Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Method Article
Identificación de células quiescentes en un modelo de leucemia linfoblástica aguda de células T de pez cebra mediante tinción de proliferación celular
En este artículo
Resumen
Utilizamos la tinción de proliferación celular para identificar células quiescentes en el modelo de leucemia linfoblástica aguda T de pez cebra. La tinción se retiene en las células que no se dividen y se reduce durante la proliferación celular, lo que permite la selección de células inactivas para su posterior interrogación. Este protocolo proporciona una herramienta funcional para estudiar la autorrenovación en el contexto de la quiescencia celular.
Resumen
La quiescencia celular es un estado de detención del crecimiento o proliferación lenta que se describe en las células madre normales y cancerosas (CSC). La quiescencia puede proteger a las CSC de los fármacos quimioterapéuticos antiproliferativos. En los modelos de ratón de xenoinjerto derivado de pacientes (PDX) de leucemia linfoblástica aguda de células T (LLA-T), las células quiescentes se relacionan con la resistencia al tratamiento y la madre. Los tintes para la proliferación celular son herramientas populares para el seguimiento de la división celular. El colorante fluorescente se ancla covalentemente en grupos amina en la membrana y macromoléculas dentro de la célula. Esto permite el seguimiento de las células marcadas hasta 10 divisiones, que pueden resolverse mediante citometría de flujo.
En última instancia, las células con las tasas de proliferación más altas tendrán una baja retención de colorante, ya que se diluirá con cada división celular, mientras que las células inactivas y de división más lenta tendrán la mayor retención. El uso de colorantes de proliferación celular para aislar células inactivas se ha optimizado y descrito en modelos de ratón con LLA-T. Complementario a los modelos de ratón existentes, el modelo de LLA-ALL de pez cebra derivado de rag2:Myc proporciona un excelente lugar para interrogar la autorrenovación en la LLA-T debido a la alta frecuencia de células madre leucémicas (LSC) y la conveniencia del pez cebra para experimentos de trasplante a gran escala.
Aquí, describimos el flujo de trabajo para la tinción de células T-ALL de pez cebra con un colorante de proliferación celular, optimizando la concentración del colorante para células de pez cebra, pasando células teñidas con éxito in vivo y la recolección de células con diferentes niveles de retención de colorante mediante la clasificación de células vivas de animales trasplantados. Dada la ausencia de creadores de superficie celular bien establecidos para las LSC en la LLA-T, este enfoque proporciona un medio funcional para interrogar a las células inactivas in vivo. Para obtener resultados representativos, describimos la eficiencia del injerto y la frecuencia de LSC de celdas de alta y baja retención de colorante. Este método puede ayudar a investigar propiedades adicionales de las células quiescentes, incluida la respuesta a los fármacos, los perfiles transcripcionales y la morfología.
Introducción
Las células madre adultas son responsables de la regeneración de tipos celulares diferenciados en un órgano determinado y están presentes predominantemente en un estado latente y no dividido 1,2. Por ejemplo, las células madre hematopoyéticas (HSC), que mantienen la sangre, permanecen en gran medida inactivas, y solo una pequeña fracción ingresa al ciclo celular para autorenovarse o diferenciarse paragenerar componentes sanguíneos maduros. De manera similar, en los cánceres, una subpoblación rara de células llamadas células madre cancerosas (CSC) poseen la capacidad de autorrenovación y son responsables del mantenimiento a largo plazo de la neoplasiamaligna. Las células madre cancerosas existen in vivo en un estado de quietud o crecimiento lento, lo que puede permitirles escapar de los tratamientos antiproliferativos contra el cáncer5, evadir la eliminación del sistema inmunológico6, reducir el estrés oxidativo y mejorar sus vías de reparación del ADN7. Incluso un número bajo de CSC que quedan después del tratamiento puede potencialmente repoblar el tumor, lo que resulta en la recaída del paciente8. En consecuencia, la comprensión de la quiescencia celular es muy prometedora para la identificación de posibles vulnerabilidades de las CSC y el desarrollo de nuevas formas de abordarlas.
Los colorantes de proliferación celular, como la tinción de éster de carboxifluoresceína succinimidilo (CFSE) y sus derivados, se utilizan comúnmente para rastrear la frecuencia de las divisiones celulares9. El colorante penetra a través de la membrana celular y, una vez dentro de la célula, se activa mediante esterasas intracelulares en un producto fluorescente. El compuesto fluorescente resultante se retiene dentro de la célula a través de los enlaces amida covalentes formados entre la fracción succinimidil y los grupos funcionales amina de las proteínas intracelulares10. Con cada división celular, el compuesto fluorescente se divide en partes iguales entre las dos células resultantes, lo que provoca una dilución de señal doble. Este colorante permite la detección de hasta 10 divisiones celulares mediante análisis de citometría de flujo11.
Este enfoque se ha utilizado previamente para enriquecer las poblaciones de CSC in vitro mediante la identificación de poblaciones de células de ciclo lento con alta retención del colorante11,12. En la LLA-T, la CFSE se ha utilizado para rastrear el crecimiento tumoral in vivo en xenoinjertos derivados de pacientes en ratones. Después del marcaje celular y tres semanas de trasplante, el análisis de citometría de flujo mostró una población rara de células que aún conservaban la fluorescencia de CFSE. Esta población se asoció con la madre, la resistencia al tratamiento y la alta similitud con las células causantes de recaídas en los pacientes13. En consecuencia, este colorante proporciona una herramienta útil para el estudio de los fenotipos de células madre de leucemia (LSC) en la LLA-T.
El objetivo del trabajo es extender la aplicación del colorante de proliferación celular para estudiar la quiescencia in vivo utilizando un modelo de LLA-T de pez cebra. En particular, el modelo14 de pez cebra T-ALL impulsado por rag2:Myc proporciona un excelente lugar para el estudio de la autorrenovación debido a la alta frecuencia de LSC en comparación con los modelos de ratón y las enfermedades humanas15. Además, el uso del pez cebra permite realizar estudios de trasplante a gran escala, que pueden realizarse a un costo mucho menor de cuidado y mantenimiento en comparación con sus contrapartes de ratón16. El pez cebra también es excelente para aplicaciones de imágenes en vivo, ya que las células tumorales marcadas con fluorescencia se pueden ver fácilmente utilizando un microscopio de fluorescencia simple para estimar la tasa de desarrollotumoral.
En este protocolo, describimos el flujo de trabajo para la tinción de células T-ALL de pez cebra con colorante de proliferación celular seguido de la propagación in vivo de células teñidas en pez cebra singénico CG1. Tras el desarrollo de la leucemia, describimos la clasificación de las células que retuvieron el colorante y su uso para un posterior experimento de trasplante de dilución limitante para cuantificar las tasas de autorrenovación de LSC. Este protocolo puede ampliarse para aplicaciones adicionales, incluido el cribado in vivo de fármacos de posibles compuestos para dirigirse a las LSC inactivas. Además, las células recolectadas se pueden utilizar para diferentes análisis posteriores, como el perfil transcriptómico, la proteómica y la metabolómica, lo que ofrece información única sobre el comportamiento de las LSC inactivas en la LLA-T.
Protocolo
En este protocolo, estamos utilizando células T-ALL de pez cebra marcadas con GFP que se generaron previamente en la cepa CG1 y, por lo tanto, pueden inyectarse directamente en el pez cebra CG1 singénicoreceptor 15. En resumen, la leucemia se generó por microinyección de ADN de rag2:Myc y rag2:GFP en embriones unicelulares de pez cebra CG1. Los animales fueron monitoreados para el desarrollo de leucemia a partir de las 3 semanas posteriores a la inyección, utilizando microscopía de fluorescencia. Las células leucémicas positivas para GFP se aislaron en FACS y se trasplantaron en serie en el pez cebra receptor CG1 para generar clones con una alta frecuencia de LSC. Los detalles de todo el protocolo son descritos por Blackburn et al.15.
Alternativamente, la T-ALL derivada de rag2:Myc primaria puede generarse mediante microinyección de ADN de embriones de pez cebra17. La microinyección de ADN de rag2:Myc con un reportero fluorescente impulsado por rag2, como GFP, puede dar lugar al desarrollo de células B, células T y ALL18 mixtas. Se verificó previamente que los clones de leucemia utilizados en este protocolo eran T-ALL15. Todos los procedimientos experimentales con pez cebra fueron revisados y aprobados por el Comité Institucional de Cuidado y Uso de Animales de la Universidad de Kentucky, protocolo 2019-3399.
1. Propagación de células de LLA-T de pez cebra in vivo
- Descongele un vial que contenga 1 ml de células T-ALL de pez cebra congeladas marcadas con GFP en un baño de agua a 37 °C con agitación suave, hasta que se descongele. Una vez descongelado, transfiéralo a hielo.
- Pipetee lentamente el contenido del tubo en un tubo cónico de 15 mL con 4 mL de medio de pescado (0,9x PBS + 5% FBS) para diluir el medio de congelación.
- Centrifugar durante 5 min a 2.500 × g a 4 °C. Retire los medios del pellet. Vuelva a suspender en 0,5 ml de medio para peces y mantenga las células en hielo.
- Cuente las células y dilúyalas si es necesario hasta 100.000 células/5 μL.
- Anestesiar el pez cebra CG1 adulto añadiendo 200 μL de 4 mg/mL de anestésico (MS-222) a 25 mL de agua del sistema de peces en una placa de Petri. Sostenga el pez CG1 con la parte ventral hacia arriba e inyecte 5-6 μL en el espacio intraperitoneal (IP) con una jeringa de microlitros Hamilton. Mueva a los animales de regreso a sus tanques y controle si vuelven a nadar normalmente antes de volver a colocarlos en el sistema.
NOTA: Se utilizaron peces cebra adultos, de 60 días o más, para los estudios de trasplante descritos en este protocolo. - Controle el crecimiento de la leucemia una vez por semana con un microscopio de fluorescencia. Consulte la sección 2 a continuación para obtener detalles sobre el procedimiento de detección.
2. Recolección de células leucémicas marcadas con fluorescencia
- Aproximadamente 21-28 días después del trasplante, anestesiar al pez cebra CG1 adulto añadiendo 200 μL (4-5 gotas) de 4 mg/mL de anestésico a 25 mL de agua del sistema de peces en una placa de Petri.
- Examinar el pez cebra CG1 para detectar la carga de leucemia evaluando el porcentaje de células leucémicas marcadas con GFP en el animal con un microscopio epifluorescente, utilizando el filtro adecuado para detectar la fluorescencia de GFP. La leucemia GFP positiva está lista para ser cosechada si se ha diseminado en el >70% del animal.
- Eutanasiar al animal añadiendo 1 mL de anestésico de 4 mg/mL en una placa de Petri que contenga 9 mL de agua del sistema de peces. Permite que cesen todas las señales de vida; Por ejemplo, observe el cese del movimiento opercular de los peces (~5 min).
- Mueva el pez cebra a una nueva placa de Petri y agregue 1 ml de medio de pescado para que sirva como amortiguador para las células. Con una nueva hoja de afeitar, primero decapita al pez cebra y luego macera el tejido con la misma hoja de afeitar. Pipetear hacia arriba y hacia abajo para desalojar grandes grupos de células.
- Pase las células a través de un filtro celular de 40 μm a un tubo cónico de 50 mL para disociarlas en una suspensión de una sola célula. Mantenga las células en hielo.
3. Optimización de la concentración del colorante de proliferación celular (CellTrace Far Red) para la tinción y la viabilidad celular del pez cebra
NOTA: Para este protocolo, y dado que las células tumorales están marcadas con GFP, utilizamos un colorante de proliferación de glóbulos rojos lejanos (CellTrace Far Red) para evitar la superposición espectral, que se denominará CT-FR.
- Prepare una solución de 1 mM del tinte fluorescente inmediatamente antes de usarlo agregando el volumen apropiado de DMSO según las recomendaciones del fabricante. Tienen soluciones de trabajo de 1 mM, 0,5 mM, 0,1 mM y 0,01 mM; diluir según sea necesario en medios de pescado para probar la viabilidad celular después de la tinción.
- Cuente las células y recoja 1 × 106 células en tubos de microcentrífuga de 1,5 ml.
- Centrifugar a 2.500 × g a 4 °C durante 5 min. Retire el líquido y vuelva a suspender las células en 1 ml de 0,9x PBS.
- Divida la suspensión celular en cuatro tubos de 250 μL cada uno para el tratamiento con CT-FR.
- Añada 250 μL de PBS 0,9x para elevar el volumen a 500 μL cada uno con aproximadamente 250.000 células/tubo.
- Añada las cantidades necesarias de las soluciones de trabajo descritas anteriormente a cada uno de los cuatro tubos para alcanzar las siguientes concentraciones finales: 1 μM, 0,5 μM, 0,1 μM y 0,05 μM. Incubar durante 20 minutos a 37 °C, protegido de la luz.
- Granule las células girando a 2.500 × g durante 5 min a temperatura ambiente. Retire el líquido y lave las células con 500 μL de medio de pescado para eliminar el exceso de colorante.
- Vuelva a pelar, retire el líquido y vuelva a suspender en 25 μL de medio de pescado. Utilice 1 μL para contar las células en una dilución 1:10 en 50% de Azul de Tripán.
- Examinar las células bajo el microscopio para determinar su viabilidad celular; Las células vivas no retendrán el azul tripán y se verán brillantes bajo el microscopio, mientras que las células muertas absorberán el tinte y se verán oscuras. Examine primero las células bajo el canal de fluorescencia apropiado para identificar las células tumorales y luego use el canal de campo claro para evaluar la viabilidad celular.
- Seleccione la concentración que dé como resultado una tinción exitosa mientras se mantiene la viabilidad celular (>90% de células tripan-azul negativas).
NOTA: Para las células T-ALL de pez cebra probadas en este experimento, se utilizó una concentración de 1 μM para una tinción exitosa y un >90% de la viabilidad celular.
4. Propagación de células de pez cebra T-ALL teñidas con CT-FR in vivo
- Usando la concentración optimizada de CT-FR de la Sección 3, tiña las células de pez cebra. Deje algunas células tumorales sin teñir para la generación del tumor T-ALL marcado con GFP, como control positivo para GFP durante la clasificación de FACS. Diluir las células teñidas y no teñidas a 50.000 células/5 μL para el trasplante.
- Anestesiar el pez cebra CG1 adulto añadiendo 200 μL de 4 mg/mL de anestésico a 25 mL de agua del sistema de peces en una placa de Petri.
- Inyecte 5 μL de la suspensión celular en la cavidad IP del pez cebra como se describe en la sección 1 tanto para las células teñidas como para las no teñidas. Inyecte 5-6 peces cebra por grupo para tener en cuenta la mortalidad potencial después de la inyección.
- Examinar a los animales mediante microscopía fluorescente bajo sedación 2 veces por semana para detectar el desarrollo de leucemia.
NOTA: Después de ~ 10-14 días, la leucemia debería ocupar aproximadamente el 30-40% de este cuerpo. Planifique la recolección de leucemia y la clasificación posterior dentro de este período de tiempo. Esperar a que el tumor se expanda a un tamaño grande puede resultar en una mayor dilución del tinte celular fluorescente y dificultad para detectar su señal. Considere la optimización del momento de la extracción del tumor para el modelo tumoral elegido. Además, se recomienda un seguimiento tumoral más frecuente para garantizar la captura del tamaño tumoral deseado.
5. Preparación para la clasificación de células T-ALL de pez cebra teñidas con CT-FR
- Prepare los siguientes controles para la clasificación de células: Sin control de color (sin teñir, no transgénico, suspensión unicelular, de un pez cebra de tipo salvaje), células T-ALL marcadas con GFP y células de pez cebra CT-FR WT recién teñidas (para establecer un umbral máximo de señal de rojo lejano).
- Preparación de controles sin teñir y CT-FR
- Recoja células de peces de tipo silvestre (WT) mediante la eutanasia de un pez cebra CG1 no trasplantado agregando 1 mL de anestésico de 4 mg/mL en una placa de Petri que contenga 9 mL de agua del sistema de peces.
- Mueva el pez cebra a una nueva placa de Petri y agregue 1 ml de medio de pescado para que sirva como amortiguador para las células. Use una nueva hoja de afeitar para decapitar primero y luego macerar al pez cebra con la misma hoja de afeitar; pipetear hacia arriba y hacia abajo para desalojar los grandes grupos de células.
- Pase las células a través de un filtro celular de 40 μm a un tubo cónico de 50 mL para disociarlas en una suspensión de una sola célula. Mantenga las células en hielo.
- Para el control CT-FR, transfiera 250.000 células WT a un tubo de microcentrífuga y granule las células por centrifugación a 2.500 × g durante 5 minutos a temperatura ambiente. Retire el medio de pescado y agregue 500 μL de 0,9x PBS+ 1% FBS.
- Añadir 0,5 μL de la solución madre de colorante CT-FR de 1 mM para obtener una concentración final de 1 μM. Pipetear suavemente con 1.000 μL de pipeta para mezclar. Incubar a 37 °C durante 20 min, protegido de la luz.
- Retire el líquido y lave las células con 500 μL de medio de pescado para eliminar el exceso de colorante.
- Vuelva a granular las células por centrifugación, retire el líquido y vuelva a suspender las células en 500 μL de 0,9x PBS+ 1% FBS y páselas a través de una tapa de filtro de 35 μm a un tubo FACS. Mantener en hielo.
- Preparación de la placa del donante
NOTA: La placa donante es una placa inferior en V de 96 pocillos en la que se clasificarán las células T-ALL teñidas con CT-FR del pez cebra trasplantado. Cada pocillo de la placa contiene 5.000 células WT CG1 sin teñir en 50 μL de medio de pescado para servir como portador y ayudar a pelar las células clasificadas en los pasos siguientes.- Cuente 500.000 células WT CG1 y transfiéralas a un tubo cónico de 15 ml.
- Diluya este caldo celular a 100 células/μL añadiendo 5 mL de medio de pescado.
- Dispense 50 μL de la suspensión celular en cada pocillo de la placa de 96 pocillos. Mezcle el tubo de suspensión celular después de cada fila para mantener la homogeneidad de la suspensión celular. Mantenga la placa a 4 °C hasta la clasificación.
- Preparación de las muestras de peces trasplantados
- Seleccione peces trasplantados con una carga de T-ALL del 30-40%. Recoja peces trasplantados con células teñidas con CT-FR y células tumorales GFP sin teñir.
- Recolectar células como se describe en la Sección 2.
NOTA: Dado que se espera que las células retenedoras de colorante estén presentes en una abundancia baja, prepárese para clasificar una gran cantidad de células de la muestra de GFP CT-FR. - Diluir en la concentración adecuada para clasificar ~ 3-5 × 106 celdas/mL en 0.9x PBS + 1% FBS y pasar a través de una tapa de filtro de 35 μm a un tubo FACS. Agregue DAPI (1 mg/mL) en dilución 1:1,000 como un colorante vital para excluir las células muertas. Mantener en hielo.
- En el caso de las células tumorales GFP no teñidas, transfiera 250.000 células a un tubo de microcentrífuga y granule a 2.500 × g durante 5 minutos a temperatura ambiente. Retire el medio de pescado, agregue 500 μL de PBS y pase a través de una tapa de filtro de 35 μm a un tubo FACS. Mantener en hielo.
6. Clasificación
NOTA: Mantenga todos los tubos y la placa donante en hielo todo el tiempo, excepto cuando se use para clasificar.
- Para ordenar los parámetros y las puertas, comience por aplicar la compuerta de dispersión frontal y lateral para identificar las celdas de interés en función de su tamaño y eliminar los desechos de celda. A continuación, utilice la altura de dispersión hacia adelante frente al área de dispersión hacia adelante para excluir las celdas duplicadas y mantener solo los singletes. Por último, utilice los controles sin color y de un solo color para dibujar los cuadrantes e identificar las poblaciones de células positivas para GFP y CT-FR positivas.
NOTA: Se espera que el control de CT-FR sea mucho más brillante que las muestras para clasificar, ya que la tinción para el control se realizó fresca sin divisiones celulares; Se espera que las células de las muestras de GFP de CT-FR aparezcan en el extremo inferior de la puerta positiva de CT-FR. - Clasifique el número de células que se trasplantarán en cada pez en un pocillo de la placa donante.
NOTA: Para este experimento, utilizamos un ensayo de dilución limitante para estimar la frecuencia de células madre de leucemia en CT-FR High y CT-FR Low. Este ensayo utilizó una dosis de 25 células, trasplantadas a 3 animales, y una dosis de 10 células, trasplantadas a 10 animales. Un ensayo de dilución limitante típico utilizando la LLA-ALL derivada del pez cebra rag2:Myc involucraría un grupo con un mayor número de células (500 o 1.000), ya que la frecuencia de LSC en este modelo se estima en 1 LSC en cientos de células. Sin embargo, en este ensayo, estamos utilizando uno de los clones de T-ALL previamente descritos por Blackburn et al.15. La frecuencia de LSC en la muestra utilizada aquí es ~1 LSC en decenas de células; Predecimos que la leucemia se detectará en animales trasplantados en el grupo de 25 células. Al optimizar este ensayo para su modelo de enfermedad, se debe tener cuidado al seleccionar el grupo de número de células más alto para garantizar el injerto del tumor. - Después de clasificar, mantenga la placa en hielo hasta que esté lista para el trasplante.
NOTA: Los procedimientos de clasificación pueden ser estresantes y afectar la viabilidad de la célula. Antes de ejecutar el experimento de dilución limitante real, se realizó un experimento piloto de clasificación. Se trasplantaron las células seleccionadas y se monitoreó el desarrollo de la leucemia para determinar si la clasificación era perjudicial para la viabilidad celular. Alternativamente, la viabilidad celular se puede evaluar tiñendo las células clasificadas con azul de tripán y examinándolas bajo el microscopio antes del trasplante.
7. Trasplante de células clasificadas en la dilución límite y seguimiento de la aparición del tumor
- Gire la placa con una centrífuga de sobremesa grande a 2.500 × g a 4 °C.
- Retire con cuidado 45 μL del sobrenadante de cada pocillo, dejando 5 μL de líquido y asegurándose de evitar tocar el pellet de celda en el fondo del pocillo.
- Vuelva a suspender las células con una pipeta de 20 μL. Vuelva a suspender 2-3 pocillos con la pipeta y luego, con la jeringa de microlitro Hamilton, inyecte las suspensiones celulares de cada pocillo en el número deseado de pez cebra CG1 mediante trasplante IP. Luego, vuelva a suspender las células en el siguiente grupo de pocillos para evitar el reasentamiento de las células.
- Examinar el pez cebra mediante microscopía de fluorescencia bajo sedación una vez a la semana para detectar el desarrollo de LLA-T durante al menos 6 semanas.
8. Determinación de la frecuencia de células madre leucémicas
- Registre el número de animales positivos por dosis de célula y grupo de tratamiento a las 6 semanas después del trasplante, considerando que los animales con cualquier cantidad de señal de GFP son positivos. Se considera que los animales tienen una carga significativa de leucemia cuando la señal GFP ocupa el >50% del cuerpo.
- Utilice el software estadístico ELDA (Extreme Limiting Dilution Analysis) (http://bioinf.wehi.edu.au/software/elda/)19 basado en la web para calcular la frecuencia de LSC dentro de cada población celular.
NOTA: En la Figura 1 se proporciona una ilustración esquemática del flujo de trabajo.
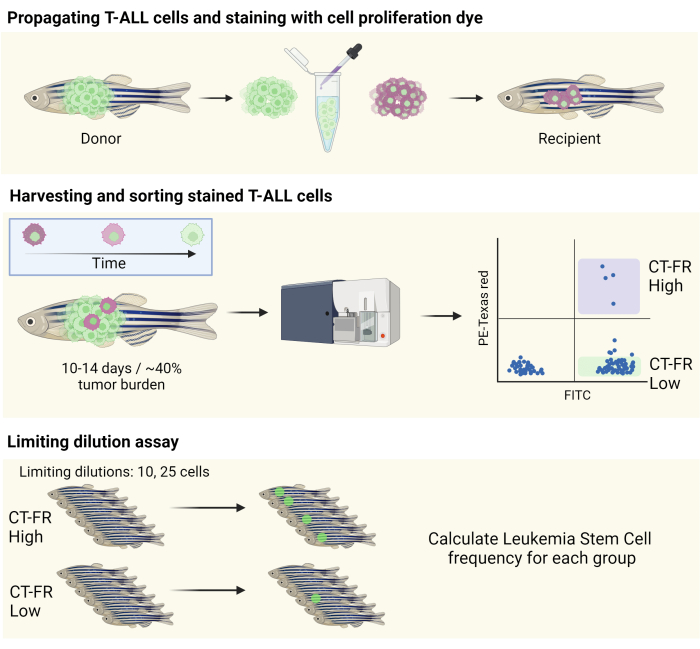
Figura 1: Flujo de trabajo para el uso de la tinción de seguimiento celular para aislar células inactivas en el modelo T-ALL de pez cebra. Ilustración esquemática de la tinción de células T-ALL de pez cebra con la tinción de proliferación celular, la propagación en un pez cebra CG1 (panel superior) y la clasificación de las células en función de la retención de la tinción de proliferación celular (panel central). Las células recolectadas se utilizaron para un ensayo de dilución limitante para determinar la frecuencia de LSC (panel inferior). Abreviaturas: LLA-T = leucemia linfoblástica aguda de células T; LSC = células madre leucémicas; CT-FR = CellTrace rojo lejano; FITC = isotiocianato de fluoresceína; PE = ficoeritrina. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
Resultados
Seguimos el protocolo descrito anteriormente para clasificar las células que han retenido el colorante de proliferación celular, CT-FR, y las utilizamos para un ensayo de dilución limitante (LDA) para estimar la frecuencia de LSC en las poblaciones de CT-FR High y CT-FR Low. Para establecer la compuerta para el experimento de citometría de flujo, utilizamos un control sin fluoróforo (sin color) además de controles de un solo color (Figura 2A).<...
Discusión
Se sabe que las LSC son resistentes a los tratamientos convencionales de quimioterapia antiproliferativa, y el hallazgo de terapias dirigidas contra estas células es muy prometedor para reducir la aparición de recaídas y mejorar el pronóstico de los pacientes20. Investigaciones previas describieron el uso de tinciones de proliferación celular fluorescente para identificar una pequeña población de células quiescentes asociadas con resistencia a medicamentos...
Divulgaciones
Los autores no tienen conflictos de intereses que revelar.
Agradecimientos
La financiación de esta investigación fue proporcionada por el Instituto Nacional del Cáncer (R37CA227656 a JSB). Esta investigación también fue apoyada por los Recursos Compartidos de Citometría de Flujo y Monitoreo Inmunológico del Centro Oncológico Markey de la Universidad de Kentucky (P30CA177558).
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 26 G/2” micro-syringe | Hamilton | 87930 | NA |
| 35 µm filter cap FACS tubes | Falcon | 352235 | NA |
| 40 µm cell strainer | CELLTREAT | 229482 | NA |
| 96-well skirted PCR plate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AB0800 | NA |
| Cell sorter | Sony Biotechnology | SY3200 | NA |
| CellTrace Far Red | Thermo Fisher Scientific | C34564 | NA |
| Conical tubes | VWR | 10026-078 | NA |
| DAPI | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 62248 | NA |
| DMSO | Sigma-Aldrich | D4818 | NA |
| Dulbecco'sPhosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | Caisson Labs | 22110001 | NA |
| Epifluorescence stereo microscope | Nikon | SMZ25 | NA |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Sigma-Aldrich | 12306C | NA |
| Fish system water | N/A | N/A | 0.03-0.05% salinity, pH 6.5-8, buffered with sodium bicarbonate |
| Microcentrifuge tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | C2171 | NA |
| MS-222 | Pentaire | TRS-1 | tricaine mesylate, an anesthetic |
| Petri dishes | Corning | 07-202-011 | NA |
| Razor blades | American Line | 66-0089 | NA |
| Trypan Blue | Thermo Fisher Scientific | T10282 | NA |
Referencias
- Reya, T., Morrison, S. J., Clarke, M. F., Weissman, I. L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 414 (6859), 105-111 (2001).
- Arai, F., et al. Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell. 118 (2), 149-161 (2004).
- Li, L., Bhatia, R. Stem cell quiescence. Clin. Cancer Res. 17 (15), 4936-4941 (2011).
- Kreso, A., Dick, J. E. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 14 (3), 275-291 (2014).
- Chen, W., Dong, J., Haiech, J., Kilhoffer, M. -. C., Zeniou, M. Cancer stem cell quiescence and plasticity as major challenges in cancer therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 1740936 (2016).
- Kleffel, S., Schatton, T. Tumor dormancy and cancer stem cells: Two sides of the same coin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 734, 145-179 (2013).
- Tuy, K., Rickenbacker, L., Hjelmeland, A. B. Reactive oxygen species produced by altered tumor metabolism impacts cancer stem cell maintenance. Redox Biol. 44, 101953 (2021).
- Zhou, B. -. B. S., et al. Tumour-initiating cells: Challenges and opportunities for anticancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8 (10), 806-823 (2009).
- Lyons, A. B., Blake, S. J., Doherty, K. V. Flow cytometric analysis of cell division by dilution of cfse and related dyes. Curr Protoc Cytom. 64 (1), 11-12 (2013).
- Lyons, A. B. Analysing cell division in vivo and in vitro using flow cytometric measurement of cfse dye dilution. J Immunol Methods. 243 (1-2), 147-154 (2000).
- Azari, H., Deleyrolle, L. P., Reynolds, B. A. Using carboxy fluorescein succinimidyl ester (cfse) to identify quiescent glioblastoma stem-like cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1686, 59-67 (2018).
- Deleyrolle, L. P., Rohaus, M. R., Fortin, J. M., Reynolds, B. A., Azari, H. Identification and isolation of slow-dividing cells in human glioblastoma using carboxy fluorescein succinimidyl ester (cfse). J Vis Exp. (62), e3918 (2012).
- Ebinger, S., et al. Characterization of rare, dormant, and therapy-resistant cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 30 (6), 849-862 (2016).
- Langenau, D. M., et al. Myc-induced t cell leukemia in transgenic zebrafish. Science. 299 (5608), 887-890 (2003).
- Blackburn, J. S., et al. Clonal evolution enhances leukemia-propagating cell frequency in t cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia through akt/mtorc1 pathway activation. Cancer Cell. 25 (3), 366-378 (2014).
- Al-Hamaly, M. A., Turner, L. T., Rivera-Martinez, A., Rodriguez, A., Blackburn, J. S. Zebrafish cancer avatars: A translational platform for analyzing tumor heterogeneity and predicting patient outcomes. Int J Mol Sci. 24 (3), 2288 (2023).
- Blackburn, J. S., Liu, S., Langenau, D. M. Quantifying the frequency of tumor-propagating cells using limiting dilution cell transplantation in syngeneic zebrafish. J Vis Exp. (53), e2790 (2011).
- Borga, C., et al. Simultaneous b and t cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias in zebrafish driven by transgenic myc: Implications for oncogenesis and lymphopoiesis. Leukemia. 33 (2), 333-347 (2019).
- Hu, Y., Smyth, G. K. Elda: Extreme limiting dilution analysis for comparing depleted and enriched populations in stem cell and other assays. J Immunol Methods. 347 (1-2), 70-78 (2009).
- Bhojwani, D., Pui, C. -. H. Relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 14 (6), e205-e217 (2013).
- Zon, L. I., Peterson, R. T. In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4 (1), 35-44 (2005).
- Al-Hamaly, M. A., et al. Zebrafish drug screening identifies erlotinib as an inhibitor of wnt/β-catenin signaling and self-renewal in t-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biomed Pharmacother. 170, 116013 (2024).
- Yan, C., et al. Visualizing engrafted human cancer and therapy responses in immunodeficient zebrafish. Cell. 177 (7), 1903-1914 (2019).
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoExplorar más artículos
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados