Для просмотра этого контента требуется подписка на Jove Войдите в систему или начните бесплатную пробную версию.
Method Article
Геном редактирование в Mammalian клеток линии, используя ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas
В этой статье
Резюме
ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas — это мощная технология инженер комплекс геномов растений и животных. Здесь мы подробно протокол эффективно редактировать генома человека с использованием различных эндонуклеазами Cas. Мы отмечаем важные соображения и расчетные параметры для оптимизации эффективности редактирования.
Аннотация
Кластерный системы регулярно interspaced короткие палиндром повторяется (ТРИФОСФАТЫ) функции естественно в бактериальных адаптивного иммунитета, но успешно многократно использовать для генома инженерии в многих различных живых организмов. Чаще всего Cas12a эндонуклеазы используется прилепится определенных сайтов в геноме, после чего перерыв двуцепочечной ДНК будет восстановлена через не гомологичных конце присоединения (NHEJ) путь или ориентированные на гомологии ремонт (или wildtype ТРИФОСФАТЫ связанные 9 (Cas9) HDR) путь в зависимости от того, является ли шаблон доноров отсутствует или представить соответственно. На сегодняшний день, ТРИФОСФАТЫ систем от различных видов бактерий было показано, чтобы быть способными выполнять изменения генома в mammalian клетках. Однако несмотря на кажущуюся простоту технологии, несколько конструктивных параметров должны рассматриваться, которые часто оставляют пользователи недоумевали о том, как лучше всего выполнять их геном редактирования экспериментов. Здесь мы описываем полный рабочий процесс из экспериментального дизайна для идентификации ячейки клонов, которые несут желаемые изменения ДНК, с целью облегчения успешного выполнения редактирования эксперименты в mammalian клетки линии генома. Мы подчеркиваем основные соображения для пользователей, чтобы принять к сведению, включая выбор системы ТРИФОСФАТЫ, длина распорку и дизайн шаблона доноров одноцепочечной oligodeoxynucleotide (ssODN). Мы предполагаем, что этот процесс будет полезен для гена нокаут исследований, моделирования усилия, болезни или поколения репортер мобильных линий.
Введение
Способность инженер геном любого живого организма имеет много биомедицинских и биотехнологических приложений, например коррекции болезнетворные мутации, строительство точных моделей для исследования заболеваний, или поколения сельскохозяйственных культур с желательные черты. С начала века, различные технологии были разработаны для техники генома клеток млекопитающих, включая meganucleases1,2,3, цинковый палец nucleases4,5, или Транскрипция эффекторных активатор как nucleases (Таленс)6,,78,9. Однако эти более ранних технологий трудно программы или утомительно собрать, препятствуя тем самым их широкое распространение в научных исследований и промышленности.
В последние годы кластеризованный регулярно interspaced короткие палиндром повторяется (ТРИФОСФАТЫ) - связанные ТРИФОСФАТЫ (Cas) системы стала мощной новой генома, инженерные технологии10,11. Первоначально адаптивной иммунной системы в бактерии, он был успешно развернут для модификации генома растений и животных, включая человека. Основная причина, почему ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas популярность так много за такое короткое время, что элемент, который приносит ключевых эндонуклеазы Cas, например Cas9 или Cas12a (также известный как Cpf1), в нужное место в геноме это просто небольшой фрагмент химерных единого руководства RN A (sgRNA), которая является простой дизайн и дешевые синтезировать. После набираются на целевой сайт, Cas фермента функционирует как молекулярные ножницы и расщепляет ДНК связанного с его RuvC, HNH или КНУ доменов12,,1314. Результате двойной мель перерыв (DSB) впоследствии отремонтированы клетки через ориентированные на гомологии ремонт (HDR) путь или не гомологичных конце присоединения (NHEJ). В отсутствие шаблона ремонт DSB отремонтированы по ошибкам NHEJ пути, который может привести к псевдо-случайных вставки или удаления нуклеотидов (indels) в месте разреза, потенциально вызывая фреймшифт мутации в генах, белок кодирования. Однако в присутствии доноров шаблон, содержащий требуемые изменения ДНК, DSB восстановлена дорожка HDR высокой верности. Общие типы доноров шаблоны включают одноцепочечной олигонуклеотиды (ssODNs) и плазмид. Бывший обычно используется, если предполагаемого изменения ДНК небольшие (например, изменение одной пары базы), в то время как последние обычно используется, если один хочет, чтобы вставить относительно длинная последовательность (например, кодирующая последовательность зеленого флуоресцентного белка или GFP) в целевой Локус.
Эндонуклеазы активность белка Cas требует наличия protospacer прилегающие мотив (PAM) на целевой сайт15. Пэм Cas9 находится в конце 3' protospacer, в то время как Пэм Cas12a (также называемый Cpf1) находится в конце 5' вместо16. Cas руководство РНК комплекс не в состоянии представить DSB, если PAM отсутствует17. Следовательно PAM места ограничения в геномной местах, где особенно нуклеиназы Cas способен расщеплять. К счастью Cas nucleases из различных видов бактерий обычно демонстрируют различные требования PAM. Таким образом путем интеграции различных систем ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas в наших инженерных инструментов, мы можем расширить круг сайтов, которые могут быть направлены в геноме. Кроме того естественный фермент Cas может быть спроектирован или эволюционировали признать альтернативных последовательностей PAM, дальнейшего расширения масштабов геномной целей доступным для манипуляции18,19,20.
Хотя несколько ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas системы доступны для технических целей генома, большинство пользователей технологии полагались главным образом на Cas9 Нуклеаза от Streptococcus pyogenes (SpCas9) по нескольким причинам. Во-первых он требует относительно просто NGG Пэм, в отличие от многих других белков Cas, которые может только расщеплять при наличии более сложных пам. Во-вторых это первый Cas эндонуклеазы успешно развернуты в клетки человека21,,2223,24. В-третьих SpCas9 является на сегодняшний день лучше всего характеризуется фермент на сегодняшний день. Если исследователь хочет использовать другой нуклеиназы Cas, он или она часто будет ясно о том, как лучше разработать эксперимент, и насколько хорошо другие ферменты будет выполнять в различных биологических условиях по сравнению с SpCas9.
Чтобы внести ясность в относительной эффективности различных систем ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas, мы провели недавно систематическое сравнение пяти Cas эндонуклеазами – SpCas9, Cas9 фермента от золотистого стафилококка (SaCas9), энзим Cas9 от Neisseria meningitidis (NmCas9), Cas12a фермента от Acidaminococcus sp. BV3L6 (AsCas12a) и Cas12a фермента от бактерия Lachnospiraceae ND2006 (LbCas12a)25. За справедливое сравнение мы оценивали различные Cas nucleases, используя тот же набор целевых объектов и других экспериментальных условий. Исследование также определила дизайн параметры для каждой системы ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas, которая будет служить полезным справочным материалом для пользователей технологии. Здесь, чтобы лучше включить исследователей использовать ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas системы, мы предоставляем пошаговые протокол для оптимального генома техники с различными Cas9 и Cas12a ферменты (см. Рисунок 1). Протокол включает не только экспериментальных детали, но также важных конструктивных соображений необходимо максимизировать вероятность успешного генома инженерных решений в mammalian клетках.

Рисунок 1 : Обзор рабочего процесса для создания генома линий клеток человека отредактированы. Пожалуйста, нажмите здесь, чтобы посмотреть большую версию этой фигуры.
протокол
1. дизайн sgRNAs
- Выберите соответствующую систему ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas.
- Во-первых проверьте целевого региона для PAM последовательности всех Cas9 и Cas12a nucleases, которые показали, чтобы быть функциональным в mammalian клетках16,21-32. Пять часто используемые ферменты приведены в таблице 1 вместе с их соответствующими пам.
Примечание: Помимо эндонуклеазами, перечисленных в таблице 1, существуют другие менее часто используемые Cas ферменты, которые были успешно развернуты в mammalian клетках также, как Cas9 Нуклеаза от Streptococcus thermophilus (St1Cas9), признает PAM NNAGAAW. Если нужного целевого сайта не содержит известный PAM, тогда одно не сможет использовать систему ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas для генома техники. - Во-вторых рассмотрим любые известные свойства целевой геномной Локус или гена. Некоторые свойства, чтобы принимать во внимание включают уровни выражения гена или доступность хроматина и ли есть другие тесно связанные последовательности также.
Примечание: Определенные ферменты лучше подходят для биологических контекстами. Например, чтобы изменить повторяющиеся геномной Локус или гена с несколькими другими закрыть паралоги, рекомендуется использовать либо AsCas12a (из-за его низкий допуск для несоответствия между sgRNA и ДНАО цели чем SpCas9 и LbCas12a) или SaCas9 (из-за его требование более распорки, который обеспечивает выше таргетинга специфика)25.
- Во-первых проверьте целевого региона для PAM последовательности всех Cas9 и Cas12a nucleases, которые показали, чтобы быть функциональным в mammalian клетках16,21-32. Пять часто используемые ферменты приведены в таблице 1 вместе с их соответствующими пам.
| CAS эндонуклеазы | ПЭМ | Длина Оптимальная прокладка |
| SpCas9 | НЭС | 17-22 nt включительно |
| SaCas9 | NNGRRT | ≥ 21 nt |
| NmCas9 | NNNNGATT | ≥ 19 nt |
| AsCas12a и LbCas12a | TTTV | ≥ 19 nt |
Таблица 1: некоторые часто используемые Cas ферментов с их родственных ПАМС и оптимальной sgRNA длин. N = любой нуклеотидов (A, T, G или C); R = A или G; V = A, C, или G.
- Выберите подходящий заполнитель последовательности. Определить как уникальную последовательность как можно свести к минимуму риск расщепление пробить событий, либо путем изучения целевой генома с ДОМЕННАЯ33 , или с помощью несколько бесплатных онлайн инструментов, таких как: (в) программу из лаборатории Чжан Фэн34 (http://crispr.mit.edu/); (b) CHOPCHOP35 (http://chopchop.cbu.uib.no/); (c) E-ХРУСТЯЩИЙ36 (http://www.e-crisp.org/E-CRISP/); (d) CRISPOR37 (http://crispor.tefor.net/); (e) Cas-OFFinder38 (http://www.rgenome.net/cas-offinder/).
Примечание: Оптимальная длина распорка может варьироваться от 17-25 нуклеотидов (nt) включительно, в зависимости от которой Cas используется фермент (см. таблицу 1). Для Cas9, распорка вверх по течению от PAM, а для Cas12a, распорку вниз по течению от PAM. Дополнительно, HDR эффективность падает быстро с увеличением расстояния от отрезока сайта. Таким образом для точного редактирования ДНК, позиция sgRNA как можно ближе к месту предполагаемого изменения. - Синтез олигонуклеотидов ДНК с соответствующей свесы для плазмида ТРИФОСФАТЫ, которая используется.
- Добавление G нуклеотидов перед распорку если первая позиция руководства не G. определить обратный взаимодополняющих последовательность распорку. Добавьте необходимые свесы для клонирования целей.
Примечание: Иллюстрации, для плазмид, используемых в нашей оценке исследования25, олигонуклеотиды синтезироваться показано в таблице 2. При необходимости, используйте пример, приведенный на рисунке 2 в качестве ориентира. Многие ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмид доступны из коммерческих источников (например, Addgene). Некоторые из более популярных плазмид, приведены в Таблице материалов.
- Добавление G нуклеотидов перед распорку если первая позиция руководства не G. определить обратный взаимодополняющих последовательность распорку. Добавьте необходимые свесы для клонирования целей.
| ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмиды | Последовательность |
| pSpCas9 и pSaCas9 | Смысл: 5' - CACC (G) NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN - 3' Antisense: 3' - (C) NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNCAAA - 5' |
| pNmCas9 | Смысл: 5' - CACC (G) NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN - 3' Antisense: 3' - (C) NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNCAAC - 5' |
| pAsCas12a и pLbCas12a | Смысл: 5' - AGATNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN - 3' Antisense: 3' - NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNAAAA - 5' |
Таблица 2: олигонуклеотиды, необходимых для клонирования sgRNA последовательности в ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмид, используемых в ходе недавней оценки изучить25. Свесы выделены курсивом.
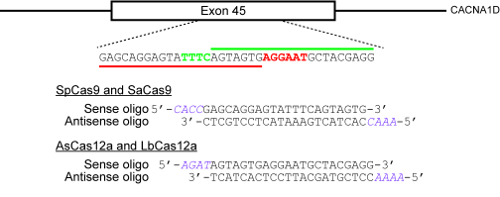
Рисунок 2 : Пример как выбрать целевые сайты и дизайн олигонуклеотиды для клонирования в ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмидов. Цель genomic Локус здесь — 45 экзона гена человека CACNA1D. Пам SpCas9 и SaCas9 являются NGG и NNGRRT соответственно и выделяются красным цветом, а PAM для AsCas12a и LbCas12a TTTN и подсвечивается зеленым цветом. Красная горизонтальная полоса показывает protospacer для SpCas9 и SaCas9, в то время как зеленая горизонтальная полоса показывает protospacer для двух Cas12a ферменты. Пожалуйста, нажмите здесь, чтобы посмотреть большую версию этой фигуры.
2. клонирование в олигонуклеотиды в вектор позвоночника
- Фосфорилировать и отжига смысл и antisense олигонуклеотидов.
- Если лиофилизированный олигонуклеотиды, Ресуспензируйте их к концентрации 100 мкм в трис Этилендиаминтетрауксусная кислота (ЭДТА) (TE буфера, смотрите Таблицу материалы) или ddH2O.
- Подготовка 10 мкл реакция смеси, содержащие 1 мкл смысл олигонуклеотида, 1 мкл антисмысловых олигонуклеотидов, 1 мкл T4 ДНК лигаза буфера (10 x), 1 мкл T4 полинуклеотид киназы (ПНК) и 6 мкл ddH2O. Mix хорошо закупорить и поместите смесь реакции в тепловой cy Клер, используя следующие параметры: 37 ° C за 30 мин., 95 ° C за 5 мин и пандус до 25 ° C на 6 ° C/мин.
- Разбавьте реакции смесь 1: 100 ddH2O (например, 2 мкл реакции микс + 198 мкл ddH2O).

Рисунок 3 : Пример ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмида. () A карта с указанием различных важных особенностей плазмиды. Здесь EF-1a промоутер диски выражение Cas9, в то время как промоутер U6 диски выражение sgRNA. Amp(R) указывает, ампициллина сопротивление гена в плазмиду. (b) последовательность «BbsI-BplI клонирования сайт» в плазмиды. Признание последовательность BbsI GAAGAC и указывается в красном, в то время как признание последовательность BplI, кляп-N5- КТК и указывается в зеленый. (c) грунты, которые могут использоваться для проверки, является ли последовательность sgRNA был успешно клонирован в плазмиду для колонии PCR. HU6_forward грунтовка обозначается фиолетовые стрелки на карте плазмида, в то время как Универсальный грунт M13R(-20) обозначается розовыми стрелками на карте плазмиды. Пожалуйста, нажмите здесь, чтобы посмотреть большую версию этой фигуры.
- Дайджест ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмида с соответствующей энзима ограничения.
Примечание: Клонирование sgRNAs обычно полагаются на Золотые ворота Ассамблеи с типом энзимов ограничения IIs. Различные ферменты могут использоваться для различных ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмид. Для pSpCas9, используйте BbsI или BplI (см. рис. 3). Для pSaCas9, pNmCas9, pAsCas12a и pLbCas12a используйте BsmBI.- Подготовка 20 мкл реакция смеси, содержащие 1 мкг вектор плазмиды циркуляр, 2 мкл буфера (10 x), 1 мкл энзима ограничения (например, BbsI, BplI или BsmBI), и ddH2O в окончательный объем 20 мкл. Инкубируйте реакции при 37 ° C для 2,5 ч.
- 1 мкл креветок щелочной фосфатазы (SAP) в реакции и инкубировать при 37 ° C для еще 30 мин.
- Утолить реакции, добавив 5 мкл 6 x ДНК загрузки красителя (см. Таблицу материалы), смесь хорошо и разрешить реакцию на 0,8% агарозном геле с 1 x буфер tris ацетат ЭДТА (ТЭ). Затем, акцизный правильные группы и приступить к гель Очистить линеаризованного вектора.
- Перевязать отожженная олигонуклеотиды в переваривается ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмиду.
- Подготовка смесь реакции 10 мкл: 50 нг линеаризованного вектора, 1 мкл разбавленного отожженная олигонуклеотиды, 1 мкл T4 ДНК лигаза буфера (10 x), 1 мкл T4 ДНК лигаза, и ddH2O в окончательный объем 10 мкл (см. Таблицу материалы). Инкубируйте реакции на 16 ° C в одночасье или при комнатной температуре в течение 2 ч.
Примечание: Чтобы ускорить процесс перевязки, используйте концентрированный T4 ДНК лигаза и инкубировать и реакция смеси при комнатной температуре в течение 15 мин (см. Таблицу материалы).
- Подготовка смесь реакции 10 мкл: 50 нг линеаризованного вектора, 1 мкл разбавленного отожженная олигонуклеотиды, 1 мкл T4 ДНК лигаза буфера (10 x), 1 мкл T4 ДНК лигаза, и ddH2O в окончательный объем 10 мкл (см. Таблицу материалы). Инкубируйте реакции на 16 ° C в одночасье или при комнатной температуре в течение 2 ч.
- Трансформировать перевязаны продуктов в химически сведущее Escherichia coli клеток (см. дополнительный файл 1). Распространять преобразованный бактериальные клетки на плите агар LB с 100 мкг/мл ампициллина.
- Выполните колонии полимеразной цепной реакции (ПЦР) для идентификации бактерий с вставкой.
- Подготовьте два комплекта стерильную ПЦР газа трубы. В набор 1 4.7 мкл ddH2O, в набор 2, 50 мкл LB отвара с соответствующим антибиотиком (например, 100 мкг/мл ампициллин).
- С наконечником стерильной пипеткой выбрать колонии от пластины, проведите его кратко в Set 1 трубку и оставлять чаевые в набор 2 трубки. Повторите для нескольких колоний, убедившись использовать различные трубы ПЦР каждый раз.
Примечание: Как правило, скрининг четыре колонии является достаточным. Однако это может варьироваться в зависимости от эффективности клонирования. - Добавьте следующие реагентов к каждой пробке набор 1 (для 10 мкл ПЦР): 5 мкл 2 x PCR мастер смеси (с загрузкой краситель, см. Таблицу материалы), 0,15 мкл смысл или antisense олигонуклеотида (100 мкм), 0,15 мкл праймера (100 мкм) ориентация ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмида вниз по течению или вверх поток sgRNA кассеты соответственно (см. рис. 3).
Примечание: Продукт PCR в идеале должна принести размер продукта приблизительно 150 bp или больше, так что любые положительные полосы не ошибаюсь как Димеры праймера. - Запустите ГКДЗ в тепловая велосипедист, используя следующие параметры: 95 ° C в течение 3 мин., 95 ° C за 30 s (шаг 2), 60 ° C за 30 s (шаг 3), 72 ° C для 30 s (шаг 4), повторите шаги 2\u20124 для еще 34 циклов, 72 ° C за 5 мин и провести на 4 ° C.
Примечание: Отжига температура 60 ° C может потребоваться быть оптимизированы для грунтовки разработаны. Удлинение времени 30 s может также варьироваться в зависимости от ожидаемого размера Ампликон ПЦР и ДНК-полимераза используется. - Разрешить реакции на геле агарозы 1% с использованием 1 x TAE буфера.
- Прививать колонии, что дает Позитив Бэнд в PCR путём перевода 50 мкл своей культуры из соответствующий набор 2 трубки в больших конических трубка, содержащая 5 мл фунтов с соответствующим антибиотиком. Пусть растут на ночь в 37 ° C шейкер инкубатор культуры.
- Изолируйте плазмиды от ночи культуры с использованием алкалический комплекта (см. Таблицу материалы) и последовательность образца с помощью колонии PCR праймер, это не смысл или antisense олигонуклеотида (hU6_forward или M13R(-20) на рис. 3).
Примечание: При необходимости, выполните maxiprep проверку последовательности ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмиды для получения большей суммы по течению экспериментов.
3. дизайн и синтез ремонт шаблонов
Примечание: Для точности инженерии генома, указав желаемые изменения ДНК шаблон необходимо предоставить вместе с ТРИФОСФАТЫ реагентов. Для небольших изменения ДНК такие изменения одного нуклеотида ssODN доноров шаблоны являются наиболее подходящим (см. раздел 3.1). Для большего изменения ДНК как вставки GFP тег 5' и 3' определенного белка кодирование гена, плазмида доноров шаблоны являются наиболее подходящим (см. раздел 3.2).
- Дизайн и синтезировать ssODN доноров шаблон (см. Рисунок 4).
- Определите, что правильный нити которого последовательности, шаблон должен следовать.
Примечание: Cas12a экспонатов предпочтение ssODNs прядь не являющихся объектом последовательности, в то время как Cas9 экспонатов предпочтение для ssODNs стренги целевой последовательности вместо25 (см. Рисунок 4). - Убедитесь, что восстановленной последовательности не ориентации по выбранной нуклеиназы Cas снова. Например мутировать Пэм таким образом, что нет никаких изменений аминокислоты или устранить PAM от доноров шаблона, если он не имеет никаких функциональных последствий. Используйте пример, приведенный на рисунке 4b как руководство, при необходимости.
- Решите, если шаблон симметричный или асимметричный доноров пожелан. Для симметричных доноров что обеспечивает каждый гомологии руку фланговые сайт модификации ДНК по меньшей мере 17 nt длиной25. Для асимметричных доноров шаблонов используйте больше оружия 5′ желаемых изменений ДНК (см. Рисунок 4). Главное, убедитесь, что короче руку около 37 nt в длину, в то время как другой рукой гомологии составляет около 77 nt в длину25,39.
- Синтезировать разработан шаблон как кусок одноцепочечной ДНК.
Примечание: Асимметричной ssODNs можно, но не всегда, демонстрируют более высокую эффективность HDR, чем симметричные ssODNs. В общем асимметричной доноров обычно выполняет по крайней мере а также симметричный доноров, когда разработаны правильно. Однако асимметричные шаблон стоит гораздо дороже, потому что это длиннее и поэтому требует очищения геля полиакриламида электрофореза (страница) или специальные синтеза процедуры. Рутинной гена нокауты обычно полагаются на путь NHEJ ремонт и ремонт шаблон не требуется. Однако, если нокаут эффективность низка, шаблон ssODN доноров, содержащий фреймшифт мутации и по крайней мере 120 nt в длину25,40.
- Определите, что правильный нити которого последовательности, шаблон должен следовать.
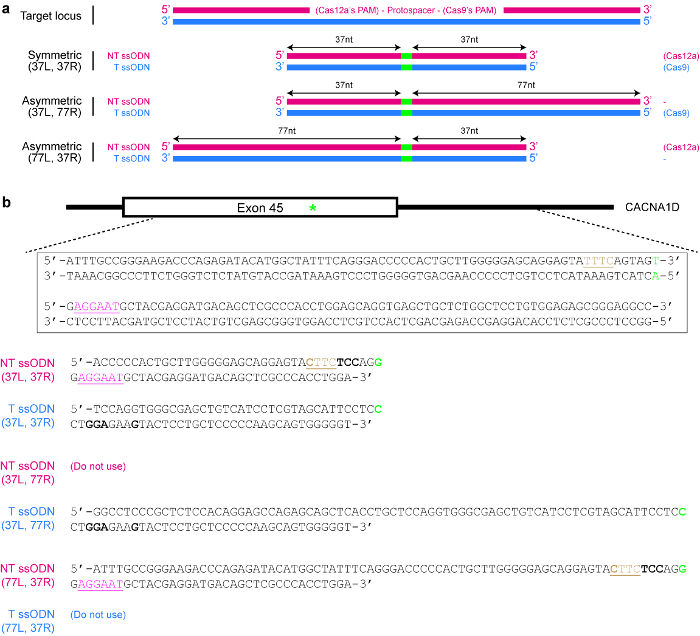
Рисунок 4 : Дизайн шаблонов доноров ssODN. () схемы, иллюстрирующие различные возможные конструкции. Красные горизонтальные прямоугольники указывают стренги непромысловых (NT), в то время как синие прямоугольники указывают стренги целевой (T). Кроме того небольшие зеленые прямоугольники показывают желаемые изменения ДНК (например единичных нуклеотидных изменений). Когда используется симметричный ssODN, минимальная длина каждого гомологии руку должно быть по меньшей мере 17 nt (но может быть больше). Для асимметричных ssODNs ssODN 37/77 T, как представляется, быть оптимальной для SpCas9-индуцированной HDR, в то время как NT ssODN 77/37, как представляется, является оптимальным для Cas12a-индуцированной HDR. L = левый гомологии руку; R = правый гомологии руку. (b) конкретный пример, чтобы продемонстрировать как ssODN шаблоны дизайна. Целевой геномной Локус вот экзона 45 CACNA1D гена человека. PAM для Cas9 розовый и подчеркнул, в то время как PAM для Cas12a коричневый и подчеркнул. Целью является создание Миссенс мутация (выделенный в зеленый) путем преобразования АГУ (кодирование Серин) для общ (кодирование аргинина). Для предотвращения повторной ориентации, Cas12a, TTTC PAM является мутировал КТТК. Обратите внимание, что нет никаких изменений в аминокислоты (СХУ и UAC, оба кода для тирозин). Для дальнейшего предотвращения, требуемой по Cas9, AGU кодон заменяется UCC кодон (жирный), оба из которых код для серина. Пожалуйста, нажмите здесь, чтобы посмотреть большую версию этой фигуры.
- Дизайн и клонировать шаблон доноров соответствующие плазмиды. Например, он может содержать последовательность GFP, обрамленная длинные руки, которые гомологических целевой геномной локус (см. Рисунок 5).
- Убедитесь, что изменение последовательности не ориентации по выбранной нуклеиназы Cas снова. Например protospacer может разделяться вставить тег (ГПУП). Кроме того PAM могут быть мутировал или удалены из доноров шаблон таким образом, что не влияет на функции гена.
- Усилить гомологии оружия от геномной ДНК с помощью ПЦР. Длина каждого гомологии рука обычно является 1000 до 1500 bp.
Примечание: Чтобы облегчить клонирование, убедитесь, что вперед грунтовка для левой гомологии руку и обратный грунтовка для правой гомологии руку каждый имеет по крайней мере 20 nt перекрывающихся последовательности с выбранного вектора позвоночника. Кроме того убедитесь, что обратный грунтовка для левой гомологии руку и вперед грунтовка для правой гомологии рука имеет некоторые перекрытия последовательности с тегом epitope также. - Клонировать две руки гомологии и тег (ГПУП) в основу вектор с помощью Гибсон Ассамблеи41 (см. Таблицу материалов). Проверьте плазмида Сэнгером виртуализации с помощью вперед и обратить вспять праймеры которые вверх и вниз по течению от доноров шаблона соответственно.
Примечание: Сэнгер последовательности дешево и широко доступны в качестве коммерческой службы. Отправьте Алиготе плазмида вместе с грунтовки последовательности к поставщику услуг. - Линеаризации доноров шаблон с энзима ограничения, что сокращение плазмида, только один раз вверх по течению от левой гомологии руку или ниже по течению от руки правой гомологии.
Примечание: Недавно, двойной cut донора, который является параллельной последовательности sgRNA Пэм и освобождается от плазмида после расщепления от соответствующего нуклеиназы Cas, было показано для увеличения эффективности HDR42. Когда sgRNA-PAM последовательности вставляются вверх и вниз по течению от левого и правого гомологии оружия соответственно (например Ассамблеей Гибсон), длина плеча гомологии может быть уменьшена до 300 bp и нет необходимости для линеаризации плазмиды.
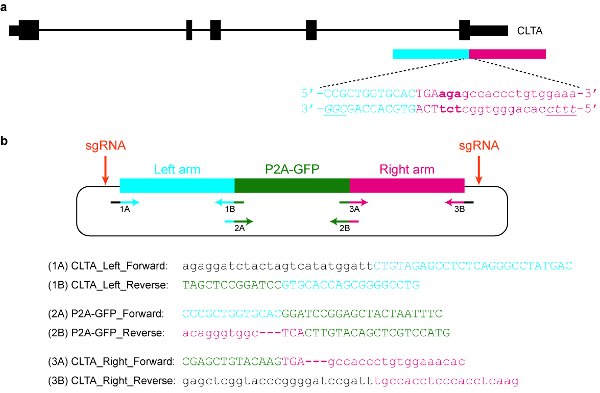
Рисунок 5 : Дизайн и клонирование плазмиды доноров шаблона. () цель в этот конкретный пример является предохранитель P2A-ГФП в C-конечная CLTA белка. Синий горизонтальный прямоугольник указывает гомологии левой руки, а красный прямоугольник горизонтальной руку правой гомологии. Прописные буквы указывать белка кодирование последовательностей, тогда как строчные буквы некодирующих последовательностей. Пам SpCas9 и Cas12a курсив и подчеркнул. (b) донором плазмида шаблон, который может использоваться для эндогенно тег P2A-ГФП в C-terminus CLTA. Предоставленный грунтовка последовательности может использоваться для клонирования плазмиды Ассамблеей Гибсон. Условия PCR заключаются в следующем: 98 ° С в течение 3 мин, 98 ° C за 30 s (шаг 2), 63 ° C за 30 s (шаг 3), 72 ° C в течение 1 мин (шаг 4), повторите шаги 2\u20124 для еще 34 циклов, 72 ° C на 3 мин и провести на 4 ° C. Черные буквы соответствуют последовательности вектор, синие буквы соответствуют руку левой гомологии, зеленый письма соответствуют P2A-GFP и красные буквы соответствуют руку правой гомологии. Обратите внимание, что после последовательности кодирования P2A-GFP успешно интегрированы в целевой локус, требуемой по SpCas9 будет невозможно, поскольку лишь 9 nt protospacer (GTGCACCAG) останутся нетронутыми. Кроме того во избежание повторного таргетинга, Cas12a, три basepairs сразу ниже по течению от остановки кодон (выделено жирным шрифтом) удаляются из последовательности плазмиды. Пожалуйста, нажмите здесь, чтобы посмотреть большую версию этой фигуры.
4. клетки Трансфекция
Примечание: Оставшиеся части протокола записываются с HEK293T клеток в виду. Культура средних используется состоит из Дульбекко изменение Eagle среднего (DMEM) дополнены глюкозы 4,5 г/Л, 10% плода бычьим сывороточным (ФБС), 2 мм L-глютамина и 0.1% пенициллина/стрептомицина. Различные этапы протокола может должны быть изменены согласно фактической клеток линии. Все клетки культуры работа в кабинете биологической безопасности II класса обеспечить стерильный рабочей среды.
- Семя 1.8 x 105 клеток в культуре ткани 24-ну пластины за один день до transfection.
- Разбить ячейки, аспирационных СМИ и затем добавив 150 мкл 0,25% трипсина-ЭДТА в колодец. Инкубируйте клетки при 37 ° C на 2 мин.
- Нейтрализовать трипсина, добавив 150 мкл (или 1 x объем) клетки культуры средств массовой информации. Суспензию клеток передавать Конические трубки. Спин вниз клетки в центрифугу скамейке Топ на 1000 x g 5 мин.
- Аспирационная супернатанта и Ресуспензируйте с 5 мл клетки культуры средств массовой информации. В отдельном пластиковых пробирок, кратные 10 мкл раствора Трипановый синий 0,4%. Затем добавьте в 10 мкл высокомобильна клеток из шага 4.1.2 и тщательно перемешать.
- Пипетка 10 мкл смеси (клетки + Трипановый синий) в Горяева. Перейти к подсчитать количество ячеек вручную или с помощью автоматизированных ячейки счетчика.
- Семя 1.8 x 105 клеток в одну скважину пластины 24-ну тканевые культуры.
- Подготовить трансфекции смеси, содержащие либо 500 нг плазмида ТРИФОСФАТЫ (для NHEJ-опосредованной редактирования) или 300 нг ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмиды и 300 нг доноров шаблон (для HDR-опосредованной редактирования), согласно инструкциям, прилагаемым к трансфекции реагента (см Таблица материалов). Инкубации при комнатной температуре в течение рекомендованного времени (обычно вокруг 10\u201220 мин).
- Добавить смесь transfection клетки в прикапывают моды, и слегка взболтать пластины после.
- Инкубировать при 37 ° C в увлажненные 5% CO2 воздуха инкубатор на 24 ч (для экспериментов на основе NHEJ) или 72 ч (для HDR-основе экспериментов).
5. флуоресценции активации клеток сортируя (FACS) transfected клеток
- Разбить ячейки, аспирационных СМИ и затем добавив 150 мкл трипсин 0.25%-ЭДТА за хорошо. Инкубируйте клетки при 37 ° C на 2 мин.
- Нейтрализовать трипсина, добавив 150 мкл (или 1 x объем) клетки культуры средств массовой информации. Суспензию клеток передавать пластиковых пробирок. Спин вниз клетки в microcentrifuge на 235 x g за 5 мин.
- Аспирационная супернатант и Ресуспензируйте клетки с 2% плода бычьим сывороточным (ФБС) в фосфат амортизированное saline (PBS). Фильтр клетки через сетку 30 мкм или ячейки фильтра в трубке 5 мл СУИМ.
- Подготовить еще один пластиковых пробирок с приблизительно 100 мкл культуры средств массовой информации или 2% FBS в PBS для сбора клеток.
- На проточный цитометр ворота клетки с не transfected клеток как отрицательный контроль. Сортировка и сбор transfected клеток, согласно которой флуоресценции маркер на ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмида используется. Например если плазмида несет ген mCherry, сортировка для ЗП положительных клеток.
Примечание: Различные ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмиды будет иметь различные выбираемые маркеры. Набор плазмид (pSpCas9, pSaCas9, pNmCas9, pAsCpf1 и pLbCpf1), используемые в данном исследовании оценки носить оранжевый флуоресцентный белок (ОФП) или гена mCherry.
6. расширение индивидуальных клонов
- Центрифуга для сортировки клеток в скамейке Топ центрифуги на максимальной скорости (18 000 x g) для 5 минут аспирата супернатант и Ресуспензируйте лепешка с 300 мкл культуры средств массовой информации. Семя 200 мкл клетки в культуре ткани 24-ну пластины и пусть они восстановить за несколько дней в инкубаторе 37 ° C. Сохранить оставшиеся 100 мкл клетки для раздела 7.
- После того, как клетки начинают становится вырожденная, проход их согласно 4.1.1\u20124.1.3 шаги. Семя клетки негусто в 100 мм тканевой культуры блюдо Обеспечьте достаточное пространство для отдельных колоний расти. Инкубировать при 37 ° C в увлажненные 5% CO2 воздуха инкубатора.
Примечание: Попробуйте различных разведениях. Отдельные ячейки должны достаточное пространство для роста как отдельных колоний. Однако, они также не может быть слишком мало, как некоторые линии клетки не растут хорошо, когда количество ячеек слишком мало. - Как только колониях начинает форме, забрать их под микроскопом (с 4-кратным увеличением) и поместите каждый клон в отдельных также 24-ну плиты, содержащий ячейку культуры средств массовой информации. Инкубировать при 37 ° C в увлажненные 5% CO2 инкубатора воздуха до тех пор, пока клетки становятся вырожденная.
Примечание: Альтернативой серийных разведений и собирание колонии является использование проточной цитометрии для сортировки для одиночных клеток в 96-луночных плиту. Однако это может не работать для некоторых клеточных линий, которые не растут хорошо, когда присутствует только одна ячейка.
7. Оценка эффективности редактирования
- Экстракт геномной ДНК центрифугированием оставшиеся 100 мкл сортировка клеток (от шага 6.1) в центрифугу Топ скамейке на максимальной скорости (18 000 x g) для 5 минут аспирата супернатант и приступить к изолировать genomic дна с помощью извлечения kit (см. таблицы Материалы).
- Выполните T7 эндонуклеазы I (T7EI) расщепления пробы (см. рис. 6).
- Настройка 50 мкл ПЦР, содержащие 10 мкл ПЦР реакции буфера (5 x), 1 мкл dNTP смеси (10 мм), 2,5 мкл определяемые пользователем вперед праймера (10 мкм), 2,5 мкл определяемые пользователем обратный праймера (10 мкм), 0.5 мкл ДНК-полимеразы, 2\u20125 мкл геномной ДНК шаблона (в зависимости от того, сколько ячеек были отсортированы), затем сверху до 50 мкл с ddH2O (см. Таблицу материалы).
Примечание: Праймеры предназначены для фланка целевой геномной Локус и доходность, которую продукт PCR вокруг 400\u2012700 bp. обычно одна грунтовка позиционируется ближе к месту отрезока Cas фермента, чем грунт, так что результат T7EI assay два отдельных полос на ag возник гель (см. рис. 6). - Запустите ПЦР в тепловая велосипедист со следующими параметрами: 98 ° С в течение 3 мин, 98 ° C за 30 s (шаг 2), 63 ° C за 30 s (шаг 3), 72 ° C для 30 s (шаг 4), повторите шаги 2\u20124 для еще 34 циклов, 72 ° C на 2 мин и провести на 4 ° C.
- Разрешить реакции на 2% агарозном геле с использованием 1 x TAE буфера.
- Акцизный продукт PCR от геля с чистым, резким скальпелем и очистить ДНК, используя набор для извлечения геля, согласно инструкциям производителя. Измерить концентрацию ПЦР продукта, используя спектрофотометр на длине волны поглощения 260 Нм (см. Таблицу материалы).
- Подготовка анализа смеси, содержащие 200 ng ДНК, 2 мкл T7EI реакции буфера (10 x) и превысила до 19 мкл с ddH2O (см. Таблицу материалы).
- Повторно отжига продукт PCR в тепловая велосипедист, используя следующие параметры: 95 ° C за 5 мин, рампы до 25 ° C на 6 ° C/мин, затем провести на 4 ° C.
- Добавить 5 U T7EI повторно отожженная продукт PCR, смешайте хорошо закупорить и инкубировать при 37 ° C 50 мин.
- Разрешения T7EI-переваривается ДНК на 2,5% агарозном геле с использованием 1 x TAE буфера.
- Изображение гель, количественную оценку интенсивности группы, используя ImageJ и рассчитать скорость indel образования с использованием следующей формулы:
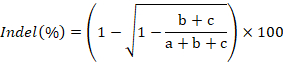
где представляет интенсивность неповрежденной продукта PCR и b и c соответствуют интенсивность расщепления продуктов43.- Для количественного определения интенсивности полосы в ImageJ, сначала нарисуйте прямоугольник вокруг группы как вблизи ее границы как можно. Во-вторых нажмите на анализ , а затем Задать измерения. Убедитесь, что проверяются параметры области, означает значение серогои комплексной плотности . Закройте окно настроек, нажав кнопку ОК. В-третьих нажмите на анализ , а затем меру. Среднее или RawIntDen значение используется как группа интенсивности.
- Настройка 50 мкл ПЦР, содержащие 10 мкл ПЦР реакции буфера (5 x), 1 мкл dNTP смеси (10 мм), 2,5 мкл определяемые пользователем вперед праймера (10 мкм), 2,5 мкл определяемые пользователем обратный праймера (10 мкм), 0.5 мкл ДНК-полимеразы, 2\u20125 мкл геномной ДНК шаблона (в зависимости от того, сколько ячеек были отсортированы), затем сверху до 50 мкл с ddH2O (см. Таблицу материалы).
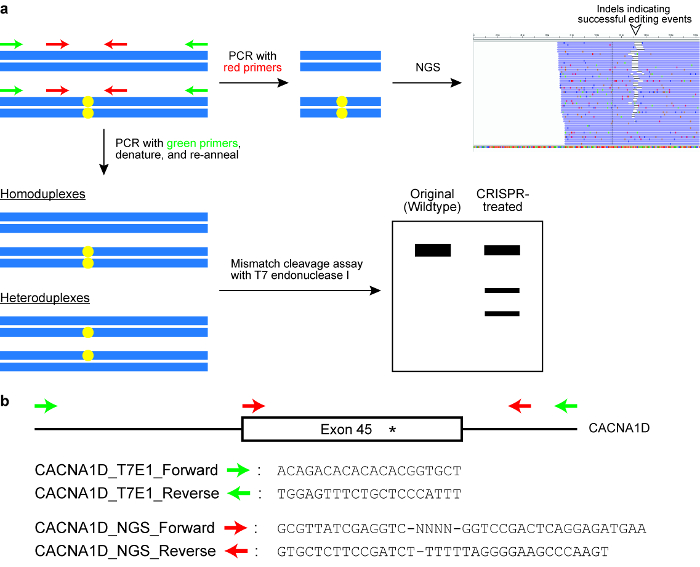
Рисунок 6 : Проверка клетки для редактирования результатов успешного генома. () A схема, иллюстрирующая два часто используемых анализов, а именно несоответствие расщепления пробирного с T7 эндонуклеазы я фермента (T7EI) и следующего поколения последовательности (НГС) или целевых ампликон последовательности. Синие горизонтальные прямоугольники указывают, что ДНК и желтые круги показывают изменения, вызванные системе ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas. Праймеры для T7E1 assay обозначены зеленым цветом, в то время как праймеры для генерации ампликонов для NGS обозначаются красным цветом. (b) дизайн праймера последовательности для assay расщепление T7EI и NGS. Целевой геномной Локус вот экзона 45 CACNA1D гена человека. На сайте предполагаемого изменения обозначается звездочкой. Пожалуйста, нажмите здесь, чтобы посмотреть большую версию этой фигуры.
- Выполнение целевых ампликон последовательности (см. рис. 6).
- Праймеры PCR дизайн для усиления целевой геномной Локус. Позиция одной из грунтовки до менее чем 100 bp, но более чем 20 bp от protospacer.
Примечание: Как правило, общий размер продукта PCR предназначен для быть вокруг 150\u2012300 bp (см. рис. 6). - Добавить дополнительные последовательности праймеры следующим образом: (a) 5' \u2012GCGTTATCGAGGTC - NNNN-[вперед грунт] – 3'; (b) 5' - GTGCTCTTCCGATCT-[обратный грунт] – 3».
- Настройка 50 мкл смесь ПЦР реакции, содержащие 10 мкл буфера реакции PCR (5 x), 1 мкл dNTP (10 мм), 5 мкл праймера (10 мкм), 5 мкл грунтовка б (10 мкм), 0.5 мкл ДНК-полимеразы, 2\u20125 мкл геномной ДНК шаблон (в зависимости от того, сколько клеток были отсортированы) , затем сверху до 50 мкл с ddH20.
- Запустите ПЦР в тепловая велосипедист со следующими параметрами: 98 ° С в течение 3 мин, 98 ° C за 30 s (шаг 2), 63 ° C за 30 s (шаг 3), 72 ° C для 15 s (шаг 4), повторите шаги 2\u20124 для еще 34 циклов, 72 ° C на 2 мин и провести на 4 ° C.
- Разрешить реакции на 2% агарозном геле и очистить продукт PCR, используя набор извлечения геля согласно инструкциям производителя. Количественного определения ДНК, используя спектрофотометр на длине волны поглощения 260 Нм (см. Таблицу материалов).
- Синтезировать следующий раунд 2 праймеры PCR: (c) 5' \u2012 AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACCCTACACGAGCGTTATCGAGGTC-3'; (d) 5' \u2012CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGAT-[штрих] - GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCT-3'
- Настройка реакции PCR 20 мкл смешать содержащий 4 мкл 0.4 мкл dNTP (10 мм), 2 мкл грунтовка c (10 мкм), 2 мкл грунтовка d (10 мкм), 0,2 мкл ДНК-полимеразы, 2 мкл шаблона дна (от шага 7.3.5 ПЦР реакции буфера (5 x), разбавленный масштаба 1: 100) и 9,4 мкл ddH2O.
Примечание: Коэффициент разрежения для шаблона ДНК может варьироваться в зависимости от его оригинальной концентрации. Если концентрация вокруг 20\u201240 нг/мкл, используйте коэффициент разбавления 1: 100. Кроме того, выбрать различные штрих-кодов для каждого экспериментального образца, если же грунт и грунтовка б в шаге 7.3.3. - Запустите ПЦР в тепловая велосипедист со следующими параметрами: 98 ° С в течение 3 мин, 98 ° C за 30 s (шаг 2), 65 ° C для 30 s (шаг 3), 72 ° C для 30 s (шаг 4), повторите шаги 2\u20124 для еще 14 циклов, 72 ° C на 2 мин и удерживайте 4 ° C.
- Разрешить 5 мкл каждой реакции на 2% агарозном геле для определения успеха комбайна ГКДЗ. все образцы вместе (предполагая, что различные штрих-код был использован для каждого образца) и очистка пула ДНК, используя комплект для очистки ПЦР по данным производителя инструкции. Если некоторые из ГКДЗ exhibit более чем одной группы (указывающих на наличие неспецифичные продукты), выполните шаг извлечения дополнительных геля.
- Последовательность в библиотеку на инструмент виртуализации высокой пропускной способности (см. Таблицу материалы) согласно инструкциям изготовителя производить парных 151 bp читает. Грунтовка последовательности чтения 1 специально и предоставляться отдельно. Его последовательность является следующим: Read1_seq: 5'-CCACCGAGATCTACACCCTACACGAGCGTTATCGAGGTC-3'. Читать 2 Последовательность праймера и индекс последовательности грунтовка являются стандартными и предоставляются в картридже реагента.
Примечание: T7EI пробирного и целевых ампликон последовательности обычно используются для проверки эффективности изменения генома. Однако другие эксперименты могут проводиться для оценки эффективности редактирования, в зависимости от типа ДНК внесенные. Например если ограничение сайт создается на целевом сайте, пробирного полиморфизма (фрагментов ПДРФ) длина фрагмента ограничение может выполняться. Это похоже на T7EI assay, за исключением того, что эндонуклеазы ограничения используется вместо переваривать продукт PCR.
- Праймеры PCR дизайн для усиления целевой геномной Локус. Позиция одной из грунтовки до менее чем 100 bp, но более чем 20 bp от protospacer.
8. Проверка отдельных клонов
- С шагом 6.3 разбить ячейки после того, как они начинают получать вырожденная. Для каждого индивидуального клон собрать оставшиеся ячейки и извлечь геномной ДНК согласно шаг 7.1.
- Выполните T7EI assay для всех индивидуальных клонов согласно статье 7.2, за исключением одной модификации. Усилить целевой геномной Локус от wildtype клеток и в шаге 7.2.5, вместо 200 нг теста ДНК только, смесь 100 нг теста ДНК с 100 нг wildtype ДНК.
Примечание: Изменение шага причина что некоторые клоны могут прошли успешные biallelic преобразования и гомозиготных мутанты. В таких случаях будет не расщепления полос в T7EI assay если wildtype ДНК не смешивается. - Последовательность целевого сайта в клоны, которые демонстрируют расщепления полосы в T7EI assay.
- Усиливают изменение геномной Локус согласно 7.2.1–7.2.4 шаги.
- Настройка следующих клонирования реакции: 4 мкл продукт PCR, 1 мкл раствора соли, 1 мкл TOPO вектора (см. Таблицу материалов).
- Осторожно перемешать, закупорить и инкубации при комнатной температуре по крайней мере 5 минут.
- Преобразование 3 мкл реакция смеси в химически сведущее Escherichia coli клетки (например, TOP10 или Stbl3) (см. дополнительный файл 1). Распространять преобразованный бактериальные клетки на плите агар LB с 50 мкг/мл канамицин.
- Следующий день, прививок по крайней мере 10 колоний в LB жидких сред, содержащих 50 мкг/мл канамицин.
- При бактериальных культур мутная, изолировать плазмид, используя алкалический комплекта (см. Таблицу материалы) и последовательность их с помощью стандартных M13 вперед или обратный грунтовка M13.
- Выполните западную помарку (также известный как иммуноблот) чтобы определить отсутствие или наличие целевого белка (если генома, редактирования эксперимент предполагает, выбив через фреймшифт мутации гена, белок кодирование). Смотрите Дополнительные файл 1.
Примечание: Другие эксперименты могут выполняться для выявления клонов, перевозящих геномной желаемые изменения. Например фенотипического анализа может производиться, если стучать вне определенного гена, как известно, вызывают определенные изменения в клеточных поведение.
Результаты
Для выполнения генома редактирования эксперимент, ТРИФОСФАТЫ плазмида, выражая sgRNA ориентации, локус интерес должен быть клонированы. Во-первых плазмида переваривается с энзима ограничения (обычно типа IIs фермент) для линеаризации его. Рекомендуется для устранения переваривается прод...
Обсуждение
Система ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas является мощным, революционная технология для инженер геномов и transcriptomes растений и животных. Содержат ТРИФОСФАТЫ-Cas систем, которые потенциально могут быть адаптированы для генома и транскриптом инженерных целей44были найдены многочисленные виды бак...
Раскрытие информации
Авторы не имеют конкурирующих финансовых интересов.
Благодарности
M.H.T. поддерживается агентства грант для Объединенного бюро Совета науки, технологий и научных исследований (1431AFG103), Национальный совет медицинских исследований Грант (OFIRG/0017/2016), Национальный исследовательский фонд предоставляет (NRF2013-THE001-046 и NRF2013-THE001-093), Министерство образования Tier 1 Грант (RG50/17 (S)), запуска грант от Nanyang технологический университет и фондов для генетически Инженерная машина (МПСЭ) международного конкурса от Nanyang технологический университет.
Материалы
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| T4 Polynucleotide Kinase (PNK) | NEB | M0201 | |
| Shrimp Alkaline Phosphatase (rSAP) | NEB | M0371 | |
| Tris-Acetate-EDTA (TAE) Buffer, 50X | 1st Base | BUF-3000-50X4L | Dilute to 1X before use. The 1X solution contains 40 mM Tris, 20 mM acetic acid, and 1 mM EDTA. |
| Tris-EDTA (TE) Buffer, 10X | 1st Base | BUF-3020-10X4L | Dilute to 1X before use. The 1X solution contains 10 mM Tris (pH 8.0) and 1 mM EDTA. |
| BbsI | NEB | R0539 | |
| BsmBI | NEB | R0580 | |
| T4 DNA Ligase | NEB | M0202 | 400,000 units/ml |
| Quick Ligation Kit | NEB | M2200 | An alternative to T4 DNA Ligase. |
| Rapid DNA Ligation Kit | Thermo Scientific | K1423 | An alternative to T4 DNA Ligase. |
| Zero Blunt TOPO PCR Cloning Kit | Thermo Scientific | 451245 | The salt solution comes with the TOPO vector in the kit. |
| NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix | NEB | E2621L | Kit for Gibson assembly. |
| One Shot Stbl3 Chemically Competent E.Coli | Thermo Scientific | C737303 | |
| LB Broth (Lennox), powder | Sigma Aldrich | L3022 | Reconstitute in ddH20, and autoclave before use |
| LB Broth with Agar (Lennox), powder | Sigma Aldrich | L2897 | Reconstitute in ddH20, and autoclave before use |
| SOC media | - | - | 2.5 mM KCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 20 mM glucose in 1 L of LB Broth |
| Ampicillin (Sodium), USP Grade | Gold Biotechnology | A-301 | |
| REDiant 2X PCR Mastermix | 1st Base | BIO-5185 | |
| Agarose | 1st Base | BIO-1000 | |
| T7 Endonuclease I | NEB | M0302 | |
| Plasmid DNA Extraction Miniprep Kit | Favorgen | FAPDE 300 | |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), High Glucose | Hyclone | SH30081.01 | 4.5 g/L Glucose, no L-glutamine, HEPES and Sodium Pyruvate |
| L-Glutamine, 200mM | Gibco | 25030 | |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin, 10, 000U/mL | Gibco | 15140 | |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA, 1X | Gibco | 25200 | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Hyclone | SV30160 | FBS is heat inactivated before use at 56 oC for 30 min |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline, 1X | Gibco | 20012 | |
| jetPRIME transfection reagent | Polyplus Transfection | 114-75 | |
| QuickExtract DNA Extraction Solution, 1.0 | Epicentre | LUCG-QE09050 | |
| ISOLATE II Genomic DNA Kit | Bioline | BIO-52067 | An alternative to QuickExtract |
| Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase | NEB | M0491 | |
| Deoxynucleotide (dNTP) Solution Mix | NEB | N0447 | |
| 6X DNA Loading Dye | Thermo Scientific | R0611 | 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) 0.03% bromophenol blue, 0.03% xylene cyanol FF, 60% glycerol, 60 mM EDTA |
| Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Set3 | Merck | 539134 | |
| Nitrocellulose membrane, 0.2µm | Bio-Rad | 1620112 | |
| Tris-glycine-SDS buffer, 10X | Bio-Rad | 1610772 | Dilute to 1X before use. The 1x solution contains 25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, and 0.1% SDS. |
| Tris-glycine buffer, 10X | 1st base | BUF-2020 | Dilute to 1X before use. The 1x solution contains 25 mM Tris and 192 mM glycine. |
| Ponceau S solution | Sigma Aldrich | P7170 | |
| TBS, 20X | 1st base | BUF-3030 | Dilute to 1X before use. The 1x solution contains 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) and 150 mM NaCl. |
| Tween 20 | Sigma Aldrich | P9416 | |
| Skim Milk for immunoassay | Nacalai Tesque | 31149-75 | |
| WesternBright Sirius-femtogram HRP | Advansta | K12043 | |
| Antibody for β-actin (C4) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-47778 | Lot number: C0916 |
| MiSeq system | Illumina | SY-410-1003 | |
| NanoDrop spectrophotometer | Thermo Scientific | ND-2000 | |
| Qubit fluorometer | Thermo Scientific | Q33226 | |
| EVOS FL Cell Imaging System | Thermo Scientific | AMF4300 | |
| CRISPR plasmid: pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP (PX458) | Addgene | 48138 | Single vector system: The gRNA is expressed from the same plasmid. |
| CRISPR plasmid: pX601-AAV-CMV::NLS-SaCas9-NLS-3xHA-bGHpA | Addgene | 61591 | Single vector system: The gRNA is expressed from the same plasmid. |
| CRISPR plasmid: xCas9 3.7 | Addgene | 108379 | Dual vector system: The gRNA is expressed from a different plasmid. |
| CRISPR plasmid: pX330-U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 | Addgene | 42230 | Single vector system: The gRNA is expressed from the same plasmid. |
| CRISPR plasmid: hCas9 | Addgene | 41815 | Dual vector system: The gRNA is expressed from a different plasmid. |
| CRISPR plasmid: eSpCas9(1.1) | Addgene | 71814 | Single vector system: The gRNA is expressed from the same plasmid. |
| CRISPR plasmid: VP12 (SpCas9-HF1) | Addgene | 72247 | Dual vector system: The gRNA is expressed from a different plasmid. |
Ссылки
- Epinat, J. C., et al. A novel engineered meganuclease induces homologous recombination in yeast and mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Research. 31 (11), 2952-2962 (2003).
- Arnould, S., et al. Engineered I-CreI derivatives cleaving sequences from the human XPC gene can induce highly efficient gene correction in mammalian cells. Journal of Molecular Biology. 371 (1), 49-65 (2007).
- Chapdelaine, P., Pichavant, C., Rousseau, J., Paques, F., Tremblay, J. P. Meganucleases can restore the reading frame of a mutated dystrophin. Gene Therapy. 17 (7), 846-858 (2010).
- Carroll, D. Genome engineering with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics. 188 (4), 773-782 (2011).
- Urnov, F. D., Rebar, E. J., Holmes, M. C., Zhang, H. S., Gregory, P. D. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nature Reviews Genetics. 11 (9), 636-646 (2010).
- Miller, J. C., et al. A TALE nuclease architecture for efficient genome editing. Nature Biotechnology. 29 (2), 143-148 (2011).
- Zhang, F., et al. Efficient construction of sequence-specific TAL effectors for modulating mammalian transcription. Nature Biotechnology. 29 (2), 149-153 (2011).
- Boch, J., et al. Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science. 326 (5959), 1509-1512 (2009).
- Moscou, M. J., Bogdanove, A. J. A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors. Science. 326 (5959), 1501 (2009).
- Hsu, P. D., Lander, E. S., Zhang, F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell. 157 (6), 1262-1278 (2014).
- Sander, J. D., Joung, J. K. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nature Biotechnology. 32 (4), 347-355 (2014).
- Jinek, M., et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science. 337 (6096), 816-821 (2012).
- Nishimasu, H., et al. Crystal structure of Cas9 in complex with guide RNA and target DNA. Cell. 156 (5), 935-949 (2014).
- Yamano, T., et al. Crystal Structure of Cpf1 in Complex with Guide RNA and Target DNA. Cell. 165 (4), 949-962 (2016).
- Swarts, D. C., Mosterd, C., van Passel, M. W., Brouns, S. J. CRISPR interference directs strand specific spacer acquisition. PLoS One. 7 (4), e35888 (2012).
- Zetsche, B., et al. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system. Cell. 163 (3), 759-771 (2015).
- Sternberg, S. H., Redding, S., Jinek, M., Greene, E. C., Doudna, J. A. DNA interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9. Nature. 507 (7490), 62-67 (2014).
- Hu, J. H., et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity. Nature. 556 (7699), 57-63 (2018).
- Kleinstiver, B. P., et al. Broadening the targeting range of Staphylococcus aureus CRISPR-Cas9 by modifying PAM recognition. Nature Biotechnology. 33 (12), 1293-1298 (2015).
- Kleinstiver, B. P., et al. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with altered PAM specificities. Nature. 523 (7561), 481-485 (2015).
- Cong, L., et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science. 339 (6121), 819-823 (2013).
- Mali, P., et al. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science. 339 (6121), 823-826 (2013).
- Jinek, M., et al. RNA-programmed genome editing in human cells. Elife. 2, e00471 (2013).
- Cho, S. W., Kim, S., Kim, J. M., Kim, J. S. Targeted genome engineering in human cells with the Cas9 RNA-guided endonuclease. Nature Biotechnology. 31 (3), 230-232 (2013).
- Wang, Y., et al. Systematic evaluation of CRISPR-Cas systems reveals design principles for genome editing in human cells. Genome Biology. 19 (1), 62 (2018).
- Ran, F. A., et al. In vivo genome editing using Staphylococcus aureus Cas9. Nature. 520 (7546), 186-191 (2015).
- Hou, Z., et al. Efficient genome engineering in human pluripotent stem cells using Cas9 from Neisseria meningitidis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A. 110 (39), 15644-15649 (2013).
- Kim, E., et al. In vivo genome editing with a small Cas9 orthologue derived from Campylobacter jejuni. Nature Communications. 8, 14500 (2017).
- Edraki, A., et al. A Compact, High-Accuracy Cas9 with a Dinucleotide PAM for In Vivo Genome Editing. Molecular Cell. , (2018).
- Chatterjee, P., Jakimo, N., Jacobson, J. M. Minimal PAM specificity of a highly similar SpCas9 ortholog. Science Advances. 4 (10), (2018).
- Muller, M., et al. Streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR-Cas9 Systems Enable Specific Editing of the Human Genome. Mol Therapy. 24 (3), 636-644 (2016).
- Esvelt, K. M., et al. Orthogonal Cas9 proteins for RNA-guided gene regulation and editing. Nature Methods. 10 (11), 1116-1121 (2013).
- Boratyn, G. M., et al. BLAST: a more efficient report with usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Research. 41 (Web Server issue), W29-W33 (2013).
- Hsu, P. D., et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nature Biotechnology. 31 (9), 827-832 (2013).
- Montague, T. G., Cruz, J. M., Gagnon, J. A., Church, G. M., Valen, E. CHOPCHOP: a CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN web tool for genome editing. Nucleic Acids Research. 42 (Web Server issue), W401-W407 (2014).
- Heigwer, F., Kerr, G., Boutros, M. E-CRISP: fast CRISPR target site identification. Nature Methods. 11 (2), 122-123 (2014).
- Haeussler, M., et al. Evaluation of off-target and on-target scoring algorithms and integration into the guide RNA selection tool CRISPOR. Genome Biology. 17 (1), 148 (2016).
- Bae, S., Park, J., Kim, J. S. Cas-OFFinder: a fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off-target sites of Cas9 RNA-guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics. 30 (10), 1473-1475 (2014).
- Richardson, C. D., Ray, G. J., DeWitt, M. A., Curie, G. L., Corn, J. E. Enhancing homology-directed genome editing by catalytically active and inactive CRISPR-Cas9 using asymmetric donor DNA. Nature Biotechnology. 34 (3), 339-344 (2016).
- Richardson, C. D., Ray, G. J., Bray, N. L., Corn, J. E. Non-homologous DNA increases gene disruption efficiency by altering DNA repair outcomes. Nature Communications. 7, 12463 (2016).
- Gibson, D. G., et al. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nature Methods. 6 (5), 343-345 (2009).
- Zhang, J. P., et al. Efficient precise knockin with a double cut HDR donor after CRISPR/Cas9-mediated double-stranded DNA cleavage. Genome Biology. 18 (1), 35 (2017).
- Ran, F. A., et al. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nature Protocols. 8 (11), 2281-2308 (2013).
- Shmakov, S., et al. Diversity and evolution of class 2 CRISPR-Cas systems. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 15 (3), 169-182 (2017).
- Moreno-Mateos, M. A., et al. CRISPR-Cpf1 mediates efficient homology-directed repair and temperature-controlled genome editing. Nature Communications. 8 (1), 2024 (2017).
- Lin, S., Staahl, B. T., Alla, R. K., Doudna, J. A. Enhanced homology-directed human genome engineering by controlled timing of CRISPR/Cas9 delivery. Elife. 3, e04766 (2014).
- Yang, L., et al. Optimization of scarless human stem cell genome editing. Nucleic Acids Research. 41 (19), 9049-9061 (2013).
- Watanabe, K., et al. A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nature Biotechnology. 25 (6), 681-686 (2007).
Перепечатки и разрешения
Запросить разрешение на использование текста или рисунков этого JoVE статьи
Запросить разрешениеThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Авторские права © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Все права защищены