A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
יישום סדרתית של הזכוכית Coverslips להעריך את הדחיסה הנוקשת של עדשות העכבר: ניתוח זנים ואת morphometric
In This Article
Summary
Age-related increases in eye lens stiffness are linked to presbyopia. This protocol describes a simple, cost-effective method for measuring mouse lens stiffness. Mouse lenses, like human lenses, become stiffer with age. This method is precise and can be adapted for lenses from larger animals.
Abstract
עדשת העין היא איבר שקוף כי ומשגרת ומתמקד אור כדי ליצור תמונה ברורה על הרשתית. אצל בני אדם, שרירים מתכווצים ריסים כדי לעוות את העדשה, מה שמוביל לעלייה בכוחה האופטי 'העדשה להתמקד בעצמים קרובים, תהליך המכונה אירוח. גיל הקשורים שינויים נוקשים עדשה קושרו פרסביופיה, הפחתת העדשה 'היכולת להכיל, ובהרחבה, את הצורך במשקפי קריאה. למרות עדשות עכבר אינה להתאים או לפתח פרסביופיה, במודלים של עכברים יכולים לספק כלי רב ערך עבור גנטי פתולוגיות עדשת הבנה, וההזדקנות המואצת נצפתה בעכברים מאפשרת הלימוד של שינויים הקשורים בגיל בעדשה. פרוטוקול זה מדגים שיטה פשוטה, מדויקת, וחסכונית לקביעת נוקשות עדשת עכבר, באמצעות coverslips זכוכית ליישם ברצף הגדלת עומסי דחיסה על גבי העדשה. נציג נתונים לאשר עדשות העכבר להיות נוקשה עם הגיל, כמועדשות אדם. שיטה זו היא מאוד לשחזור ואף עלול להיות מדורג עד מכנית עדשות מבחן מחיות גדולות יותר.
Introduction
The lens is a transparent and avascular organ in the anterior chamber of the eye that is responsible for fine focusing of light onto the retina. A clear basement membrane, called the lens capsule, surrounds a bulk of elongated fiber cells covered by an anterior monolayer of epithelial cells1,2. Life-long growth of the lens depends on the continuous proliferation and differentiation of epithelial cells at the lens equator into new fiber cells that are added onto previous generations of fiber cells in a concentric manner2. Over time, lens fiber cells undergo compaction, resulting in a rigid center in the middle of the lens called the nucleus1. Accommodation, defined as a dioptric change in the optical power of the eye, occurs in humans when the ciliary muscles contract to deform the lens and allow a true increase in optical power to focus on near objects3-5. In the unaccommodated eye, the lens is held in a relatively flattened state due to tension from zonular fibers. When the ciliary muscles contract, the tension on the lens is released, leading to decreased lens equatorial diameter and increased axial thickness. Age-related changes in the lens cause presbyopia, a progressive loss of lens accommodation, which leads to the need for reading glasses.
Several studies have linked presbyopia to age-related increase in the intrinsic stiffness of the lens6-11. Stiffness is defined as the resistance of an elastic object to deform under applied load. A variety of methods have been used to examine stiffness of human lenses, including spin compression12-14, actuator compression15, probe indentation16, dynamic mechanical analysis 6,10 and bubble-based acoustic radiation force17. While mouse lenses do not accommodate or develop presbyopia, mouse models for lens pathologies are valuable tools because mice are less expensive than larger animals, well characterized genetically and undergo accelerated age-related changes due to rapid aging. A handful of studies have examined mouse lens stiffness with compression methods and demonstrated changes in lens stiffness due to aging or targeted genetic disruptions18-21. Thus, mouse lenses are good models for studying age-related changes in lens stiffness.
This protocol describes a simple and inexpensive, yet precise and reproducible, compression method for determining mouse lens stiffness based on application of glass coverslips onto the lens in conjunction with photographing the lens through a dissection microscope and mirror. This method yields robust strain and morphometric data with an easily fabricated and assembled apparatus. The representative results confirm that mouse lenses increase in stiffness with age.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
הנהלים כל חיה בוצעו בהתאם ההמלצות מדריך לטיפול ושימוש בחיות מעבדה על ידי המכונים הלאומיים לבריאות ותחת פרוטוקול שאושר על ידי ועדת טיפול בבעלי חיים מוסדיים השתמש במכון המחקר סקריפס.
1. עדשות Dissection
- להרדים עכברים על פי המלצות המכונים הלאומיים לבריאות "מדריך לטיפול והשימוש בחי מעבדה" ופרוטוקולי שימוש בבעלי חיים במוסד שאושר.
- Enucleate העין מעכברים באמצעות מלקחיים מעוקלים. לדכא את הרקמה סביב העין עם מלקחיים כדי להביא את העין מתוך השקע, ואז לקטוף את העין מהשקע עם מלקחיים. עבר עיניים בופר פוספט 1x הטרי (PBS) בצלחת לנתיחה.
- חותכים את עצב הראייה קרוב גלגל העין ככל האפשר. בעדינות ובזהירות להכניס פינצטה ישר עדין אל תוך גלגל העין דרך wher חורדואר עצב הראייה יוצא האחורי.
- בזהירות עושים חתך במספריים לתוך גלגל העין מן אחורי אל הקצה של הקרנית. עדשות מכרסמות לכבוש ~ 30% של העין. ודא חתכים אלה בזהירות, ואל תכניס פינצטה או מספריים עמוק מדי לתוך העין כדי למנוע נזק העדשה.
- חותכים לאורך המפגש בין הקרנית בלובן העין בבית חצי הדרך לפחות סביב גלגל העין.
- דחוף בעדינות את הקרנית כדי להסיר את העדשה מהעין דרך הפתח שנעשה צעדי 1.4 ו -1.5.
- שימוש במלקחיים ישר טיפ נאים כדי להסיר כל פסולת גדולה בזהירות כי הוא עדיין מחובר העדשה. ראייה לבדוק את העדשה לכל נזק לפני שתמשיך המדידות נוקשות.
2. מדידות נוקשות
- לשקול לפחות 10 coverslips מאותה תיבה באמצעות איזון אנליטיים. מצא את המשקל הממוצע של coverslips. לקבלת עקביות, השתמש באותה קופסת coverslips עבור כל הניסויים. טרום רטובבמראה coverslips ו-זווית ישרה ב PBS 1x בטמפרטורת החדר למשך שעה לפחות 2 לפני תחילת הניסויים.
- ממלא את החדר המדיד (ראה איור 1) עם 65 - 75 מיליליטר של 1x PBS. תא המדידה נעשה מתוך פרספקס ידי חנות מכונת in-house, ואת divots בתא נעשה על ידי מקדחה מוגדרת לעומק הרצוי עם מקדח מתאים. עדשות לשמור על שקיפות ב 1x PBS בטמפרטורת החדר למשך בדיקות מכניות.

איור 1:. נוקשות מדידת לשכת תצלום מראה את הממדים של חדר המדידה נוקשת מחוייט עם מגוון רחב של divots עומקים שונים ובצורות שונות. Divots העגול 200 מיקרומטר או 300 מיקרומטר עמוק (ראשי חץ צהובים) משמש את המידות על עדשות עכבר. Divots הם 2 מ"מ בקוטר ~ 13-. 14 מ"מ מהקצה של החדר אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
- מניחים המראים בזווית ישר לתוך התא במרחק קבוע מן השקע אשר ישמש כדי להחזיק את העדשה. ודא במראה לא זז במהלך הניסוי.
- עדשות העברת גזור לתא מדידה בקפידה עם מלקחיים לתפוס או מלקחיים מעוקלים.
- קח תמונה עליונה לאור העדשה פרקה ישר מלמעלה. קח תמונות העדשה העכבר 30X הגדלה עם תאורה מ מיקרוסקופ לנתח (למטה) ומקור אור סיבים אופטיים על הצדדים על ימין ועל שמאל. הגדר את אספקת החשמל סיבים אופטיים עד 80% של עוצמת האור המקסימלית. התאם את פלט אספקת החשמל מבוסס על תאורה מפוזרת, העדפות המשתמש ואת איכות התמונה לפי הצורך.
- קח תמונת נוף בצד של העדשה לא הטעונה, אשר ניתן לראות דרך רימראה ght-זווית. אם המצלמה אינה מכוילת, לצלם תמונה של הקצה המראה בפוקוס. קצה המראה באורך 5 מ"מ, מדידה זו ניתן להשתמש מאוחר יותר כדי לקבוע את הפיקסלים / מ"מ ולשמש סרגל קנה המידה של תמונות.
- עדשת מקום לתוך השקע, ולאשר כי העדשה מונחת כהלכה ו ישר את השקע. קח תמונה של העדשה לפני הטעינה. העדשה צריכה להיות נחה את השקע על הקדמי שלה או בקוטב אחורי.
- מקום 1 coverslip בעדינות על העדשה. חכה 2 דקות כדי לאפשר שרץ, ולקחת עוד תמונת הצד להציג של העדשה הטעונה.
- ממשיכים להוסיף coverslips כמו בשלב 2.8 וצילמו-מבט מהצד לאחר תוספת של כל coverslip כמו בשלב 2.8 עד סך של 10 coverslips מוחלים.
- הסר את כל coverslips. חכה 2 דקות, ולצלם תמונת נוף בצד של העדשה (ומחוץ לה את השקע) לאחר הסרת כל coverslips.
3. מדידת העדשה Nucleus
- כדי determine בגודל גרעין העדשה, להזיז את העדשה אל צלחת נקייה פטרי מלא 1x PBS.
- בעדינות decapsulate העדשה באמצעות מלקחיים ישר בסדר.
- להשיל את תאי סיבי קליפת המוח על ידי גלגול העדשה בין אצבע עטוית כפפה. גרעין העדשה הנותר ירגיש כמו גולה קשה. השתמש בהליך זה כדי לבודד את הגרעין על עדשות מבוגרות מתחיל ב -1 לחודש של גיל. מאז הגרעין המבודד הוא גוף נוקשה, בדיקה מכאנית נוספת של גרעין העדשה לא יכולה להתבצע באמצעות שיטה מתוארת זה.
- לשטוף בעדינות את גרעין העדשה 1x PBS בצלחת פטרי.
- מניחים את גרעין העדשה בחזרה לתוך תא המדידה (לא את השקע), ולקחת תמונה של גרעין העדשה דרך המראה בזווית ישרה.
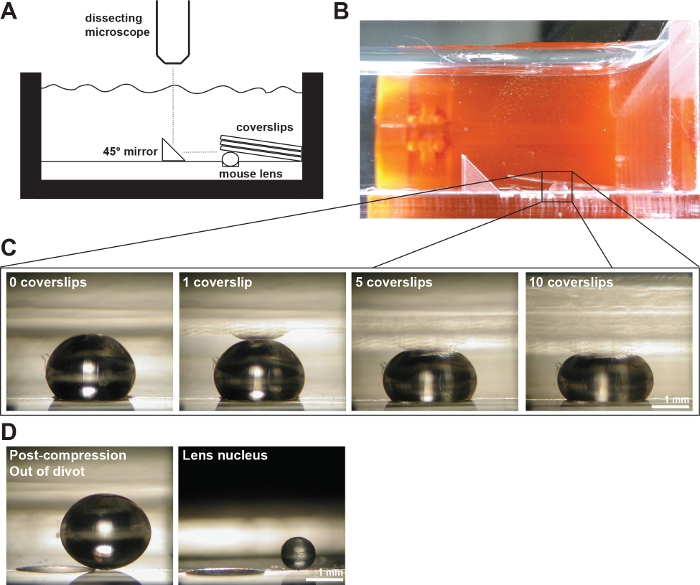
איור 2:. עדשות עכבר דחוסים ידי Coverslips (א) סכמטי ו- (ב) תצלום של האקסהתקנת perimental מראה עדשת עכבר 2 בן חודש בתוך שקע 200 מיקרומטר עמוק בתוך תא המדידה מלא 1x PBS. מראה זווית נכונה ומצלמה דיגיטלית רכובה על מיקרוסקופ לנתיחה שמשו כדי לאסוף תמונות של העדשה במהלך דחיסה על ידי coverslips. (C) תמונות של נופי sagittal של עדשת wild-type 2-בן חודש הדחוסה על ידי מספר הגדל והולך של coverslips ברציפות ספקו את הנתונים הגולמיים למדידת קטרים ציריים משווניים וחישוב זנים ציריים משווניים במהלך בדיקת דחיסה מבוססת coverslip. השתקפות של העדשה ניתן לראות לפעמים את coverslips (רוב נראה בבירור בתמונה 1 coverslip). בעת ביצוע מדידות, להתעלם ההשתקפות ולמדוד אל הקודקוד של העדשה. (ד) תמונות של נופי sagittal של עדשת wild-type בן חודש 2-דחיסת הדואר ועל גרעין העדשה המבודד. עדשת פוסט-דחיסת הגרעין מבודד ישב מחוץ את השקע. ברי סולם, 1 מ"מ. נתון זה שונה מן Gokhב, et al. PLoS ONE, 2012 19. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
ניתוח תמונה 4.
- מדוד בקטרים משווניים ו ציריים של עדשות לפני טעינה ואחרי כל שלב טעינה באמצעות ImageJ או תוכנה דומה. מדוד את הקוטר של כל גרעין העדשה. גרעין העדשה כמעט כדורי כך מדידה בכל אורינטציה תספיק 19,21.
- תקן את העדשה צירית בקטרים ידי הוספת עומק השקע בשימוש. בתא המדידה, את השקע הסתיר 200 מיקרומטר (עדשות עכבר 2-בן חודש) או 300 מיקרומטר (4 בן חודש ו -8 חודשים ישנות עדשות עכבר) של העובי הצירי של העדשה.
- חשבת את צירית זנים משווניים מן מדידות קוטר עדשה באמצעות המשוואה, ε = (d - d 0) / ד 0, שם ε הוא זן, d הוא צירי או דוארקוטר quatorial בעומס נתון, ד 0 הוא בקוטר צירי או משווני המקביל בעומס אפס.
- מגרש את צירית זנים משווניים כפונקציה של העומס המוטל (במ"ג).
- מגרש את צירי, הקו משווה ובקטרים גרעיניים. לחשב ולתכנן את יחס ממדי עדשה על ידי חלוקה בקוטר הצירי ידי הקוטר המשווני.
- לחשב ולתכנן את היקף העדשה באמצעות המשוואה, נפח = 4/3 × π × r E 2 × r A, כאשר r E הוא רדיוס r המשווני הוא הרדיוס הצירי נמדד על פי התמונה לקחה צעד 2.6. משוואה זו מניחה העדשה היא אליפטית oblate (אליפסואיד) 1,22.
- לחשב ולתכנן את היקף גרעיני באמצעות המשוואה, נפח = 4/3 × π × r N 3, כאשר r N הוא רדיוס של גרעין העדשה כפי שהן נמדדות תמונה לקחה צעד 3.5. משוואה זו מניחה את i גרעין העדשהsa בתחום 19,21.
- לחשב ולתכנן את השבר גרעיני כיחס בין היקף גרעיני בהיקף העדשה.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
תוצאות
הנוקשות והממדים של 2, 4 ו 8 חודשים ישני עדשות עכבר נמדדו. עכברים היו כל wild-type חיות על רקע המתח טהור C57BL6 המתקבל מתקן גידול בעלי חיים TSRI, ואת כל עדשה היתה עמוסה 1 עד 10 coverslips. הזנים הציריים משווניים חושבו כפונקציה של עומס המופעל על ידי מדידה הצירית ובקטרי קו ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
ישנם מספר שיקולים מרכזיים בעת שימוש בשיטה זו כדי למדוד נוקשות עדשה. ראשית, coverslips מוחלים על העדשה בזווית אלכסונית מעט (8 - 8.5 °) ביחס לחלק התחתון של החדר (θ). זה יחול מרכיב קטן מאוד של עומס equatorially ולא axially. עם זאת, עומס משווני זה נחשב זניח בגלל חטא θ ≈ 0.1 19. אם שיטה זו מות...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
החוקרים אין לי מה לחשוף.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Eye Institute Grant R01 EY017724 (VMF) and National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Grant K99 AR066534 (DSG).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Fine tip straight forceps | Fine Scientific Tools | 11252-40 | |
| Microdissection scissors, straight edge | Fine Scientific Tools | 15000-00 | |
| Curved forceps | Fine Scientific Tools | 11272-40 | |
| Seizing forceps | Hammacher | HSC 702-93 | Optional |
| Dissection dish | Fisher Scientific | 12565154 | |
| 60 mm Petri dish | Fisher Scientific | 0875713A | |
| 1x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | Life Technologies | 14190 | |
| 18 x 18 mm glass coverslips | Fisher Scientific | 12-542A | |
| Measurement chamber with divots to hold lenses | Custom-made (see Figure 1) | ||
| Right-angle mirror | Edmund Optics | 45-591 | |
| Light source | Schott/Fostec | 8375 | |
| Illuminated dissecting microscope | Olympus | SZX-ILLD100 | With SZ-PT phototube |
| Digital camera | Nikon | Coolpix 990 |
References
- Lovicu, F. J., Robinson, M. L. Development of the ocular lens. , Cambridge University Press. (2004).
- Piatigorsky, J. Lens differentiation in vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features. Differentiation. 19 (3), 134-153 (1981).
- Glasser, A. Restoration of accommodation: surgical options for correction of presbyopia. Clin Exp Optom. 91 (3), 279-295 (2008).
- Keeney, A. H., Hagman, R. E., Fratello, C. J. Dictionary of ophthalmic optics. , Butterworth-Heinemann. (1995).
- Millodot, M. Dictionary of optometry and visual science. 7, Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann. (2009).
- Heys, K. R., Cram, S. L., Truscott, R. J. Massive increase in the stiffness of the human lens nucleus with age: the basis for presbyopia. Mol Vis. 10, 956-963 (2004).
- Heys, K. R., Friedrich, M. G., Truscott, R. J. Presbyopia and heat: changes associated with aging of the human lens suggest a functional role for the small heat shock protein, alpha-crystallin, in maintaining lens flexibility. Aging Cell. 6 (6), 807-815 (2007).
- Pierscionek, B. K. Age-related response of human lenses to stretching forces. Exp Eye Res. 60 (3), 325-332 (1995).
- Glasser, A., Biometric Campbell, M. C. optical and physical changes in the isolated human crystalline lens with age in relation to presbyopia. Vision Res. 39 (11), 1991-2015 (1999).
- Weeber, H. A., van der Heijde, R. G. On the relationship between lens stiffness and accommodative amplitude. Exp Eye Res. 85 (5), 602-607 (2007).
- Weeber, H. A., et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of human lenses. Exp Eye Res. 80 (3), 425-434 (2005).
- Fisher, R. F. Elastic properties of the human lens. Exp Eye Res. 11 (1), 143(1971).
- Krueger, R. R., Sun, X. K., Stroh, J., Myers, R. Experimental increase in accommodative potential after neodymium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser photodisruption of paired cadaver lenses. Ophthalmology. 108 (11), 2122-2129 (2001).
- Burd, H. J., Wilde, G. S., Judge, S. J. An improved spinning lens test to determine the stiffness of the human lens. Exp Eye Res. 92 (1), 28-39 (2011).
- Glasser, A., Campbell, M. C. Presbyopia and the optical changes in the human crystalline lens with age. Vision Res. 38 (2), 209-229 (1998).
- Pau, H., Kranz, J. The increasing sclerosis of the human lens with age and its relevance to accommodation and presbyopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 229 (3), 294-296 (1991).
- Hollman, K. W., O'Donnell, M., Erpelding, T. N. Mapping elasticity in human lenses using bubble-based acoustic radiation force. Exp Eye Res. 85 (6), 890-893 (2007).
- Baradia, H., Nikahd, N., Glasser, A. Mouse lens stiffness measurements. Exp Eye Res. 91 (2), 300-307 (2010).
- Gokhin, D. S., et al. Tmod1 and CP49 synergize to control the fiber cell geometry, transparency, and mechanical stiffness of the mouse lens. PLoS One. 7 (11), e48734(2012).
- Sindhu Kumari, S., et al. Role of Aquaporin 0 in lens biomechanics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. , (2015).
- Fudge, D. S., et al. Intermediate filaments regulate tissue size and stiffness in the murine lens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52 (6), 3860-3867 (2011).
- Kuszak, J. R., Mazurkiewicz, M., Zoltoski, R. Computer modeling of secondary fiber development and growth: I. Nonprimate lenses. Mol Vis. 12, 251-270 (2006).
- Scarcelli, G., Kim, P., Yun, S. H. In vivo measurement of age-related stiffening in the crystalline lens by Brillouin optical microscopy. Biophys J. 101 (6), 1539-1545 (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved