A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
الأنسجة المفروم في المضغوط الكولاجين: وBiotransplant التي تحتوي على خلية لإصلاح الترميمية نظموا وحيد
In This Article
Summary
وغالبا ما تتضمن هندسة الأنسجة في التوسع في المختبر من أجل خلق طعم ذاتي لتجديد الأنسجة. في هذه الدراسة تم تطوير طريقة لتوسيع الأنسجة، وتجديد، وإعادة البناء في الجسم الحي من أجل تقليل تجهيز الخلايا والمواد البيولوجية خارج الجسم.
Abstract
Conventional techniques for cell expansion and transplantation of autologous cells for tissue engineering purposes can take place in specially equipped human cell culture facilities. These methods include isolation of cells in single cell suspension and several laborious and time-consuming events before transplantation back to the patient. Previous studies suggest that the body itself could be used as a bioreactor for cell expansion and regeneration of tissue in order to minimize ex vivo manipulations of tissues and cells before transplanting to the patient. The aim of this study was to demonstrate a method for tissue harvesting, isolation of continuous epithelium, mincing of the epithelium into small pieces and incorporating them into a three-layered biomaterial. The three-layered biomaterial then served as a delivery vehicle, to allow surgical handling, exchange of nutrition across the transplant, and a controlled degradation. The biomaterial consisted of two outer layers of collagen and a core of a mechanically stable and slowly degradable polymer. The minced epithelium was incorporated into one of the collagen layers before transplantation. By mincing the epithelial tissue into small pieces, the pieces could be spread and thereby the propagation of cells was stimulated. After the initial take of the transplants, cell expansion and reorganization would take place and extracellular matrix mature to allow ingrowth of capillaries and nerves and further maturation of the extracellular matrix. The technique minimizes ex vivo manipulations and allow cell harvesting, preparation of autograft, and transplantation to the patient as a simple one-stage intervention. In the future, tissue expansion could be initiated around a 3D mold inside the body itself, according to the specific needs of the patient. Additionally, the technique could be performed in an ordinary surgical setting without the need for sophisticated cell culturing facilities.
Introduction
وتشمل معظم الدراسات هندسة الأنسجة على زرع على الجلد والجهاز البولي التناسلي المحاصيل خلية ذاتي من الأنسجة السليمة وتوسيع الخلية في مرافق زراعة الخلايا مجهزة خصيصا 1،2.
بعد توسيع الخلية، وعادة ما تكون مخزنة الخلايا لاستخدامها لاحقا عندما يتم تحضير المريض لتلقي الطعم الذاتي. المجمدات النيتروجين تسمح التخزين على المدى الطويل في درجات حرارة منخفضة من -150 درجة مئوية أو أقل. ويجب أن تكون عملية تجميد دقيق والتحكم حتى لا تفقد الخلايا. خطر واحد من موت الخلايا وتبلور الماء داخل الخلايا أثناء عملية ذوبان الجليد، والتي يمكن أن تؤدي إلى تمزق أغشية الخلايا. عادة ما يتم إجراء تجميد الخلية عن طريق بطيئة وتسيطر التبريد (-1 ° C لكل دقيقة)، وذلك باستخدام تركيز عال من الخلايا، مصل بقري جنيني، وسلفوكسيد ثنائي ميثيل. بعد ذوبان الجليد، تحتاج الخلايا التي سيتم تجهيزها مرة أخرى عن طريق إزالة المتوسطة تجميد وزرع على البلاستيك زراعة الخلايا أومادة بيولوجية قبل الزرع إلى المريض.
جميع الخطوات المذكورة أعلاه تستغرق وقتا طويلا، وشاقة، وتكلفة 3. وبالإضافة إلى ذلك، كل في المختبر تجهيز خلايا المعدة للزرع المريض درجة عالية من التنظيم ويتطلب موظفين مدربين تدريبا جيدا والمعتمدين ومختبرات 4. جميع في كل شيء، لشراء عملية التصنيع آمنة وموثوق بها، ويمكن وضع هذه التقنية إلا في عدد قليل جدا من المراكز المتقدمة تقنيا واستخدامها على نطاق أوسع في اضطرابات الجراحية المشتركة أمر مشكوك فيه.
من أجل التغلب على القيود المفروضة على زراعة الخلايا في بيئة المختبر، يتم تقديم مفهوم من زرع الأنسجة المفروم للتوسع خلية في الجسم الحي باستخدام الجسم نفسه بأنه مفاعل حيوي. لهذه الأغراض، فإن تفضيلي يتم زرعها على طعم ذاتي على العفن 3D وفقا للشكل أن هناك حاجة لإعادة إعمار النهائي للجهاز طnterest 5-7.
في الأصل، تم تقديم فكرة زرع ظهارة مفروم التي كتبها ميك عام 1958 عندما وصف كيف ينمو ظهارة من حواف الجرح. وقد أوضح أن قطعة صغيرة من الجلد من شأنه أن يزيد من هوامش أرباحها وبالتالي قدرته على توسيع الخلية بنسبة 100٪ عن طريق قطع قطعة مرتين في الاتجاهات المتعامدة (الشكل 1) 8. وقد تم دعم هذه النظرية عن طريق استخدام الطعوم سماكة الجلد جزئية مزجها لزرع الجلد 9 وفي الجلد التئام الجروح نماذج 10.
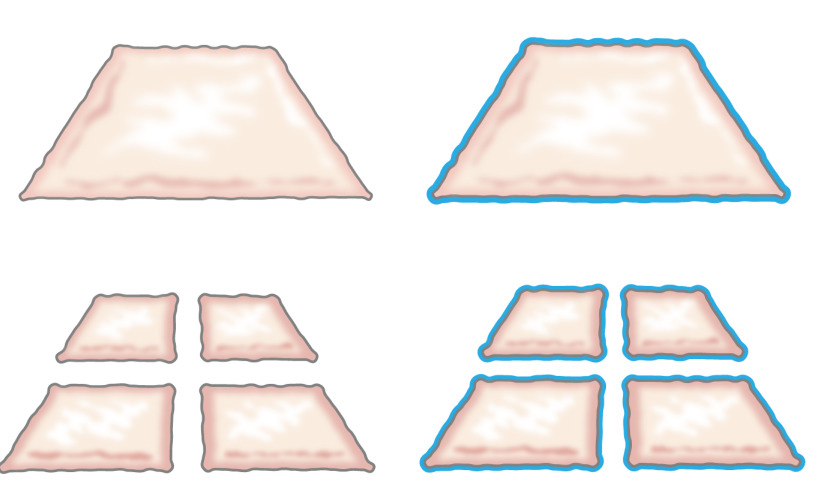
الشكل 1: نظرية وديع وفقا لنظرية ميك، وظهارة تنمو على حواف الجرح. من خلال زيادة مساحة كشفها بواسطة تكنولوجيا تنميق، الأنسجة المفروم epithelializes الجروح من العديد من المواقع.
وتعتمد الدراسة الحالية على فراش لا تسببأطروحة أن نفس المبدأ يمكن تطبيقها على الأنسجة تحت الجلد عن طريق وضع ظهارة مفروم حول القالب. إن الخلايا الظهارية حشد من زرع مفروم (تنظيم)، وتغطي مناطق الجرح (تهاجر) والقسمة (توسيع) من أجل تشكيل neoepithelium المستمر الذي يغطي منطقة الجرح ويفصل جسم غريب (القالب) من الجسم الداخلية ( الشكل 2).
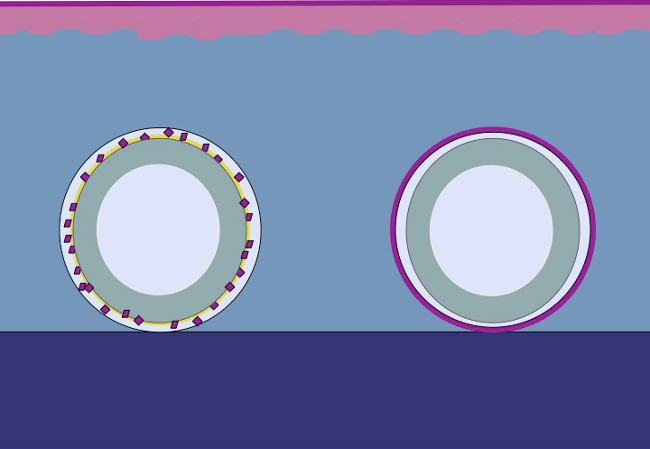
الشكل 2: كارتون من قالب 3D مع ظهارة المفروم في الجسم الحي توسيع الأنسجة intracorporal وفقا لنظرية ميك باستخدام الأنسجة المفروم وضعت على قالب ثم زرعها في الأنسجة تحت الجلد، والفرضية هي أن الخلايا الظهارية تهاجر من حواف الأنسجة المفروم وإعادة تنظيم وتوسيع ذلك لتشكيل neoepithelium المستمر الذي يغطي منطقة الجرح ويفصل جسم غريب (القالب) من الجسم الداخلية.
على الرغم من أن الدراسات السابقة في الجسم الحي تظهر نتائج واعدة، ويمكن تحقيق مزيد من التحسينات من خلال تعزيز طعم ذاتي بحيث ظهارة مجدد يمكن أن تحمل الصدمات الميكانيكية أفضل 7. لهذه الأغراض، تم تحديد أهم الشروط الأساسية لمادة بيولوجية الناجحة، مثل: نشر السهل من المواد الغذائية والفضلات، إمكانية العفن بطريقة 3D وسهولة التعامل الجراحي. وقدمت النتائج أن هذه الاحتياجات يمكن تلبيتها عن طريق إضافة مادة بيولوجية المركبة إلى الأنسجة المفروم.
الدراسة الحالية تهدف إلى تطوير سقالة تتكون من الأنسجة المفروم في الكولاجين البلاستيك ضغط تحتوي على نواة يعزز من نسيج القابلة للتحلل. بهذه الوسائل، يمكن أن خلايا قابلة للحياة تهاجر من جزيئات الأنسجة المفروم وتتكاثر مع الميزات المورفولوجية سمة من ظهارة الأصلية (الجلد أو الظهارة البولية). باستخدام ضغط من البلاستيك، وكانت سقالة الحدتم المغطى د في حجمها من 1 سم إلى حوالي 420 ميكرون كما الجسيمات المفروم في الكولاجين الطبقة العليا. النسيج الأساسية يمكن أن يكون أي البوليمر ولكن يحتاج إلى تعديل مع سطح ماء من أجل الربط بين مع تغطي طبقات الكولاجين 11.
توفير طريقة لسلامة سقالة معززة من خلال دمج شبكة محبوك تتكون من بولي (ε-caprolactone) (PCL) في غضون سنتين من البلاستيك المضغوط والمواد الهلامية الكولاجين باستخدام بأنها سقالة لزراعة مفروم مخاطية المثانة أو الجلد مفروم من الخنازير. وقد حافظت على بناء في ظروف زراعة الخلايا لمدة تصل إلى 6 أسابيع في المختبر، مما يدل على تشكيل الناجح لالطبقية، الظهارة البولية متعدد الطبقات أو الحرشفية ظهارة الجلد على الجزء العلوي من بناء الهجين موحد بشكل جيد. كان بناء السهل التعامل معها ويمكن خياطة في مكان لأغراض المثانة زيادة أو تغطية عيوب البشرة. جميع أجزاء من سقالة الأنسجة وادارة الاغذية والعقاقير وافق وتقنيةيمكن استخدامها في إجراءات مرحلة واحدة من قبل الحصاد الأنسجة، تنميق، وضغط من البلاستيك، وزرع العودة إلى المريض كتدخل واحد على مراحل. يمكن إجراء العملية للتوسع الأنسجة وإعادة الإعمار تحت ظروف معقمة في أي وحدة الجراحة العامة.
Protocol
وقبل الموافقة على جميع البروتوكولات الحيوان من قبل لجنة مقاطعة ستوكهولم على الحيوانات ويتفق جميع الإجراءات لوائح للاستخدام الحيواني، وكذلك القوانين الاتحادية ذات الصلة.
1. إجراءات الحيوان
- إعداد الحيوان للجراحة
- إعداد طاولة الجراحة مع جميع المواد والأدوات اللازمة لتشغيل تحت ظروف معقمة. إجراء عملية جراحية على وجه الحصر تحت ظروف معقمة للحد من خطر العدوى وتحسين الأوضاع في جراحة بقاء.
- صيام الحيوان لمدة 12 ساعة قبل الجراحة وقياس وزنه. إدارة الحقن العضلي من azaperone (2 ملغ / كغ) للتخدير. تخدير الحيوانات مع حقن في العضل من hypochloride تلييتامين (2.5 ملغ / كلغ)، hypochloride zolazepam (2.5 ملغ / كلغ)، medetomidine (25 ميكروغرام / كغ) والأتروبين (25 ميكروغرام / كغ).
- حقن phenobarbiturate (15 ملغ / كلغ) قبل endotracheآل التنبيب ويستمر التخدير العام مع 0.8٪ -2٪ الأيزوفلورين. ادخال قسطرة الوريد الطرفية في أذن واحدة ويبث الجلوكوز (25 ملغ / مل) عن طريق الوريد أثناء إجراء للحفاظ على رفاهية الحيوان.
- وضع الأجهزة على الأذن أو الذيل رصد لفحص درجة حرارة وضغط الدم والتشبع، والنبض المحيطي. التخدير السيطرة عن طريق تحفيز آلام الأذنين أو الحوافر. تطبيق مرهم للعين لمنع جفاف بينما تحت التخدير.
- استئصال المثانة خزعة عينة
- يقثطر المثانة باستخدام القسطرة سيليكون 10-الفرنسية عن طريق إدخال منظار لعرض مجرى البول وادخال القسطرة عن طريق مجرى البول وإلى المثانة البولية لإفراغ البول تحت ظروف شبه معقمة. ملء المثانة مع محلول ملحي معقم لضغط من 20-25 سم H 2 O، حوالي 100-300 مل، ومن ثم فارغة إلى 20 سم H 2 O (حوالي 8 مل / كجم من وزن الجسم).
- مع الالبريد الخنازير تحولت بعناية لموقف الجانب، إجراء التعقيم قبل الجراحة الأساسية من الجلد مع تطبيق غلوكونات الكلورهيكسيدين. تطبيق لوحة الإنفاذ الحراري في الكتف بعد إزالة نتف الشعر مع مقص الحلاقة.
- تحويل خنزير بعناية في موقف ضعيف وإزالة نتف الشعر في البطن باستخدام مقص الحلاقة والقيام التعقيم قبل الجراحة الأساسية للجلد البطن مع تطبيق غلوكونات الكلورهيكسيدين.
- تضمين الأطراف مع الثياب الناعمة للحد من خطر تلف تمدد مفرط في المفاصل في الأطراف. تعقيم الجلد في منطقة البطن للحيوان مع تطبيقات المتعاقبة من غلوكونات الكلورهيكسيدين ووضع اللف العقيمة حول الجراحي الميداني.
- قبل شق الجلد، وتطبيق مسكن في الوريد يتكون من البوبرينورفين (45 ميكروغرام / كغ)، كاربروفين (3 ملغ / كغ)، والحقن المحلي ليدوكائين في خط الوسط تحت السرة. تحقق من وجود رد فعل الألم عن طريق استيعاب كورونافي بالملقط. جعل انخفاض شق خط الوسط من خلال لفافة والغشاء البريتوني باستخدام الإنفاذ الحراري للسيطرة على النزيف. توطين المثانة لديها موقف داخل الصفاق تماما في خنزير ويمكن أن يتعرض بحرية من خلال تعبئة من خلال الجروح.
- اتخاذ اجراء من المثانة مع ملقط وقياسه مع شريط قياس تعقيمها وعلامة على عينة الخزعة على شكل بيضاوي الشكل تقريبا 2 سم طوليا و 1 سم عرضيا، أو أصغر، وذلك باستخدام قلم تعقيمها (الخنزير تتسامح انخفاض ربع حجم المثانة ممتاز). استئصال منطقة ملحوظة، وذلك باستخدام مشرط، ووضع عينة المثانة خزعة في DMEM تحت ظروف معقمة.
- أداء الزرع الذاتي مع biotransplant أو إغلاق المثانة عن طريق خياطة مع 5-0 Vicryl في طبقتين. إغلاق رباط البطن بعناية مع 2-0 أو 3-0 تشغيل Vicryl. إغلاق تحت الجلد مع 3-0 Vicryl والجلد مع 3-0 Ethilon. وضع ضمادة على الجرح وبعناية فيتميل للحيوان حتى تعافى بشكل كاف من التخدير ولا يعبر عن الألم.
- نقل الحيوانات إلى مرفق رعاية الحيوانات لتأمين الظروف الملائمة لرعاية ما بعد الجراحة. وضع الحيوان في قفص واحد مع مصباح التدفئة وحضور للحيوان حتى الشفاء التام من التخدير ومن ثم السماح أن المتوقفة الحيوانات في أزواج.
- توفير الانتعاش هادئ حول الألم ورفاه وإدارة البوبرينورفين (45 ميكروغرام / كغ) عضليا لتسكين الألم بعد العملية الجراحية وtrimetoprim (4 ملغ / كلغ) والسلفوناميد (20 ملغ / كلغ) مرتين يوميا لمدة ثلاثة أيام ومرة واحدة يوميا لمدة خمسة أيام للحد من خطر العدوى بعد الجراحة.
- استئصال خزعة الجلد عينة
- إعداد طاولة الجراحة مع جميع المواد اللازمة. تخدير الحيوانات كما هو موضح سابقا في 1.1. إزالة نتف الشعر باستخدام الشمع، وغسل وتعقيم المنطقة شق مع betadine والكحول 70٪ وبعد ذلك وضعت اللف العقيمة أروند منطقة شق.
- استخدام جلدي لحصاد 0.3 مم سمك جزئي خزعة الجلد. ضع عينة الجلد في DMEM قبل تنميق، كما هو موضح في 2.2. تغطية منطقة الجرح مع مرهم الدهنية وخلع الملابس.
2. مفروم الأنسجة التحضير
- المثانة الغشاء المخاطي
- غسل خزعة المثانة مرتين في DMEM. ضع العينة المثانة خزعة على طبق من ذهب تشريح تعقيمها مع الغشاء المخاطي التي تواجه صعودا وإصلاح واحد من الجانبين لوحة باستخدام دبابيس تشريح.
- فصل الأنسجة المخاطية من عضلة النافصة باستخدام مقص الجميلة وملقط (الشكل 3) والحفاظ على الأغشية المخاطية رطبة بسبب يقطر المالحة أو DMEM أكثر من ذلك.
- استخدام جهاز تنميق عن طريق وضعها على الغشاء المخاطي ومن ثم تمرير الجهاز من نهاية واحدة إلى أخرى عموديا وأفقيا، وتطبيق الضغط اليدوي للحصول على قطعة من نسيج مفروم 0.8 مم × 0.8 مم (0.8 ملم هي المسافة بين rotatinز مناشير).
- بشرة
- إذا كان biopsis الجلد سميكة: وضع الجلد على طبق من ذهب تشريح معقمة واستخدام مقص جراحي لفصل البشرة من الدهون تحت الجلد والأدمة. البشرة رقيقة وشفافة (حوالي 0.3 مم) عندما يكون جاهزا لتنميق.
- استخدام جهاز تنميق عن طريق وضعه على البشرة. مع الضغط، وتمرير الجهاز من نهاية واحدة إلى أخرى عموديا وأفقيا للحصول على قطعة من نسيج مفروم 0.8 مم × 0.8 مم.
3. إعداد البلاستيك المضغوط PCL / الكولاجين طعم ذاتي
- ضع كل المكونات على الجليد للحفاظ على برودة. الأواني اللازمة: أنبوب الصقر، 10X DMEM، 1X DMEM، 1 N هيدروكسيد الصوديوم وذيل فأر نوع الكولاجين 1.
- مزيج 2 مل من 10X DMEM (بعناية لتجنب الفقاعات) مع 12 مل من نوع الكولاجين 1. إضافة 1 N هيدروكسيد الصوديوم، قطرة قطرة، لتحقيق درجة الحموضة تصل إلى 7،4-8 (اللون في المتوسط يجب أن تشير إلى درجة الحموضة عن طريق تغيير من شدة الأصفر إلى دبوسك). وبالإضافة إلى ذلك، استخدم شريط الأس الهيدروجيني.
- بعناية إضافة 2 مل من 1X DMEM ومزيج الحل. لوحة ما يقرب من 2 مل من الكولاجين في كل بئر من العفن مستطيل الصلب (20x30x10 مم)، واحتضان في 37 ° مئوية في 5٪ CO 2 لمدة 10 دقيقة.
ملاحظة: يجب أن يكون تركيز الكولاجين 2.06 ملغ / مل في حمض الخليك 0.6٪ وكمية الكولاجين 1 مل / سم 2. - مرة واحدة يحدد الكولاجين في القالب، ضع مادة بيولوجية (PCL) على أعلى من هلام الكولاجين (20 ملم × 30 ملم) وتصب الكولاجين المتبقية (حوالي 6 مل) على أعلى من ذلك. احتضان عند 37 درجة مئوية في 5٪ CO 2 لمدة 20 دقيقة.
- وضع الأنسجة المفروم (لمدة 1: 6 التوسع) في الجزء العلوي من هلام الكولاجين. اضغط على المياه من بناء بالقوة الميكانيكية باستخدام ضغط البلاستيك على النحو التالي (الأرقام 3 و 4).
- وضع طبقة سميكة من قطع من الشاش على سطح العقيمة. مكان واحد مش الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ (400 ميكرون سميكة) على رأس gauzمنصات ه ثم ورقة من شبكة من النايلون (110 ميكرون سميكة). نقل بعناية الجل الكولاجين / الأنسجة المفروم على شبكة من النايلون وإزالة بعناية القالب الصلب مستطيلة.
- وضع طبقة جديدة من شبكة من النايلون على رأس هلام الكولاجين / الأنسجة المفروم. وضع شبكة من الصلب الثانية على رأس شبكة من النايلون. وضع في موقف لوحة الضغط أو تحميل وزنها لا يقل عن 120 غرام (أي لوحة من الزجاج) لمدة 5 دقائق.
- إزالة تنسجم الوزن، والنايلون، والصلب. وطعم ذاتي هي الآن جاهزة للخياطة إلى المثانة خنزير في الجروح الجلدية كامل سماكة أو مثقف في المختبر.
- لفي المختبر زراعة، وقطع بناء رقيقة إلى قطع صغيرة تركيب لوحات 12-جيدا. إضافة 1 مل من المتوسط القرنية. وضع لوحات في الحاضنة عند 37 درجة مئوية، و 5٪ CO 2 والثقافة تصل إلى 6 أسابيع وتغيير المتوسطة 3 مرات في الأسبوع.
4. خياطة لطعم ذاتي
- خياطة من الطعم الذاتي مع مفروم مخاطية المثانة إلى المثانة خنزير
- الحفاظ على الطعم الذاتي رطبة في DMEM خلال فترة الانتظار. خياطة الطعم الذاتي مع غرامة خيوط تشغيل حيدة. استخدام غير قابل للامتصاص 5-0 Ethilon لأغراض البحث.
- معرفة ما اذا كان للماء عن طريق ملء المثانة مع المياه المالحة عن طريق القسطرة البولية مسستقر. إذا كان ذلك ممكنا، وتغطية الطعم الذاتي مع طبقة من الثرب الكبير. إغلاق جدار البطن، الأنسجة تحت الجلد، والجلد كما هو موضح في 1.2.6. تطبيق تضميد الجراح.
- خياطة من بأسلوب الطعم الذاتي مع البشرة الجلد مفروم إلى الجرح كامل سماكة
- الحفاظ على الطعم الذاتي رطبة في DMEM خلال فترة الانتظار.
- خياطة الطعم الذاتي في الجزء السفلي من الجلد كامل سماكة الجرح بواسطة الغرز انقطاع في الزوايا وفي منتصف الطعم الذاتي للحفاظ على الطعم الذاتي متمسكة السطح السفلي.
- تغطية الجرح بضمادة البلاستيكية التي تحافظ على رطوبة الجرح.
الحمار = "jove_title"> 5. نهاية
- رزين الحيوان مع الحقن العضلي من hypochloride zolazepam (2.5 ملغ / كلغ) وmedetomidine (25 ميكروغرام / كغ) قبل إنهاء وتطبيق أجهزة الرصد إلى الأذن أو الذيل للتحقق من النبض وضغط الدم.
- الموت ببطء الحيوان بإعطاء جرعة قاتلة من الصوديوم بنتوباربيتال (60-140 ملغ / كلغ) عن طريق الوريد. تحقق النبض وضغط الدم إلى حين وقوع الوفاة.
6. في المختبر الثقافة
ملاحظة: تقييم تشريحيا تطور النسيج المفروم في بنيات PCL / الكولاجين في المختبر، والكولاجين / PCL / بقع مفروم يتم تربيتها في لوحات 12-جيدا باستخدام المتوسطة القرنية.
- إعداد المتوسطة القرنية:
- تعقيم زجاجة 500 مل.
- مزيج 400 مل من DMEM مع 100 مل من F12 هام (4: 1 خليط). تكملة مع 10٪ مصل بقري جنيني، والانسولين 5 ميكروغرام / مل،0.4 ميكروغرام / مل الهيدروكورتيزون، 21 ميكروغرام / مل الأدنين، 10 -10 مول / لتر الكوليرا السم، 2 × 10 -9 مول / لتر ثلاثي يودوثيرونين، 5 ميكروغرام / مل ترانسفيرين، 10 نانوغرام / مل عامل نمو البشرة، 50 U / مل البنسلين و 50 ميكروغرام / مل الستربتومايسين.
- تعقيم بواسطة الترشيح من خلال مرشح 0.2 ميكرومتر وجمع الرشاحة في زجاجة 500 مل العقيمة.
7. المناعية
ملاحظة: يتم تقسيم بروتوكول المناعية عموما إلى الخطوات التالية: (1) تثبيت والبارافين التضمين، (2) الصغيرة باجتزاء إلى 5 ميكرون شرائح والتنسيب على الشرائح، deparaffination، والإماهة، (3) المستضد إماطة اللثام، تلطيخ وتتصاعد . قبل البدء في الخطوات الأخيرة في إجراء المناعية، وإعداد مخازن الغسيل والحل فضح مستضد (انظر التفاصيل المادية منفصلة). إعداد الحل ABC معقدة لا يقل عن 30 دقيقة قبل الاستخدام.
- تثبيت
لاالشركة المصرية للاتصالات: في نهاية الثقافة في المختبر، وتحديد بقع على النحو التالي:- إعداد أنابيب إيبندورف مع 1 مل من 4٪ الفورمالديهايد مخزنة (PFA) (تحذير: الفورمالديهايد السامة يرجى قراءة ورقة بيانات السلامة المادية قبل العمل مع هذه المادة الكيميائية ارتداء القفازات والنظارات الواقية وإعداد الحل داخل غطاء الدخان).
- نقل كل من بقع الكولاجين لأنبوب إيبندورف تحتوي على 4٪ PFA. إصلاح أكثر من ليلة في درجة حرارة الغرفة.
- عينات مكان في الايثانول 70٪ للتخزين طويل الأجل عند 4 درجات مئوية. عينات جاهزة الآن للجفاف وتضمينها في كتل البارافين قبل باجتزاء.
- الإماهة
- ضع الشرائح في جرة تلطيخ مع يذاب X-هيئة تنظيم الاتصالات لمدة 15 دقيقة. كرر باستخدام جرة تلطيخ جديدة مع يذاب X-هيئة تنظيم الاتصالات. ضع الشرائح في جرة تلطيخ مع الايثانول المطلق لمدة 10 دقيقة. كرر باستخدام جرة تلطيخ جديدة مع الايثانول المطلق. ضع الشرائح في جرة تلطيخ مع 95٪ من الإيثانول لمدة 10 دقيقة وبعد ذلكفي وعاء تلطيخ مع 70٪ من الإيثانول لمدة 10 دقيقة. أخيرا غسل الشرائح مرتين لمدة 5 دقائق مع الماء المقطر.
- مستضد نزع القناع
- وضع الشرائح في جرة Coplin مع TE-حل ووضع الجرة في حمام الماء ليغلي لمدة 20 دقيقة. خذ جرة من حمام الماء بعناية. تبريد الشرائح إلى درجة حرارة الغرفة لمدة 30 دقيقة ويغسل مرتين لمدة 5 دقائق في المخزن تريس. ضع الشرائح في جرة تلطيخ مع 3٪ بيروكسيد الهيدروجين لمدة 10 دقيقة. تغسل الشرائح مرتين لمدة 5 دقائق في المخزن تريس. رسم دائرة حول العينات باستخدام طارد المياه بمناسبة القلم.
- منع انوعي ملزمة من الأجسام المضادة باستخدام 100-300 ميكرولتر من عرقلة الحل. إزالة عرقلة الحل وإضافة 100-300 ميكرولتر من الأجسام المضادة الأولية حل في التركيز الموصى به في عازلة تريس. احتضان بين عشية وضحاها. إزالة حل الأجسام المضادة وغسل أقسام العازلة في تريس مرتين لمدة 5 دقائق.
- احتضان مع الأجسام المضادة الثانوية لمدة 1 ساعة في غرفة temperatلدى عودتهم. يغسل مرتين لمدة 5 دقائق في المخزن تريس. احتضان 30 دقيقة باستخدام أدوات ABC النخبة (اتبع إرشادات الشركة المصنعة). يغسل مرتين في المخزن تريس.
- تطوير رد فعل الأجسام المضادة باستخدام VIP عدة ناقلات، باتباع إرشادات الشركة المصنعة (تنتج 1-7 دقيقة الحضانة عادة كثافة اللون البنفسجي واضحة). وضع الشرائح في الماء المقطر. مباين مع الهيماتوكسيلين ماير لمدة 30 ثانية.
- يغسل في الماء الجاري لمدة 5 دقائق. ضع الشرائح في جرة تلطيخ مع 70٪ من الإيثانول لمدة 1 دقيقة. كرر باستخدام جرة تلطيخ جديدة مع 70٪ من الإيثانول. ضع الشرائح في جرة تلطيخ مع 95٪ من الإيثانول لمدة 1 دقيقة. كرر باستخدام جرة تلطيخ جديدة مع 95٪ من الإيثانول.
- ضع الشرائح في جرة تلطيخ مع يذاب X-هيئة تنظيم الاتصالات لمدة 5 دقائق. إزالة، في وقت واحد للحفاظ على رطوبة. ضع قطرة من تصاعد المتوسطة على رأس كل شريحة ووضع غطاء زجاجي على رأس (تفعل ذلك بعناية لتجنب فقاعات الهواء). السماح للشرائح الجافة بين عشية وضحاها وعرض الشرائح تحت الجزئينطاق.
النتائج
تقدم هذه الدراسة طريقة يوضح كيفية إنتاج مادة بيولوجية للزرع باستخدام ضغط البلاستيك الكولاجين والأنسجة المفروم.
مخاطية المثانة والجلد ويمكن أن تحصد ثم مفروم ميكانيكيا الى جزيئات صغيرة (الشكل 3). بواسطة ضغط من البلاستيك، ...
Discussion
تقدم هذه الدراسة مقاربة الاستخدام السهل أن تنتج بقع جدار المثانة مع الأنسجة ذاتي للزرع على طاولة العمليات الجراحية. تتشكل بقع من قبل مجموعة من الحياكة بوليمر قابلة للتحلل في الوسط والكولاجين مع وبدون الأنسجة المفروم في الأسطح الخارجية في تركيبة مع ضغط من البلاستيك. ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Swedish Society for Medical Research, the Promobilia Foundation, the Crown Princess Lovisa Foundation, the Freemason Foundation for Children’s Welfare, the Swedish Society of Medicine, the Solstickan Foundation, Karolinska Institutet, and the Stockholm City Council for financial support.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Silicone catheter 10-French | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| DMEM 10x | Gibco | 31885-023 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| 24 well plates | Falcon | 08-772-1 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| 3',3',5-Triiodothyronine | Sigma-Aldrich | IRMM469 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| 4% PFA | Labmed Solutions | 200-001-8 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| 70% ethanol | Histolab | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 | |
| ABC Elite kit: Biotin-Streptavidin detection kit | Vector | PK6102 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Absolute ethanol | Histolab | 1399.01 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Adenine | Sigma-Aldrich | A8626 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Atropine 25 μg/kg | Temgesic, RB Pharmaceuticals, Great Britain | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Azaperone 2 mg/kg | Stresnil, Janssen-Cilag, Pharma, Austria | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Biosafety Level 2 hood | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Blocking solution: Normal serum from the same species as the secondary secondary antibody was generated in. | Vector | The blocking solution depends of the origin of first antibody | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Buprenorphine 45 μg/kg | Atropin, Mylan Inc, Canonsburg, PA | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Carprofen 3 mg/kg | Rimadyl, Orion Pharma, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Chlorhexidine gluconate | Hibiscrub 40 mg/mL, Regent Medical, England | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Cholera toxin | Sigma-Aldrich | C8052 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Coplin jar: staining jar for boiling | Histolab | 6150 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Stainless mold (33 mm x 22 mm x 10 mm) custom made | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| DMEM | Gibco | 3188-5023 | Plastic compression section 4. Keep on ice when using it in plastic compression |
| Epidermal growth factor | Sigma-Aldrich | E9644 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Ethilon (non-absorbable monofilament for skin sutures) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Gibco | 10437-036 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Forceps (Adison with tooth) | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Gauze (Gazin Mullkompresse) | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Ham's F12 | Gibco | 31765-027 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Hematoxylin | Histolab | 1820 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Humidity chamber | DALAB | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 | |
| Hydrocortisone | Sigma-Aldrich | H0888 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Hydrogen peroxide Solution 30% | Sigma-Aldrich | H1009 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Insulin | Sigma-Aldrich | I3536 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Isoflurane | Isoflurane, Baxter, Deerfield, IL | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Lidocaine 5 mg/ml | Xylocaine, AstraZeneca, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Lucose 25 mg/ml | Baxter, Deerfield, IL | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Marker pen pap pen | Sigma-Aldrich | Z377821-1EA | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Medetomidine 25 μg/kg | Domitor, Orion Pharma, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Mincing device | Applied Tissue Technologies LLC | Minced tissue preparation, section 2 | |
| Monocryl (absorbable monofilament) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | S7653 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| NaOH 1 N | Merck Millipore | 106462 | Plastic compression section 4 and cell culture |
| Nylon mesh, 110 μM thick pore size 0.04 sqmm | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Oculentum simplex APL: ointment for eye protection | APL | Vnr 336164 | Surgery, Section 1 |
| PBS | Gibco | 14190-094 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Phenobarbiturate 15 mg/kg | Pentobarbital, APL, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| PCL Knitted fabric | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Rat-tail collagen | First LINK, Ltd, UK | 60-30-810 | Plastic compression section 4, keep on ice |
| Scalpel blade - 15 | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Shaving shears | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Stainless stell mesh, 400 μM thick pore size | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Steril gloves | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Sterile gowns | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Sterile drapes | |||
| Sterilium | Bode Chemie HAMBURG | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Suture Thread Ethilon | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| TE-solution (antigen unmasking solution) consist of 10 mM Tris and 1 mM EDTA, pH 9.0 | 10 mM Tris/1 mM EDTA, adjust pH to 9.0 | ||
| Tiletamine hypochloride 2.5 mg/kg | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Transferrin | Sigma-Aldrich | T8158 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Trizma Base, H2NC | Sigma-Aldrich | T6066 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Vector VIP kit: Enzyme peroxidase substrate kit | Vector | SK4600 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Vicryl (absorbable braded) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| Tris buffer pH 7.6 (washing buffer) | TE solution: Make 10x (0.5 M Tris, 1.5 M NaCl) by mixing: 60.6 g Tris (Trizma Base, H2NC(CH2OH)3, M=121.14 g/mol), add 800 ml distilled water adjust the pH till 7.6, add 87.7 g NaCl and fill to 1,000 ml with distilled water. Dilute to 1x with distilled water. | ||
| X-tra solv (solvent) | DALAB | 41-5213-810 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6. Use under fume hood |
| Zolazepam hypochloride | Zoletil, Virbac, France | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Depilatory wax strips | Veet | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Pentobarbital sodium | Lundbeck | Termination, Section 3 |
References
- Rheinwald, J. G., Green, H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 6, 331-343 (1975).
- Fossum, M., Nordenskjold, A., Kratz, G. Engineering of multilayered urinary tissue in vitro. Tissue Engineering. 10, 175-180 (2004).
- Salmikangas, P., et al. Manufacturing, characterization and control of cell-based medicinal products: challenging paradigms toward commercial use. Regen Med. 10, 65-78 (2015).
- Fossum, M., et al. Minced skin for tissue engineering of epithelialized subcutaneous tunnels. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 15, 2085-2092 (2009).
- Fossum, M., et al. Minced urothelium to create epithelialized subcutaneous conduits. The Journal of Urology. 184, 757-761 (2010).
- Reinfeldt Engberg, G., Lundberg, J., Chamorro, C. L., Nordenskjold, A., Fossum, M. Transplantation of autologous minced bladder mucosa for a one-step reconstruction of a tissue engineered bladder conduit. BioMed Research International. 2013, 212734 (2013).
- Meek, C. P. Successful microdermagrafting using the Meek-Wall microdermatome. Am J Surg. 96, 557-558 (1958).
- Tanner, J. C., Vandeput, J., Olley, J. F. The Mesh skin graft. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 34, 287-292 (1964).
- Svensjo, T., et al. Autologous skin transplantation: comparison of minced skin to other techniques. The Journal of Surgical Research. 103, 19-29 (2002).
- Ajalloueian, F., Zeiai, S., Rojas, R., Fossum, M., Hilborn, J. One-stage tissue engineering of bladder wall patches for an easy-to-use approach at the surgical table. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods. 19, 688-696 (2013).
- Engelhardt, E. M., et al. A collagen-poly(lactic acid-co-varepsilon-caprolactone) hybrid scaffold for bladder tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 32, 3969-3976 (2011).
- Brown, R. A., Wiseman, M., Chuo, C. B., Cheema, U., Nazhat, S. N. Ultrarapid engineering of biomimetic materials and tissues: fabrication of nano- and microstructures by plastic compression. Adv Funct Mater. 15, 1762-1770 (2005).
- Fumagalli Romario, U., Puccetti, F., Elmore, U., Massaron, S., Rosati, R. Self-gripping mesh versus staple fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a prospective comparison. Surg Endosc. 27, 1798-1802 (2013).
- Muangman, P., et al. Complex Wound Management Utilizing an Artificial Dermal Matrix. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 57, 199-202 (2006).
- Ajalloueian, F., Zeiai, S., Fossum, M., Hilborn, J. G. Constructs of electrospun PLGA, compressed collagen and minced urothelium for minimally manipulated autologous bladder tissue expansion. Biomaterials. 35, 5741-5748 (2014).
- Orabi, H., AbouShwareb, T., Zhang, Y., Yoo, J. J., Atala, A. Cell-seeded tubularized scaffolds for reconstruction of long urethral defects: a preclinical study. Eur Urol. 63, 531-538 (2013).
- Blais, M., Parenteau-Bareil, R., Cadau, S., Berthod, F. Concise review: tissue-engineered skin and nerve regeneration in burn treatment. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2, 545-551 (2013).
- Serpooshan, V., Muja, N., Marelli, B., Nazhat, S. N. Fibroblast contractility and growth in plastic compressed collagen gel scaffolds with microstructures correlated with hydraulic permeability. J Biomed Mater Res A. 96, 609-620 (2011).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved