このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
単一セル材料特性を決定するためのせん断アッセイプロトコル
* これらの著者は同等に貢献しました
要約
このプロトコルは、 in vitroでの癌性および非癌性細胞株の機械的特性の定量化の概要を示しています。がん細胞と正常細胞の機構における保存された違いは、予後と診断に影響を与える可能性のあるバイオマーカーとして機能する可能性があります。
要約
不規則なバイオメカニクスは、広範な研究の対象となる癌生物学の特徴です。セルの機械的特性は、材料の機械的特性と似ています。ストレスやひずみに対する細胞の耐性、緩和時間、弾力性はすべて、他のタイプの細胞と比較することができる特性です。癌性(悪性)細胞と正常(非悪性)細胞の機械的特性を定量化することで、研究者はこの病気の生物物理学的基礎をさらに明らかにすることができます。がん細胞の機械的性質は、正常細胞の機械的性質とは一貫して異なることが知られているが、培養中の細胞からこれらの性質を推定する標準的な実験手順は不足している。
この論文では、流体せん断アッセイを使用して in vitro で単一細胞の機械的特性を定量化する手順の概要を説明します。このアッセイの背後にある原理は、単一の細胞に流体せん断応力を適用し、結果として生じる細胞の変形を経時的に光学的に監視することです。その後、デジタル画像相関(DIC)解析を使用して細胞の機械的特性を特徴付け、DIC解析から生成された実験データに適切な粘弾性モデルをフィッティングします。全体として、ここで概説するプロトコルは、治療が困難な癌の診断のためのより効果的で標的を絞った方法を提供することを目的としています。
概要
がん細胞と非がん細胞の生物物理学的な違いを研究することで、新しい診断および治療の機会が可能になります1。バイオメカニクス/メカノバイオロジーの違いが腫瘍の進行と治療抵抗性にどのように寄与するかを理解することで、標的療法と早期診断の新しい道が明らかになります2。
がん細胞の機械的性質(原形質膜や核膜の粘弾性など)は正常細胞と異なることが知られていますが3,4,5、生細胞でこれらの性質を測定するための堅牢で再現性のある方法は不足しています6。せん断アッセイ法は、単一細胞を流体せん断応力にさらし、加えられた応力に対する個々の応答および抵抗を分析することにより、細胞の機械的特性を定量化するために使用されます3,4,5,7,8,9。単一細胞の機械的特性を特徴付けるためにいくつかの方法および技術が使用されてきたが、これらは、i)原子間力顕微鏡(AFM)10,11に関連するくぼみの深さ、複雑な先端形状、または基板硬化による細胞膜の穿孔/損傷、ii)光学トラップ中に細胞の光損傷を誘発することによって細胞材料特性に影響を与える傾向がある12、図13、又はiii)マイクロピペット吸引に関連する複雑なストレス状態を誘導する14、15。これらの外部効果は、細胞粘弾性測定の精度における重大な不確実性と関連している6、16、17。
これらの制限に対処するために、ここで説明するせん断アッセイ法は、プロセス中の細胞材料特性に影響を与えることなく、体内の生理学的流れをシミュレートするための高度に制御可能で簡単なアプローチを提供します。このアッセイにおける流体せん断応力は、循環中に腫瘍間質内の流体または血液中の流体のいずれかによって体内の細胞が受ける機械的ストレスを表す18、19、20。さらに、これらの流体ストレスは、腫瘍原性細胞と非腫瘍性細胞の間で異なる進行、遊走、転移、および細胞死を含む、癌細胞における様々な悪性挙動を促進する19,21,22,23。さらに、癌細胞の変化した機械的特徴(すなわち、それらはしばしば同じ器官内に見られる正常細胞よりも「柔らかい」)は、それらが敵対的な腫瘍微小環境に存続し、周囲の正常組織に浸潤し、そして遠隔部位に転移することを可能にする24,25,26。細胞が生理学的レベルの流体せん断応力を経験する疑似生物学的環境を作り出すことによって、生理学的に関連し、細胞に破壊されないプロセスが達成される。これらの加えられた流体せん断応力に対する細胞応答により、細胞の機械的特性を特徴付けることができます。
この論文は、せん断応力が加えられた下での癌性および非癌性の細胞の機械的特性と挙動の広範な研究のためのせん断アッセイプロトコルを提供します。細胞は弾性的かつ粘性のある方法で外力に応答するため、粘弾性材料3として理想化することができます。この手法は、(i)分散した単一細胞の細胞培養、(ii)流体せん断応力の制御された適用、(iii)細胞の挙動(ストレスおよび変形に対する抵抗性を含む)の in situ イメージングおよび観察、(iv)変形の程度を決定するための細胞のひずみ解析、および(v)単一細胞の粘弾性特性の特性評価に分類されます。これらの機械的特性と挙動を調べることにより、複雑な細胞メカノバイオロジーを定量化可能なデータに蒸留することができます。この方法を概説するプロトコルは、様々な悪性および非悪性細胞タイプのカタログ化および比較を可能にする。これらの違いを定量化することで、診断および治療バイオマーカーを確立する可能性があります。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
プロトコル
1. シングルセルせん断アッセイの調製
- 細胞培養
- 約50,000個の懸濁単細胞を、2 mLの培地を含む35 mm x 10 mmのシャーレに播種します。
注:播種前に懸濁細胞を渦流して、細胞凝集塊を分解します。 - 細胞を37°Cでインキュベートし、細胞付着と完全な細胞骨格タンパク質形成のために10〜48時間待ちます。
注:細胞凝集を回避しながら適切な細胞増殖と付着を確保するために、細胞付着の期間、ならびに増殖および増殖速度を考慮してください。これらのパラメータは細胞の種類によって異なります。
- 約50,000個の懸濁単細胞を、2 mLの培地を含む35 mm x 10 mmのシャーレに播種します。
2. せん断アッセイ実験
- せん断アッセイ粘性流動媒体の調製
- わずかに粘性のある流動媒体(0.015-0.02 Pa·s)を確保するには、0.05 wt%の非毒性および非アレルギー性メチルセルロース(4 Pa·s)を測定し、培地に加えます。
- 均一な混合を確保するには、マグネチックスターラー/ホットプレートを使用して、ベース培養培地を~60-70°Cの温度で~10-20分間予熱します。メディアを連続的に攪拌しながら、メチルセルロース粒子の凝固を避けるために、メチルセルロースが迅速に分散するように穏やかに添加する。このプロセスを~15-24時間継続して、培地+セルロースの透明な溶液を確保します。
注意: 溶液を過度に加熱しないでください。 - 流動媒体の粘度を測定するには、レオメーターを使用して代表的な流動媒体の~0.5-1 mLをテストします。読み出しから流体粘度を決定し、この値を使用してせん断流体媒体の粘度(μ)を表し、式(2)を使用してせん断応力を計算します。
- せん断装置のセットアップ
- 粘性培養培地の注入と回収のためにプログラム可能なシリンジポンプに接続されたデュアルシリンジ(60 mLまたは100 mL)のせん断アッセイシステムをセットアップします(図1)。
- 両方のシリンジを1/16インチチューブとチューブコネクタ を介して フローチャンバーに取り付けます。
- ゴム製ガスケットを固定して、流路に沿った単一セルに制御された均一な流れを提供します(図1)。ゴム製ガスケットは、達成する流れプロファイル(層流または乱流)と目的の観察領域(長さ22.5 mm、幅2.5 mm、高さ0.254 mmなど)に応じてさまざまなサイズがあります(図1)。
- 一定量の液体(例:60 mL)を指定された速度(例:1 mL/分)で注入および回収するようにポンプをプログラムし、対応するシリンジ(例:60 mL)を選択します。
注意: 詰まりや誤動作を防ぐために、最大注入量と引き出し量のプリセットを考慮してください。必要なポンプせん断速度の計算には、式(2)を使用します(必要な応力と粘度がわかっていると仮定します)。
- プリシアのセットアップ
- 準備した粘性流動媒体をシリンジに充填します。
- 60 mLまたは100 mL(または必要に応じて)の粘性流動媒体で満たされたシリンジと空の60 mLシリンジを、プログラム可能なシリンジポンプのそれぞれの場所に取り付けます。チューブとチューブコネクタ を介して 、両方のシリンジをフローチャンバーに接続します。
- 単一セルの識別を容易にし、フローチャンバーとペトリ皿を固定するために、ゴム製ガスケットをフローチャンバーに取り付けます。
- 目的の細胞を含むシャーレから細胞培養培地を吸引します。
- リン酸緩衝生理食塩水(PBS)を使用して、死んだ細胞と緩く付着した細胞を洗い流します。
- PBSを吸引します。
- フローチャンバーとゴム製ガスケット(~34 mm x 9 mm)を、取り付けられたセルが入っているペトリ皿(35 mm x 10 mm)に挿入して固定します。
- 培養皿に装着したマイクロ流体フローチャンバー+細胞を倒立顕微鏡に置き、高ピクセル値(通常は 40倍から63 倍の 倍 率)で高品質の画像を得るのに十分な高さの顕微鏡対物レンズとディスプレイモニターを使用します。
- ディスプレイモニターの顕微鏡ソフトウェアから ライブ画像 (一部のソフトウェアではタイムラプス)オプションを選択します。PCの顕微鏡ソフトウェアにt(タイムラプス)機能があるか、ビデオ録画できることを確認してください。
- 顕微鏡対物レンズの焦点を合わせ、適切なコントラストと明瞭な細胞エッジを確保します。これは、せん断後の画像解析に必要です。顕微鏡ステージを動かして、細胞がディスプレイモニターにはっきりと見え、ライブ画像であることを確認します。
- フィットフローチャンバー+ペトリ皿のイメージング/流路内のセルまたは複数の異なるセル(フローチャンバーへのガスケットのフィッティングによって作成された領域/パス)を選択します。
- せん断とイメージング
- 連続的に均一な流れを維持するには、同様の注入速度と離脱速度を選択し、流体の層流(通常は 1 mL / minから 5 mL / minの間)を確保します。層流が低いレジームでは、Re < 100のレイノルズ数を確保します。
- せん断ポンプの [実行 ]をクリックして、せん断液(準備された粘性媒体)を連続速度で注入および引き出します。輸液中に気泡がないことを確認すると、細胞に外部の説明されていないストレスがかかる可能性があります。
- 注入されたせん断液が顕微鏡下で目的の細胞に接触する前に、顕微鏡ソフトウェアの録画をクリックしてビデオの 録画 を開始します。
- 7分間、またはストレス曝露の希望期間、または目的の細胞が皿の底から剪断されるまで記録を続けます。必要に応じて実行が完了したら、顕微鏡ソフトウェアで 記録の停止 をクリックします。
- 録音を保存し 、.tiffファイルとして抽出します。好ましくは、容易な解析のために 毎秒1フレームで 画像を抽出する。
3. データ処理
- デジタル画像相関手順(画像解析)
- 顕微鏡からの記録をビデオファイルとして抽出した場合は、画像フレーム(できれば.tiffファイル形式)に変換します。
- せん断アッセイ記録から得られた画像をDavis 10.1.2ソフトウェア(DICソフトウェア)にインポートし、それぞれの新しい画像(変形画像)内の参照画像のピクセル(サブセット)の各ブロックを特定することにより、細胞の自然にパターン化された構造の動きを追跡します(図2)。
- 最適な相関関係を得るには、 31 x 31 ピクセルのサブセット サイズ、 20 ピクセルのステップ サイズ (各サブセットの変形距離)、および最後の画像に対する新しい画像の変形を追跡する 差動トラック オプションの合計 を利用します。この相関の結果はひずみ時間プロット(図3)であり、MATLABでさらに分析するために.csvファイルとしてエクスポートできます。
- 選択した単一セルの対象領域をマップします。マップされたセル内の任意の点を選択して、変形を追跡します。セルなどの不規則な形状の場合は、 ポリゴン マスク を使用してセルのジオメトリをマップします。
- マッピング後、[ひずみゲージの追加]をクリックし、定義された細胞境界内のポイントで個々の ひずみゲージ を描画して、解析する細胞上の特定のポイント(核または細胞質)を選択します。
- [実行]をクリックしてひずみ処理を開始し、ひずみ対時間データを取得します。
- 生成されたひずみ時間プロットをダブルクリック(または右クリック)し、 データをスプレッドシートとしてエクスポートを選択します。
4. 機械的特性評価
- 粘弾性特性の特性評価
- DICソフトウェアのひずみ時間データを含む.csvファイルは、MATLABで読みやすいように別のフォルダに保存します。
- MATLABを実行し、エディタータブをクリックして エディター ページを開き、スプレッドシートをセルごとに読み取るコードを記述します。
- MATLAB パス (目的のファイルにアクセスするフォルダー パス) を変更して、分析するデータを含むフォルダー ( ユーザー/ユーザー名/デスクトップ/データなど) にアクセスします。
- MATLAB エディター ページで、カスタマイズされたコードを使用してスプレッドシート データにアクセスします。たとえば、a1= xlsread('data','run1','A4:A183') の場合、a1 は識別子を表し、xlsread は.csv ファイル (この場合はスプレッドシートとして) を読み取る MATLAB 関数、data はファイル名、run1 はシート名、A4:A183 は分析対象のスプレッドシート データのセル A に含まれるデータの範囲です。完全に適合するには、xとy(それぞれ時間とひずみ)を分析します。例えば:
a1=xlsread('data','run1','A4:A183');
b1=xlsread('data','run1','B4:B183');
a1 = x (時間)、および b1 = y (ひずみ)。 - MATLAB で、[ アプリ |カーブフィッター |カスタム方程式。代表的なカスタム式をクリアし、粘弾性モデル式[式(1)]を入力します(εはx変数、tはy変数を表します。
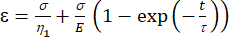 (1)
(1)
ここで、εはひずみを表し、σはせん断応力を表し、η1は粘度を表し、Eは弾性を表し、tは時間を表し、τは緩和時間を表し、一次変形後にセルが元の形状に戻るのに必要な最大時間を特徴付ける。これはτ=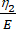 として表され、ここでη 2は2番目のダッシュポットの二次粘度項です(図4)。
として表され、ここでη 2は2番目のダッシュポットの二次粘度項です(図4)。 - 新しい変数をカスタム方程式インターフェース内の粘弾性パラメータに再割り当てします。(ε, η1, E, σ, t, τ =
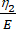 )は (x, a, b, K, y, c) をそれぞれ表します。ここで、xとyはそれぞれ独立変数と従属変数です。せん断応力(σ)は、式 (2) を使用して求めることができます。
)は (x, a, b, K, y, c) をそれぞれ表します。ここで、xとyはそれぞれ独立変数と従属変数です。せん断応力(σ)は、式 (2) を使用して求めることができます。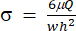 (2)
(2)
ここで、μはせん断流体媒体の粘度を表し、Qはポンプ流量であり、 w および h はそれぞれ 図1Cに示す流路の幅および高さである。 - [データの選択]をクリックして、各データセットの時間(a1)と歪み(b1)を選択します。
- [ 自動調整ボックス]オプション がオンになっていることを確認します。これにより、データ(xとy)が選択されたときに自動的にフィットが実行されます。
- 境界条件を締め付けるフィット方法を選択します。[方法]カテゴリの下にある[詳細オプション]をクリックし、[非線形最小二乗法]を選択します。[堅牢] で [オフ] を選択し、[アルゴリズム] で [信頼リージョン] を選択します。他のすべてのパラメーターはそのままにしておきます。
- フィッティング後の新しい変数(a、b、c)は、それぞれセルの粘弾性特性、粘度、弾性、および緩和時間(η1、E、EQUAT)を表します(図5)。
- 適合値の高いR2乗値(R2 >80%)を探して、データ出力が粘弾性モデルの真の適合と見なすことができることを確認します(図3)
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
結果
DICと粘弾性モデルを使用した変形解析と組み合わせたせん断アッセイプロトコルは、in vitroで単一細胞の機械的特性を定量化することに成功しています。この方法は、正常ヒト乳細胞(MCF-10A)3,4,9、低転移性トリプルネガティブ乳がん細胞(MDA-MB-468)3、トリプルネガティブ乳がん細胞(MDA-MB-231)3、ヒト?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
ディスカッション
せん断アッセイ法は、細胞と周囲の機械的微小環境との相互作用および機械的ストレスに対するそれらの応答をシミュレートするための疑似機械生物学的環境の設定を含み、そのパターンが癌性細胞株間の保存された物理的異型を示す細胞機械的特性のカタログを作成しました3,4,5,7,8
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
開示事項
著者には、開示すべき競合する金銭的利益はありません。
謝辞
著者らは、この技術を最初に開拓したウースター工科大学のソボエジョグループの以前の研究者であるYifang Cao博士、Jingjie Hu博士、Vanessa Uzonwanne博士に感謝します。この研究は、米国国立がん研究所(NIH/NCI K22 CA258410 to M.D.)の支援を受けた。図は BioRender.com で作成されました。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| CELL CULTURE | |||
| .25% Trypsin, 2.21 mM EDTA, 1x[-] sodium bicarbonate | Corning | 25-053-ci | For cellular detachment from substrate in cell culture |
| 15 mL Centrifuge tubes | Falcon by Corning | 05-527-90 | |
| 35 mm Petri dishes | Corning | 430165 | |
| 50 mL Centrifuge tubes | Falcon by Corning | 14-432-22 | |
| Centrifuge | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Dulbecco's Modification of Eagle's Medium (DMEM) 1x | Corning | 10-013-cv | Or any other media for culturing cells. DMEM was used for culturing U87 cells |
| Gloves | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Heracell Vios 160i CO2 Incubator | Thermo Scientific | 51033770 | For Incubation during cell culture |
| Hood | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Micropipette | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Micropipette tips | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Microscope | Leica/any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline without calcium and magnesium PBS, 1x | Corning | 21-040-CM | |
| Pipetman | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Pipette tips | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Precision GP 10 liquid incubator | Thermo Scientific | TSGP02 | |
| T25 Flask | Corning | 430639 | |
| T75 Flask | Corning | 430641U | |
| SHEAR ASSAY | |||
| 100 mL beaker | any | For creating DMEM + methyl cellulose viscous shear media | |
| DMEM | Corning | ||
| Flow chamber + rubber gasket | Glycotech | 31-001 | Circular Flow chamber Kit ( for 35 mm tissue culture dishes) |
| Hybrid Rheometer | HR-2 Discovery Hybrid Rheometer | For determination of shear fluid viscosity | |
| Magnetic stir bar | any | For creating DMEM + methyl cellulose viscous shear media | |
| Magnetic stir plate | any | For creating DMEM + methyl cellulose viscous shear media | |
| Methyl cellulose | any | To increase viscosity of DMEM in flow media | |
| Syringe Pump | KD Scientific Geminin 88 plus | 788088 | For programming fluid infusion and withdrawal |
| Syringes, tubing, and connectors | For shear apparatus setup | ||
| SOFTWARE | |||
| ABAQUS software | Simulia | ||
| Digitial Image Correlation software | LaVision, Germany | DAVIS 10.1.2 | |
| Imaging software | Leica/any microscope software | ||
| MATLAB | MATLAB | MATLAB_R2020B |
参考文献
- Sethi, S., Ali, S., Philip, P. A., Sarkar, F. H. Clinical advances in molecular biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 14 (7), 14771-14784 (2013).
- Runel, G., Lopez-Ramirez, N., Chlasta, J., Masse, I. Biomechanical properties of cancer cells. Cells. 10 (4), 887(2021).
- Hu, J., Zhou, Y., Obayemi, J. D., Du, J., Soboyejo, W. O. An investigation of the viscoelastic properties and the actin cytoskeletal structure of triple negative breast cancer cells. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 86, 1-13 (2018).
- Onwudiwe, K., et al. Investigation of creep properties and the cytoskeletal structures of non-tumorigenic breast cells and triple-negative breast cancer cells. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A. 110 (5), 1004-1020 (2022).
- Ani, C. J., et al. A shear assay study of single normal/breast cancer cell deformation and detachment from poly-di-methyl-siloxane (PDMS) surfaces. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 91, 76-90 (2019).
- Suresh, S. Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 3 (4), 413-438 (2007).
- Cao, Y., et al. Investigation of the viscoelasticity of human osteosarcoma cells using a shear assay method. Journal of Materials Research. 21 (8), 1922-1930 (2006).
- Cao, Y. On the measurement of human osteosarcoma cell elastic modulus using shear assay experiments. Journal of Materials Science. Materials in Medicine. 18 (1), 103-109 (2007).
- Onwudiwe, K., et al. Actin cytoskeletal structure and the statistical variations of the mechanical properties of non-tumorigenic breast and triple-negative breast cancer cells. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 119, 104505(2021).
- Kirmizis, D., Logothetidis, S. Atomic force microscopy probing in the measurement of cell mechanics. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 5, 137-145 (2010).
- Haase, K., Pelling, A. E. Investigating cell mechanics with atomic force microscopy. Journal of the Royal Society. Interface. 12 (104), 20140970(2015).
- Zhang, H., Liu, K. K. Optical tweezers for single cells. Journal of the Royal Society. Interface. 5 (24), 671-690 (2008).
- Peterman, E. J. G., Gittes, F., Schmidt, C. F. Laser-induced heating in optical traps. Biophysical Journal. 84, 1308-1316 (2003).
- Hochmuth, R. M. Micropipette aspiration of living cells. Journal of Biomechanics. 33 (1), 15-22 (2000).
- Evans, E., Yeung, A. Apparent viscosity and corticcal tension of blood granulocytes determined by micropipet aspiration. Biophysical Journal. 56 (1), 151-160 (1989).
- Van Vliet, K. J., Bao, G., Suresh, S. The biomechanics toolbox: experimental approaches for living cells and biomolecules. Acta Materialia. 51 (19), 5881-5905 (2003).
- Moeendarbary, E., Harris, A. R. Cell mechanics: principles, practices, and prospects. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Systems Biology and Medicine. 6 (5), 371-388 (2014).
- Choi, H. Y., et al. Hydrodynamic shear stress promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by downregulating ERK and GSK3beta activities. Breast Cancer Research. 21 (1), 6(2019).
- Northcott, J. M., Dean, I. S., Mouw, J. K., Weaver, V. M. Feeling stress: The mechanics of cancer progression and aggression. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 6, 17(2018).
- Onwudiwe, K., Najera, J., Siri, S., Datta, M. Do tumor mechanical stresses promote cancer immune escape. Cells. 11 (23), 3840(2022).
- Heldin, C. H., Rubin, K., Pietras, K., Ostman, A. High interstitial fluid pressure - an obstacle in cancer therapy. Nature Reviews. Cancer. 4 (10), 806-813 (2004).
- Krog, B. L., Henry, M. D. Biomechanics of the circulating tumor cell microenvironment. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 1092, 209-233 (2018).
- Moose, D. L., et al. Cancer cells resist mechanical destruction in circulation via RhoA/actomyosin-dependent mechano-adaptation. Cell Reports. 30 (11), 3864-3874 (2020).
- Mao, B. H., Nguyen Thi, K. M., Tang, M. J., Kamm, R. D., Tu, T. Y. The interface stiffness and topographic feature dictate interfacial invasiveness of cancer spheroids. Biofabrication. 15 (1), (2023).
- Kashani, A. S., Packirisamy, M. Cancer cells optimize elasticity for efficient migration. Royal Society Open Science. 7 (10), 200747(2020).
- Riehl, B. D., Kim, E., Bouzid, T., Lim, J. Y. The role of microenvironmental cues and mechanical loading milieus in breast cancer cell progression and metastasis. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 8, 608526(2021).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved