A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Concanavalin A-Based Sedimentation Assay to Measure Substrate Binding of Glucan Phosphatases
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This method describes a lectin-based in vitro sedimentation assay to quantify the binding affinity of glucan phosphatase and amylopectin. This co-sedimentation assay is reliable for measuring glucan phosphatase substrate binding and can be applied to various solubilized glucan substrates.
Abstract
Glucan phosphatases belong to the larger family of dual specificity phosphatases (DSP) that dephosphorylate glucan substrates, such as glycogen in animals and starch in plants. The crystal structures of glucan phosphatase with model glucan substrates reveal distinct glucan-binding interfaces made of DSP and carbohydrate-binding domains. However, quantitative measurements of glucan-glucan phosphatase interactions with physiologically relevant substrates are fundamental to the biological understanding of the glucan phosphatase family of enzymes and the regulation of energy metabolism. This manuscript reports a Concanavalin A (ConA)-based in vitro sedimentation assay designed to detect the substrate binding affinity of glucan phosphatases against different glucan substrates. As a proof of concept, the dissociation constant (KD) of glucan phosphatase Arabidopsis thaliana Starch Excess4 (SEX4) and amylopectin was determined. The characterization of SEX4 mutants and other members of the glucan phosphatase family of enzymes further demonstrates the utility of this assay to assess the differential binding of protein- carbohydrate interactions. These data demonstrate the suitability of this assay to characterize a wide range of starch and glycogen interacting proteins.
Introduction
Glucan phosphatases are members of a functionally diverse subfamily of dual specificity phosphatases (DSPs) within the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) superfamily1. They have been found in most life forms, including widely divergent photosynthetic organisms, humans, vertebrates, and some invertebrates and protists2,3,4. Plants contain three known glucan phosphatases: Starch Excess4 (SEX4), Like Sex Four1 (LSF1), and Like Sex Four2 (LSF2)5,6,7. Plants that lack glucan phosphatases display decreased rates of transitory starch degradation and accumulation of starch in the leaves8,9. Laforin is the founding member of the glucan phosphatase family that dephosphorylates glycogen in vertebrates and humans3,10. The mutations of laforin result in neurodegenerative Lafora disease, a fatal autosomal recessive form of epilepsy11. Glucan phosphatases are necessary for glycogen and starch metabolism and have emerged as important enzymes for modulating starch content in plants and treating neurodegenerative Lafora disease12,13. Recent X-ray crystallography studies on glucan phosphatases with model glucan substrates have shed light on substrate binding and the catalytic mechanism of glucan dephosphorylation14,15,16,17. However, the current understanding of how glucan phosphatases bind to their physiological substrates is incomplete.
Starch is an insoluble polymer of glucose made of 80%-90% amylopectin and 10%-20% amylose18. The substrates for plant glucan phosphatases are phosphorylated carbohydrate molecules, such as glycogen and starch granules. The phosphorylated glucosyl residues are present at a 1:600 phosphate:glucosyl residue ratio. Interestingly, the phosphates are present only on the amylopectin molecules19. The main plant glucan phosphatase SEX4 acts on the starch granule to dephosphorylate amylopectin molecules. The X-ray crystal structure of SEX4 combined with structure-guided mutagenesis studies has demonstrated the unique substrate specificities of SEX4 for different positions within a glucan structure15. We recently showed that the biologically relevant activity of SEX4 can only be observed when acting on its solubilized amylopectin substrates20. However, understanding glucan-SEX4 interactions has proven to be difficult due to the structural complexity of the substrate, broader binding specificities, and low binding affinities between the protein and its substrates. These issues have hindered the ability to utilize methods commonly used in protein-ligand interactions, such as isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)-based assays.
Interestingly, much of our understanding of carbohydrate-protein interactions have come from studying lectins. Concanavalin A (ConA) is a legume lectin family of proteins originally extracted from the jack bean. ConA binds carbohydrates with high specificity, which is advantageous for its use in drug targeting and delivery applications. The binding of ConA to a variety of substrates containing nonreducing α-D-mannosyl and α-D-glucosyl has been extensively studied19,20. Commercially available ConA-bound Sepharose beads are commonly used to purify glycoproteins and glycolipids21. ConA binds to these glucans via C3, C4, and C6 hydroxyl groups of the glucose residues. ConA-Sepharose beads have also been successfully used to measure the binding of glycogen-protein and starch-protein interactions22,23. In this study, we used ConA-Sepharose beads to develop a binding assay to measure the binding specificities of glucan phosphatase-amylopectin interactions.
Previously, a ConA-based sedimentation assay was employed to assess glucan phosphatase substrate binding ability14,20,24. In this study, the same strategy was used to develop a novel method to determine the binding affinity of glucan-glucan phosphatase and carbohydrate interactions. This method also has an advantage for investigating various solubilized carbohydrate-protein interactions.
Protocol
1. Preparation of ConA-Sepharose beads
- Make 250 mL of a binding buffer containing 67 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, and 0.2 mM CaCl2. Adjust the pH using 1 M NaOH solution.
- Pipette 250 μL of ConA-Sepharose bead suspension into a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge the contents at 10,000 x g for 30 s at 4 °C. Discard the supernatant.
NOTE: 250 µL of ConA-Sepharose beads in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube is needed for each amylopectin concentration used for the assay. - Add 750 µL of the binding buffer to each tube containing 250 µL of ConA-Sepharose beads. Centrifuge the tubes at 10,000 x g for 1 min at 4 °C. Remove the supernatant. Repeat this step 2x to ensure that the beads are appropriately washed and equilibrated with the binding buffer.
2. Preparation of amylopectin solutions
- Make a stock solution of 10 mg/mL potato amylopectin. Amylopectin is water-insoluble and can be solubilized by heat. To solubilize, add 0.1 g of potato amylopectin to 10 mL of distilled water. Heat the suspension in a water bath at 80 °C for 1 h or until the solution is no longer cloudy.
- Allow the solution to return to room temperature (RT), with repeated vortexing to avoid clumping.
- Alcohol-alkaline treatment is an alternative method to solubilize amylopectin substrates. To solubilize using this method, follow the steps below.
- Suspend 0.5 g of amylopectin substrate in 5 mL of 20% ethanol and 5 mL of 2 M NaOH. Stir the contents vigorously for 15-20 min at RT.
- Next, add 10 mL of water, and adjust the pH of the solution to 6.5 by adding 2 M HCl. Bring up the volume of the resulting solution to 50 mL with distilled water to make a 10 mg/mL amylopectin solution.
- Dilute the 10 mg/mL solubilized amylopectin solution to make a series of 2 mL of diluted amylopectin solutions. For example, perform half dilutions of 10 mg/mL to prepare a series of amylopectin concentrations (5 mg/mL, 2.5 mg/mL, 1.25 mg/mL, 0.625 mg/mL, 0.3125 mg/mL, 0.156 mg/mL, 0.078 mg/mL, 0.039 mg/mL, 0.019 mg/mL, and 0 mg/mL).
3. Preparation of ConA-Sepharose: amylopectin beads
- Add 250 µL of each diluted amylopectin solution to 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes containing 250 µL of ConA-Sepharose beads pre-equilibrated in binding buffer. Mix the contents well. Label the tubes with the corresponding amylopectin concentration.
- Incubate the contents on a rotating wheel at 4 °C for 30 min.
NOTE: There is no change in the ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin bound complex over time after 20 min. The 30 min incubation time was chosen by varying incubation times from 10 min to 1 h to ensure equilibrium was reached. - Centrifuge the tubes at 10,000 x g for 1 min. Collect the supernatant in a newly labeled 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube. Save these supernatant fractions to perform D-glucose assay12 (acid hydrolysis of amylopectin followed by UV determination of glucose via enzymatic assay). This step is necessary to ensure all amylopectin is bound to the beads.
- Add 750 µL of binding buffer to the ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin beads. Centrifuge the tubes at 10,000 x g for 1 min. Discard the supernatant to remove any unbound amylopectin molecules.
- Repeat step 3.4 to ensure sufficient washing. Each tube now contains ConA-Sepharose beads bound to varying amounts of amylopectin substrates.
4. Incubating SEX4 with ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin beads
- Mix 250 µL of ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin beads with 100 µL of the binding buffer which includes 10 µg of SEX4 protein, 10 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), and 10 µM protease inhibitor cocktail (PIC). Note that the total volume in each tube is 350 µL.
NOTE: A protease inhibitor cocktail is added as a precautionary step to avoid any unnecessary SEX4 degradation. This is an optional step. In this assay, the recombinant protein Arabidopsis thaliana SEX4 (AtSEX4) is used. The purified protein contains an N-terminal histidine tag necessary for detecting the protein via chemiluminescence. Detailed information on glucan phosphatase purifications is described in previous publications14,20,24. - Incubate the protein and ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin bead suspension at 4 °C for 45 min with gentle rotation.
NOTE: The 45 min incubation time is chosen to ensure equilibrium is reached for the complex. - Centrifuge the tubes at 10,000 x g for 1 min. Pipette 50 µL of the supernatant carefully using a gel loading tip into a new 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube. Add 20 µL of 4x SDS-PAGE dye and 10 µL of water to each tube containing 50 µL of the collected supernatant fractions. Heat the samples at 95 °C for 10 min. Save these samples for running the SDS-PAGE gels. Ensure 10 new tubes labeled "supernatant (S)" have the corresponding substrate concentrations.
- Add 750 µL of the binding buffer to the ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin: SEX4 beads to remove any unbound protein from the beads. Centrifuge the tubes at 10,000 x g for 1 min. Repeat this step one more time to ensure proper washing. Discard the supernatant.
- Add 20 µL of 4x SDS-PAGE dye and 80 µL of distilled water into the tubes containing washed ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin:SEX4 beads. Heat the samples at 95 °C for 10 min and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 1 min.
- Discard the pellet and save the supernatant for running the SDS-PAGE gels. Pipette 80 µL of the supernatant into new tubes and label them as "pellet (P)".
5. Running SDS-PAGE gels
- Load 40 µL of the unbound protein samples (made in step 2.3, labeled S) into 4%-12% precast polyacrylamide gel wells from the lowest substrate concentration to the highest, but keep the first lane free to load the protein molecular weight marker. Use a second gel to load 10 bound protein samples made in step 2.5 (labeled as P).
- Add freshly prepared 1x SDS-PAGE running buffer to both chambers of the apparatus. Run the gel at 150 V for 35 min or until the dye front reaches the bottom of the gel.
- Remove the run gel from the apparatus and remove the spacers and glass plates. Use the separated gel to run a western blot analysis.
6. Western blotting for chemiluminescence detection14,15
NOTE: This method can be easily modified/adapted depending on the western blotting equipment that users have in their labs.
- Make 1 L of transfer buffer containing 5.8 g of Tris base, 2.9 g of glycine, 0.37 g of SDS, and 200 mL of methanol.
- Transfer the size-separated proteins from the polyacrylamide gel to a nitrocellulose membrane. Briefly assemble the sponges, filter papers, gel, and nitrocellulose membrane according to western transfer protocol14,15. Run at 70 V for 1 h.
- To prevent nonspecific protein binding, incubatethe nitrocellulose membrane containing the protein solution of 1%-5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) or milk protein in 50 mL of TBST buffer (20 mM Tris [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% Tween 20) for 1 h. Wash the membrane 3x using TBST buffer to remove any unbound blocking solution.
- Incubate the membrane with a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-linked antibody specific for His-tagged protein for 1 h. Wash the membrane 3x in TBST buffer to remove any unbound antibodies. Use a 1:2,000 dilution of antibody to TBST for optimal reproducibility and sensitivity.
- The HRP enzyme-linked antibody binds specifically to the histidine tag of the SEX4 protein, which yields a band in the presence of chemiluminescence reagents. For digital imaging, make a solution of equal parts of chemiluminescent substrate solutions (750 µL each) in a 1.5 mL tube. Incubate the membrane for at least 5 min in the solution.
- Place the membrane protein side down on the blot scanner and run the acquisition software to quantify the protein in both the pellet and supernatant fractions.
7. Data analysis
- Perform the quantitative signal measurements using the acquisition software with the blot scanner. Normalize all quantitative measurements in the supernatant and pellet fractions to the total protein loaded.
NOTE: The software allows to quantify the intensity of each protein band in the supernatant and pellet fractions. - In the saturating binding experiment, plot the percentage of protein-bound versus amylopectin concentration. Fit the data to Y = Bmax x X/(KD + X), using data analysis software to calculate KD.
NOTE: Bmax is the maximum specific binding, the Y-axis is the percentage of protein bound, the and X-axis is the amylopectin concentration.
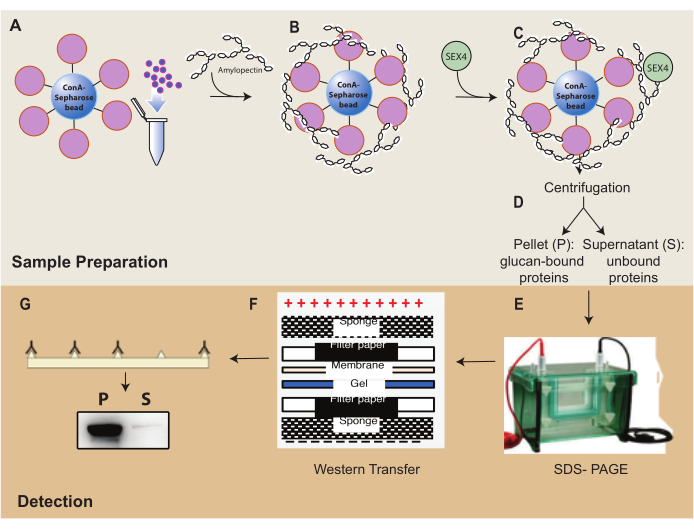
Figure 1: Overview of the ConA-Sepharose sedimentation assay workflow. (A) Preparation of ConA-Sepharose beads. (B) Incubation with amylopectin substrate. (C) Incubation with SEX4 protein. (D) Separation of bound and unbound protein fractions through centrifugation. (E) Separation of protein through SDS-PAGE. (F) Western-blot analysis. (G) Chemiluminescence detection of His-tagged SEX4 protein. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
One of the key features of the glucan phosphatase family of proteins is their ability to bind to glucan substrates. First, the binding capacity of SEX4 to ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin beads was analyzed using SDS-PAGE (Figure 2A). Bovine serum albumin (BSA) served as a negative control to detect any nonspecific binding of proteins to the ConA-Sepharose:amylopectin beads. The SDS-PAGE analysis of proteins showed the presence of SEX4 protein in the pellet fraction and BSA in the supernatant frac...
Discussion
This study demonstrates the successful development of a novel in vitro sedimentation assay that allows determination of the binding affinity of glucan-glucan phosphatase interactions. The assay design takes advantage of the specific binding of lectin ConA to glucans via the hydroxyl residues of glucose to indirectly capture solubilized carbohydrate substrates onto Sepharose beads. This allows the separation of bound and unbound protein fractions via centrifugation and determination of the bindi...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation award MCB-2012074. The authors thank Dr. Craig W. Vander Kooi of the University of Florida Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology for valuable discussions and support. The authors also thank Dr. Matthew S. Gentry of the University of Florida Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology for his support. We would like to thank Dr. Sara Lagalwar, chair of the Skidmore College Neuroscience program, for allowing us to use the LICOR C-digit blot scanner for western blot imaging.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 6x-His Tag monoclonal antibody (HIS.H8), HRP | Therm Fisher Scientific | MA1-21315-HRP | |
| Biorad gel electrophoresis and Western blot kit | Biorad | 1703930 | |
| Calcium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | 208291 | |
| C-Digit blot scanner | LICOR | 3600-00 | Blot scanner |
| Complete protease inhibitor cocktail | Sigma-Aldrich | 11836170001 | |
| Concanavalin A-sepharose beads | Sigma-Aldrich | C9017 | This product contains in 0.1 M acetate buffer, pH 6, containing 1 M NaCl, 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MnCl2, and 1 mM MgCl2 in 20% ethanol |
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5425R | |
| Glycine | Fisher Scientific | BP381-5 | |
| GraphPad Prism 8.0 software | GraphPad | Version 8.0 | Data analysis software |
| HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | H8651 | |
| Image Studio | LICOR | 3600-501 | Acquisition Software |
| Magnesium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | M2670 | |
| Methanol | Fisher Scientific | A452SK-4 | |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | Fisher Scientific | PI28312 | |
| Potato amylopectin | Sigma-Aldrich | A8515 | |
| Precast SDSPAGE Gels | Genscript | M00653S | |
| Tris base | Fisher Scientific | BP154-1 | |
| Tween 20 | Fisher Scientific | MP1TWEEN201 | |
| Westernsure premium chemiluminescence substrate | LI-COR | 926-95000 |
References
- Meekins, D. A., Vander Kooi, C. W., Gentry, M. S. Structural mechanisms of plant glucan phosphatases in starch metabolism. The FEBS Journal. 283 (13), 2427-2447 (2016).
- Gentry, M. S., et al. The phosphatase laforin crosses evolutionary boundaries and links carbohydrate metabolism to neuronal disease. The Journal of Cell Biology. 178 (3), 477-488 (2007).
- Worby, C. A., Gentry, M. S., Dixon, J. E. Laforin, a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates complex carbohydrates. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (41), 30412-30418 (2006).
- Gentry, M. S., Pace, R. M. Conservation of the glucan phosphatase laforin is linked to rates of molecular evolution and the glucan metabolism of the organism. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 9, 138 (2009).
- Niittyla, T., et al. Similar protein phosphatases control starch metabolism in plants and glycogen metabolism in mammals. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (17), 11815-11818 (2006).
- Kotting, O., et al. STARCH-EXCESS4 is a laforin-like Phosphoglucan phosphatase required for starch degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell. 21 (1), 334-346 (2009).
- Comparot-Moss, S., et al. A putative phosphatase, LSF1, is required for normal starch turnover in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiology. 152 (2), 685-697 (2010).
- Zeeman, S. C., Northrop, F., Smith, A. M., Rees, T. A starch-accumulating mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana deficient in a chloroplastic starch-hydrolysing enzyme. The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology. 15 (3), 357-365 (1998).
- Kotting, O., et al. Identification of a novel enzyme required for starch metabolism in Arabidopsis leaves. The phosphoglucan, water dikinase. Plant Physiology. 137 (1), 242-252 (2005).
- Tagliabracci, V. S., et al. Laforin is a glycogen phosphatase, deficiency of which leads to elevated phosphorylation of glycogen in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 104 (49), 19262-19266 (2007).
- Gentry, M. S., Guinovart, J. J., Minassian, B. A., Roach, P. J., Serratosa, J. M. Lafora disease offers a unique window into neuronal glycogen metabolism. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 293 (19), 7117-7125 (2018).
- Brewer, M. K., et al. Targeting pathogenic lafora bodies in lafora disease using an antibody-enzyme fusion. Cell Metabolism. 30 (4), 689-705 (2019).
- Santelia, D., Zeeman, S. C. Progress in Arabidopsis starch research and potential biotechnological applications. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 22 (2), 271-280 (2011).
- Raththagala, M., et al. Structural mechanism of laforin function in glycogen dephosphorylation and lafora disease. Molecular Cell. 57 (2), 261-272 (2015).
- Meekins, D. A., et al. Phosphoglucan-bound structure of starch phosphatase Starch Excess4 reveals the mechanism for C6 specificity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (20), 7272-7277 (2014).
- Vander Kooi, C. W., et al. Structural basis for the glucan phosphatase activity of Starch Excess4. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (35), 15379-15384 (2010).
- Meekins, D. A., et al. Structure of the Arabidopsis glucan phosphatase like sex four2 reveals a unique mechanism for starch dephosphorylation. The Plant Cell. 25 (6), 2302-2314 (2013).
- Smith, A. M., Zeeman, S. C. Starch: A flexible, adaptable carbon store coupled to plant growth. Annual Review of Plant Biology. 71, 217-245 (2020).
- Jane, J., Kasemuwan, T., Chen, J. F., Juliano, B. O. Phosphorus in rice and other starches. Cereal Foods World. 41 (11), 827-832 (1996).
- Mak, C. A., et al. Cooperative kinetics of the glucan phosphatase starch excess4. Biochemistry. 60 (31), 2425-2435 (2021).
- Campbell, K. P., MacLennan, D. H. Purification and characterization of the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 256 (9), 4626-4632 (1981).
- Campbell, K. P., MacLennan, D. H., Jorgensen, A. O., Mintzer, M. C. Purification and characterization of calsequestrin from canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and identification of the 53,000 dalton glycoprotein. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 258 (2), 1197-1204 (1983).
- Davey, M. W., Sulkowski, E., Carter, W. A. Binding of human fibroblast interferon to concanavalin A-agarose. Involvement of carbohydrate recognition and hydrophobic interaction. Biochemistry. 15 (3), 704-713 (1976).
- Meekins, D. A., et al. Mechanistic insights into glucan phosphatase activity against polyglucan substrates. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 290 (38), 23361-23370 (2015).
- Wilkens, C., et al. Plant α-glucan phosphatases SEX4 and LSF2 display different affinity for amylopectin and amylose. FEBS Letters. 590 (1), 118-128 (2016).
- Atanasova, M., Bagdonas, H., Agirre, J. Structural glycobiology in the age of electron cryo-microscopy. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 62, 70-78 (2020).
- Doyle, M. L. Characterization of binding interactions by isothermal titration calorimetry. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 8 (1), 31-35 (1997).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved