A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
In vivo Bioluminescence Imaging of Tumor Hypoxia Dynamics of Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis in a Mouse Model
In This Article
Summary
Bioluminescence imaging of hypoxia inducible factor-1α activity is applied to monitor intracranial tumor hypoxia development in a breast cancer brain metastasis mouse model.
Abstract
It is well recognized that tumor hypoxia plays an important role in promoting malignant progression and affecting therapeutic response negatively. There is little knowledge about in situ, in vivo, tumor hypoxia during intracranial development of malignant brain tumors because of lack of efficient means to monitor it in these deep-seated orthotopic tumors. Bioluminescence imaging (BLI), based on the detection of light emitted by living cells expressing a luciferase gene, has been rapidly adopted for cancer research, in particular, to evaluate tumor growth or tumor size changes in response to treatment in preclinical animal studies. Moreover, by expressing a reporter gene under the control of a promoter sequence, the specific gene expression can be monitored non-invasively by BLI. Under hypoxic stress, signaling responses are mediated mainly via the hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) to drive transcription of various genes. Therefore, we have used a HIF-1α reporter construct, 5HRE-ODD-luc, stably transfected into human breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells (MDA-MB231/5HRE-ODD-luc). In vitro HIF-1α bioluminescence assay is performed by incubating the transfected cells in a hypoxic chamber (0.1% O2) for 24 hr before BLI, while the cells in normoxia (21% O2) serve as a control. Significantly higher photon flux observed for the cells under hypoxia suggests an increased HIF-1α binding to its promoter (HRE elements), as compared to those in normoxia. Cells are injected directly into the mouse brain to establish a breast cancer brain metastasis model. In vivo bioluminescence imaging of tumor hypoxia dynamics is initiated 2 wks after implantation and repeated once a week. BLI reveals increasing light signals from the brain as the tumor progresses, indicating increased intracranial tumor hypoxia. Histological and immunohistochemical studies are used to confirm the in vivo imaging results. Here, we will introduce approaches of in vitro HIF-1α bioluminescence assay, surgical establishment of a breast cancer brain metastasis in a nude mouse and application of in vivo bioluminescence imaging to monitor intracranial tumor hypoxia.
Protocol
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
1. In vitro HIF-1α bioluminescence assay
- Materials and Methods:
- Human metastatic breast cancer cell line MDA-MB231 transfected with a novel HIF-1-dependent reporter gene, 5HRE-ODD-luc was generated by Dr. Harada.
- In hypoxic condition, the enhanced expression of oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODD)-Luciferase fusion protein is driven by 5 copies of hypoxia-response element (5HRE). The presence of ODD causes the degradation of ODD-Luc protein resulting in extremely low background luciferase activity in normoxic conditions. Therefore, this novel system can be used to detect hypoxic regions in a tumor by real time imaging. The construction of this 5HRE-ODD-luc expression vector has been reported by Harada et al1,2.
- Culture cells under normoxia or hypoxia:
- Maintain the recombinant MDA-MB231 cells in 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)-DMEM medium containing 1% glutamine, antibiotics of 400 μg/ml of G418 and 1% penicillin/streptomycin.
- For the in vitro HIF-1α bioluminescence assay, plate 3 x 105 MDA-MB231 cells expressing 5HRE-ODD-luc vector in each well of two six well dish.
- Allow cells to attach the dish wall after overnight incubation and then transfer one dish into a hypoxia chamber (Billups-Rothenberg, Inc. Del Mar, CA) for hypoxia studies, while keep the other dish under normoxic condition (21% O2).
- Reassemble the chamber and gas the chamber with 0.1% O2 by connecting the inlet port tubing with a gas cylinder.
Note: Both inlet and outlet port clamps must be open during this procedure. - Disconnect gas source after chamber has been purged and seal chamber by closing plastic clamps.
- Place the chamber in a 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2.
Note: The chamber must be humidified to prevent excessive evaporation of cultures. This can be accomplished by placing 10 - 20 ml sterile water in the chamber.
- Bioluminescence assay:
- After 24 hr incubation, remove the medium and wash the cells quickly with ice cold PBS (2X).
- Add 1 ml of cold PBS with 100 μl of Luciferin (Gold Biotechnology, St Louis, MO).
- Acquire BL imaging (IVIS Spectrum system, Caliper Life Sciences, Hopkinton, MA) with various exposure times (1, 30, 60, 180 s).
- Measure light intensity in each well using the Living Image software (Caliper Life Sciences).
2. Establishment of a breast cancer brain metastasis model
- Preparation of the MDA-MB231/5HRE-ODD-luc cells
- Retrieve and culture the MDA-MB231/5HRE-ODD-luc cells in DEME medium containing 10% FBS, 1% glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin.
- Replace medium every 2-3 days. Tripsinize and wash the cells when they reach 80% confluence.
- Count appropriate number of cells and resuspend them in serum free DEME medium with 25% Matrigel (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) with a final concentration of 105 cells in 4 μl volume.
- Place cells on ice prior to intracranial injection.
- Surgical implantation
- Female nude mice (BALB/c nu/nu; National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD) at 4-6 weeks old are used in this study.
- Anesthetize (3% isoflurane/ O2 in an induction chamber; isoflurane from Baxter International Inc., Deerfield, IL, USA) and maintain the animals with isoflurane (1%) in oxygen (1 dm3/min) during the surgical procedure3.
- The right parietal skin should be prepped with betadine and then 70% alcohol prior to incision.
- Using a high-speed drill, burr a 1 mm hole in the right hemisphere of the skull, 1mm anterior to the coronal suture and 2 mm lateral to saggital suture.
- Draw 4 μl cell mixture (105 cells) using a 10 μl Hamilton syringe (Hamilton Company, Reno, NV). Inject the cells directly into right caudal diencephalon, 1.5 mm beneath the dura mater using a custom-made 32G Hamilton needle. Keep the needle in place for about 30 s before withdrawal. Usage of a 32G fine needle minimizes tissue damage.
- Fill the burr hole with bone wax and close the scalp with absorbable sutures.
- Prepare the incision region with 70% alcohol.
- Apply buprenorphine analgesia every 12 hrs for two days.
3. In vivo bioluminescence imaging of tumor hypoxia dynamics in breast cancer brain metastasis
- Initiate longitudinal bioluminescence imaging (IVIS Spectrum system) two weeks after intracranial implantation and repeat once a week for 8-10 weeks.
- Anesthetize three mice at a time (3% isoflurane/ O2 in an induction chamber)
- Administer a solution of D-luciferin (120 mg/kg in PBS in a total volume of 80 μl; Gold Biotechnology) subcutaneously in the neck region of each mouse as described in detail previously4.
D-luciferin is non-toxic and has been shown to be capable of penetrating intact blood-brain barrier (BBB) and cell membranes3,5.
- Place the 3 mice in the imaging chamber and maintained with isoflurane (1%) in oxygen (1 dm3/min) during imaging.
- Five minutes after luciferin injection, acquire BL imaging with an array of various exposure time (1, 30, 60, 180 s).
Our observations show that the peak light emission time is about 5 mins after subcutaneous administration of luciferin in the neck region3,4.
- Analyze data with the Living Imaging software (Caliper Life Sciences) by using absolute photon counts (photons/s) in a region of interest (ROI), manually drawn to outline the BLI signal of the brain.
- Plot time course curve of photon counts to indicate tumor hypoxia dynamics.
- Immediately after the last BLI, administer pimonidazole, the hypoxia marker and 1 hr later, sacrifice the mice and dissect the brains. Embed the whole brains in Optimal Cutting Temperature (O.C.T.) medium and freeze in -80 °C freezer. Subsequent histological Cresyl violet staining and immunohistochemical staining against luciferase, hypoxia marker pimonidazole, and HIF-1α performed to validate imaging observations.
4. Representative results:
As shown in Fig.1, significantly higher BLI signal was observed after the transfected cells incubated in the hypoxic chamber (1% O2) for 24 hrs. Weak light emission was observed from the control cells under normoxia. This may result from the overcrowded cell population after 24 hr culture of 3 x 105 cells, which induced a stress signal to the cells to overexpress HIF-1α. Nonetheless, in vivo BLI results were validated by immunohistochemical staining showing colocalization between tumor hypoxia and luciferase expression.
An automated array of exposure times enables continuous acquisitions of a series of images, which facilitates capture of a weak signal with longer exposure time, and strong signals using a shorter time without saturating the CCD.
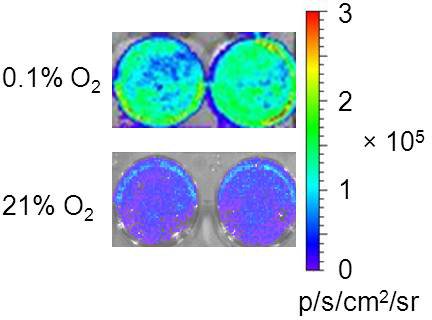
Figure 1 In vitro HIF-1α bioluminescence assay. Top row: 3 x 105 MDA-MB231/5HRE-ODD-luc cells incubated in each well of a 6-well-dish in a hypoxia chamber (0.1% O2) for 24 hr before the medium was removed, washed and replaced with 1 ml PBS. Immediately after 100 μl luciferin was added into each well, BLI was acquired with an array of exposure times (1, 30, 60, 180 s). Strong luminescence was observed from representative wells. Bottom row: As a control, 3 x 105 cells incubated under normoxia (21% O2) emitted weak light.
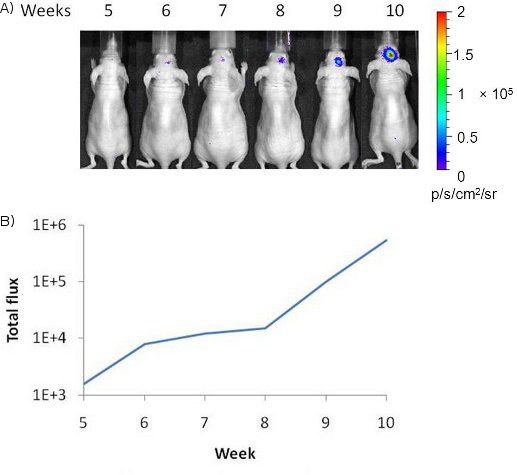
Figure 2 In vivo bioluminescence imaging of tumor hypoxia dynamics. A) A weak light signal from right side of mouse brain was first visualized 5 weeks after intracranial implantation of MDA-MB231/5HRE-ODD-luc breast cancer cells. Increased optical signal was observed over additional 6 weeks, indicating increased tumor hypoxia. B) The plot showed the time course curve of quantitative photon counts of light signal.
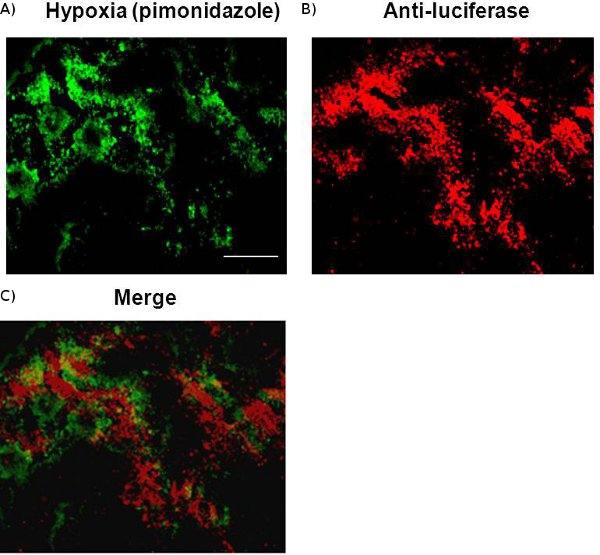
Figure 3 Colocaliztion of luciferase and hypoxia detected by immunohisto-chemical staining. A frozen mouse brain bearing a metastasis of breast cancer MDA-MB231/5HRE-ODD-luc embedded in O.C.T. was sectioned. A 10 μm section immunostained with hypoxic marker, pimonidazole, revealed intratumoral heterogeneity of hypoxia, which was found to correlate spatially with luciferase expression detected by anti-luciferase staining. Scale bar, 100 μm.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Breast cancer brain metastasis occurs in 30% of breast cancer patients at stage IV. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality and has a median survival of 13 months6. There is a need to have appropriate animal models to mimic this clinically devastating disease in order to facilitate our understanding of its intracranial initiation and progression as well as pathophysiological profiles. Here, we have developed an orthotopic breast cancer brain metastasis model by injecting human breast cancer cells, d...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported in part by DOD Breast Cancer IDEA Award W81XWH-08-1-0583 and NIH/NCI CA141348-01A1 (DZ) and FAMRI clinical scientist award (DS). Imaging infrastructure is provided by Southwestern Small Animal Imaging Research Program supported in part by U24 CA126608 and Simmons Cancer Center (P30 CA142543) and NIH 1S10RR024757-01.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| D-luciferin | Gold Biotechnology | L-123 | 120 mg/kg in PBS in a total volume of 80 μl for in vivo study |
| Isoflurane | Baxter Internationl Inc. | 1001936060 | |
| Matrigel | BD Biosciences | 354234 | |
| Hamilton syringe | Hamilton Co | 1701 | |
| 32G Hamilton needle | Hamilton Co | 7803-04 | |
| Hypoxia chamber | Billups-Rothenberg, Inc. | MIC-101 | |
| Bioluminescence imaging system | Caliper Life Sciences | IVIS Spectrum system | |
| G418 | Fisher Scientific | SV3006901 |
References
- Harada, H. The combination of hypoxia-response enhancers and an oxygen-dependent proteolytic motif enables real-time imaging of absolute HIF-1 activity in tumor xenografts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360, 791-796 (2007).
- Ou, G. Usefulness of HIF-1 imaging for determining optimal timing of combining bevacizumab and radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75, 463-467 (2009).
- Zhou, H. Dynamic near-infrared optical imaging of 2-deoxyglucose uptake by intracranial glioma of athymic mice. PLoS One. 4, e8051-e8051 (2009).
- Contero, A., Richer, E., Gondim, A., Mason, R. P. High-throughput quantitative bioluminescence imaging for assessing tumor burden. Methods Mol Biol. 574, 37-45 (2009).
- Zhao, D., Richer, E., Antich, P. P., Mason, R. P. Antivascular effects of combretastatin A4 phosphate in breast cancer xenograft assessed using dynamic bioluminescence imaging and confirmed by MRI. FASEB J. 22, 2245-2451 (2008).
- Chang, E. L., Lo, S. Diagnosis and management of central nervous system metastases from breast cancer. Oncologist. 8, 398-410 (2003).
- Palmieri, D. Vorinostat inhibits brain metastatic colonization in a model of triple-negative breast cancer and induces DNA double-strand breaks. Clin Cancer Res. 15, 6148-6157 (2009).
- Mason, R. P. Multimodality imaging of hypoxia in preclinical settings. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 54, 259-280 (2010).
- Tatum, J. L. Hypoxia: importance in tumor biology, noninvasive measurement by imaging, and value of its measurement in the management of cancer therapy. Int J Radiat Biol. 82, 699-757 (2006).
- Moeller, B. J. Pleiotropic effects of HIF-1 blockade on tumor radiosensitivity. Cancer Cell. 8, 99-110 (2005).
- Lu, X. In vivo dynamics and distinct functions of hypoxia in primary tumor growth and organotropic metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 70, 3905-3914 (2010).
- Zhao, D., Chang, C. H., Kim, J. G., Liu, H., Mason, R. P. In vivo Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Monitoring of Tumor Response to Combretastatin A-4-Phosphate Correlated With Therapeutic Outcome. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80, 574-581 (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved