このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
ヒト筋肉間脂肪組織からの核の単離と下流の単一核RNAシーケンシング
要約
筋肉間脂肪組織(IMAT)の生物学は、ヒト組織のアクセス性が限られているため、ほとんど未踏です。ここでは、このユニークな脂肪貯蔵庫の細胞組成を特定するための単一核RNAシーケンシングのための凍結ヒトIMATの核単離とライブラリ調製のための詳細なプロトコルを紹介します。
要約
筋肉間脂肪組織(IMAT)は、筋繊維の間に位置する比較的研究されていない脂肪貯蔵庫です。IMAT含有量は、年齢とBMIとともに増加し、代謝性疾患および筋肉変性疾患に関連しています。しかし、IMATの生物学的特性と周囲の筋線維との相互作用についての理解は著しく不足しています。近年、シングルセルおよび核RNAシーケンシングにより、いくつかのヒト組織の細胞タイプ特異的なアトラスが得られました。しかし、ヒトIMATの細胞組成は、ヒトの生検収集からのアクセス可能性に固有の課題のために、ほとんど調査されていないままです。ヒトIMATは、採取される組織の量が限られていることに加え、骨格筋組織や筋膜に近いため、処理が複雑になります。脂肪細胞の脂質を多く含む性質により、脂肪細胞は単一細胞の単離と互換性がありません。したがって、単一核RNAシーケンシングは、単一細胞分解能で高次元トランスクリプトミクスを得るのに最適であり、IMATの正確な細胞組成を含むこのデポの生物学を明らかにする可能性を提供します。ここでは、単一核RNAシーケンシングのための凍結ヒトIMATの核単離とライブラリ調製のための詳細なプロトコルを紹介します。このプロトコルでは、液滴ベースのアプローチを使用して数千の核をプロファイリングできるため、希少で存在量が少ない細胞タイプを検出する能力が得られます。
概要
筋肉間脂肪組織(IMAT)は、筋線維1の間および周囲に存在する異所性脂肪貯蔵庫です。Goodpasterらによる最近のレビューで詳細に説明されているように、IMATは、高解像度のコンピュータ断層撮影法(CT)および磁気共鳴画像法(MRI)(図1A、B)を使用して検出でき、全身の筋線維の周囲および内部に見られます1。IMATの量は個人によって大きく異なり、BMI、年齢、性別、人種、座りがちな状況に影響されます2,3,4。さらに、IMAT沈着は、筋肉の変性5に関連する病的状態によく見られ、多くの研究で、肥満、2型糖尿病、メタボリックシンドローム、およびインスリン抵抗性6,7,8,9の個人におけるIMAT量の増加が記録されています。それにもかかわらず、IMATの細胞的および生物学的特性は解明され始めたばかりです。アクセス性が限られていること、IMATの位置と内容物が全身に異なることが、このユニークな脂肪貯蔵所2からのサンプル収集を困難にしています。さらに、サンプルは収集時に骨格筋(SM)で容易に「汚染」されるため、異なる組織からの生物学的寄与の分離を解読するのが困難になります(図1C)。そのため、過去10年間で大きな注目を集めている一核RNAシーケンシング(snRNA-seq)は、IMATおよびSM由来の遺伝子発現パターンをシングルセルの分解能で分離するための理想的な方法論として機能します。さらに、核の単離は、脂質を多く含む脂肪細胞が大きいため、脂肪組織に特に有用であり、細胞の完全性を損なうことなく単一細胞懸濁液に解離することは不可能です。最後に、この技術は、IMAT特異的脂肪細胞の新規マーカーを発見し、異なる前駆細胞集団の組成と存在を明らかにするだけでなく、病理学的および正常な状態での細胞組成の変動を研究する可能性を秘めています。
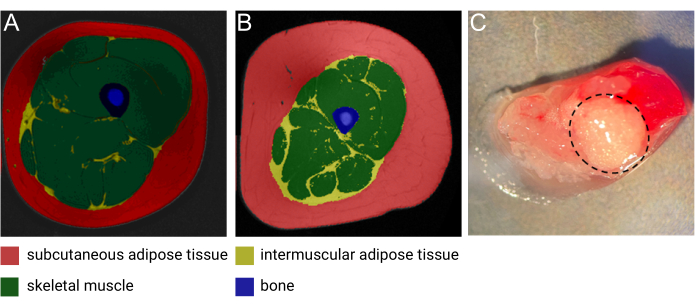
図1:IMATの画像。 (A)中年の痩せた女性と(B)肥満の中年男性からのIMATの代表的な磁気共鳴(MRI)画像。赤:皮下脂肪組織、黄:筋肉間脂肪組織、緑:骨格筋、青:骨。画像提供:Heather Cornnell氏、AdventHealth Translational Research Institute。(C)IMATを使用した新鮮な組織サンプル(黒の破線で囲まれています)。画像提供:AdventHealth Translational Research Institute の Meghan Hopf 氏とコロラド大学の Bryan Bergman 氏。この図は、Goodpaster et al.1 の許可を得て変更されています。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
豚、鶏、牛の肉の霜降り(特にIMAT)をシングルセル(sc)とsnRNA-seq10を用いて調査した畜産業界から多くの研究が発表されています。これらの研究により、脂肪細胞のいくつかの亜集団とIMATの潜在的な前駆細胞のマーカーが特定されました11,12,13;しかし、これらの細胞組成物がヒトIMATに翻訳されるかどうかは不明です。私たちの知る限り、変形性股関節症の男性患者から得られた、脂肪浸潤を伴うヒト筋肉の細胞の不均一性をsnRNA-seq14を使用して調べた研究は1つだけです。研究者らは、小さな脂肪細胞集団といくつかの線維脂肪形成前駆細胞(FAP)亜集団を報告しました 筋核14の大規模な集団内。私たちの研究は、snRNA-seqを使用して、ヒトの筋肉から手動で解剖したIMATの細胞組成を直接調べる方法を開発した最初の研究です。
重要なことは、snRNA-seqのプロトコールは、利用可能な組織の量と特定の組織の物理的特性によって最適な処理ステップが決まるため、研究対象の特定の組織に合わせてカスタマイズする必要があるということです。IMATの組織収量は通常小さく、超音波ガイド下生検を行う場合でも、50 mgを超えないことがよくあります。したがって、この希少な組織の適切な処理が不可欠です。このプロトコルは、ヒトIMATを研究する研究者にとって貴重なリソースとなると考えています。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
プロトコル
このプロトコルに使用されたサンプルは、Western IRB-Copernicus Group(WCG)の治験審査委員会によって承認され、ヘルシンキ宣言に従って実施されたStudy of Muscle Mobility, and Aging(SOMMA)15の一部でした。参加者は、研究への参加について書面によるインフォームドコンセントを提供しました。
注:このプロトコルは、ナノウェルベースのプラットフォーム16上で100mgのヒト腹部皮下脂肪組織を使用した以前のプロトコルから適応されています。現在のプロトコールは、50 mgのヒトIMATおよび液滴ベースのプラットフォームを使用したライブラリ調製に最適化されています。非ヒトIMATまたは他の脂肪デポーからの核単離のためのこのプロトコルのさらなる最適化が必要となる場合があります。
1. バッファーと試薬の調製(表1、表2)
注:実験当日にバッファーを新たに調製し、再利用しないでください。
- 遠心分離機を4°Cに予冷します。
- 均質化バッファーと核分離培地を調製します。
- 氷のバケツ2つを用意し、2 x 15 mLコニカルチューブを予冷します。
- ホモジナイズバッファー(HB)用のすべての試薬を、 表1に記載されている順序で15 mLのコニカルチューブに混合します。氷の上を保ってください。ボルテックスで混ぜます。
- 核単離培地(NIM)用のすべての試薬を、 表2の順序付きリストにある15 mLのコニカルチューブに混合します。氷の上を保ってください。ボルテックスで混ぜます。
- 100 μL の Triton X-100 を 900 μL のヌクレアーゼフリー水に加えて、10% Triton-X を調製します。適切な混合を確保するための渦巻き。室温(RT)で保管してください。
| 試薬 | 容量 (μL) | 最終濃度(mM) | |
| 1倍 | 2倍 | ||
| 1 M MgCl2 | 10 | 20 | 5 |
| 1 M トリスバッファー、pH 8.0 | 20 | 40 | 10 |
| 2 M KCl | 25 | 50 | 25 |
| 1.5 Mショ糖(-4°C) | 334 | 668 | 250 |
| 1mM DTT | 2 | 4 | 0.001 (~1 μM) |
| 100xプロテアーゼ阻害剤 | 20 | 40 | 1倍 |
| スーパーアシン 20 U/μL | 40 | 80 | 0.4 U/μL |
| ヌクレアーゼフリー水 | 1549 | 3098 | - |
| 総ボリューム | 2000 | 4000 | - |
表1:均質化バッファー(HB)。 氷の上を保ってください。ボルテックスで混ぜます。
| 試薬 | 容量 (μL) | 最終濃度(mM) | |
| 1倍 | 2倍 | ||
| EDTAの | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.1 |
| リボロックRNAse阻害剤(40U/μL) | 40 | 80 | 0.8 U/μL |
| 1%BSA-PBS(-/-) | 1959.6 | 3919.2 | - |
| 総ボリューム | 2000 | 4000 | - |
表2:核分離培地(NIM)。 氷の上を保ってください。ボルテックスで混ぜます。
2. 凍結組織の粉砕(図2A)
- 均質化のためにワークステーションをセットアップします。
- キャニスターに液体窒素(LN2)を入れます。
注意: LN 2で作業するときは、 常にゴーグルとクライオグローブを着用してください。 - 自動ダンサー用に、2x乳鉢、1x乳棒、1xマイクロスコップヘラ、1xガラスドンス、および1xステンレス鋼乳棒を入手します。
- 自動ダンサーを設定します。
- ビーカーに氷を入れ、グラスダンスを予冷します。
- キャニスターに液体窒素(LN2)を入れます。
- 2つの乳鉢(乳棒とへらを含む)にLN2 を充填して、器具を冷やします。LN2 を蒸発させて繰り返します。
- 機器が冷えている間に、グラスドンスにHB1mLを追加します。.
- 最後にもう一度両方のモルタルにLN2 を充填し、50 mgのIMATサンプルをモルタルの1つに注ぎます。
- 乳棒を使用してIMATをティッシュピースにそっと押し付けて粉砕し、細かく砕きます。すべてのピースが粉砕されていることを確認してください。
- LN2は、組織を粉砕しながらゆっくりと蒸発します。組織が適切に粉砕され、LN2のモルタルの1/4〜1/2がまだ残っている場合は、モルタルをモルタルのリップに向かって傾けて、粉砕された組織をリップで収集します。LN2を完全に蒸発させます。
- 最後のLN2 が蒸発した直後に、粉砕した組織を1mLのHBが入ったガラス製菓にすくい取ります。
3. 粉砕組織の均質化
- 自動ダウンサーを使用して粉砕された組織を均質化します。ガラスをステンレス製の乳棒を上下に動かし、順方向に10ストローク、続いて逆方向に10ストロークします。
- 均質化後の溶液が濁り、目に見える組織片が含まれていないことを確認してください。淡いピンク色は、筋肉組織による汚染のためにしばしば予想されます。
- ホモジネートを氷上で予冷した1.7 mL低結合チューブに移します。
- 400μLのHBを使用してダウンスをすすぎ、すべての材料が転写されていることを確認し、チューブに追加します。
注:一度に2つのサンプルを処理できます。これを行うには、HB と NIM の量を 2 倍にします。1つの組織サンプルを粉砕して均質化し、その直後に2番目の組織サンプルを粉砕して均質化することで、単離とクリーンアップのステップを並行して実行できるようにします。
4. 原子核の単離とクリーンアップ(図2B)
- ホモジネートに14 μLのTriton-X(10%)を加えて、0.1%濃度にします。
- チューブを氷の上と暗闇に10〜15分間置き、3分ごとにボルテックスします。
- 100 μmセルストレーナー1個と40 μmセルストレーナー1個(サンプルあたり)を、それぞれ100 μLのRT DPBSで50 mLコニカルチューブにプレウェットします。
- 100 μmのセルストレーナーでホモジネートをろ過します。
- 1.7 mLチューブを400 μLのHBですすぎ、100 μmセルストレーナーでろ過します。
- 次に、40 μmセルストレーナーで溶液をろ過します。
- 各チューブ内の~900 μLに対応する2本の予冷済み1.7 mL低結合チューブに同量の溶液を移します。
- チューブを2700 x g 、4°Cで10分間遠心分離します。 遠心分離後に小さなペレットが見える必要があります。
- 上部の脂質層と残りの上清を取り出して廃棄し、最初のチューブから~50 μLの溶液を残します。
- 2番目のチューブについても繰り返します。
- 20倍に静かにピペッティングしてペレットを最初のチューブに完全に再懸濁し、新しい1.7 mL低結合チューブに移します。バブルの作成は避けてください。
- 2番目のチューブについてこの手順を繰り返し、再懸濁溶液を同じチューブに移します。
- NIM500μLを加え、ピペッティングで混合します。
- バランスを1000 x g にしてチューブを4°Cで10分間遠心分離します。
- 上清を取り出し、~50 μL を残し、ペレットが再懸濁されるまでゆっくりと上下にピペットで動かします。オプションで、チューブの側面に脂質が残っている場合は、再懸濁したペレットを新しいきれいなチューブに移します。
- NIM200μLを加え、ピペッティングで混合します。
5. 核の染色とカウント(図2C および 図3)
注:カウントを容易にするために、明視野とDAPIチャネルの調整がカウントに大きく影響する可能性があるため、自動セルカウンターで「核カウント」プロトコルを設定します。破片ではなく原子核のみが捕捉されるようにチャネルを調整します。明視野チャンネルが、DAPI染色も持っている「オブジェクト」のみをマークするようにしてください。
- 生細胞染色液を1滴加え、氷の上、暗所に15分間放置します。
- 30 μmセルストレーナーで溶液をろ過します。
- ピペッティングで核溶液を混合し、10 μLの溶液をセルカウンティングチャンバースライドに加えます。
- 自動セルカウンターを使用して核をカウントします。
注:最適濃度は、1.0 x 106/mLに対応する1000 nuclei/μLです。- 核の塊が存在しないことを確認すると、チップを詰まらせて単一核の液滴を生成する可能性があります(図3)。
- 核濃度が十分に高くない場合は、溶液を1000 x g で4°Cで10分間スピンダウンしてペレットを取得し、上清を除去し、少量で再懸濁します。
- 溶液中の破片の程度が高い場合は、核溶液をより大容量のNIM(すなわち、1 mL)に再懸濁し、30 μmの細胞ストレーナーで再度ろ過します。次に、1000 x g で4°Cで10分間スピンダウンし、核の濃度に対して適切な量で再懸濁します。
- 核濃度を取得したら、ライブラリ調製の最初のステップに直接進みます。
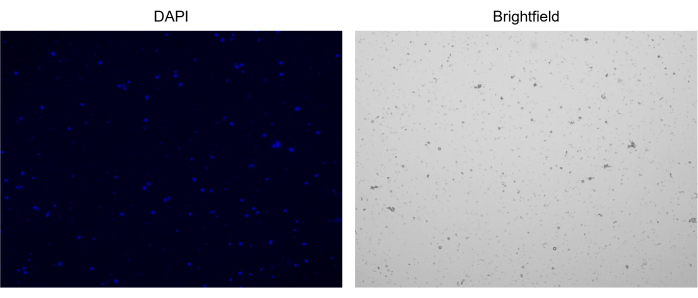
図3:単離された核の染色。 NucBlue/DAPIで染色した核のセルカウンターからの画像(左の画像)と対応する明視野の画像(右の画像)。微量の破片の存在は、明視野画像で明らかです。ここで使用する自動セルカウンターには、スケールバーを含めるオプションはありません。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
6. ライブラリ調製およびシーケンシングパラメータ
- プロバイダーのWebページ17で入手可能な液滴ベースの単一核アプローチを使用したライブラリ調製のための詳細なプロトコルを参照してください。
- 目標核回収率10,000を目標にしてください。ただし、高レベルの破片や壊れやすい核を持つサンプルの場合、回収される核の数は少なくなると予想されます。
- ステップ2.3の後、サンプルを4°Cで最大72時間保存します。ライブラリ調製プロトコルでは、より多くのサンプルの処理を並行して組み合わせます。これを行うには、ステップ 2.3 までの 2 つのサンプルを 2 日間連続して処理し、3 日目にはステップ 3 の 4 つのサンプルを一緒に処理し、ライブラリ調製プロトコルで進めます。
- シーケンシングパラメータ:核あたり50,000ペアエンドリードを目指すシーケンシングプラットフォーム上でのシーケンシング。
注:このプロトコルで示されたデータは、NovaSeq 6000プラットフォームでシーケンシングされ、核あたり50,000のペアエンドリードを目指しました。
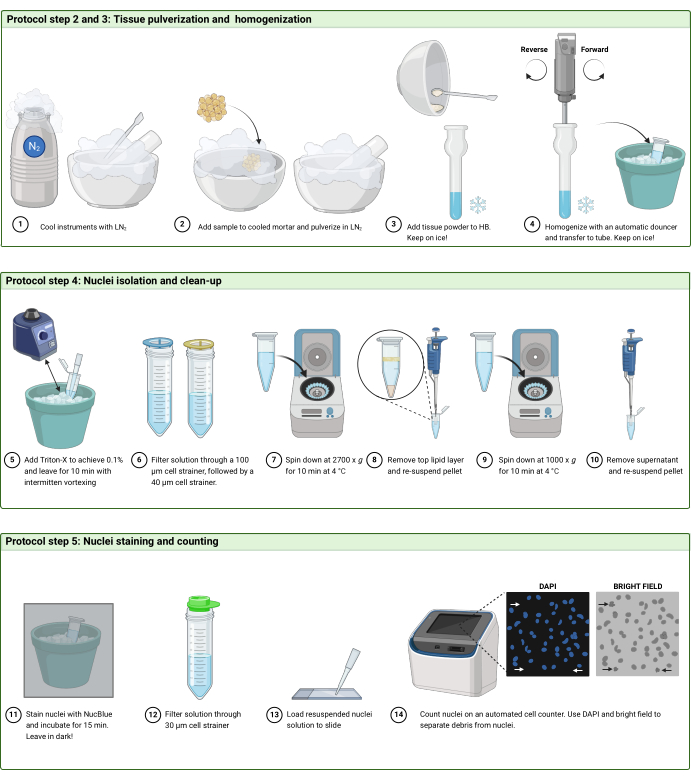
図2:プロトコルワークフロー。 プロトコルの(A)ステップ2および3、(B)ステップ4、および(C)ステップ5のワークフローの概略図。フィギュアは BioRender.com で作成しました。 この図の拡大版を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
7. データ処理と分析
注:このプロトコルでは、結果として得られるシーケンシングデータの処理に使用される推奨ソフトウェアとRパッケージの一部が、初期前処理後のステップに焦点を当てて簡単に紹介されています(表3)。この研究では、一般的な品質管理(QC)メトリクスと、 図4の均一多様体近似および投影(UMAP)の例を提供します。ただし、バイオインフォマティクス分析の詳細な説明は、このプロトコルの範囲外です。したがって、読者はHeumosらによるシングルセル解析のベストプラクティスに関する最近のレビューを参照することができます18。
- シーケンシングデータの前処理
- 読み取った単一核をヒト参照ゲノムGRCh38にマッピングします。
- イントロンリードをカウントに含めます。
- Seurat Rパッケージ19を使用してデータのQCとフィルタリングを実行します。
- 細胞複雑性スコアは、検出された遺伝子のlog(10)数を検出されたlog(10)リード数で割ることにより、細胞複雑性スコアを計算します。
- ヒストグラムまたはバイオリンプロットを使用して、核ごとに検出された遺伝子の数、ミトコンドリアの読み取り率、細胞の複雑さのスコアなど、最も重要なQC指標をプロットします。
- 核あたりの遺伝子数が200未満または10,000個以上、ミトコンドリアの読み取りが10%を超え、複雑さのスコアが0.8未満の核をフィルタリングします。
- データを正規化し、次元削減を実行します。
- Seurat の SCTransform 関数を使用して、2000 個の変数機能を使用してデータを正規化します。
- Seurat R パッケージの RunPCA、FindNeighbors、FindClusters、RunUMAP の関数を使用してデータをクラスター化します。
- UMAP をプロットして、データのクラスタリングを可視化します。
- DoubletFinder R パッケージ20 を使用して予測されたダブレットを除外し、データを再クラスタリングします。
- 組織内に存在すると予想される細胞タイプの既知の遺伝子マーカーを使用してクラスターにアノテーションを付けるか(教師ありアプローチ)、またはクラスター間で発現差のある上位5つの遺伝子に基づいて(教師なしアプローチ)。
- decontX21を使用して、アンビエントRNAの汚染度を測定し、アンビエントRNAの遺伝子発現マトリックスを調整します。
- 生の遺伝子マトリックスをバックグラウンドとして含めます。
- Seurat オブジェクトを保存して、後でデータを探索することができます。
注: QC およびクラスタリング分析のコードは、 補足ファイル 1 にあります。
| データワークフローで使用されるソフトウェア/Rパッケージ | 代替ソフトウェア/パッケージ | 処理ステップ |
| セルレンジャー | スターソロ、カリスト | トリミング、整列、マッピング |
| スーラ | SingleCellExperiment、セルレンジャー | QC、分析、データ探索 |
| ダブレットファインダー | scds、scdblFinder、スクラブレット | ダブレット検出 |
| デコントX | SoupX、セルベンダー | アンビエントRNA調整 |
表3:データワークフロー用のソフトウェア/ツール。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
結果
このワークフローは、凍結ヒトIMATサンプルの処理をガイドして、単一核の分解能で遺伝子発現プロファイルを取得し、細胞タイプの同定を可能にするように設計されています。ここでは、SOMMA試験の参加者から代表的なIMATサンプルを1つ紹介します。
snRNA-seqデータの解析の最初のステップは、データの品質を評価して、データセットから削除する必要がある可能性のある...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
ディスカッション
IMATとの連携には、いくつかの固有の課題があります。その限られたアクセス性に加えて、サンプル材料の収量は非常に少ないことが多く、骨格筋の「汚染」を避けることはほとんど不可能です。最高品質のサンプルを得るためには、生検針を挿入する際に筋筋膜を貫通し(皮下脂肪組織を採取しないようにするため)、採取後すぐに顕微鏡でサンプルを解剖してできるだけ多くの筋肉組織を切?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
開示事項
著者は何も開示していません。
謝辞
著者らは、コロラド大学のBryan Bergman博士が、MoTrIMAT研究(R01AG077956)の図1CのIMAT生検の画像を提供してくれたことに感謝の意を表します。私たちは、代表的な結果セクションにデータが示されているIMATサンプルを提供した筋肉、可動性、老化の研究に感謝しています。国立老化研究所(NIA)は、筋肉、可動性、老化の研究(SOMMA;R01AG059416)およびその補助的な研究SOMMA AT(R01AG066474)およびSOMMA Knee OA(R01AG070647)。研究インフラストラクチャのサポートは、ピッツバーグ大学(P30AG024827)とウェイクフォレスト大学(P30AG021332)のNIAクロード・D・ペッパー高齢者アメリカ独立センターと、ウェイクフォレスト大学の国立トランスレーショナルサイエンス推進センター(UL1 0TR001420)が資金提供した臨床およびトランスレーショナルサイエンス研究所によって部分的に資金提供されました。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.2 µm corning syringe filters | Millipore Sigma | CLS431229 | |
| 1.7 mL DNA LoBind tubes | Eppendorf | 22431021 | low-bind tubes |
| 10% Tween 20 | Bio-Rad | 1662404 | |
| 100x protease inhibitor | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 78437 | |
| 10X Magnetic Separator | 10X Genomics | 230003 | |
| 10X Vortex Adapter | 10X Genomics | 330002 | |
| 15 mL canonical tubes | Sarstedt | 6,25,54,502 | |
| 2100 Bioanalyzer | Agilent | G2939BA | |
| 50 mL conical tubes | Sarstedt | 6,25,47,254 | |
| CellRanger | Genomics | N/A | |
| Chromium iX accesory kit | 10X Genomics | PN1000323 | |
| Chromium iX Controller | 10X Genomics | PN1000326 | |
| Chromium Next GEM Chip G Single Cell Kit | 10X Genomics | PN1000127 | |
| Chromium Next GEM Single Cell 3' Gel Bead Kit v3.1 | 10X Genomics | PN1000129 | |
| Chromium Next GEM Single Cell GEM Kit v3.1 | 10X Genomics | PN1000130 | |
| Countess 3 Automated Cell Counter | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AMQAX2000 | Automated cell counter |
| Countess cell counting chamber slides | Thermo Fisher Scientific | C10228 | |
| DoubletFinder | R | N/A | |
| DPBS (no calcium, no magnesium) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 14190144 | |
| DTT | Thermo Fisher Scientific | R0861 | |
| Dual Index Kit TT Set A, 96 rxns | 10X Genomics | PN1000215 | |
| Dynabeads MyOne SILANE | 10X Genomics | PN2000048 | |
| Falcon 100 µm Cell strainer | Corning Life Science | 352360 | |
| Falcon 40 µm Cell strainer | Corning Life Science | 352340 | |
| Glycerin (glycerol), 50% (v/v) Aqueous Solution | Ricca Chemical Company | 3290-32 | |
| KCL | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AM9640G | |
| Library Construction Kit v3.1 | 10X Genomics | PN1000196 | |
| MACS SmartStrainers (30µm) | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-098-458 | |
| Mastercycler Nexus Gradient Thermal cycler | Eppendorf | 6331000017 | |
| MgCl2 | Ambion | AM9530G | |
| Mortar and pestel | Health care logistics | 14075 | |
| NucBlue Live Ready Probes Reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | R37605 | |
| Nuclease Free Water (not DEPC treated) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AM9930 | |
| Probumin Bovine Serum Albumin Fatty Acid Free, Powder | Sigma-Aldrich | 820024 | |
| Qiagen Buffer EB | Qiagen | 19086 | |
| Ribolock RNAse inhibitor | Thermo Fisher Scientific | EO0382 | |
| Seurat | R | N/A | |
| Sucrose | Sigma-Aldrich | S0389 | |
| SUPERasin 20 U/µL | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AM2695 | |
| ThermoMixer C | Eppendorf | 5382000015 | |
| Tissue homogenizer | Glass-Col | 099C K54 | |
| Tris buffer pH 8.0 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AM9855G | |
| Triton X-100 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AC327372500 | |
| UltraPure 0.5M EDTA pH 8.0 | Gibco | 15575020 |
参考文献
- Goodpaster, B. H., Bergman, B. C., Brennan, A. M., Sparks, L. M. Intermuscular adipose tissue in metabolic disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 19 (5), 285-298 (2023).
- Sparks, L. M., Goodpaster, B. H., Bergman, B. C. The metabolic significance of intermuscular adipose tissue: Is IMAT a friend or a foe to metabolic health. Diabetes. 70 (11), 2457-2467 (2021).
- Gallagher, D., et al. Adipose tissue in muscle: A novel depot similar in size to visceral adipose tissue. Am J Clin Nutr. 81 (4), 903-910 (2005).
- Manini, T. M., et al. Reduced physical activity increases intermuscular adipose tissue in healthy young adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 85 (2), 377-384 (2007).
- Addison, O., Marcus, R. L., LaStayo, P. C., Ryan, A. S. Intermuscular fat: A review of the consequences and causes. Int J Endocrinol. 2014, 309570(2014).
- Goodpaster, B. H., et al. Obesity, regional body fat distribution, and the metabolic syndrome in older men and women. Arch Intern Med. 165 (7), 777-783 (2005).
- Goodpaster, B. H., Thaete, F. L., Kelley, D. E. Thigh adipose tissue distribution is associated with insulin resistance in obesity and in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr. 71 (4), 885-892 (2000).
- Goodpaster, B. H., et al. Association between regional adipose tissue distribution and both type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in elderly men. Diabetes Care. 26 (2), 372-379 (2003).
- Sachs, S., et al. Intermuscular adipose tissue directly modulates skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 316 (5), E866-E879 (2019).
- Ford, H., Liu, Q., Fu, X., Strieder-Barboza, C. White adipose tissue heterogeneity in the single-cell era: From mice and humans to cattle. Biology (Basel). 12 (10), 1289(2023).
- Wang, L., et al. Single-nucleus and bulk RNA sequencing reveal cellular and transcriptional mechanisms underlying lipid dynamics in high marbled pork. NPJ Sci Food. 7 (1), 23(2023).
- Li, J., et al. Identification of diverse cell populations in skeletal muscles and biomarkers for intramuscular fat of chicken by single-cell RNA sequencing. BMC Genomics. 21 (1), 752(2020).
- Lyu, P., Qi, Y., Tu, Z. J., Jiang, H. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals heterogeneity of cultured bovine satellite cells. Front Genet. 12, 742077(2021).
- Fitzgerald, G., et al. MME+ fibro-adipogenic progenitors are the dominant adipogenic population during fatty infiltration in human skeletal muscle. Commun Biol. 6 (1), 111(2023).
- Cummings, S. R., et al. The study of muscle, mobility and aging (SOMMA): A unique cohort study about the cellular biology of aging and age-related loss of mobility. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 78 (11), 2083-2093 (2023).
- Whytock, K. L., et al. Isolation of nuclei from frozen human subcutaneous adipose tissue for full-length single-nuclei transcriptional profiling. STAR Protoc. 4 (1), 102054(2023).
- 10x Genomics. Chromium Single Cell 3' Reagent Kits User Guide (v3.1 Chemistry Dual Index), Document Number CG000315 RevE. , Available from: https://cdn.10xgenomics.com/image/upload/v1668017706/support-documents/CG000315_ChromiumNextGEMSingleCell3-_GeneExpression_v3.1_DualIndex__RevE.pdf (2022).
- Heumos, L., et al. Best practices for single-cell analysis across modalities. Nat Rev Genet. 24 (1), 550-572 (2023).
- Hao, Y., et al. Dictionary learning for integrative, multimodal and scalable single-cell analysis. Nat Biotechnol. 42 (2), 293-304 (2023).
- McGinnis, C. S., Murrow, L. M., Gartner, Z. J. DoubletFinder: Doublet detection in single-cell RNA sequencing data using artificial nearest neighbors. Cell Syst. 8 (4), 329-337 (2019).
- Yang, S., et al. Decontamination of ambient RNA in single-cell RNA-seq with DecontX. Genome Biol. 21 (2), 57(2020).
- Common considerations for quality control filters for single cell RNA-seq data. 10X Genomics. , Available from: https://www.10xgenomics.com/analysis-guides/common-considerations-for-quality-control-filters-for-single-cell-rna-seq-data (2022).
- Luecken, M. D., Theis, F. J. Current best practices in single-cell RNA-seq analysis: a tutorial. Mol Syst Biol. 15 (6), e8746(2019).
- Emont, M. P., et al. A single-cell atlas of human and mouse white adipose tissue. Nature. 603 (7903), 926-933 (2022).
- Hildreth, A. D., et al. Single-cell sequencing of human white adipose tissue identifies new cell states in health and obesity. Nat Immunol. 22 (5), 639-653 (2021).
- Whytock, K. L., et al. Single cell full-length transcriptome of human subcutaneous adipose tissue reveals unique and heterogeneous cell populations. iScience. 25 (8), 104772(2022).
- Probst, V., et al. Benchmarking full-length transcript single cell mRNA sequencing protocols. BMC Genomics. 23 (1), 860(2022).
- CG000148 Rev A Technical Note - Resolving cell types as a function of read depth and cell number. Technical note. 10X Genomics. , Available from: https://assets.ctfassets.net/an68im79xiti/6gDArDPBTOg4IIkYEO2Sis/803be2286bb a5ca67f353e6baf68d276/CG000148_10x_Technical _Note_Resolving_Cell_Types_as_Function_of_ Read_Depth_Cell_Number_RevA.pdf (2018).
- Gupta, A., et al. Characterization of transcript enrichment and detection bias in single-nucleus RNA-seq for mapping of distinct human adipocyte lineages. Genome Res. 32 (2), 242-257 (2022).
- Bakken, T. E., et al. Single-nucleus and single-cell transcriptomes compared in matched cortical cell types. PLoS One. 13 (12), e0209648(2018).
- Wu, H., Kirita, Y., Donnelly, E. L., Humphreys, B. D. Advantages of single-nucleus over single-cell RNA sequencing of adult kidney: Rare cell types and novel cell states revealed in fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 30 (1), 23-32 (2019).
- Kim, N., Kang, H., Jo, A., Yoo, S. -A., Lee, H. -O. Perspectives on single-nucleus RNA sequencing in different cell types and tissues. J Pathol Transl Med. 57 (1), 52-59 (2023).
- Avila Cobos, F., Alquicira-Hernandez, J., Powell, J. E., Mestdagh, P., De Preter, K. Benchmarking of cell type deconvolution pipelines for transcriptomics data. Nat Commun. 11 (1), 5650(2020).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved