillo. Agite suavemente las placas para distribuir uniformemente las células.
- Coloque las placas de 6 pocillos en una incubadora de CO2 e incube durante 2-3 semanas a 37 °C con 5% de CO2. Cambie el medio de cultivo una vez cada 5 días. Grabe las imágenes con un microscopio invertido equipado con lentes de objetivo de 10x y 20x. Cosecha las células cuando las colonias sean visibles (cientos de células dentro de un clon).
- Para estudiar los efectos del GSK923295, cultive las células en las placas de 6 pocillos durante 24 h y agregue 2 ml de GSK923295 a las concentraciones finales de 10, 25, 50, 100 y 200 nM.
NOTA: No mueva la placa de cultivo en la etapa temprana de la formación del clon para evitar el desprendimiento celular, que puede formar nuevos clones y afectar el cribado de las células transfectadas. - Deseche el medio de cultivo y fije las células con PFA al 1% a temperatura ambiente durante 10 min. Tiñir las colonias con una solución de tinción de violeta cristalina al 0,1% a temperatura ambiente durante 15 min. Enjuague las muestras con 1x PBS tres veces. Registre las imágenes de las colonias celulares y cuantifique los diámetros de cada colonia utilizando el software ImageJ. Elija la herramienta de selección de línea recta , haga clic en Analizar, elija Medir y registre la longitud.
- Enjuague las colonias con 1 ml de solución de ácido acético al 10% durante 5 min. Transfiera 200 μL de las soluciones sobrenadantes en una placa de 96 pocillos y mida los valores de absorbancia utilizando un espectrofotómetro de microplacas aA 600 nm.
6. Ensayo de viabilidad celular
- Siembre las células en las placas de 24 pocillos y cultive las células durante 48 h a una densidad del 80-90%.
- Incubar las células con 100 μL de tripsina/EDTA al 0,25% a 37 °C durante 3 min.
- Mezclar 400 μL de PBS con las células con una pistola de pipetas. Transfiera 100 μL de las suspensiones celulares a la placa de 96 pocillos.
- Añadir 20 μL de solución MTS en cada pocillo con una concentración final de 317 μg/mL y mezclar suavemente según los protocolos del fabricante. Incubar las muestras a 37 °C durante 1-3 h en una incubadora deCO2 .
- Registre los valores de absorbancia de cada pocillo en el pico de absorbancia de A490 nm utilizando un espectrofotómetro de microplacas. Utilice una longitud de onda de referencia de A630 nm para restar el fondo aportado por los restos celulares y la absorbancia inespecífica (viabilidad celular = A490 nm-A 630 nm).
Resultados
Las células CENP-E-/- HeLa se generaron con éxito utilizando el sistema CRISPR/Cas9 (Figura 1). La línea de tiempo y los pasos experimentales críticos de este método se muestran en la Figura 1. En primer lugar, diseñamos y sintetizamos los sgRNAs específicos de CENP-E, recocimos y ligamos los sgRNAs en el plásmido pX458, transfectamos el plásmido en células HeLa y las cultivamos durante 48 h. Las células transfectadas se d...
Discusión
La quinesina-7 CENP-E es un regulador clave en la alineación cromosómica y el punto de control de ensamblaje del huso durante la división celular 17,19,20. La deleción genética de CENP-E generalmente resulta en la activación del punto de control del ensamblaje del huso, la detención del ciclo celular y la muerte celular 27,29,51,52.
Divulgaciones
Los autores no tienen conflictos de intereses que revelar.
Agradecimientos
Agradecemos a todos los miembros del Laboratorio de Citoesqueletos de la Universidad Médica de Fujian por sus útiles discusiones. Agradecemos a Jun-Jin Lin, Zhi-Hong Huang, Ling Lin, Li-Li Pang, Lin-Ying Zhou, Xi Lin y Min-Xia Wu del Centro de Servicios Públicos de Tecnología de la Universidad Médica de Fujian por su asistencia técnica. Agradecemos a Si-Yi Zheng, Ying Lin y Qi Ke del Centro de Enseñanza Experimental de Ciencias Médicas Básicas de la Universidad Médica de Fujian por su apoyo. Este estudio contó con el apoyo de las siguientes subvenciones: Fundación Nacional de Ciencias Naturales de China (subvención número 82001608 y 82101678), Fundación de Ciencias Naturales de la provincia de Fujian, China (subvención número 2019J05071), los Fondos Conjuntos para la Innovación de la Ciencia y la Tecnología, la provincia de Fujian, China (subvención número 2021Y9160) y el proyecto de financiación de la investigación científica de alto nivel de talentos de la Universidad Médica de Fujian (número de subvención XRCZX2017025).
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA | Gibco | 25200056 | |
| 1.5 mL centrifuge tube | Axygen | MCT-150-C | |
| 24-well plate | Corning | 3524 | |
| 4S Gelred, 10,000x in water | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) | A616697 | |
| 50 mL centrifuge tube | Corning | 430828 | |
| 6 cm Petri dish | Corning | 430166 | |
| 95% ethanol | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 10009164 | |
| 96-well plate | Corning | 3599 | |
| Acetic acid | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 10000218 | Dissolve in H2O to prepare a 10% working solution. |
| Agarose | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) | A620014 | |
| Alexa Fluor 488-labeled Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L) | Beyotime | A0428 | For immunofluorescence. Dissolve in 1% BSA/PBST. 1:500 dilution. |
| Alexa Fluor 488-labeled Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) | Beyotime | A0423 | For immunofluorescence. Dissolve in 1% BSA/PBST. 1:500 dilution. |
| Alexa Fluor 555-labeled Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L) | Beyotime | A0460 | For immunofluorescence. Dissolve in 1% BSA/PBST. 1:500 dilution. |
| Anhydrous ethanol | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 100092690 | |
| Anti-BubR1 rabbit monoclonal antibody | Abcam | ab254326 | For immunofluorescence. Dissolve in 1% BSA/PBST. 1:100 dilution |
| Anti-CENP-B mouse monoclonal antibody | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-376392 | For immunofluorescence. Dissolve in 1% BSA/PBST. 1:50 dilution. |
| Anti-CENP-E rabbit monoclonal antibody | Abcam | ab133583 | For immunofluorescence. Dissolve in 1% BSA/PBST. 1:100 dilution. |
| Anti-fade mounting medium | Beyotime | P0131 | Slowing down the quenching of fluorescent signals. |
| Anti-α-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibody | Abcam | ab7291 | For immunofluorescence. Dissolve in 1% BSA/PBST. 1:100 dilution. |
| Biotek Epoch Microplate Spectrophotometer | Biotek Instruments | Biotek Epoch | |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 69003435 | |
| BpiI (BbsI) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | ER1011 | |
| CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution cell proliferation assay | Promega | G3580 | |
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5424BK745380 | |
| Colchicine | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 61001563 | |
| Confocal scanning microscope | Leica | Leica TCS SP8 | |
| Coverslip | CITOTEST | 80344-1220 | |
| DAPI | Beyotime | C1006 | |
| DH5α competent cells | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) | B528413 | |
| DL2000 DNA marker | TaKaRa | 3427A | |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) | Gibco | C11995500BT | |
Endo-free plasmid mini kit  | Omega | D6950 | |
| Ezup Column Animal Genomic DNA Purification Kit | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) | B518251 | |
| Fetal bovine serum | Zhejiang Tianhang Biotechnology | 11011-8611 | |
| Gentian violet | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 71019944 | Dissolve in PBS to prepare 0.1% gentian violet/PBS. |
| Giemsa staining solution | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 71020260 | |
| GraphPad Prism version 8.0 software | GraphPad | www.graphpad.com | Statistical analysis. |
| GSK923295 | MedChemExpress | HY-10299 | |
| HeLa cell line | ATCC | CCL-2 | |
| Humidified incubator | Heal Force | HF90/HF240 | |
| Image J software | National Institutes of Health | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ | Image processing and analysis. |
| Inverted microscope | Nanjing Jiangnan Novel Optics | XD-202 | |
| LB agar powder | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) | A507003 | |
| Lipo6000 transfection reagent | Beyotime | C0526 | |
| Nikon Ti-S2 microscope | Nikon | Ti-S2 | |
| Opti-MEM reduced serum medium | Gibco | 31985070 | |
| Paraformaldehyde | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 80096618 | Dissolve in PBS to prepare 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS. |
| Penicillin-streptomycin solution | HyClone | SV30010 | |
| SanPrep column DNA gel extraction kit | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) | B518131 | |
| SanPrep column plasmid mini-preps kit | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) | B518191 | |
| T4 DNA ligase | TaKaRa | 2011A | |
| T4 polynucleotide kinase | TaKaRa | 2021A | |
| TaKaRa Ex Taq | TaKaRa | RR001A | |
| Triton X-100 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 30188928 | Dissolve in PBS to prepare 0.25% Triton X-100/PBS. |
| Tween 20 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent | 30189328 | Dissolve in PBS to prepare 0.1% Tween 20/PBS. |
Referencias
- Jiang, W., Bikard, D., Cox, D., Zhang, F., Marraffini, L. A. RNA-guided editing of bacterial genomes using CRISPR-Cas systems. Nature Biotechnology. 31 (3), 233-239 (2013).
- Bibikova, M., Beumer, K., Trautman, J. K., Carroll, D. Enhancing gene targeting with designed zinc finger nucleases. Science. 300 (5620), 764 (2003).
- Urnov, F. D., Rebar, E. J., Holmes, M. C., Zhang, H. S., Gregory, P. D. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nature Reviews Genetics. 11 (9), 636-646 (2010).
- Joung, J. K., Sander, J. D. TALENs: a widely applicable technology for targeted genome editing. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 14 (1), 49-55 (2013).
- Wood, A. J., et al. Targeted genome editing across species using ZFNs and TALENs. Science. 333 (6040), 307 (2011).
- Stoddard, B. L. Homing endonuclease structure and function. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics. 38 (1), 49-95 (2005).
- Pâques, F., Duchateau, P. Meganucleases and DNA double-strand break-induced recombination: perspectives for gene therapy. Current Gene Therapy. 7 (1), 49-66 (2007).
- Cong, L., et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science. 339 (6121), 819-823 (2013).
- Shmakov, S., et al. Discovery and functional characterization of diverse class 2 CRISPR-Cas systems. Molecular Cell. 60 (3), 385-397 (2015).
- Ran, F. A., et al. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nature Protocols. 8 (11), 2281-2308 (2013).
- Jia, N., Patel, D. J. Structure-based functional mechanisms and biotechnology applications of anti-CRISPR proteins. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 22 (8), 563-579 (2021).
- Hsu, P. D., Lander, E. S., Zhang, F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell. 157 (6), 1262-1278 (2014).
- Horvath, P., Barrangou, R. CRISPR/Cas, the immune system of bacteria and archaea. Science. 327 (5962), 167-170 (2010).
- Gasiunas, G., Barrangou, R., Horvath, P., Siksnys, V. Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (39), E2579-E2586 (2012).
- Jinek, M., et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science. 337 (6096), 816-821 (2012).
- Jackson, S. A., et al. CRISPR-Cas: Adapting to change. Science. 356 (6333), eaal5056 (2017).
- Wood, K. W., Sakowicz, R., Goldstein, L. S., Cleveland, D. W. CENP-E is a plus end-directed kinetochore motor required for metaphase chromosome alignment. Cell. 91 (3), 357-366 (1997).
- Craske, B., Welburn, J. P. I. Leaving no-one behind: how CENP-E facilitates chromosome alignment. Essays in Biochemistry. 64 (2), 313-324 (2020).
- Yu, K. W., Zhong, N., Xiao, Y., She, Z. Y. Mechanisms of kinesin-7 CENP-E in kinetochore-microtubule capture and chromosome alignment during cell division. Biology of the Cell. 111 (6), 143-160 (2019).
- Schaar, B. T., Chan, G. K., Maddox, P., Salmon, E. D., Yen, T. J. CENP-E function at kinetochores is essential for chromosome alignment. Journal of Cell Biology. 139 (6), 1373-1382 (1997).
- McEwen, B. F., et al. CENP-E is essential for reliable bioriented spindle attachment, but chromosome alignment can be achieved via redundant mechanisms in mammalian cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 12 (9), 2776-2789 (2001).
- Yao, X., Abrieu, A., Zheng, Y., Sullivan, K. F., Cleveland, D. W. CENP-E forms a link between attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochores and the mitotic checkpoint. Nature Cell Biology. 2 (8), 484-491 (2000).
- Kim, Y., Heuser, J. E., Waterman, C. M., Cleveland, D. W. CENP-E combines a slow, processive motor and a flexible coiled coil to produce an essential motile kinetochore tether. Journal of Cell Biology. 181 (3), 411-419 (2008).
- Qian, X., et al. Discovery of the first potent and selective inhibitor of Centromere-Associated Protein E: GSK923295. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 1 (1), 30-34 (2010).
- Wood, K. W., et al. Antitumor activity of an allosteric inhibitor of centromere-associated protein-E. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (13), 5839-5844 (2010).
- Pisa, R., Phua, D. Y. Z., Kapoor, T. M. Distinct mechanisms of resistance to a CENP-E inhibitor emerge in near-haploid and diploid cancer cells. Cell Chemical Biology. 27 (7), 850.e6-857.e6 (2020).
- Putkey, F. R., et al. Unstable kinetochore-microtubule capture and chromosomal instability following deletion of CENP-E. Developmental Cell. 3 (3), 351-365 (2002).
- Weaver, B. A., Silk, A. D., Montagna, C., Verdier-Pinard, P., Cleveland, D. W. Aneuploidy acts both oncogenically and as a tumor suppressor. Cancer Cell. 11 (1), 25-36 (2007).
- Silk, A. D., et al. Chromosome missegregation rate predicts whether aneuploidy will promote or suppress tumors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (44), E4134-E4141 (2013).
- Guo, Y., Kim, C., Ahmad, S., Zhang, J., Mao, Y. CENP-E-dependent BubR1 autophosphorylation enhances chromosome alignment and the mitotic checkpoint. Journal of Cell Biology. 198 (2), 205-217 (2012).
- Weaver, B. A., Cleveland, D. W. Aneuploidy: instigator and inhibitor of tumorigenesis. Cancer Research. 67 (21), 10103-10105 (2007).
- Nishimura, K., Fukagawa, T. An efficient method to generate conditional knockout cell lines for essential genes by combination of auxin-inducible degron tag and CRISPR/Cas9. Chromosome Research. 25 (3-4), 253-260 (2017).
- Owa, M., Dynlacht, B. A non-canonical function for Centromere-associated protein-E controls centrosome integrity and orientation of cell division. Communications Biology. 4 (1), 358 (2021).
- Barabási, A. L., Oltvai, Z. N. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nature Reviews Genetics. 5 (2), 101-113 (2004).
- Rossi, A., et al. Genetic compensation induced by deleterious mutations but not gene knockdowns. Nature. 524 (7564), 230-233 (2015).
- Ma, Z., et al. PTC-bearing mRNA elicits a genetic compensation response via Upf3a and COMPASS components. Nature. 568 (7751), 259-263 (2019).
- El-Brolosy, M. A., et al. Genetic compensation triggered by mutant mRNA degradation. Nature. 568 (7751), 193-197 (2019).
- Kung, P. P., et al. Chemogenetic evaluation of the mitotic kinesin CENP-E reveals a critical role in triple-negative breast cancer. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 13 (8), 2104-2115 (2014).
- Kim, J. H., et al. Development of a novel HAC-based "gain of signal" quantitative assay for measuring chromosome instability (CIN) in cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7 (12), 14841-14856 (2016).
- Hirayama, T., et al. Synthetic studies of centromere-associated protein-E (CENP-E) inhibitors: 1. Exploration of fused bicyclic core scaffolds using electrostatic potential map. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 21 (17), 5488-5502 (2013).
- Hirayama, T., et al. Synthetic studies on Centromere-associated protein-E (CENP-E) inhibitors: 2. Application of electrostatic potential map (EPM) and structure-based modeling to Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives as anti-tumor agents. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 58 (20), 8036-8053 (2015).
- Ohashi, A., et al. A novel time-dependent CENP-E inhibitor with potent antitumor activity. PLoS One. 10 (12), e0144675 (2015).
- Ohashi, A., et al. Aneuploidy generates proteotoxic stress and DNA damage concurrently with p53-mediated post-mitotic apoptosis in SAC-impaired cells. Nature Communications. 6, 7668 (2015).
- Ding, X., et al. Probing CENP-E function in chromosome dynamics using small molecule inhibitor syntelin. Cell Research. 20 (12), 1386-1389 (2010).
- Liu, X., et al. Phase separation drives decision making in cell division. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 295 (39), 13419-13431 (2020).
- Henderson, M. C., et al. UA62784, a novel inhibitor of centromere protein E kinesin-like protein. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 8 (1), 36-44 (2009).
- Yamane, M., et al. Identification of benzo[d]pyrrolo[2,1-b]thiazole derivatives as CENP-E inhibitors. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 519 (3), 505-511 (2019).
- Lock, R. B., et al. Initial testing of the CENP-E inhibitor GSK923295A by the pediatric preclinical testing program. Pediatric Blood & Cancer. 58 (6), 916-923 (2012).
- Chung, V., et al. First-time-in-human study of GSK923295, a novel antimitotic inhibitor of centromere-associated protein E (CENP-E), in patients with refractory cancer. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology. 69 (3), 733-741 (2012).
- Hsu, P. D., et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nature biotechnology. 31 (9), 827-832 (2013).
- Weaver, B. A., Cleveland, D. W. Decoding the links between mitosis, cancer, and chemotherapy: The mitotic checkpoint, adaptation, and cell death. Cancer Cell. 8 (1), 7-12 (2005).
- Manchado, E., Guillamot, M., Malumbres, M. Killing cells by targeting mitosis. Cell Death and Differentiation. 19 (3), 369-377 (2012).
- Dang, Y., et al. Optimizing sgRNA structure to improve CRISPR-Cas9 knockout efficiency. Genome Biology. 16, 280 (2015).
- Ratz, M., Testa, I., Hell, S. W., Jakobs, S. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated endogenous protein tagging for RESOLFT super-resolution microscopy of living human cells. Scientific Reports. 5, 9592 (2015).
- Koch, B., et al. Generation and validation of homozygous fluorescent knock-in cells using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. Nature Protocols. 13 (6), 1465-1487 (2018).
- Yan, Q., et al. Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9-based genome engineering enhanced by Drosha-mediated sgRNA-shRNA structure. Scientific Reports. 6, 38970 (2016).
- Cheng, Y., et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated chicken TBK1 gene knockout and its essential role in STING-mediated IFN-β induction in chicken cells. Frontiers in Immunology. 9, 3010 (2019).
- Zhou, Y., et al. High-throughput screening of a CRISPR/Cas9 library for functional genomics in human cells. Nature. 509 (7501), 487-491 (2014).
- Zeng, W., Guo, L., Xu, S., Chen, J., Zhou, J. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology. Trends in Biotechnology. 38 (8), 888-906 (2020).
- Tsai, S. Q., et al. GUIDE-seq enables genome-wide profiling of off-target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas nucleases. Nature Biotechnology. 33 (2), 187-197 (2015).
- Kim, D., et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals specificities of Cpf1 endonucleases in human cells. Nature Biotechnology. 34 (8), 863-868 (2016).
- Komor, A. C., Kim, Y. B., Packer, M. S., Zuris, J. A., Liu, D. R. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature. 533 (7603), 420-424 (2016).
- Nishimasu, H., et al. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease with expanded targeting space. Science. 361 (6408), 1259-1262 (2018).
- Wang, H., et al. One-step generation of mice carrying mutations in multiple genes by CRISPR/Cas-mediated genome engineering. Cell. 153 (4), 910-918 (2013).
- Ablain, J., Durand, E. M., Yang, S., Zhou, Y., Zon, L. I. A CRISPR/Cas9 vector system for tissue-specific gene disruption in zebrafish. Developmental Cell. 32 (6), 756-764 (2015).
- Pickar-Oliver, A., Gersbach, C. A. The next generation of CRISPR-Cas technologies and applications. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 20 (8), 490-507 (2019).
- Nalawansha, D. A., Gomes, I. D., Wambua, M. K., Pflum, M. K. H. HDAC inhibitor-induced mitotic arrest is mediated by Eg5/KIF11 acetylation. Cell Chemical Biology. 24 (4), 481.e5-492.e5 (2017).
- Kavalapure, R. S., et al. Design, synthesis, and molecular docking study of some 2-((7-chloroquinolin-4-yl) amino) benzohydrazide Schiff bases as potential Eg5 inhibitory agents. Bioorganic Chemistry. 116, 105381 (2021).
- Calligaris, D., Lafitte, D. Chemical inhibitors: the challenge of finding the right target. Chemistry & Biology. 18 (5), 555-557 (2011).
- Łomzik, M., et al. Metal-dependent cytotoxic and kinesin spindle protein inhibitory activity of Ru, Os, Rh, and Ir half-sandwich complexes of Ispinesib-derived ligands. Inorganic Chemistry. 59 (20), 14879-14890 (2020).
- Ferro, L. S., et al. Structural and functional insight into regulation of kinesin-1 by microtubule-associated protein MAP7. Science (New York, N.Y.). 375 (6578), 326-331 (2022).
- Atherton, J., et al. The mechanism of kinesin inhibition by kinesin-binding protein. eLife. 9, e61481 (2020).
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoExplorar más artículos
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados