A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Screening of Tobacco Genotypes for Phytophthora nicotianae Resistance
In This Article
Summary
Here, a protocol is presented for the efficient and accurate screening of tobacco genotypes for Phytophthora nicotianae resistance in seedlings. This is a practical approach for precision breeding, as well as molecular mechanism research.
Abstract
Black shank, caused by the oomycetes Phytophthora nicotianae, is destructive to tobacco, and this pathogen is highly pathogenic to many solanaceous crops. P. nicotianae is well adapted to high temperatures; therefore, research on this pathogen is gaining importance in agriculture worldwide because of global warming. P. nicotianae-resistant varieties of tobacco plants are commonly screened by inoculation with oat grains colonized by P. nicotianae and monitoring for the disease symptoms. However, it is difficult to quantify the inoculation intensity since accurate inoculation is crucial in this case. This study aimed to develop an efficient and reliable method for evaluating the resistance of tobacco to infection with P. nicotianae. This method has been successfully used to identify resistant varieties, and the inoculation efficiency was confirmed by real-time PCR. The resistance evaluation method presented in this study is efficient and practical for precision breeding, as well as molecular mechanism research.
Introduction
P. nicotianae is destructive to many solanaceous crops. It can cause tobacco "black shank"1, potato foliar and tuber rot2, tomato and sweet pepper crown and root rot3, and Goji collar and root rot4. P. nicotianae can attack all parts of tobacco plants, including the roots, stems, and leaves at any growing stage5. The most common symptom of the disease is the black base of the stalk. The roots are initially visible as water-soaked and then become necrotic, and the leaves show large circular lesions5. This disease can be devastating to a tobacco plant in the greenhouse, as well as in the field6. The most practical and economical method for controlling P. nicotianae is the use of resistant varieties7. However, an effective screening protocol is required for the identification of P. nicotianae-resistant accessions from tobacco germplasm collections.
Various identification methods have been described to assess P. nicotianae resistance in tobacco7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16. In general, three major approaches have been used for the identification of P. nicotianae-resistant tobacco genotypes. The first includes mixing mycelia with agar medium on Petri plates containing P. nicotianae. The mycelia are then cultivated in the dark at room temperature for 2 weeks. 1 L of deionized water is added to the mycelia and homogenized for 30 s. The inoculum is kept on ice until needed. Two holes (1 cm in diameter and 4-5 cm deep) are made on each side of the plant, and 10 mL of the inoculum is poured into each hole. The holes are then filled with the surrounding soil, and disease development is monitored daily for 2 weeks8,10.
In the second method, the plants are inoculated with pathogen-infested toothpicks. For this approach, the plants should be used approximately 6 weeks after transplanting and should have a minimum height of 30 cm. Autoclaved toothpicks are placed on the surface of cultures containing P. nicotianae mycelia. The culture dishes are then stored under the light at room temperature for 7 days. Then, colonized toothpicks are used to inoculate the plants. Toothpicks are inserted into the tobacco stems between the fourth and fifth nodes. The plants are monitored daily for 5 days9,15. This method is not applicable for small seedlings. As the inoculum is pathogen-infested toothpicks, the inoculation intensity cannot be precisely controlled.
The most frequently used approach involves oat grains for inoculation. In this case, oat grains are prepared by autoclaving 500 mL of oats and 300 mL of deionized water at 121 °C for 1 h once per day for 3 days. Then, oat grains are added to the pathogen-colonized culture medium. The dishes are sealed with paraffin film and incubated at 25 °C in light for 7-12 days. Four separate 5 cm deep holes are madeon the potting soil, 4 cm from each plant, and one pathogen-infested oat grain is placed into each hole. The incubation period is determined based on when the first aboveground symptom occurrs7,11,12,13,14,15,16. This method is efficient and applicable for large-scale resistance screening. However, one limitation of this approach is that the inoculum is pathogen-infested oat grains, hence the inoculation intensity cannot be precisely controlled.
However, presented here is a more accurate method that is applicable to growth chamber resistance evaluation. Compared to the other approaches, the inoculum is zoospore suspension, hence the inoculation intensity is controllable and adjustable. As the tobacco plants in this study are cultivated without soil, the results are easier to observe. Moreover, sampling plant roots from soil always causes damage to the roots, which induces a series of physiological responses17. In this method, as plants are cultivated without soil, the interference in root damage can be eliminated. In conclusion, this method is more practical for molecular mechanism research and precision breeding. Using this protocol, data are typically obtained within 5 days, with more than 200 plants evaluated in a single experiment.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Materials
- Obtain tobacco varieties.
NOTE: For this experiment "Beinhart1000-1" (a selection of Beinhart 1000) (BH) and "Xiaohuangjin1025" (XHJ) were obtained from the National Medium-term Genbank of the Tobacco Germplasm Resource of China. BH is resistant, whereas XHJ is susceptible to P. nicotianae infection16. A field isolate of P. nicotianae race 0, which was preserved in the Tobacco Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, was used for all inoculations throughout the study.
2. Planting tobacco genotypes for P. nicotianae resistance evaluation
- Mix tobacco seeds with vermiculite and broadcast the seeds gently on the sterilized potting soil. Place the pots in the growth chamber. Maintain a constant temperature of 25 °C, under a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod.
- Prepare hydroponic devices with trays and foam sheets. After the seeds germinate, prick seedlings out from the potting soil, wash the roots gently with sterile deionized water, and transplant them into the hydroponic devices.
- Place the devices in climate chambers at 25 °C under a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod for 24 h.
- Prepare Hoagland nutrient solution beforehand (Table 1). Transplant the seedlings to hydroponic devices with Hoagland nutrient solution (approximately 125 mL per plant).
- Place the devices in a climate chamber at 25 °C under a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod for 2 weeks.
3. Preparation of P. nicotianae zoospore suspension
- Prepare oatmeal agar medium.
- Weigh 33 g of oatmeal and transfer to glassware and add 1,000 mL of sterile water. Boil on an electromagnetic stovetop oven.
- After the oatmeal becomes sticky, strain the liquid solution through a piece of sterile gauze.
- Pour the liquid solution into a 1,000 mL graduated cylinder and adjust the volume to 1,000 mL with sterile water.
- Pour the liquid solution into a glass reagent bottle and add 18 g of agar. Shake well and autoclave the mixture (oatmeal agar medium) at 121 °C for 15 min. Leave it at room temperature for 30 min.
- Pour around 20 mL of the sterilized oatmeal agar medium into each Petri dish. Leave the Petri dishes at room temperature to cool thoroughly before mycelial cultivation.
- Carry out mycelial cultivation.
- Prepare 1 cm diameter punches and toothpicks beforehand by autoclaving them at 121 °Cfor 15 min.
- Punch holes in the P. nicotianae mycelial agar cultures to make round mycelial mats.
- Pick out the mycelial mats, place the mycelial side down on the oatmeal agar medium, and incubate the mycelium at 25 °C in the dark for 14 days.
- Prepare P. nicotianae zoospore suspension.
- Add 0.1% KNO3 solution to each mycelial cultivation (15 mL/dish), followed by culturing at 4 °C for 20 min to induce sporangium.
- Keep the dishes at 25 °C for 25 min to release zoospores.
- Collect the zoospore suspension in a beaker and measure the zoospore concentration using a microscope andhemocytometer.
- Adjust the zoospore concentration to 1 x 104 zoospores/mL with sterile water.
4. Identification of disease-resistant tobacco varieties
- Take the seedlings from the Hoagland nutrient solution and inoculate them by immersing the roots in 20 mL of P. nicotianae zoospore suspension in a Petri dish (90 mm) at 25 °C for 3 h in the dark.
- After inoculation, put the tobacco seedlings into new Petri dishes with 10 mL of sterile water immersing the roots. Keep the roots moist by covering with two pieces of filter paper. Keep the dishes at 25 °C with a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod.
- After 2-3 days, observe the disease severity.
- For the control treatment, put the tobacco seedlings directly in the Petri dishes with 10 mL sterile water immersing the roots, and cover the roots with two pieces of filter paper.
NOTE: Each treatment had three replications, with 8 plants per experiment.
- For the control treatment, put the tobacco seedlings directly in the Petri dishes with 10 mL sterile water immersing the roots, and cover the roots with two pieces of filter paper.
5. Evaluation of P. nicotianae infection
- Evaluate the disease severity 4-5 days after inoculation. Based on the Chinese national standard18, score individual plant disease severity on a scale from 0 to 9 (Table 2, Figure 1).
- Calculate the disease index using the following formula18:
Disease index =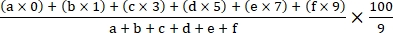
where a, b, c, d, e, and f are the number of plants in each disease severity grade.
NOTE: Disease severity was divided into 6 grades18 (Table 3).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
4-week-old plants of the resistant variety BH and susceptible variety XHJ were challenged with P. nicotianae using the method presented in this article. The experiment was designed with three replicates, each with 8 plants per group. P. nicotianae infection of the two tobacco varieties, BH and XHJ, is presented in Figure 2. At 3 days post inoculation, for XHJ, stem lesions covered approximately one-half of the stem girth, and one-half of the leaves were slightly wilted; in ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Multiple resistance sources have been used to improve P. nicotianae resistance in cultivated tobacco. Single dominant R genes, Php and Phl, have been introgressed from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia and Nicotiana longiflora, respectively10. The cigar tobacco variety Beinhart 1000 has the highest reported level of quantitative resistance to P. nicotianae13. Multiple interval mapping experiments have suggested that at least six...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31571738) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of China (ASTIP-TRIC01).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| (NH4)2SO4 | Sinopharm | 10002917 | Analytical Reagent |
| (NH4)6 Mo7O24•2 H2O | Sinopharm | XW131067681 | Analytical Reagent |
| 1.5 ml Safe-lock Microcentrifuge Tubes | Eppendorf | 30120086 | Used for Sample Extarction |
| 2 ml Safe-lock Microcentrifuge Tubes | Eppendorf | 30120094 | Used for Sample Extarction |
| Agar | MDBio, Inc | 9002-18-0 | Materials of Culture Medium |
| Analytical Balance | AOHAOSI | AX2202ZH | Equipment |
| Autoclave | Yamatuo | SQ510C | Equipment |
| Autoclave | YAMATUO | SQ510C | Equipment |
| Beaker | Bio Best | DHSB-2L | Materials of Culture Medium |
| Biological Incubator | JINGHONG | SHP-250 | Equipment |
| Ca(NO3)2•4 H2O | Sinopharm | 80029062 | Analytical Reagent |
| CaCl2 | Sinopharm | 10005817 | Analytical Reagent |
| CuSO4•5 H2O | Sinopharm | 10008218 | Analytical Reagent |
| Electromagnetic Oven | Bio Best | DHDCL | Equipment |
| FeSO4•7 H2O | Sinopharm | 10002918 | Analytical Reagent |
| Filter Paper | Bio Best | DHLZ-9CM | Material |
| Fluorescence Ration PCR Instrument | Roche | LightCycler96 | Equipment |
| Gauze | Bio Best | 17071202 | Materials of Culture Medium |
| H3BO3 | Phytotechnology | B210-500G | Analytical Reagent |
| Hemocytometer | Solarbio | 17072801 | Material for disease-resistant identification |
| K2SO4 | Sinopharm | 10017918 | Analytical Reagent |
| KNO3 | Sinopharm | 10017218 | Analytical Reagent |
| KT Foam Sheet | Bio Best | DHKTB | Material for Seedling |
| Low Constant Incubator | Jinghong | SHP-250 | Equipment |
| Measuring Cylinder | Bio Best | DHBLLT-1000ML | Materials of Culture Medium |
| MgSO4•7 H2O | Sinopharm | 10013080 | Analytical Reagent |
| Microscope | ECHO | RVL-100-G | Equipment |
| MnCl2•4 H2O | Sinopharm | G5468154 | Analytical Reagent |
| Na2-EDTA | Sinopharm | G21410-250 | Analytical Reagent |
| NaH2PO4•2 H2O | Sinopharm | 20040717 | Analytical Reagent |
| NH4NO3 | Sinopharm | B64586-100g | Analytical Reagent |
| Oatmeal | Bio Best | DHYMP-1.5KG | Materials of Culture Medium |
| Petri Dish | Bio Best | DHPYM-9CM | Material for disease-resistant identification |
| Pipettor | THERMO | S1 | Equipment |
| Potting | Bio Best | DHYCXHP-12CM | Material for Seedling |
| Potting Soil | Bio Best | DHYMJZ-50L | Seedling Material |
| Punch | Bio Best | DHDKW | Material |
| qRT-PCR Plate | Monad | MQ50401S | qRT-PCR Plate |
| SYBR Green Premix Pro Taq HS qPCR Kit | Accurate Biology | AG11718 | PCR Reagent |
| Toothpick | Bio Best | DHYQ-900 | Material |
| Total RNA Kit II | Omega | R6934-01 | PCR Reagent |
| TransScript® II One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix | Transgen | AH311-02 | PCR Reagent |
| Trays | Bio Best | DHYMTP-90G | Material for Seedling |
| Vermiculite | Bio Best | DHZS | Seedling Material |
| Water Purification System | HEAL FORCE | HSE68-2 | Equipment |
| ZnSO4•7 H2O | Sinopharm | 10024018 | Analytical Reagent |
References
- Antonopoulos, D. F., Melton, T., Mila, A. L. Effects of chemical control, cultivar resistance, and structure of cultivar root system on black shank incidence of tobacco. Plant Disease. 94 (5), 613-620 (2010).
- Taylor, R. J., Pasche, J. S., Gallup, C. A., Shew, H. D., Gudmestad, N. C. A foliar blight and tuber rot of potato caused by Phytophthora nicotianae: New occurrences and characterization of isolates. Plant Disease. 92 (4), 492-503 (2008).
- Amalia, B. R., José, I. M. G., Miguel, D. C. G., Francisco, C. F., Julio, C. T. M. Pathogenicity of plant and soil isolates of Phytophthora parasitica on tomato and pepper. European Journal of Plant Pathology. 148 (3), 607-615 (2017).
- Corrado, C., Annamari, M., Leonardo, S., Antonio, I., Simona, M. S. First report of collar and root rot caused by Phytophthora nicotianae on Lycium barbarum. Journal of Plant Pathology. 100 (2), (2018).
- Meng, Y. L., Zhang, Q., Ding, W., Shan, W. X. Phytophthora parasitica.: a model oomycete plant pathogen. Mycology. 5 (2), 43-51 (2014).
- Biasi, A., Martin, F. N., Cacciola, S. O., Lio, G. M., Grunwald, N. J., Schena, L. Genetic analysis of Phytophthora nicotianae populations from different hosts using microsatellite markers. Phytopathology. 106 (9), 1006-1014 (2016).
- Sullivan, M. J., Melton, T. A., Shew, H. D. Fitness of races 0 and 1 of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. Plant Disease. 89 (11), 1220-1228 (2005).
- Carlson, S. R., Wolff, M. A. F., Shew, H. D., Wernsman, E. A. Inheritance of resistance to Race 0 of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae from the flue-cured tobacco cultivar Coker 371-Gold. Plant Disease. 81 (11), 1269-1274 (1997).
- Csinos, A. S. Stem and root resistance to tobacco black shank. Plant Disease. 83 (8), 777-780 (1999).
- Johnson, E. S., Wolff, M. F., Wernsman, E. A., Atchley, W. R., Shew, H. D. Origin of the black shank resistance gene, Ph, in tobacco cultivar coker 371-Gold. Plant Disease. 86 (10), 1080-1084 (2002).
- Osmany, C., Ingrid, H., Roxana, P., Yunior, L., Merardo, P., Orlando, B. H. Identification of defense-related genes in tobacco responding to black shank disease. Plant Science. 177 (3), 175-180 (2009).
- Hernández, I., et al. Black shank resistant tobacco by silencing of glutathione S-transferase. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 387 (2), 300-304 (2009).
- Vontimitta, V., Lewis, R. S. Growth chamber evaluation of a tobacco 'Beinhart 1000' × 'Hicks' mapping population for quantitative trait loci affecting resistance to multiple races of Phytophthora nicotianae. Crop Science. 52 (1), 91-98 (2012).
- Xiao, B., et al. Location of genomic regions contributing to Phytophthora nicotianae resistance in tobacco cultivar florida 301. Crop Science. 53 (2), 473-481 (2013).
- McCorkle, K., Lewis, R., Shew, D. Resistance to Phytophthora nicotianae in tobacco breeding lines derived from variety Beinhart 1000. Plant Disease. 97 (2), 252-258 (2013).
- Zhang, Y., et al. Identification of stably expressed QTL for resistance to black shank disease in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) line Beinhart 1000-1. The Crop Journal. 6 (3), 282-290 (2018).
- Yu, X., Feng, B., He, P., Shan, L. From chaos to harmony: responses and signaling upon microbial pattern recognition. Annual Review of Phytopathology. 55, 109-137 (2017).
- Ren, G., et al. GB/T 23222 Grade and Investigation Method of Tobacco Diseases and Insect Pests. , China Standard Press. Beijing. (2008).
- Doyle, J. J., Doyle, J. L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemical Bulletin. 19 (11), 11-15 (1987).
- Yan, H. Z., Liou, R. F. Selection of internal control genes for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assays in the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora parasitica. Fungal Genetics and Biology. 43, 430-438 (2006).
- Chacón, O., Hernández, I., Portieles, R., López, Y., Pujol, M., Borrás-Hidalgo, O. Identification of defense-related genes in tobacco responding to black shank disease. Plant Science. 117 (3), 175-180 (2009).
- Vijay, V., Ramsey, S. L. Mapping of quantitative trait loci affecting resistance to Phytophthora nicotianae in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) line Beinhart-1000. Molecular Breeding. 29 (1), 89-98 (2012).
- McCorkle, K. L., Drake-Stowe, K., Lewis, R. S., Shew, D. Characterization of Phytophthora nicotianae resistance conferred by the introgressed Nicotiana rustica region, Wz, in flue-cured tobacco. Plant Disease. 102 (2), 309-317 (2018).
- Drake, K. E., Moore, J. M., Bertrand, P., Fortnum, B., Peterson, P., Lewis, R. S. Black shank resistance and agronomic performance of flue-cured tobacco lines and hybrids carrying the introgressed Nicotiana rustica Region. Wz. Crop Science. 55 (1), 79-86 (2015).
- Kebdani, N., Pieuchot, L., Deleury, E., Panabières, F., Berre, J. -Y. L., Gourgues, M. Cellular and molecular characterization of Phytophthora parasitica appressorium-mediated penetration. New Phytologist. 185 (1), 248-257 (2010).
- Huang, G., et al. An RXLR effector secreted by Phytophthora parasitica is a virulence factor and triggers cell death in various plants. Molecular Plant Pathology. 20 (3), 1-16 (2019).
- Agnès, A., Mathieu, G., Nicolas, C. -T., Harald, K. The immediate activation of defense responses in Arabidopsis roots is not sufficient to prevent Phytophthora parasitica infection. New Phytologist. 187 (2), 229(2010).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved