A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Shear Assay Protocol for the Determination of Single-Cell Material Properties
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This protocol outlines the quantification of the mechanical properties of cancerous and non-cancerous cell lines in vitro. Conserved differences in the mechanics of cancerous and normal cells can act as a biomarker that may have implications in prognosis and diagnosis.
Abstract
Irregular biomechanics are a hallmark of cancer biology subject to extensive study. The mechanical properties of a cell are similar to those of a material. A cell's resistance to stress and strain, its relaxation time, and its elasticity are all properties that can be derived and compared to other types of cells. Quantifying the mechanical properties of cancerous (malignant) versus normal (non-malignant) cells allows researchers to further uncover the biophysical fundamentals of this disease. While the mechanical properties of cancer cells are known to consistently differ from the mechanical properties of normal cells, a standard experimental procedure to deduce these properties from cells in culture is lacking.
This paper outlines a procedure to quantify the mechanical properties of single cells in vitro using a fluid shear assay. The principle behind this assay involves applying fluid shear stress onto a single cell and optically monitoring the resulting cellular deformation over time. Cell mechanical properties are subsequently characterized using digital image correlation (DIC) analysis and fitting an appropriate viscoelastic model to the experimental data generated from the DIC analysis. Overall, the protocol outlined here aims to provide a more effective and targeted method for the diagnosis of difficult-to-treat cancers.
Introduction
Studying the biophysical differences between cancerous and non-cancerous cells allows for novel diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities1. Understanding how differences in biomechanics/mechanobiology contribute to tumor progression and treatment resistance will reveal new avenues for targeted therapy and early diagnosis2.
While it is known that cancer cell mechanical properties differ from normal cells (e.g., viscoelasticity of the plasma membrane and nuclear envelope)3,4,5, robust and reproducible methods for measuring these properties in live cells are lacking6. The shear assay method is used to quantify the mechanical properties of cells by subjecting single cells to fluid shear stress and analyzing their individual responses and resistance to the applied stress3,4,5,7,8,9. Although several methods and techniques have been used to characterize the mechanical properties of single cells, these tend to affect cell material properties by i) perforating/damaging the cell membrane due to the indentation depth, complex tip geometries, or substrate stiffening associated with atomic force microscopy (AFM)10,11, ii) inducing cellular photodamage during optical trapping12,13, or iii) inducing complex stress states associated with micropipette aspiration14,15. These external effects are associated with significant uncertainties in the accuracy of cell viscoelasticity measurements6,16,17.
To address these limitations, the shear assay method described here provides a highly controllable and simple approach to simulate physiological flow in the body without affecting cellular material properties in the process. Fluid shear stresses in this assay represent mechanical stresses experienced by cells in the body either by fluids within the tumor interstitium or in the blood during circulation18,19,20. Further, these fluid stresses promote various malignant behaviors in cancer cells, including progression, migration, metastasis, and cell death19,21,22,23 which vary between tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic cells. Moreover, the altered mechanical features of cancer cells (i.e., they are often "softer" than normal cells found within the same organ) allow them to persist in hostile tumor microenvironments, invade surrounding normal tissues, and metastasize to distant sites24,25,26. By creating a pseudo-biological environment where cells experience physiological levels of fluid shear stress, a process that is physiologically relevant and not destructive to the cell is achieved. The cellular responses to these applied fluid shear stresses allow us to characterize cell mechanical properties.
This paper provides a shear assay protocol for the extensive study of the mechanical properties and behavior of cancerous and non-cancerous cells under applied shear stress. Cells respond to external forces in an elastic and viscous manner and can therefore be idealized as a viscoelastic material3. This technique is categorized into: (i) cell culture of dispersed single cells, (ii) controlled application of fluid shear stress, (iii) in situ imaging and observation of cellular behavior (including resistance to stress and deformation), (iv) strain analysis of cells to determine the extent of deformation, and (v) characterization of the viscoelastic properties of single cells. By interrogating these mechanical properties and behaviors, complex cellular mechanobiology can be distilled to quantifiable data. A protocol outlining this method allows for the cataloging of and comparison between various malignant and non-malignant cell types. Quantifying these differences has the potential to establish diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers.
Protocol
1. Preparation for the single-cell shear assay
- Cell culture
- Seed approximately 50,000 suspended single cells in a 35 mm x 10 mm Petri dish containing 2 mL of culture media.
NOTE: Vortex the suspended cells prior to seeding to break apart cell aggregates. - Incubate the cells at 37 °C and allow between 10 to 48 h for cell attachment and complete cytoskeletal protein formation.
NOTE: Consider the duration of cellular attachment, as well as proliferation and growth rates, to ensure adequate cellular growth and attachment while avoiding cell aggregation. These parameters vary with cell type.
- Seed approximately 50,000 suspended single cells in a 35 mm x 10 mm Petri dish containing 2 mL of culture media.
2. Shear assay experiment
- Preparation of shear assay viscous flow media
- To ensure a slightly viscous flow media (0.015-0.02 Pa·s), measure and add 0.05 wt% of non-toxic and non-allergenic methylcellulose (4 Pa·s) to the culture media.
- To ensure a homogeneous mix, preheat the base culture media for ~10-20 min at a temperature of ~60-70 °C with a magnetic stirrer/hot plate. While continually stirring the media, gently add the methylcellulose such that it quickly disperses, to avoid coagulation of the methylcellulose particles. Allow this process to continue for ~15-24 h to ensure a clear solution of media + cellulose.
NOTE: Avoid excessive heating of the solution. - To measure the viscosity of the flow media, test ~0.5-1 mL of the representative flow media using a rheometer. From the readout, determine the fluid viscosity and utilize this value to represent the viscosity of the shear fluid medium (μ) to compute shear stress using equation (2).
- Shear apparatus setup
- Set up the shear assay system of dual syringes (60 mL or 100 mL) connected to a programmable syringe pump for infusion and withdrawal of the viscous culture media (Figure 1).
- Attach both syringes to the flow chamber via 1/16 inch tubing and tubing connectors.
- Fasten a rubber gasket to provide a controlled, uniform flow on single cells along the flow path (Figure 1). The rubber gasket comes in different sizes depending on the flow profile to be attained (laminar or turbulent) and the desired area of observation (e.g., length of 22.5 mm, width of 2.5 mm, and height of 0.254 mm) (Figure 1).
- Program the pump to infuse and withdraw a certain volume of fluid (e.g., 60 mL) at a designated rate (e.g., 1 mL/min) and select the corresponding syringes (e.g., 60 mL).
NOTE: Account for the maximum infusion and withdrawal volume presets to avoid jamming or malfunction. Use equation (2) for the calculation of the required pump shear rate (assuming the required stress and viscosity are known).
- Pre-shear setup
- Fill the syringe with the prepared viscous flow media.
- Attach the syringe, filled with 60 or 100 mL (or as needed) of viscous flow media, and an empty 60 mL syringe to their respective locations on the programmable syringe pump. Via tubing and tubing connectors, connect both syringes to the flow chamber.
- To ensure easy identification of single cells and a fastened connection between the flow chamber and the Petri dish, attach the rubber gasket to the flow chamber.
- Aspirate the cell culture media from the Petri dish containing the cells of interest.
- Wash off dead cells and loosely attached cells using phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
- Aspirate the PBS.
- Insert and fix the flow chamber and rubber gasket (~34 mm x 9 mm) onto the Petri dish (35 mm x 10 mm) containing the attached cells.
- Place the fitted microfluidic flow chamber + cells on a cultured dish onto an inverted microscope, with a microscope objective high enough to obtain high-quality images with high pixel values (usually between 40x and 63x magnification) and a display monitor.
- Select the live image (time-lapse on some software) option from the microscope software on the display monitor. Ensure the microscope software on the PC has either a t (time-lapse) functionality or can take video recordings.
- Focus the microscope objective, ensuring adequate contrast and distinct cell edges. This is necessary for the image analysis post-shear. Move the microscope stage to ensure the cells are clearly visible on the display monitor and are live images.
- Select a cell or multiple distinct cells within the imaging/flow path of the fitted flow chamber + Petri dish (the area/path created by the fitting of the gasket to the flow chamber).
- Shear and imaging
- To maintain a continuous uniform flow, select similar infusion and withdrawal rates and ensure laminar flow of the fluid, usually between 1 mL/min and 5 mL/min. For low laminar flow regimes, ensure a Reynold's number of Re < 100.
- Click on Run on the shear pump to inject and withdraw the shear fluid (prepared viscous media) at a continuous rate. Ensure that there are no bubbles during fluid infusion, as this might introduce external unaccounted stress on the cells.
- Begin recording a video by clicking record on the microscope software before the infused shear fluid makes contact with the cell(s) of interest under the microscope.
- Continue to record for 7 min, or for the desired duration of stress exposure, or until the cell(s) of interest shears off the bottom of the dish. Click stop recording on the microscope software when the run is completed as desired.
- Save the recording and extract as .tiff files. Preferably, extract images at 1 frame per second for facile analysis.
3. Data processing
- Digital image correlation procedure (image analysis)
- If the recording from the microscope was extracted as a video file, convert it to image frames (preferably .tiff file format).
- Import the images derived from the shear assay recording to Davis 10.1.2 software (DIC software) to track the movement of the naturally patterned structures of the cell by locating each block of pixel (subset) of the reference image in the respective new images (deformed images) (Figure 2).
- For an optimized correlation, utilize a subset size of 31 x 31 pixels, a step size (deformation distance of each subset) of 20 pixels, and the sum of the differential track option, which tracks the deformation of a new image with respect to the last image. The result of this correlation is a strain-time plot (Figure 3) that can be exported as a .csv file for further analysis in MATLAB.
- Map out the region of interest for a chosen single cell. Select arbitrary points within the mapped cell to track deformation. For an irregular shape, such as the cell, use a polygon mask to map out the cell's geometry.
- After mapping, choose specific points on the cell (nucleus or cytoplasm) to be analyzed by clicking add strain gauge and drawing out individual strain gauges at points within the defined cellular boundary.
- Click on Run to begin the strain processing and obtain strain versus time data.
- Double-click (or right-click) on the generated strain-time plot and select export data as a spreadsheet.
4. Mechanical property characterization
- Viscoelastic property characterization
- Save the .csv file containing the strain-time data from the DIC software in a separate folder for easy readability by MATLAB.
- Run MATLAB and click on the editor tab to open an editor page to write a code that reads the spreadsheet, cell by cell.
- Change the MATLAB path (the folder path that accesses the file of interest) to access the folder containing the data to be analyzed, for example, Users/Username/Desktop/data.
- On the MATLAB editor page, access the spreadsheet data using the customized code. For example: a1= xlsread('data','run1','A4:A183'), where a1 represents the identifier, xlsread is the MATLAB function that reads the .csv file (in this case, as a spreadsheet), data is the file name, run1 is the sheet name, and A4:A183 is the range of data of interest in cell A of the spreadsheet data to be analyzed. For a complete fit, analyze x and y (time and strain, respectively). For example:
a1=xlsread('data','run1','A4:A183');
b1=xlsread('data','run1','B4:B183');
a1 = x (time), and b1 = y (strain). - In MATLAB, click Apps | Curve Fitter | Custom Equation. Clear the representative custom equation and input the viscoelastic model equation [equation (1)], where ε represents the x variable and t represents the y variable.
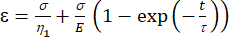 (1)
(1)
Here, ε represents the strain, σ represents the shear stress, η1 represents the viscosity, E represents the elasticity, t represents the time, and τ represents the relaxation time, which characterizes the maximum time required for the cell to return to its original shape after primary deformation. It is expressed as τ =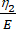 , where η2 is the secondary viscosity term for the second dashpot (Figure 4).
, where η2 is the secondary viscosity term for the second dashpot (Figure 4). - Reassign new variables to the viscoelastic parameters within the custom equation interface. (ε, η1, E, σ, t, and τ =
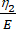 ) will represent (x, a, b, K, y, and c), respectively. Here, x and y are the independent and dependent variables, respectively. Shear stress (σ) can be determined using equation (2):
) will represent (x, a, b, K, y, and c), respectively. Here, x and y are the independent and dependent variables, respectively. Shear stress (σ) can be determined using equation (2):
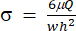 (2)
(2)
Here, μ represents the viscosity of the shear fluid medium, Q is the pump flow rate, and w and h are the width and height of the flow channel shown in Figure 1C, respectively. - Click on Select Data to select the Time (a1) and Strain (b1) for each set of data.
- Ensure the Auto Fit box option is checked. This runs the fit automatically when data (x and y) are selected.
- Select the fitting methods to tighten the boundary conditions. Click on Advanced Options under the Methods category and select Nonlinear Least Squares. Under Robust, select Off, and under Algorithm, select Trust-Region. Leave every other parameter as it is.
- The new variables post-fitting (a, b, and c) represent the viscoelastic properties, viscosity, elasticity, and relaxation time (η1, E, EQUAT), of the cell, respectively (Figure 5).
- Look for a high R-square value of the fit (R2 > 80%) to ensure that the data output can be considered a true fit of the viscoelastic model (Figure 3)
Results
The shear assay protocol coupled with deformation analysis using DIC and a viscoelastic model is successful in quantifying the mechanical properties of a single cell in vitro. This method has been tested on human and murine cell lines, including normal human breast cells (MCF-10A)3,4,9, less metastatic triple-negative breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-468)3, triple-negative breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-...
Discussion
The shear assay method, which includes setting up an pseudo-mechanobiological environment to simulate the interaction of cells with the surrounding mechanical microenvironment and their responses to mechanical stresses, has produced a catalog of cellular mechanical properties, whose patterns show conserved physical atypia among cancerous cell lines3,4,5,7,8. T...
Disclosures
The authors have no competing financial interests to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank previous researchers from the Soboyejo group at Worcester Polytechnic Institute who first pioneered this technique: Drs. Yifang Cao, Jingjie Hu, and Vanessa Uzonwanne. This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute (NIH/NCI K22 CA258410 to M.D.). Figures were created with BioRender.com.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| CELL CULTURE | |||
| .25% Trypsin, 2.21 mM EDTA, 1x[-] sodium bicarbonate | Corning | 25-053-ci | For cellular detachment from substrate in cell culture |
| 15 mL centrifuge tubes | Falcon by Corning | 05-527-90 | |
| 35 mm Petri dishes | Corning | 430165 | |
| 50 mL centrifuge tubes | Falcon by Corning | 14-432-22 | |
| centrifuge | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Dulbecco's Modification of Eagle's Medium (DMEM) 1x | Corning | 10-013-cv | Or any other media for culturing cells. DMEM was used for culturing U87 cells |
| gloves | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Heracell Vios 160i CO2 Incubator | Thermo Scientific | 51033770 | For Incubation during cell culture |
| Hood | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| micropipette | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| micropipette tips | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Microscope | Leica/any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline without calcium and magnesium PBS, 1x | Corning | 21-040-CM | |
| pipetman | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| pipette tips | any | For sterile cell culture | |
| Precision GP 10 liquid incubator | Thermo Scientific | TSGP02 | |
| T25 flask | Corning | 430639 | |
| T75 flask | Corning | 430641U | |
| SHEAR ASSAY | |||
| 100 mL beaker | any | For creating DMEM + methyl cellulose viscous shear media | |
| DMEM | Corning | ||
| Flow chamber + rubber gasket | Glycotech | 31-001 | Circular Flow chamber Kit ( for 35 mm tissue culture dishes) |
| Hybrid Rheometer | HR-2 Discovery Hybrid Rheometer | For determination of shear fluid viscosity | |
| magnetic stir bar | any | For creating DMEM + methyl cellulose viscous shear media | |
| magnetic stir plate | any | For creating DMEM + methyl cellulose viscous shear media | |
| methyl cellulose | any | To increase viscosity of DMEM in flow media | |
| Syringe Pump | KD Scientific Geminin 88 plus | 788088 | For programming fluid infusion and withdrawal |
| syringes, tubing, and connectors | For shear apparatus setup | ||
| SOFTWARE | |||
| ABAQUS software | Simulia | ||
| Digitial Image Correlation software | LaVision, Germany | DAVIS 10.1.2 | |
| Imaging software | Leica/any microscope software | ||
| MATLAB | MATLAB | MATLAB_R2020B |
References
- Sethi, S., Ali, S., Philip, P. A., Sarkar, F. H. Clinical advances in molecular biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 14 (7), 14771-14784 (2013).
- Runel, G., Lopez-Ramirez, N., Chlasta, J., Masse, I. Biomechanical properties of cancer cells. Cells. 10 (4), 887 (2021).
- Hu, J., Zhou, Y., Obayemi, J. D., Du, J., Soboyejo, W. O. An investigation of the viscoelastic properties and the actin cytoskeletal structure of triple negative breast cancer cells. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 86, 1-13 (2018).
- Onwudiwe, K., et al. Investigation of creep properties and the cytoskeletal structures of non-tumorigenic breast cells and triple-negative breast cancer cells. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A. 110 (5), 1004-1020 (2022).
- Ani, C. J., et al. A shear assay study of single normal/breast cancer cell deformation and detachment from poly-di-methyl-siloxane (PDMS) surfaces. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 91, 76-90 (2019).
- Suresh, S. Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 3 (4), 413-438 (2007).
- Cao, Y., et al. Investigation of the viscoelasticity of human osteosarcoma cells using a shear assay method. Journal of Materials Research. 21 (8), 1922-1930 (2006).
- Cao, Y. On the measurement of human osteosarcoma cell elastic modulus using shear assay experiments. Journal of Materials Science. Materials in Medicine. 18 (1), 103-109 (2007).
- Onwudiwe, K., et al. Actin cytoskeletal structure and the statistical variations of the mechanical properties of non-tumorigenic breast and triple-negative breast cancer cells. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 119, 104505 (2021).
- Kirmizis, D., Logothetidis, S. Atomic force microscopy probing in the measurement of cell mechanics. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 5, 137-145 (2010).
- Haase, K., Pelling, A. E. Investigating cell mechanics with atomic force microscopy. Journal of the Royal Society. Interface. 12 (104), 20140970 (2015).
- Zhang, H., Liu, K. K. Optical tweezers for single cells. Journal of the Royal Society. Interface. 5 (24), 671-690 (2008).
- Peterman, E. J. G., Gittes, F., Schmidt, C. F. Laser-induced heating in optical traps. Biophysical Journal. 84, 1308-1316 (2003).
- Hochmuth, R. M. Micropipette aspiration of living cells. Journal of Biomechanics. 33 (1), 15-22 (2000).
- Evans, E., Yeung, A. Apparent viscosity and corticcal tension of blood granulocytes determined by micropipet aspiration. Biophysical Journal. 56 (1), 151-160 (1989).
- Van Vliet, K. J., Bao, G., Suresh, S. The biomechanics toolbox: experimental approaches for living cells and biomolecules. Acta Materialia. 51 (19), 5881-5905 (2003).
- Moeendarbary, E., Harris, A. R. Cell mechanics: principles, practices, and prospects. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Systems Biology and Medicine. 6 (5), 371-388 (2014).
- Choi, H. Y., et al. Hydrodynamic shear stress promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by downregulating ERK and GSK3beta activities. Breast Cancer Research. 21 (1), 6 (2019).
- Northcott, J. M., Dean, I. S., Mouw, J. K., Weaver, V. M. Feeling stress: The mechanics of cancer progression and aggression. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 6, 17 (2018).
- Onwudiwe, K., Najera, J., Siri, S., Datta, M. Do tumor mechanical stresses promote cancer immune escape. Cells. 11 (23), 3840 (2022).
- Heldin, C. H., Rubin, K., Pietras, K., Ostman, A. High interstitial fluid pressure - an obstacle in cancer therapy. Nature Reviews. Cancer. 4 (10), 806-813 (2004).
- Krog, B. L., Henry, M. D. Biomechanics of the circulating tumor cell microenvironment. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 1092, 209-233 (2018).
- Moose, D. L., et al. Cancer cells resist mechanical destruction in circulation via RhoA/actomyosin-dependent mechano-adaptation. Cell Reports. 30 (11), 3864-3874 (2020).
- Mao, B. H., Nguyen Thi, K. M., Tang, M. J., Kamm, R. D., Tu, T. Y. The interface stiffness and topographic feature dictate interfacial invasiveness of cancer spheroids. Biofabrication. 15 (1), (2023).
- Kashani, A. S., Packirisamy, M. Cancer cells optimize elasticity for efficient migration. Royal Society Open Science. 7 (10), 200747 (2020).
- Riehl, B. D., Kim, E., Bouzid, T., Lim, J. Y. The role of microenvironmental cues and mechanical loading milieus in breast cancer cell progression and metastasis. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 8, 608526 (2021).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved