A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Sequential Application of Glass Coverslips to Assess the Compressive Stiffness of the Mouse Lens: Strain and Morphometric Analyses
In This Article
Summary
Age-related increases in eye lens stiffness are linked to presbyopia. This protocol describes a simple, cost-effective method for measuring mouse lens stiffness. Mouse lenses, like human lenses, become stiffer with age. This method is precise and can be adapted for lenses from larger animals.
Abstract
The eye lens is a transparent organ that refracts and focuses light to form a clear image on the retina. In humans, ciliary muscles contract to deform the lens, leading to an increase in the lens' optical power to focus on nearby objects, a process known as accommodation. Age-related changes in lens stiffness have been linked to presbyopia, a reduction in the lens' ability to accommodate, and, by extension, the need for reading glasses. Even though mouse lenses do not accommodate or develop presbyopia, mouse models can provide an invaluable genetic tool for understanding lens pathologies, and the accelerated aging observed in mice enables the study of age-related changes in the lens. This protocol demonstrates a simple, precise, and cost-effective method for determining mouse lens stiffness, using glass coverslips to apply sequentially increasing compressive loads onto the lens. Representative data confirm that mouse lenses become stiffer with age, like human lenses. This method is highly reproducible and can potentially be scaled up to mechanically test lenses from larger animals.
Introduction
The lens is a transparent and avascular organ in the anterior chamber of the eye that is responsible for fine focusing of light onto the retina. A clear basement membrane, called the lens capsule, surrounds a bulk of elongated fiber cells covered by an anterior monolayer of epithelial cells1,2. Life-long growth of the lens depends on the continuous proliferation and differentiation of epithelial cells at the lens equator into new fiber cells that are added onto previous generations of fiber cells in a concentric manner2. Over time, lens fiber cells undergo compaction, resulting in a rigid center in the middle of the lens called the nucleus1. Accommodation, defined as a dioptric change in the optical power of the eye, occurs in humans when the ciliary muscles contract to deform the lens and allow a true increase in optical power to focus on near objects3-5. In the unaccommodated eye, the lens is held in a relatively flattened state due to tension from zonular fibers. When the ciliary muscles contract, the tension on the lens is released, leading to decreased lens equatorial diameter and increased axial thickness. Age-related changes in the lens cause presbyopia, a progressive loss of lens accommodation, which leads to the need for reading glasses.
Several studies have linked presbyopia to age-related increase in the intrinsic stiffness of the lens6-11. Stiffness is defined as the resistance of an elastic object to deform under applied load. A variety of methods have been used to examine stiffness of human lenses, including spin compression12-14, actuator compression15, probe indentation16, dynamic mechanical analysis 6,10 and bubble-based acoustic radiation force17. While mouse lenses do not accommodate or develop presbyopia, mouse models for lens pathologies are valuable tools because mice are less expensive than larger animals, well characterized genetically and undergo accelerated age-related changes due to rapid aging. A handful of studies have examined mouse lens stiffness with compression methods and demonstrated changes in lens stiffness due to aging or targeted genetic disruptions18-21. Thus, mouse lenses are good models for studying age-related changes in lens stiffness.
This protocol describes a simple and inexpensive, yet precise and reproducible, compression method for determining mouse lens stiffness based on application of glass coverslips onto the lens in conjunction with photographing the lens through a dissection microscope and mirror. This method yields robust strain and morphometric data with an easily fabricated and assembled apparatus. The representative results confirm that mouse lenses increase in stiffness with age.
Protocol
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals by the National Institutes of Health and under an approved protocol by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at The Scripps Research Institute.
1. Lens Dissection
- Euthanize mice according to recommendations in the National Institutes of Health "Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals" and approved institution animal use protocols.
- Enucleate the eye from mice using curved forceps. Depress the tissue around the eye with the forceps to bring the eye out of the socket, and then pluck the eye from the socket with the forceps. Transfer eyes to fresh 1x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) in dissection dish.
- Cut off the optic nerve as close to the eyeball as possible. Gently and carefully insert fine straight tweezers into the eyeball through the hole where the optic nerve exits the posterior.
- Carefully make an incision with scissors into the eyeball from the posterior to the edge of the cornea. Rodent lenses occupy ~30% of the eye. Make these incisions carefully, and do not insert tweezers or scissors too deep into the eye to avoid damaging the lens.
- Cut along the junction between the cornea and sclera at least half way around the eyeball.
- Gently push on the cornea to remove the lens from the eye through the opening made in steps 1.4 and 1.5.
- Use fine tip straight forceps to carefully remove any large debris that is still attached to the lens. Visually inspect the lens for any damage before proceeding to the stiffness measurements.
2. Stiffness Measurements
- Weigh at least 10 coverslips from the same box using an analytical balance. Find the average weight of the coverslips. For consistency, use the same box of coverslips for all experiments. Pre-wet the coverslips and right-angle mirror in 1x PBS at room temperature for at least 2 hr before starting experiments.
- Fill the measurement chamber (see Figure 1) with 65 - 75 ml of 1x PBS. The measurement chamber was made out of Plexiglas by an in-house machine shop, and divots in the chamber were made by a drill press set to the desired depth with an appropriate drill bit. Lenses remain transparent in 1x PBS at room temperature for the duration of mechanical testing.

Figure 1: Stiffness Measurement Chamber. A photo showing the dimensions of the custom-made stiffness measurement chamber with a variety of divots of different depths and shapes. The round divots that are 200 µm or 300 µm deep (yellow arrowheads) are used for the measurements on mouse lenses. Divots are 2 mm in diameter and ~13 - 14 mm from the edge of the chamber. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Place right-angle mirror into the chamber at a constant distance from the divot that will be used to hold the lens. Make sure the mirror does not move during the experiment.
- Transfer dissected lenses to measurement chamber carefully with seizing forceps or curved forceps.
- Take a top-view picture of the unloaded lens from directly overhead. Take mouse lens photos at 30X magnification with illumination from dissecting microscope (bottom) and a fiber optic light source on the left and right sides. Set the fiber optic power supply to 80% of the maximum light intensity. Adjust the power supply output based on ambient lighting, user preference and picture quality as needed.
- Take a side-view picture of the unloaded lens, which can be seen through the right-angle mirror. If camera is not calibrated, take a picture of the mirror edge in focus. The mirror edge is 5 mm long, and this measurement can later be used to determine the pixels/mm and serve as a scale bar in the images.
- Place lens into the divot, and confirm that the lens is seated securely and straight in the divot. Take a picture of the lens before loading. The lens should be resting in the divot on its anterior or posterior pole.
- Place 1 coverslip gently onto the lens. Wait 2 min to permit creep, and take another side-view picture of the loaded lens.
- Continue adding coverslips as in step 2.8 and taking side-view pictures after the addition of each coverslip as in step 2.8 until a total of 10 coverslips are applied.
- Remove all coverslips. Wait 2 min, and take a side-view picture of the lens (inside and outside of the divot) after removing all coverslips.
3. Lens Nucleus Measurement
- To determine the lens nucleus size, move the lens to a clean Petri dish filled with 1x PBS.
- Gently decapsulate the lens using fine straight forceps.
- Slough off the cortical fiber cells by rolling the lens between gloved fingers. The remaining lens nucleus will feel like a hard marble. Use this procedure to isolate the nucleus on adult lenses starting at 1 month of age. Since the isolated nucleus is a rigid body, further mechanical testing of the lens nucleus cannot be performed using this described method.
- Gently rinse the lens nucleus in 1x PBS in the Petri dish.
- Place the lens nucleus back into the measurement chamber (not in the divot), and take an image of the lens nucleus through the right-angle mirror.
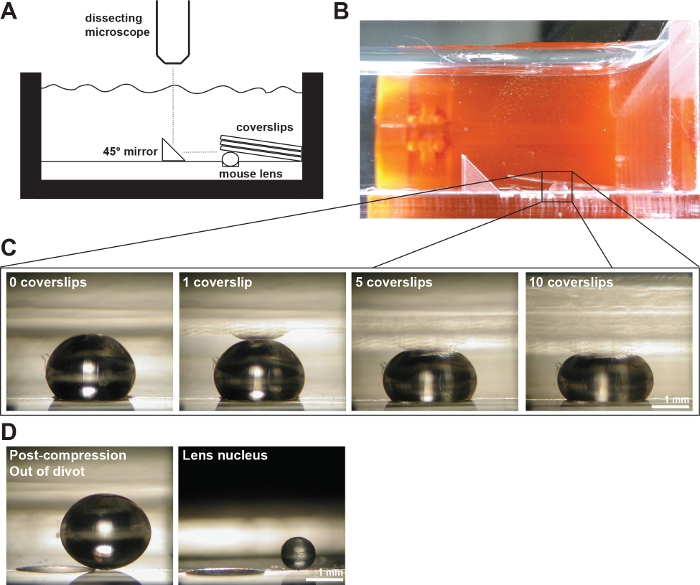
Figure 2: A Mouse Lenses Compressed by Coverslips. (A) Schematic and (B) photograph of the experimental setup showing a 2-month-old mouse lens in a 200-µm-deep divot in the measurement chamber filled with 1x PBS. A right angle mirror and a digital camera mounted on a dissection microscope were used to collect images of the lens during compression by coverslips. (C) Photos of sagittal views of a 2-month-old wild-type lens compressed by successively increasing numbers of coverslips provided the raw data for measuring axial and equatorial diameters and calculating axial and equatorial strains during coverslip-based compression testing. A reflection of the lens can sometimes be seen in the coverslips (most clearly visible in the 1 coverslip image). When making measurements, ignore the reflection and measure to the apex of the lens. (D) Photos of sagittal views of the 2-month-old wild-type lens post-compression and the isolated lens nucleus. The post-compression lens and isolated nucleus are sitting outside of the divot. Scale bars, 1 mm. This figure is modified from Gokhin, et al. PloS one, 201219. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Image Analysis
- Measure equatorial and axial diameters of lenses before loading and after each loading step using ImageJ or similar software. Measure the diameter of each lens nucleus. The lens nucleus is nearly spherical so a measurement at any orientation will suffice19,21.
- Correct the lens axial diameters by adding the depth of the divot used. In the measurement chamber, the divot obscured 200 µm (2-month-old mouse lenses) or 300 µm (4-month-old and 8-month-old mouse lenses) of the axial thickness of the lens.
- Calculate the axial and equatorial strains from the lens diameter measurements using the equation, ε = (d - d0) / d0, where ε is strain, d is the axial or equatorial diameter at a given load, and d0 is the corresponding axial or equatorial diameter at zero load.
- Plot the axial and equatorial strains as functions of the imposed load (in mg).
- Plot the axial, equatorial and nuclear diameters. Calculate and plot the lens aspect ratio by dividing the axial diameter by the equatorial diameter.
- Calculate and plot the lens volume using the equation, volume = 4/3 × π × rE2 × rA, where rE is the equatorial radius and rA is the axial radius measured from the picture taken in step 2.6. This equation assumes the lens is an oblate spheroid (ellipsoid)1,22.
- Calculate and plot the nuclear volume using the equation, volume = 4/3 × π × rN3, where rN is the radius of the lens nucleus as measured from the picture taken in step 3.5. This equation assumes the lens nucleus is a sphere19,21.
- Calculate and plot the nuclear fraction as the ratio of the nuclear volume to the lens volume.
Results
The stiffness and dimensions of 2-, 4- and 8-month-old mouse lenses were measured. Mice were all wild-type animals on a pure C57BL6 strain background obtained from the TSRI Animal Breeding Facility, and each lens was loaded with 1 to 10 coverslips. The axial and equatorial strains were calculated as a function of applied load by measuring the axial and equatorial diameters of the lens after the addition of each coverslip, and then normalizing each change in diameter to the corresponding u...
Discussion
There are several key considerations when using this method to measure lens stiffness. First, the coverslips are applied to the lens at a slightly oblique angle (8 - 8.5°) with respect to the bottom of the chamber (θ). This will apply a very small component of the load equatorially rather than axially. However, this equatorial load is considered negligible because sin θ ≈ 0.119. If this method is adapted for larger lenses, the angle of the coverslips to the bottom of the chamber would need...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Eye Institute Grant R01 EY017724 (VMF) and National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Grant K99 AR066534 (DSG).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Fine tip straight forceps | Fine Scientific Tools | 11252-40 | |
| Microdissection scissors, straight edge | Fine Scientific Tools | 15000-00 | |
| Curved forceps | Fine Scientific Tools | 11272-40 | |
| Seizing forceps | Hammacher | HSC 702-93 | Optional |
| Dissection dish | Fisher Scientific | 12565154 | |
| 60 mm Petri dish | Fisher Scientific | 0875713A | |
| 1x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | Life Technologies | 14190 | |
| 18 x 18 mm glass coverslips | Fisher Scientific | 12-542A | |
| Measurement chamber with divots to hold lenses | Custom-made (see Figure 1) | ||
| Right-angle mirror | Edmund Optics | 45-591 | |
| Light source | Schott/Fostec | 8375 | |
| Illuminated dissecting microscope | Olympus | SZX-ILLD100 | With SZ-PT phototube |
| Digital camera | Nikon | Coolpix 990 |
References
- Lovicu, F. J., Robinson, M. L. . Development of the ocular lens. , (2004).
- Piatigorsky, J. Lens differentiation in vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features. Differentiation. 19 (3), 134-153 (1981).
- Glasser, A. Restoration of accommodation: surgical options for correction of presbyopia. Clin Exp Optom. 91 (3), 279-295 (2008).
- Keeney, A. H., Hagman, R. E., Fratello, C. J. . Dictionary of ophthalmic optics. , (1995).
- Millodot, M. . Dictionary of optometry and visual science. 7, (2009).
- Heys, K. R., Cram, S. L., Truscott, R. J. Massive increase in the stiffness of the human lens nucleus with age: the basis for presbyopia. Mol Vis. 10, 956-963 (2004).
- Heys, K. R., Friedrich, M. G., Truscott, R. J. Presbyopia and heat: changes associated with aging of the human lens suggest a functional role for the small heat shock protein, alpha-crystallin, in maintaining lens flexibility. Aging Cell. 6 (6), 807-815 (2007).
- Pierscionek, B. K. Age-related response of human lenses to stretching forces. Exp Eye Res. 60 (3), 325-332 (1995).
- Glasser, A., Biometric Campbell, M. C. optical and physical changes in the isolated human crystalline lens with age in relation to presbyopia. Vision Res. 39 (11), 1991-2015 (1999).
- Weeber, H. A., van der Heijde, R. G. On the relationship between lens stiffness and accommodative amplitude. Exp Eye Res. 85 (5), 602-607 (2007).
- Weeber, H. A., et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of human lenses. Exp Eye Res. 80 (3), 425-434 (2005).
- Fisher, R. F. Elastic properties of the human lens. Exp Eye Res. 11 (1), 143 (1971).
- Krueger, R. R., Sun, X. K., Stroh, J., Myers, R. Experimental increase in accommodative potential after neodymium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser photodisruption of paired cadaver lenses. Ophthalmology. 108 (11), 2122-2129 (2001).
- Burd, H. J., Wilde, G. S., Judge, S. J. An improved spinning lens test to determine the stiffness of the human lens. Exp Eye Res. 92 (1), 28-39 (2011).
- Glasser, A., Campbell, M. C. Presbyopia and the optical changes in the human crystalline lens with age. Vision Res. 38 (2), 209-229 (1998).
- Pau, H., Kranz, J. The increasing sclerosis of the human lens with age and its relevance to accommodation and presbyopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 229 (3), 294-296 (1991).
- Hollman, K. W., O'Donnell, M., Erpelding, T. N. Mapping elasticity in human lenses using bubble-based acoustic radiation force. Exp Eye Res. 85 (6), 890-893 (2007).
- Baradia, H., Nikahd, N., Glasser, A. Mouse lens stiffness measurements. Exp Eye Res. 91 (2), 300-307 (2010).
- Gokhin, D. S., et al. Tmod1 and CP49 synergize to control the fiber cell geometry, transparency, and mechanical stiffness of the mouse lens. PLoS One. 7 (11), e48734 (2012).
- Sindhu Kumari, S., et al. Role of Aquaporin 0 in lens biomechanics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. , (2015).
- Fudge, D. S., et al. Intermediate filaments regulate tissue size and stiffness in the murine lens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52 (6), 3860-3867 (2011).
- Kuszak, J. R., Mazurkiewicz, M., Zoltoski, R. Computer modeling of secondary fiber development and growth: I. Nonprimate lenses. Mol Vis. 12, 251-270 (2006).
- Scarcelli, G., Kim, P., Yun, S. H. In vivo measurement of age-related stiffening in the crystalline lens by Brillouin optical microscopy. Biophys J. 101 (6), 1539-1545 (2011).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved