このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
の剛性を測定します
要約
We present detailed protocols for isolation of aortas from mouse and measurement of their elastic modulus using atomic force microscopy.
要約
動脈硬化は、心血管疾患や老化の顕著な特徴のための重要な危険因子とバイオマーカーです。原子間力顕微鏡(AFM)( 等のプラスチック、ガラス、金属、)ハードに至るまで様々な材料のための粘弾性の機械的性質を特徴付けるための多目的な分析ツールである任意の基板上のセルに表面。広く、細胞の剛性を測定するために使用されるが、あまり頻繁に大動脈の剛性を測定するために使用されてきました。本稿では、無負荷マウスの動脈のex vivoでの弾性率を測定するために、接触モードでAFMを使用するための手順について説明します。我々は、マウスの大動脈の単離のために私たちの手順を説明し、その後、AFM分析のための詳細な情報を提供します。これは、レーザービームのアライメント、ばね定数とAFMプローブの偏向感度のキャリブレーション、および力曲線を取得するためのステップバイステップの手順が含まれています。また、データANALYための詳細なプロトコルを提供します力曲線のsisの。
概要
The biomechanical properties of arteries are a critical determinant in cardiovascular disease (CVD) and aging. Arterial stiffness, a major cholesterol independent risk factor and an indicator for the progression of CVD, increases with vascular injury, atherosclerosis, age, and diabetes1-8. Arterial wall stiffening is associated with increased dedifferentiation, migration, and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells9-12. In addition, increased arterial stiffness has been linked to enhanced macrophage adhesion1, endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration13, and vessel wall remodeling14,15. Thus, therapies that could prevent arterial stiffening in CVD or aging might complement currently available pharmacological interventions that treat CVD by reducing high blood cholesterol.
AFM is a powerful analytical tool used for various physical and biological applications. AFM is increasingly used to obtain the high-resolution images and characterize the biomechanical properties of soft biological samples such as tissues and cells1,2,10,16,17 with a great degree of accuracy at nanoscale levels. A major advantage of AFM is the fact that it can be used with living cells.
This paper describes our method for measuring the elastic modulus of mouse arteries ex vivo using AFM. The described method shows how we 1) properly isolate mouse arteries (descending aorta and aortic arch) and 2) measure the elastic modulus of these tissues by AFM. Measurements of unloaded elastic moduli in arteries can help to elucidate changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) that occur in response to vascular injury, CVD, and aging.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
プロトコル
この研究における動物の作業は、ペンシルバニア大学の施設内動物管理使用委員会によって承認されました。方法は承認されたガイドラインに従って行いました。
1.マウスと大動脈の分離の準備します
- 腹腔内に - (2ミリグラム/ kgの1) - ( - 100ミリグラム/ kgを80)、キシラジン(8に10mg / kg)およびアセプロマジンケタミンでマウスを麻酔。テールピンチテストで麻酔を確認してください。マウスが完全に麻酔された後、頚椎脱臼によりマウスを安楽死させます。
- その背中の上でマウスを置き、解剖ボードにマウスをピン。 70%(v / v)エタノールのワイプと腹部エリアを清掃してください。
- ミッドラインで皮膚をつまみ、腹部での中規模顕微はさみと小さな初期切開を行います。鉗子で皮膚を保持しながら、胸骨に腹部から皮膚や腹膜をカットする中規模の顕微はさみを使用しています。
- bのリブを切り取ります中規模顕微はさみとOTH側面。慎重に小型マイクロサージェリーのハサミで肺と肝臓を除去し、心臓および大動脈を残します。解剖顕微鏡にマウスや解剖ボードを転送します。
- 小さな鉗子で大動脈の周囲の脂肪をつかみ、慎重に大動脈の周りに脂肪を切り取るために、小さなはさみを使用しています。
- 優しく、鉗子で大動脈をつかむだけで腹部大動脈の上、上行大動脈と下行大動脈の終わりに別のカットの開始時に小型マイクロサージェリーハサミで1カットをします。
- (;カルシウムとマグネシウムを含まないPBS)1×リン酸緩衝生理食塩水を含む60-mmディッシュに解剖し、大動脈を転送します。
- 小型顕微はさみを使用して、大動脈から残りの脂肪組織を離れて解剖し続けます。縦方向に大動脈を開くには、小さなはさみを使用してください。
- 下行大動脈とaortiの小片(〜2×4 mm)をカットする小型顕微はさみを使用AFM分析用Cアーチ( 図1)。 60 mmのプラスチック皿に組織を置き、PBSのドロップに湿ったそれを保ちます。
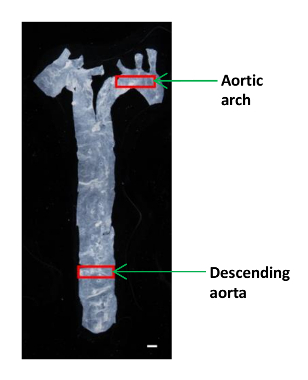
図1:マウスにおける異なる大動脈セグメントの位置を示す画像大動脈は、横隔膜に心臓から単離し、下行大動脈の小部分および大動脈弓は、弾性率を測定しました。スケールバー、1ミリメートル。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
AFM測定のための2の準備組織サンプル
- 慎重に大動脈に触れることなく、ラボワイプを使用してPBSを除去します。組織の管腔側が上を向いていることを必ず。
- 静かに追加することによってプレートに開かれた大動脈の各端部を接着 5る-ゲルローディングチップでシアノアクリレート接着剤を10μl( 図2)。
注:しっかりと各端部に組織を取り付けるために必要な接着剤の量は、経験的に決定されなければなりません。大動脈が、このプロセスの間に張られていないことが重要です。 - それが折り畳まれたり、フローティングされていないことを特定するために接着され、大動脈を確認してください。大動脈に接着剤を空気が乾燥した後(30から60秒)、静かにPBSを追加し、サンプルを沈めます。
注:準備AFM(手順3 - 5)は、組織を分析のために準備されている間に行うことができます。

図2:大動脈セグメントの漫画は、シアノアクリレート接着剤を使用して、60 mmの培養皿に接着シアノアクリレート接着剤は、AFM測定の準備のために大動脈試料のエッジに適用されています。コム/ファイル/ ftp_upload / 54630 / 54630fig2large.jpg "ターゲット=" _空白 ">この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
3.プローブのロード
- プローブ負荷スタンド上に流体プローブホルダをマウントします。
- ピンセットを使用して、球状の先端を有する窒化シリコンAFMプローブ(0.06 N / mのカンチレバー)をスライドさせ、プローブホルダに(我々は1μmの直径のSiO 2粒子を使用しているが、より大きなサイズを使用してもよいです)。 AFMプローブがしっかりとプローブホルダに固定されていることを確認します。
- AFMヘッドのZスキャナマウント上にプローブホルダーをスライドさせ、プローブホルダーがしっかり取り付けられていることを確認。
4.プローブにレーザーを揃えます
- AFMのソフトウェアを開きます。ソフトウェア上の実験のタイプを選択し、 実験のカテゴリーは、流体中にモードを問い合わせする流体と実験でモードを問い合わせするモード、 実験グループに連絡します。 ロードEXPをクリックしますソフトウェアでeriment。これは、レーザーがオンになります。
- 50 mmのガラスボトムディッシュに、蒸留水の3ミリリットルを追加し、レーザーアライメントユニットのステージに皿を置きます。このユニットは、カンチレバーの背面にレーザビームを集束するプロセスを簡素化します。
- レーザーアライメントユニットにレーザーアライメントユニットと電源の上に直立位置にAFMヘッドをマウントします。 AFMチップ上の液滴を形成するために、蒸留水約50μlを添加。
- ジョイスティックを使用して、AFMチップが皿内の水と接触するように、AFMヘッドを下げます。接触は、皿にAFMチップと水との間で行われていない場合は接触が行われるまで、静かに皿を上げます。 AFMチップは、アライメントユニットのLCD画面上の表示になっているので、ピント、明るさとXY位置を調整します。
- AFMヘッドのレーザー位置決めノブを調整することにより、AFMプローブの先端にレーザースポットの位置を調整します。 AFMヘッドに検出器の位置ノブを使用して、仮定を調整0と-1 Vの間の値まで、フォトダイオードのイオンは、垂直偏向のために得られ、〜0Vが水平偏向のために得られます。
- レーザー和信号が最大化されているかどうかを確認してください。必要であれば、繰り返しステップ4.5は、AFMチップ上のレーザビームと、最大の和信号を得るために、フォトダイオードの位置の位置を再調整します。
注:ステップ4.5を繰り返した場合でも最大の和信号を得るために、プローブホルダのAFMプローブを再配置する必要があるかもしれません。
5.偏向感度とAFMプローブのばね定数をキャリブレーション
- 鉗子で60 mmの培養皿上のスクラッチを行い、蒸留水で皿を埋めます。試料ホルダープレート上で培養皿を置きます。この場合、倒立顕微鏡の電動式XYスキャンステージ上に皿をマウントします。
- 撮像中に固定し、それを維持するために、プレートの上に磁気プレートホルダーを置きます。
- クリック AFMプローブは、皿に手を触れないようにするために、ほぼ最も高い位置にAFMヘッドを上に移動するためのソフトウェアのナビゲーションメニューの矢印「アップ」。
注:それはAFMチップを壊す回避し、この手順は非常に重要です。 - 顕微鏡ステージ上AFMヘッドを配置します。
- プレートの傷に集中する顕微鏡を使用してください。ジョイスティックを使用するか、ゆっくりと慎重にPBSにAFMプローブを下げるために、ナビゲーションメニューの「停止中」の矢印をクリックします。わずかプレート内のスクラッチの上に頭を置きます。
注:AFMヘッドの初期位置は、試料に近い場合、係合する時間が大幅に短縮されます。 - 係合前に、必要に応じて最大SUM信号を得るために、AFMチップおよびフォトダイオードの位置にレーザビームの位置を再調整します。
- セットアップメニューで変更プローブをクリックすることで、チップの種類を選択します。
- 20 nmのスキャンを1Hz〜0〜 サイズ 、 スキャンレート 、256 サンプル/ラインとたわみ設定値 : パラメータをチェックして 、パラメータを設定する]をクリックします。エンゲージクリックしてください。プローブは、プレートの表面に接触するまでエンゲージステータス]ウィンドウが開いたままになります。プローブに係合後、 ランプをクリックします。
- スキャンツールバーメニューの拡張モード ] をクリックし、パラメータを設定します。nmおよび1〜500μmの間にランプサイズ 、 ランプ・レート 2 Hzの、256 サンプル数 、 先端半径 500 nmまで、 サンプルポアソン比を0.5にすると、(材料を前提としてい測定することが20〜100nmの間に相対的とトリガしきい値を0にヒント半角 、 トリガーモード 、)完全に非圧縮性です。
- obtaにランプツールバーメニューで連続ランプをクリックしてくださいプレート( 図3A)に力曲線インチこのフォースカーブでは、 偏向エラーにチャンネル1を設定します。
注:これは、ソフトウェアがz位置対垂直偏向として結果をグラフ化することができます。- 力曲線の左または右の端でクリックして、力曲線( 図3A、破線の赤線)の線形領域を包含するようにカーソルをドラッグします。直線で収まるように、傾斜領域の境界をマークするために、これらの2行を使用します。
- ツールバーのランプを選択し、Update感度 ] をクリックします。値を記録し、この手順を4回繰り返します。ツールバーのキャリブレーションを選択し、[ 検出 ] をクリックします。入力偏向感度ボックス内の 5回の測定から平均値。
- AFMヘッドを上げるために3回- 2の撤回 ]をクリックします。このステップは、防止することが重要です熱チューニングプロセス中にAFMチップと基板の間の相互作用。ツールバーの熱チューンをクリックします。
- 長方形のカンチレバーのためのV字型カンチレバーのための1.144と1.106に100 kHzの(この情報はメーカーのカタログから取得することができる)と偏向感度補正 - サーマル 1のチューニング範囲を設定します 。
- 熱チューンメニューでは、熱同調曲線( 図3B)を取得するためにデータを取得する ]をクリックします。 AFMソフトウェアを使用して、場所の赤フィッティングのための境界を定義するために、グラフのエッジからでマウスをドラッグして( 図3(b)に示すように )曲線の両側に破線。 ローレンツ(空気)以上のデータをフィット応じたシンプルな高調波発振器(流体)モデルのいずれかを選択します。
- フィットデータは 、その後、 春Kを計算し、この値を保存]をクリックします。リバネ定数キャリブレーションを数回泥炭および平均値を使用します。数回の撤回 ]をクリックします。
- 顕微鏡ステージからAFMヘッドを外し、アライメントユニットの上に置きます。顕微鏡ステージから皿を取り出します。
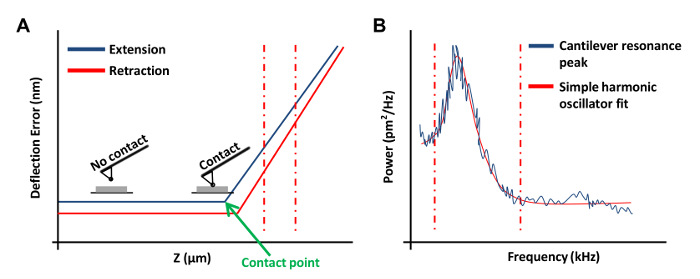
図3:AFMプローブのキャリブレーションに使用されるAFMフォースカーブ。 (A)代表的なAFM力曲線(検量線)。垂直方向の赤との間の力の曲線の延長部は、破線カンチレバー偏向感度を決定するために使用した。(B)は、以前に 20を説明したように、カンチレバーのバネ定数を計算するために使用される単純な調和振動子フィットグラフ。 ご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。この図の拡大版。
6。マウスの動脈ex vivoでの弾性率を測定します
- 顕微鏡ステージ上の大動脈組織を含む60 mmの培養皿を置き、磁気プレートホルダーにプレートを固定します。
- 顕微鏡ステージ上AFMヘッドを配置します。 AFMプローブは、大動脈と接触することなく、静かにPBSで接触し、メニスカスを形成していないことを確認してください。必要に応じて、アライメントユニットにAFMヘッドを配置し、クリックして接触を防止するのに十分な隙間があるまで撤退 、その後、顕微鏡ステージ上AFMヘッドを配置します。
- 移動をクリックします。ジョイスティックを使用して、または「停止中」の矢印をクリックすると、ゆっくりと大動脈の上にカンチレバーを配置するためにAFMプローブを下げます。必要に応じて、AFMヘッド上の検出器の位置決めノブを使用して、フォトダイオードの位置を調整します。
- カンチレバーは、大動脈との接触を行うことができるようにエンゲージクリックしてください。
- かつて大動脈が締結され、ピエゾセンターが安定していることを確認し、 ランプをクリックします。ピエゾ中心が変動している場合、これは偽の係合の結果であり得ます。プローブを撤回し、少しずつフォトダイオードにレーザーの垂直オフセットを増加させる(〜0.5 V)と再係合します。
- プローブが遠い試料表面上にある場合にも、手動近い試料表面にプローブを下げる再係合する前に。前の手順は、変動を排除していない場合は、プローブを交換してみてください。
- 3ミクロン、相対的にトリガモードと100 nmのトリガしきい値にランプのサイズを設定し、 ランプが連続 ]をクリックします。探針と試料との間の接触点がZランプ・サイクルの3/4下のほぼ中央で発生することを確認します。これは観察されない場合は、試料を必要に応じて、ランプのサイズを調整し、かつ再係合し、サンプルから外れます。
- メニューバーに顕微鏡をクリックし、[ 設定 ] をエンゲージ 。 SPMが 30μmに撤退変更します。ランプツールバーメニューのランプが連続 ]をクリックします。
- 力曲線を観察した後、メニューバーのキャプチャをクリックし、[ ファイル名をキャプチャします。エンディング「0.000」(これは追加のキャプチャしたファイルは、1により数が増加することができます)で、目的のファイル名を入力します。指定されたフォルダを選択して、データを保存します。
- 撮影ツールバー]メニューの[ キャプチャ ] をクリックします。 撤退した後、 移動します ]をクリックします。大動脈の他の領域の上にカンチレバーを配置するジョイスティックやソフトウェアのコントロールを使用します(次の当初測定点に、 図4を参照)。
- 、 ランプを エンゲージクリックして、それぞれ、 連続上昇します。力曲線を観察した後、[ 停止 ] をクリックします、次にキャプチャします。
- 6.10 - を繰り返して、6.9を繰り返します。 図 4に示すように、面積当たり少なくとも5回の測定をキャプチャ注:私たちは、典型的には15収集- 図4に示すように、それぞれ、各組織における5つの異なる場所- 3から25の力曲線を。
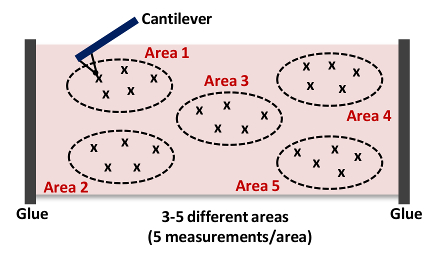
。図4:全体的の剛性を獲得するために、各動脈内- 5異なる場所(5エリア1 - ) - 3から25回カンチレバー組織へのアプローチとインデント(エリア1)の漫画のこのAFM測定は15まで繰り返します組織サンプル。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
7.データ解析
- オープンフォースカーブ解析ソフトウェア。
- Cl嫌な検索とメニューバーで開くと、ファイルをダブルクリックして、分析されます。
- 偏向感度、定数春、ヒント半径、ヒント半角とポアソン比を確認するには、ツールバーメニューの変更を強制パラメータをクリックします。パラメータを変更するには、その横にあるチェックボックスをオンにして、新しい値]列に正しい値を入力します。 [ 実行 ]をクリックします。
- 力曲線はノイズが多い場合は、 ボックスカーフィルタをクリックして、0 番目に3とフィルタの順序に、 平均ポイントを拡張する方向のための入力を設定します。データを平滑化するために実行をクリックします。
- メニューバーのベースラインの修正をクリックして、強制的に、 プロット・ユニットを拡張する方向の入力を設定し、分離するタイプ 、1 回目に是正命令とベースラインソースを拡張 拡張します。力曲線の平坦な部分を包含するように縦の点線の青い線を調整し、[ 実行 ]をクリックします。
- ツールバーメニューでインデントをクリックして、のようなフィット変数を扱うためにポイントベース、 コンタクトポイントアルゴリズムを問い合わせするように拡張され、 フィット法にアクティブカーブの入力を設定し、Noに粘着力 、 マックスフォースフィットバウンダリ 30%に、 ミン・フォースフィット境界にを含めますヘルツ(球面)に0%とモデルのフィット 。
注:我々の測定では、先端と試料(後退曲線のカンチレバーの陰性波)との間に有意な密着性はほとんど認められませんでした。このような付着が観察される場合には、適切なモデル(DMTまたはJKR)が分析18,19のために使用されるべきです。 - ヤング率の値を保存します。 3の各々のヤング(弾性)係数を分析- 図4に示すように、5つの領域(面積あたり5の力曲線)は、互いに短い距離以内に撮影されました。
注:、アーチファクトを除去分析からヤング率> 100キロパスカル(総測定値の正常〜10%)を除外するには。 - 3のそれぞれの平均ヤング率の値を計算 - (測定された)5つの領域を、全体として大動脈の平均弾性率を計算するためにこれらの値を使用します。
注:少なくとも3、より多くの場合、4から6個々の大動脈は、動脈硬化の正確な評価を得るために使用されます。最終結果は、「n」個の独立した実験の平均±SEMとしてプロットされています。必要な大動脈の正確な数は、当然のことながら、要求される精度のレベルに依存します。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
結果
図5Aは、6ヶ月齢、雄のC57BL / 6マウスから降順(胸部)大動脈の位相コントラスト画像を示しています。 AFMカンチレバーは、直接組織上記の場所にあり、インデントのための準備ができました。 図5Bおよび5Cは、コンタクトモードでのAFMインデントによって得られた代表的な力曲線を示しています。 図5B及び図5Cに示す緑色の...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
ディスカッション
AFMのインデントは、細胞および組織の剛性(弾性率)を特徴付けるために使用することができます。本稿では、マウスで下行大動脈および大動脈弓を隔離し、これらの動脈領域のex vivoでの弾性係数を決定するための詳細なステップバイステップのプロトコルを提供します。私たちは今、要約し、この論文に記載された方法の技術的な問題と制限事項について説明します。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
開示事項
The authors have nothing to disclose.
謝辞
AFM analysis was performed on instrumentation supported by the Pennsylvania Muscle Institute and the Institute for Translational Medicine and Therapeutics, Perelman School of Medicine, the University of Pennsylvania. This work was supported by NIH grants HL62250 and AG047373. YHB was supported by post-doctoral fellowship from the American Heart Association.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| BioScope Catalyst AFM system | Bruker | ||
| Nikon Eclipse TE 200 inverted microscope | Nikon Instruments | ||
| Silicon nitride AFM probe | Novascan Technologies | PT.SI02.SN.1 | 0.06 N/m cantilever; 1 µm SiO2 particle |
| Dumont #5 forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11251-10 | See section 1.4 |
| Dumont #5SF forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11252-00 | See section 1.8 |
| Fine Scissors-ToughCut | Fine Science Tools | 14058-11 | See section 1.4 (medium sized) |
| Vannas-Tübingen spring scissors | Fine Science Tools | 15008-08 | See section 1.6 (small sized) |
| 60 mm TC-treated cell culture dish | Corning | 353004 | |
| Dulbecco's Phosphate-Buffered Saline, 1x | Corning | 21-031-CM | Without calcium and magnesium |
| Krazy Glue instant all purpose liquid | Krazy Glue | KG58548R | See section 2.2 |
| Gel-loading tips, 1 - 200 µl | Fisher | 02-707-139 | See section 2.2 |
| Tip Tweezers | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 78092-CP | See section 3.2 |
| 50-mm, clear wall glass bottom dishes | TED PELLA | 14027-20 | See section 4.4 |
参考文献
- Kothapalli, D., et al. Cardiovascular Protection by ApoE and ApoE-HDL Linked to Suppression of ECM Gene Expression and Arterial Stiffening. Cell Rep. 2, 1259-1271 (2012).
- Liu, S. -L., et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-12 is an essential mediator of acute and chronic arterial stiffening. Sci Rep. 5, 17189(2015).
- Lakatta, E. G. Central arterial aging and the epidemic of systolic hypertension and atherosclerosis. J Am Soc Hypertens. 1, 302-340 (2007).
- Stehouwer, C. D. A., Henry, R. M. A., Ferreira, I. Arterial stiffness in diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: a pathway to cardiovascular disease. Diabetologia. 51, 527-539 (2008).
- Steppan, J., Barodka, V., Berkowitz, D. E., Nyhan, D. Vascular Stiffness and Increased Pulse Pressure in the Aging Cardiovascular System. Cardiol Res Pract. 2011, 263585(2011).
- Duprez, D. A., Cohn, J. N. Arterial stiffness as a risk factor for coronary atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 9, 139-144 (2007).
- Mitchell, G. F., et al. Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Events: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 121, 505-511 (2010).
- Sutton-Tyrrell, K., et al. Elevated Aortic Pulse Wave Velocity, a Marker of Arterial Stiffness, Predicts Cardiovascular Events in Well-Functioning Older Adults. Circulation. 111, 3384-3390 (2005).
- Klein, E. A., et al. Cell-Cycle Control by Physiological Matrix Elasticity and In Vivo Tissue Stiffening. Curr Biol. 19, 1511-1518 (2009).
- Bae, Y. H., et al. A FAK-Cas-Rac-lamellipodin signaling module transduces extracellular matrix stiffness into mechanosensitive cell cycling. Sci signal. 7, ra57(2014).
- Thyberg, J., Hedin, U., Sjölund, M., Palmberg, L., Bottger, B. A. Regulation of differentiated properties and proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 10, 966-990 (1990).
- Owens, G. K., Kumar, M. S., Wamhoff, B. R. Molecular Regulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation in Development and Disease. Physiol Rev. 84, 767-801 (2004).
- Huynh, J., et al. Age-Related Intimal Stiffening Enhances Endothelial Permeability and Leukocyte Transmigration. Sci Transl Med. 3, 112ra122(2011).
- Safar, M. E., Levy, B. I., Struijker-Boudier, H. Current Perspectives on Arterial Stiffness and Pulse Pressure in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation. 107, 2864-2869 (2003).
- Raffetto, J. D., Khalil, R. A. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 75, 346-359 (2008).
- Muller, D. J., Dufrene, Y. F. Atomic force microscopy as a multifunctional molecular toolbox in nanobiotechnology. Nat Nanotechnol. 3, 261-269 (2008).
- Hsu, B. Y., Bae, Y. H., Mui, K. L., Liu, S. -L., Assoian, R. K. Apolipoprotein E3 Inhibits Rho to Regulate the Mechanosensitive Expression of Cox2. PLoS ONE. 10, e0128974(2015).
- Johnson, K. L., Kendall, K., Roberts, A. D. Surface Energy and the Contact of Elastic Solids. Proc R Soc Lond A. 324, 301-313 (1971).
- Derjaguin, B. V., Muller, V. M., Toporov, Y. P. Effect of contact deformations on the adhesion of particles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 53, 314-326 (1975).
- Hutter, J. L., Bechhoefer, J. Calibration of atomic-force microscope tips. Rev Sci Instrum. 64, 1868-1873 (1993).
- Pries, A. R., Secomb, T. W., Gaehtgens, P. The endothelial surface layer. Pflugers Arch EJP. 440, 653-666 (2000).
- Pogoda, K., et al. Depth-sensing analysis of cytoskeleton organization based on AFM data. Eur Biophys J. 41, 79-87 (2012).
- Mendez, M. G., Restle, D., Janmey, P. A. Vimentin Enhances Cell Elastic Behavior and Protects against Compressive Stress. Biophys J. 107, 314-323 (2014).
- Moreno-Flores, S., Benitez, R., Md Vivanco,, Toca-Herrera, J. L. Stress relaxation and creep on living cells with the atomic force microscope: a means to calculate elastic moduli and viscosities of cell components. Nanotechnology. 21, 445101(2010).
- Darling, E. M., Topel, M., Zauscher, S., Vail, T. P., Guilak, F. Viscoelastic properties of human mesenchymally-derived stem cells and primary osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes. J Biomech. 41, 454-464 (2008).
- Dimitriadis, E. K., Horkay, F., Maresca, J., Kachar, B., Chadwick, R. S. Determination of Elastic Moduli of Thin Layers of Soft Material Using the Atomic Force Microscope. Biophys J. 82, 2798-2810 (2002).
- Mahaffy, R. E., Shih, C. K., MacKintosh, F. C., Käs, J. Scanning Probe-Based Frequency-Dependent Microrheology of Polymer Gels and Biological Cells. Phys Rev Lett. 85, 880-883 (2000).
- Amin, M., Le, V. P., Wagenseil, J. E. Mechanical Testing of Mouse Carotid Arteries: from Newborn to Adult. J Vis Exp. , e3733(2012).
- Laurent, S., et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J. 27, 2588-2605 (2006).
- Plodinec, M., et al. The nanomechanical signature of breast cancer. Nat Nano. 7, 757-765 (2012).
- Raman, A., et al. Mapping nanomechanical properties of live cells using multi-harmonic atomic force microscopy. Nat Nano. 6, 809-814 (2011).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved