A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Assay for Neural Induction in the Chick Embryo
In This Article
Summary
Neural induction is the first step in the formation of the brain. It is a mechanism by which Hensen's node (organizer), instructs adjacent tissue to adopt a neural fate, i.e. to give rise to the nervous system. This video demonstrates an assay for neural induction in chick embryo.
Abstract
Protocol
I. Schematic Overview:

This video demonstrates the different steps in assay for neural induction in chick embryo. First, the host embryo is explanted in New culture [NI1]. Then, the donnor embryo is explanted in saline and Hensen’s node (the “organizer” in chick) is labelled with fluorescent dye DiI [NI2]. Hensen’s node is excised from the donnor embryo [NI3] and transplanted to the host embryo [NI4, NI5]. The host embryo is then cultured for up to 22 hrs, after which period the donnor tissue has induced an ectopic axis in the host area opaca [NI6]. Following culture, the host embryo is fixed and processed for photooxidation in the presence of DAB: By this chemical reaction, donnor derived cells, which appear red under FITC fluorescence prior to photooxidation [NI7], become brown following reaction with DAB [NI8]. The embryo is then processed for in situ hybridization with a neural marker [NI8]; host derived tissue has formed neural tissue in the presence of the donnor graft. This tissue appears blue.
1: Preparing the host embryo for New culture
- This neural induction assay protocol begins with eggs that have been incubated to Hamburger & Hamilton stage 3+ (or HH3+). These eggs have been incubated laid on their side in a humid incubator for 13 hours.
- Prepare the host embryo for New culture (steps 3.1. to 5.59).
- Cover the surface of the host embryo with 200 μl saline. This will facilitate later transfer and positioning of the donnor graft.
- Finally, cover the assembly with an inverted Falcon 35 mm culture dish.
2: Explanting the donnor embryo in saline
- Open the egg by tapping on the shell with forceps and removing pieces of the shell, all around the shell. Remove top of shell and discard.
- Remove the thick albumin with forceps, and tilt the yolk sac with coarse forceps so that the embryo faces upwards.
- Using fine scissors, cut a square of yolk sac around the embryo. Remove the embryo from the yolk with a spoon, and place in a dish containing PBS.
- Using forceps, detach the donnor embryo from area pellucida.
- Transfer donnor embryo to a Sylgard covered dish containing PBS.
3: Labeling, excising and transplanting the donnor graft
- Using an microelectrode puller, pull 50 μl glass microcapillary pipettes. Under the microscope, cut the tip of the micropipette using fine forceps. Place micropipette in a petri dish lined with a ribbon of plasteline.
- Prepare the dye solution which will be used to label the graft prior to transplantation: carbocyanine dye DiI (1,1’-dioctadecyl-3,3,3’,3’-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate): First, prepare a stock of DiI in 1ml absolute ethanol at 0.5%. This stock can be stored at -20C in dark. In a water bath set at 42°C, mix prewarmed 40 μl DiI stock to 360μl 0.3M sucrose. The water bath temperature is necessary in order to prevent precipitation of DiI and formation of insoluble crystals. Briefly spin the solution on a mini spectrafuge (for 5-10 seconds). The DiI solution is now ready to use.
- Using insect pins, secure the donnor embryo on the bottom of the Sylgard covered dish.
- Back-fill the micropipette with DiI. By applying gentle pressure using an aspirator tube assembly, apply a small bolus of DiI to Hensen’s node. Make sure the entire Hensen’s node is labelled.
- Using a microcapillary pipette or a microdissecting knife, cut Hensen’s node (“organizer”, donnor graft).
- Mark the ventral side and posterior end of the graft with carmine. This will ensure that the graft is positioned with proper dorso-ventral orientation in step 4.3.
- Using a 200μl Gilson pipette, transfer the graft to the host embryo.
4: Securing the graft and culturing the host embryo
- Remove saline from host embryo, making sure the graft remains positioned in close proximity with host site.
- Using a microcapillary pipette or a microdissecting knife, make a small incision (80-100μm) in the area pellucida/area opaca boundary region, at the level of Hensen’s node of host embryo.
- Using a microcapillary pipette or a microdissecting knife, position the graft so that ventral side faces towards you and the posterior end is parallel to equivalent region in host embryo.
- Remove remaining saline, and process the host embryo for New culture for 81-22 hr (steps 6.1 to 6.69).
- The host embryo is then fixed overnight at 4°C (steps 7.1 to 7.79).
5: Photooxidise the graft under fluorescence
- Under fume hood, prepare a DAB working solution in Tris buffer: Dissolve DAB substrate (3,3’-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride) in Tris buffer (100mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4) at 500μg/ml; keep solution in dark, on ice.
- Wash the embryo twice in PBS for 5 mn each and once in Tris buffer for 5 mn.
- Transfer the embryo to a glass cavity slide containing 1 ml Tris buffer.
- Replace the Tris buffer solution with 1.5 ml DAB solution. Dispose of Eppendorf tip in bucket containing a 10% bleach solution in order to decontaminate DAB. Place a coverslip on top of cavity slide.
- Under FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate) fluorescence, focus the objective of the microscope on the graft (donnor cells will appear fluorescent red) and expose to FITC fluorescence until all fluorescent red cells have become brown (this happens as a result of the DiI fluorochrome being photoconverted to insoluble brown crystals, by exposure to FITC excitation wavelength (488nm) in the presence of DAB. This process takes between 20 mn and 2 hours.
- Following completion of the photooxidation reaction, remove the coverslip using fine forceps. Transfer embryo to glass a 20 ml scintillation vial containing PBTw (or PBS with 0.1% Tween-20).
- Deactivate DAB from coverslip and glass cavity slide by incubating in 10% bleach solution.
6: Process the embryo for in situ hybridization, photography and sectioning
- Proceed with in situ hybridization (steps 3.7 to 6.59), incubating the embryo for only DIG labelled probe.
- Proceed with photographing (step 8.2 9) and sectioning (steps 8.3 and 8.49).
Representative Results
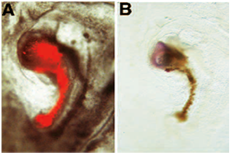
In the following example of neural induction assay, the donnor graft is shown induce the expression of the neural marker Tailless from host derived tissue. In this particular example, we assessed the acquisition of neural inducing ability of embryonic regions which normally do not have “organizer” abilities: the donnor graft originates from an embryo in which the “organizer” region has been surgically removed from the donnor embryo at stage 3+. Following ablation, the donnor embryo is allowed to develop in New culture, until the hole has healed and a structure resembling Hensen’s node has formed. This structure is then labelled with DiI, excised from the donnor embryo and grafted to area pellucida/area opaca boundary of a host embryo. Following New culture, a miniature axis is formed adjacent to the host embryo: this miniature axis consists of a rod of red cells (donnor derived) and a head-like structure (host derived): In (A), donnor-derived DiI labelled cells are shown prior to fixation under FITC fluorescence microscopy. These donnor-derived cells have proliferated to form a miniature notochord, which appears as rod of red cells. (B) Following photoconversion of DiI, these donnor-derived cells appear brown. The donnor graft has induced the formation of neural tissue from the host: this tissue consists of precursors for brain, as revealed by their expression for the marker Tailless following in situ hybridization [reprinted from 6].
Note: In this procedure, we have used DiI labelled cells in order to differentiate neural inducing donnor tissue (red/brown) from host derived “neural” tissue (blue). Instead of using a chick derived, DiI labelled donnor graft, some authors also use donnor tissue derived from quail embryos instead of chick [e.g. 6]. This alternative method also allows to differentiate donnor from host tissue. In this case, the graft (donnor tissue) originates from quail eggs instead of chicken eggs. Following step 4.5, the host is processed for whole mount immunohistochemistry with an antibody specific to quail tissue (QCP1) and steps 3.1 to 3.4 and 5.1 to 5.7 are omitted from the protocol. An example of this alternative procedure is shown below: In this case, we used the same experimental procedure as in A,B, but we used quail-derived donnor tissue (as shown by the expression of QCPN antibody [brown]): The regenerated node derived from quail embryo has induced the expression of pan-neural marker Sox2 in the host [reprinted from 6]:

Discussion
This video demonstrates the different steps in performing an assay for neural induction; This assay is essentially used for the characterization of putative neural inducing molecules in chick, and thus can be used for a wide variety of applications, ranging from embryological micromanipulations 1-4; 6 to unraveling new signaling cascades 7,8, all aiming to the understanding of the initial step in the formation of the brain and remaining nervous system.
Acknowledgements
D.P is recipient of Ruth Kirschstein Award 1F32 DA021977-01A1 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. This work was supported by the Margaret M. Alkek Foundation to RHF.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |
| Eggs | Animal | Charles River Laboratories | Premium Fertile | Fertilized, HH3+ (14 hr) |
| Stereomicroscope | Microscope | Leica Microsystems | MZ9.5 or similar | |
| Hybridization Incubator | Equipment | Robbins Scientific, SciGene | M1000 | Use with inverted Pyrex dish and 500 ml ddH2O beaker |
| Marsh Automatic Incubator | Equipment | Lyon | RX | |
| Pyrex dish | ||||
| Watchmaker’s glass 50mm | Tool | VWR international | 66112-060 | |
| Glass rings | Tool | Physical Plant facility | cut 4 mm thick sections of glass tubing (27 mm outer diam, 25 mm inner diam). Do not fine polish. | |
| Curved Forceps (1) | Tool | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 72991-4C | |
| Forceps (2) | Tool | Fine Science Tools | 11002-13 | blunt ended using sharpening Stone and 100ul mineral oil |
| Fine scissors | Tool | Fine Science Tools | 14161-10 | |
| Plastic dishes | Tool | Falcon BD | 353001 | |
| Rubber Bulb | Tool | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 70980 | |
| DiI | Reagent | Invitrogen | D-282 | |
| Aspirator tube assembly | Tool | Sigma-Aldrich | A5177-5EA | |
| Micr–lectrode puller | Equipment | Sutter Instrument Co. | Sutter InstrumentsP-97 Flaming/Brown Micropipette | |
| Pasteur Capillary Pipette | Tool | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 70950-12 | round edge under flame |
| Culture chamber | Tool | Pioneer Plastics | 030C | |
| Microcapillary tube | Tool | Sigma-Aldrich | P1049-1PAK | |
| Microdissecting knife | Tool | Fine Science Tools | 10056-12 | Use to puncture cavities prior to in situ hybridization |
| Minuten pins 0.2mm diam | Tool | Fine Science Tools | 26002-20 | Mix 1 part Curing Agent, 9 parts Base; set O/N at 37C |
| Diethylpyrocarbonate (depc) | Reagent | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710 | |
| Sylgard 184 Silicon Elastomer Curing Agent and Base | Dow Corning | 0001986475 | Mix 1 part Curing Agent, 9 parts Base; set O/N at 37C | |
| Diethylpyrocarbonate (depc) | Acros Organics | 10025025 | Add 1ml depc to 1l PBS; shake; autoclave | |
| 16% PFA | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710 |
References
- Waddington, C. H. Experiments on the development of chick and duck embryos, cultivated in vitro. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 221, 179-230 (1932).
- Waddington, C. H. Induction by the primitive streak and its derivatives in the chick. J. Exp. Biol. 10, 38-46 (1933).
- Gallera, J. Excision et transplantation des différentes régions de la ligne primitive chez le poulet. C. R. Ass. Anat. 49, 632-639 (1964).
- Gallera, J. Primary induction in birds. Adv. Morph. 9. , 149-180 (1971).
- Serbedzija, G. N., Fraser, S. E., Bronner-Fraser, M. Pathways of neural crest cell migration in the mouse embryo as revealed by vital dye labeling. Development 108. , 605-612 (1990).
- Psychoyos, D., Stern, C. D. Restoration of the organizer after radical ablation of Hensen's node and the anterior primitive streak in the chick embryo. Development 122. , 3263-3273 (1996).
- Joubin, K., Stern, C. D. Molecular interactions continuously define the organizer during the cell movements of gastrulation. Cell. 98, 559-571 (1999).
- Streit, A., Berliner, A. J., Papanayotou, C., Sirulnik, A., Stern, C. D. Initiation of neural induction by FGF signaling before gastrulation. Nature. , 406-474 (2000).
- Psychoyos, D., Finnell, R. Method for Culture of Early Chick Embryos ex vivo (New Culture. JoVE. 20, 10-3791 (2008).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved