A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Implantation of Human-Sized Coronary Stents into Rat Abdominal Aorta Using a Trans-Femoral Access
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes the implantation of human coronary stents into the abdominal aorta of rats with an apoE-/- background using a trans-femoral access. Compared with other animal models, murine models carry the advantages of high throughput, reproducibility, ease of handling and housing, and a broad availability of molecular markers.
Abstract
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), combined with the deployment of a coronary stent, represents the gold standard in interventional treatment of coronary artery disease. In-stent restenosis (ISR) is determined by an excessive proliferation of neointimal tissue within the stent and limits the long-term success of stents. A variety of animal models have been used to elucidate pathophysiological processes underlying in-stent restenosis (ISR), with the porcine coronary and the rabbit iliac artery models being the most frequently used. Murine models provide the advantages of high throughput, ease of handling and housing, reproducibility, and a broad availability of molecular markers. The apolipoprotein E deficient (apoE-/- ) mouse model has been widely used to study cardiovascular diseases. However, stents must be miniaturized to be implanted into mice, involving important changes of their mechanical and (potentially) biological properties. The use of apoE-/- rats can overcome these shortcomings as apoE-/- rats allow for the evaluation of human-sized coronary stents while at the same time providing an atherogenic phenotype. This makes them an excellent and reliable model to investigate ISR after stent implantation. Here, we describe, in detail, the implantation of commercially available human coronary stents into the abdominal aorta of rats with an apoE-/- background using a trans-femoral access.
Introduction
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), combined with the deployment of a coronary stent, represents the gold standard in interventional treatment of coronary artery disease1. The long-term success of stents, however, can be limited by the occurrence of in-stent restenosis (ISR) that is determined by an excessive proliferation of neointimal tissue within the stent2,3. ISR may require a re-intervention either with coronary artery bypass or re-PCI. A variety of animal models have been suggested for the study of ISR, each of them featuring advantages and shortcomings. The major drawbacks of the most commonly used porcine coronary and rabbit iliac artery models, albeit developing lesions markedly similar to humans after stent implantation4,5, are large animal and housing costs which brings up logistical difficulties especially in long-term studies, as well as limitations in handling and equipment. Furthermore, availability of antibodies to cellular proteins of swine and rabbits is limited. On the other hand, murine models provide the major advantages of high throughput and reproducibility, as well as ease of handling, housing, and therefore cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, a higher number of antibodies are available. However, while apolipoprotein E-deficient (apoE-/-) mice have been broadly used for the study of atherosclerosis6,7,8, they are unsuitable for the study of ISR as stents have to be miniaturized to be implanted into mice, potentially changing the stents’ mechanical properties. Moreover, the aortic wall of mice measures between 50 µm in young mice and 85 µm in old mice9, and stents have to be deployed using pressure levels as low as 2 atm, which might lead to malapposition of the stent10. Rats, however, allow for the implantation of commercially available human coronary stents, and demonstrate a vascular healing course similar to larger animals after aortic stent implantation, first reported by Langeveld et al.11. This technique originally required a trans-abdominal access, which necessitated a physical constriction of the aorta to achieve a temporary interruption of blood flow. To avoid the potentially associated vessel injury and inflammatory reactions, the technique was later refined by the introduction of a trans-iliac access, which additionally resulted in a higher survival rate of the animals12.
Because wildtype rats do not develop atherosclerotic lesions13, apoE-/- rats have been generated using nuclease techniques such as Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nuclease (TALEN)14, Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR/Cas9)15, and Zinc Finger (ZF)16. ApoE-/- rats have been commercially available since 2011. Providing an atherogenic background, apoE-/- rats allow for a more realistic evaluation of human-sized coronary stents, especially with regards to ISR.
Herein, we describe the method via the transfemoral access route and using a commercially available thin-strut cobalt-chromium drug-eluting stent (DES), however, it can also be applied for the study of other stent types, such as bare metal stents (BMS) or biodegradable stents.
Protocol
The experiments were performed in accordance with the German animal welfare law (TSchG) and Directive 2010/63/EU pertaining to the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. The official approval for this study was granted by the Governmental Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol No.: AZ 87-51.04.2010.A065; Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz Nordrhein-Westfalen, Recklinghausen, Germany). The study protocol complied with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Postoperative pain treatment is based on the recommendations of the German Society for Laboratory Animal Science (GV-SOLAS) as well as Initiative Veterinary Pain Therapy.
1. Basic techniques and common procedures
- Use homozygous apoE-/- Sprague-Dawley rats. Identify the genotype of each animal by using standard methods17.
- Keep the animals under identical conditions (21 °C ± 2 °C, 60% ± 5% humidity, and a 12 h light/dark cycle) and ensure free access to water and food.
- Carry out all procedures under clean but nonsterile conditions.
- Once the rat is anesthetized, perform all procedures under a surgical microscope at a magnification of 16x.
- Use cotton swabs for compression hemostasis. Gauze swabs (5 cm x 5 cm) soaked with lactated Ringer solution are helpful to keep the groin moist.
- Follow waste disposal regulations to dispose used materials.
2. Preparations before surgery
- Prepare the veterinary drugs before starting the operation. Keep all solutions at room temperature, unless otherwise indicated.
- Thirty minutes before the procedure, administer 0.03-0.05 mg/kg buprenorphine subcutaneously.
- Anesthetize the rat with an intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg body weight (BW) (S)-ketamine and 8 mg/kg BW xylazine.
- Assess the rat’s weight using a weighing scale.
- Place the rat on a heating pad and fix the upper and lower limbs using medical tape. Position the rat with its left hind limb fully extended and as much in line with its spine as possible so as to create a straight line between femoral artery and aorta. This will facilitate advancing the balloon-mounted stent through the aortic bifurcation.
- Maintain anesthesia with inhalation of 1.5 vol% isoflurane in 97.5% oxygen at a flow rate of 2 L/min.
NOTE: Allow the rat to breathe spontaneously, without intubation. - Apply eye ointment to prevent eye damage during unconsciousness.
- Shave the fur from the groin and lower abdomen area of the rat and sterilize the corresponding skin with a povidone-iodine solution.
- Before starting the surgery, verify adequate depth of anesthesia by pinching the tail tip and the interdigital tissue.
3. Surgery
- Make a medial incision of ~0.5‒1 cm in the left groin to open the skin and the underlying fascia.
- Bluntly dissect and probe in the depths until the pulsating left femoral artery can be identified.
- Using very fine forceps, prepare the femoral artery by gently removing the surrounding connective tissue. Be careful to harm neither the femoral nerve nor the femoral vein, which is medial to the artery.
- Prepare about 1 cm of the femoral artery. Carefully put the tip of the forceps under the vessel to gently lift it.
- Thread pieces of 4-0 silk suture under the distal and proximal parts of the artery and form slings. Clamp the ends of each of the two thread slings between the branches of a surgical clamp. Use the surgical clamps to control the artery. Gently stretch and lift the slings in order to temporarily interrupt blood flow.
NOTE: Work fast to avoid a prolonged tourniquet which may lead to tissue damage. - Using sharp micro scissors, perform an arteriotomy in the middle of the femoral artery.
- Introduce a guide wire through the arteriotomy. When reaching the proximal thread sling, release the tension of the thread by moving the surgical clamp and advance the guide wire further towards the abdominal aorta.
NOTE: Cut the guide wire using a wire cutter to facilitate handling. - Place the proximal end of the guide wire between the diaphragm and the renal arteries.
NOTE: Advancing the guide wire too far bears the risk of aortic or cardiac injury. We recommend opening the abdomen to ensure adequate positioning of the guide wire and the stent at least for the first several animals. - Introduce a crimped and balloon-mounted coronary stent measuring 2.25 mm x 8 mm (max. 2.5 mm x 8 mm) over the guide wire into the femoral artery and advance it to the abdominal aorta.
- Place the stent just above the aortic bifurcation but below the renal arteries. Deploy the stent by inflating the balloon catheter to 12 atm for 15 s by using an inflation syringe system.
- Deflate the balloon catheter and maintain negative pressure according to the manufacturer’s recommendations for the stent in use.
- Slowly withdraw the deflated catheter while leaving the stent in place.
- Just before taking out the catheter, create tension on the thread loop above the incision with the surgical clamp to interrupt blood flow again. Then remove the balloon catheter and directly ligate the vessel proximally.
- Tie the proximal and the distal thread loops to ligate the femoral artery and confirm adequate hemostasis of the arteriotomy. Collateral arteries will ensure further perfusion to the limb.
- Close the muscle overlying the artery, as well as the skin incision by using 10-0 non-resorbable sutures.
4. Animal care after stent implantation
- Immediately after the operation, allow the rat to recover for 60 min in a special intensive care unit cage with warmed air (30‒35 °C) and an oxygen supply.
- Watch the animals carefully until fully recovered. Afterwards, move the rats into a normal cage. Provide ad libitum access to water and food.
- Administer postoperative analgesia every 6-12 hours with 0.03-0.05 mg/kg buprenorphine (s.c., in 500µl NaCl) for a total of 72 hours under clinical assessment.
- Have the food mixed with clopidogrel (15 mg/kg) to avoid thrombosis of the implanted stent.
- To enhance hypercholesterolemic conditions and plaque formation, start western diet feeding at 6‒8 weeks after birth and continue until euthanasia. If desired, a cohort of animals fed normal rat chow can serve as control.
5. Tissue collection and processing
- Before starting the tissue explantation at the designated time point, euthanize the animal according to IACUC guidelines. Harvest the stented aorta for histological analysis at the end of the observation period.
- Open the abdomen by a midline incision and remove the stented segment of the aorta as well as adjacent non-stented parts of the aorta, measuring 0.5 cm each.
- Place the tissue into a solution of 4% buffered formalin for 24 h for fixation.
- Embed the stented arterial tissue in plastic and perform histological and immunohistochemical staining according to standard protocols18,19.
6. Histomorphometric analysis
- Perform histomorphometric analysis of sequential sections of the proximal, middle, and distal part of the stented aorta by means of a microscope linked to a computer with an appropriate image analysis software.
- Trace the contours of the external elastic lamina (EEL, between adventitia and media), internal elastic lamina (IEL, between media and neointima), and lumen with a graphic drawing tablet. From these values, calculate EEL area, IEL area, and lumen area with the software.
- Calculate the percent cross-sectional area in-stent restenosis (ISR):
![figure-protocol-8647 ISR formula: 100 × (1 - [Lumen area/IEL area]); mathematical equation; vascular study.](/files/ftp_upload/61442/61442equ01.jpg)
- Calculate the total neointimal area (Ai):
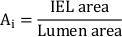
- Measure the neointimal thickness (NIT) over each stent strut as the distance between strut and lumen. Measure the NIT between the stent struts as the distance between IEL and lumen.
NOTE: Alternatively, calculate NIT as
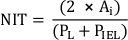
where PL and PIEL are the lumen and internal elastic lamina perimeter, respectively20. - Perform additional analyses according to the requirements of the study.
Results
This protocol describes stent implantation in the abdominal aorta of rats using a trans-femoral access route (Figure 1). The first central point of this animal model is that it allows for the deployment of human-sized coronary stents. A commercially available crimped and balloon-mounted coronary stent can be placed into the abdominal aorta of rats. Thus, in addition, the same principle of stent deployment as in humans can be applied. Another advantage of the use of rats is the availability o...
Discussion
This protocol describes the implantation of human-sized coronary stents into the abdominal aorta of apoE-/- rats. Several technical points are worth emphasizing. First, a mismatch between the stent size and the size of the aorta should be avoided. Placing too small a stent can lead to stent malapposition, whereas implantation of a stent that is too large for the aorta can cause overstretch, tearing, and injury of the vessel. Therefore, we recommend using stents between 2.0 and 2.5 mm in diameter, and to keep i...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mrs. Angela Freund for her invaluable technical assistance with embedding and slides production. We would also like to thank Mr. Tadeusz Stopinski at the Institute for Laboratory Animal Science & Experimental Surgery for his insightful help with the veterinary work.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Diet | |||
| SNIFF High Fat diet + Clopidogrel (15 mg/kg) | SNIFF Spezialdiäten GmbH, Soest | custom prepared | Western Diet |
| Drugs and Anesthetics | |||
| Buprenorphine | Essex Pharma | 997.00.00 | |
| ISOFLO (Isoflurane Vapor) vaporiser | Eickemeyer | 4802885 | |
| Isoflurane | Forene Abbott | B 506 | |
| Isotonic (0.9%) NaCl solution | DeltaSelect GmbH | PZN 00765145 | |
| Ringer's lactate solution | Baxter Deutschland GmbH | 3775380 | |
| (S)-ketamine | CEVA Germany | ||
| Xylazine | Medistar Germany | ||
| Consumable supplies | |||
| 10 mL syringes | BD Plastipak | 4606108V | |
| 2 mL syringes | BD Plastipak | 4606027V | |
| 6-0 prolene suture | ETHICON | N-2719K | |
| 4-0 silk suture | Seraflex | IC 158000 | |
| Bepanthen Eye and Nose Ointment | Bayer Vital GmbH | 6029009.00.00 | |
| Cotton Gauze swabs | Fuhrmann GmbH | 32014 | |
| Durapore silk tape | 3M | 1538-1 | |
| Poly-Alcohol Skin Desinfection Solution | Antiseptica GmbH | 72PAH200 | |
| Sterican needle 18 G | B. Braun | 304622 | |
| Sterican needle 27 3/4 G | B.Braun | 4657705 | |
| Tissue Paper | commercially available | ||
| Surgical instruments | |||
| Graefe forceps curved x1 | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 11151-10 | |
| Graefe forceps straight | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 11050-10 | |
| Needle holder Mathieu | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 12010-14 | |
| Scissors | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 14074-11 | |
| Semken forceps | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 11008-13 | |
| Small surgical scissors curved | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 14029-10 | |
| Small surgical scissors straight | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 14028-10 | |
| Standard pattern forceps | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 11000-12 | |
| Vannas spring scissors | Fine Science Tools Inc. | 15000-08 | |
| Equipment | |||
| Dissecting microscope | Leica MZ9 | ||
| Temperature controlled heating pad | Sygonix | 26857617 | |
| Equipment for stent implantation | |||
| Drug-eluting stent Xience 2,25mm x 8mm | Abbott Vascular USA | 1009544-18 | |
| Guide wire Fielder XT PTCA guide wire: 0.014" x 300cm | ASAHI INTECC CO., LTD Japan | AGP140302 | |
| Inflation syringe system | Abbott 20/30 Priority Pack | 1000186 | |
| Tissue processing and analysis | |||
| 30% H2O2 | Roth | 9681 | Histology |
| Ethanol | Roth | K928.1 | Histology |
| Giemsas Azur-Eosin-Methylenblau | Merck | 109204 | Histology |
| Graphic Drawing Tablet | WACOM Europe GmbH | CTL-6100WLK-S | |
| Roti Histofix, Formaldehyd 4% buffered | Roth | P087 | Histology |
| Technovit 9100 | Morphisto | 12225.K1000 | Histology |
References
- Patel, M. R., et al. ACC/AATS/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/STS 2017 Appropriate Use Criteria for Coronary Revascularization in Patients With Stable Ischemic Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Heart Association, American Society of Echocardiography, American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, Society for Cardiovasular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 69 (17), 2212-2241 (2017).
- Virmani, R., Farb, A. Pathology of in-stent restenosis. Current Opinion in Lipidology. 10 (6), 499-506 (1999).
- Buccheri, D., Piraino, D., Andolina, G., Cortese, B. Understanding and managing in-stent restenosis: a review of clinical data, from pathogenesis to treatment. Journal of Thoracic Disease. 8 (10), 1150-1162 (2016).
- Perkins, L. E. Preclinical models of restenosis and their application in the evaluation of drug-eluting stent systems. Veterinary Pathology. 47 (1), 58-76 (2010).
- Kim, W. H., et al. Histopathologic analysis of in-stent neointimal regression in a porcine coronary model. Coronary Artery Disease. 11 (3), 273-277 (2000).
- Plump, A. S., et al. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 71 (2), 343-353 (1992).
- Breslow, J. L. Transgenic mouse models of lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (18), 8314-8318 (1993).
- Knowles, J. W., Maeda, N. Genetic modifiers of atherosclerosis in mice. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 20 (11), 2336-2345 (2000).
- Wheeler, J. B., Mukherjee, R., Stroud, R. E., Jones, J. A., Ikonomidis, J. S. Relation of murine thoracic aortic structural and cellular changes with aging to passive and active mechanical properties. Journal of the American Heart Association. 4 (3), 001744 (2015).
- Rodriguez-Menocal, L., et al. A novel mouse model of in-stent restenosis. Atherosclerosis. 209 (2), 359-366 (2010).
- Langeveld, B., et al. Rat abdominal aorta stenting: a new and reliable small animal model for in-stent restenosis. Journal of Vascular Research. 41 (5), 377-386 (2004).
- Oyamada, S., et al. Trans-iliac rat aorta stenting: a novel high throughput preclinical stent model for restenosis and thrombosis. Journal of Surgical Research. 166 (1), 9 (2011).
- Touchard, A. G., Schwartz, R. S. Preclinical restenosis models: challenges and successes. Toxicologic Pathology. 34 (1), 11-18 (2006).
- Wei, S., et al. Apolipoprotein E-deficient rats develop atherosclerotic plaques in partially ligated carotid arteries. Atherosclerosis. 243 (2), 589-592 (2015).
- Zhao, Y., et al. Hyperlipidemia induces typical atherosclerosis development in Ldlr and Apoe deficient rats. Atherosclerosis. 271, 26-35 (2018).
- Ekuni, D., et al. Occlusal disharmony accelerates the initiation of atherosclerosis in apoE knockout rats. Lipids in Health and Disease. 13 (144), 13 (2014).
- Bhattacharya, D., Van Meir, E. G. A simple genotyping method to detect small CRISPR-Cas9 induced indels by agarose gel electrophoresis. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 39950 (2019).
- Malik, N., et al. Intravascular stents: a new technique for tissue processing for histology, immunohistochemistry, and transmission electron microscopy. Heart. 80 (5), 509-516 (1998).
- Kumar, A. H., McCauley, S. D., Hynes, B. G., O'Dea, J., Caplice, N. M. Improved protocol for processing stented porcine coronary arteries for immunostaining. Journal of Molecular Histology. 42 (2), 187-193 (2011).
- Jiang, Z., et al. A novel vein graft model: adaptation to differential flow environments. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 286 (1), 18 (2004).
- Cornelissen, A., et al. Apolipoprotein E deficient rats generated via zinc-finger nucleases exhibit pronounced in-stent restenosis. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 54541 (2019).
- Ritskes-Hoitinga, M. G. T., Jensen, T. L., Mikkelsen, L. F. . The Laboratory Mouse (Second Edition). , 567-599 (2012).
- Rune, I., et al. Long-term Western diet fed apolipoprotein E-deficient rats exhibit only modest early atherosclerotic characteristics. Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 23835 (2018).
- Daemen, J., et al. Early and late coronary stent thrombosis of sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in routine clinical practice: data from a large two-institutional cohort study. Lancet. 369 (9562), 667-678 (2007).
- Cornelissen, A., Vogt, F. J. The effects of stenting on coronary endothelium from a molecular biological view: Time for improvement. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 23 (1), 39-46 (2019).
- Mori, H., et al. Pathological mechanisms of left main stent failure. International Journal of Cardiology. 263, 9-16 (2018).
- Wolinsky, H., Glagov, S. Comparison of abdominal and thoracic aortic medial structure in mammals. Deviation of man from the usual pattern. Circulation Research. 25 (6), 677-686 (1969).
- Lowe, H. C., James, B., Khachigian, L. M. A novel model of in-stent restenosis: rat aortic stenting. Heart. 91 (3), 393-395 (2005).
- Unthank, J. L., Nixon, J. C., Lash, J. M. Early adaptations in collateral and microvascular resistances after ligation of the rat femoral artery. Journal of Applied Physiology. 79 (1), 73-82 (1985).
- Nevzati, E., et al. Biodegradable Magnesium Stent Treatment of Saccular Aneurysms in a Rat Model - Introduction of the Surgical Technique. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (128), e56359 (2017).
- Aquarius, R., Smits, D., Gounis, M. J., Leenders, W. P. J., de Vries, J. Flow diverter implantation in a rat model of sidewall aneurysm: a feasibility study. Journal of NeuroInterventional Surgery. 10 (1), 88-92 (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved