Un abonnement à JoVE est nécessaire pour voir ce contenu. Connectez-vous ou commencez votre essai gratuit.
Method Article
In vitro Cartographie chimique des structures de l’ADN G-quadruplex par Bis-3-chloropipéridines
Dans cet article
Résumé
Les bis-3-chloropipéridines (B-CePs) sont des sondes chimiques utiles pour identifier et caractériser les structures G-quadruplex dans les matrices d’ADN in vitro. Ce protocole détaille la procédure permettant d’effectuer des réactions de sondage avec des B-CeP et de résoudre les produits de réaction par électrophorèse sur gel de polyacrylamide à haute résolution.
Résumé
Les G-quadruplexes (G4s) sont des structures d’ADN biologiquement pertinentes, non canoniques, qui jouent un rôle important dans l’expression des gènes et les maladies, représentant des cibles thérapeutiques importantes. Des méthodes accessibles sont nécessaires pour la caractérisation in vitro de l’ADN dans les séquences potentielles de formation de G-quadruplex (PQS). Les B-CeP sont une classe d’agents alkylants qui se sont avérés être des sondes chimiques utiles pour l’étude de la structure d’ordre supérieur des acides nucléiques. Cet article décrit un nouveau test de cartographie chimique exploitant la réactivité spécifique des B-CeP avec le N7 des guanines, suivi d’un clivage direct des brins au niveau des G alkylés.
En effet, pour distinguer les plis G4 des formes d’ADN dépliées, nous utilisons B-CeP 1 pour sonder l’aptamère de liaison à la thrombine (TBA), un ADN de 15 mères capable d’assumer l’arrangement G4. La réaction des guanines répondant au B-CeP avec le B-CeP 1 permet d’obtenir des produits qui peuvent être résolus par électrophorèse sur gel de polyacrylamide (PAGE) à haute résolution au niveau d’un seul nucléotide en localisant les adduits d’alkylation individuels et le clivage des brins d’ADN au niveau des guanines alkylées. La cartographie à l’aide de B-CePs est un outil simple et puissant pour la caractérisation in vitro de séquences d’ADN formant G-quadruplex, permettant la localisation précise des guanines impliquées dans la formation des G-tétrades.
Introduction
En plus de la double hélice typique de Watson-Crick, les acides nucléiques peuvent adopter diverses structures secondaires, telles que la forme alternative G-quadruplex (G4), en raison de leurs séquences riches en guanine. La structure G4 est basée sur la formation de tétramères planaires, appelés G-tétrades, dans lesquels quatre guanines interagissent par l’intermédiaire de liaisons hydrogène Hoogsteen. Les G-tétrades sont empilées et stabilisées par des cations monovalents qui sont coordonnés au centre du noyau de guanine (Figure 1)1.
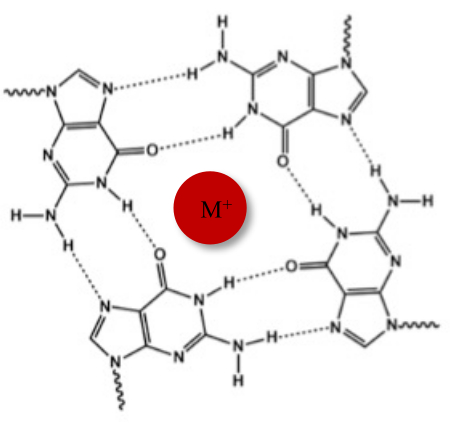
Figure 1 : Représentation schématique d’une structure G-quadruplex. (A) Représentation schématique d’une tétrade G. Le réseau planaire est stabilisé par l’appariement de bases de Hoogsteen et par un cation central (M+). Veuillez cliquer ici pour voir une version agrandie de cette figure.
Les séquences comportant quatre cycles ou plus d’au moins deux nucléotides consécutifs de guanine sont des séquences potentielles formant des G-quadruplex (PQS) qui peuvent se replier dans des structures G-quadruplex. Les PQS sont situés dans de nombreux contextes cellulaires différents, tels que les télomères, les promoteurs de gènes, l’ADN ribosomique et les sites de recombinaison, et sont impliqués dans la régulation de nombreux processus biologiques2. Par conséquent, l’identification et la validation expérimentale des G4 dans le génome humain, qui sont actuellement effectuées principalement à l’aide d’outils informatiques, est une question biologiquement pertinente3. Afin de soutenir les prédictions computationnelles ou de détecter des structures G4 non prédites, une méthode accessible basée sur la cartographie chimique pour identifier la formation de G4 dans une matrice d’ADN est présentée ici, permettant l’identification précise des guanines formant la structure G-tétrade.
Le test de cartographie chimique rapporté exploite la réactivité différente des bis-3-chloropipéridines (B-CePs) avec les guanines suite à la formation de structures G4. En raison de leur forte réactivité avec les nucléophiles 4,5,6,7,8,9, les B-CeP sont des agents alkylants d’acides nucléiques ayant la capacité de réagir très efficacement avec la position N 7 des nucléotides de guanine10. L’alkylation est suivie de la dépurination et du clivage des brins dans les constructions d’ADN simple et double brin. Au contraire, les guanines impliquées dans la formation des G-tétrades dans les arrangements G4 sont imperméables à l’alkylation B-CeP, car la position N7 des guanines est impliquée dans les liaisons hydrogène de Hoogsteen. Cette réactivité spécifique des B-CePs permet non seulement la détection des structures G4, mais aussi l’identification des guanines formant la ou les tétrades, telles qu’elles peuvent être déduites de leur protection relative contre l’alkylation par rapport aux guanines dans l’ADN simple et double brin.
Le protocole de cartographie chimique est présenté ici en utilisant B-CeP 1 (Figure 2A) comme sonde pour la caractérisation de l’aptamère de liaison à la thrombine (TBA), un ADN de 15 mères capable d’assumer l’arrangement G4 en présence de cations potassiques11,12. L’arrangement G4 de TBA (G4-TBA) est directement comparé à deux témoins, à savoir TBA sous la forme simple brin (ssTBA) et TBA recuit à sa séquence complémentaire pour former la construction double brin (dsTBA) (tableau 1). Les produits des réactions de sondage sont résolus par électrophorèse sur gel de polyacrylamide à haute résolution (PAGE) au niveau du mononucléotide en localisant les adduits d’alkylation individuels et le clivage des brins d’ADN au niveau des guanines alkylées. La visualisation sur le gel est rendue possible par la conjugaison de l’oligonucléotide TBA avec un fluorophore à son extrémité 3' (Tableau 1). Ce protocole montre comment plier TBA dans ses différentes conformations (G4 et témoins), et comment effectuer des réactions de sondage avec des B-CeP suivis de PAGE.
Protocole
1. Préparation de la sonde d’acide nucléique et chimique
- Acides nucléiques
REMARQUE : L’oligonucléotide nommé « TBA » est la séquence d’ADN 5'-GGT-TGG-TGT-GGT-TGG-TGG-3' de 15 mères marquée à l’extrémité 3' par le fluorophore 5-carboxyfluorescéine (FAM) pour permettre la visualisation sur le gel. L’oligonucléotide non marqué « cTBA » est sa séquence complémentaire d’ADN 5'-CCA-ACC-ACA-CCA-ACC-3'. TBA et cTBA sont utilisés pour obtenir les trois structures différentes, comme le montre le tableau 1.- Embouts d’autoclave et tubes de 0,5 mL afin d’obtenir des produits jetables stériles et d’éviter la contamination.
- Préparer des solutions mères solubilisant chaque oligonucléotide dans de l’eau ultrapure jusqu’à une concentration finale de 100 μM. Déterminer la concentration exacte d’oligonucléotides à l’aide d’un spectrophotomètre ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis), en utilisant le coefficient d’extinction à 260 nm fourni par le fabricant.
NOTE : Coefficients d’extinction : 164 300 M-1 cm-1 et 138 600 M-1 cm-1 ont été utilisés pour la TBA et la cTBA, respectivement. - Conserver les solutions mères TBA et cTBA à -20 °C (pendant des mois dans ces conditions).
- Composé B-CeP 1
REMARQUE : Le composé B-CeP 1 est synthétisé comme indiqué précédemment6.- Préparer la solution mère B-CeP 1 à ~10 mM. Peser ~1 mg du composé lyophilisé à l’aide d’une balance analytique située dans une hotte et le solubiliser dans du diméthylsulfoxyde à 100 % (DMSO).
- Calculer la concentration exacte du composé en fonction de la quantité réelle de composé et de DMSO (d = 1,1 g/cm3) utilisée.
REMARQUE : Manipuler le composé avec des gants en tout temps (à la fois lorsqu’il est lyophilisé et lorsqu’il est dissous dans le DMSO)13,14.
Tableau 1 : Structures oligonucléotidiques utilisées dans ce protocole. Veuillez cliquer ici pour télécharger ce tableau.
2. Repliement des constructions d’acides nucléiques
- Préparation des tampons
- Préparer une solution tampon BPE (acide biphosphate-éthylènediaminetétraacétique [EDTA], 5x : 2 mM NaH 2 PO 4, 6 mM Na 2 HPO 4, 1 mMNa2EDTA, pH7,4) et une solution de 500 mM KCl dans de l’eau ultrapure. Filtrez les solutions à travers des filtres de taille de pores de 0,22 μm.
REMARQUE : Pour de meilleurs résultats, utilisez des solutions fraîchement préparées. Le tampon BPE peut être stocké à 4 °C jusqu’à 15 jours.
- Préparer une solution tampon BPE (acide biphosphate-éthylènediaminetétraacétique [EDTA], 5x : 2 mM NaH 2 PO 4, 6 mM Na 2 HPO 4, 1 mMNa2EDTA, pH7,4) et une solution de 500 mM KCl dans de l’eau ultrapure. Filtrez les solutions à travers des filtres de taille de pores de 0,22 μm.
- Pliage d’échantillons G4-TBA, ssTBA et dsTBA par la procédure de repliage à chaud
REMARQUE : Les cations potassiques sont nécessaires pour replier la structure G4 (G4-TBA). N’ajoutez pas de cations potassiques dans la solution de repliement des témoins ssTBA et dsTBA.- Préparez 40 μL d’une solution de 4 μM de G4-TBA dans 1x BPE et 100 mM de KCl. Dénaturez la solution d’oligonucléotide G4-TBA en chauffant le tube à 95 °C pendant 5 min et refroidissez-le lentement à température ambiante (RT) pour permettre au TBA de se replier en G-quadruplexes.
- Préparer 40 μL d’une solution de 4 μM de ssTBA dans 1x BPE. Effectuez la procédure de repliage à chaud, comme mentionné à l’étape 2.2.1, pour plier TBA sous sa forme monobrin.
- Préparer 40 μL d’une solution de 4 μM de dsTBA en mélangeant des quantités équimolaires de TBA et de cTBA dans 1x BPE. Effectuez la procédure de repliement à chaud comme mentionné ci-dessus (étape 2.2.1) pour que le TBA se recuit à sa séquence complémentaire cTBA et forme la forme double brin du TBA.
REMARQUE : Le volume final de chaque solution de repliement est basé sur le nombre d’échantillons pour les réactions de palpage, étant donné que 5 μL de solution de 4 μM seront nécessaires pour chaque échantillon. Préparez un peu d’excédent de volume de chaque solution pour éviter les erreurs de pipetage.
3. Réactions de sondage
REMARQUE : Les réactions de palpage doivent être effectuées immédiatement après la procédure de repliage à chaud.
- Lorsque les solutions de repliement de G4-TBA, ssTBA et dsTBA ont refroidi à RT, effectuez une centrifugation à rotation courte (7 000 × g pendant 5 à 8 s à RT) et démarrez les réactions de sonde.
- Préparez 21 tubes vides de 0,5 ml autoclavés. Organisez-les en trois ensembles de sept tubes chacun dans le rack pour les échantillons de laboratoire, comme indiqué dans le tableau 2.
REMARQUE : Chaque jeu de colonnes correspond aux trois conditions de pliage TBA différentes G4-TBA, ssTBA et dsTBA. Chaque rang correspond à trois temps d’incubation différents. Chaque cellule de la colonne correspond à la concentration finale de la sonde B-CeP 1 (tableau 2). Assurez-vous d’étiqueter clairement les tubes. - Ajoutez 3 μL d’eau ultrapure dans chaque tube.
- Ajouter 5 μL de G4-TBA plié dans chaque tube de la première série (étape 3.2). Ajouter 5 μL de ssTBA plié dans chaque tube de la deuxième série. Ajouter 5 μL de dsTBA plié dans chaque tube de la troisième série.
- Diluer la solution mère de B-CeP 1 à 250 μM et 25 μM dans de l’eau ultra-pure.
REMARQUE : Les dilutions de la sonde chimique B-CeP 1 doivent être fraîchement préparées et réagir immédiatement avec le substrat d’ADN pour éviter les réactions concurrentes avec l’eau. - Ajouter 2 μL de la dilution B-CeP 1 appropriée (25 μM et 250 μM) aux échantillons. Remplacer le composé par de l’eau ultra-pure dans les trois échantillons de contrôle (C) pour l’analyse des TBA différemment pliés en l’absence du composé. Incuber tous les échantillons à 37 °C.
- Après 1 h, 4 h et 15 h d’incubation, arrêtez la réaction en plaçant les tubes à -20 °C jusqu’à l’étape suivante.
REMARQUE : Les échantillons peuvent être stockés dans ces conditions pendant quelques jours. - Séchez les échantillons dans une centrifugeuse sous vide.
REMARQUE : Les échantillons séchés peuvent être conservés à -20 °C pendant des semaines avant de procéder à l’analyse PAGE.
Tableau 2 : Échantillons pour les réactions de sondage (structures, concentrations de la sonde et temps d’incubation). Chaque ensemble de colonnes correspond aux trois conditions de pliage TBA différentes (G4-TBA, ssTBA et dsTBA). Chaque rang correspond à trois temps d’incubation différents (1, 4, 15 h). Chaque cellule de la colonne correspond à la concentration finale de la sonde B-CeP 1 (5 ou 50 μM). Le témoin (C) pour chaque série correspond à un échantillon de TBA différemment pliés incubés pendant une période plus longue (15 h) en l’absence de composé. Veuillez cliquer ici pour télécharger ce tableau.
4. PAGE haute résolution
- Préparation de la solution de polyacrylamide dénaturant
REMARQUE : Préparer à l’avance 500 mL de solution de gel de polyacrylamide dénaturant à 20 %. Environ 80 mL de cette solution seront utilisés pour chaque expérience. Utilisez une bouteille en verre ambré ou couvrez une bouteille en verre de papier d’aluminium pour stocker la solution à RT.
ATTENTION : Le polyacrylamide est neurotoxique. Pendant toutes les étapes de la préparation et du versement du gel, portez des gants et une blouse de laboratoire. Jeter l’acrylamide polymérisé dans une boîte appropriée pour les matériaux contaminés.- Peser 210 g d’urée dans un bécher de 1 L. Ajouter 250 mL de solution d’acrylamide/bisacrylamide (19/1) à 40 % et 50 mL de 10x TBE (890 mM de Tris-HCl, 890 mM de borate, 20 mM d’EDTA, pH 8).
- Placez le bécher sur une plaque d’agitation et mélangez la solution à l’aide d’une tige d’agitation. Couvrez le bécher avec du papier d’aluminium pendant le mélange pour éviter les éclaboussures et la contamination.
- Mélangez la solution jusqu’à ce que l’urée soit complètement dissoute et que la solution soit claire.
REMARQUE : Cette étape peut prendre plusieurs heures. Pour favoriser la dissolution de l’urée, ajoutez une petite aliquote d’eau sans dépasser le volume final souhaité. - Retirez la tige d’agitation. Versez la solution dans un cylindre et ajoutez de l’eau jusqu’à obtenir un volume final exact de 500 ml.
- Mise en place d’un appareil de gel
- Nettoyez deux plaques (une entaillée et une non entaillée) avec de l’éthanol à 70 %, laissez-les sécher, puis traitez les plaques avec une solution de diméthyldichlorosilane.
REMARQUE : La silanisation peut être sautée, bien qu’elle aide à la libération du gel de l’une des plaques lorsque le sandwich de gel est démonté.
ATTENTION : Manipulez la solution de silanisation avec des gants et effectuez le traitement de la plaque avec cette solution dans une hotte. - Placez les entretoises de 0,4 mm le long des bords longs de la plaque la plus longue, placez la plaque courte l’une sur l’autre et alignez les deux plaques en bas.
- Placez plusieurs couches de ruban adhésif en papier le long de tous les bords, à l’exception du haut.
- Pour éviter les fuites lors de la coulée, ajoutez une couche supplémentaire de ruban adhésif au fond du gel.
- Clipsez les côtés du sandwich en verre avec des pinces propres en suivant les instructions du fournisseur (différents fournisseurs utilisent des appareils, des pinces sandwich et des joints légèrement différents).
- Nettoyez deux plaques (une entaillée et une non entaillée) avec de l’éthanol à 70 %, laissez-les sécher, puis traitez les plaques avec une solution de diméthyldichlorosilane.
- Verser le gel
REMARQUE : Versez le gel à RT (25 °C), car la polymérisation du polyacrylamide est sensible à la température.- Dans un bécher, verser 80 mL de la solution de polyacrylamide dénaturant préparée précédemment (étape 4.1), 450 μL d’une solution de persulfate d’ammonium (APS) à 10 % m/V et 45 μL de tétraméthyléthylènediamine (TEMED) immédiatement avant l’utilisation.
- Mélangez la solution et versez-la rapidement entre les plaques de verre à l’aide d’une seringue de 50 ml. Introduisez le peigne avec le nombre souhaité de puits entre les plaques de verre, en évitant les bulles. Ajouter une solution de gel pour remplir complètement le sandwich, si nécessaire. Placez quatre pinces sur le peigne pour appuyer et permettre une distribution uniforme des puits.
- Laissez le gel polymériser pendant au moins 45 min.
- Exécution du gel
- Après la polymérisation, retirez toutes les pinces et les couches de ruban adhésif en papier. Retirez lentement le peigne et rincez abondamment les puits avec de l’eau distillée.
- Suivez les instructions du fournisseur spécifique pour placer correctement le sandwich de gel dans l’appareil d’électrophorèse verticale sur gel.
- Préparez le tampon de fonctionnement TBE (1x : 89 mM Tris-HCl, 89 mM de borate, 2 mM EDTA, pH 8) dans de l’eau déminéralisée et remplissez les réservoirs supérieur et inférieur avec le tampon.
- Réchauffez les plaques en effectuant un pré-fonctionnement de l’électrophorèse sur gel pendant au moins 30 min à 50 W.
- Préparer un tampon de charge de gel dénaturant (DGLB : 1 M de Tris-HCl, 80 % de formamide, 50 % de glycérol, 0,05 % de bleu de bromophénol) dans de l’eau ultra-pure.
REMARQUE : GLB aide à suivre le mouvement des échantillons d’oligonucléotides dans le système de gel et permet de charger les échantillons dans les puits du gel. La présence de l’agent dénaturant formamide permet aux espèces d’ADN de se séparer en fonction de leur taille, même dans un PAGE non dénaturant. - Remettre en suspension les échantillons séchés (échantillons de l’étape 3.8) dans 5 μL de DGLB.
- Avant de charger les échantillons, nettoyez les puits à l’aide d’une petite seringue et du tampon TBE dans la chambre tampon supérieure pour éliminer l’urée des puits.
REMARQUE : Répétez cette étape plusieurs fois pour nettoyer avec précision les puits, évitant ainsi les bandes difficiles à interpréter. - Chargez les échantillons dans les puits propres et notez l’ordre de chargement.
- Faire fonctionner l’électrophorèse sur gel pendant 2 h à 50 W, ou au moins jusqu’à ce que le colorant bleu de bromophénol ait coulé aux 2/3 du gel.
- Imagerie du gel
- Après l’électrophorèse, coupez l’alimentation électrique, retirez le sandwich en verre et nettoyez les verres.
- Détectez la fluorescence des bandes oligonucléotidiques marquées par FAM en scannant à l’aide d’un imageur sur gel.
Résultats
La figure 2 montre un résultat représentatif d’un test de cartographie chimique effectué, tel que décrit dans le protocole avec B-CeP 1 sur l’oligonucléotide TBA replié dans trois structures différentes. L’arrangement G-quadruplex de TBA (G4-TBA) a été obtenu en repliant l’oligonucléotide dans le BPE et en présence du cation K+, tandis que la forme simple brin de la même séquence TBA (ssTBA) a été repliée en l’absence de potassium. La construction double ...
Discussion
Les G-quadruplexes sont des structures secondaires d’acides nucléiques qui se replient généralement dans des séquences d’ADN riches en guanine et sont des cibles de recherche importantes en raison de leur association avec le contrôle génétique et les maladies. La cartographie chimique par B-CePs est un protocole utile pour la caractérisation des G4 de l’ADN, qui peut être utilisé pour identifier les bases de guanine impliquées dans la formation des G-tétrades dans des conditions physiologiques de sel.
Déclarations de divulgation
Les auteurs n’ont aucun conflit d’intérêts à divulguer.
Remerciements
Ce travail a été soutenu par le Département des Sciences Pharmaceutiques et Pharmacologiques de l’Université de Padoue (PRIDJ-BIRD2019).
matériels
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acrylamide/bis-acrylamide solution 40% | Applichem | A3658 | R45-46-20/21-25-36/38-43-48/23/ 24/25-62 |
| Ammonium per-sulfate (APS) | Sigma Aldrich | A7460 | |
| Analytical balance | Mettler Toledo | ||
| Autoclave | pbi international | ||
| Boric acid | Sigma Aldrich | B0252 | |
| Bromophenol blue Brilliant blue R | Sigma Aldrich | B0149 | |
| di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate | Fluka | 71649 | |
| DMSO | Sigma Aldrich | 276855 | |
| DNA oligonucleotides | Integrated DNA Technologies | synthesis of custom sequences | |
| EDTA disodium | Sigma Aldrich | E5134 | |
| Formamide | Fluka | 40248 | H351-360D-373 |
| Gel imager | GE Healtcare | STORM B40 | |
| Glycerol | Sigma Aldrich | G5516 | |
| Micro tubes 0.5 mL | Sarstedt | 72.704 | |
| Potassium Chloride | Sigma Aldrich | P9541 | |
| Sequencing apparatus | Biometra | Model S2 | |
| Silanization solution I | Fluka | 85126 | H225, 314, 318, 336, 304, 400, 410 |
| Sodium phosphate monobasic | Carlo Erba | 480086 | |
| Speedvac concentrator | Thermo Scientific | Savant DNA 120 | |
| TEMED | Fluka | 87689 | R11-21/22-23-34 |
| Tris-HCl | MERCK | 1.08387.2500 | |
| Urea | Sigma Aldrich | 51456 | |
| UV-Vis spectrophotometer | Thermo Scientific | Nanodrop 1000 |
Références
- Davis, J. T. G-quartets 40 years later: from 5'-GMP to molecular biology and supramolecular chemistry. Angewandte Chemie. 43 (6), 668-698 (2004).
- Varshney, D., Spiegel, J., Zyner, K., Tannahill, D., Balasubramanian, S. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 21 (8), 459-474 (2020).
- Chambers, V. S., et al. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nature Biotechnology. 33 (8), 877-881 (2015).
- Zuravka, I., Sosic, A., Gatto, B., Gottlich, R. Synthesis and evaluation of a bis-3-chloropiperidine derivative incorporating an anthraquinone pharmacophore. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 25 (20), 4606-4609 (2015).
- Zuravka, I., Roesmann, R., Sosic, A., Gottlich, R., Gatto, B. Bis-3-chloropiperidines containing bridging lysine linkers: Influence of side chain structure on DNA alkylating activity. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 23 (6), 1241-1250 (2015).
- Zuravka, I., et al. Synthesis and DNA cleavage activity of bis-3-chloropiperidines as alkylating agents. ChemMedChem. 9 (9), 2178-2185 (2014).
- Sosic, A., Gottlich, R., Fabris, D., Gatto, B. B-CePs as cross-linking probes for the investigation of RNA higher-order structure. Nucleic Acids Research. 49 (12), 6660-6672 (2021).
- Sosic, A., et al. Bis-3-chloropiperidines targeting TAR RNA as a novel strategy to impair the HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein. Molecules. 26 (7), 1874 (2021).
- Sosic, A., et al. In vitro evaluation of bis-3-chloropiperidines as RNA modulators targeting TAR and TAR-protein interaction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23 (2), 582 (2022).
- Sosic, A., et al. Direct and topoisomerase II mediated DNA damage by bis-3-chloropiperidines: The importance of being an earnest G. ChemMedChem. 12 (17), 1471-1479 (2017).
- Bock, L. C., Griffin, L. C., Latham, J. A., Vermaas, E. H., Toole, J. J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature. 355 (6360), 564-566 (1992).
- Paborsky, L. R., McCurdy, S. N., Griffin, L. C., Toole, J. J., Leung, L. L. The single-stranded DNA aptamer-binding site of human thrombin. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (28), 20808-20811 (1993).
- Carraro, C., et al. Behind the mirror: chirality tunes the reactivity and cytotoxicity of chloropiperidines as potential anticancer agents. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 10 (4), 552-557 (2019).
- Carraro, C., et al. Appended aromatic moieties in flexible bis-3-chloropiperidines confer tropism against pancreatic cancer cells. ChemMedChem. 16 (5), 860-868 (2021).
- Kypr, J., Kejnovska, I., Renciuk, D., Vorlickova, M. Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (6), 1713-1725 (2009).
- Onel, B., Wu, G., Sun, D., Lin, C., Yang, D. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay and dimethyl sulfate footprinting for characterization of G-quadruplexes and G-quadruplex-protein complexes. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2035, 201-222 (2019).
Réimpressions et Autorisations
Demande d’autorisation pour utiliser le texte ou les figures de cet article JoVE
Demande d’autorisationThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon