A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Micro-Colony Forming Unit Assay for Efficacy Evaluation of Vaccines Against Tuberculosis
In This Article
Summary
The determination of colony-forming units (CFU) is the gold-standard technique for quantifying bacteria, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis which can take weeks to form visible colonies. Here we describe a micro-CFU for CFU determination with increased time efficiency, reduced lab space and reagent cost, and scalability to medium and high throughput experiments.
Abstract
Tuberculosis (TB), the leading cause of death worldwide by an infectious agent, killed 1.6 million people in 2022, only being surpassed by COVID-19 during the 2019-2021 pandemic. The disease is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb). The Mycobacterium bovis strain Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), the only TB vaccine, is the oldest licensed vaccine in the world, still in use. Currently, there are 12 vaccines in clinical trials and dozens of vaccines under pre-clinical development. The method of choice used to assess the efficacy of TB vaccines in pre-clinical studies is the enumeration of bacterial colonies by the colony-forming units (CFU) assay. This time-consuming assay takes 4 to 6 weeks to conclude, requires substantial laboratory and incubator space, has high reagent costs, and is prone to contamination. Here we describe an optimized method for colony enumeration, the micro-CFU (mCFU), that offers a simple and rapid solution to analyze M.tb vaccine efficacy results. The mCFU assay requires tenfold fewer reagents, reduces the incubation period threefold, taking 1 to 2 weeks to conclude, reduces lab space and reagent cost, and minimizes the health and safety risks associated with working with large numbers of M.tb. Moreover, to evaluate the efficacy of a TB vaccine, samples may be obtained from a variety of sources, including tissues from vaccinated animals infected with Mycobacteria. We also describe an optimized method to produce a unicellular, uniform, and high-quality mycobacterial culture for infection studies. Finally, we propose that these methods should be universally adopted for pre-clinical studies of vaccine efficacy determination, ultimately leading to time reduction in the development of vaccines against TB.
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death worldwide by a single infectious agent, bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb), killing more people than any other pathogen. In 2021, TB was responsible for 1.6 million deaths and was surpassed by COVID-19 during the 2019-2021 pandemic1. Moreover, according to the World Health Organization´s global TB report of 2022, the COVID-19 pandemic was responsible for an increase in new TB cases. The WHO also reports large drops in the number of people diagnosed with TB during this period, which could increase further the number of TB cases1.
The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a live-attenuated strain of the pathogenic Mycobacterium bovis, used for the first time as a vaccine more than 100 years ago. This is the only vaccine against TB and is the oldest licensed vaccine in the world still in use2,3. Currently, there are 12 vaccines in different phases of clinical trials4, and dozens of vaccines are under pre-clinical development5,6. Pre-clinical assessment of vaccines against TB includes the evaluation of the safety and immunogenicity7, which can be obtained in diverse animal models such as zebrafish, mice, guinea pigs, rabbits, cattle, and non-human primates8,9,10. Additionally, assessing the capacity of a vaccine to induce protection against M.tb infection and/or transmission, i.e., the vaccine efficacy, requires an M.tb challenge in vivo5,11. Interestingly, BCG vaccination induces non-specific effects that affect the survival of other bacterial and viral pathogens12,13 through the mechanism of trained immunity14. To quantify the viable bacterial burden in an infected animal, the method of choice is the enumeration of bacterial colonies through the colony-forming units (CFU) assay5,15. CFU is a unit that estimates the number of microorganisms (bacteria or fungi) that form colonies under specific growth conditions. CFUs originate from viable and replicative microorganisms, and the absolute number of living microorganisms within each colony is difficult to estimate. It is uncertain whether a colony has originated from one or more microorganisms. The CFU unit reflects this uncertainty, hence a great variability can be observed in replicates of the same sample. This time-consuming assay requires specialized technicians trained to work in a biosafety level 3 (BSL3) facility, substantial laboratory and incubator space, takes from 4 to 6 weeks to conclude, and is prone to contamination.
In this study, we describe an optimized method for colony enumeration, the micro-CFU (mCFU), and offer a simple and rapid solution to analyze the results15,16,17,18,19,20. The mCFU assay requires tenfold fewer reagents, reduces the incubation period threefold, taking 1 to 2 weeks to conclude, reduces lab space and reagent cost, and minimizes the health and safety risks associated with working with large numbers of M.tb. We propose that this method should be universally adopted for pre-clinical studies of vaccine efficacy determination, ultimately leading to time reduction in the development of vaccines against TB. Finally, this optimized method of CFU enumeration has been used to quantify not only Mycobacteria but also other bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Ralstonia solanacearum21.
Protocol
NOTE: The protocol described here is for BCG but can be applied to any Mycobacteria. BCG can be used as a surrogate bacterium for TB experiments when BSL3 facilities are not available22. The following procedures using BCG should be performed under a biosafety level 2 (BSL2) laboratory and follow the appropriate biosafety guidelines and good laboratory practices for the manipulation of hazard group 2 microorganisms.
1. Culture media preparation
- Prepare Middlebrook 7H9 broth supplemented with 10% (v/v) oleic acid, albumin, dextrose, and catalase (OADC) enrichment, according to the supplier's instructions. Supplement the broth with 0.05% (v/v) of tyloxapol.
NOTE: Tyloxapol is a non-ionic liquid polymer that has been used as a surfactant to prevent bacterial clump formation16. - Prepare Middlebrook 7H10 solid medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) OADC enrichment according to the supplier's instructions.
- Distribute 40 mL of medium per square Petri dish (120 mm x 120 mm). Allow the plates to dry to minimize condensation at the surface of the agar.
NOTE: This specific size of petri dish is fundamental to allow direct transposal of at least 96 droplets from a 96-well plate. Effective drying of the plates will later facilitate the plating of small droplets of bacterial suspension and prevent the droplets from spreading. - Prepare either Roswell Park Memorial Institute Medium (RPMI 1640) or Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) to produce the infection medium. In either case, supplement the medium with 10% fetal calf serum, 1% L-glutamine, and 1 mM sodium pyruvate. Do not add penicillin and streptomycin to the medium.
2. Sample preparation
- Obtain samples from a variety of sources. Typically, to quantify CFU to evaluate the efficacy of a TB vaccine, acquire samples from vaccinated and unvaccinated animal tissues. For example, mouse lung and spleen11 or macaque lung, thoracic and peripheral lymph nodes, spleen, liver, skin, blood, bone marrow, and bronchoalveolar lavage wash23. Alternatively, obtain samples from in vitro cultures of macrophages/dendritic cells/neutrophils infected with BCG18,19,20, 24,25,26.
3. Production of BCG culture
NOTE: For in vivo studies of TB vaccines, the aim is to improve the efficacy of BCG. Therefore, BCG-vaccinated groups are usually used as control. BCG strains used for human vaccination are ideal for testing in animal models. In this case, a culture of BCG must be reconstituted according to the supplier's instructions27. However, a BCG culture for in vivo studies can also be produced in-house11. The production of unicellular, uniform, and high-quality BCG culture for in vitro infection protocols has been produced very successfully in several studies11, 16, 18,19,20, 26, 28, 29, using the following protocol, which can also be used for animal challenge studies.
- Culture 50 mL of BCG in 7H9 broth, at 37 °C, with agitation at 200 rpm. Vary the volume according to the needs of the experiment.
- Every day, for 8-10 days, collect 100 µL of the culture and dilute it by adding 900 µL of PBS in a 1 mL cuvette. Then proceed by measuring the optical density of bacteria (OD at λ=600 nm; OD600) in a spectrophotometer. Draw a growth curve from those values. Identify the mid-log phase of the culture (when the OD is doubling consistently per unit of time).
- Prepare a subsequent culture and incubate until reaching the mid/late log growth phase as in steps 3.1 and 3.2. Use the values obtained in the previous step as guidance. Ensure that the culture does not reach the stationary growth phase (when the OD starts stabilizing) to maintain a good quality culture of viable bacteria.
- Collect the culture at the mid/late log growth phase. Centrifuge at 3000 x g for 10 min. Remove the supernatant.
- Add 10 mL of PBS to wash the bacteria. Centrifuge at 3000 x g for 10 min. Remove the supernatant.
- Resuspend the bacteria with 5 mL of infection media. Place the tube in an ultrasound bath for 15 min, full power at 80 Hz.
- Centrifuge at 1000 x g for 10 min. Collect the supernatant avoiding the pellet as it is rich in bacterial clumps that should be avoided in a high-quality BCG culture and discard it.
- Measure the OD of the supernatant. Here, cultures at the exponential growth phase, with an OD600 of 0.1, are equivalent to 1 x 107 CFU/mL.
NOTE: Each laboratory should produce its own BCG growth curves before starting experiments to establish a linear regression between OD600 and CFU using the spectrophotometer. Please note that spectrophotometers have different light path distances, which can vary the readings obtained for the same sample. - Carry out simple calculations to establish the number of bacteria to add to each host cell culture. The number of bacteria per host cell is the Multiplicity of Infection (MOI). Use an MOI of 10 bacteria per host cell, which is the most common MOI used for BCG infection experiments.
4. Micro-colony forming unit assay
NOTE: After an in vivo or in vitro infection experiment is completed, the enumeration of bacteria can be performed by mCFU. For in vivo studies, samples must be first homogenized in a bead beater or another tissue homogenizer. For in vitro cultures of macrophages/dendritic cells/neutrophils infected with BCG, samples must be lysed using a non-ionic detergent (e.g., 0.05% solution of non-ionic, non-denaturing detergent).
- Serial dilutions using a 96-well plate: perform serial 10-fold dilutions of the lysates, in a sterile 96-well plate according to the scheme in Figure 1A. Distribute the lysates on rows A and E. For each plate, the maximum number of samples and/or replicates is 24.
- Add 180 µL of dH2O to the remaining wells to perform the serial dilution.
- Using a 12-channel pipette, resuspend the lysates in row A and transfer 20 µL to row B (20 µL lysate + 180 µL dH2O). Homogenize well. Sequentially repeat this step for rows B and C until reaching the last dilution in row D.
NOTE: We usually perform three dilutions (100, 101, 102, 103), thus using 4 rows of the plate (A-D or E-H) for each set of 12 samples and/or replicates. - Micro droplet plating: use a 0.5-10 µL (thin tips are preferred) multichannel pipette to transfer 5 µL from each row of the 96-well plate to the solid medium square plate, according to Figure 1B.
- While slowly pipetting the 5 µL droplets, allow them to slightly touch the agar. This will help to take off the droplet from the tip towards the agar and reduce the possibility of retention of the liquid inside the tip.
- Allow the droplets to dry, close the agar plate, and incubate it at 37 °C while monitoring bacterial growth. Optionally, incubate the agar plates in a sealed plastic bag to prevent the plates from drying.
- Micro-colony counting: following approximately 6-10 days of incubation, check for individual colonies, visible to the naked eye (Figure 2).
- Count the colonies using the lowest magnification objective (4x or lower) of an inverted optical microscope or magnifying glass. Counts should be performed in the dilutions where the number of colonies is lower than 300 and higher than 30. Alternatively, use a camera to take a picture of the droplet to manually count colonies on the computer or use software such as ImageJ to automate colony counting.
- To express cell numbers in CFU/mL, use the following equation:
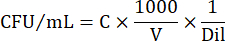
Where C = number of colonies counted, V = volume plated in µL, and Dil = dilution where the colonies were counted (100, 101, 102, 103). For example, if 30 colonies were counted in a 5 µL droplet in dilution 102, then:
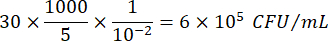
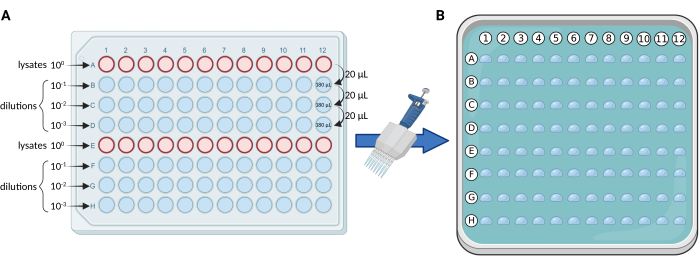
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the mCFU protocol. (A) Serial 10-fold dilutions of the BCG-containing lysates in a 96-well plate. (B) Square Petri dish containing solid culture medium and overlayed by 96 droplets of 5 µL each. Droplets are pipetted directly from the 96-well plate using a multichannel pipette. Created with BioRender.com. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
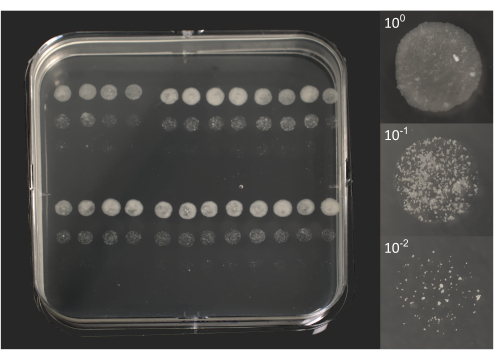
Figure 2. Micro-colony forming units of BCG following 10 days of incubation. On the left, a photo of a square Petri dish overlayed by 96 droplets of 5 µL each, as previously represented in Figure 1B. On the right, individual photos of 3 droplets correspond to an original lysate (100) and two dilutions (101, 102). Photos were taken using a DSRL camera equipped with an 18-55 mm zoom lens (plate) or a 105 mm macro lens (droplets). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Micro-colony forming unit counting in Fiji (ImageJ)
NOTE: The mCFU method allows CFU quantification of large sets of samples. Pictures of the droplets may be recorded for posterior analysis to facilitate colony counting. Several photographic devices can produce images with sufficient quality for this purpose. These include digital cameras, webcams, camera-attached microscopes and magnifying glasses, and cell phones. Free image analysis software such as ImageJ offers the possibility of manual or automated colony counting in those images. To demonstrate both methods, Fiji will be used, which is a distribution of ImageJ that packages several tools for scientific image analysis30. Fiji can be downloaded from https://fiji.sc/.
- Manual counting method
- Open the image containing the mCFU in Fiji. Select Plugins > Analyze > Cell Counter.
- On the Cell Counter menu, select Initialize and then select a counter (e.g., Type 1).
- Proceed by clicking on each colony. Each click will be shown on the picture and will update the counter (Figure 3). To undo accidental clicks, select Delete.
- Register the value displayed on the counter. Click the Reset button to reset the count and open a new image to count additional samples.
NOTE: Further instructions on this plugin can be found at https://imagej.net/plugins/cell-counter.
- Automated counting method
- Open the image containing the mCFU in Fiji. Select Image > Type > 8 -bit. This will convert the image to an 8-bit gray-scale image.
- Select the Oval tool in the tool bar and draw an oval around the area with the colonies (Figure 4A). The oval may be adjusted after being drawn.
- Select Edit > Clear Outside, to remove any interference from the outside area (Figure 4B). Select Image > Adjust > Threshold.
- Move the sliders in the threshold menu until the colonies appear in red and background noise is minimized (Figure 4C).
- Select Apply and exit the threshold window. A black-and-white image is generated (Figure 4D).
- Select Analyze > Analyze Particles. In the analyze particles window, specify the range for colony area (between 1 and infinity, measured in squared pixels) and circularity (between 0 and 1, where 1 is a perfect circle; Figure 4E).
- Select Outlines in the show popup menu. Check Display Results for detailed measurements for each colony in the results window. Check Clear Results to erase any previous measurements. Check the Summarize box to display the summarized results of the measurements (Figure 4E).
- Initiate the analyzer by selecting OK. A new window appears, displaying all the outlined colonies that were detected and counted. The results window displays the details for each colony, and the summarized results window shows the total colonies counted (Figure 4F).
NOTE: The settings for size and circularity will vary with the image's resolution and magnification and the colonies' size and shape. Repeat the process several times until the best settings are found that detect all colonies. Further instructions on the analyze particles plugin can be found at https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/docs/menus/analyze.html#ap.
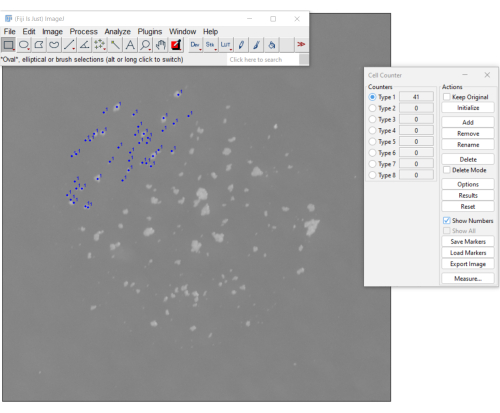
Figure 3. A manual method for counting mCFU using the cell counter plugin on Fiji software. The blue dots indicate colonies already clicked on by the user. The menu on the right displays the number of colonies counted so far (the count is 41). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
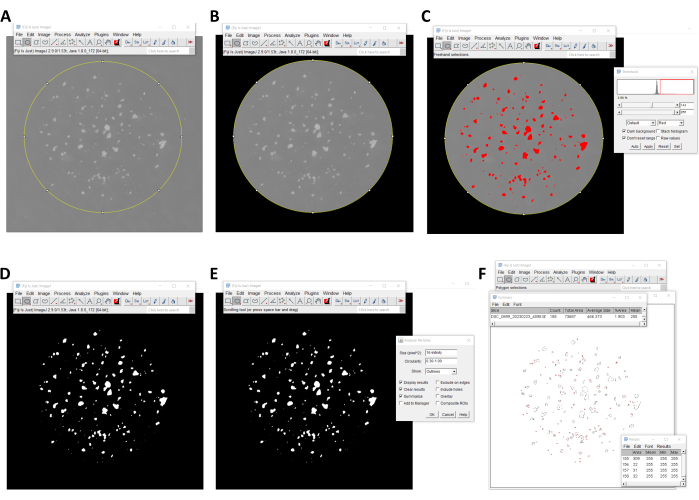
Figure 4. An automated method for counting mCFU using Fiji software. (A, B) The region of interest with the colonies is selected using the oval selection tool, and the outside area is removed using the clear outside command. (C, D) A black-and-white image of the colonies is generated using the threshold tool. (E, F) The number of colonies is quantified using the analyze particles tool. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
The mCFU assay described here increases the amount of information that can be retrieved from a single Petri dish to at least 96-fold. Figure 5 depicts a comparison of two drug-delivery methods for the repurposed use of saquinavir (SQV)31,32 as a host-directed drug to treat tuberculosis. In this assay, four different strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis were used to infect primary human macrophages. M. tubercul...
Discussion
TB is an important public health problem with increasing importance, particularly in low and middle-income countries. The disruption of healthcare settings to diagnose and treat TB during the COVID-19 pandemic caused a negative impact on the incidence of new cases1. In addition, the multi-drug and extensively-drug resistant M.tb strains, and the co-infection of M.tb and HIV must be urgently addressed to control this epidemic1,3...
Disclosures
DP and PJGB declare that the study was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by internal funding from the Faculty of Medicine, Universidade Católica Portuguesa, and external funding from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), under the grants UIDP/04279/2020, UIDB/04279/2020, and EXPL/SAU-INF/0742/2021.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 96-well plates | VWR | 734-2781 | |
| DSLR 15-55 mm lens | Nikon | AF-P DX NIKKOR 18-55mm f/3.5-5.6G VR | |
| DSLR camera | Nikon | D3400 | |
| DSLR macro lens | Sigma | MACRO 105mm F2.8 EX DG OS HSM | |
| Fetal calf serum | Gibco | 10270106 | |
| Fiji Software | https://fiji.sc/ | Fiji is an open-source software supported by several laboratories, institutions, and individuals. All the required plugins are included. | |
| Igepal CA-630 | Sigma-Aldrich | 18896 | |
| L-glutamine | Gibco | 25030-081 | |
| Middlebrook 7H10 | BD | 262710 | |
| Middlebrook 7H9 | BD | 271310 | |
| Multichannel pipette (0.5 - 10 µl) | Gilson | FA10013 | |
| Multichannel pipette (20 - 200 µl) | Gilson | FA10011 | |
| Mycobacterium bovis BCG | American Type Culture Collection | ATCC35734 | strain TMC 1011 [BCG Pasteur] |
| OADC enrichment | BD | 211886 | |
| Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | NZYTech | MB25201 | |
| RPMI 1640 medium | Gibco | 21875091 | |
| Sodium pyruvate | Gibco | 11360-070 | |
| Spectrophotometer UV-6300PC | VWR | 634-6041 | |
| Square Petri dish 120 x 120 mm | Corning | BP124-05 | |
| Tyloxapol | Sigma-Aldrich | T8761 | |
| Ultrasound bath Elma P 30 H | VWR | 142-0051 |
References
- World Health Organization. . Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. , (2022).
- Bettencourt, P. J. G., Joosten, S. A., Lindestam Arlehamn, C. S., Behr, M. A., Locht, C., Neyrolles, O. 100 years of the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine. Vaccine. 39 (50), 7221-7222 (2021).
- Bettencourt, P. J. G. The 100th anniversary of bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) and the latest vaccines against COVID-19. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 25 (8), 611-613 (2021).
- Scriba, T. J., Netea, M. G., Ginsberg, A. M. Key recent advances in TB vaccine development and understanding of protective immune responses against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Seminars in Immunology. 50, 101431 (2020).
- McShane, H., Williams, A. A review of preclinical animal models utilised for TB vaccine evaluation in the context of recent human efficacy data. Tuberculosis. 94 (2), 105-110 (2014).
- Voss, G., et al. Progress and challenges in TB vaccine development. F1000Research. 7, 199 (2018).
- Satti, I., McShane, H. Current approaches toward identifying a correlate of immune protection from tuberculosis. Expert Review of Vaccines. 18 (1), 43-59 (2019).
- Young, D. Animal models of tuberculosis. European Journal of Immunology. 39 (8), 2011-2014 (2009).
- Pedroza-Roldán, C., Flores-Valdez, M. A. Recent mouse models and vaccine candidates for preventing chronic/latent tuberculosis infection and its reactivation. Pathogens and disease. 75 (6), (2017).
- Gong, W., Liang, Y., Wu, X. Animal Models of Tuberculosis Vaccine Research: An Important Component in the Fight against Tuberculosis. BioMed Research International. 2020, 1-21 (2020).
- Bettencourt, P., et al. Identification of antigens presented by MHC for vaccines against tuberculosis. NPJ vaccines. 5 (1), 2 (2020).
- Moorlag, S. J. C. F. M., Arts, R. J. W., van Crevel, R., Netea, M. G. Non-specific effects of BCG vaccine on viral infections. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 25 (12), 1473-1478 (2019).
- Wilkie, M., et al. Functional in-vitro evaluation of the non-specific effects of BCG vaccination in a randomised controlled clinical study. Scientific Reports. 12 (1), 7808 (2022).
- Netea, M. G., et al. Trained immunity: A program of innate immune memory in health and disease. Science. 352 (6284), aaf1098 (2016).
- Bettencourt, P., Pires, D., Carmo, N., Anes, E. Application of Confocal Microscopy for Quantification of Intracellular Mycobacteria in Macrophages. Microscopy: Science, Technology, Applications and Education. 1, 614-621 (2010).
- Bettencourt, P., Carmo, N., Pires, D., Timóteo, P., Anes, E. Mycobacterial infection of macrophages: the effect of the multiplicity of infection. Antimicrobial research: Novel bioknowledge and educational programs. , 651-664 (2017).
- Pires, D., Bettencourt, P., Carmo, N., Niederweis, M., Anes, E. Role of Mycobacterium tuberculosis outer-membrane porins in bacterial survival within macrophages. Drug Discovery Today. 15 (23-24), 1112-1113 (2010).
- Pires, D., et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Modulates miR-106b-5p to Control Cathepsin S Expression Resulting in Higher Pathogen Survival and Poor T-Cell Activation. Frontiers in immunology. 8 (DEC), 1819 (2017).
- Pires, D., et al. Role of Cathepsins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Survival in Human Macrophages. Scientific reports. 6 (August), 32247 (2016).
- Bettencourt, P., et al. Actin-binding protein regulation by microRNAs as a novel microbial strategy to modulate phagocytosis by host cells: the case of N-Wasp and miR-142-3p. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology. 3 (June), 19 (2013).
- Bhuyan, S., et al. Microliter spotting and micro-colony observation: A rapid and simple approach for counting bacterial colony forming units. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 207, 106707 (2023).
- Jackson, S., McShane, H. Challenges in Developing a Controlled Human Tuberculosis Challenge Model. Current topics in microbiology and immunology. , 1-27 (2022).
- Darrah, P. A., et al. Prevention of tuberculosis in macaques after intravenous BCG immunization. Nature. 577 (7788), 95-102 (2020).
- Madura Larsen, J., et al. BCG stimulated dendritic cells induce an interleukin-10 producing T-cell population with no T helper 1 or T helper 2 bias in vitro. Immunology. 121 (2), 276-282 (2007).
- Bickett, T. E., et al. Characterizing the BCG-Induced Macrophage and Neutrophil Mechanisms for Defense Against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Frontiers in immunology. 11, 1202 (2020).
- Pires, D., et al. Interference of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with the endocytic pathways on macrophages and dendritic cells from healthy donors: role of cathepsins. Drug Discovery Today. 15 (23-24), 1112-1112 (2010).
- Betts, G., et al. Optimising Immunogenicity with Viral Vectors: Mixing MVA and HAdV-5 Expressing the Mycobacterial Antigen Ag85A in a Single Injection. PLoS ONE. 7 (12), e50447 (2012).
- Tanner, R., et al. The influence of haemoglobin and iron on in vitro mycobacterial growth inhibition assays. Scientific reports. 7 (1), 43478 (2017).
- McNeill, E., et al. Regulation of mycobacterial infection by macrophage Gch1 and tetrahydrobiopterin. Nature communications. 9 (1), 5409 (2018).
- Schindelin, J., et al. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods. 9 (7), 676-682 (2012).
- Pereira, M., Vale, N. Saquinavir: From HIV to COVID-19 and Cancer Treatment. Biomolecules. 12 (7), 944 (2022).
- Pires, D., et al. Repurposing Saquinavir for Host-Directed Therapy to Control Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection. Frontiers in immunology. 12, 647728 (2021).
- Pires, D., et al. Liposomal Delivery of Saquinavir to Macrophages Overcomes Cathepsin Blockade by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Helps Control the Phagosomal Replicative Niches. International journal of molecular sciences. 24 (2), (2023).
- Maartens, G., Wilkinson, R. J. Tuberculosis. The Lancet. 370 (9604), 2030-2043 (2007).
- Matarazzo, L., Bettencourt, P. J. G. mRNA vaccines: a new opportunity for malaria, tuberculosis and HIV. Frontiers in Immunology. 14, 1172691 (2023).
- Young, D., Dye, C. The Development and Impact of Tuberculosis Vaccines. Cell. 124 (4), 683-687 (2006).
- Kommareddi, S., Abramowsky, C. R., Swinehart, G. L., Hrabak, L. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections: Comparison of the fluorescent auramine-o and Ziehl-Neelsen techniques in tissue diagnosis. Human Pathology. 15 (11), 1085-1089 (1984).
- Sabiiti, W., et al. A Tuberculosis Molecular Bacterial Load Assay (TB-MBLA). Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE. (158), e60460 (2020).
- Somoskövi, A., et al. Comparison of Recoveries of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using the Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 System, the BACTEC 460 TB System, and Löwenstein-Jensen Medium. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 38 (6), 2395-2397 (2000).
- Tanner, R., et al. The in vitro direct mycobacterial growth inhibition assay (MGIA) for the early evaluation of TB vaccine candidates and assessment of protective immunity: a protocol for non-human primate cells. F1000Research. 10, 257 (2021).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved