A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Whole-mount Immunohistochemical Analysis for Embryonic Limb Skin Vasculature: a Model System to Study Vascular Branching Morphogenesis in Embryo
In This Article
Summary
We introduce a whole-mount immunohistochemistry and laser scanning confocal microscopy with multiple labelling for analyzing intricate vascular network formation in mouse embryonic limb skin.
Abstract
Whole-mount immunohistochemical analysis for imaging the entire vasculature is pivotal for understanding the cellular mechanisms of branching morphogenesis. We have developed the limb skin vasculature model to study vascular development in which a pre-existing primitive capillary plexus is reorganized into a hierarchically branched vascular network. Whole-mount confocal microscopy with multiple labelling allows for robust imaging of intact blood vessels as well as their cellular components including endothelial cells, pericytes and smooth muscle cells, using specific fluorescent markers. Advances in this limb skin vasculature model with genetic studies have improved understanding molecular mechanisms of vascular development and patterning. The limb skin vasculature model has been used to study how peripheral nerves provide a spatial template for the differentiation and patterning of arteries. This video article describes a simple and robust protocol to stain intact blood vessels with vascular specific antibodies and fluorescent secondary antibodies, which is applicable for vascularized embryonic organs where we are able to follow the process of vascular development.
Protocol
1. Collecting Mouse Embryonic Limb Skin (E13.5~E17.5)
- Euthanize plugged females by approved procedure. According to our approved animal protocol, the females are euthanized by CO2 exposure and then assured by cervical dislocation. Lay the animal on its absorbent paper towel and soak it thoroughly in 70% EtOH/H2O from a squeeze bottle.
- Dissect the uterus intact and place it in a 100 x 15 mm Petri dish containing ice-cold Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) to wash out blood.
- Separate and dissect the embryo. Remove the very thin amnion from the embryo.
- (Option) Dissect a single embryo in a 35 x 10 mm Petri dish if each embryo needs to be genotyped. Dissected tail is transferred to a 0.2 ml PCR tube for genotyping.
- Cut off the forelimbs of embryo and transfer forelimbs by a ring forceps into 24 well plate containing 2 ml of ice-cold fresh 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) in Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS).
- Fix the forelimbs with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at 4°C overnight.
- On the following day, remove the PFA and wash three times for 5 min in 2 ml of PBS with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature.
- Transfer the forelimbs in 100% methanol (MeOH) and store them at -20°C enzyme freezer (the freezer with critical temperature control and without automatic defrost function). Primary antibodies listed in Table 1 work after the 100% MeOH treatment.
- Peel off skin from the forelimb using fine tweezers. Limb skin, when dehydrated, should separate easily from the limb. First place the limb with ventral side (palm side) facing up. Then using fine tweezers, cut the skin as shown in the video. Next dissect around the entire limb, peeling the skin off gently without any damage.
2. Whole-mount Immunohistochemical Staining of Limb Skins
- Rehydrate the limb skins in 5ml polypropylene round-bottom tube by incubating through the graded series of MeOH/PBT (PBS + 0.2%Triton X-100) (75%, 50%, 25%) for 5 min each. Note that exchanging solutions should be careful to avoid damaging the limb skins.
- Wash twice for 5 min in PBT with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature.
- Block the limb skins with either 10%Goat serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 blocking buffer for goat secondary antibodies or 10%Donkey serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 blocking buffer for donkey secondary antibodies for 2 hours with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature.
- Place the limb skins on a 35 x 10 mm Petri dish and transfer by a ring forceps into 2ml-microcentrifuge tube with 800μl of primary antibodies (appropriate dilution as listed in Tables) in the blocking buffer (either 10%Goat serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 or 10%Donkey serum/PBS+0.2%TX100). Incubate the limb skins with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at 4°C overnight. Note that multiple primary antibodies derived from different species (e.g., rat monoclonal antibody+ rabbit polyclonal antibody) can be used simultaneously.
- On the following day, place the limb skins on a 35 x 10 mm Petri dish and transfer by a ring forceps into 5ml polypropylene round-bottom tube with 4ml of the washing buffer (either 2%Goat serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 or 2%Donkey serum/PBS+0.2%TX100).
- Wash five times for 15 min with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature.
- Place the limb skins on a 35 x 10 mm Petri dish and transfer by a ring forceps into 2ml-microcentrifuge tube with 800μl of secondary antibodies in the blocking buffer (either 10%Goat serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 or 10%Donkey serum/PBS+0.2%TX100). Typically we use secondary antibodies from Jackson ImmunoResearch (Cy3, Cy5, 1:300 dilutions) or Invitrogen (Alexa Fluor 488, Alexa Fluor 568, Alexa Fluor 633, 1:250 dilution). Filter the secondary antibody solution using 0.22μm PVDF membrane syringe filters to remove aggregated particles of the secondary antibodies. Incubate the limb skins in the dark or wrapped with aluminum foil for 1 hour with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature. Note that different fluorescent conjugated secondary antibodies derived from different species can be used simultaneously.
- Place the limb skins on a 35 x 10 mm Petri dish and transfer by a ring forceps into 5ml polypropylene round-bottom tube with 4ml of the washing buffer (either 2%Goat serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 or 2%Donkey serum/PBS+0.2%TX100). Wash five times for 15 min in the dark or wrapped with aluminum foil with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature.
- (Option for counterstaining against nucleus) Incubate the limb skins with 4ml of the washing buffer (either 2%Goat serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 or 2%Donkey serum/PBS+0.2%TX100) with To-Pro-3 (Invitrogen T3605, 1:3000 dilution) in the dark or wrapped with aluminum foil for 10 min with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature. Then, wash three times for 5 min with 4ml of the washing buffer (either 2%Goat serum/PBS+0.2%TX100 or 2%Donkey serum/PBS+0.2%TX100) in the dark or wrapped by aluminum foil with gentle mixing on the Nutator Mixer at room temperature. Note that strong and specific staining for nuclei is observed for To-pro-3 in a specific emission (HeNe 633 nm excitation).
3. Mounting the Limb Skins on Slide
- Place the limb skins on a 35 x 10 mm Petri dish. Remove dusts, crystals, fibers from the inner layer of the skins using fine tweezers under the stereomicroscope with low illumination to avoid extensive photo bleaching.
- Transfer the limb skins to adhesive microscopic slide by a ring forceps. Place the skins with the inner layer lying upward on the slide (i.e. towards coverslip). Flatten the skins carefully using fine tweezers and remove carry-over washing buffer by Kimwipe.
- Mount in anti-fade mounting media without air bubbles. We use 25"x25" coverslip. Cure on a flat surface in the dark (e.g., the samples mounted using ProLong Gold reagent are placed overnight in the dark at room temperature before viewing). For long-term storage, seal the coverslip to the slide and store at 4°C.
4. Confocal Microscopy
- Set up appropriate lasers for fluorophores. We use Leica TCS SP5 confocal microscope with three laser sources including Argon 488nm (for Alexa Fluor 488 and GFP), DPSS 561nm (for Alexa Fluor 568 and Cy3)and HeNe 633nm (for Alexa Fluor 633, Cy5 and To-Pro-3).
- Use sequential scan tool to avoid or reduce crosstalk in which all dyes in double or triple-stained samples will be excited at the same time. In the sequential scan mode, images will be recorded in a sequential order.
- More general information about fluorescent dyes and lasers for excitation may be founded in "Confocal Microscopy for Biologists" by Hibbs (2004)
5. Representative Results
Whole-mount triple-label confocal immnofluorescence microscopy in mouse forelimb skin at E15.5 with antibodies to the pan-endothelial cell marker PECAM-1 (Figure 1A-C, D blue), the neurofilament marker 2H3 (Figure 1A green), and the smooth muscle cell marker αSMA (Figure 1A, B red) revealed a characteristic branching pattern of αSMA+ arteries, aligned with 2H3+ peripheral nerves in the limb skin. In addition to blood vessel branching, this limb skin vasculature model is used to study patterning of lymphatic vessel branching using antibodies to the lymphatic endothelial cell marker LYVE-1 (Figure 1D, E red) and Neuropilin2 (NRP2) (Figure 1D, F green).
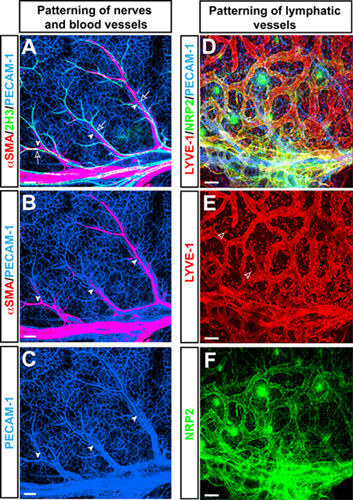
Figure 1. (A-C) Arteries align with peripheral nerves in the embryonic limb skin. Whole-mount triple-label confocal immnofluorescence microscopy with antibodies to the pan-endothelial cell marker PECAM-1 (A-C, blue), the neurofilament marker 2H3 (A, green), and the smooth muscle cell marker αSMA (A and B, red) is shown. At E15.5, 2H3+ peripheral nerves (open arrows) associate with arteries (arrowheads) which are covered by αSMA+ smooth muscle cells. (D-F) Lymphatic vasculature in the embryonic limb skin. Triple-label confocal immnofluorescence microscopy with antibodies to the pan-endothelial cell marker PECAM-1 (D, blue), the lymphatic endothelial cell marker LYVE-1 (D and E, red) and Neuropilin2 (NRP2) (D and F, green) is shown. Lymphatic vessels are visualized by both LYVE-1 and NRP2, whereas LYVE-1 is also expressed by a subset of macrophages (open arrowheads). Scale bar: 100μm.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The vascular system is crucial for organ development during embryogenesis as well as for organ maintenance and reproductive functions in the adults, because it supplies sufficient oxygen and nutrients to the organs. Proper vascular network is well-established with complex and multi-step processes by angiogenesis in which pre-existing capillary network is reorganized with highly branched and hierarchical structures. Although numerous works have been shown that a variety of molecules is involved in these processes, it has ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Gill for assistance with mouse breeding and care and for laboratory management. Thanks also to Mukoyama lab members for technical help. Funding was provided by Intramural Research Program of Naitonal Institutes of Health.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Antibodies Pan-endothelial cell marker
Arterial endothelial cell marker
Venous endothelial cell marker
Lymphatic endothelial cell marker
Smooth muscle cell/pericyte marker
Antibodies forGFP reporter
Antibodies for LacZ reporter
Antibodies for peripheral axon
Antibodies for migrating Schwann cells
(P): polyclonal antibody, (M): monoclonal antibody #1: Goat anti-Armenian hamster-Cy3 (Jackson ImmunoResearch 127-165-160) antibody should be used as a secondary antibody. #2: The Collagen IV antibody can be used to detect blood vessels after in situ hybridization. #3: The Neuropilin1 antibody is kindly provided by the Alex Kolodkin’s lab in the Johns Hopkins University. Sheep anti-human Neuropilin1 antibody is available in R&D (AF3870), although we have not tested it yet. #4: The LYVE-1 antibodies also detect a subset of macrophages in the embryonic skin. #5: The anti-αSMA antibody is mouse IgG2a monoclonal antibody. #6: The Cy3-conjugated αSMA antibody is incubated for 1 hour at room temperature together with secondary antibodies for other primary antibodies. #7: 2H3 antibody is mouse IgG1 monoclonal antibody against neurofilament. #8: Tuj1 antibody is mouse IgG2a monoclonal antibody against Neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin. #9: The BFABP (brain-specific fatty acid binding protein) antibody is kindly provided by the Thomas Müller’s lab in Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Mukouyama, Y. S., Shin, D., Britsch, S., Taniguchi, M., Anderson, D. J. Sensory nerves determine the pattern of arterial differentiation and blood vessel branching in the skin. Cell. 109, 693-705 (2002).
- Mukouyama, Y. S., Gerber, H. P., Ferrara, N., Gu, C., Anderson, D. J. Peripheral nerve-derived VEGF promotes arterial differentiation via neuropilin 1-mediated positive feedback. Development. 132, 941-952 (2005).
- Wang, H. U., Chen, Z. F., Anderson, D. J. Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell. 93, 741-753 (1998).
- Gerety, S. S., Wang, H. U., Chen, Z. F., Anderson, D. J. Symmetrical mutant phenotypes of the receptor EphB4 and its specific transmembrane ligand ephrin-B2 in cardiovascular development. Mol Cell. 4, 403-414 (1999).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved