A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Revealing Subtle Changes in Cardiac Function using Transthoracic Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography in Mice
In This Article
Summary
Left ventricular dysfunction constitutes the final common pathway for a host of cardiac disorders. We here provide a detailed protocol of transthoracic dobutamine stress echocardiography approach for comprehensive evaluation of the left ventricular function of mouse models of cardiac disease as well as cardiac phenotyping.
Abstract
Left ventricular (LV) dysfunction paves the final pathway for a multitude of cardiac disorders. With the non-invasive high-frequency transthoracic dobutamine stress echocardiography in humans, a reductionist investigation approach to unmask subtle changes in cardiac function has become possible. Here, we provide a protocol for using this technique in mice to facilitate expanded analysis of LV architecture and function in physiology and pathology enabling the observation of alterations in models of cardiac disease hidden in unstressed hearts. This investigation can be performed in one and the same animal and allows both, basal and pharmacologically stress-induced measurements. We outline detailed criteria for appropriate anesthesia, imaging-based LV analysis, consideration of intra- and interobserver variability, and obtaining positive inotrope response that can be attained in mice after intraperitoneal injection of dobutamine under near physiological conditions. To recapitulate the characteristics of human physiology and disease in small animal models, we highlight critical pitfalls in evaluation, e.g., a pronounced Bowditch effect in mice. To further meet translational objectives, we compare stress-induced effects in humans and mice. When used in translational studies, attention must be paid to physiological differences between mice and human. Experimental rigor dictates that some parameters assessed in patients can only be used with caution due to restrictions in spatial and temporal resolution in mouse models.
Introduction
The hallmark of many cardiac diseases in human is a systolic and/or diastolic functional impairment of the left ventricle (LV). For the detection of structural abnormalities, the diagnosis, and the management of systolic heart failure as well as the evaluation of diastolic function in patients with symptoms of heart failure, echocardiography is used as a fundamental assessment modality.
Since the symptoms are unspecific and more than one third of patients with the clinical syndrome of heart failure may not suffer from the actual heart failure, it is important to find an objective echocardiographic correlate for the patient's clinical presentation1. Furthermore, some symptoms which are occult in the resting or static state may occur under conditions of activity or stress. In patients with coronary artery disease, already minor changes in coronary perfusion can lead to regional wall motion abnormalities. However, these subtle changes cannot be evaluated using conventional echocardiography as alterations of cardiac disease can be hidden in unstressed hearts. To gain a deeper understanding of the cardiac physiopathology, stress echocardiography provides a dynamic evaluation of myocardial structure and function under conditions of exercise or pharmacological induced stress, permitting matching symptoms with cardiac findings2. Also, in small animals, this method represents a non-invasive reliable in-vivo tool3,4,5. In-line with humans, stress reaction of the myocardium can be induced via pharmacological agents in mice and rats. Dobutamine is a frequently used drug and dobutamine stress echocardiography is widely performed in humans6,7 but only sometimes used in small animal models to assess cardiac stress reaction8,9,10,11. Dobutamine is a synthetical catecholamine with a predominantly β1-agonistic effect resulting in positive inotropy and chronotropy of the heart. To achieve a correct translation from human to mouse, the technology and the conceptual framework of echocardiography, technical limitations related to e.g., the small size and rapid heart rate in the mouse must be considered. The human target heart rate in dobutamine stress echocardiography is [(220-age) x 0.85] resulting in an average heart rate increase of about 150 ± 10% in healthy volunteers12,13. For mice, such a formula is missing. The ejection fraction (EF) is described to be increased by stress echocardiography in humans by 5-20%12,14. The EF in mice is, depending on the heart rate, reported between 58 ± 11% (< 450 bpm) and 71 ± 11% (≥ 450 bpm) and changes by nearly 20% with higher heart rates4. The main mechanism in mice to increase the cardiac output is an increase in the heart rate. Partly responsible for this mechanism is the Bowditch effect or staircase phenomenon, a frequency-dependent calcium-mediated positive-inotropic cardiac response, that is more pronounced in mice than in humans15,16. In addition, (stress) echocardiography underlies intra- and interobserver variability. Therefore, a highly standardized procedure is indispensable17,18.
Here we present the detailed procedure of dobutamine stress echocardiography to acquire standardized images to unravel subtle changes in cardiac function in mice in models of health and disease. Key components include adequate anesthesia, adequate heart rate monitoring and possible pitfalls in stress-induced imaging in mice. Key parameters are the evaluation of systolic and diastolic function including consideration of the LVEF. Because mice are resistant to afterload-induced cardiac dysfunction17, this protocol may add valuable information for the use in models of valvular heart disease as well.
Protocol
All methods and procedures were performed in accordance and compliance with all relevant regulations ('European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and other Scientific Purposes' (Directive 2010/63/EU) and animal care was in accordance with institutional guidelines. Data from human subjects were analyzed in compliance with all institutional, national, and international guidelines for human welfare and was approved by the Local Ethics Committee (20-9218-BO). All experiments have been performed with male C57BL/6JRj at the age of 12 weeks.
1. Preparation of materials and equipment
NOTE: Figure 1 shows an example of a small-animal ultrasound workplace.
- Make sure to operate in a silent controlled environment with dimmable light.
- Pre-heat the ultrasound gel, e.g., using a gel warmer. Allow the gel to warm to 37 °C. This may take a while.
- Clean all instruments including the platform with a disinfectant wipe.
- Turn on and pre-heat the platform to 37 °C.
- Turn on the ultrasound machine. Enter the animal ID and protocol ID as well as other relevant information. Use a high-frequency ultrasound transducer with a center transmit of 30 MHz for mice with approximately 30 g body weight.
- Make sure to work with an active gas exhaustion system.
NOTE: If using an activated charcoal filter for adsorbing the isoflurane in the exhaled flow, make sure to check the weight and replace the filter once the indicated maximal weight increase is reached. - If necessary, fill the vaporizer with the adequate amount of isoflurane.
CAUTION: Do not inhale volatile anesthetics. - Prepare a dobutamine working solution of 2.5 µg/µL either by dilution of a ready-to-use injection solution or by dissolving dobutamine hydrochloride powder in 0.9% saline according to the manufacturer's instruction. The solution is stable at least for 24 h when stored at room temperature.
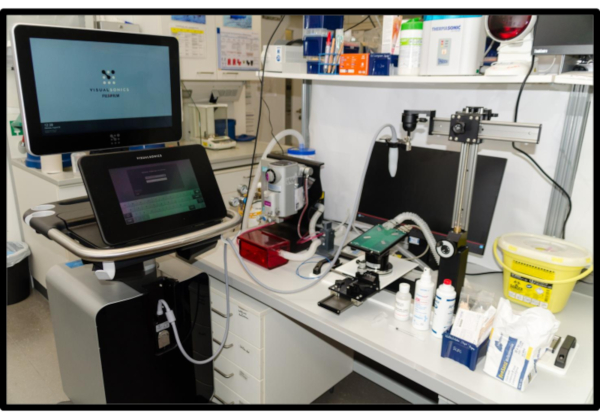

Figure 1: Small-animal cardiac ultrasound workplace. An ergonomic setting is indispensable for small-animal stress echocardiography as examination times must remain short. The workplace consists of an ultrasound machine, a small-animal anesthesia system with oxygen supply and active gas exhaust, a heated echocardiography platform with embedded ECG and movement capabilities via micromanipulators as part of an integrated rail system as well as a physiological monitoring unit. A gel warmer to warm ultrasound gel and a heat lamp are useful aids. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Preparation of the mouse for imaging and induction of anesthesia
- Fill the induction chamber with 3%-4% v/v isoflurane in an oxygen-enriched gas mixture (with 1 L/min 100% O2).
- Weigh the mouse. Gently pick up the mouse by the tail and transfer it to the induction chamber. Ensure that the animal is sedated within a few seconds by closely observing the animal's movements.
- If necessary, change the gas flow to the nose cone connected to the anesthesia system (1.0-1.5 vol% isoflurane with 1 L/min 100 % O2 to maintain a stable sedation). Remove the mouse from the induction chamber and place it carefully on the pre-heated platform. Ensure that the paws lie on the ECG sensors embedded in the platform.
- To prevent drying of the sclera, apply ointment gel to both eyes.
NOTE: Stress measurements will take their time. - Apply a very small amount of electrode cream to the ECG sensors. Gently secure the animal with adhesive tape on all four limbs. Use a small part of adhesive tape to secure the animal's head position in the nose cone. The ECG is used to record the heart rate during image acquisition. Adjust the physiological imaging system for a stable and clear ECG signal.
NOTE: Too much electrode cream may result in bad ECG signal quality. - To protect the animal from stress during the procedure, check the adequate depth of sedation by maintaining the heart rate range at 400-450 bpm. The heart rate is obtained by the ECG. A variation of 50 bpm within the range is acceptable.
NOTE: Movements of the animal may indicate a too narrow level of sedation. The anesthesia must not lead to cardio-depression of the mouse. The sedation can be adjusted to obtain the above-mentioned target heart rate. - Using lubrication, gently insert a rectal thermometer for continuous monitoring of the body temperature. Keep the temperature in the physiological range (normally between 36.5 °C and 37.5 °C depending on the mouse strain and experimental setup). In a non-environmentally controlled animal cardiac ultrasound laboratory, the use of infrared lighting may be considered.
- Use chemical depilatory cream to remove the body hair from the chest. Use a clean damp paper towel to wipe clean the chest. Make sure to remove all remaining cream components (Figure 2A).
NOTE: An electric clipper can be used before depilatory application as well. The animal is now prepared for imaging. As it is critical to keep imaging time short, the whole preparation before imaging should take less than 3 min.
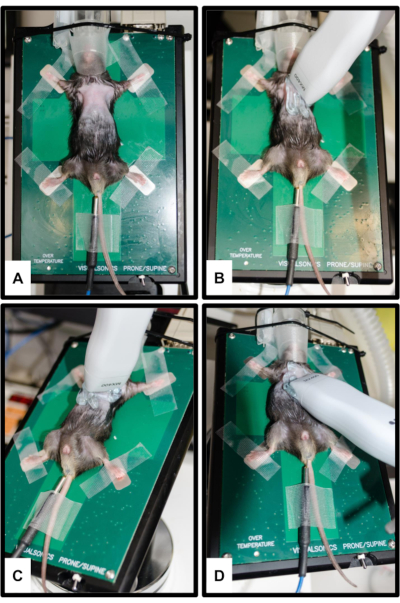
Figure 2: Animal and transducer positioning. (A) The mouse is attached to the heated platform with all four limbs fixed on the silver ECG electrodes. A rectal thermometer is inserted for body temperature measurement. The snout is gently inserted to the nose cone of the anesthesia system. (B) Probe orientation for parasternal long axis view (PSLAX); see step 3.2. (C) Probe orientation for parasternal short axis view (PSSAX); see step 3.3. (D) Probe orientation for apical four chamber view (4CH); see step 3.4. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Basic cardiovascular imaging
NOTE: Images can be acquired using two basic transducer positions (parasternal and apical ultrasound window) (Figure 2) and at least three ultrasound modalities (B(rightness)-mode, M(otion)-mode and Doppler-mode (color doppler and pulsed-wave (PW) doppler) (Figure 3,Figure 4,Figure 5). For basics of imaging please refer to previously published articles16,18. It is critical to obtain clear images for the comparison with later acquired stress images.
- Apply pre-heated ultrasound gel bubble-free to the chest.
NOTE: Non-heated ultrasound gel will result in rapid body temperature loss which will affect the heart rate. - Perform parasternal long axis (PSLAX) view.
NOTE: PSLAX is performed to visualize the LV in its long axis. With this, e.g., the aortic root dimensions and proximal aorta dimension as well as the LV length can be obtained.- With the head facing away from the investigator, tilt the table approximately 10-20° to the left and 5-10° to the front to bring the heart as anterior as possible. Place the transducer parasternally in line with the long axis of the heart with the marker (notch) pointing towards the animal's right shoulder (Figure 2B).
- Use micromanipulators to adjust the optimal view. Use image control panel controls to optimize the image. Acquire at least one 2D B-mode picture and one M-mode picture in midventricular level.
- Acquire any additional images if need for the specific question. Acquire at least 100 frames and at least 3(-6) full cardiac cycles.
- Perform parasternal short axis (PSSAX) view.
NOTE: PSSAX is performed to visualize the LV in its short axis. From this view, e.g., left-ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), left-ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), stroke volume (SV) and cardiac output (CO) can be calculated.- Rotate the transducer 90° clockwise without changing of the angulation (marker now pointing towards the animal's left shoulder) (Figure 2C). Acquire at least one B-mode image in the basal, midventricular (level of the papillary muscles), and apical view.
- To define the most basal and the most apical view, scroll along the long axis to the most distant points, where the full cardiac cycle of the LV chamber is still visible. Take images on the midventricular level approximately in an intermediate position at the level of the papillary muscles.
- Acquire at least one M-mode image in the midventricular view.
NOTE: Some ultrasound machines provide presets for the different views; it is recommended to check for the adequate preset before acquiring images.
- Perform apical four chamber (4CH) view.
NOTE: 4CH is important because it can be primarily used to evaluate the mitral valve using PW doppler.- Tilt the platform that the animal is in a modified Trendelenburg position with the head down. Angle the transducer towards the head of the mouse, the marker facing towards the animal's left side (Figure 2D).
- Acquire at least one B-mode image as well as color doppler and PW doppler image of the mitral- and tricuspid valve. Depending on the experimental question, apply tissue doppler in the 4CH view.
NOTE: The easiest way to reach apical 4CH position is to tilt the table from the PSAX view and to angulate the transducer. Be careful not to apply too much pressure to the thorax as this may interfere with measurements e.g. of diastolic function.
4. Dobutamine stress imaging
NOTE: Once the target heart rate is reached, standardized views should be acquired as long as the target heart rate is stable. This typically requires more than one switch between PSLAX and PSSAX. Because the switch between PSLAX and PSSAX only requires a 90° rotation, the views can be imaged easily.
- Perform dobutamine stress testing in one and the same animal maintaining the same anesthesia to ensure comparability. Make sure the starting heart rate remains stable in the range of 400-450 bpm. Record the ECG readings and save it together with and on the acquired images. Make sure the ECG signal is clear. Otherwise, try to re-tape all four limbs until a clear ECG signal is displayed.
- Again, perform PSLAX view (B-mode and M-mode images). Save the images as "baseline" image. Be sure, to save and keep in mind the initial heart rate as well.
- Prefill the syringe and inject 5 µg/g body weight dobutamine intraperitoneally using a 27 G needle and 1 mL syringe. Closely watch for the heart rate. Record echocardiographic images until the target heart rate is reached and use the increase of the heart rate for later analysis. A sustainable significant dobutamine-induced heart rate increase is reached after an increase of 15-30% after about 1 min, depending on the dobutamine dose.
NOTE: Always use single-use sterile injection needles for every animal to prevent from infections. The dobutamine susceptibility and the (sub)maximal load may vary with the mouse strain and may be dependent on the experimental setup and should be defined in pre-experiments. It is recommended adjusting the dobutamine dose to the experimental setup.
CAUTION: Follow institutional guidelines for the use of sharp and potential infectious items. Always dispose the needle into an approved medical waste container! - Once the target heart rate is reached and remains stable for approximately 30 s, acquire PSLAX B-mode and M-mode images as described in step 3.
- Again, rotate the transducer clockwise to obtain PSSAX view as described in step 3. Here, acquire B-mode images of the basal, midventricular (level of papillary muscles) and apical level and M-mode images of the midventricular (level of the papillary muscles) level. Reassure, that the target heart rate remains stable. Otherwise, switch back to PSLAX position and start imaging again.
NOTE: As the heart rate will drop without continuous infusion of dobutamine12 (not covered in this article), the images should be acquired within two minutes. PSLAX and PSSAX images are essential for most of the relevant stress-induced measurements (see "Representative Results" section). - Now, perform apical 4CH view again (as explained in step 3.4.). Using PW doppler, measure the flow patterns of interest (as explained in step 3.4.2.). Under unstressed conditions, two characteristic waves are measured using PW doppler, one representing the passive filling of the ventricle (E(arly) wave) and one representing the active filling after atrial contraction (A(trial) wave). With increasing heart rates, these waves tend to fuse and may not be measurable distinctively under dobutamine induced stress.
5. Final steps
- After approximately 5 min when the heart rate will start to decrease again, make sure all views are captured.
- Gently remove the ultrasound gel from the chest using a clean damp paper towel. Carefully remove the tape fixation. Pay special attention to the tape fixing the animal's head to avoid pulling out the whiskers.
- Turn off the anesthesia. If using an active gas exhaust, make sure to continue gas exhaustion. Place the animal on a paper towel in a separated heated cage during the wake-up period. Observe the animal closely. It must not be left unattended until it has regained sufficient consciousness to maintain sternal recumbency. Once awake and fully recovered, transfer the animal to its cage.
NOTE: Due to the non-final character of this technique, the animal may stay within the experiment in accordance with all relevant regulations.
6. Offline evaluation
- Transfer the image data to the offline analysis software on a working-station to perform detailed evaluation of the cardiac function. Pay special attention to the difference between unstressed and stressed heart function. The heart rate should always be recorded and presented.
NOTE: Because software analysis varies between different software, it is not covered in this protocol. Please refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
Results
A physiological unstressed echocardiographic image acquired in PSLAX is shown in Figure 3. In diastole, the ventricle walls appear uniformly (Figure 3A) and thicken to a certain degree (Figure 3B,C). The injection of 5 µg/g body weight dobutamine i.p. leads to a significant increase of the heart rate (positive chronotropic effect)12 and the LVEF (positive...
Discussion
Stress-induced evaluation of the cardiac function is widely used in humans in a clinical setting using exercise testing or pharmacological stress testing6,7. Because immediate post-exercise echocardiography of mice is very limited due to the need for sedation, dobutamine-induced stress echocardiography is likely to be the most translational method to assess stress-induced cardiac physiopathology. Reliable information on cardiac function can be obtained using real...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the following funding sources: German Research Foundation (UMEA Junior Clinician Scientist, Stephan Settelmeier; RA 969/12-1, Tienush Rassaf; HE 6317/2-1, Ulrike Hendgen-Cotta), Else-Kroener-Fresenius-Stiftung (2014_A216, Tienush Rassaf).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Activated Charcoal Filter | UNO BV | 180000140 | http://www.unobv.com/Rest%20Gas%20Filters.html |
| Aquasonic 100 Ultrasound Transmission Gel | Parker Laboratories | 001-02 | https://www.parkerlabs.com/aquasonic-100.asp |
| Chemical Hair removal lotion | General Supply | - | |
| Cotton Swaps | General Supply | - | |
| ddH2O | General Supply | - | |
| Dobutamine | Carinopharm | 71685.00.00 | https://www.carinopharm.de/stammsortiment/#103 |
| Flowmeter for laboratory animal anesthesia | UNO BV | SF3 | http://www.unobv.com/Flowmeters.html |
| Gas Exhaust Unit | UNO BV | - | http://www.unobv.com/Gas%20Exhaust%20Unit.html |
| Heating Lamp | Philips | - | |
| Induction Box | UNO BV | - | http://www.unobv.com/Induction%20box.html |
| Medical Sharps Container | BD | 305626 | https://legacy.bd.com/europe/safety/de/products/sharps/ |
| MX400 ultrasound transducer (20-46 Mhz) | VisualSonics | MX400 | https://www.visualsonics.com/product/transducers/mx-series-transducers |
| Octenisept disinfectant | Schuelke | 173711 | https://www.schuelke.com/de-de/produkte/octenisept.php |
| Omnican F syringe with needle 1ml | B. Braun | 9161502S | https://www.bbraun.de/de/products/b60/omnican-f.html |
| Paper Towels | General Supply | - | |
| Signacreme Electrode Cream | Parker Laboratories | 017-05 | https://www.parkerlabs.com/Signacreme.asp |
| Standard Gauze Pads | BeeSana Meditrade | 4852728 | https://www.meditrade.de/de/wundversorgung/verbandstoffe/beesana-mullkompresse/ |
| Thermasonic Gel Warmer | Parker Laboratories | 82-03-20 CE | https://www.parkerlabs.com/thermasonic_apta_sbp.asp |
| Transpore Tape | 3M | 1527NP-0 | https://www.3mdeutschland.de/3M/de_DE/unternehmen-de/produkte/~/3M-Transpore-Fixierpflaster/ |
| Vaporizer Sigma Delta | UNO BV | - | http://www.unobv.com/Vaporizers.html |
| Vevo 3100 high-frequency preclinical ultrasound imaging system | VisualSonics | Vevo3100 | https://www.visualsonics.com/product/imaging-systems/vevo-3100 * required software package: Cardiovascular package; B-mode, M-mode, pulsed-wave doppler mode |
| Vevo Imaging Station with integrated rail system, heated platform and physiological monitoring unit | VisualSonics | - | https://www.visualsonics.com/product/accessories/imaging-stations |
| VevoLab Analysis Software | VisualSonics | Vers. 3.2.5 | https://www.visualsonics.com/product/software/vevo-lab *required software package: Vevo Strain, LV analysis |
References
- Oh, J. Echocardiography in heart failure: Beyond diagnosis. European Journal of Echocardiography. 8 (1), 4-14 (2007).
- Lancellotti, P., et al. The clinical use of stress echocardiography in non-ischaemic heart disease: Recommendations from the european association of cardiovascular imaging and the american society of echocardiography. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 30 (2), 101-138 (2017).
- Lindsey, M. L., Kassiri, Z., Virag, J. A. I., de Castro Bras, L. E., Scherrer-Crosbie, M. Guidelines for measuring cardiac physiology in mice. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 314 (4), 733-752 (2018).
- Zacchigna, S., et al. Toward standardization of echocardiography for the evaluation of left ventricular function in adult rodents: a position paper of the ESC Working Group on myocardial function. Cardiovascular Research. , 110 (2020).
- Hendgen-Cotta, U. B., et al. A novel physiological role for cardiac myoglobin in lipid metabolism. Scientific Reports. 7, 43219 (2017).
- Al-Lamee, R. K., et al. Dobutamine stress echocardiography ischemia as a predictor of the placebo-controlled efficacy of percutaneous coronary intervention in stable coronary artery disease: The stress echocardiography-stratified analysis of ORBITA. Circulation. 140 (24), 1971-1980 (2019).
- Cadeddu Dessalvi, C., Deidda, M., Farci, S., Longu, G., Mercuro, G. Early ischemia identification employing 2D speckle tracking selective layers analysis during dobutamine stress echocardiography. Echocardiography. 36 (12), 2202-2208 (2019).
- Li, Z., et al. Reduced myocardial reserve in young x-linked muscular dystrophy mice diagnosed by two-dimensional strain analysis combined with stress echocardiography. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 30 (8), 815-827 (2017).
- Puhl, S. L., Weeks, K. L., Ranieri, A., Avkiran, M. Assessing structural and functional responses of murine hearts to acute and sustained beta-adrenergic stimulation in vivo. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 79, 60-71 (2016).
- Ferferieva, V., et al. Assessment of strain and strain rate by two-dimensional speckle tracking in mice: comparison with tissue Doppler echocardiography and conductance catheter measurements. European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging. 14 (8), 765-773 (2013).
- Wiesmann, F., et al. Dobutamine-stress magnetic resonance microimaging in mice : acute changes of cardiac geometry and function in normal and failing murine hearts. Circulation Research. 88 (6), 563-569 (2001).
- Pellikka, P. A., et al. Guidelines for performance, interpretation, and application of stress echocardiography in ischemic heart disease: From the American Society of Echocardiography. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 33 (1), 1-41 (2020).
- Ahonen, J., et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship of dobutamine and heart rate, stroke volume and cardiac output in healthy volunteers. Clinical Drug Investigation. 28 (2), 121-127 (2008).
- Nath Das, R. Determinants of cardiac ejection fraction for the patients with dobutamine stress echocardiography. Epidemiology. 07 (03), (2017).
- Balcazar, D., et al. SERCA is critical to control the Bowditch effect in the heart. Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 12447 (2018).
- Zhang, B., Davis, J. P., Ziolo, M. T. Cardiac catheterization in mice to measure the pressure volume relationship: Investigating the Bowditch Effect. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (100), e52618 (2015).
- Casaclang-Verzosa, G., Enriquez-Sarano, M., Villaraga, H. R., Miller, J. D. Echocardiographic approaches and protocols for comprehensive phenotypic characterization of valvular heart disease in mice. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (120), e54110 (2017).
- Respress, J. L., Wehrens, X. H. Transthoracic echocardiography in mice. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (39), e1738 (2010).
- Rea, D., et al. Strain analysis in the assessment of a mouse model of cardiotoxicity due to chemotherapy: Sample for preclinical research. In Vivo. 30 (3), 279-290 (2016).
- Beyhoff, N., et al. Application of speckle-tracking echocardiography in an experimental model of isolated subendocardial damage. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 30 (12), 1239-1250 (2017).
- Pappritz, K., et al. Speckle-tracking echocardiography combined with imaging mass spectrometry assesses region-dependent alterations. Scientific Reports. 10 (1), 3629 (2020).
- Krahwinkel, W., et al. Dobutamine stress echocardiography. European Heart Journal. 18, 9-15 (1997).
- Michel, L., et al. Real-time pressure-volume analysis of acute myocardial infarction in mice. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (137), e57621 (2018).
- Baumgartner, H., et al. ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. European Heart Journal. 38 (36), 2739-2791 (2017).
- Knuuti, J., et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. European Heart Journal. 41 (3), 407-477 (2020).
- Schoensiegel, F., et al. High throughput echocardiography in conscious mice: Training and primary screens. European Journal of Ultrasound. 32, 124-129 (2011).
- Gao, S., Ho, D., Vatner, D. E., Vatner, S. F. Echocardiography in Mice. Current Protocols in Mouse Biology. 1, 71-83 (2011).
- Scherrer-Crosbie, M., Thibault, H. B. Echocardiography in translational research: of mice and men. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 21 (10), 1083-1092 (2008).
- Tanaka, N., et al. Transthoracic echocardiography in models of cardiac disease in the mouse. Circulation. 94 (5), 1109-1117 (1996).
- Roth, D. M., et al. Cardiac-directed adenylyl cyclase expression improves heart function in murine cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 99 (24), 3099-3102 (1999).
- Castle, P. E., et al. Anatomical location, sex, and age influence murine arterial circumferential cyclic strain before and during dobutamine infusion. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 49 (1), 69-80 (2019).
- Ren, S., et al. Implantation of an isoproterenol mini-pump to induce heart failure in mice. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (152), e59646 (2019).
- Carillion, A., Biais, M., Riou, B., Amour, J. Comparison of Dobutamine with Isoproterenol in echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac β-adrenergic response in rats: 4AP8-9. European Journal of Anaesthesiology. 29, (2012).
- Lang, R. M., et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging. 16 (3), 233-270 (2015).
- Lindsey, M. L., et al. Guidelines for experimental models of myocardial ischemia and infarction. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 314 (4), 812-838 (2018).
- Pieske, B., et al. How to diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: the HFA-PEFF diagnostic algorithm: a consensus recommendation from the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal. 40 (40), 3297-3317 (2019).
- Riehle, C., Bauersachs, J. Small animal models of heart failure. Cardiovascular Research. 115 (13), 1838-1849 (2019).
- Rammos, C., et al. Impact of dietary nitrate on age-related diastolic dysfunction. European Journal of Heart Failure. 18 (6), 599-610 (2016).
- Koshizuka, R., et al. Longitudinal strain impairment as a marker of the progression of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a rat model. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 26 (3), 316-323 (2013).
- Bunting, K. V., et al. A practical guide to assess the reproducibility of echocardiographic measurements. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 32 (12), 1505-1515 (2019).
- Grune, J., et al. Accurate assessment of LV function using the first automated 2D-border detection algorithm for small animals - evaluation and application to models of LV dysfunction. Cardiovascular Ultrasound. 17 (1), 7 (2019).
- Lau, E. M. T., et al. Dobutamine stress echocardiography for the assessment of pressure-flow relationships of the pulmonary circulation. Chest. 146 (4), 959-966 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved