JoVE 비디오를 활용하시려면 도서관을 통한 기관 구독이 필요합니다. 전체 비디오를 보시려면 로그인하거나 무료 트라이얼을 시작하세요.
Method Article
압축 된 콜라겐에 다진 조직 : 단일 무대 재건 복구를위한 세포 함유 Biotransplant
요약
조직 공학은 종종 조직 재생을위한자가 이식을 만들기 위해 체외 확장에 포함되어 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 조직 확장 재생 및 생체 내에서 재구성하기위한 방법이 체외 세포 및 생체 물질의 처리를 최소화하기 위해 개발되었다.
초록
Conventional techniques for cell expansion and transplantation of autologous cells for tissue engineering purposes can take place in specially equipped human cell culture facilities. These methods include isolation of cells in single cell suspension and several laborious and time-consuming events before transplantation back to the patient. Previous studies suggest that the body itself could be used as a bioreactor for cell expansion and regeneration of tissue in order to minimize ex vivo manipulations of tissues and cells before transplanting to the patient. The aim of this study was to demonstrate a method for tissue harvesting, isolation of continuous epithelium, mincing of the epithelium into small pieces and incorporating them into a three-layered biomaterial. The three-layered biomaterial then served as a delivery vehicle, to allow surgical handling, exchange of nutrition across the transplant, and a controlled degradation. The biomaterial consisted of two outer layers of collagen and a core of a mechanically stable and slowly degradable polymer. The minced epithelium was incorporated into one of the collagen layers before transplantation. By mincing the epithelial tissue into small pieces, the pieces could be spread and thereby the propagation of cells was stimulated. After the initial take of the transplants, cell expansion and reorganization would take place and extracellular matrix mature to allow ingrowth of capillaries and nerves and further maturation of the extracellular matrix. The technique minimizes ex vivo manipulations and allow cell harvesting, preparation of autograft, and transplantation to the patient as a simple one-stage intervention. In the future, tissue expansion could be initiated around a 3D mold inside the body itself, according to the specific needs of the patient. Additionally, the technique could be performed in an ordinary surgical setting without the need for sophisticated cell culturing facilities.
서문
피부와 비뇨 기관에 이식에 대부분의 조직 공학 연구는 특별히 장착 된 세포 배양 시설 1, 2의 건강한 조직과 세포의 확장에서자가 세포 수확을 포함한다.
환자 이식술을 수신 할 준비가되었을 때 셀 전개 후, 세포는 일반적으로 나중에 사용하기 위해 저장된다. 질소 냉동고 -150 ° C 이하의 낮은 온도에서의 장기간 저장을 허용한다. 동결 프로세스는 신중하고 세포 손실하지 않도록 제어되어야한다. 세포 사멸의 한 위험 세포막의 파괴로 이어질 수 해동 과정 중 세포 내 물이 결정화된다. 동결 세포는 일반적으로 세포를 소 태아 혈청 및 디메틸 술폭 시드의 고 농도를 사용하여 천천히 제어 냉각 (-11 ° C 당 분)에 의해 수행된다. 해동 후, 세포를 동결 배지를 제거하고 세포 배양 용 플라스틱 또는 배양에 의해 다시 처리 될 필요다시 환자에게 이식하기 전에 생체 재료.
모든 상기 언급 된 단계는 시간 소모, 번잡하고 고비용 3. 또한, 환자의 이식을위한 세포의 모든 체외 처리는 매우 규제하고 잘 훈련 된 공인 인력과 실험실 4 필요합니다. 전부, 기술은 기술적으로 진보 센터 극소수에 설립 될 수 있고, 일반적인 수술 질환을 넓게 사용하기 어렵다, 안전하고 신뢰할 수있는 제조 공정을 조달.
실험실 환경에서 세포 배양의 한계를 극복하기 위해, 생체 내에서 세포 확장 다진 조직 이식의 개념은 바이오 리액터로서 본체 자체를 사용하여 도입된다. 이러한 목적을 위해,자가 이식 우선적 I의 장기의 최종 재구성에 필요한 형상에 따라 3D 금형에 이식 될5-7 nterest.
원래, 다진 상피 세포를 이식의 아이디어는 그가 상피 세포가 상처의 가장자리에서 성장하는 방법을 설명 할 때 1958 년 온순한 제시했다. 그 피부의 작은 조각 (도 1) (8)를 수직 방향으로 두 조각을 절단하여 100 %로함으로써, 셀 확장 가능성을 마진을 증가한다고 입증 하였다. 이론은 피부 이식 9 맞물린 부분 층 피부 이식의 사용에 의해 지원 피부 모델 10 상처 치유되었다.
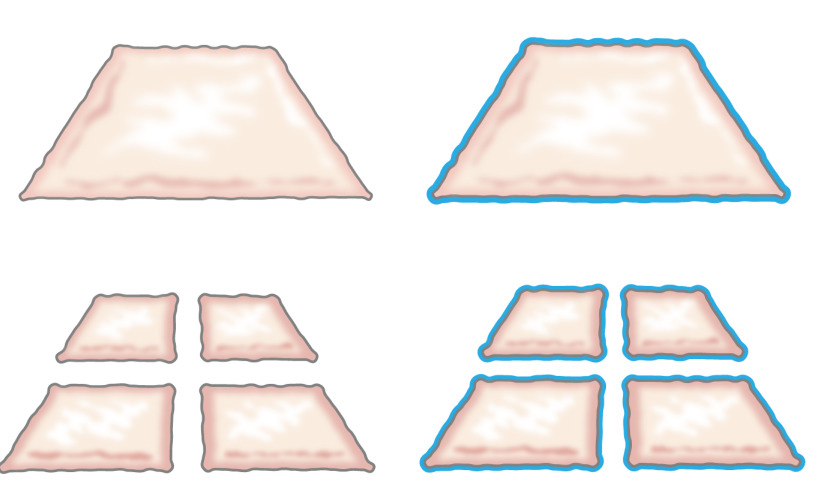
그림 1 :. 온순한 이론은 미크의 이론에 따르면, 상피 세포는 상처의 가장자리에서 성장. 닦지 기술에 의해 노출되는 면적을 증가시킴으로써, 다진 조직은 많은 점에서 상처를 epithelializes.
본 연구는 저자에 기초동일한 원리가 주형 주위 다진 상피 배치하여 피하 조직에 적용될 수 논문. (상기 내부 몸체로부터 이물 (금형) 상처 면적 분리 연속 neoepithelium을 형성하기 위해 상피 세포는 상처 영역 (마이그레이션) 커버 다진 이식 (재구성)로부터 동원 것이고 분할기 (확장) 그림 2).
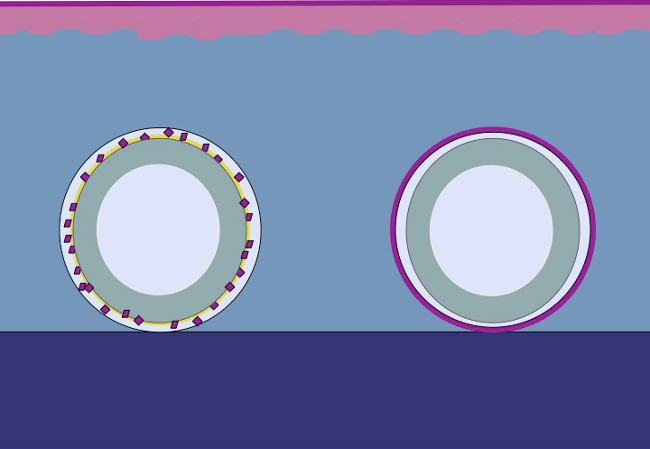
그림 2. 선량의 이론에 따른 생체 intracorporal 조직 확장 다진 상피 3D 금형 만화 피하 조직에 금형에 배치 한 후 이식 다진 조직을 이용하여 상기 가설은 상피 세포에서 마이그레이션 있다는 다진 조직의 가장자리는 재구성 및 상처 면적 본체 내부에서 이물질 (몰드)을 분리하는 연속 neoepithelium을 형성하도록 확장.
이전의 생체 내 연구는 유망한 결과를 보여하지만 재생 된 상피 더 나은 7 기계적 충격에 견딜 수 있도록, 더 개선은자가 이식을 강화함으로써 달성 될 수있다. 쉬운 영양소와 폐기물의 확산 가능성 금형 3D 방식 외과 취급 용이성 이러한 목적을 위해 성공적인 생체 중요한 전제 같은 확인되었다. 결론이 요구 다진 티슈 복합 생체 재료를 첨가함으로써 충족 될 수 있다고 하였다.
에 다진 조직으로 구성된 인공 지지체의 개발을 목표로 현재 연구 생분해 성 섬유의 보강 코어를 포함하는 콜라겐을 플라스틱 압축. 이러한 방법으로, 실행 가능한 세포는 다진 조직의 입자에서 마이그레이션 수 있고 원래의 상피 (피부 또는 요로 상피)의 형태 학적 기능 특성으로 확산. 플라스틱 압축을 사용하여 비계 감소했다약 420 μm의 다진 입자로에 1cm의 크기 d는 상위 계층 콜라겐에 싸여 있었다. 코어 섬유는 중합체 일 수 있지만, 피복 콜라겐 층 11 인터링크하기 위해 친수성 표면으로 변형 될 필요가 있었다.
이 방법은 다진 방광 점막 또는 돼지에서 다진 피부를 배양하기위한 발판으로 사용하여 두 개의 플라스틱 압축 된 콜라겐 젤 내에서 폴리 (ε 카프로 락톤을)로 구성된 니트 메쉬 (PCL)를 통합하여 향상된 발판 무결성을 제공했다. 구조는 잘 통합 하이브리드 구조물의 위에 층화 다층 요로 상피 또는 피부 편평 상피의 성공적인 형성을 입증하는 시험 관내에서 6 주 동안 세포 배양 조건에서 유지되었다. 구조는 취급이 용이이었고, 방광 확대 술의 목적이나 피부 결점 커버 장소에 봉합 될 수있다. 조직 골격의 모든 부분은 FDA 승인 및 기술되어있다티슈 닦지 수확 플라스틱 압축 및 단일 스테이지 개입 같은 환자에게 다시 이식하여 단일 단계 과정에 이용 될 수있다. 절차는 임의의 외과 부 멸균 조건 하에서 조직 팽창과 복원에 대해 수행 될 수있다.
프로토콜
모든 동물 프로토콜은 동물의 스톡홀름 카운티위원회의 사전 승인을하고, 모든 절차는 동물의 사용뿐만 아니라 관련 연방법의 규정을 따른다.
1. 동물 절차
- 수술에 대한 동물 준비
- 무균 조건 하에서 작동에 필요한 모든 재료와 도구로 수술 테이블을 준비합니다. 감염의 위험을 감소시키고 생존 수술 조건을 최적화하기 위해 멸균 조건하에 단독으로 수술을 수행한다.
- 수술 전 12 시간 동안 동물을 빠르고 무게를 측정한다. 전 처치 용 된 azaperone의 근육 내 주사 (2 ㎎ / ㎏)을 관리 할 수 있습니다. tiletamine의 차아 염소산 (2.5 ㎎ / ㎏), zolazepam의 차아 염소산 (2.5 ㎎ / ㎏), 메데 토미 (25 μg의 / kg) 및 아트로핀 (/ kg 25 μg의)의 근육 내 주사와 함께 동물을 마취.
- phenobarbiturate을 주입 (15 ㎎ / ㎏) endotrache하기 전에알 삽관 0.8 % -2 %의 이소 플루 란과 전신 마취를 계속합니다. 한쪽 귀에서 주변 정맥 카테터를 삽입하고 동물의 복지를 유지하기 위해 정맥 절차를 수행하는 동안 포도당 (25 ㎎ / ㎖)을 주입.
- 온도, 혈압, 채도 및 말초 맥박을 확인하는 귀 또는 꼬리 모니터링 장치 놓는다. 귀 또는 발굽의 통증 자극에 의해 제어 마취. 마취 동안 건조를 방지하기 위해 눈 연고를 적용합니다.
- 방광 생검 표본의 절단
- 세미 무균 조건 하에서 소변 비우기 요도를보고 요도를 통해 카테터를 삽입 검경 도입에 의해 방광에 10 프랑스어 실리콘 카테터를 사용하여 방광 카테 테르를 꽂다. 20~25cm의 H 2 O, 약 100-300 ml의 압력을 무균 생리 식염수로 방광을 채우고 다음 빈 O H 2 형상 (20) (약 70. 8 ㎖ / 체중 kg).
- 번째로전자 돼지 신중하게, 측면 위치로 회전 클로르헥시딘 글루코 네이트의 응용 프로그램과 함께 피부의 기본 수술 전 소독을 수행합니다. 면도 가위로 털 가죽을 제거한 후 어깨에 투열 요법 판을 적용합니다.
- 앙와위로 조심스럽게 돼지를 켜고 면도 가위를 사용하여 복부 털 가죽을 제거하고 클로르헥시딘 글루코 네이트의 응용 프로그램과 복부 피부의 기본 수술 전 소독을한다.
- 부드러운 옷을 사지를 포함하면 사지의 관절 과신전 손상의 위험을 최소화합니다. 클로르헥시딘 글루 콘산의 연속 응용 프로그램과 동물의 복부 피부를 소독하고 수술 부위의 주위에 멸균 입체 재단을 배치합니다.
- 피부 절개하기 전에, 배꼽 아래의 중간 선에서 프레 노르 핀 (45 μg의 / kg), 카프로 펜 (3 ㎎ / ㎏) 및 리도카인 국소 주입으로 구성된 정맥 진통제를 적용합니다. SK를 잡고 통증 반응 확인집게로한다. 근막을 통해 낮은 중간 선 절개를 확인하고 출혈의 제어를위한 투열 요법을 사용하여 복막. 돼지 완전히 복강 위치가 자유롭게 수술 상처를 통해 동원에 의해 노출 될 수 블래 지역화.
- 집게와 방광의 보류를 타고 멸균 측정 테이프를 측정하고 멸균 펜을 사용하여 세로 방향으로 약 2cm 및 횡 방향으로 1cm, 또는 작은 타원 모양의 생검 표본을 표시 (돼지 방광 크기의 분기 감소를 용인 아주 잘). , 표시된 영역을 절제 메스를 사용하고 무균 조건 하에서 DMEM에서 방광 생검 표본을 배치합니다.
- biotransplant으로자가 이식을 수행하거나 두 개의 층에 5-0 Vicryl로 봉합하여 방광을 닫습니다. 2-0 또는 3-0 Vicryl을 실행 조심스럽게 복부 근막을 닫습니다. 3-0 Vicryl와 피하와 3-0 에틸 론으로 피부를 닫습니다. 상처에 조심스럽게에서 드레싱을 배치이 마취에서 충분히 회복과 고통을 표현하지 않을 때까지 동물 경향이있다.
- 수술 후 관리를위한 조건을 확보하기 위해 동물 보호 시설로 동물을 이동합니다. 가열 램프 하나의 새장에 동물을 넣고 참석 동물 마취에서 완전히 회복 될 때까지 다음 동물이 쌍으로 정체 될 수 있습니다.
- 고통과 웰빙에 관한 사건이 복구를 제공하고 5 일 동안 하루에 한 번씩 사흘 동안 매일 두 번 근육 수술 후 통증 및 trimetoprim (4 ㎎ / ㎏) 및 술폰 아미드 (20 ㎎ / ㎏)에 대한 프레 노르 핀 (45 μg의 / kg)을 관리하고 수술 후 감염의 위험을 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 피부 생검 표본의 절단
- 필요한 모든 재료와 수술 테이블을 준비합니다. 앞서 설명한 바와 같이 1.1 동물을 마취. 왁스를 사용하여 털 가죽을 제거 씻어 betadine 70 % 알코올로 절개 영역을 소독하고 멸균 입체 재단을 aroun를 배치절개 영역 거라고.
- 0.3 mm 부분 층 피부 생검 표본을 수확 피부 분절을 사용합니다. 2.2에 설명 된대로 닦지 전에 DMEM의 피부 표본을 놓습니다. 지방 연고 및 드레싱 상처 영역을 커버.
2. 다진 조직 준비
- 방광 점막
- DMEM 두 번 방광 조직 검사를 씻으십시오. 위쪽으로 향하게 점막과 멸균 해부 접시에 방광 생검 표본을 놓고 해부 핀을 사용하여 판에 측면 중 하나를 수정합니다.
- 미세 가위와 집게 (그림 3)를 사용하여 배뇨근 근육의 점막 조직을 분리하고 그 위에 식염수 또는 DMEM 떨어지는하여 촉촉한 점막을 유지합니다.
- 점막에 배치하여 닦지 장치를 사용하고, 0.8 mm X 0.8 mm의 다진 조직 조각을 얻기 수동 압력을 적용, 상하 좌우 한쪽에서 다른 장치를 통과 (0.8 mm가 rotatin 간의 거리이다g) 블레이드를 절단.
- 피부
- 피부 biopsis 경우 두꺼운 : 멸균 해부 접시에 피부를 배치하고 피하 지방과 진피에서 표피를 분리하는 수술 가위를 사용합니다. 표피가 얇고 반투명 (약. 0.3 mm)는 닦지위한 준비가되었을 때.
- 표피에 배치하여 닦지 장치를 사용하십시오. 압력이 0.8 mm X 0.8 mm의 다진 조직 조각을 얻었다 가로 세로 한쪽에서 다른 장치를 통과.
플라스틱 압축 PCL / 콜라겐자가 이식 3. 준비
- 차가운 유지하기 위해 얼음에 모든 재료를 놓습니다. 필요한기구 : 팔콘 튜브, 10 배 DMEM, 1 배 DMEM, 1 N 수산화 나트륨과 쥐의 꼬리 콜라겐 유형 1.
- 1. 1 N의 NaOH, 적가 추가 강렬한에서 변경하여 pH를 나타내야 매체 7.4-8 (색의 pH까지 가져 콜라겐 타입 12 ml의 10 배 DMEM (신중 거품을 방지하기 위해) 2 ㎖ 믹스 핀에 노란색케이). 또한, pH가 스트립을 사용한다.
- 조심 1X DMEM 2 ㎖를 추가하고, 용액을 혼합한다. 플레이트 스틸 직사각형 금형 (20x30x10 mm)의 각 웰 콜라겐의 약 2 mL 및 37 부화 10 분 동안 5 % CO 2에서 C를 °.
주 : 콜라겐의 농도가 2.06 밀리그램 / 0.6 % 아세트산 용액과 콜라겐 1 ㎖ / cm 2의 양이어야한다. - 콜라겐은 금형에 설정되면, 콜라겐 겔 (20mm X 30mm)의 상단에있는 생체 재료 (PCL)를 배치하고 그 위에 남아있는 콜라겐 (약 6 ml)에 붓는다. 20 분 동안 5 % CO 2에서 37 ℃에서 인큐베이션.
- 콜라겐 젤의 상단에 : 다진 조직 (6 확장 1) 놓습니다. 다음 플라스틱 압축을 사용하여 기계력 구조에서 물을 누르면 (도 3 및도 4).
- 멸균 표면에 거즈 패드의 두꺼운 층을 배치합니다. gauz 위에 하나의 스테인레스 스틸 메쉬 (400 ㎛의 두께)를 놓고전자 패드와 나일론 메쉬 (두께 110 μm의)의 다음 시트. 조심스럽게 나일론 메쉬로 콜라겐 젤 / 다진 조직을 전송하고 조심스럽게 사각형 스틸 몰드를 제거합니다.
- 콜라겐 젤 / 다진 조직의 상부에 나일론 메쉬의 새 레이어를 놓습니다. 나일론 메쉬의 상단에 두 번째 스틸 메쉬를 놓습니다. 위치 5 분 동안 120g (즉, 유리 플레이트)의 최소 계량 압력이나 하중 판을 놓는다.
- 무게, 나일론, 철강 메쉬를 제거합니다. 자가 이식은 이제 전체 두께 피부 상처에 돼지 방광에 봉합 또는 체외에서 배양 할 준비가 된 것입니다.
- 체외 배양를 들어, 12 웰 플레이트 피팅 작은 조각으로 얇은 구조를 잘라. 각질 세포 매체의 1 ML을 추가합니다. 37 ° C 6 주까지 5 % CO 2와 문화의 인큐베이터에서 접시를 놓고 일주일 중 3 번을 변경합니다.
자가 이식 4. 봉합
- 자가 이식의 봉합과 함께돼지 방광에 다진 방광 점막
- 대기 시간 동안 DMEM에 촉촉한 이식술을 유지합니다. 잘 실행 모노 필라멘트 봉합사와 이식술을 봉합. 연구 목적으로 비 흡수성 5-0 에틸 론을 사용합니다.
- 내주 요도 카테터를 통해 생리 식염수로 방광을 작성하여 방수 있는지 확인합니다. 가능하면 더 대망의 층 이식술을 커버. 1.2.6에 설명 된 바와 같이 복벽, 피하 조직, 피부를 닫는다. 상처 드레싱을 적용합니다.
- 전체 두께 상처에 다진 피부 표피와 이식술의 봉합
- 대기 시간 동안 DMEM에 촉촉한 이식술을 유지합니다.
- 밀접 하부 표면에 부착 이식술 유지 모서리 단속 봉합 의해 이식술의 중간에 권취 피부 전층의 바닥 이식술 봉합사.
- 상처가 촉촉하게 유지하는 플라스틱 드레싱 상처를 커버.
5. 종료
- 근육 zolazepam의 차아 염소산의 주입 (2.5 ㎎ / ㎏) 및 메데 토미 (25 μg의 / kg) 이전에 종료 및 귀 또는 꼬리에 감시 장치를 적용와 조용한 동물 펄스와 혈압을 확인합니다.
- 정맥 내 펜토 바르 비탈 나트륨 (60-140 ㎎ / ㎏)의 치사량을 투여함으로써 동물을 안락사. 죽음이 발생 될 때까지 맥박과 혈압을 확인합니다.
6. 체외 문화
주 : 조직 학적 시험 관내 PCL / 콜라겐 구조물은 다진 조직의 진행을 평가하기는 콜라겐 / PCL / 다진 패치 각질 매체를 이용하여 12- 웰 플레이트에서 배양 하였다.
- 각질 매체의 제조 :
- 500 ml의 유리 병을 소독.
- (1 혼합물을 4) 햄 F12 100㎖로 DMEM 400ml를 섞는다. 10 % 소 태아 혈청으로 보충 5 μg의 / ㎖ 인슐린,0.4 μg의 / ㎖의 하이드로 코르티손, 21 μg의 / ㎖ 아데닌, 10-10 몰 / L 콜레라 독소, 2 × 10-9 몰 / L의 트리 요오 도티 로닌, / ㎖ 트랜스페린, 10 ng / ml의 상피 세포 성장 인자, 50 U / ㎖ 페니실린 5㎍을 및 / ㎖ 스트렙토 마이신 50 μg의.
- 0.2 μm의 필터를 통해 여과하여 소독 및 멸균 500ml의 병에 여과 액을 수집합니다.
7. 면역 조직 화학
참고 : 면역 조직 화학 프로토콜은 일반적으로 다음과 같은 단계로 나뉘어집니다 : (1) 고정 및 파라핀 삽입, (2) 마이크로 절편 5 μm의 조각, 슬라이드, 탈 파라핀과 재수에 배치로는, (3) 항원에 마스크, 염색 및 설치 . 면역 조직 화학 절차의 마지막 단계를 시작하기 전에 세척 버퍼와 항원 마스크를 제거 용액 (별도 자료의 자세한 사항 참조) 준비합니다. 사용하기 전에 ABC 복잡한 솔루션을 최소 30 분을 준비합니다.
- 정착
아니오TE 다음과 같이 시험 관내 배양의 마지막 패치 FIX :- 4 % 버퍼링 포름 알데히드 (PFA)의 1 ㎖의 에펜 도르프 튜브를 준비 (주의 :.. 포름 알데히드는 독성이 화학 물질을 사용하기 전에 물질 안전 보건 자료를 읽어 장갑과 보안경을 착용하고 흄 후드 내부의 용액을 제조하십시오).
- 4 % PFA를 함유하는 에펜 도르프 튜브로 콜라겐 패치 각각 옮긴다. 실온에서 밤새 수정.
- 4 ℃에서의 장기 저장을 위해 70 % 에탄올에 넣어 샘플. 샘플은 현재 탈수에 대한 준비 및 단면 처리하기 전에 파라핀 블록에 포함됩니다.
- 재수
- 15 분 동안 X-TRA의 SOLV와 염색 항아리에 슬라이드를 놓습니다. X-TRA의 SOLV로 새로운 염색 항아리를 사용하여 반복합니다. 10 분 동안 무수 에탄올과 염색 항아리에 슬라이드를 놓습니다. 무수 에탄올로 새로운 염색 항아리를 사용하여 반복합니다. 95 % 에탄올로 염색 항아리에 슬라이드를 10 분 동안 한 후, 배치10 분 동안 70 % 에탄올로 염색 단지에. 마지막으로 증류수로 5 분 동안 두 번 슬라이드를 씻는다.
- 항원 폭로
- TE-솔루션 코 플린 항아리에 슬라이드를 넣고 20 분간 끓여 물을 욕조에 병을 넣어. 조심스럽게 물을 욕조 밖으로 항아리를 가져 가라. 30 분 동안 실온으로 냉각시키고, 슬라이드 트리스 완충액에서 5 분 동안 두 번 세척 하였다. 10 분 동안 3 % 과산화수소로 염색 단지에 슬라이드를 놓는다. 트리스 버퍼에 5 분 동안 두 번 슬라이드를 씻으십시오. 펜 마킹 발수를 사용하여 샘플 주위에 원을 그립니다.
- 용액을 차단 100-300 μL를 사용하여 항체의 비특이적 결합을 차단. 차단 솔루션을 제거하고 트리스 버퍼에 권장 농도로 용해 차 항체의 100 ~ 300 μl를 추가합니다. 밤새 품어. 항체 용액을 제거하고 5 분 동안 두 번 트리스 버퍼 섹션을 씻는다.
- 객실 temperat에서 1 시간 동안 차 항체와 함께 품어URE. 트리스 버퍼에 5 분 동안 두 번 씻으십시오. ABC 엘리트 키트 (제조업체의 지침에 따라)를 사용하여 30 분을 품어. 트리스 버퍼에 두 번 씻으십시오.
- 제조업체의 지침 (1-7 분 배양은 일반적으로 맑은 보라색의 강도를 생산), 벡터 VIP 키트를 사용하여 따라 항체 반응을 개발할 수 있습니다. 증류수에 슬라이드를 넣습니다. 30 초 동안 마이어의 헤 마톡 실린과 Counterstain과.
- 5 분 동안 흐르는 물에 씻으십시오. 1 분 동안 70 % 에탄올로 염색 항아리에 슬라이드를 놓습니다. 70 % 에탄올로 새로운 염색 항아리를 사용하여 반복합니다. 1 분 동안 95 % 에탄올로 염색 항아리에 슬라이드를 놓습니다. 95 % 에탄올로 새로운 염색 항아리를 사용하여 반복합니다.
- 5 분 동안 X-TRA의 SOLV와 염색 항아리에 슬라이드를 놓습니다. 촉촉한 유지하기 위해 한 번에 하나를 제거합니다. 각 슬라이드의 상단에 장착 매체의 방울을 넣고 위에 덮개 유리 (공기 방울을 피하기 위해 매우 조심스럽게 수행)했습니다. 슬라이드 밤새 건조하자 마이크로에서 슬라이드를 보려면범위.
결과
이 연구는 콜라겐과 다진 조직의 플라스틱 압축을 사용하여 이식 생체 재료를 생산하는 방법을 보여줍니다 방법을 제시한다.
방광 점막 및 피부는 수확 후 기계적으로 작은 입자 (그림 3)에 다진 할 수 있습니다. 플라스틱 압축하여 다진 입자 콜라겐 겔 (도 4)의 외층 내에 기계적으로 강한 중앙 배치 생분해 성 고분자로 이루어지는 복합체 지지체 내?...
토론
이 연구는 수술 테이블에 이식자가 조직과 방광 벽에 패치를 생성하기 위해 사용하기 쉬운 방법을 제공합니다. 패치와 플라스틱의 압축과 함께 외면 다진 조직없이 중간 및 콜라겐 분해성 중합체 편성의 조합에 의해 형성된다. 압축 성형 방법은, 이전에 다른 저자에 의해 기재된 콜라겐 겔 (12, 13)에서 유체의 급속 제적으로 정의 될 수있다. 방광 점막이나 피부 조직 다진이 지지체에 ?...
공개
The authors have nothing to disclose.
감사의 말
The authors thank the Swedish Society for Medical Research, the Promobilia Foundation, the Crown Princess Lovisa Foundation, the Freemason Foundation for Children’s Welfare, the Swedish Society of Medicine, the Solstickan Foundation, Karolinska Institutet, and the Stockholm City Council for financial support.
자료
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Silicone catheter 10-French | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| DMEM 10x | Gibco | 31885-023 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| 24 well plates | Falcon | 08-772-1 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| 3',3',5-Triiodothyronine | Sigma-Aldrich | IRMM469 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| 4% PFA | Labmed Solutions | 200-001-8 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| 70% ethanol | Histolab | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 | |
| ABC Elite kit: Biotin-Streptavidin detection kit | Vector | PK6102 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Absolute ethanol | Histolab | 1399.01 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Adenine | Sigma-Aldrich | A8626 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Atropine 25 μg/kg | Temgesic, RB Pharmaceuticals, Great Britain | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Azaperone 2 mg/kg | Stresnil, Janssen-Cilag, Pharma, Austria | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Biosafety Level 2 hood | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Blocking solution: Normal serum from the same species as the secondary secondary antibody was generated in. | Vector | The blocking solution depends of the origin of first antibody | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Buprenorphine 45 μg/kg | Atropin, Mylan Inc, Canonsburg, PA | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Carprofen 3 mg/kg | Rimadyl, Orion Pharma, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Chlorhexidine gluconate | Hibiscrub 40 mg/mL, Regent Medical, England | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Cholera toxin | Sigma-Aldrich | C8052 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Coplin jar: staining jar for boiling | Histolab | 6150 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Stainless mold (33 mm x 22 mm x 10 mm) custom made | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| DMEM | Gibco | 3188-5023 | Plastic compression section 4. Keep on ice when using it in plastic compression |
| Epidermal growth factor | Sigma-Aldrich | E9644 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Ethilon (non-absorbable monofilament for skin sutures) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Gibco | 10437-036 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Forceps (Adison with tooth) | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Gauze (Gazin Mullkompresse) | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Ham's F12 | Gibco | 31765-027 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Hematoxylin | Histolab | 1820 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Humidity chamber | DALAB | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 | |
| Hydrocortisone | Sigma-Aldrich | H0888 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Hydrogen peroxide Solution 30% | Sigma-Aldrich | H1009 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Insulin | Sigma-Aldrich | I3536 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Isoflurane | Isoflurane, Baxter, Deerfield, IL | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Lidocaine 5 mg/ml | Xylocaine, AstraZeneca, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Lucose 25 mg/ml | Baxter, Deerfield, IL | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Marker pen pap pen | Sigma-Aldrich | Z377821-1EA | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Medetomidine 25 μg/kg | Domitor, Orion Pharma, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Mincing device | Applied Tissue Technologies LLC | Minced tissue preparation, section 2 | |
| Monocryl (absorbable monofilament) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | S7653 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| NaOH 1 N | Merck Millipore | 106462 | Plastic compression section 4 and cell culture |
| Nylon mesh, 110 μM thick pore size 0.04 sqmm | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Oculentum simplex APL: ointment for eye protection | APL | Vnr 336164 | Surgery, Section 1 |
| PBS | Gibco | 14190-094 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Phenobarbiturate 15 mg/kg | Pentobarbital, APL, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| PCL Knitted fabric | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Rat-tail collagen | First LINK, Ltd, UK | 60-30-810 | Plastic compression section 4, keep on ice |
| Scalpel blade - 15 | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Shaving shears | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Stainless stell mesh, 400 μM thick pore size | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Steril gloves | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Sterile gowns | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Sterile drapes | |||
| Sterilium | Bode Chemie HAMBURG | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Suture Thread Ethilon | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| TE-solution (antigen unmasking solution) consist of 10 mM Tris and 1 mM EDTA, pH 9.0 | 10 mM Tris/1 mM EDTA, adjust pH to 9.0 | ||
| Tiletamine hypochloride 2.5 mg/kg | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Transferrin | Sigma-Aldrich | T8158 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Trizma Base, H2NC | Sigma-Aldrich | T6066 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Vector VIP kit: Enzyme peroxidase substrate kit | Vector | SK4600 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Vicryl (absorbable braded) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| Tris buffer pH 7.6 (washing buffer) | TE solution: Make 10x (0.5 M Tris, 1.5 M NaCl) by mixing: 60.6 g Tris (Trizma Base, H2NC(CH2OH)3, M=121.14 g/mol), add 800 ml distilled water adjust the pH till 7.6, add 87.7 g NaCl and fill to 1,000 ml with distilled water. Dilute to 1x with distilled water. | ||
| X-tra solv (solvent) | DALAB | 41-5213-810 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6. Use under fume hood |
| Zolazepam hypochloride | Zoletil, Virbac, France | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Depilatory wax strips | Veet | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Pentobarbital sodium | Lundbeck | Termination, Section 3 |
참고문헌
- Rheinwald, J. G., Green, H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 6, 331-343 (1975).
- Fossum, M., Nordenskjold, A., Kratz, G. Engineering of multilayered urinary tissue in vitro. Tissue Engineering. 10, 175-180 (2004).
- Salmikangas, P., et al. Manufacturing, characterization and control of cell-based medicinal products: challenging paradigms toward commercial use. Regen Med. 10, 65-78 (2015).
- Fossum, M., et al. Minced skin for tissue engineering of epithelialized subcutaneous tunnels. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 15, 2085-2092 (2009).
- Fossum, M., et al. Minced urothelium to create epithelialized subcutaneous conduits. The Journal of Urology. 184, 757-761 (2010).
- Reinfeldt Engberg, G., Lundberg, J., Chamorro, C. L., Nordenskjold, A., Fossum, M. Transplantation of autologous minced bladder mucosa for a one-step reconstruction of a tissue engineered bladder conduit. BioMed Research International. 2013, 212734 (2013).
- Meek, C. P. Successful microdermagrafting using the Meek-Wall microdermatome. Am J Surg. 96, 557-558 (1958).
- Tanner, J. C., Vandeput, J., Olley, J. F. The Mesh skin graft. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 34, 287-292 (1964).
- Svensjo, T., et al. Autologous skin transplantation: comparison of minced skin to other techniques. The Journal of Surgical Research. 103, 19-29 (2002).
- Ajalloueian, F., Zeiai, S., Rojas, R., Fossum, M., Hilborn, J. One-stage tissue engineering of bladder wall patches for an easy-to-use approach at the surgical table. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods. 19, 688-696 (2013).
- Engelhardt, E. M., et al. A collagen-poly(lactic acid-co-varepsilon-caprolactone) hybrid scaffold for bladder tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 32, 3969-3976 (2011).
- Brown, R. A., Wiseman, M., Chuo, C. B., Cheema, U., Nazhat, S. N. Ultrarapid engineering of biomimetic materials and tissues: fabrication of nano- and microstructures by plastic compression. Adv Funct Mater. 15, 1762-1770 (2005).
- Fumagalli Romario, U., Puccetti, F., Elmore, U., Massaron, S., Rosati, R. Self-gripping mesh versus staple fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a prospective comparison. Surg Endosc. 27, 1798-1802 (2013).
- Muangman, P., et al. Complex Wound Management Utilizing an Artificial Dermal Matrix. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 57, 199-202 (2006).
- Ajalloueian, F., Zeiai, S., Fossum, M., Hilborn, J. G. Constructs of electrospun PLGA, compressed collagen and minced urothelium for minimally manipulated autologous bladder tissue expansion. Biomaterials. 35, 5741-5748 (2014).
- Orabi, H., AbouShwareb, T., Zhang, Y., Yoo, J. J., Atala, A. Cell-seeded tubularized scaffolds for reconstruction of long urethral defects: a preclinical study. Eur Urol. 63, 531-538 (2013).
- Blais, M., Parenteau-Bareil, R., Cadau, S., Berthod, F. Concise review: tissue-engineered skin and nerve regeneration in burn treatment. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2, 545-551 (2013).
- Serpooshan, V., Muja, N., Marelli, B., Nazhat, S. N. Fibroblast contractility and growth in plastic compressed collagen gel scaffolds with microstructures correlated with hydraulic permeability. J Biomed Mater Res A. 96, 609-620 (2011).
재인쇄 및 허가
JoVE'article의 텍스트 или 그림을 다시 사용하시려면 허가 살펴보기
허가 살펴보기더 많은 기사 탐색
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유