A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Time-Lapse Imaging of Neuronal Arborization using Sparse Adeno-Associated Virus Labeling of Genetically Targeted Retinal Cell Populations
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a method for investigating neurite morphogenesis in postnatal mouse retinal explants by time-lapse confocal microscopy. We describe an approach for sparse labeling and acquisition of retinal cell types and their fine processes using recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors that express membrane-targeted fluorescent proteins in a Cre-dependent manner.
Abstract
Discovering mechanisms that pattern dendritic arbors requires methods to visualize, image, and analyze dendrites during development. The mouse retina is a powerful model system for the investigation of cell type-specific mechanisms of neuronal morphogenesis and connectivity. The organization and composition of retinal subtypes are well-defined, and genetic tools are available to access specific types during development. Many retinal cell types also constrain their dendrites and/or axons to narrow layers, which facilitates time-lapse imaging. Mouse retina explant cultures are well suited for live-cell imaging using confocal or multiphoton microscopy, but methods optimized for imaging dendrite dynamics with temporal and structural resolution are lacking. Presented here is a method to sparsely label and image the development of specific retinal populations marked by the Cre-Lox system. Commercially available adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) used here expressed membrane-targeted fluorescent proteins in a Cre-dependent manner. Intraocular delivery of AAVs in neonatal mice produces fluorescent labeling of targeted cell types by 4-5 days post-injection (dpi). The membrane fluorescent signals are detectable by confocal imaging and resolve fine branch structures and dynamics. High-quality videos spanning 2-4 h are acquired from imaging retinal flat-mounts perfused with oxygenated artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF). Also provided is an image postprocessing pipeline for deconvolution and three-dimensional (3D) drift correction. This protocol can be used to capture several cellular behaviors in the intact retina and to identify novel factors controlling neurite morphogenesis. Many developmental strategies learned in the retina will be relevant for understanding the formation of neural circuits elsewhere in the central nervous system.
Introduction
Dendrites of retinal neurons form intricate, yet specific, patterns that influence their function within neural circuits. In the vertebrate retina, diverse types of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and amacrine cell interneurons bear unique dendritic morphologies that differ in arbor size, location, branch length, and density1. During postnatal development, RGCs and amacrine cells extend exuberant dendritic processes into a neuropil called the inner plexiform layer (IPL), where they receive bipolar cell inputs transmitting photoreceptor signals2. As captured by time-lapse imaging of fluorescently labelled retinal populations in chick or zebrafish larvae, dendrite morphogenesis is highly dynamic3,4,5. Within days, dendritic arbors expand, remodel, and ramify to narrow sublayers of the IPL, where they synapse with select partners. The arbors exhibit different structural dynamics over development, with changes in relative rates of branch addition, retraction, and stabilization. Amacrine and RGC dendrites also exhibit different outgrowth and remodeling behaviors that might reflect type-specific arborization. However, these studies tracked broad amacrine or RGC populations and focused on laminar targeting, which is just one aspect of morphology.
The mechanisms that produce the vast morphological diversity observed across retinal subtypes are poorly understood. The objective of this group was to develop a method to capture dendrite dynamics and arbor remodeling of defined retinal subtypes in mice. Identifying cell type-specific mechanisms of dendrite patterning requires methods to visualize and measure dendrite behaviors of cells of interest. Organotypic cultures of mouse retinas are well suited for live-cell imaging studies using confocal or multiphoton microscopy. Developing retinas are dissected and mounted into a flat explant that can be imaged for several hours in a recording chamber or cultured over a few days with limited effects on the circuitry6,7. Live retinal neurons can be labeled by a variety of techniques, including dye-filling by electrodes, electroporation, biolistic delivery of particles coated with lipophilic dyes or plasmids encoding fluorescent proteins (e.g., Gene Gun), as well as genetically encoded cell labels7,8,9,10. However, these approaches are inefficient for imaging dendrite dynamics of specific retinal subtypes. For instance, dye-filling methods are low-throughput and require electrophysiology apparatus and additional genetic labels to reliably target cells of interest. Moreover, the strong fluorescence signals in the soma can obscure nearby dendrites.
Biolistic gene delivery methods can simultaneously label dozens of cells, but steps involving high-pressure particle delivery and overnight incubation of isolated retina can compromise cell physiology and dendritic outgrowth. This paper proposes that recent genetic tools can be employed to capture early dendrite dynamics with cell type and structural resolution, given the following experimental criteria. First, to resolve the fine branches and filopodia that dominate developing arbors, the method should label neurons with bright, fluorescent proteins that fill processes in the entire arbor. The fluorescence labeling should not fade due to photobleaching during the imaging period. A variety of fluorescent protein variants have been generated and compared for suitability for in vivo/ex vivo imaging11 based on brightness and photostability. Second, the fluorescent proteins (XFPs) must be expressed at sufficiently high levels by the earliest stage of dendrite morphogenesis, so that the narrow developmental window is not missed. In analyses of static timepoints in the mouse retina, dendrite development occurs during the first postnatal week and includes phases of outgrowth, remodeling, and stabilization10,12,13,14,15. Third, the method should lead to selective labelling or to an increased probability of labelling of the neuronal subpopulation of interest. Fourth, labelling of the target subpopulation must be sufficiently sparse so that the entire neuronal arbor can be identified and traced. Although RGC and amacrine subtypes can be distinguished by their mature morphological characteristics and IPL stratification patterns16,17,18,19,20, the challenge is to identify subtypes during development based on immature structures. This task is facilitated by the expansion of transgenic tools to label specific retinal cell types during development.
Transgenic and knock-in mouse lines in which cellular and temporal expression of fluorescent proteins or Cre is determined by gene regulatory elements are widely used to study retinal cell types13,21,22,23. Key observations on subtype-specific patterns of dendrite development have come from studies of transgenic mouse retinas at static timepoints10,14,24,25. The Cre-Lox system, in particular, enables exquisite gene manipulation and monitoring of subtypes using a variety of recombinase-dependent reporters, sensors, and optogenetic activators. These tools have led to discoveries of subtype-specific molecular programs and functional properties that underlie retinal circuit assembly26,27,28,29,30. However, they have yet to be leveraged to study subtype-specific dendrite dynamics in the mouse retina. Low-density labeling can be achieved by combining Cre mouse lines with transgenes introduced by electroporation or by recombinant AAVs. If available, tamoxifen-inducible Cre lines or intersectional genetic strategies can also be used. Finally, the cell should be labelled in a minimally invasive manner and imaged using acquisition parameters so as not to compromise the tissue or interfere with cellular function required for dendrite morphogenesis.
Presented here is a method to apply transgenic tools and confocal microscopy to investigate dendrite dynamics in live mouse retinal explants. Cre transgenic mouse lines have been combined with AAV vectors that express fluorescent proteins upon Cre recombination, which allows for sparse labeling of retinal cells of interest. Commercially available AAVs are delivered to neonatal retina by intravitreal injections. This paper demonstrates that AAVs produce significantly high and cell type-specific fluorescent expression by 4 dpi, allowing access to postnatal time points. To illustrate this approach, the cholinergic "starburst" amacrine interneuron was labelled by delivering Brainbow AAV in neonatal mice expressing the choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-Cre transgene, which is active in the early postnatal retina31,32. Starburst amacrine cells develop a stereotyped and radial arbor morphology that is shaped by dendrite self-avoidance mediated by the clustered protocadherins33,34. This paper shows that the resolution of starburst dendrites and filopodia is significantly improved by XFPs to the plasma membrane with the addition of the CAAX motif which undergoes farnesylation, as used for the Brainbow AAVs31. Finally, time-lapse imaging and post-processing protocols have been determined that produce high-quality images amenable for dendrite reconstruction and morphometric quantification. This protocol can be used to identify factors controlling dendrite morphogenesis and to capture several cellular behaviors in the intact retina.
Protocol
NOTE: This protocol spans 2 days with a minimum period of 4-5 days for viral transduction between experimental days (Figure 1A). Animal experiments are performed in accordance with the Canadian Council on Animal Care Guidelines for Use of Animals in Research and Laboratory Animal Care under protocols approved by the Laboratory of Animal Services Animal Use and Care Committee at the Hospital for Sick Children (Toronto, Canada).
1. Preparations for the neonatal AAV injections and imaging experiments
- Select a Cre mouse line to label the retinal cell populations of interest. Confirm Cre recombinase expression at the time of AAV injections by crossing to a Cre transgenic reporter or through immunostaining with a Cre antibody.
- Breed transgenic Cre mice (8-16 weeks old) to generate Cre-positive neonatal animals.
NOTE: For this demonstration, ChAT-IRES-Cre knock-in mice were used to target the cholinergic Starburst amacrine cells. - Obtain recombinase-dependent AAV virus encoding fluorescent protein(s). For optimal labeling of fine processes, select vectors that express modified XFPs targeting the plasma membrane.
NOTE: This study used the Brainbow virus (BBV), AAV-EF1a-BbTagBY and AAV9-EF1a-BbChT (see Table of Materials), which provide the option for multicolour labeling (Figure 1B). Farnesylated enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) and monomeric Cherry (mCherry) expression produced the strongest fluorescent signals for live imaging. A single BBV can be used to image individual arbors, while co-injection of BBVs can be used to label more cells or neighboring arbors with distinct fluorophores. If using multiple fluorescent proteins, ensure minimal emission spectrum overlap (Figure 1C). Microscope acquisition parameters must be adjusted to capture distinct XFP signals. - Prepare ∼3-5 µL aliquots of AAVs in individual low-binding tubes for single-use stocks to avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Store at -80 °C.
- Prepare borosilicate glass micropipettes with very fine tips using a micropipette puller.
NOTE: Puller settings vary depending on filament and puller being used; see Figure 2A for final tip size and shape. Typical droplet diameters are 600 µm. - Obtain a microinjection system and associated tubing. Connect the microinjector to a pressurized air port.

Figure 1: Experimental overview. (A) This protocol spans 2 days of experiments with a minimum of 4-5-day infection period between experimental days. Intraocular injections are performed on neonatal mice no older than postnatal day 3. Retinas are then dissected, flat-mounted, and live-imaged to capture the desired developmental window. Labelled cells can be imaged any time after the required 4-5 days needed for viral expression, as there are no apparent effects of prolonged AAV expression on dendrite morphology. (B) Cre-dependent Brainbow AAV vectors (BBV) are injected into animals expressing Cre31. In this study, ChAT-Cre knock-in mice were used to drive Cre recombination in starburst amacrine cells. The two BBVs encode modified eYFP or tagBFP, or mCherry and mTFP, which terminate in a CAAX motif that is sequentially farnesylated for membrane localization. Lox sites are depicted with triangles. The vectors express either farnesylated XFPs in a stochastic and combinatorial manner dependent on Cre recombination. The EF1α promoter includes regulatory elements from the elongation factor 1α gene. W represents elements from the woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element, and pA indicates the polyadenylation sequence. (C) The excitation and emission spectra of mCherry and eYFP, the BBV fluorophores imaged in this study. When live-imaging multiple fluorescent proteins, the detection parameters must be arranged to adequately separate emission spectra into distinct channels. Abbreviations: AAV = adeno-associated virus; BBV = Brainbow AAV; ChAT = choline acetyltransferase; iRES = internal ribosome entry site; eYFP = enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; iTR = inverted terminal repeat; tagBP = Tag-blue fluorescent protein; mCherry = monomeric Cherry; mTFP = teal fluorescent protein; XFP = any fluorescent protein; EF1α= elongation factor 1 alpha. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Intravitreal injections of AAVs in neonatal mice
- Thaw an AAV aliquot on ice. Prepare a ~1:4 AAV dilution using sterile saline or phosphate-buffered saline. Prepare ~0.5 µL of AAV dilution per animal (~0.25 µL per eye) in case the micropipette breaks, and a new pipette needs to be filled. Store the remaining undiluted AAV at 4 °C, and use within 2 weeks.
NOTE: In this experiment, the supplier AAV concentration was ~1-2 × 1013 genome content (GC)/mL and diluted to a final concentration of 4 × 1012 GC/mL. Optimize the viral concentration to obtain the desired labeling density. - To visualize the injections, add approximately 1 µL of 0.02% Fast Green FCF dye solution for every 15 µL of AAV dilution to color the solution blue.
- Transfer a mouse cage with dam and newborn litter (postnatal day (P) 0.5-3) to a procedure room with microinjection equipment. Keep the animals in the same cage with nests and bedding to minimize maternal stress and rejection of pups.
- Sterilize the injection area with 70% ethanol, and place sterile diaper pads on bench surfaces. Prepare a warm platform (e.g., a heating pad) for recovery from hypothermia-induced anesthesia.
- Backfill the micropipette with the AAV dilution using a microsyringe. Under a stereomicroscope, break the micropipette tip with a 30 G needle to unseal the tip.
NOTE: Figure 2A shows the backfilled tip-both sealed (top) and unsealed (middle). - Anesthetize neonatal mice by hypothermia by placing 1-2 animals on ice. Place animals onto a latex glove to protect skin from direct contact with ice. Once the animal no longer moves in response to paw pinch (~2 min), place the animal under a stereomicroscope. If desired, tattoo paw pads with tattoo ink and 30 G needle, and collect tail clippings for DNA isolationto identify animals by genotyping.
NOTE: Appropriate monitoring of depth of anesthesia must occur throughout the procedure. - Swab the skin overlying the eyes with 70% ethanol. Use a 30 G needle to open the fused eyelid (Figure 2B). Apply light pressure with the fingers to open the eye, and poke a small hole through the cornea at the cornea-sclera junction (Figure 2C).
- Insert the glass micropipette into the hole, and press the microinjector foot pedal 2-4 times to inject the AAV into the intravitreal space. Slowly remove the micropipette, and confirm AAV injection by visualizing blue dye through the pupil (Figure 2D).
NOTE: With an ejection pressure of 6-8 psi and pulse time of 600-800 ms, a 600 µm diameter droplet is ejected (Figure 2A, bottom). Approximately 0.23-0.45 µL of AAV solution is injected per eye. Blue solution outside the eye indicates that the AAV was not injected into the eye. Blue solution leaking from the injection site indicates that the AAV may have leaked out, reducing transfection efficiency. - Gently press the eyelids together to re-seal, and place the pup onto a heated pad. Once the animals recover a pinkish color and are responsive, gently transfer them back to the housing cage.
NOTE: Ensure appropriate precautions are taken to avoid too rapid re-warming of the pups. - Repeat the injection procedure for the remaining animals in the litter. Allow a minimum of 4-5 days for viral transduction before imaging the retina.

Figure 2: Neonatal intraocular injections. (A) Backfilled micropipette shows the shape of the pipette tip when sealed (top) and after the tip is unsealed (bottom, left). Pico-injection pressure of 6-8 psi and pulse time of 600-800 ms produces a 600 µm diameter droplet (bottom, right). Scale bar = 1 mm.(B) Anesthetized P0 pup under 16x magnification. The fused eyelid junction (white) is slit open using a sharp 30 G needle. Scale bar = 2 mm. (C) Light pressure applied to the eye exposes the cornea; scale bar = 2 mm. Zoomed section (red) shows the small hole at the cornea-sclera junction (yellow) created with a 30 G needle; scale bar = 0.5 mm. (D) Withdrawal of the pipette tip after injection (left). Fast Green dye in the AAV solution appears as blue-grey through the pupil (middle), as compared to the light pupil color before injection (right). Scale bar = 1 mm. (E) After 4 days, the eyelid has healed and fused shut (left); scale bar = 2 mm. Upon enucleation, the healed injection site is visible (yellow); scale bar = 1 mm. Note the location of the injection site at the border between the cornea and sclera. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Retinal dissections for imaging experiment
- Prepare retinal aCSF (119 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM KCl, 1.3 mM MgCl2·6H2O, 2.5 mM CaCl2·2H2O, 1 mM NaH2PO4, 11 mM glucose, and 20 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES free acid)35. If desired, prepare and freeze 10x solution; thaw and dilute to 1x as needed.
- Oxygenate the retinal aCSF by bubbling with carbogen (95% O2, 5% CO2) for a minimum of 15 min. Adjust the pH to 7.4. Keep in a sealed container until use to ensure that the aCSF remains oxygenated.
NOTE: Retinas require a high concentration of O2. It is important to keep aCSF oxygenated throughout the experiment. - Embed a 60 mm diameter Petri dish into an ice tray (fashion an ice tray out of lab plastic, e.g., a pipette box lid), and place it under a stereomicroscope. Fill the Petri dish with oxygenated retinal aCSF.
- Euthanize mice P9 and younger by decapitation. Euthanize mice P10 and older by isoflurane induction, or an alternate method approved under the animal protocol, followed by decapitation.
- If the eyelids are sealed, cut the eyelid flap to expose the eye. Use forceps to enucleate the eyes, and transfer them into the cold retinal aCSF from step 3.3.
- To dissect the retinal cup, under a stereomicroscope (magnification 25x), stabilize the eye by clasping the optic nerve using a Dumont #5 forcep (Figure 3A).
- Poke a hole in the center of the cornea with a 30 G needle, and then insert one tip of the microscissors into the hole to make an incision from the hole to the end of the cornea. Repeat to make 4 slices in the cardinal directions, creating 4 "flaps" (Figure 3A).
- With two Dumont #5 forceps, grasp and pull the two adjacent flaps apart, gently peeling the sclera from the retina. Repeat with the remaining cornea flaps, and remove the sclera from the retina (Figure 3B).
- Remove the lens from the retinal cup using the forceps. With microscissors, make 4 radial incisions from the edge of the retina towards the optic nerve, creating 4 equal petals (Figure 3B). Repeat steps 3.4-3.7 for the second eye.
4. Retinal flat-mount preparation
- Prepare grey mixed cellulose ester (MCE) membrane filter discs for mounting. If using large diameter MCE membrane filters, cut the disc into quadrants (roughly 1 cm across). Place the MCE disc onto the center of a larger white filter paper (Figure 3D).
NOTE: MCE filters are also available in 1 cm diameter discs. The MCE filter disc must be large enough to fit 1-2 retinas, but small enough to fit into the imaging chamber. As MCE membranes hold a static charge, minimize contact and handling of the MCE membrane. - Handling retinas using two size 3/0 paint brushes, flip one retinal cup onto a paintbrush with the retinal ganglion cell side down. Gently lift the retina out of the aCSF, making sure the water tension does not tear the retina (Figure 3C).
- While still holding the paintbrush with the retina, use a transfer pipette to place a droplet of aCSF in the center of the MCE filter paper (Figure 3C, right). Float the retina into the droplet of aCSF created by the surface tension. Use paint brushes to position the retina RGC side up within the droplet and to unfold the four petals.
- Once positioned, create a water bridge between the paintbrush and white filter paper to break the surface tension of the droplet.
NOTE: When aCSF is wicked away, the retina will adhere to the MCE filter paper (Figure 3D,E). Flat-mounted retinas can be handled by grasping the MCE disc with forceps. If the aCSF droplet quickly wicks away prior to forming a water bridge, this may indicate that the MCE membrane is not charged. Use a fresh MCE membrane, and minimize the time between enucleation and imaging by dissecting and flat-mounting retinas immediately before moving retinas into the imaging chamber.

Figure 3: Retinal dissection and flat-mounting onto mixed cellulose ester filter membranes. (A) Left, an enucleated eye is stabilized by grasping the optic nerve with Dumont #5 forceps (left). A small hole is created in the center of the cornea using a 30 G needle (center). Micro-dissection scissors are used to cut the cornea into 4 equal flaps (right). Scale bar = 1 mm. (B) Dissected retina with the sclera peeled off using two Dumont #5 forceps (left) and with the lens removed (center). Retina with 4 equal cuts halfway into the retina (right). Scale bar = 1 mm. (C) Handling of retina with two fine paintbrushes (size 3/0, left). Retina flipped with retinal ganglion cells side down onto a paintbrush (center) and lifted out of aCSF, making sure the water tension does not tear the retina (right). Scale bar = 2 mm. (D) Grey MCE membrane disc placed onto a white filter paper (left). A droplet of aCSF on the MCE disc (right). Scale bar = 1 cm. (E) After floating the retinas into the droplet and positioning them, create a water bridge with the white filter paper to wick the aCSF, pulling the retina onto the charged MCE paper (left); scale bar = 1 cm. Zoomed image of the MCE membrane (red) shows 2 retinas mounted with retinal ganglion cells side up (right); scale bar = 2 mm. One retina is outlined in white. Abbreviations: MCE = mixed cellulose ester; aCSF = artificial cerebrospinal fluid. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Time-lapse confocal imaging of live whole-mount retina preparations
- Assemble the live-imaging incubation chamber for an upright confocal microscope as seen in Figure 4.
NOTE: For inverted confocal systems, flat-mounts are placed RGC side down directly onto the glass bottom coverslip of the incubation chamber. Once the retinas make contact with the coverslip, they cannot be moved. - Fill the chamber with oxygenated aCSF, and turn on the pump and temperature controller (temperature 32-34 °C, flow rate 1 mL/min). Do not allow temperature to rise above 34 °C.
- To transfer the retinal flat-mount to the perfusion chamber, stop the pump, and remove the aCSF that is in the chamber. Place the MCE disc with the retinal flat-mount into the (empty) incubation chamber.
- Place a sample weight onto the flat-mount; pre-wet the weight to break surface tension. Refill the chamber with the warmed aCSF, and circulate aCSF at ~1 mL/min.
- Position the nosepiece with the 25x water dipping objective (numerical aperture 0.95) into the imaging chamber. Screen for labelled cells of interest using epifluorescent light (Figure 4C).
- Adjust the imaging volume to capture dendritic features of interest.
NOTE: This study captured the complete dendritic arbor at 1024 x 1024 pixels per frame, z-step 1 µm, and a frame rate of 2 min between each z-stack. Final image sizes are ~100 µm x 100 µm x 20 µm. - To adjust the laser power to an optimal setting, use a look-up table that identifies both oversaturated and undersaturated pixels. While scanning, adjust the laser power such that no pixels are oversaturated (i.e., at an intensity of 255 or above). Continue imaging as long as required, or until the there is a significant and detectable decline in fluorescent signal and increase in noise (typically 2-4 h).
NOTE: Reduced laser power is recommended as deconvolution algorithms work optimally when pixels are distributed over the full dynamic range. Pixel intensity should not exceed 254; empirical analyses of neurites revealed that pixel values below 170 are ideal for deconvolution. Fast scan speeds (400-600 Hz) with line averaging (2-3) are preferable to single, slower scans of the same total pixel dwell time. The area of prolonged imaging often photobleaches, but other explant sections remain viable. Multiple regions in a flat-mount can be imaged, each for 2-4 h, with a total incubation time of 6 hours. Imaging sessions beyond 6 h have not been systematically tested. Neurite degradation and blebbing are signs that the explant viability is declining. - After imaging, fix the retinal flat-mounts and membrane filter with cold 4% paraformaldehyde for 1-2 h at 4 °C. Amplify the fluorescent labels in the fixed retinas by immunohistochemistry for further analyses.
NOTE: Post-imaging fixation is not possible when using an inverted confocal; retinas are not removable without destroying the tissue.
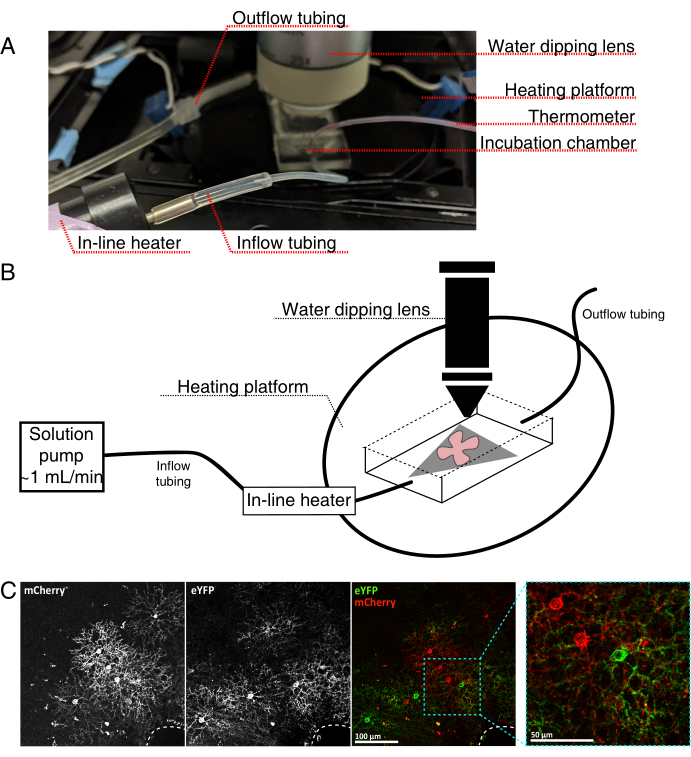
Figure 4: Live-cell imaging incubation chamber setup. (A) Live-imaging incubation apparatus showing heating, solution, and imaging components. Dual heater includes a heated incubation chamber platform (back circle with blue connector electrodes) and an in-line solution heater. (B) Schematic diagram of 4A. Retinal flat-mount (red) on MCE membrane (grey) is placed in the incubation chamber. The in-line solution heater is connected to a solution pump (not pictured in 4A). Imaging chamber dimensions allow a good working area for the dipping objective nose. (C) 25x view a retinal explant injected with 0.23-0.45 µL of 4 × 1012 GC/mL of AAV dilution; scale bar = 100 µm. Dense labeling of cells often surrounds the optic nerve head (dashed line, bottom right); scale bar = 50 µm. Abbreviations: MCE = mixed cellulose ester; GC = genome copies; mCherry = monomeric Cherry; eYFP = enhanced yellow fluorescent protein. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
6. Image deconvolution and post-processing in ImageJ
- Import the image series, split the series by time, and color if it is a multi-color image. Ensure that all time points for one color are contained in the same folder.
NOTE: Import Bio-formats if using ImageJ (Bio-formats is automatically included in FIJI). - Create a theoretical point-spread function (PSF) using the ImageJ plugin, Diffraction PSF 3D.
NOTE: Each imaging channel requires its own PSF as fluorescent protein emission wavelength impacts the PSF. - Use Plugins | Macros | Run to perform batch Parallel Iterative Deconvolution for all timepoints using the provided macro (Supplementary File 1).
NOTE: This macro runs 25 iterations of the Wiener Filter Preconditioned Landweber (WPL) iterative algorithm. Each color channel must be deconvolved separately. - Merge the color channels, and compile all time points into a Hyperstack (Image | Hyperstacks | Stacks to Hyperstack). Correct the 3D drift using Plugins | Registration | Correct 3D Drift.
- Return the image to a regular stack (Image | Hyperstacks | Hyperstack to Stack), and split the time points (Image | Stacks | Tools | Stack Splitter). Use batch processing to create maximum projection for all time points (Process | Batch | Macro | run("Z Project...", "projection=[Max Intensity]"); ).
- Import the time-lapse image sequence (File | Import | Image Sequence). Use conventional ImageJ tools for desired analysis of deconvolved and post-processed two-dimensional (2D) video.
NOTE: Four-dimensional (3D + time) deconvolved and drift-corrected videos can be viewed as a hyperstack. Omit the previous step to maintain 3D time points.
Results
Using the above protocol, a high-resolution 3D video of developing starburst cell dendrites was acquired, deconvolved, and corrected for 3D drift. Z-plane maximum projections were produced to make 2D videos for analysis (Supplementary Video 1, Figure 5A). 3D deconvolution of each time point increased the resolution of fine filopodia projections (Figure 5B,C). Fine filopodia protrusions are a feature of developing retinal dendrit...
Discussion
This video demonstrates an experimental pipeline that utilizes existing genetic tools to image dendrite dynamics of developing retinal neurons with confocal live-imaging. Also demonstrated are intraocular injections of Cre-dependent AAVs encoding membrane-targeted fluorescent proteins into neonatal mice. Single cells of genetically targeted populations are brightly labelled as early as 4-5 dpi. Retinal flat-mounts were prepared for standard imaging chambers to perform live-cell confocal imaging. This method produces high...
Disclosures
The authors do not have anything to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We thank Madison Gray for giving me a hand when I didn't have any. This research was supported by an NSERC Discovery Grant (RGPIN-2016-06128), a Sloan Fellowship in Neuroscience and a Canada Research Chair Tier 2 (to J.L.L). S. Ing-Esteves was supported by the Vision Science Research Program and NSERC Postgraduate Scholarships-Doctoral.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Addgene viral prep #45185-AAV9 | |||
| Addgene viral prep #45186-AAV9 | |||
| Dissection tools | |||
| Cellulose filter paper | Whatman | 1001-070 | |
| Dumont #5 fine forceps | FST | 11252-20 | Two Dumont #5 forceps are required for retinal micro-dissection |
| Dumont forceps | VWR | 82027-426 | |
| Fine Scissors | FST | 14058-09 | |
| Mixed cellulose ester membrane (MCE) filter papers, hydrophilic, 0.45 µm pore size | Millipore | HABG01 300 | |
| Petri Dish, 50 × 15 mm | VWR | 470313-352 | |
| Polyethylene disposable transfer pipette | VWR | 470225-034 | |
| Round tip paint brush, size 3/0 | Conventional art supply store | Two size 3/0 paint brushes (or smaller) are required for retinal flat-mounting | |
| Surgical Scissors | FST | 14007-14 | |
| Vannas Spring Scissors - 2.5 mm Cutting Edge | FST | 15000-08 | |
| Live-imaging incubation system | |||
| Chamber polyethylene tubing, PE-160 10' | Warner Instruments | 64-0755 | |
| Dual channel heater controller, Model TC-344C | Warner Instruments | 64-2401 | |
| HC FLUOTAR L 25x/0.95 W VISIR dipping objective | Leica | 15506374 | |
| Heater controller cable | Warner Instruments | CC-28 | |
| Large bath incubation chamber with slice support | Warner Instruments | RC-27L | |
| MPII Mini-Peristaltic Pump | Harvard Apparatus | 70-2027 | |
| PM-6D Magnetic Heated Platform (incubation chamber heater) | Warner Instruments | PM-6D | |
| Pump Head Tubing Pieces For MPII Mini-Peristaltic Pump | Harvard Apparatus | 55-4148 | |
| Sample anchor (Harps) | Warner Instruments | 64-0260 | Sample anchor must be compatible with incubation chamber |
| Sloflo In-line Solution Heater | Warner Instruments | SF-28 | |
| Neonatal Injections | |||
| 10 µL Microliter Syringe Series 700, Removable Needle | Hamilton Company | 80314 | |
| 30 G Hypodermic Needles (0.5 inch) | BD PrecisionGlide | 305106 | |
| 4 inch thinwall glass capillary, no filament (1.0 mm outer diameter/0.75 mm) | WPI World Precision Instruments | TW100-4 | |
| Ethanol 99.8% (to dilute to 70% with double-distilled water [ddH2O]) | Sigma-Aldrich | V001229 | |
| AAV9.hEF1a.lox.TagBFP. lox.eYFP.lox.WPRE.hGH-InvBYF | Penn Vector Core | AV-9-PV2453 | Addgene Plasmid #45185 |
| AAV9.hEF1a.lox.mCherry.lox.mTFP 1.lox.WPRE.hGH-InvCheTF | Penn Vector Core | AV-9-PV2454 | Addgene Plasmid #45186 |
| ChAT-IRES-Cre knock-in transgenic mouse line | The Jackson Laboratory | 6410 | |
| Fast Green FCF Dye content ≥85 % | Sigma-Aldrich | F7252-25G | |
| Flaming/Brown Micropipette Puller, model P-97 | Sutter Instrument Co. | P-97 | |
| Green tattoo paste | Ketchum MFG Co | 329A | |
| Phosphate-Buffered Saline, pH 7.4, liquid, sterile-filtered, suitable for cell culture | Sigma-Aldrich | 806552 | |
| Pneumatic PicoPump | WPI World Precision Instruments | PV-820 | |
| Oxygenated artifiial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) Reagents | |||
| Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) | Sigma-Aldrich | C7902 | |
| Carbogen (5% CO2, 95% O2) | AirGas | X02OX95C2003102 | Supplier may vary depending on region |
| D-(+)-Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | G7021 | |
| HEPES, Free Acid | Bio Basic | HB0264 | |
| Hydrochloric acid solution, 1 N | Sigma-Aldrich | H9892 | |
| Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2·6H2O) | Sigma-Aldrich | M2670 | |
| pH-Test strips (6.0-7.7) | VWR | BDH35317.604 | |
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Sigma-Aldrich | P9541 | |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Bio Basic | DB0483 | |
| Sodium phosphate monobasic (NaH2PO4) | Sigma-Aldrich | RDD007 | |
| Software | |||
| ImageJ | National Institutes of Health (NIH) | Open source |
References
- Lefebvre, J. L., Sanes, J. R., Kay, J. N. Development of dendritic form and function. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 31, 741-777 (2015).
- Graham, H. K., Duan, X. Molecular mechanisms regulating synaptic specificity and retinal circuit formation. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Developmental biology. 10 (1), 379 (2021).
- Godinho, L., et al. Targeting of amacrine cell neurites to appropriate synaptic laminae in the developing zebrafish retina. Development. 132 (22), 5069-5079 (2005).
- Mumm, J. S., et al. In vivo imaging reveals dendritic targeting of laminated afferents by zebrafish retinal ganglion cells. Neuron. 52 (4), 609-621 (2006).
- Wong, W. T., Faulkner-Jones, B. E., Sanes, J. R., Wong, R. O. Rapid dendritic remodeling in the developing retina: dependence on neurotransmission and reciprocal regulation by Rac and Rho. The Journal of Neuroscience. 20 (13), 5024-5036 (2000).
- Wei, W., Elstrott, J., Feller, M. B. Two-photon targeted recording of GFP-expressing neurons for light responses and live-cell imaging in the mouse retina. Nature Protocols. 5 (7), 1347-1352 (2010).
- Morgan, J. L., Wong, R. O. L. Ballistic labeling with fluorescent dyes and indicators. Current Protocols in Neuroscience. 43 (1), 1-10 (2008).
- Nickerson, P. E. B., et al. Live imaging and analysis of postnatal mouse retinal development. BMC Developmental Biology. 13, 24 (2013).
- Morgan, J. L., Dhingra, A., Vardi, N., Wong, R. O. L. Axons and dendrites originate from neuroepithelial-like processes of retinal bipolar cells. Nature Neuroscience. 9 (1), 85-92 (2006).
- Coombs, J. L., Van Der List, D., Chalupa, L. M. Morphological properties of mouse retinal ganglion cells during postnatal development. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 503 (6), 803-814 (2007).
- Cranfill, P. J., et al. Quantitative assessment of fluorescent proteins. Nature Methods. 13 (7), 557-562 (2016).
- Stacy, R. C., Wong, R. O. L. Developmental relationship between cholinergic amacrine cell processes and ganglion cell dendrites of the mouse retina. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 456 (2), 154-166 (2003).
- Kay, J. N., et al. Retinal ganglion cells with distinct directional preferences differ in molecular identity, structure, and central projections. The Journal of Neuroscience. 31 (21), 7753-7762 (2011).
- Liu, J., Sanes, J. R. Cellular and molecular analysis of dendritic morphogenesis in a retinal cell type that senses color contrast and ventral motion. The Journal of Neuroscience. 37 (50), 12247-12262 (2017).
- Diao, L., Sun, W., Deng, Q., He, S. Development of the mouse retina: emerging morphological diversity of the ganglion cells. Journal of Neurobiology. 61 (2), 236-249 (2004).
- Coombs, J., vander List, D., Wang, G. Y., Chalupa, L. M. Morphological properties of mouse retinal ganglion cells. Neuroscience. 140 (1), 123-136 (2006).
- Sanes, J. R., Masland, R. H. The types of retinal ganglion cells: current status and implications for neuronal classification. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 38, 221-246 (2015).
- Sümbül, U., et al. A genetic and computational approach to structurally classify neuronal types. Nature Communications. 5, 3512 (2014).
- Lin, B., Masland, R. H. Populations of wide-field amacrine cells in the mouse retina. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 499 (5), 797-809 (2006).
- Macneil, M. A., Heussy, J. K., Dacheux, R. F., Raviola, E., Masland, R. H. The shapes and numbers of amacrine cells: Matching of photofilled with Golgi-stained cells in the rabbit retina and comparison with other mammalian species. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 413 (2), 305-326 (1999).
- Ivanova, E., Hwang, G. S., Pan, Z. H. Characterization of transgenic mouse lines expressing Cre recombinase in the retina. Neuroscience. 165 (1), 233-243 (2010).
- Jo, A., Xu, J., Deniz, S., Cherian, S., DeVries, S. H., Zhu, Y. Intersectional strategies for targeting amacrine and ganglion cell types in the mouse retina. Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 12, 66 (2018).
- Siegert, S., et al. Genetic address book for retinal cell types. Nature Neuroscience. 12 (9), 1197-1204 (2009).
- Kim, I. -. J., Zhang, Y., Meister, M., Sanes, J. R. Laminar restriction of retinal ganglion cell dendrites and axons: subtype-specific developmental patterns revealed with transgenic markers. The Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (4), 1452-1462 (2010).
- Peng, Y. -. R., Tran, N. M., Krishnaswamy, A., Kostadinov, D., Martersteck, E. M., Sanes, J. R. Satb1 regulates contactin 5 to pattern dendrites of a mammalian retinal ganglion cell. Neuron. 95 (4), 869-883 (2017).
- Duan, X., Krishnaswamy, A., Dela Huerta, I., Sanes, J. R. Type II cadherins guide assembly of a direction-selective retinal circuit. Cell. 158 (4), 793-807 (2014).
- Ray, T. A., et al. Formation of retinal direction-selective circuitry initiated by starburst amacrine cell homotypic contact. eLife. 7, 34241 (2018).
- Krishnaswamy, A., Yamagata, M., Duan, X., Hong, Y. K., Sanes, J. R. Sidekick 2 directs formation of a retinal circuit that detects differential motion. Nature. 524 (7566), 466-470 (2015).
- Caval-Holme, F., Zhang, Y., Feller, M. B. Gap junction coupling shapes the encoding of light in the developing retina. Current Biology. 29 (23), 4024-4035 (2019).
- Lucas, J. A., Schmidt, T. M. Cellular properties of intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells during postnatal development. Neural Development. 14 (1), 8 (2019).
- Cai, D., Cohen, K. B., Luo, T., Lichtman, J. W., Sanes, J. R. Improved tools for the Brainbow toolbox. Nature Methods. 10 (6), 540-547 (2013).
- Rossi, J., et al. Melanocortin-4 receptors expressed by cholinergic neurons regulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Cell Metabolism. 13 (2), 195-204 (2011).
- Lefebvre, J. L., Kostadinov, D., Chen, W. V., Maniatis, T., Sanes, J. R. Protocadherins mediate dendritic self-avoidance in the mammalian nervous system. Nature. 488 (7412), 517-521 (2012).
- Ing-Esteves, S., et al. Combinatorial effects of alpha- and gamma-protocadherins on neuronal survival and dendritic self-avoidance. The Journal of Neuroscience. 38 (11), 2713-2729 (2018).
- Williams, P. R., Morgan, J. L., Kerschensteiner, D., Wong, R. O. L. In vitro imaging of retinal whole mounts. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2013 (1), (2013).
- Ramoa, A. S., Campbell, G., Shatz, C. J. Transient morphological features of identified ganglion cells in living fetal and neonatal retina. Science. 237 (4814), 522-525 (1987).
- Schindelin, J., et al. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods. 9, 676-682 (2012).
- Peng, H., Ruan, Z., Long, F., Simpson, J. H., Myers, E. W. V3D enables real-time 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of large-scale biological image data sets. Nature Biotechnology. 28 (4), 348-353 (2010).
- Cuntz, H., Forstner, F., Borst, A., Häusser, M. One rule to grow them all: a general theory of neuronal branching and its practical application. PLoS Computational Biology. 6 (8), 1000877 (2010).
- Xiao, H., Peng, H. APP2: automatic tracing of 3D neuron morphology based on hierarchical pruning of a gray-weighted image distance-tree. Bioinformatics. 29 (11), 1448-1454 (2013).
- Nanda, S., et al. Design and implementation of multi-signal and time-varying neural reconstructions. Scientific data. 5, 170207 (2018).
- Sherry, D. M., Wang, M. M., Bates, J., Frishman, L. J. Expression of vesicular glutamate transporter 1 in the mouse retina reveals temporal ordering in development of rod vs. cone and ON vs. OFF circuits. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 465 (4), 480-498 (2003).
- Johnson, J., et al. Vesicular neurotransmitter transporter expression in developing postnatal rodent retina: GABA and glycine precede glutamate. The Journal of Neuroscience. 23 (2), 518-529 (2003).
- Jüttner, J., et al. Targeting neuronal and glial cell types with synthetic promoter AAVs in mice, non-human primates and humans. Nature Neuroscience. 22 (8), 1345-1356 (2019).
- Zincarelli, C., Soltys, S., Rengo, G., Rabinowitz, J. E. Analysis of AAV serotypes 1-9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Molecular Therapy. 16 (6), 1073-1080 (2008).
- Petros, T. J., Rebsam, A., Mason, C. A. In utero and ex vivo electroporation for gene expression in mouse retinal ganglion cells. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (31), e1333 (2009).
- Lye, M. H., Jakobs, T. C., Masland, R. H., Koizumi, A. Organotypic culture of adult rabbit retina. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (3), e190 (2007).
- Pignatelli, V., Strettoi, E. Bipolar cells of the mouse retina: a gene gun, morphological study. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 476 (3), 254-266 (2004).
- Huckfeldt, R. M., et al. Transient neurites of retinal horizontal cells exhibit columnar tiling via homotypic interactions. Nature Neuroscience. 12 (1), 35-43 (2009).
- Prahst, C., et al. Mouse retinal cell behaviour in space and time using light sheet fluorescence microscopy. eLife. 9, 49779 (2020).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved