A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Examining the Dynamics of Cellular Adhesion and Spreading of Epithelial Cells on Fibronectin During Oxidative Stress
In This Article
Summary
This method is useful for quantifying the early dynamics of cellular adhesion and spreading of anchorage-dependent cells onto the fibronectin. Furthermore, this assay can be used to investigate the effects of altered redox homeostasis on cell spreading and/or cell adhesion-related intracellular signaling pathways.
Abstract
The adhesion and spreading of cells onto the extracellular matrix (ECM) are essential cellular processes during organismal development and for the homeostasis of adult tissues. Interestingly, oxidative stress can alter these processes, thus contributing to the pathophysiology of diseases such as metastatic cancer. Therefore, understanding the mechanism(s) of how cells attach and spread on the ECM during perturbations in redox status can provide insight into normal and disease states. Described below is a step-wise protocol that utilizes an immunofluorescence-based assay to specifically quantify cell adhesion and spreading of immortalized fibroblast cells on fibronectin (FN) in vitro. Briefly, anchorage-dependent cells are held in suspension and exposed to the ATM kinase inhibitor Ku55933 to induce oxidative stress. Cells are then plated on FN-coated surface and allowed to attach for predetermined periods of time. Cells that remain attached are fixed and labeled with fluorescence-based antibody markers of adhesion (e.g., paxillin) and spreading (e.g., F-actin). Data acquisition and analysis are performed using commonly available laboratory equipment, including an epifluorescence microscope and freely available Fiji software. This procedure is highly versatile and can be modified for a variety of cell lines, ECM proteins, or inhibitors in order to examine a broad range of biological questions.
Introduction
Cell-matrix adhesions (i.e., focal adhesions) are large and dynamic multimolecular protein complexes which mediate cell adhesion and spreading. These processes are critical for tissue development, maintenance, and physiological function. Focal adhesions are composed of membrane-bound receptors, such as integrins, as well as scaffolding proteins that link cytoskeletal actin to the extracellular matrix (ECM)1. These complexes are capable of responding to physiochemical cues present in the extracellular environment through the activation of various signaling transduction pathways. As such, focal adhesions serve as signaling centers to propagate extracellular mechanical cues into a number of cellular processes including directed migration, cell cycle regulation, differentiation, and survival1,2. One group of signaling molecules that regulate and interact with focal adhesions includes members of the Rho family of small GTPases. Rho GTPases are key proteins that regulate cell migration and adhesion dynamics through their specific spatiotemporal activation3. Not surprisingly, dysregulation of Rho protein function has been implicated in a number of human pathologies such as metastasis, angiogenesis, and others. Of particular interest, cellular redox status plays a predominant role in the modulation of cell migration and adhesion. Alterations in redox homeostasis, such as increases in reactive oxygen species (ROS), have been demonstrated to regulate Rho protein activity, as well as adhesion, in a number of cell types and human diseases4,5,6,7,8. For example, individuals suffering from the neurological disorder ataxia-telangiectasia (A-T), which is caused by a mutation in the DNA damage repair serine/threonine kinase A-T-mutated (ATM), have an increased risk of metastatic cancer9,10. Loss of ATM kinase activity in these patients and cell lines, either through genetic mutation or chemical inhibition, results in high levels of oxidative stress due to dysfunction of the pentose phosphate pathway7,11,12. Moreover, recent studies from the laboratory have highlighted a pathophysiological role for ROS in A-T by altering cytoskeletal dynamics (i.e. adhesion and spreading) as a direct result of activating Rho family GTPases in vitro5. Ultimately, these alterations in cytoskeletal dynamics caused by Rho family activation may lead to the increased risk of metastatic cancer noted in A-T patients5,13. Therefore, understanding the interplay between cell-matrix interactions during oxidative stress can provide insights into the regulation of adhesion and spreading. These studies can also set the stage for further investigations into a possible role for Rho family GTPases in these signaling processes.
Described herein is a protocol to study the early cellular dynamics of adhesion assembly and spreading during oxidative stress caused by inhibition of ATM kinase activity. This assay is based on the well-characterized mechanism of anchorage-dependent cells adhesion to the ECM protein fibronectin (FN). When cells maintained in suspension are plated onto FN, several Rho GTPases coordinate the control of the actin cytoskeletal remodeling3,14. Morphological changes are observed as cells shift from round and circular in appearance to flattened and expanded. Concomitant with these observations is the development of numerous matrix adhesions with the ECM. These changes are attributed to the biphasic activation of RhoA with Rac1 during the first hour as cells adhere and spread 15,16.
A variety of methods have been utilized to examine adhesion morphology and dynamics as well as cell spreading. However, these methods rely on sophisticated long-term, live-imaging total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) or confocal microscopy systems. Thus, users must have access to specialized equipment and software. Furthermore, the set-up time required by these bio-imaging systems makes capturing early adhesion events challenging, especially when testing multiple inhibitors or treatment conditions concurrently.
The methods detailed, herein, provide a straightforward, economical, yet quantitative way to assess parameters that govern the adhesion assembly and spreading in vitro. The protocol is performed using commonly available laboratory equipment, such as an epifluorescence microscope and CCD camera. This assay involves applying anchorage-dependent cells to an FN-coated surface after a period of oxidative stress caused by chemical inhibition of ATM kinase activity, which has been demonstrated previously5. Following plating, cells are allowed to attach and adhere for specified lengths of time. Unattached cells are washed away, while attached cells are fixed and labeled with fluorescence-based antibodies to markers of adhesion (e.g., paxillin) and spreading (e.g., F-actin)2,5. These proteins are then visualized and recorded using an epifluorescence microscope. Subsequent data analysis is performed using freely available Fiji software. Moreover, this method can be adapted to examine adhesion dynamics under a wide range of conditions including different ECM proteins, treatment with various oxidants/cell culture conditions or a variety of anchorage-dependent cell lines to address a broad range of biological questions.
Protocol
1. Preparations
NOTE: The protocol described below has been optimized for the use with REF52 cells and ATM+/+ or ATM-/- human fibroblasts. Other cell types may require further optimization as described in the notes and troubleshooting sections below.
- Make 500 mL of complete cell culture medium for REF52 cells. To 500 mL of high-glucose containing Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) add 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 100 units/mL penicillin-streptomycin.
- Prepare a 25 μg/mL solution of fibronectin (FN) by adding 300 μL of 1 mg/mL FN solution to 12 mL of sterile 1x phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4. Mix well.
- Prepare a 0.5% (w/v) delipidated (i.e., fatty acid free) bovine serum albumin (dlBSA) solution in serum free DMEM cell culture medium. Add 0.5 g of dlBSA to 100 mL of serum free DMEM medium. Mix the solution well, but do not vortex. Sterile filter the solution into a new sterile container, using a 0.22 μM syringe filter before use. Store at 4 °C.
- Make 3.7% paraformaldehyde solution by dissolving 3.7 g of paraformaldehyde in 100 mL of 1x PBS. Use gentle heat and stirring to get the paraformaldehyde into solution.
NOTE: The paraformaldehyde solution is light sensitive and should be protected from light. It is good for up to one week when stored at 4 °C.
CAUTION: Paraformaldehyde is toxic, flammable, corrosive and a health hazard. Review the material safety data sheet for paraformaldehyde prior to use. Use the appropriate personal protective equipment when handling including eye shield, face shield, full-face particle respirator, gloves, and lab coat. - Prepare the permeabilization solution containing 0.2% non-ionic surfactant in 1x PBS (v/v). For 100 mL, slowly add 0.2 mL of Triton X-100 to 100 mL of 1x PBS, while stirring.
- Make the immunofluorescence blocking buffer containing 2.5% BSA, 5% goat serum, and 0.05% non-ionic surfactant (w/v/v) dissolved in 1x PBS solution. For 100 mL, add 5 mL of goat serum, 2.5 g of BSA and 0.05 mL of Triton X-100 in ~ 95 mL 1x PBS, while stirring.
- Grow REF52 cells in DMEM complete culture medium in a 10 cm2 (or any other vessel size) cell culture-treated plate in a cell culture incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
2. Coating cell culture plates with the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin
NOTE: Perform this section using aseptic technique and sterile reagents in a BSL-2 certified laminar flow hood. Refer to Figure 1A for an overview of key steps prior to beginning.
- Using a tissue culture certified 24-well plate, place one glass coverslip (12-Cir-1) in each well. Label the plate according to Figure 1B.
- Pipette 500 μL of the 25 μg/mL FN solution to each well of a 24-well plate.
- Pipette the solution over each coverslip a few times to ensure even coating and complete submersion. Place the lid back on the plate.
- Incubate the plate in a cell culture incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 1 h.
NOTE: Alternatively, incubate overnight at 4 °C. - After 1 h, remove the plate from the incubator and aspirate the FN solution from the wells.
- Wash wells three times with 500 μL of 1x PBS. Aspirate the final wash of 1x PBS.
- Block wells with 500 μL of 0.5% dlBSA solution for a minimum of 15 min at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Aspirate the dlBSA solution prior to plating cells in step 3 below.
NOTE: If storing plates, add 500 μL of 1x PBS to each coverslip after aspiration of the dlBSA solution. Plates can then be kept at 4 °C for up to one week.
3. Preparing anchorage-dependent cells for the adhesion assay
NOTE: Perform this section using aseptic technique and sterile reagents in a BSL-2 certified laminar flow hood.
- At least 30 min prior to the cell plating, pre-warm the following solutions: DMEM complete medium, dlBSA solution, 1x PBS, 0.5% trypsin-EDTA solution, and trypsin neutralizing serum (TNS) in a 37°C water bath.
- Starting with a confluent monolayer of REF52 cells in a 10 cm2 dish, wash cells twice with 6 mL of warm 1x PBS. Serum starve the cells for at least 1 h (depending on cell type) in 6 mL of warm dlBSA solution at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Wash cells with 6 mL of warmed 1x PBS, aspirate PBS and add 1.5 mL of warm 0.5% Trypsin-EDTA solution.
- Place cells in a cell culture incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for ~2 min.
- Observe cells under a light microscope to ensure the detachment is complete. If cells are still adherent after tapping the plate on the bench top, return to the 37 °C incubator for an additional 2 min. Trypsinize the cells for as little time as is necessary.
- Pipette 1.5 mL of warm trypsin neutralizing solution (TNS) to the dish to stop trypsinization and collect detached cells. Pipette the solution up and down over the bottom of the plate numerous times to remove all remaining adherent cells. If cells appear clumpy, further triturate the cell suspension by gently pipetting up and down over the back of the dish.
- Count cells using trypan blue exclusion and a hemocytometer under a light microscope. Alternatively, use an automated cell counter.
- Remove an appropriate amount of cells to create a 1.0 - 3.0 x 104 cells/mL cell suspension in 5 mL of dlBSA in a 15 mL conical tube.
- Centrifuge cells at ~ 300 x g for 5 min using a fixed angle rotor in a table-top centrifuge.
- Aspirate the supernatant from the cell pellet, and resuspend cells in a total of 7 mL of warm dlBSA solution. Do not allow the cells to be overly confluent upon coverslip plating, but evenly distributed with few cells touching one another.
- Evenly divide the cell suspension into two 15 mL conical tubes, one for the vehicle alone control (DMSO) and one for Ku55933 (ATM kinase inhibitor, oxidant)5. Ensure each tube contains 3.5 mL of the cell suspension.
- Using a tube rotator, revolve the tubes at 37 °C for 90-120 min in a cell culture incubator.
- 30 min before plating, add a final concentration of 10 μM Ku55933 and DMSO (1:1,000) to each respective tube. Place the cell suspension back on the rotator for the remaining time.
- Immediately prior to plating the cells, retrieve the 24-well plate from the incubator and aspirate the dlBSA solution.
- After revolving the cell suspension for 90-120 min, remove 500 μL of cell suspension from each treatment group and add to one FN coated coverslip in the 24-well plate from step 2 as illustrated (Figure 1B). Return the plate to the 37 °C and 5% CO2 cell culture incubator and the cell suspension back to the rotation.
- After plating the cell suspension on the FN covered-coverslips, allow cells to adhere for the desired length of time (e.g., 10 min, 15 min, 20 min, 30 min) and then immediately proceed to step 4.
4. Cell fixation and antibody staining for immunofluorescence
NOTE: The following steps are performed under non-sterile conditions and at room temperature unless otherwise stated.
- After the desired time for adhesion has passed, aspirate the cell solution from each coverslip in the plate.
- Using the sides of the well, gently dispense 500 μL of 3.7% paraformaldehyde solution onto each coverslip and wait 10-15 min.
- Remove the paraformaldehyde solution and wash each coverslip with 500 μL of 1x PBS for a total of two times.
NOTE: Dispose of paraformaldehyde waste responsibly, according to the institution’s environmental health and safety plan. - Aspirate the PBS, and permeabilize cells on each coverslip with 500 μL of 0.2% Triton X-100 in 1x PBS (v/v) for 10-15 min at room temperature.
- Wash each coverslip with 500 μL of 1x PBS three times.
- Block cells on each coverslip with 500 μL of immunofluorescence blocking buffer containing 5% goat serum, 2.5% BSA and 0.05% Triton X-100 dissolved in a 1 x PBS solution for 30-60 minutes.
- Dilute the primary anti-paxillin antibody (1:250) in the blocking buffer. Mix well and add 200 μL of the antibody solution to each coverslip. Incubate at room temperature for at least 1 h.
NOTE: Alternatively, the primary antibody solution can be incubated overnight at 4 °C. There are many common focal adhesion markers that could be used for staining adhesion complexes and subsequent FA analysis. These include antibodies against the following proteins: integrin subunits (β1, α5, or αV), talin, or vinculin2. - Aspirate the antibody solution, and wash each coverslip with 500 μL of 1x PBS three times for 10 min each. Protect the samples from light from this point forward.
- Dilute the phalloidin F-actin probe conjugated to the red fluorescent Alexa 594 dye (1:1000) and goat-anti mouse 488 fluorescent secondary antibody (1:400) in the same blocking buffer solution. Mix well and add 200 μL of the antibody solution to each coverslip for 30 min.
NOTE: Fluorescently conjugated secondary antibodies from other species may be used as well. However, the use of antibodies from other species will require modification of the blocking buffer serum. - Aspirate the antibody solution, and wash each coverslip with 500 μL of 1x PBS three times for 10 min each.
- Aspirate the 1x PBS and rinse one time with 500 μL of dIH2O.
- Mount coverslips onto microscope slides using anti-fade mounting medium containing DAPI.
- Leave microscope slides to set overnight in the dark at room temperature.
- Store microscope slides in the dark at 4 ˚C for the long-term storage and until imaging.
NOTE: Image using standard immunofluorescence techniques. It is recommended to use a high-powered oil immersion 60x objective lens to ensure enough resolution to note the focal adhesions and peripheral ruffles at cell edges. Acquire images of 20-30 cells in multiple fields of view for each coverslip under each treatment condition and time. From combined replicates, this should yield at least 60 cells in order to perform statistical analysis. Save and export fluorescence images as a .TIFF file with a minimum of 300 dpi resolution.
5. Quantifying stress fibers, cell circularity, and focal adhesion formation
NOTE: The following image analyses are performed using the latest version of the open source imaging processing package Fiji Is Just Image J (Fiji), which can be downloaded free of charge at (http://fiji.sc/).
- General image processing
NOTE: All images will need to be prepared for computational analyses by performing steps 5.1.1-5.1.5 below (Figure 2). Afterward, any or all subsequent quantification procedures may be selected.- Open the .TIFF fluorescence image using Fiji. Ensure the images are 8-bit and grayscale.
- Select Image-Adjust-Window/level and select Auto (Figure 2A).
- Select Process-Subtract Background to subtract the background fluorescence. Check Sliding Paraboloid and select the option of a Rolling Ball Radius of 50 pixels (Figure 2B).
NOTE: To verify the proper size for the rolling ball radius, select the Line Tool and draw a radius on the largest adhesion in the image. Select Measure to verify the length of the line drawn. If the value of the radius is too large, features including adhesions will be lost in the image. If the radius is too small, it will give rise to artifacts in the processed image due to background noise. - Select Image-Adjust- Brightness/Contrast to check the intensity of the adhesion over the background. Adjust if necessary.
NOTE: To optimize the brightness/contrast and avoid saturating the signal, use the lookup tool of the image to examine its histogram to adjust the brightness/contrast. - Select the following parameters under Analyze-Set Measurements: Area, Mean Gray Value, Shape Descriptors, and Integrated Density.
- Stress fiber formation analysis
NOTE: Stress fibers can be quantified multiple ways depending on the phenotype.- Count the number of cells with stress fibers as a percentage over the total number of cells. This analysis is best if there are visual differences in the number of stress fibers formed under different experimental conditions.
- Count the number of stress fibers that transverse the cell. This analysis allows for the comparison of the number of stress fibers formed per cell.
- Measure the total fluorescence intensity given by the phalloidin (e.g., F-actin) staining per cell17,18. This method will highlight drastic increases/decreases in fluorescence intensity due to F-actin staining.
- Set the measurement parameters in step 5.1.5 above.
- Select the Freehand Tool in the Fiji toolbar and manually trace the cell(s) of interest. Select Analyze-Measure. A new window will appear showing the selected measurement parameters.
- Select the Freehand Tool in the Fiji toolbar and manually trace an empty space with no cells present. Select Analyze-Measure. This measurement will serve as the background fluorescence.
- Use the equation below to determine the total F-actin fluorescence per cell:
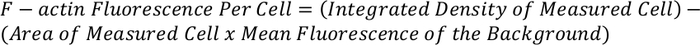
NOTE: The resulting measurement can be normalized and compared to other cells to give F-actin fluorescence per cell.
- Cell circularity analysis
NOTE: Information on cell area (an indicator of cell spreading over time), as well as, the circularity can also be recorded. This measurement is given as a ratio between 0 to 1 as a way to quantify cells that are elongated to round, respectively.- Select the Freehand Tool in the Fiji toolbar, and trace an individual cell. Select Image-Measure and record the cell area and perimeter measurements for each cell. Repeat this procedure for each cell.
NOTE: Under the Set Measurements function, circularity is provided as the Shape Descriptors measurement (step 5.1.5). - Manually count actin-enriched ruffling or protrusions per cell as depicted in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
- Select the Freehand Tool in the Fiji toolbar, and trace an individual cell. Select Image-Measure and record the cell area and perimeter measurements for each cell. Repeat this procedure for each cell.
- Focal adhesion analysis
NOTE: Before performing focal adhesion analysis, install the Mexican Hat Filter plugin on the latest version of Fiji. The following protocol has been modified from previous studies19,20,21.- Select Process-Enhance Local Contrast (Clahe) using a block size of 19, histogram bins 256, and a maximum slope of 6, with no mask and not fast. (Figure 2C)
- Select Process-Filters- Gaussian Blur with a Sigma (Radius) of 2.0 to filter the image (Figure 2D).
- Select Plugins-Mexican Hat Filter (Mhf) with a Radius of 2.0 (Figure 2E).
- Run Threshold and select Dark Background and Over/Under using either Huang or Isodata as the thresholding method. Select Auto-Threshold.
NOTE: This step ensures that adhesions are highlighted, but also distinct from one another. - Select Analyze-Analyze Particles with the following parameters selected: size=20, pixels-infinity and circularity=0.00-0.99. Check the outlines to ensure the proper detection and separation of focal adhesions.
NOTE: These results yield the number, area, and shape description of individual focal adhesions.
Results
A general schema of the experimental set-up
Figure 1 represents the general schema for the cell adhesion and spreading protocol beginning with serum starvation of REF52 cells and ending with computational analysis of acquired fluorescence images. Key steps in the protocol are illustrated in the timeline. Of note, step 2 of the protocol describes the preparation of the FN-coated coverslips, which should be performed concurrently with step 3: serum starving REF52 cell...
Discussion
The protocol described here is a versatile and economical way to rapidly screen a number of anchorage-dependent cell types for dynamic cytoskeleton remodeling during cell spreading. In particular, this method quantitatively examines stress fiber and focal adhesion formation during oxidative stress when cells adhere to FN (Figure 1A). Moreover, these cellular phenotypes may suggest a regulatory role for members of the Rho family of small GTPases since they have documented roles during cell at...
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Drs. Scott R. Hutton and Meghan S. Blackledge for the critical review of the manuscript. This work was funded by High Point University’s Research and Sponsored Programs (MCS) and the Biotechnology Program at North Carolina State University (MCS).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA (1x) | Gibco by Life Technologies | 25300-054 | cell dissociation |
| 10 cm2 dishes | Cell Treat | 229620 | sterile, tissue culture treated |
| 15 mL conical tubes | Fisher Scientific | 05-539-5 | sterile |
| 1X Phosphate Buffered Saline | Corning Cellgro | 21-031-CV | PBS, sterile, free of Mg2+ and Ca2+ |
| 24-well cell culture treated plates | Fisher Scientific | 07-200-740 | sterile, tissue culture treated |
| 4°C refrigerator | Fisher Scientific | ||
| Mouse IgG anti-paxillin primary antibody (clone 165) | BD Transduction Laboratories | 610620 | marker of focal adhesions |
| Aspirator | Argos | EV310 | |
| Biosafety cabinet | Nuair | NU-477-400 | Class II, Type A, series 5 |
| Delipidated Bovine Serum Albumin (Fatty Acid Free) Powder | Fisher Scientific | BP9704-100 | dlBSA |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide | Fisher Scientific | BP231-100 | organic solvent to dissolve Ku55933 |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Media, High Glucose | Fisher Scientific | 11965092 | REF52 base cell culture medium |
| Fetal bovine serum | Fisher Scientific | 16000044 | certified, cell culture medium supplement |
| Fiji | National Institutes of Health | http://fiji.sc/ | image analysis program |
| Filter syringe | Fisher Scientific | 6900-2502 | 0.2 µM, sterile |
| Glass coverslips (12-Cir-1.5) | Fisher Scientific | 12-545-81 | autoclave in foil to sterilize |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | A11001 | fluorescent secondary antibody, light sensitive |
| Goat Serum | Gibco by Life Technologies | 16210-064 | component of blocking solution for immunofluorescence |
| Hemocytometer | Fisher Scientific | 22-600-107 | for cell counting |
| Human Plasma Fibronectin | Gibco by Life Technologies | 33016-015 | FN |
| IX73 Fluorescence Inverted Microscope | Olympus | microscope to visualize fluorescence, cell morphology, counting and dissociation | |
| Ku55933 | Sigma-Aldrich | SML1109-25MG | ATM kinase inhibitor, inducer of reactive oxygen species |
| L-glutamine | Fisher Scientific | 25-030-081 | cell culture medium supplement |
| Monochrome CMOS 16 bit camera | Optimos | ||
| Paraformaldehyde | Sigma-Aldrich | P6148-500G | PFA, fixative for immunofluorescence |
| Penicillin-streptomycin | Fisher Scientific | 15-140-122 | P/S, antibiotic solution for culture medium |
| Alexa Fluor 594 phalloidin (F-actin probe) | Invitrogen | A12381 | marker of F-actin, light sensitive |
| ProLong Gold Anti-fade reagent with DAPI | Invitrogen | P36941 | cover slip mounting media including nuclear dye DAPI, light sensitive |
| REF52 cells | Graham, D.M. et. al. Journal of Cell Biology 2018 | ||
| Stir plate with heat control | Corning Incorporated | PC-420D | |
| Syringe | BD Biosciences | 309653 | 60 mL syringe |
| Tissue culture incubator | Nuair | ||
| Triton X-100 | Fisher Scientific | BP151-500 | detergent used to permeabilize cell membranes |
| Trypan Blue Solution | Fisher Scientific | 15-250-061 | for cell counting |
| Trypsin Neutralizing Solution (1x) | Gibco by Life Technologies | R-002-100 | TNS, neutralizes trypsin instead of fetal bovine serum |
| tube rotator | Fisher Scientific | 11-676-341 | |
| water bath | Fisher Scientific | FSGPD02 |
References
- Geiger, B., Bershadsky, A., Pankov, R., Yamada, K. M. Transmembrane crosstalk between the extracellular matrix--cytoskeleton crosstalk. Nature Reviews: Molecular Cell Biology. 2 (11), 793-805 (2001).
- Geiger, B., Yamada, K. M. Molecular architecture and function of matrix adhesions. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 3 (5), (2011).
- Lawson, C. D., Burridge, K. The on-off relationship of Rho and Rac during integrin-mediated adhesion and cell migration. Small GTPases. 5, e27958 (2014).
- Heo, J., Campbell, S. L. Mechanism of redox-mediated guanine nucleotide exchange on redox-active Rho GTPases. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (35), 31003-31010 (2005).
- Tolbert, C. E., Beck, M. V., Kilmer, C. E., Srougi, M. C. Loss of ATM positively regulates Rac1 activity and cellular migration through oxidative stress. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 508 (4), 1155-1161 (2019).
- Hobbs, G. A., et al. Redox regulation of Rac1 by thiol oxidation. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 79, 237-250 (2015).
- Zhang, Y., et al. Mitochondrial redox sensing by the kinase ATM maintains cellular antioxidant capacity. Science Signaling. 11 (538), (2018).
- Hobbs, G. A., Zhou, B., Cox, A. D., Campbell, S. L. Rho GTPases, oxidation, and cell redox control. Small GTPases. 5, e28579 (2014).
- Shiloh, Y., Ziv, Y. The ATM protein kinase: regulating the cellular response to genotoxic stress, and more. Nature Reviews: Molecular Cell Biology. 14 (4), 197-210 (2013).
- Lang, L., et al. ATM-Mediated Phosphorylation of Cortactin Involved in Actin Polymerization Promotes Breast Cancer Cells Migration and Invasion. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 51 (6), 2972-2988 (2018).
- Peter, Y., et al. Elevated Cu/Zn-SOD exacerbates radiation sensitivity and hematopoietic abnormalities of Atm-deficient mice. European Molecular Biology Organization Journal. 20 (7), 1538-1546 (2001).
- Takao, N., Li, Y., Yamamoto, K. Protective roles for ATM in cellular response to oxidative stress. Federation of European Biochemical Societies Letters. 472 (1), 133-136 (2000).
- Jansen, S., Gosens, R., Wieland, T., Schmidt, M. Paving the Rho in cancer metastasis: Rho GTPases and beyond. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 183, 1-21 (2018).
- Berrier, A. L., Martinez, R., Bokoch, G. M., LaFlamme, S. E. The integrin beta tail is required and sufficient to regulate adhesion signaling to Rac1. Journal of Cell Science. 115 (Pt 22), 4285-4291 (2002).
- Arthur, W. T., Petch, L. A., Burridge, K. Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Current Biology. 10 (12), 719-722 (2000).
- Arthur, W. T., Burridge, K. RhoA inactivation by p190RhoGAP regulates cell spreading and migration by promoting membrane protrusion and polarity. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 12 (9), 2711-2720 (2001).
- Chandra, S., Kalaivani, R., Kumar, M., Srinivasan, N., Sarkar, D. P. Sendai virus recruits cellular villin to remodel actin cytoskeleton during fusion with hepatocytes. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 28 (26), 3801-3814 (2017).
- Fitzpatrick, M. . Measuring Cell Fluorescence Using ImageJ. , (2014).
- Berginski, M. E., Vitriol, E. A., Hahn, K. M., Gomez, S. M. High-resolution quantification of focal adhesion spatiotemporal dynamics in living cells. PLoS One. 6 (7), e22025 (2011).
- Horzum, U., Ozdil, B., Pesen-Okvur, D. Step-by-step quantitative analysis of focal adhesions. MethodsX. 1, 56-59 (2014).
- Elosegui-Artola, A., et al. Image analysis for the quantitative comparison of stress fibers and focal adhesions. PLoS One. 9 (9), e107393 (2014).
- Meller, J., Vidali, L., Schwartz, M. A. Endogenous RhoG is dispensable for integrin-mediated cell spreading but contributes to Rac-independent migration. Journal of Cell Science. 121 (Pt 12), 1981-1989 (2008).
- Donaldson, J. G. Immunofluorescence Staining. Current Protocols in Cell Biology. 69 (43), 1-7 (2015).
- Burry, R. W. Controls for immunocytochemistry: an update. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 59 (1), 6-12 (2011).
- Grashoff, C., et al. Measuring mechanical tension across vinculin reveals regulation of focal adhesion dynamics. Nature. 466 (7303), 263-266 (2010).
- Kumar, A., et al. Correction: Talin tension sensor reveals novel features of focal adhesion force transmission and mechanosensitivity. Journal of Cell Biology. 214 (2), 231 (2016).
- Kumar, A., et al. Talin tension sensor reveals novel features of focal adhesion force transmission and mechanosensitivity. Journal of Cell Biology. 213 (3), 371-383 (2016).
- Friedrichs, J., Helenius, J., Muller, D. J. Quantifying cellular adhesion to extracellular matrix components by single-cell force spectroscopy. Nature Protocols. 5 (7), 1353-1361 (2010).
- Brown, M. A., et al. The use of mild trypsinization conditions in the detachment of endothelial cells to promote subsequent endothelialization on synthetic surfaces. Biomaterials. 28 (27), 3928-3935 (2007).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved