A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
רקמות טחונות ב הדחוס קולגן: A Biotransplant המכיל נייד עבור תיקון Reconstructive המבוים יחיד
In This Article
Summary
הנדסת רקמות קרובות כולל בהרחבת חוץ גופית על מנת ליצור autografts לשחזור רקמות. במחקר זה שיטה להרחבת רקמות, התחדשות, ושחזור in vivo פותחה על מנת למזער את העיבוד של תאים וחומרים ביולוגיים מחוץ לגוף.
Abstract
Conventional techniques for cell expansion and transplantation of autologous cells for tissue engineering purposes can take place in specially equipped human cell culture facilities. These methods include isolation of cells in single cell suspension and several laborious and time-consuming events before transplantation back to the patient. Previous studies suggest that the body itself could be used as a bioreactor for cell expansion and regeneration of tissue in order to minimize ex vivo manipulations of tissues and cells before transplanting to the patient. The aim of this study was to demonstrate a method for tissue harvesting, isolation of continuous epithelium, mincing of the epithelium into small pieces and incorporating them into a three-layered biomaterial. The three-layered biomaterial then served as a delivery vehicle, to allow surgical handling, exchange of nutrition across the transplant, and a controlled degradation. The biomaterial consisted of two outer layers of collagen and a core of a mechanically stable and slowly degradable polymer. The minced epithelium was incorporated into one of the collagen layers before transplantation. By mincing the epithelial tissue into small pieces, the pieces could be spread and thereby the propagation of cells was stimulated. After the initial take of the transplants, cell expansion and reorganization would take place and extracellular matrix mature to allow ingrowth of capillaries and nerves and further maturation of the extracellular matrix. The technique minimizes ex vivo manipulations and allow cell harvesting, preparation of autograft, and transplantation to the patient as a simple one-stage intervention. In the future, tissue expansion could be initiated around a 3D mold inside the body itself, according to the specific needs of the patient. Additionally, the technique could be performed in an ordinary surgical setting without the need for sophisticated cell culturing facilities.
Introduction
רוב המחקרים בהנדסת רקמות על השתלה לעור בדרכי השתן ואברי המין כוללים יבולי תא אוטולוגי מרקמות בריאות הרחבת תא במתקנים-culturing תא מאובזר במיוחד 1,2.
לאחר הרחבת התא, התאים בדרך כלל מאוחסנים לשימוש מאוחר יותר כאשר החולה הוא מוכן לקבל את autograft. מקפיאי חנקן לאפשר אחסון לטווח ארוך בטמפרטורות נמוכות של -150 מעלות צלזיוס ומטה. תהליך ההקפאה חייב להיזהר ומבוקר על מנת לא לאבד את התאים. אחת הסכנות של מוות של תאים הוא התגבשות של מים תאיים במהלך תהליך ההפשרה, מה שעלול להוביל לקרע של קרום התא. תא הקפאה מתבצעת לרוב על ידי קירור איטי ומבוקר (-1 ° C לדקה), באמצעות ריכוז גבוה של תאים, בסרום שור העובר, וכן sulfoxide דימתיל. לאחר הפשרה, תאים צריכים להיות מעובד שוב על ידי הסרה בינוני מקפיא culturing על פלסטיק תרבית תאים אוביולוגי לפני ההשתלה בחזרה לחולה.
כל השלבים הנ"ל הן זמן רב, מייגע, ויקר 3. בנוסף, כל במבחנת העיבוד של תאים המיועדים להשתלה לחולה נמצא תחת הרגולציה מאוד ודורש ומוכרים מאומנים היטב אנשים ומעבדות 4. בסיכומו של דבר, כדי להשיג תהליך הייצור בטוח ואמין, הטכניקה יכול יוקם רק במספר קטן מאוד של מרכזי מתקדם מבחינה טכנית לשימוש רחב יותר בהפרעות כירורגית משותפות מוטל בספק.
על מנת להתגבר על המגבלות של culturing תא בסביבת מעבדה, הרעיון של השתלת רקמות טחון עבור הרחבת התא in vivo הוא הציג באמצעות הגוף עצמו בתור bioreactor. למטרות אלה, autografts יהיה להשתיל מועדף על תבנית 3D על פי הצורה מה שצריך לשיקום הסופי של האיבר של interest 5-7.
במקור, הרעיון של השתלת אפיתל טחון הוצגה על ידי מיק בשנת 1958 כשתיאר כיצד האפיתל צומחת מן הקצוות של פצע. הוא הוכיח כי חתיכה קטנה של עור תגדיל את שולי רווח שלה ובכך פוטנציאל שלה הרחבת התא ב -100% על ידי חיתוך הפיסה פעמים בכיוונים ניצב (איור 1) 8. התאוריה כבר נתמכה על ידי שימוש בשתלי עור בעובי חלקי מרושתים להשתלת עור 9 וב עור ריפוי פצעי מודלים 10.
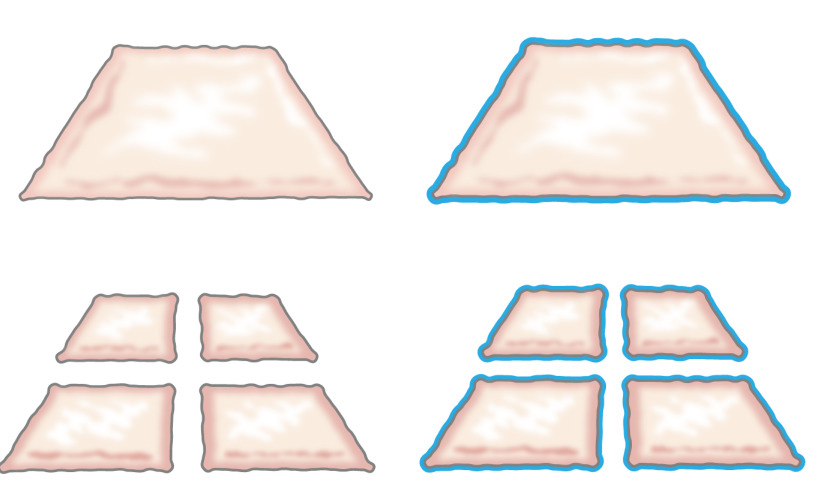
איור 1:. התיאוריה מיק על פי התיאוריה של מיק, האפיתל צומחת מן הקצוות של פצע. על ידי הגדלת שטח החשופה על ידי הטכנולוגיה מתייפייף, רקמות טחונות epithelializes פצעי כתמים רבים.
המחקר הנוכחי מבוסס על היפוהתזה כי אותו עיקרון יכול להיות מיושם על הרקמה התת עורית על ידי הצבת האפיתל טחון סביב עובש. לתאי האפיתל יגייסו מ השתלות טחונות (מחדש), לכסות את אזורי הפצע (להעביר) ומתחלקים (להרחיב) על מנת לגבש neoepithelium רציפה המכסה את אזור הפצע ומפריד הגוף הזר (העובש) מהגוף הפנימי ( איור 2).
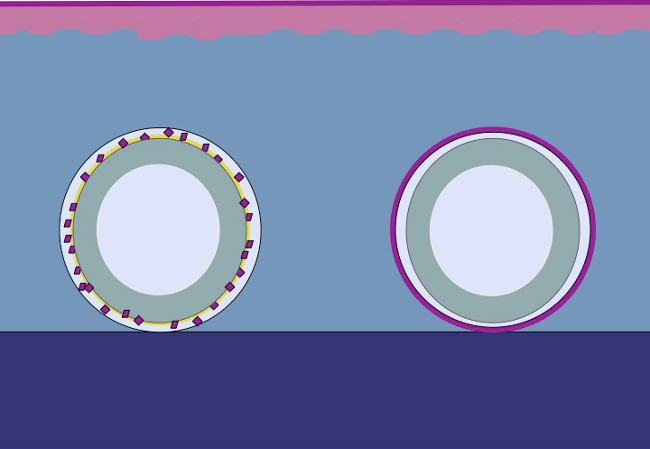
איור 2:. קריקטורה של עובש 3D עם אפיתל טחון עבור in vivo להרחבת רקמות intracorporal פי התיאוריה של מיק באמצעות רקמות טחון דגש על תבנית ולאחר מכן להשתיל את הרקמה התת עורית, ההשערה היא כי תאי אפיתל להגר מן שולי הרקמה טחון, להתארגן מחדש ולהרחיב כדי לגבש neoepithelium רציפה המכסה את אזור הפצע ומפריד הגוף הזר (עובש) מהגוף הפנימי.
למרות שמחקרי in vivo קודמים הראו תוצאות מבטיחות, שיפורים נוספים ניתן להשיג על ידי חיזוק autografts כך האפיתל מחדש יכול לעמוד טראומה מכאנית 7 טוב יותר. לעניין זה, תנאים מוקדמים חשובים עבור ביולוגי מוצלח זוהו, כגון: דיפוזיה קל של חומרים מזינים ופסולת, אפשרות לעצב באופן 3D ונינוחות של טיפול כירורגים. מסקנות נעשו כי הצרכים הללו יכול להיות נפגשו על ידי הוספת ביולוגי מרוכבים אל הרקמה טחון.
המחקר הנוכחי במטרה לפתח פיגום מורכב רקמות טחונות בפלסטיק-דחוס המכיל קולגן גרעין חיזוק של בד מתכלה. תודות לאמצעים אלה תאי קיימא עשויים להגר מ- חלקיקי הרקמות הטחונים מתרבים עם מאפיין תכונות מורפולוגיות של האפיתל המקורי (עור או urothelium). באמצעות דחיסת פלסטיק, הפיגום היה להפחיתד בגודל 1 ס"מ לכ 420 מיקרומטר כמו חלקיקים טחון היו נתונות קולגן השכבה העליונה. בד הליבה יכול להיות כל פולימר אבל צריך להיות שונים עם משטח הידרופילי כדי interlink עם שכבות קולגן הכוללים 11.
השיטה סיפק שלמות פיגום משופרת על ידי שילוב של רשת סרוגים המורכב פולי (ε-caprolactone) (PCL) בתוך שני ג'ל קולגן דחוס פלסטיק להשתמש בה כמו פיגום עבור culturing רירית שלפוחית השתן טחון או העור טחון חזירים. הבונה נשמרה בתנאי תרבית תאים עד 6 שבועות במבחנה, הוכחת היווצרות מוצלחת של urothelium מרובדת, רב שכבתי או אפיתל עור קשקש על חלק עליון של מבנה היברידי אוחד גם. הבונה הייתה קלה לטפל ניתן לצורך איחוי במקום למטרות הגדלת שלפוחית או כיסוי של פגמים בעור. כל החלקים של הפיגום רקמות ה- FDA ואת הטכניקהיוכל לשמש עבור הליכים חד-שלבי על ידי קצירת רקמות, מגונדרת, דחיסה פלסטיק, השתלה בחזרה לחולה כמו התערבות חד מבוים. ההליך יכול להתבצע להרחבת רקמות ושיקום בתנאים סטריליים בכל יחידת כירורגיה כללית.
Protocol
כל פרוטוקולים החיים היו שאושרו מראש על ידי ועדת מחוז סטוקהולם על בעלי חיים וכל הליכים תאמו לתקנון שימוש בבעלי חיים, כמו גם חוקים פדרליים רלוונטיים.
1. נהלים בעלי חיים
- הכנת בעלי חיים לכירורגיה
- הכן את השולחן כירורגית עם כל החומרים והכלים הדרושים המבצע בתנאים סטריליים. לבצע את הניתוח באופן בלעדי בתנאים סטריליים כדי להפחית את הסיכון לזיהום ו לייעל את התנאים בניתוחי הישרדות.
- לצום החיה במשך 12 שעות לפני הניתוח ולמדוד את משקלו. נהל זריקה תוך שרירית של azaperone (2 מ"ג / ק"ג) עבור premedication. להרדים את החיה עם זריקה תוך שרירית של היפוכלוריד tiletamine (2.5 מ"ג / ק"ג), היפוכלוריד zolazepam (2.5 מ"ג / ק"ג), medetomidine (25 מיקרוגרם / ק"ג) אטרופין (25 מיקרוגרם / ק"ג).
- להזריק phenobarbiturate (15 מ"ג / ק"ג) לפני endotracheאל אינטובציה ולהמשיך הרדמה כללית עם 0.8% -2% isoflurane. הכנס וריד קטטר היקפי באוזן אחת להחדיר גלוקוז (25 מ"ג / מ"ל) לווריד במהלך ההליך כדי לשמור על רווחתם של בעלי החיים.
- מניח ניטור התקנים על אוזן או הזנב לבדוק טמפרטורה, לחץ דם, רוויה, ודופק פריפריה. בקרת הרדמה על ידי גירוי כאב של אוזניים או פרסות. החל משחה לעיניים למניעת יובש לאחר הרדמה.
- כריתה של שלפוחית השתן ביופסיה הדגימה
- קטטר לשלפוחית השתן באמצעות קטטר סיליקון 10-צרפתית על ידי החדרת ספקולום כדי להציג את השופכה והכנס קטטר דרך השופכה לתוך שלפוחית השתן לרוקן את השתן בתנאים חצי סטרילי. מלאו את השלפוחית עם תמיסת מלח סטרילית כדי בלחץ של 20-25 ס"מ H 2 O, על 100-300 מ"ל, ואז ריק עד 20 ס"מ H 2 O (כ. 8 מ"ל / ק"ג משקל גוף).
- עם החזיר דואר סובב בזהירות בעמדה בצד, לבצע עיקור לפני ניתוח בסיסי של עור עם יישום של gluconate chlorhexidine. החל צלחת דיאתרמיה לכתף לאחר הסרת pelage עם מספרי גילוח.
- סובב את החזיר בזהירות לתוך במצב שכיבה ולהסיר את pelage הבטן באמצעות מספרי גילוח ולעשות עיקור לפני ניתוח בסיסי של עור הבטן עם יישום של gluconate chlorhexidine.
- שבץ הגפיים עם בגדים רכים כדי למזער את הסיכון לנזק hyperextension למפרקים בגפיים. לעקר את עור הבטן של חיה עם יישומים רצופים של gluconate chlorhexidine ומניח כורך סטרילי סביב השדה כירורגית.
- לפני החתך בעור, להחיל משכך כאבים תוך ורידי המורכב עצירות (45 מיקרוגרם / ק"ג), carprofen (3 מ"ג / ק"ג) ו זריקה מקומית של לידוקאין קו האמצע מתחת לטבור. בדקו אם תגובה לכאב ידי אחיזת skעם מלקחיים. ביצוע חתך קו אמצע תחתון דרך fascia הצפק באמצעות דיאתרמיה על שליטת דימום. לוקליזציה של שלפוחית השתן, כי יש עמדת intraperitoneal במלואו החזיר יכול להיחשף באופן חופשי על ידי הניע אותו דרך הפצע כירורגית.
- החזיקו את השלפוחית עם המלקחיים ומודדים אותו עם סרט המדידה מעוקר וסמן דגימת ביופסיה בצורת אליפטי כ 2 סנטימטרי אורכים או 1 סנטימטר transversally, או קטנים יותר, באמצעות עט מעוקר (חזיר סובל הפחתת רבע גודל שלפוחית שתן טוב מאוד). ובלו האזור מסומן, באמצעות אזמל, ומקום דגימת ביופסית שלפוחית שתן DMEM בתנאים סטריליים.
- בצע autotransplantation עם biotransplant או לסגור את שלפוחית השתן על ידי תפירה זה עם 5-0 Vicryl בשתי שכבות. סגור את fascia הבטן בזהירות עם 2-0 או 3-0 ריצה Vicryl. סגור את subcutis עם 3-0 Vicryl והעור עם 3-0 Ethilon. מניח הלבשה על פצע בקפידהנוטה את החיה עד שהוא התאושש מספיק מן ההרדמה ואינו להביע כאב.
- הזז את החיה למתקן הטיפול בבעלי החיים כדי לזכות בתנאים נוחים עבור טיפול לאחר ניתוח. שים את החיה בכלוב אחד עם מנורת חימום ולטפל החיה עד להחלמה מלאה מן ההרדמה ולאחר מכן תן לחיות לְהֵאָבֵס בזוגות.
- לספק התאוששות ללא אירועים מיוחדים לגבי כאב ורווחה ולנהל עצירות (45 מיקרוגרם / ק"ג) לשריר על שיכוך כאבים לאחר הניתוח trimetoprim (4 מ"ג / ק"ג) ו sulfonamide (20 מ"ג / ק"ג) פעמיים ביום למשך שלושה ימים, פעם ביום, במשך חמישה ימים כדי להפחית את הסיכון לזיהומים לאחר ניתוח.
- כריתה של עור ביופסית הדגימה
- הכן את השולחן כירורגית עם כל החומרים הדרושים. להרדים את החיה כפי שתואר לעיל ב 1.1. הסר את pelage באמצעות שעווה, לרחוץ ולחטא את אזור החתך בבטאדין 70% אלכוהול ולאחר מכן למקם כורכת סטרילי לאיזורד את אזור החתך.
- השתמש dermatome למסוק דגימה לביופסיה העור עובי חלקי 0.3 מ"מ. מניח את דגימת עור DMEM לפני מיותר, כמתואר 2.2. מכסה את אזור הפצע עם משחת שומן רוטב.
2. רקמות טחונות הכנה
- שלפוחית שתן רירי
- שטוף את ביופסית שלפוחית השתן פעמים DMEM. מניח את דגימת הביופסיה בשלפוחית לצלחת לנתח מעוקרים עם הרירית כלפי מעלה ולתקן אחד צדדים לצלחת באמצעות סיכות לנתיחה.
- הפרד את הרקמה הרירית מן השריר detrusor באמצעות מספרי מלקחי קנס (איור 3) ולשמור את רירית לח ידי נוטף מלוח או DMEM מעליו.
- השתמש במכשיר מתייפייף ידי הצבתו על רירית ולאחר מכן להעביר את המכשיר מקצה אחד לקצה השני אנכית ואופקית, הפעלת לחץ ידני כדי להשיג חתיכות של רקמות טחון של 0.8 מ"מ x 0.8 מ"מ (0.8 מ"מ הוא המרחק בין rotating להבים חותכים).
- עור
- אם biopsis העור עבה: למקם את העור לצלחת לנתח סטרילי ולהשתמש מספרי כירורגיות להפריד האפידרמיס משומן תת עורי הדרמיס. האפידרמיס הוא דק ושקוף (כ. 0.3 מ"מ) כאשר הוא מוכן עבור מיותרות.
- השתמשו במכשיר המיותר ידי הצבתו על האפידרמיס. עם לחץ, להעביר את המכשיר מקצה אחד לקצה שני האנכי ואופקי להשיג חתיכות של רקמות טחונות של 0.8 מ"מ x 0.8 מ"מ.
3. הכנת פלסטיק דחוס PCL / קולגן Autografts
- מניחים את כל המרכיבים על קרח כדי לשמור על קור. הכלים הדרושים: צינור פלקון, 10x DMEM, 1x DMEM, 1 N NaOH וסוג קולגן זנב עכברוש 1.
- מערבבים 2 מ"ל של 10x DMEM (בזהירות כדי למנוע בועות) עם 12 מ"ל של קולגן מסוג 1. הוסף 1 N NaOH, טיפה אחר טיפה, כדי להעלות את ה- pH 7.4-8 (צבע בטווח הבינוני צריך לציין את ה- pH על ידי שינוי מן אינטנסיבי צהוב להצמידיא). בנוסף, השתמש ברב pH.
- בזהירות להוסיף 2 מ"ל של 1x DMEM ומערבבים הפתרון. פלייט כ 2 מ"ל של קולגן היטב כל עובש מלבני פלדה (20x30x10 מ"מ) ו לדגור על 37 ° C ב 5% CO 2 למשך 10 דקות.
הערה: ריכוז קולגן צריך להיות 2.06 מ"ג / מ"ל ב 0.6% חומצה אצטית ואת כמות הקולגן 1 מ"ל / 2 ס"מ. - לאחר קולגן קובע לתוך התבנית, מניחים את ביולוגי (PCL) על גבי ג'ל קולגן (20 מ"מ x 30 מ"מ) ושופכים את הקולגן הנותרים (כ -6 מ"ל) על גבי זה. לדגור על 37 מעלות צלזיוס ב 5% CO 2 עבור 20 דקות.
- הנח את רקמת טחון (1: 6 הרחבה) על החלק העליון של ג'ל קולגן. לחצו על המים מתוך המבנה בכוח מכני באמצעות דחיסת פלסטיק כדלקמן (איורים 3 ו -4).
- מניחים שכבה עבה של פדי גזה על משטח סטרילי. מניחים רשת נירוסטה אחד (400 מיקרומטר עבה) על גבי gauzרפידות דואר ולאחר מכן גיליון רשת ניילון (110 מיקרומטר עבה). להעביר בזהירות את קולגן ג'ל / רקמות טחונות על רשת הניילון ובזהירות להסיר את תבנית פלדה המלבנית.
- מניח שכבה חדשה של רשת ניילון על גבי רקמת קולגן ג'ל / הטחון. מניח רשת פלדה שנייה על גבי רשת הניילון. מניח בעמדת צלחת הלחץ או טעינה במשקל מינימום של 120 גר '(כלומר, צלחת זכוכית) במשך 5 דקות.
- הסר את המשקל, ניילון, משתלב פלדה. Autografts מוכן כעת להיות איחוי לשלפוחית חזיר הפצעים בעור בעובי המלא או מתורבת במבחנה.
- עבור culturing במבחנה, לחתוך את המבנה הדק לחתיכות קטנות ההולמות 12 גם צלחות. הוסף 1 מ"ל של מדיום keratinocyte. מניחים את הצלחות בחממה ב 37 מעלות צלזיוס, 5% CO 2 והתרבות עד 6 שבועות ולשנות את המדיום 3 פעמים בשבוע.
4. קשירת Autografts
- תפר של autograft עם רירית שלפוחית השתן טחון לשלפוחית חזיר
- שמור את autograft לח ב DMEM בזמן ההמתנה. לתפור את autograft עם התפרים monofilament פועל בסדר. שימוש בלתי נספג 5-0 Ethilon למטרות מחקר.
- בדקו אם אטום למים על ידי מילוי השלפוחית עם מי מלח דרך קטטר שתן השכינה. במידת האפשר, לכסות את autograft בשכבת omentum יותר. סגור את דופן הבטן, הרקמה התת עורית, והעור כמתואר 1.2.6. החלת הלבשת פצע.
- תפר של Autograft עם עור טחון אפידרמיס כדי פצע בעובי מלא
- שמור את autograft לח ב DMEM בזמן ההמתנה.
- לתפור את autograft לתחתית של בעובי מלא העור הפצע על ידי תפרים קטע בפינות ובאמצע של autograft לשמור על autograft המצורפת הדוק משטח הבסיס.
- מכסה את הפצע עם תחבושת פלסטיק שמחזיק את הפצע לח.
התחת = "jove_title"> 5. סִיוּם
- החיה שלווים עם זריקה תוך שרירית של היפוכלוריד zolazepam (2.5 מ"ג / ק"ג) ו medetomidine (25 מיקרוגרם / ק"ג) לפני סיומה ולהחיל מכשירי ניטור לאוזן או הזנב כדי לבדוק את הדופק ואת לחץ הדם.
- להרדימו על ידי מתן מנה קטלנית של נתרן pentobarbital (60-140 מ"ג / ק"ג) לווריד. בדוק את הדופק ואת לחץ הדם עד המוות התרחשה.
6. במבחנה תרבות
הערה: כדי להעריך את ההתקדמות היסטולוגית של הרקמה הטחונה מבני PCL / קולגן במבחנה, קולגן / PCL / הטלאים טחונים מתורבתות 12 גם צלחות באמצעות מדיום keratinocyte.
- הכנת בינוני keratinocyte:
- לעקר בקבוק זכוכית 500 מ"ל.
- מערבבים 400 מ"ל של DMEM עם 100 מ"ל של F12 של חם (4: 1 תערובת). מוסף עם 10% בסרום שור עוברי, 5 מיקרוגרם / מיליליטר אינסולין,0.4 מיקרוגרם / מ"ל הידרוקורטיזון, 21 מיקרוגרם / מ"ל אדנין, 10 -10 mol / L רעלן הכולרה, 2 x 10 -9 mol / L triiodothyronine, 5 מיקרוגרם / מ"ל transferrin, 10 ng / ml גורם הגדילה באפידרמיס, 50 U / ml פניצילין ו -50 מיקרוגרם / מ"ל סטרפטומיצין.
- לעקר ידי filtrating דרך פילטר 0.2 מיקרומטר ולאסוף תסנין בבקבוק 500 מ"ל סטרילי.
7. אימונוהיסטוכימיה
הערה: פרוטוקול אימונוהיסטוכימיה מחולק בדרך כלל אל השלבים הבאים: (1) קיבעון פרפין והטבעה, (2) מיקרו-חתך עד 5 מיקרומטר פרוסות, מיקום בשקופיות, deparaffination, ו התייבשות, (3) הסרת המסכות אנטיגן, מכתים ואת הרכבה . לפני שמתחילים את הצעדים האחרונים בהליך אימונוהיסטוכימיה, להכין מאגרי כביסת פתרון חשיפת אנטיגן (ראה פירוט חומר נפרד). הכן את הפתרון מורכב ABC לפחות 30 דקות לפני השימוש.
- קיבוע
לאTE: בסוף התרבות במבחנה, לתקן את התיקונים כדלקמן:- הכן צינורות Eppendorf עם 1 מ"ל של 4% פורמלין שנאגרו (PFA) (זהירות:. פורמלדהיד הוא רעיל אנא קרא גיליונות נתוני בטיחות חומרים לפני עבודה עם חומר כימי זה יש להשתמש בכפפות ומשקפי בטיחות ולהכין את הפתרון בתוך במנדף.).
- העברת כל התיקונים קולגן צינור Eppendorf המכיל 4% PFA. תקן במשך הלילה בטמפרטורת החדר.
- מקום דגימות באתנול 70% עבור אחסון לטווח ארוך ב 4 מעלות צלזיוס. דוגמאות מוכנות כעת עבור התייבשות והטבעה בבלוקי פרפין לפני החתך.
- rehydration
- מניח את השקופיות בצנצנת מכתימה עם solv X-tra במשך 15 דקות. חזור באמצעות בצנצנת מכתים חדשה עם solv X-TRA. מניח את השקופיות בצנצנת מכתימה עם אתנול אבסולוטי למשך 10 דקות. חזור באמצעות בצנצנת מכתים חדשה עם אתנול אבסולוטי. מניח את השקופיות בצנצנת מכתימה עם אתנול 95% למשך 10 דקות ולאחר מכןלצנצנת מכתימה עם אתנול 70% למשך 10 דקות. לבסוף לשטוף את שקופיות פעמים במשך 5 דקות עם מים מזוקקים.
- חשיפת Antigen
- שים שקופיות בצנצנת Coplin עם TE-פתרון ולשים בצנצנת באמבט מים להרתיח במשך 20 דקות. קח את הצנצנת מתוך אמבט במים בזהירות. מצננים את השקופיות בטמפרטורת החדר למשך 30 דקות ולשטוף פעמיים במשך 5 דקות ב טריס חיץ. מניח את השקופיות בצנצנת מכתימה עם מי חמצן 3% למשך 10 דקות. שטפו את השקופיות פעמיים במשך 5 דקות ב טריס חיץ. צייר עיגול סביב הדגימות באמצעות דוחה מי סימון עט.
- חסום ספציפי מחייב של הנוגדנים באמצעות 100-300 μl של פתרון לחסימה. הסר את הפתרון חוסם ולהוסיף 100-300 μl של נוגדן ראשוני מומס בריכוז המומלץ ב טריס חיץ. דגירת הלילה. הסר את פתרון הנוגדן ולשטוף פרקים, טריס חיץ פעמים במשך 5 דקות.
- דגירה עם נוגדנים משני עבור שעה 1 ב חדר לטמפרטורותיור. שטפו פעמיים במשך 5 דקות ב טריס חיץ. דגירה 30 דקות באמצעות ערכת עלית ABC (בהתאם להוראות היצרן). לשטוף פעמיים ב טריס חיץ.
- לפתח תגובת נוגדן באמצעות ערכת VIP הווקטור, בעקבות הוראות יצרן (דגירת דקות 1-7 בדרך כלל מייצרת עוצמת סגולה ברורה). שים את השקופיות במים מזוקקים. Counterstain עם hematoxylin מאיר למשך 30 שניות.
- לשטוף במים זורמים למשך 5 דקות. מניח את השקופיות בצנצנת מכתימה עם אתנול 70% דקות 1. חזור באמצעות בצנצנת מכתים חדשה עם 70% אתנול. מניח את השקופיות בצנצנת מכתימה עם אתנול 95% דקות 1. חזור באמצעות בצנצנת מכתים חדשה עם 95% אתנול.
- מניחים את השקופיות בצנצנת מכתים עם solv X-tra למשך 5 דקות. הסר, אחד בכל פעם, כדי לשמור על לחות. מניחים ירידה של המדיום גובר על גבי כל שקופית ולשים כוס על גבי העטיפה (לעשות זאת בזהירות כדי למנוע בועות אוויר). בואו השקופיות לייבוש למשך הלילה ולהציג שקופיות תחת מיקרותְחוּם.
תוצאות
מחקר זה מציג שיטה שמראה איך לייצר ביולוגי להשתלה באמצעות דחיסת פלסטיק של הקולגן ולבניית רקמות טחון.
רירית שלפוחית שתן ועור ניתן לקצור ואז טחון מכאני לחלקיקים קטנים (איור 3). על ידי דחיסת פלסטיק, חלקיקים הטחונים משולבי?...
Discussion
המחקר זה מציג גישה קלה לשימוש לייצר תיקונים לדופן שלפוחית עם רקמה עצמית להשתלה ליד השולחן כירורגית. המדבקות נוצרות על ידי השילוב של סריגת פולימר מתכלה באמצע וקולגן עם ובלי רקמות טחונות ב המשטחים החיצוניים בשילוב עם דחיסת פלסטיק. דחיסת פלסטיק היא שיטה שתוארה לעיל ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Swedish Society for Medical Research, the Promobilia Foundation, the Crown Princess Lovisa Foundation, the Freemason Foundation for Children’s Welfare, the Swedish Society of Medicine, the Solstickan Foundation, Karolinska Institutet, and the Stockholm City Council for financial support.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Silicone catheter 10-French | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| DMEM 10x | Gibco | 31885-023 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| 24 well plates | Falcon | 08-772-1 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| 3',3',5-Triiodothyronine | Sigma-Aldrich | IRMM469 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| 4% PFA | Labmed Solutions | 200-001-8 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| 70% ethanol | Histolab | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 | |
| ABC Elite kit: Biotin-Streptavidin detection kit | Vector | PK6102 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Absolute ethanol | Histolab | 1399.01 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Adenine | Sigma-Aldrich | A8626 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Atropine 25 μg/kg | Temgesic, RB Pharmaceuticals, Great Britain | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Azaperone 2 mg/kg | Stresnil, Janssen-Cilag, Pharma, Austria | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Biosafety Level 2 hood | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Blocking solution: Normal serum from the same species as the secondary secondary antibody was generated in. | Vector | The blocking solution depends of the origin of first antibody | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Buprenorphine 45 μg/kg | Atropin, Mylan Inc, Canonsburg, PA | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Carprofen 3 mg/kg | Rimadyl, Orion Pharma, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Chlorhexidine gluconate | Hibiscrub 40 mg/mL, Regent Medical, England | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Cholera toxin | Sigma-Aldrich | C8052 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Coplin jar: staining jar for boiling | Histolab | 6150 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Stainless mold (33 mm x 22 mm x 10 mm) custom made | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| DMEM | Gibco | 3188-5023 | Plastic compression section 4. Keep on ice when using it in plastic compression |
| Epidermal growth factor | Sigma-Aldrich | E9644 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Ethilon (non-absorbable monofilament for skin sutures) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Gibco | 10437-036 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Forceps (Adison with tooth) | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Gauze (Gazin Mullkompresse) | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Ham's F12 | Gibco | 31765-027 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Hematoxylin | Histolab | 1820 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Humidity chamber | DALAB | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 | |
| Hydrocortisone | Sigma-Aldrich | H0888 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Hydrogen peroxide Solution 30% | Sigma-Aldrich | H1009 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Insulin | Sigma-Aldrich | I3536 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Isoflurane | Isoflurane, Baxter, Deerfield, IL | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Lidocaine 5 mg/ml | Xylocaine, AstraZeneca, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Lucose 25 mg/ml | Baxter, Deerfield, IL | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Marker pen pap pen | Sigma-Aldrich | Z377821-1EA | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Medetomidine 25 μg/kg | Domitor, Orion Pharma, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Mincing device | Applied Tissue Technologies LLC | Minced tissue preparation, section 2 | |
| Monocryl (absorbable monofilament) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | S7653 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| NaOH 1 N | Merck Millipore | 106462 | Plastic compression section 4 and cell culture |
| Nylon mesh, 110 μM thick pore size 0.04 sqmm | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Oculentum simplex APL: ointment for eye protection | APL | Vnr 336164 | Surgery, Section 1 |
| PBS | Gibco | 14190-094 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | Plastic compression section 4 |
| Phenobarbiturate 15 mg/kg | Pentobarbital, APL, Sweden | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| PCL Knitted fabric | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Rat-tail collagen | First LINK, Ltd, UK | 60-30-810 | Plastic compression section 4, keep on ice |
| Scalpel blade - 15 | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Shaving shears | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Stainless stell mesh, 400 μM thick pore size | Plastic compression; Section 4 | ||
| Steril gloves | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Sterile gowns | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Sterile drapes | |||
| Sterilium | Bode Chemie HAMBURG | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Suture Thread Ethilon | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| TE-solution (antigen unmasking solution) consist of 10 mM Tris and 1 mM EDTA, pH 9.0 | 10 mM Tris/1 mM EDTA, adjust pH to 9.0 | ||
| Tiletamine hypochloride 2.5 mg/kg | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | ||
| Transferrin | Sigma-Aldrich | T8158 | In vitro culture; Section 5 |
| Trizma Base, H2NC | Sigma-Aldrich | T6066 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Vector VIP kit: Enzyme peroxidase substrate kit | Vector | SK4600 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6 |
| Vicryl (absorbable braded) | Ethicon | Surgery, Section 1 | |
| Tris buffer pH 7.6 (washing buffer) | TE solution: Make 10x (0.5 M Tris, 1.5 M NaCl) by mixing: 60.6 g Tris (Trizma Base, H2NC(CH2OH)3, M=121.14 g/mol), add 800 ml distilled water adjust the pH till 7.6, add 87.7 g NaCl and fill to 1,000 ml with distilled water. Dilute to 1x with distilled water. | ||
| X-tra solv (solvent) | DALAB | 41-5213-810 | Immunocytochemistry; Section 6. Use under fume hood |
| Zolazepam hypochloride | Zoletil, Virbac, France | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Depilatory wax strips | Veet | Preparing the animal for surgery, Section 1 | |
| Pentobarbital sodium | Lundbeck | Termination, Section 3 |
References
- Rheinwald, J. G., Green, H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 6, 331-343 (1975).
- Fossum, M., Nordenskjold, A., Kratz, G. Engineering of multilayered urinary tissue in vitro. Tissue Engineering. 10, 175-180 (2004).
- Salmikangas, P., et al. Manufacturing, characterization and control of cell-based medicinal products: challenging paradigms toward commercial use. Regen Med. 10, 65-78 (2015).
- Fossum, M., et al. Minced skin for tissue engineering of epithelialized subcutaneous tunnels. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 15, 2085-2092 (2009).
- Fossum, M., et al. Minced urothelium to create epithelialized subcutaneous conduits. The Journal of Urology. 184, 757-761 (2010).
- Reinfeldt Engberg, G., Lundberg, J., Chamorro, C. L., Nordenskjold, A., Fossum, M. Transplantation of autologous minced bladder mucosa for a one-step reconstruction of a tissue engineered bladder conduit. BioMed Research International. 2013, 212734 (2013).
- Meek, C. P. Successful microdermagrafting using the Meek-Wall microdermatome. Am J Surg. 96, 557-558 (1958).
- Tanner, J. C., Vandeput, J., Olley, J. F. The Mesh skin graft. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 34, 287-292 (1964).
- Svensjo, T., et al. Autologous skin transplantation: comparison of minced skin to other techniques. The Journal of Surgical Research. 103, 19-29 (2002).
- Ajalloueian, F., Zeiai, S., Rojas, R., Fossum, M., Hilborn, J. One-stage tissue engineering of bladder wall patches for an easy-to-use approach at the surgical table. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods. 19, 688-696 (2013).
- Engelhardt, E. M., et al. A collagen-poly(lactic acid-co-varepsilon-caprolactone) hybrid scaffold for bladder tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 32, 3969-3976 (2011).
- Brown, R. A., Wiseman, M., Chuo, C. B., Cheema, U., Nazhat, S. N. Ultrarapid engineering of biomimetic materials and tissues: fabrication of nano- and microstructures by plastic compression. Adv Funct Mater. 15, 1762-1770 (2005).
- Fumagalli Romario, U., Puccetti, F., Elmore, U., Massaron, S., Rosati, R. Self-gripping mesh versus staple fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a prospective comparison. Surg Endosc. 27, 1798-1802 (2013).
- Muangman, P., et al. Complex Wound Management Utilizing an Artificial Dermal Matrix. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 57, 199-202 (2006).
- Ajalloueian, F., Zeiai, S., Fossum, M., Hilborn, J. G. Constructs of electrospun PLGA, compressed collagen and minced urothelium for minimally manipulated autologous bladder tissue expansion. Biomaterials. 35, 5741-5748 (2014).
- Orabi, H., AbouShwareb, T., Zhang, Y., Yoo, J. J., Atala, A. Cell-seeded tubularized scaffolds for reconstruction of long urethral defects: a preclinical study. Eur Urol. 63, 531-538 (2013).
- Blais, M., Parenteau-Bareil, R., Cadau, S., Berthod, F. Concise review: tissue-engineered skin and nerve regeneration in burn treatment. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2, 545-551 (2013).
- Serpooshan, V., Muja, N., Marelli, B., Nazhat, S. N. Fibroblast contractility and growth in plastic compressed collagen gel scaffolds with microstructures correlated with hydraulic permeability. J Biomed Mater Res A. 96, 609-620 (2011).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved