需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
测量的刚度
摘要
We present detailed protocols for isolation of aortas from mouse and measurement of their elastic modulus using atomic force microscopy.
摘要
动脉硬化是一个显著风险因子和生物标志物用于心血管病和老化的标志。原子力显微镜(AFM)是用于多种材料从硬(塑料,玻璃,金属等 )表面的任何基底上细胞的表征粘弹性的机械性能的多功能的分析工具。它已被广泛地用于测量细胞的刚度,但不经常用于测量主动脉的刚度。在本文中,我们将介绍使用AFM在接触模式下测量空载小鼠动脉离体弹性模量的过程。我们描述程序的鼠标主动脉隔离,然后提供的AFM分析的详细信息。这包括用于激光束的对准,弹簧常数和原子力显微镜探针的偏转灵敏度的校正,并采集力曲线的一步一步的说明。我们还提供了数据ANALY了详细的方案力曲线的妹妹。
引言
The biomechanical properties of arteries are a critical determinant in cardiovascular disease (CVD) and aging. Arterial stiffness, a major cholesterol independent risk factor and an indicator for the progression of CVD, increases with vascular injury, atherosclerosis, age, and diabetes1-8. Arterial wall stiffening is associated with increased dedifferentiation, migration, and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells9-12. In addition, increased arterial stiffness has been linked to enhanced macrophage adhesion1, endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration13, and vessel wall remodeling14,15. Thus, therapies that could prevent arterial stiffening in CVD or aging might complement currently available pharmacological interventions that treat CVD by reducing high blood cholesterol.
AFM is a powerful analytical tool used for various physical and biological applications. AFM is increasingly used to obtain the high-resolution images and characterize the biomechanical properties of soft biological samples such as tissues and cells1,2,10,16,17 with a great degree of accuracy at nanoscale levels. A major advantage of AFM is the fact that it can be used with living cells.
This paper describes our method for measuring the elastic modulus of mouse arteries ex vivo using AFM. The described method shows how we 1) properly isolate mouse arteries (descending aorta and aortic arch) and 2) measure the elastic modulus of these tissues by AFM. Measurements of unloaded elastic moduli in arteries can help to elucidate changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) that occur in response to vascular injury, CVD, and aging.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
研究方案
在这项研究中动物的工作是经宾夕法尼亚大学的机构动物护理和使用委员会。该方法是按照批准的指导原则进行。
1.准备老鼠和主动脉的分离
- 麻醉用氯胺酮小鼠(80 - 100毫克/千克),赛拉嗪(8 - 10毫克/千克)和乙酰丙嗪(1 - 2毫克/千克)腹膜内。确认尾掐测试麻醉。一旦鼠标被完全麻醉,安乐死通过颈脱位鼠标。
- 将在它的后面鼠标和针鼠标一个夹层板。清洗,用70%的腹部区域(体积/体积)乙醇擦拭。
- 捏住在中线的皮肤,使与腹部中型显微剪一个小切口初期。保持与镊子皮肤,用中等大小的显微剪刀剪开皮肤和腹膜从腹部到胸骨。
- 切去B上的排骨OTH两侧中型显微剪刀。仔细小型显微剪刀取出肺脏和肝脏,并保持心脏和主动脉。鼠标和夹层板传送到解剖显微镜。
- 抓住周围的小镊子主动脉脂肪和用小剪刀小心切掉脂肪主动脉周围。
- 轻轻抓住用镊子主动脉,使一个切口与小型显微剪刀在升主动脉和另一个切口在降主动脉的端部开始,正上方的腹主动脉。
- 转移解剖主动脉到含有1x磷酸盐缓冲的盐水中的60毫米培养皿(PBS;无钙和镁)。
- 继续使用小型显微剪刀主动脉解剖走任何剩余的脂肪组织。用小剪刀纵向打开的主动脉。
- 使用小型显微剪刀剪开降主动脉和aorti的一小片(〜2×4mm的)ç拱原子力显微镜分析( 图1)。放置在组织中的60毫米的塑料盘和保持水分在PBS一滴。
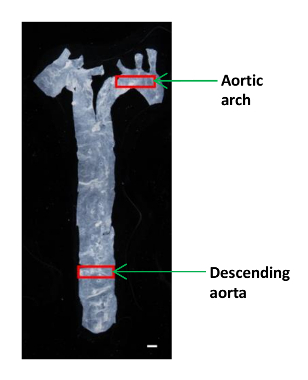
图1:一个图像显示在小鼠的不同主动脉段的位置处的主动脉是从心脏中分离至该膜片,和降主动脉的和一小部分的主动脉弓被用来确定弹性模量。比例尺,1毫米。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
2.准备组织样本的AFM测量
- 小心使用不接触主动脉实验室擦拭去除PBS。可以肯定,对组织的腔侧朝上。
- 打开主动脉的每一端轻轻粘合到板通过加 ING 5 - 10微升氰基丙烯酸酯类粘合剂的用凝胶加载尖( 图2)。
注:需要在两端牢固安装组织中的胶量必须凭经验确定。至关重要的是,主动脉未在此过程中进行拉伸。 - 检查胶合主动脉一定要确保它没有被折叠或浮动。在主动脉空气干燥该胶后(30 - 60秒),轻轻加入PBS中并浸没样品。
注:制备的原子力显微镜(步骤3 - 5)可以在所述组织被准备用于分析来进行。

图2:一个主动脉段的卡通胶合到使用氰基丙烯酸酯粘合剂的60毫米培养皿中的氰基丙烯酸酯粘合剂被施加到主动脉样品的边缘在准备AFM测量。COM /文件/ ftp_upload / 54630 / 54630fig2large.jpg"目标="_空白">点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
3.装载探头
- 挂载液体探头支架上探头负载的立场。
- 使用镊子,具有球形前端滑动的氮化硅AFM探针(0.06牛顿/米悬臂)上的探头支架(我们使用了1微米直径的 SiO 2粒子,但也可以使用更大的尺寸)。确保原子力显微镜探针被牢固地固定在探头支架。
- 探头支架滑到Z扫描器安装AFM头,并确保探头支架连接牢固。
4.校准激光探头上
- 打开AFM软件。选择软件上的实验类型; 实验范畴 ,以接触模式, 实验组 ,联系方式液和实验 ,联系方式液。点击载入EXPeriment在软件;这将开启激光器。
- 加入3毫升蒸馏水至50毫米的玻璃底培养皿并将其放置在激光对准单元的阶段的菜。这个单元简化了激光束聚焦到悬臂的背部的过程。
- 在直立位置上的激光准直单元与功率激光对准单元上安装的AFM头。添加约50微升的蒸馏水,以在针尖的液滴。
- 使用操纵杆,降低AFM头,使针尖使得在菜与水接触。如果触点没有针尖和水盘之间进行,直到接触时轻轻抬起菜。调整对焦,亮度和XY位置,使针尖是鉴于对齐单元的液晶显示屏上。
- 通过调整AFM头的激光定位旋钮激光点到AFM探针的尖端的位置。使用探测器定位旋钮上的原子力显微镜头,调整断定光电二极管直至0和-1 V范围值的离子被用于垂直偏转获得和用于水平偏转得到〜0 V.
- 查,以确保该激光和信号被最大化。如果必要,重复步骤4.5至重新调整的针尖的激光束和光电二极管的位置,以获得最大的总和信号的位置。
注意:可能需要重新定位在探头支架上的原子力显微镜探针,以获得即使步骤4.5重复最大和信号。
5.校准AFM探针的偏转灵敏度和弹簧常数
- 制作与钳子60毫米培养皿划痕和填充用蒸馏水的菜。放置在样品架板培养皿。在这种情况下,安装在倒置显微镜的电动XY扫描阶段的菜。
- 放置在板顶部上的磁性板保持器以保持其在成像期间固定。
- 点击"上"在移动的AFM头高达近最高位置的软件导航菜单箭头,以确保原子力显微镜探针不会碰的菜。
注意:这一步非常重要,因为它避免断针尖。 - 放置在AFM头显微镜舞台上。
- 使用显微镜把重点放在盘子上的划痕。使用操纵杆,或者单击"向下"箭头在导航菜单中,慢慢地,小心地将原子力显微镜探针进入PBS。在板的刮略高于头位置。
注意:如果AFM头的初始位置更接近样品时,接合时间将显著减少。 - 接合之前,重新调整的针尖的激光束和光电二极管的位置,需要获得最大SUM信号的位置。
- 通过单击更改探头在设置菜单中选择一个提示类型。
- 点击查看参数和设置参数: 扫描尺寸为0, 扫描速率为1赫兹, 采样/线 256和偏转设定点到20纳米。点击搞。直到探针使得与板的表面接触的锁上状态窗口将保持打开。从事探头后,点击斜坡 。
- 在扫描工具栏菜单中单击扩展模式和设置参数: 斜坡大小为500纳米和1微米的斜率之间,到2赫兹, 样品 256 号 , 提示半径为500纳米, 样品泊松比为0.5(假设材料待测量是完全不可压缩), 提示半角为0, 触发模式到相对和触发器阈值 ,以20至100纳米。
- 点击斜坡连续在斜坡工具栏菜单OBTA在盘上( 图3A)上的力曲线。在这种力曲线,设置通道1 偏差 。
注意:这将允许软件绘制的结果作为垂直偏转与z位置。- 点击力曲线的左边或右边结束,拖动光标以包括力曲线( 图3A,红色虚线线)的线性区域。使用这两条线来标记倾斜区域的边界要适合用一条直线。
- 选择斜坡在工具栏,然后单击更新灵敏度 。记录该值并重复此步骤四次。选择在校准工具栏,然后单击探测器 。输入从偏转灵敏度框中五次测量的平均值。
- 点击取款 2 - 3次提高AFM头。这个步骤是重要的,以防止针尖和在热调过程中的板之间的相互作用。单击工具栏热调 。
- 设置1的热调谐范围 - 100千赫(可以从制造商的产品目录中获得该信息)和偏转灵敏度更正为1.144 V形悬臂和1.106矩形悬臂。
- 在热调谐菜单中,单击获取数据以获得热调曲线( 图3B)。使用AFM软件,代替红色通过从图的边缘在拖动鼠标以限定的边界拟合虚线的曲线(如在图3B示出)的任一侧的行。选择洛伦兹(空),或者根据简谐振荡器(液)的模型上更好地满足数据。
- 点击拟合数据 ,然后计算弹簧K和保存该值。回覆泥炭弹簧常数校准几次,并使用平均值。点击撤消几次。
- 从显微镜舞台中删除AFM头,并把它对准单元。取下显微镜阶段的菜。
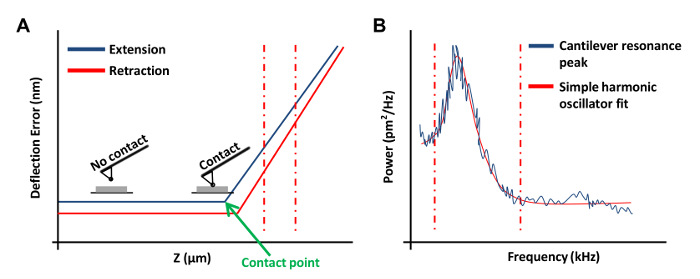
图3:AFM力曲线用于AFM探针的校准。 (A)代表AFM力曲线(校准曲线)。垂直红之间的作用力曲线的延伸部分虚线来确定悬臂偏转灵敏度。(B)用于计算悬臂如前所述20的弹簧常数的简单谐振子契合图。 请点击这里查看一个更大的版本这个数字。
6。测量弹性模量对小鼠动脉离体
- 上放置装有显微镜阶段的主动脉组织的60毫米培养皿中,并与磁性板保持固定板。
- 放置在AFM头显微镜舞台上。使一定的AFM探针不与主动脉接触而是轻轻使接触用PBS并形成一个弯月面。如果有必要,将对准单元上的原子力显微镜头和点击撤消直到有足够的空间,以防止接触,然后将AFM头显微镜舞台上。
- 点击导航 。使用操纵杆或点击"下"箭头 ,慢慢降低原子力显微镜探针定位主动脉上方的悬臂。必要时进行调整使用的原子力显微镜头探测器定位旋钮光电二极管的位置。
- 点击锁上以允许悬臂以与主动脉接触。
- 一旦主动脉从事,确保压电中心是稳定的,并单击斜坡 。如果压电中心波动,这可能是一个假啮合的结果。撤回探头和增加垂直的激光的偏移由小增量的光电二极管(〜0.5V)和重新接合。
- 此外,如果探针是远高于样品表面,手动降低探头接近样品表面之前重新接合。如果前面的步骤不排除波动,尝试更换探头。
- 设置斜坡大小为3微米, 触发方式相对和触发阈值至100纳米,然后单击斜坡持续 。观察探针和样品之间的接触点发生在大致中央与Z斜坡周期的下¾。如果这是没有观察到,从样品分离,根据需要进行调整的斜坡尺寸和重新接合样本。
- 在菜单栏中点击显微镜再搞设置 。更改SPM撤 30微米。点击斜坡在斜坡工具栏菜单持续 。
- 观察力曲线后,单击菜单栏中的捕获 ,然后捕获文件名 。与结局".000"(这将允许更多的捕捉文件由1数增加)输入所需的文件名。选择一个指定的文件夹并保存数据。
- 在捕获工具栏菜单中单击捕获 。点击退出 ,然后导航 。使用操纵杆或软件控制在主动脉的另一区域的悬臂定位(旁初始计量点; 见图4)。
- 点击参与 , 斜坡 ,分别斜坡持续 。观察力曲线后,单击停止 ,然后捕获 。
- 重复步骤6.9 - 6.10。 如图每区域捕获至少5次测量4 注:我们通常收集15 - 3 25的力曲线-在每个组织5的不同位置, 如图4中分别。
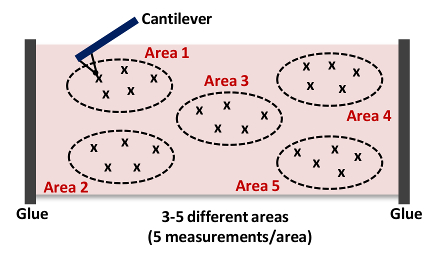
图4: -从3 25倍- 5个不同的地点(区域1 - 5)在每个动脉获得整体的刚度悬臂趋近及缩进组织(区域1)的卡通这种AFM重复测量多达15个组织样本。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
7.数据分析
- 开力曲线分析软件。
- 氯ICK 查找并在菜单栏中打开 ,并加以分析上的文件双击。
- 单击工具栏菜单修改力能参数检查偏转灵敏度,弹簧常数,刀尖半径,提示半角和泊松比。要更改参数,检查它旁边的框,然后在新值列中输入正确的值。然后单击执行 。
- 如果力曲线是嘈杂,单击棚车过滤器 ,并设置为输入方向延伸, 平均分给3和滤波器阶数为0 个 。单击执行平滑数据。
- 点击菜单栏中的基线校正 ,并为方向延伸的输入, 打印单位到部队, 键入要分离, 校正为了 1 日和扩展基准源 延伸。调整垂直蓝色虚线线涵盖力曲线的平坦部分,然后单击执行 。
- 在工具栏菜单中单击缩进并设置为活动曲线来扩展, 拟合方法输入点基, 联系点算法来联系治疗如适合的变量, 包括附着力不, 最大力适合边界至30%, 闵力适合边界来0%和拟合模型 ,以赫兹(球形)。
注意:在我们的测量,针尖和样品(在后退曲线悬臂梁的负偏转)之间显著粘附很少观察到。在观察这样的粘合的情况下,适当的模型(DMT或JKR)应该用于分析18,19。 - 减的杨氏模量的值。分析各3的杨氏(弹性)模量-第5区(每区5的力曲线), 如图4彼此的小的距离内拍摄。
注:要删除的文物,排除杨氏模量> 100千帕(通常〜测量总额的10%)的时间序列。 - 计算每个3的平均杨氏模量的值 - 第5区(已测得),并使用这些值来计算的平均弹性模量为主动脉作为一个整体。
注:至少3,更经常4 - 6个人主动脉被用于获得动脉硬度的准确评估。最后的结果被绘制为"n"的独立实验的平均值±SEM表示。需要主动脉的确切数目将当然取决于精度所要求的水平。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
结果
图5A示出了从6个月大的,雄性C57BL / 6小鼠的降(胸)主动脉的相位对比图像。原子力显微镜悬臂是直接发生在组织上面并准备缩进。 图5B和5C展示在接触模式下的AFM压痕获得代表力曲线。在图5B和5C示出绿线表示使用球体赫兹模型中获得的最佳拟合曲线。在图5D中 ,如在文中所描述的降主动脉和主动脉弓的平均刚度从...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
讨论
AFM压痕可用于表征细胞和组织的刚度(弹性模量)。在本文中,我们提供详细的一步一步的协议来隔离小鼠降主动脉和主动脉弓,并确定这些地区的动脉离体的弹性模量。我们现在总结和讨论在本文所描述的方法的技术问题和限制。
几个技术问题可以在隔离,并给予他们的小而薄的自然鼠标主动脉的分析产生。当清洗过的动脉被纵向打开,必须小心不要破坏那里的弹?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
披露声明
The authors have nothing to disclose.
致谢
AFM analysis was performed on instrumentation supported by the Pennsylvania Muscle Institute and the Institute for Translational Medicine and Therapeutics, Perelman School of Medicine, the University of Pennsylvania. This work was supported by NIH grants HL62250 and AG047373. YHB was supported by post-doctoral fellowship from the American Heart Association.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| BioScope Catalyst AFM system | Bruker | ||
| Nikon Eclipse TE 200 inverted microscope | Nikon Instruments | ||
| Silicon nitride AFM probe | Novascan Technologies | PT.SI02.SN.1 | 0.06 N/m cantilever; 1 µm SiO2 particle |
| Dumont #5 forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11251-10 | See section 1.4 |
| Dumont #5SF forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11252-00 | See section 1.8 |
| Fine Scissors-ToughCut | Fine Science Tools | 14058-11 | See section 1.4 (medium sized) |
| Vannas-Tübingen spring scissors | Fine Science Tools | 15008-08 | See section 1.6 (small sized) |
| 60 mm TC-treated cell culture dish | Corning | 353004 | |
| Dulbecco's Phosphate-Buffered Saline, 1x | Corning | 21-031-CM | Without calcium and magnesium |
| Krazy Glue instant all purpose liquid | Krazy Glue | KG58548R | See section 2.2 |
| Gel-loading tips, 1 - 200 µl | Fisher | 02-707-139 | See section 2.2 |
| Tip Tweezers | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 78092-CP | See section 3.2 |
| 50-mm, clear wall glass bottom dishes | TED PELLA | 14027-20 | See section 4.4 |
参考文献
- Kothapalli, D., et al. Cardiovascular Protection by ApoE and ApoE-HDL Linked to Suppression of ECM Gene Expression and Arterial Stiffening. Cell Rep. 2, 1259-1271 (2012).
- Liu, S. -L., et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-12 is an essential mediator of acute and chronic arterial stiffening. Sci Rep. 5, 17189(2015).
- Lakatta, E. G. Central arterial aging and the epidemic of systolic hypertension and atherosclerosis. J Am Soc Hypertens. 1, 302-340 (2007).
- Stehouwer, C. D. A., Henry, R. M. A., Ferreira, I. Arterial stiffness in diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: a pathway to cardiovascular disease. Diabetologia. 51, 527-539 (2008).
- Steppan, J., Barodka, V., Berkowitz, D. E., Nyhan, D. Vascular Stiffness and Increased Pulse Pressure in the Aging Cardiovascular System. Cardiol Res Pract. 2011, 263585(2011).
- Duprez, D. A., Cohn, J. N. Arterial stiffness as a risk factor for coronary atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 9, 139-144 (2007).
- Mitchell, G. F., et al. Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Events: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 121, 505-511 (2010).
- Sutton-Tyrrell, K., et al. Elevated Aortic Pulse Wave Velocity, a Marker of Arterial Stiffness, Predicts Cardiovascular Events in Well-Functioning Older Adults. Circulation. 111, 3384-3390 (2005).
- Klein, E. A., et al. Cell-Cycle Control by Physiological Matrix Elasticity and In Vivo Tissue Stiffening. Curr Biol. 19, 1511-1518 (2009).
- Bae, Y. H., et al. A FAK-Cas-Rac-lamellipodin signaling module transduces extracellular matrix stiffness into mechanosensitive cell cycling. Sci signal. 7, ra57(2014).
- Thyberg, J., Hedin, U., Sjölund, M., Palmberg, L., Bottger, B. A. Regulation of differentiated properties and proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 10, 966-990 (1990).
- Owens, G. K., Kumar, M. S., Wamhoff, B. R. Molecular Regulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation in Development and Disease. Physiol Rev. 84, 767-801 (2004).
- Huynh, J., et al. Age-Related Intimal Stiffening Enhances Endothelial Permeability and Leukocyte Transmigration. Sci Transl Med. 3, 112ra122(2011).
- Safar, M. E., Levy, B. I., Struijker-Boudier, H. Current Perspectives on Arterial Stiffness and Pulse Pressure in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation. 107, 2864-2869 (2003).
- Raffetto, J. D., Khalil, R. A. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 75, 346-359 (2008).
- Muller, D. J., Dufrene, Y. F. Atomic force microscopy as a multifunctional molecular toolbox in nanobiotechnology. Nat Nanotechnol. 3, 261-269 (2008).
- Hsu, B. Y., Bae, Y. H., Mui, K. L., Liu, S. -L., Assoian, R. K. Apolipoprotein E3 Inhibits Rho to Regulate the Mechanosensitive Expression of Cox2. PLoS ONE. 10, e0128974(2015).
- Johnson, K. L., Kendall, K., Roberts, A. D. Surface Energy and the Contact of Elastic Solids. Proc R Soc Lond A. 324, 301-313 (1971).
- Derjaguin, B. V., Muller, V. M., Toporov, Y. P. Effect of contact deformations on the adhesion of particles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 53, 314-326 (1975).
- Hutter, J. L., Bechhoefer, J. Calibration of atomic-force microscope tips. Rev Sci Instrum. 64, 1868-1873 (1993).
- Pries, A. R., Secomb, T. W., Gaehtgens, P. The endothelial surface layer. Pflugers Arch EJP. 440, 653-666 (2000).
- Pogoda, K., et al. Depth-sensing analysis of cytoskeleton organization based on AFM data. Eur Biophys J. 41, 79-87 (2012).
- Mendez, M. G., Restle, D., Janmey, P. A. Vimentin Enhances Cell Elastic Behavior and Protects against Compressive Stress. Biophys J. 107, 314-323 (2014).
- Moreno-Flores, S., Benitez, R., Md Vivanco,, Toca-Herrera, J. L. Stress relaxation and creep on living cells with the atomic force microscope: a means to calculate elastic moduli and viscosities of cell components. Nanotechnology. 21, 445101(2010).
- Darling, E. M., Topel, M., Zauscher, S., Vail, T. P., Guilak, F. Viscoelastic properties of human mesenchymally-derived stem cells and primary osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes. J Biomech. 41, 454-464 (2008).
- Dimitriadis, E. K., Horkay, F., Maresca, J., Kachar, B., Chadwick, R. S. Determination of Elastic Moduli of Thin Layers of Soft Material Using the Atomic Force Microscope. Biophys J. 82, 2798-2810 (2002).
- Mahaffy, R. E., Shih, C. K., MacKintosh, F. C., Käs, J. Scanning Probe-Based Frequency-Dependent Microrheology of Polymer Gels and Biological Cells. Phys Rev Lett. 85, 880-883 (2000).
- Amin, M., Le, V. P., Wagenseil, J. E. Mechanical Testing of Mouse Carotid Arteries: from Newborn to Adult. J Vis Exp. , e3733(2012).
- Laurent, S., et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J. 27, 2588-2605 (2006).
- Plodinec, M., et al. The nanomechanical signature of breast cancer. Nat Nano. 7, 757-765 (2012).
- Raman, A., et al. Mapping nanomechanical properties of live cells using multi-harmonic atomic force microscopy. Nat Nano. 6, 809-814 (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。