Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
In Vitro Chemical Mapping of G-Quadruplex DNA Structures by Bis-3-Chloropiperidines
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
Bis-3-chloropiperidines (B-CePs) are useful chemical probes to identify and characterize G-quadruplex structures in DNA templates in vitro. This protocol details the procedure to perform probing reactions with B-CePs and to resolve reaction products by high-resolution polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Streszczenie
G-quadruplexes (G4s) are biologically relevant, non-canonical DNA structures that play an important role in gene expression and diseases, representing significant therapeutic targets. Accessible methods are required for the in vitro characterization of DNA within potential G-quadruplex-forming sequences (PQSs). B-CePs are a class of alkylating agents that have proven to be useful chemical probes for investigation of the higher-order structure of nucleic acids. This paper describes a new chemical mapping assay exploiting the specific reactivity of B-CePs with the N7 of guanines, followed by direct strand cleavage at the alkylated Gs.
Namely, to distinguish G4 folds from unfolded DNA forms, we use B-CeP 1 to probe the thrombin-binding aptamer (TBA), a 15-mer DNA able to assume the G4 arrangement. Reaction of B-CeP-responding guanines with B-CeP 1 yields products that can be resolved by high-resolution polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) at a single-nucleotide level by locating individual alkylation adducts and DNA strand cleavage at the alkylated guanines. Mapping using B-CePs is a simple and powerful tool for the in vitro characterization of G-quadruplex-forming DNA sequences, enabling the precise location of guanines involved in the formation of G-tetrads.
Wprowadzenie
In addition to the typical Watson-Crick double helix, nucleic acids can adopt various secondary structures, such as the alternative G-quadruplex (G4) form, due to their guanine-rich sequences. G4 structure is based on the formation of planar tetramers, called G-tetrads, in which four guanines interact through Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds. G-tetrads are stacked and further stabilized by monovalent cations that are coordinated in the center of the guanine core (Figure 1)1.
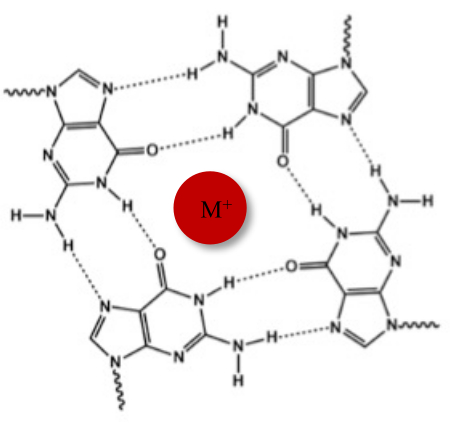
Figure 1: Schematic representation of a G-quadruplex structure. (A) Schematic representation of a G-tetrad. The planar array is stabilized by Hoogsteen base-pairing and by a central cation (M+). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Sequences with four or more runs of at least two consecutive guanine nucleotides are potential G-quadruplex-forming sequences (PQSs) that can fold in G-quadruplex structures. PQSs are located in many different cellular contexts, such as at telomeres, gene promoters, ribosomal DNA, and recombination sites, and are involved in the regulation of many biological processes2. Hence, the identification and experimental validation of G4s in the human genome, which is currently performed primarily through computational tools, is a biologically relevant issue3. In order to support computational predictions or detect unpredicted G4 structures, an accessible method based on chemical mapping to identify the G4 formation in a DNA template is shown here, enabling the precise identification of guanines forming the G-tetrad structure.
The reported chemical mapping assay exploits the different reactivity of bis-3-chloropiperidines (B-CePs) with guanines following the formation of G4 structures. Due to their high reactivity with nucleophiles4,5,6,7,8,9, B-CePs are nucleic acid-alkylating agents with the ability to react very efficiently with the N7 position of guanine nucleotides10. Alkylation is followed by depurination and strand cleavage in single- and double-stranded DNA constructs. On the contrary, guanines involved in the formation of the G-tetrads in G4 arrangements are impervious to B-CeP alkylation, as the N7 position of guanines is implicated in the Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds. This specific reactivity of B-CePs allows not only the detection of G4 structures, but also the identification of the guanines forming the tetrad(s), as they can be deduced from their relative protection from alkylation compared with guanines in single- and double-stranded DNA.
The chemical mapping protocol is reported here using B-CeP 1 (Figure 2A) as a probe for the characterization of thrombin-binding aptamer (TBA), a 15-mer DNA able to assume the G4 arrangement in the presence of potassium cations11,12. The G4 arrangement of TBA (G4-TBA) is directly compared with two controls, namely TBA in the single-stranded form (ssTBA) and TBA annealed to its complementary sequence to form the double-stranded construct (dsTBA) (Table 1). Products of probing reactions are resolved by high-resolution polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) at the single-nucleotide level by locating individual alkylation adducts and DNA strand cleavage at the alkylated guanines. Visualization on the gel is enabled by conjugation of the TBA oligonucleotide with a fluorophore at its 3'-end (Table 1). This protocol shows how to fold TBA in its different conformations (G4 and controls), and how to perform probing reactions with B-CePs followed by PAGE.
Protokół
1. Nucleic acid and chemical probe preparation
- Nucleic acids
NOTE: The oligonucleotide named "TBA" is the 15-mer DNA sequence 5'-GGT-TGG-TGT-GGT-TGG-3' labeled at the 3'-end by the fluorophore 5-carboxyfluorescein (FAM) to enable visualization on the gel. The unlabeled oligonucleotide "cTBA" is its DNA complementary sequence 5'-CCA-ACC-ACA-CCA-ACC-3'. TBA and cTBA are employed to obtain the three different structures, as shown in Table 1.- Autoclave tips and 0.5 mL tubes in order to obtain sterile disposables and avoid contamination.
- Prepare stock solutions solubilizing each oligonucleotide in ultrapure water to a final concentration of 100 µM. Determine the exact oligonucleotide concentration with a ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometer, using the extinction coefficient at 260 nm provided by the manufacturer.
NOTE: Extinction coefficients: 164,300 M-1 cm-1 and 138,600 M-1 cm-1 were used for TBA and cTBA, respectively. - Store TBA and cTBA stock solutions at -20 °C (for months in these conditions).
- Compound B-CeP 1
NOTE: The compound B-CeP 1 is synthesized as previously reported6.- Prepare the B-CeP 1 stock solution at ~10 mM. Weigh ~1 mg of the lyophilized compound using an analytical balance located in a fume hood and solubilize it in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Calculate the exact compound concentration based on the actual amount of compound and DMSO (d = 1.1 g/cm3) used.
NOTE: Handle the compound with gloves at all times (both when lyophilized and when dissolved in DMSO)13,14.
Table 1: Oligonucleotide structures used in this protocol. Please click here to download this Table.
2. Folding of nucleic acid constructs
- Preparation of buffers
- Prepare a BPE buffer solution (biphosphate-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [EDTA], 5x: 2 mM NaH2PO4, 6 mM Na2HPO4, 1 mM Na2EDTA, pH 7.4) and a solution of 500 mM KCl in ultrapure water. Filter the solutions through 0.22 µm pore size filters.
NOTE: For best results, use freshly prepared solutions. BPE buffer can be stored at 4 °C for up to 15 days.
- Prepare a BPE buffer solution (biphosphate-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [EDTA], 5x: 2 mM NaH2PO4, 6 mM Na2HPO4, 1 mM Na2EDTA, pH 7.4) and a solution of 500 mM KCl in ultrapure water. Filter the solutions through 0.22 µm pore size filters.
- Folding of G4-TBA, ssTBA, and dsTBA samples by the heat-refolding procedure
NOTE: Potassium cations are necessary to fold the G4 structure (G4-TBA). Do not add potassium cations in the folding solution of the controls ssTBA and dsTBA.- Prepare 40 µL of a 4 µM solution of G4-TBA in 1x BPE and 100 mM KCl. Denature the oligonucleotide G4-TBA solution by heating the tube to 95 °C for 5 min and slowly cool it down to room temperature (RT) to allow the TBA to fold into G-quadruplexes.
- Prepare 40 µL of a 4 µM solution of ssTBA in 1x BPE. Perform the heat-refolding procedure, as mentioned in step 2.2.1, to fold TBA in its single-stranded form.
- Prepare 40 µL of a 4 µM solution of dsTBA by mixing equimolar amounts of TBA and cTBA in 1x BPE. Perform the heat-refolding procedure as mentioned above (step 2.2.1) for TBA to anneal to its complementary sequence cTBA and form the double-stranded form of TBA.
NOTE: The final volume of each folding solution is based on the number of samples for the probing reactions, considering that 5 µL of 4 µM solution will be needed for each sample. Prepare a little excess volume of each solution to avoid pipetting errors.
3. Probing reactions
NOTE: Probing reactions must be done immediately after the heat-refolding procedure.
- When the folding solutions of G4-TBA, ssTBA, and dsTBA have cooled to RT, perform a short-spin centrifugation (7,000 × g for 5-8 s at RT) and start the probing reactions.
- Prepare 21 empty 0.5 mL autoclaved tubes. Organize them in three sets of seven tubes each in the rack for lab samples, as reported in Table 2.
NOTE: Each column set corresponds to the three different TBA folding conditions G4-TBA, ssTBA, and dsTBA. Each row corresponds to three different incubation times. Each cell within the column corresponds to the final B-CeP 1 probe concentration (Table 2). Make sure to clearly label the tubes. - Add 3 µL of ultrapure water in each tube.
- Add 5 µL of folded G4-TBA in each tube of the first set (step 3.2). Add 5 µL of folded ssTBA in each tube of the second set. Add 5 µL of folded dsTBA in each tube of the third set.
- Dilute the B-CeP 1 stock solution to 250 µM and 25 µM in ultrapure water.
NOTE: Dilutions of the B-CeP 1 chemical probe must be freshly prepared and immediately reacted with the DNA substrate to avoid competing reactions with water. - Add 2 µL of the appropriate B-CeP 1 dilution (25 µM and 250 µM) to the samples. Replace the compound with ultrapure water in the three control samples (C) for analysis of the differently folded TBAs in the absence of the compound. Incubate all the samples at 37 °C.
- After 1 h, 4 h, and 15 h of incubation, stop the reaction by placing the tubes at -20 °C until the next step.
NOTE: The samples can be stored in these conditions for a couple of days. - Dry the samples in a vacuum centrifuge.
NOTE: The dried samples can be stored at -20 °C for weeks before proceeding with the PAGE analysis.
Table 2: Samples for the probing reactions (structures, probe concentrations, and incubation time). Each column set corresponds to the three different TBA folding conditions (G4-TBA, ssTBA, and dsTBA). Each row corresponds to three different incubation times (1, 4, 15 h). Each cell within the column corresponds to the final B-CeP 1 probe concentration (5 or 50 µM). The control (C) for each set corresponds to a sample of the differently folded TBAs incubated for the longer time (15 h) in the absence of compound. Please click here to download this Table.
4. High-resolution PAGE
- Preparation of the denaturing polyacrylamide solution
NOTE: Prepare in advance 500 mL of 20% denaturing polyacrylamide gel solution. Around 80 mL of this solution will be used for each experiment. Use an amber glass bottle or cover a glass bottle with aluminum foil to store the solution at RT.
CAUTION: Polyacrylamide is neurotoxic. During all steps of gel preparation and pouring, wear gloves and a lab coat. Discard polymerized acrylamide in an appropriate box for contaminated materials.- Weigh 210 g of urea in a 1 L beaker. Add 250 mL of 40% acrylamide/bisacrylamide (19/1) solution and 50 mL of 10x TBE (890 mM Tris-HCl, 890 mM borate, 20 mM EDTA, pH 8).
- Place the beaker on a stir plate and mix the solution with a stirring rod. Cover the beaker with aluminum foil during mixing to prevent splashing and contamination.
- Mix the solution until the urea is completely dissolved and the solution is clear.
NOTE: This step can take many hours. To promote the dissolution of urea, add a small aliquot of water without going beyond the desired final volume. - Remove the stirring rod. Pour the solution in a cylinder and add water to an exact final volume of 500 mL.
- Setting up of gel apparatus
- Clean two plates (one notched and one unnotched) with 70% ethanol, let them dry, and then treat the plates with a dimethyldichlorosilane solution.
NOTE: Silanization can be skipped, although it helps the release of the gel from one of the plates when the gel sandwich is taken apart.
CAUTION: Handle the silanization solution with gloves and carry out the plate treatment with this solution in a fume hood. - Place the 0.4 mm spacers along the long edges of the longer plate, place the short plate on top of the other, and align the two plates at the bottom.
- Place multiple layers of paper tape along all the edges except for the top.
- To avoid leaks during casting, add an additional layer of tape to the bottom of the gel.
- Clip the sides of the glass sandwich with clean clamps following the supplier's instructions (different suppliers use slightly different apparatus, sandwich clamps, and gaskets).
- Clean two plates (one notched and one unnotched) with 70% ethanol, let them dry, and then treat the plates with a dimethyldichlorosilane solution.
- Pouring the gel
NOTE: Pour the gel at RT (25 °C), since polyacrylamide polymerization is temperature-sensitive.- In a beaker, pour 80 mL of the previously prepared denaturing polyacrylamide solution (step 4.1), 450 µL of a 10% m/V ammonium persulphate (APS) solution, and 45 µL of tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) immediately before use.
- Mix the solution and rapidly pour it down between the glass plates using a 50 mL syringe. Introduce the comb with the desired number of wells between the glass plates, avoiding bubbles. Add gel solution to fill the sandwich completely, if necessary. Place four clamps on the comb to press down and allow for even distribution of the wells.
- Let the gel polymerize for at least 45 min.
- Running the gel
- After the polymerization, remove all the clamps and paper tape layers. Remove the comb slowly and thoroughly rinse the wells with distilled water.
- Follow the instructions from the specific supplier to correctly place the gel sandwich in the vertical gel electrophoresis apparatus.
- Prepare TBE running buffer (1x: 89 mM Tris-HCl, 89 mM borate, 2 mM EDTA, pH 8) in deionized water and fill both the top and bottom reservoirs with the buffer.
- Warm up the plates by performing a pre-run of the gel electrophoresis for at least 30 min at 50 W.
- Prepare denaturing gel loading buffer (DGLB: 1 M Tris-HCl, 80% formamide, 50% glycerol, 0.05% bromophenol blue) in ultrapure water.
NOTE: GLB helps to track the oligonucleotide samples' movement into the gel system and allows to load the samples into the gel's wells. The presence of the denaturing agent formamide allows DNA species to separate according to size, even in a non-denaturing PAGE. - Resuspend the dried samples (samples from step 3.8) in 5 µL of DGLB.
- Before loading the samples, clean the wells using a small syringe and the TBE buffer in the upper buffer chamber to remove the urea from the wells.
NOTE: Repeat this step several times to accurately clean the wells, thus avoiding bands difficult to be interpreted. - Load the samples into the clean wells and make a note of the order of loading.
- Run the gel electrophoresis for 2 h at 50 W, or at least until the bromophenol blue dye has run 2/3 down the gel.
- Imaging the gel
- After electrophoresis, turn off the power supply, remove the glass sandwich, and clean the glasses.
- Detect the fluorescence of the FAM-labeled oligonucleotide bands by scanning using a gel imager.
Wyniki
Figure 2 shows a representative result of a chemical mapping assay performed, as described in the protocol with B-CeP 1 on the TBA oligonucleotide folded in three different structures. The G-quadruplex arrangement of TBA (G4-TBA) was obtained by folding the oligonucleotide in BPE and in the presence of the K+ cation, whereas the single-stranded form of the same TBA sequence (ssTBA) was folded in the absence of potassium. The double-stranded construct (dsTBA) was prepared by a...
Dyskusje
G-quadruplexes are nucleic acid secondary structures that typically fold within guanine-rich DNA sequences, and are significant research targets because of their association with genetic control and diseases. Chemical mapping by B-CePs is a useful protocol for the characterization of DNA G4s, which can be used to identify the guanine bases involved in the formation of G-tetrads under physiological salt conditions.
The chemical probe used in this protocol is B-CeP 1 (Figure...
Ujawnienia
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Podziękowania
This work was supported by the Department of Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Sciences, University of Padova (PRIDJ-BIRD2019).
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acrylamide/bis-acrylamide solution 40% | Applichem | A3658 | R45-46-20/21-25-36/38-43-48/23/ 24/25-62 |
| Ammonium per-sulfate (APS) | Sigma Aldrich | A7460 | |
| Analytical balance | Mettler Toledo | ||
| Autoclave | pbi international | ||
| Boric acid | Sigma Aldrich | B0252 | |
| Bromophenol blue Brilliant blue R | Sigma Aldrich | B0149 | |
| di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate | Fluka | 71649 | |
| DMSO | Sigma Aldrich | 276855 | |
| DNA oligonucleotides | Integrated DNA Technologies | synthesis of custom sequences | |
| EDTA disodium | Sigma Aldrich | E5134 | |
| Formamide | Fluka | 40248 | H351-360D-373 |
| Gel imager | GE Healtcare | STORM B40 | |
| Glycerol | Sigma Aldrich | G5516 | |
| Micro tubes 0.5 mL | Sarstedt | 72.704 | |
| Potassium Chloride | Sigma Aldrich | P9541 | |
| Sequencing apparatus | Biometra | Model S2 | |
| Silanization solution I | Fluka | 85126 | H225, 314, 318, 336, 304, 400, 410 |
| Sodium phosphate monobasic | Carlo Erba | 480086 | |
| Speedvac concentrator | Thermo Scientific | Savant DNA 120 | |
| TEMED | Fluka | 87689 | R11-21/22-23-34 |
| Tris-HCl | MERCK | 1.08387.2500 | |
| Urea | Sigma Aldrich | 51456 | |
| UV-Vis spectrophotometer | Thermo Scientific | Nanodrop 1000 |
Odniesienia
- Davis, J. T. G-quartets 40 years later: from 5'-GMP to molecular biology and supramolecular chemistry. Angewandte Chemie. 43 (6), 668-698 (2004).
- Varshney, D., Spiegel, J., Zyner, K., Tannahill, D., Balasubramanian, S. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 21 (8), 459-474 (2020).
- Chambers, V. S., et al. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nature Biotechnology. 33 (8), 877-881 (2015).
- Zuravka, I., Sosic, A., Gatto, B., Gottlich, R. Synthesis and evaluation of a bis-3-chloropiperidine derivative incorporating an anthraquinone pharmacophore. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 25 (20), 4606-4609 (2015).
- Zuravka, I., Roesmann, R., Sosic, A., Gottlich, R., Gatto, B. Bis-3-chloropiperidines containing bridging lysine linkers: Influence of side chain structure on DNA alkylating activity. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 23 (6), 1241-1250 (2015).
- Zuravka, I., et al. Synthesis and DNA cleavage activity of bis-3-chloropiperidines as alkylating agents. ChemMedChem. 9 (9), 2178-2185 (2014).
- Sosic, A., Gottlich, R., Fabris, D., Gatto, B. B-CePs as cross-linking probes for the investigation of RNA higher-order structure. Nucleic Acids Research. 49 (12), 6660-6672 (2021).
- Sosic, A., et al. Bis-3-chloropiperidines targeting TAR RNA as a novel strategy to impair the HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein. Molecules. 26 (7), 1874 (2021).
- Sosic, A., et al. In vitro evaluation of bis-3-chloropiperidines as RNA modulators targeting TAR and TAR-protein interaction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23 (2), 582 (2022).
- Sosic, A., et al. Direct and topoisomerase II mediated DNA damage by bis-3-chloropiperidines: The importance of being an earnest G. ChemMedChem. 12 (17), 1471-1479 (2017).
- Bock, L. C., Griffin, L. C., Latham, J. A., Vermaas, E. H., Toole, J. J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature. 355 (6360), 564-566 (1992).
- Paborsky, L. R., McCurdy, S. N., Griffin, L. C., Toole, J. J., Leung, L. L. The single-stranded DNA aptamer-binding site of human thrombin. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (28), 20808-20811 (1993).
- Carraro, C., et al. Behind the mirror: chirality tunes the reactivity and cytotoxicity of chloropiperidines as potential anticancer agents. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 10 (4), 552-557 (2019).
- Carraro, C., et al. Appended aromatic moieties in flexible bis-3-chloropiperidines confer tropism against pancreatic cancer cells. ChemMedChem. 16 (5), 860-868 (2021).
- Kypr, J., Kejnovska, I., Renciuk, D., Vorlickova, M. Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (6), 1713-1725 (2009).
- Onel, B., Wu, G., Sun, D., Lin, C., Yang, D. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay and dimethyl sulfate footprinting for characterization of G-quadruplexes and G-quadruplex-protein complexes. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2035, 201-222 (2019).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone