需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Methods Article
志贺氏菌上皮细胞感染分析
摘要
本方案描述了使用体外上皮细胞系询问志贺氏菌粘附、侵袭和细胞内复制的感染测定。
摘要
人类适应的肠道细菌病原体志贺氏菌每年引起数百万例感染,在儿科患者中产生长期生长效应,并且是全球腹泻死亡的主要原因。由于病原体通过胃肠道并感染结肠内壁的上皮细胞,感染会引起水样或血性腹泻。随着抗生素耐药性的惊人增加和目前缺乏批准的疫苗,标准化的研究方案对于研究这种可怕的病原体至关重要。在这里,提出了使用结肠上皮细胞中细菌粘附、侵袭和细胞内复制的体外分析来检查志贺氏菌分子发病机制的方法。在感染分析之前,志贺氏菌菌落的毒力表型通过在琼脂平板上摄取刚果红染料来验证。在细菌培养过程中,也可以考虑使用补充的实验室培养基来模拟体内条件。然后,在标准化方案中使用细菌细胞,以已建立的感染多重感染感染组织培养板中的结肠上皮细胞,并适应分析感染的每个阶段。对于依从性测定,志贺氏菌细胞与降低的培养基水平一起孵育,以促进细菌与上皮细胞的接触。对于侵袭和细胞内复制测定,庆大霉素应用于不同的时间间隔,以消除细胞外细菌并能够评估侵袭和/或细胞内复制速率的定量。所有感染方案都通过连续稀释受感染的上皮细胞裂解物并相对于感染滴度在刚果红琼脂平板上铺板细菌集落形成单位来枚举贴壁、侵袭和/或细胞内细菌。总之,这些方案能够对上皮细胞志贺氏菌感染的每个阶段进行独立的表征和比较,以成功研究这种病原体。
引言
由肠道细菌病原体引起的腹泻病是全球卫生的重大负担。2016 年,腹泻病导致全球 130 万人死亡,是 5 岁以下儿童的第四大死因 1,2。革兰氏阴性肠道细菌病原体志贺氏菌是志贺氏菌病的病原体,志贺氏菌病是全球腹泻死亡的主要原因3。志贺菌病每年在低收入和中等收入国家的儿童中造成严重的发病率和死亡率4,5,而高收入国家的感染与日托中心、食源性和水源性疫情有关6,7,8,9。无效的疫苗开发10和抗微生物药物耐药性(AMR)11,12的上升使大规模志贺氏菌疫情的管理变得复杂。美国疾病控制与预防中心最近的数据显示,2020 年美国近 46% 的志贺氏菌感染表现出耐药性13,14,而世界卫生组织已宣布志贺氏菌为 AMR 优先病原体,迫切需要新疗法15。
志贺氏菌感染在摄入受污染的食物或水后,或通过直接与人接触,很容易通过粪口途径传播。志贺氏菌已进化为一种有效的、适应人类的病原体,其感染剂量为 10-100 种细菌,足以引起疾病16。在小肠转运过程中,志贺氏菌暴露于环境信号,例如高温和胆汁17。检测这些信号可诱导转录变化以表达毒力因子,从而增强细菌感染人结肠的能力 17,18,19。志贺氏菌不会从顶端表面侵入结肠上皮,而是在被滤泡相关上皮细胞内特化的抗原呈递微折叠细胞(M 细胞)摄取后穿过上皮层20、21、22。转胞吞作用后,志贺氏菌细胞被驻留巨噬细胞吞噬。志贺氏菌迅速逃离吞噬体并触发巨噬细胞死亡,导致促炎细胞因子的释放 5,23,24。然后志贺氏菌从基底外侧侵入结肠上皮细胞,裂解巨细胞液泡,并在细胞质中建立复制生态位 5,25。促炎细胞因子,特别是白细胞介素-8 (IL-8),将多形核中性粒细胞白细胞 (PMN) 募集到感染部位,从而削弱上皮紧密连接,并使细菌浸润上皮内膜以加剧基底外侧感染5。PMN 破坏受感染的上皮内膜以控制感染,从而导致细菌性(血性)痢疾的特征性症状5。尽管侵袭和细胞内复制机制已被彻底表征,但新的研究正在证明志贺氏菌感染的重要新概念,包括胃肠道 (GI) 转运期间的毒力调节17、依从性19、通过屏障通透性改善基底外侧通路26 和营养不良儿童的无症状携带27。
志贺氏菌属引起腹泻病的能力仅限于人类和非人灵长类动物 (NHP)28。已经为斑马鱼29、小鼠30、豚鼠31、兔子21、32、33 和猪34、35 开发了志贺氏菌肠道感染模型。然而,这些模型系统都不能准确复制人类感染期间观察到的疾病特征36。尽管已经建立了志贺氏菌病的非人灵长类模型来研究志贺氏菌的发病机制,但这些模型系统的实施成本高昂,并且需要人为的高感染剂量,比人类的感染剂量高出9个数量级37,38,39,40,41,42。因此,志贺氏菌对人类宿主感染的显着适应需要使用人源性细胞培养物来重建生理相关模型,以准确询问志贺氏菌的发病机制。
在这里,描述了详细的程序,以测量 志贺氏菌 对 HT-29 结肠上皮细胞的粘附、侵袭和复制率。使用这些标准化方案,可以研究细菌毒力基因和环境信号影响 志贺氏菌 感染每一步的分子机制,以更好地了解动态宿主-病原体相互作用关系。
研究方案
1.试剂和材料的制备
注意:所有体积均与使用两个 6 孔板的测定一致。
- TSB 培养基:将 0.5 L 去离子 (DI) 水加入 15 g 胰蛋白酶大豆肉汤(TSB,参见 材料表)培养基和高压灭菌器中。在室温下储存。
- 胆汁盐培养基(TSB + BS):要制备含有0.4%(w/v)胆汁盐的TSB,将0.06g胆盐(BS,参见 材料表)重悬于15mL高压灭菌的TSB中。使用0.22μmPES过滤器过滤灭菌。
注意:胆汁盐由胆酸钠和脱氧胆酸钠的 1:1 混合物组成。使用前立即准备新鲜培养基。 - DMEM + 10% (v/v) FBS:将 5 mL 胎牛血清 (FBS) 加入 45 mL Dulbecco 改良 Eagle 培养基 (DMEM) 中。储存在4°C。
- DMEM + 庆大霉素:向 50 mL 试管中加入 50 mL DMEM 和 50 μL 50 mg/mL 庆大霉素(参见 材料表)。
注意:在每次实验之前,将新鲜等分试样在37°C水浴中加热。 - PBS + 1% (v/v) Triton X-100:将 150 μL Triton X-100 加入 15 mL 磷酸盐缓冲盐水 (PBS) 中。
注意:在每次实验之前,将新鲜等分试样在37°C水浴中加热。 - TSB + 刚果红指示板:在 1 L 瓶中加入 15 g TSB、7.5 g 精选琼脂和 0.125 g 刚果红染料(见 材料表)。加入 0.5 L 去离子水并高压灭菌。将 10-20 mL 培养基倒入单独的无菌培养皿 (100 mm x 15 mm) 中并使其凝固。
注意:刚果红是致癌的,是一种生殖毒素。确保使用适当的个人防护设备处理刚果红。有关更多信息,请参阅产品安全数据表。
注意:大约 20 块板由 0.5 升刚果红色介质制成。板可以提前 2-3 天准备好,并在室温下倒置直至使用。为了长期储存,将倒置的板放在4°C的塑料套管中长达3个月。 - DMEM + 10% (v/v) FBS 和 5% (v/v) 二甲基亚砜 (DMSO):将 42.5 mL DMEM、5 mL FBS 和 2.5 mL DMSO 加入 50 mL 试管中。储存在4°C。
2.细菌的制备
注意:所有志贺氏菌实验室培养和储存方案均改编自Payne, S. M.43。
注意: 志贺氏菌 属是风险组 2 病原体44。在 BSL-2 环境中进行所有实验室工作,并采取额外的安全措施,以限制由于 志贺氏菌 属感染剂量低而导致的意外暴露。
- 志 贺氏菌 从冷冻库存中生长
- 使用无菌施药器将少量冷冻培养物从低温小瓶转移到TSB + Congo红琼脂平板中。
- 对接种环进行火焰灭菌并使其冷却。在平板的一个象限上来回划线接种物。点燃环,让它冷却,然后从第一象限划到板的第二象限。重复上述步骤,将接种物划入平板的第三和第四象限。
注意:或者,在每个象限之间使用新鲜的无菌施药器进行条纹接种。 - 将板倒置并在37°C下孵育过夜。
注意:需要在温度≥37°C下孵育,以表达观察刚果红阳性(CR+)表型45所必需的志贺氏菌毒力因子。无毒菌落将具有白色外观,不会具有侵入性。 - 用石蜡膜密封板,并在4°C下冷藏。
注意:细菌菌落将在琼脂平板上保持活力 1-2 周。
- 志贺氏菌在液体培养物中的过夜生长
- 将 3 mL TSB 培养基等分装到无菌的 14 mL 培养管中。
- 使用无菌施药器挑选一个分离良好的红色 (CR+) 菌落,并重悬于液体培养基中。
- 将培养物在37°C下孵育过夜(16-18小时),以每分钟250转(rpm)振荡。
3. HT-29真核细胞的制备
注意:所有体积均与使用两个 6 孔板的测定一致。HT-29 细胞系购自 American Type Culture Collection (ATCC)。HT-29 维护协议改编自 ATCC建议 46。所有培养基在使用前应在37°C的水浴中预热。所有HT-29维护方案都应在生物安全柜中执行。在培养基中混合/处理 HT-29 细胞时避免产生气泡,以避免 pH 值发生剧烈变化。
- 从冷冻原液中解冻HT-29细胞
- 在37°C水浴中解冻HT-29细胞小瓶。
注意: 确保盖子完全保持在水面上方以避免污染。解冻时间应少于 2 分钟。 - 培养物完全解冻后立即将小瓶从水中取出,并用70%乙醇去污。确保从这一点开始的所有步骤都使用无菌技术执行。
- 将小瓶的所有内容物加入含有 9 mL DMEM + 10% FBS 的 15 mL 离心管中。在室温下以125× g 离心5分钟。
- 将上清液倒入废物容器中,并将沉淀重悬于10mL温热的DMEM + 10%FBS中。将重悬细胞转移到含有 10 mL 温热 DMEM + 10% FBS(总体积为 20 mL)的 75 cm2 组织培养瓶 (T75) 中。
- 在37°C下用5%CO2 孵育细胞,直到细胞达到90%汇合度(约6-7天)。
注意:汇合度是通过视觉近似来估计的。
- 在37°C水浴中解冻HT-29细胞小瓶。
- 接种 HT-29 细胞
- 在 37 °C 水浴中预热 20 mL PBS 和 50 mL DMEM + 10% FBS,并将 3 mL 0.25% (w/v) 胰蛋白酶-EDTA 预热至室温。
- 一旦HT-29细胞(从步骤3.1开始)达到90%的汇合度,将T75烧瓶中的HT-29细胞培养基倒入废物容器中。将 ~10 mL 温热的 PBS 倒入烧瓶中,轻轻旋转进行清洗。将PBS倒入废物容器中。再次用温热的PBS清洗并倒出。
- 加入 2-3 mL 0.25% (w/v) 胰蛋白酶-EDTA,并在整个表面积上轻轻旋转。在37°C与5%CO2 孵育4分钟。
- 从培养箱中取出烧瓶,轻轻旋转胰蛋白酶-EDTA,目视确保所有细胞从表面分离。
- 立即加入 6 mL 温热 DMEM + 10% FBS 以灭活胰蛋白酶。上下移液以充分混合。
- 将所有内容物转移到 15 mL 离心管中,并在室温下以 500 x g 旋转 5 分钟。
- 将上清液轻轻倒入废容器中,并将沉淀重悬于6mL温热的DMEM + 10%FBS中。
- 重悬后,立即将 10 μL 悬浮的 HT-29 细胞从培养物中间转移到 0.2 mL PCR 管中。向PCR管中加入10μL台盼蓝染料并混合。
- 将 10 μL HT-29 细胞/台盼蓝混合物加入一次性 Countess 细胞计数器室载玻片中(参见 材料表)。枚举活细胞的数量并计算细胞活力。
注意:记录样品中的细胞数时,请读取"活"细胞计数下的数字,而不是总细胞计数。或者,可以使用血细胞计数器手动进行细胞计数。 - 将 HT-29 细胞重悬于新鲜的 T75 烧瓶或 6 孔板中。
- 对于 T75 烧瓶:
- 轻轻移液混合,然后根据以下公式将 2.5 x 106 个细胞转移到新鲜的 T75 烧瓶中:
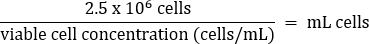
- 加入温 DMEM + 10% FBS 培养基至终体积为 20 mL(终浓度为 1.25 x 105 个细胞/mL)。
- 通过轻轻来回摇晃,将细胞均匀地分散在烧瓶中。
- 在37°C与5%CO2 孵育,直到细胞达到80%汇合度。
注意:为了获得最佳生长,每 ~3 天更换一次 T75 烧瓶中的 DMEM + 10% FBS 培养基。将培养基倒入废容器中,并向烧瓶中加入 10 mL 温热的 PBS。轻轻旋转 PBS 并将其倒入废物容器中。然后向烧瓶中加入 20 mL 新鲜、温暖的 DMEM + 10% FBS,并返回 37 °C、5% CO2 培养箱。
- 轻轻移液混合,然后根据以下公式将 2.5 x 106 个细胞转移到新鲜的 T75 烧瓶中:
- 对于 6 孔板:
- 轻轻移液混合,然后根据以下公式将 5.85 x 106 个细胞转移到新鲜的 50 mL 锥形管中:
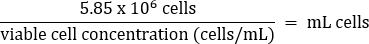
- 加入温 DMEM + 10% FBS 培养基至终体积为 26 mL(终浓度为 2.25 x 105 个细胞/mL)。
- 轻轻移液混合,然后将 2 mL(4.5 x 105 个细胞)分配到 6 孔板的单个孔中。
- 通过轻轻上下和左右摇晃 2-3 次,将细胞均匀地分散在孔中。
- 在37°C与5%CO2 一起孵育,直到细胞达到80%-95%汇合度(约3-4天)。
注意:侵袭和细胞内复制测定建议使用 85% 汇合度,而依从性测定建议汇合度为 90%-95%。孵育 48 小时后,细胞应达到 ~85% 汇合度,终浓度约为 1 x 106 个细胞/孔。可能需要调整接种的细胞数量和孵育时间。
- 轻轻移液混合,然后根据以下公式将 5.85 x 106 个细胞转移到新鲜的 50 mL 锥形管中:
- 对于 T75 烧瓶:
- 制作冷冻 HT-29 原料
- 将 1 mL DMEM + 10% FBS + 5% DMSO 培养基等分到单个低温样品瓶中。
- 将步骤 3.2.7 中的 1 x 106 HT-29 细胞添加到每个小瓶中。根据以下公式计算细胞的体积:
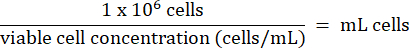
- 将HT-29电池长期储存在-130°C以下的液氮蒸气储存冰箱中。
4.依从性测定
注意:所有体积均与使用两个 6 孔板的测定一致。
- 通过1:50稀释到新鲜培养基中对志贺氏菌过夜培养。
- 涡旋,然后在适当大小的培养管中加入 100 μL 每个过夜培养物到 5 mL 新鲜 TSB 或 TSB + BS 中。
注意:将培养体积限制在培养瓶或试管体积的 <20%,以确保适当的曝气。 - 在37°C下以250rpm振荡孵育,直到细胞达到0.7的光密度(OD600)( 志贺氏菌 生长的中期对数阶段);约2-2.5小时。
注意:在传代培养期间,将50mL DMEM和足够体积的PBS等分用于所有洗涤步骤,并置于37°C水浴中。使用前让培养基达到37°C。
- 涡旋,然后在适当大小的培养管中加入 100 μL 每个过夜培养物到 5 mL 新鲜 TSB 或 TSB + BS 中。
- 将 2 x 108 个菌落形成单位 (CFU) 传代培养 的志贺氏菌 转移到单个 2 mL 微量离心管中。
注意:2 x 108 CFU 对应于 OD600 为 0.7 时约 1 mL 细菌细胞。使用 OD600 读数根据每个分光光度计的校准来近似 CFU/mL。 - 用PBS洗涤每个 志贺氏菌 样品2次。
- 通过在室温下以 17,000 x g 离心 2 分钟来沉淀细胞。吸出上清液,然后加入 1 mL 温热的 PBS 并重悬沉淀,轻轻上下移液,直到混合物完全均匀 (8-10x)。
- 重复步骤 4.3.1 1 次。
- 通过在室温下以 17,000 x g 离心 2 分钟来沉淀细胞,吸出上清液,并将沉淀重悬于 2 mL 温热的 DMEM 中。
注意:重悬细菌的最终浓度为 1 x 108 CFU/mL。
- 涡旋,然后向6孔板中制备的HT-29结肠上皮单层的每个孔中加入1mL(1×108CFU )重悬 志贺氏菌 (从步骤3.2.10.2开始)。
注意:感染通常在感染的多重性(MOI;细菌与上皮细胞的比率)为100时进行。为了测试不同的 MOI,在温 DMEM 中将重悬 志贺氏菌 稀释至所需浓度,然后将 1 mL 稀释的细菌加入 HT-29 单层。例如,要测试 MOI 为 10,将 150 μL 1 x 108 CFU/mL 细菌加入 1.35 mL 温 DMEM 中以 1:10 稀释细菌,然后将 1 mL(1 x 107 CFU)应用于 HT-29 细胞。 - 将6孔板在37°C与5%CO2 孵育3小时。
- 在孵育期间,确定细菌感染滴度。
- 将重悬 志贺氏菌 细胞(从步骤4.3.3开始)的10倍连续稀释液制备到PBS中。
- 将100μL的1×10-5 和1×10-6 稀释液培养到TSB + Congo红板上,并在37°C下孵育过夜。
注:从 1 x 10-5 和 1 x 10-6 稀释液中接种 100 μL 分别对应于 1 x 10-6 和 1 x 10-7 的最终稀释因子。
- 孵育后,用PBS洗涤单层4-5x。
- 从每个孔中抽吸培养基。
注意:从 6 孔板吸出培养基时,将吸气器的尖端沿着孔的底部引导,尽量避免与 HT-29 细胞接触。 - 向每个孔中加入 1 mL 温热的 PBS 并轻轻洗涤。
注意:要用 PBS 轻轻洗涤 6 孔单层,请在工作台上上下左右移动板。以圆周运动清洗板和/或从工作台表面取下板会导致从塑料上机械去除细胞。 - 重复步骤 4.7.1 和 4.7.2 4 次。
- 从每个孔中抽吸培养基。
- 通过抽吸除除 PBS,并通过向每个孔中加入 1 mL PBS + 1% Triton X-100 来裂解 HT-29 细胞。
- 将6孔板在37°C孵育5分钟。
- 使用细胞刮刀或弯曲的移液器吸头从孔底部刮取裂解的细胞,并将完整的 1 mL 转移到新鲜的 1.7 mL 微量离心管中。
- 确定细胞相关细菌的数量。
- 涡旋每个试管(从步骤4.10开始)至少30秒,以进一步从裂解的真核细胞中置换 志贺氏菌 。
- 将裂解物的10倍连续稀释液稀释到PBS中。
- 将 100 μL 的 1 x 10-2、1 x 10-3 和 1 x 10-4 稀释液培养到 TSB + Congo 红板上,并在 37 °C 下孵育过夜。
注:从 1 x 10-2、1 x 10-3 和 1 x 10-4 稀释液中接种 100 μL 分别对应于 1 x 10-3、1 x 10-4 和 1 x 10-5 的最终稀释因子。
5. 侵袭试验
注意:所有体积均与使用两个 6 孔板的测定一致。
- 通过1:50稀释到新鲜培养基中对志贺氏菌过夜培养。
- 涡旋,然后在适当大小的培养管中加入 100 μL 每个过夜培养物到 5 mL 新鲜 TSB 或 TSB + BS 中。
注意:将培养体积限制在培养瓶或试管体积的 <20%,以确保适当的曝气。 - 在37°C下孵育,以250rpm振荡,直到细胞达到0.7的OD600 ( 志贺氏菌 生长的中期对数期);约2-2.5小时。
注意:在传代培养期间,将50mL DMEM + 50mg / mL庆大霉素和足够体积的PBS等分用于所有洗涤步骤,并置于37°C水浴中。使用前让培养基达到37°C。
- 涡旋,然后在适当大小的培养管中加入 100 μL 每个过夜培养物到 5 mL 新鲜 TSB 或 TSB + BS 中。
- 将 2 x 108 CFU 传代培养 的志贺氏菌 转移到单独的 2 mL 微量离心管中。
注意:2 x 108 CFU 对应于 OD600 为 0.7 时约 1 mL 细菌细胞。使用 OD600 读数根据每个分光光度计的校准来近似 CFU/mL。 - 用PBS洗涤 志贺氏菌 样品1x。
- 通过在室温下以 17,000 x g 离心 2 分钟来沉淀细胞。吸出上清液,然后加入 1 mL 温热的 PBS 并重悬沉淀,轻轻上下移液,直到混合物完全均匀 (8-10x)。
- 重复步骤 5.3.1。1 倍额外时间。
- 通过在室温下以 17,000 x g 离心 2 分钟来沉淀细胞,吸出上清液,并将沉淀重悬于 2 mL 温热的 DMEM 中。
注意:重悬细菌的最终浓度为 1 x 108 CFU/mL。
- 涡旋,然后向 6 孔板中制备的 HT-29 结肠上皮单层的每个孔中加入 1 mL (1 x 108 CFU) 重悬 志贺氏菌 和 1 mL DMEM(从步骤 3.2.10.2 开始)。
注意:感染通常在感染的多重性(MOI;细菌与上皮细胞的比率)为100时进行。为了测试不同的MOI,在DMEM中将重悬 志贺氏菌 稀释至所需浓度,然后向HT-29单层中加入1mL稀释细菌。例如,要测试 MOI 为 10,将 150 μL 的 1 x 108 CFU/mL 细菌加入 1.35 mL DMEM 中,然后向 HT-29 细胞中加入 1 mL(1 x 107 CFU),以 1:10 的比例稀释细菌。 - 为了促进细菌与HT-29细胞的接触,在室温下以2,000× g 离心6孔板10分钟,如果温度设置可以调节,则为37°C。
注意:离心促进细菌与HT-29细胞的接触,从而绕过了对粘附因子的需求,并允许细菌快速侵入细胞。 - 在37°C下用5%CO2 孵育6孔板45分钟。
- 在孵育期间,确定细菌感染滴度。
- 将重悬 的志贺氏菌 细胞(从步骤5.3.3开始)的10倍连续稀释液制备到PBS中。
- 将100μL的1×10-5 和1×10-6 稀释液培养到TSB + Congo红板上,并在37°C下孵育过夜。
注:从 1 x 10-5 和 1 x 10-6 稀释液中接种 100 μL 分别对应于 1 x 10-6 和 1 x 10-7 的最终稀释因子。
- 用 1 mL PBS 彻底洗涤受感染的 HT-29 细胞 3 次。
- 从每个孔中抽吸培养基。
注意:从 6 孔板吸出培养基时,将吸气器的尖端沿着孔的底部引导,尽量避免与 HT-29 细胞接触。 - 向每个孔中加入 1 mL 温热的 PBS 并轻轻洗涤。
注意:要用 PBS 轻轻洗涤 6 孔单层,请在工作台上上下左右移动板。以圆周运动清洗板和/或从工作台表面取下板会导致从塑料上机械去除细胞。 - 重复步骤 5.8.1 和 5.8.2 2 次。
- 从每个孔中抽吸培养基。
- 通过抽吸除除PBS,然后向每个孔中加入2mL补充有50μg/ mL庆大霉素的温DMEM,并在37°C下用5%CO2孵育30分钟。
- 用 1 mL PBS 彻底洗涤受感染的 HT-29 细胞 3 次。
- 重复洗涤步骤5.8。
- 通过抽吸除除PBS,然后向每个孔中加入2mL补充有50μg/ mL庆大霉素的温DMEM,并在37°C下用5%CO2孵育60分钟。
- 用 1 mL PBS 彻底洗涤受感染的 HT-29 细胞 3 次。
- 重复洗涤步骤5.8。
- 通过抽吸除除 PBS,并通过向每个孔中加入 1 mL PBS + 1% Triton X-100 来裂解 HT-29 细胞。
- 将6孔板在37°C孵育5分钟。
- 使用细胞刮刀或弯曲的移液器吸头从孔底部刮取裂解的细胞,并将完整的 1 mL 转移到新鲜的 1.7 mL 微量离心管中。
- 确定细胞内细菌的数量。
- 涡旋每个试管(从步骤5.15开始)至少30秒,以进一步从裂解的真核细胞中置换 志贺氏菌 。
- 将裂解物的10倍连续稀释液稀释到PBS中。
- 将100μL的1×10-2 和1×10-3 稀释液培养到TSB + Congo红板上,并在37°C下孵育过夜。
注:从 1 x 10-2 和 1 x 10-3 稀释液中接种 100 μL 分别对应于 1 x 10-3 和 1 x 10-4 的最终稀释因子。
6. 细胞内复制试验
注意:所有体积均与使用两个 6 孔板的测定一致。
- 通过1:50稀释到新鲜培养基中对志贺氏菌过夜培养。
- 涡旋,然后在适当大小的培养管中加入 100 μL 每个过夜培养物到 5 mL 新鲜 TSB 或 TSB + BS 中。
注意:将培养体积限制在培养瓶或试管体积的 <20%,以确保适当的曝气。 - 在37°C下孵育,以250rpm振荡,直到细胞达到0.7的OD600 ( 志贺氏菌 生长的中期对数期);约2-2.5小时。
注意:在传代培养期间,将50mL DMEM + 50mg / mL庆大霉素和足够体积的PBS等分用于所有洗涤步骤,并置于37°C水浴中。使用前让培养基达到37°C。
- 涡旋,然后在适当大小的培养管中加入 100 μL 每个过夜培养物到 5 mL 新鲜 TSB 或 TSB + BS 中。
- 将 2 x 108 CFU 传代培养 的志贺氏菌 转移到单独的 2 mL 微量离心管中。
注意:2 x 108 CFU 对应于 OD600 为 0.7 时约 1 mL 细菌细胞。使用 OD600 读数根据每个分光光度计的校准来近似 CFU/mL。 - 用PBS洗涤 志贺氏菌 样品1x。
- 通过在室温下以 17,000 x g 离心 2 分钟来沉淀细胞。吸出上清液,然后加入 1 mL 温热的 PBS 并重悬沉淀,轻轻上下移液,直到混合物完全均匀 (8-10x)。
- 重复步骤 6.3.1。1 倍额外时间。
- 通过在室温下以 17,000 x g 离心 2 分钟来沉淀细胞,吸出上清液,并将沉淀重悬于 2 mL 温热的 DMEM 中。
注意:重悬细菌的最终浓度为 1 x 108 CFU/mL。
- 涡旋,然后向6孔板中制备的HT-29结肠上皮单层的每个孔中加入1mL(1×108 CFU)重悬 志贺氏菌 和1mL DMEM(从步骤3.2.10.2开始)。
注意:感染通常在感染的多重性(MOI;细菌与上皮细胞的比率)为100时进行。为了测试不同的MOI,在DMEM中将重悬 志贺氏菌 稀释至所需浓度,然后向HT-29单层中加入1mL稀释细菌。例如,要测试 MOI 为 10,将 150 μL 的 1 x 108 CFU/mL 细菌加入 1.35 mL DMEM 中,以 1:10 的比例稀释细菌,然后将 1 mL(1 x 107 CFU)应用于 HT-29 细胞。 - 为了促进细菌与HT-29细胞的接触,在室温下以2,000× g 离心6孔板10分钟,如果温度设置可以调节,则为37°C。
注意:离心促进细菌与HT-29细胞的接触,从而绕过了对粘附因子的需求,并允许细菌快速侵入细胞。 - 在37°C下用5%CO2 孵育6孔板45分钟。
- 在孵育期间,确定细菌感染滴度。
- 将重悬 的志贺氏菌 细胞(从步骤6.3.3开始)的10倍连续稀释液制备到PBS中。
- 将100μL的1×10-5 和1×10-6 稀释液培养到TSB + Congo红板上,并在37°C下孵育过夜。
注:从 1 x 10-5 和 1 x 10-6 稀释液中接种 100 μL 分别对应于 1 x 10-6 和 1 x 10-7 的最终稀释因子。
- 用 1 mL PBS 彻底洗涤受感染的 HT-29 细胞 3 次。
- 从每个孔中抽吸培养基。
注意:从 6 孔板吸出培养基时,将吸气器的尖端沿着孔的底部引导,尽量避免与 HT-29 细胞接触。 - 向每个孔中加入 1 mL 温热的 PBS 并轻轻洗涤。
注意:要用 PBS 轻轻洗涤 6 孔单层,请在工作台上上下左右移动板。以圆周运动清洗板和/或从工作台表面取下板会导致从塑料上机械去除细胞。 - 重复步骤 6.8.1 和 6.8.2 2 次。
- 从每个孔中抽吸培养基。
- 通过抽吸除除PBS,然后向每个孔中加入2mL补充有50μg/ mL庆大霉素的温DMEM,并在37°C下用5%CO2孵育30分钟。
- 用 1 mL PBS 彻底洗涤受感染的 HT-29 细胞 3 次。
- 重复洗涤步骤6.8。
- 通过抽吸除除PBS,然后向6孔板的每个孔中加入2mL带有50μg/ mL庆大霉素的温DMEM,并在37°C下用5%CO2 孵育所需的时间长度,以允许细胞内复制(最多24小时)。
- 用 1 mL PBS 彻底洗涤细胞 2 次。
- 重复洗涤步骤6.8。
- 通过抽吸除除 PBS,并通过向每个孔中加入 1 mL PBS + 1% Triton X-100 来裂解 HT-29 细胞。
- 将6孔板在37°C孵育5分钟。
- 使用细胞刮刀或弯曲的移液器吸头从孔底部刮取裂解的细胞,并将全部 1 mL 转移到新鲜的 1.7 mL 微量离心管中。
- 确定细胞内细菌的数量。
- 涡旋每个试管(从步骤6.15开始)至少30秒,以进一步从裂解的真核细胞中置换 志贺氏菌 。
- 将裂解物的10倍连续稀释液稀释到PBS中。
- 将 100 μL 的 1 x 10-2、1 x 10-3 和 1 x 10-4 稀释液培养到 TSB + Congo Red 板上,并在 37 °C 下孵育过夜。
注:从 1 x 10-2、1 x 10-3 和 1 x 10-4 稀释液中接种 100 μL 分别对应于 1 x 10-3、1 x 10-4 和 1 x 10-5 的最终稀释因子。
结果
将 S. flexneri 2457T 野生型 (WT) 与 S. flexneri ΔVF (ΔVF) 进行比较,后者是一种假设负调节志贺氏菌毒力的突变体。由于志贺氏菌使用胆盐作为调节毒力的信号17,18,47,因此在TSB培养基中的细菌传代培养以及补充有0.4%(w/v)胆盐的TSB中进行实验18。在传代培养步骤中暴露胆汁盐...
讨论
该方案描述了一组三种标准化测定法,用于研究志贺氏菌的粘附,侵袭和肠上皮细胞的细胞内复制。尽管这些方法只是用于研究宿主细胞内各种细菌病原体的侵袭和细胞内复制的经典庆大霉素测定法的改进版本49,50,51,但在研究志贺氏菌时必须特别考虑。
志贺氏菌是兼性厌氧菌,在37°C...
披露声明
作者声明没有利益冲突。
致谢
对作者的支持包括马萨诸塞州总医院儿科、研究临时支持基金执行委员会 (ISF) 奖 2022A009041、美国国家过敏和传染病研究所资助 R21AI146405 以及美国国家糖尿病、消化和肾脏疾病研究所资助哈佛大学营养肥胖研究中心 (NORCH) 2P30DK040561-26。资助者在研究设计、数据收集和分析、发表决定或手稿准备方面没有任何作用。
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.22 μm PES filter | Millipore-Sigma | SCGP00525 | Sterile, polyethersulfone filter for sterilizing up to 50 mL media |
| 14 mL culture tubes | Corning | 352059 | 17 mm x 100 mm polypropylene test tubes with cap |
| 50 mL conical tubes | Corning | 430829 | 50 mL clear polypropylene conical bottom centrifuge tubes with leak-proof cap |
| 6-well tissue culture plates | Corning | 3516 | Plates are treated for optimal cell attachment |
| Bile salts | Sigma-Aldrich | B8756 | 1:1 ratio of cholate to deoxycholate |
| Congo red dye | Sigma-Aldrich | C6277 | A benzidine-based anionic diazo dye, >85% purity |
| Countess cell counting chamber slide | Invitrogen | C10283 | To be used with the Countess Automated Cell Counter |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | Sigma-Aldrich | D8418 | A a highly polar organic reagent |
| Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) | Gibco | 10569-010 | DMEM is supplemented with high glucose, sodium pyruvate, GlutaMAX, and Phenol Red |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Sigma-Aldrich | F4135 | Heat-inactivated, sterile |
| Gentamicin | Sigma-Aldrich | G3632 | Stock concentration is 50 mg/mL |
| HT-29 cell line | ATCC | HTB-38 | Adenocarcinoma cell line; colorectal in origin |
| Paraffin film | Bemis | PM999 | Laboratory sealing film |
| Petri dishes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | FB0875713 | 100 mm x 15 mm Petri dishes for solid media |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 10010049 | 1x concentration; pH 7.4 |
| Select agar | Invitrogen | 30391023 | A mixture of polysaccharides extracted from red seaweed cell walls to make bacterial plating media |
| T75 flasks | Corning | 430641U | Tissue culture flasks |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma-Aldrich | T8787 | A common non-ionic surfactant and emulsifier |
| Trypan blue stain | Invitrogen | T10282 | A dye to detect dead tissue culture cells; only live cells can exclude the dye |
| Trypsin-EDTA | Gibco | 25200-056 | Reagent for cell dissociation for cell line maintenance and passaging |
| Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) | Sigma-Aldrich | T8907 | Bacterial growth media |
参考文献
- Karambizi, N. U., McMahan, C. S., Blue, C. N., Temesvari, L. A. Global estimated Disability-Adjusted Life-Years (DALYs) of diarrheal diseases: A systematic analysis of data from 28 years of the global burden of disease study. PloS one. 16 (10), e0259077 (2021).
- WHO. WHO methods and data sources for country-level causes of death 2000-2016. World Health Organization. , (2018).
- Kotloff, K. L. Shigella infection in children and adults: a formidable foe. Lancet Glob Health. 5 (12), e1166-e1167 (2017).
- Kotloff, K. L., et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet. 382 (9888), 209-222 (2013).
- Schroeder, G. N., Hilbi, H. Molecular pathogenesis of Shigella spp.: Controlling host cell signaling, invasion, and death by type III secretion. Clin Microbiol Rev. 21 (1), 134-156 (2008).
- Arvelo, W., et al. Transmission risk factors and treatment of pediatric shigellosis during a large daycare center-associated outbreak of multidrug resistant shigella sonnei: Implications for the management of shigellosis outbreaks among children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 28 (11), 976-980 (2009).
- Kozyreva, V. K., et al. Recent outbreaks of Shigellosis in California caused by two distinct populations of Shigella sonnei with either increased virulence or fluoroquinolone resistance. mSphere. 1 (6), 1-18 (2016).
- Bowen, A., et al. Importation and domestic transmission of Shigella sonnei resistant to ciprofloxacin - United States, May 2014-February 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 64 (12), 318-320 (2015).
- Tansarli, G. S., et al. Genomic reconstruction and directed interventions in a multidrug-resistant Shigellosis outbreak in Seattle, WA, USA: a genomic surveillance study. Lancet. 3099 (22), 1-11 (2023).
- Barry, E. M., et al. Progress and pitfalls in Shigella vaccine research. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10 (4), 245-255 (2013).
- Increase in Extensively Drug-Resistant Shigellosis in the United States. CDC Health Alert Network. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Available from: https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2023/han00486.asp?ACSTrackingID=USCDC_511-DM100260&ACSTrackingLabel=HAN%20486%20-%20General%20Public&deliveryName=USCDC_511-DM100260 (2023)
- Shiferaw, B., et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Shigella isolates in Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet) sites, 2000-2010. Clin Infect Dis. 54, S458-S463 (2012).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19: U.S. Impact on Antimicrobial Resistance, Special Report 2022. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. CDC. , (2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. CDC. 10 (1), (2019).
- WHO. Prioritization of pathogens to guide discovery, research and development of new antibiotics for drug-resistant bacterial infections, including tuberculosis. WHO. , (2017).
- DuPont, H. L., Levine, M. M., Hornick, R. B., Formal, S. B. Inoculum size in shigellosis and implications for expected mode of transmission. J Infect Dis. 159 (6), 1126-1128 (1989).
- Nickerson, K. P., et al. Analysis of Shigella flexneri resistance, biofilm formation, and transcriptional profile in response to bile salts. Infect Immun. 85 (6), 1-18 (2017).
- Faherty, C. S., Redman, J. C., Rasko, D. A. Shigella flexneri effectors OspE1 and OspE2 mediate induced adherence to the colonic epithelium following bile salts exposure. Mol Microbiol. 85 (1), 107-121 (2012).
- Chanin, R. B., et al. Shigella flexneri adherence factor expression in in vivo-like conditions. mSphere. 4 (6), e00751 (2019).
- Baranov, V., Hammarström, S. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and CEA-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1), apically expressed on human colonic M cells, are potential receptors for microbial adhesion. Histochem Cell Biol. 121 (2), 83-89 (2004).
- Wassef, J. S., Keren, D. F., Mailloux, J. L. Role of M cells in initial antigen uptake and in ulcer formation in the rabbit intestinal loop model of shigellosis. Infect Immun. 57 (3), 858-863 (1989).
- Sansonetti, P. J., Arondel, J., Cantey, J. R., Prévost, M. C., Huerre, M. Infection of rabbit Peyer's patches by Shigella flexneri: Effect of adhesive or invasive bacterial phenotypes on follicle-associated epithelium. Infect Immun. 64 (7), 2752-2764 (1996).
- Sansonetti, P. J., et al. Caspase-1 activation of IL-1beta and IL-18 are essential for Shigella flexneri-induced inflammation. Immunity. 12 (5), 581-590 (2000).
- Zychlinsky, A., Fitting, C., Cavaillon, J. M., Sansonetti, P. J. Interleukin 1 is released by murine macrophages during apoptosis induced by Shigella flexneri. J Clin Invest. 94 (3), 1328-1332 (1994).
- Sansonetti, P. J., Ryter, A., Clerc, P., Maurelli, A. T., Mounier, J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 51 (2), 461-469 (1986).
- Maldonado-Contreras, A., et al. Shigella depends on SepA to destabilize the intestinal epithelial integrity via cofilin activation. Gut Microbes. 8 (6), 544-560 (2017).
- Collard, J. -. M., et al. High prevalence of small intestine bacteria overgrowth and asymptomatic carriage of enteric pathogens in stunted children in Antananarivo, Madagascar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 16 (5), e0009849 (2022).
- Mattock, E., Blocker, A. J. How do the virulence factors of shigella work together to cause disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 7, 1-24 (2017).
- Mostowy, S., et al. The zebrafish as a new model for the in vivo study of Shigella flexneri interaction with phagocytes and bacterial autophagy. PLoS Pathog. 9 (9), e1003588 (2013).
- Martinez-Becerra, F. J., et al. Parenteral immunization with IpaB/IpaD protects mice against lethal pulmonary infection by Shigella. Vaccine. 31 (24), 2667-2672 (2013).
- Shim, D. -. H., et al. New animal model of shigellosis in the Guinea pig: its usefulness for protective efficacy studies. J Immunol. 178 (4), 2476-2482 (2007).
- Marteyn, B., et al. Modulation of Shigella virulence in response to available oxygen in vivo. Nature. 465 (7296), 355-358 (2010).
- West, N. P., et al. Optimization of virulence functions through glucosylation of Shigella LPS. Science. 307 (5713), 1313-1317 (2005).
- Maurelli, A. T., et al. Shigella infection as observed in the experimentally inoculated domestic pig, Sus scrofa domestica. Microbial Pathog. 25 (4), 189-196 (1998).
- Jeong, K. -. I., Zhang, Q., Nunnari, J., Tzipori, S. A piglet model of acute gastroenteritis induced by Shigella dysenteriae Type 1. J Infect Dis. 201 (6), 903-911 (2010).
- Kim, Y. -. J., Yeo, S. -. G., Park, J. -. H., Ko, H. -. J. Shigella vaccine development: prospective animal models and current status. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 14 (10), 903-912 (2013).
- Kent, T. H., Formal, S. B., LaBrec, E. H., Sprinz, H., Maenza, R. M. Gastric shigellosis in rhesus monkeys. Am J Pathol. 51 (2), 259-267 (1967).
- Shipley, S. T., et al. A challenge model for Shigella dysenteriae 1 in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Comp Med. 60 (1), 54-61 (2010).
- Higgins, R., Sauvageau, R., Bonin, P. Shigella flexneri Type 2 Infection in captive nonhuman primates. Can Vet J. 26 (12), 402-403 (1985).
- Oaks, E. V., Hale, T. L., Formal, S. B. Serum immune response to Shigella protein antigens in rhesus monkeys and humans infected with Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 53 (1), 57-63 (1986).
- Formal, S. B., et al. Protection of monkeys against experimental shigellosis with a living attenuated oral polyvalent dysentery vaccine. J Bacteriol. 92 (1), 17-22 (1966).
- Levine, M. M., Kotloff, K. L., Barry, E. M., Pasetti, M. F., Sztein, M. B. Clinical trials of Shigella vaccines: two steps forward and one step back on a long, hard road. Nat Rev Microbiol. 5 (7), 540-553 (2007).
- Payne, S. M. Laboratory cultivation and storage of Shigella. Curr Protoc Microbiol. 55 (1), 93 (2019).
- NIH Guidelines. NIH guidelines for research involving recombinant or synthetic nucleic acid molecules. NIH Guidelines. 2, 142 (2019).
- Maurelli, A. T., Blackmon, B., Curtiss, R. Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 43 (1), 397-401 (1984).
- HT-29 cell line product sheet. ATCC Available from: https://www.atcc.org/products/htb-38 (2023)
- Sistrunk, J. R., Nickerson, K. P., Chanin, R. B., Rasko, D. A., Faherty, C. S. Survival of the fittest: How bacterial pathogens utilize bile to enhance infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 29 (4), 819-836 (2016).
- Stensrud, K. F., et al. Deoxycholate interacts with IpaD of Shigella flexneri in inducing the recruitment of IpaB to the type III secretion apparatus needle tip. J Biol Chem. 283 (27), 18646-18654 (2008).
- Mandell, G. L. Interaction of intraleukocytic bacteria and antibiotics. J Clin Invest. 52 (7), 1673-1679 (1973).
- Elsinghorst, E. A. Measurement of invasion by gentamicin resistance. Methods Enzymo. 236 (1979), 405-420 (1994).
- Elsinghorst, E. A., Weitz, J. A. Epithelial cell invasion and adherence directed by the enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli tib locus is associated with a 104-kilodalton outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 62 (8), 3463-3471 (1994).
- Dorman, C. J., McKenna, S., Beloin, C. Regulation of virulence gene expression in Shigella flexneri, a facultative intracellular pathogen. Int J Med Microbiol. 291 (2), 89-96 (2001).
- Porter, M. E., Dorman, C. J. Positive regulation of Shigella flexneri virulence genes by integration host factor. J Bacteriol. 179 (21), 6537-6550 (1997).
- Maurelli, A. T., Blackmon, B., Curtiss, R. Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 43 (1), 195-201 (1984).
- Schuch, R., Maurelli, A. T. Virulence plasmid instability in Shigella flexneri 2a is induced by virulence gene expression. Infect Immun. 65 (9), 3686-3692 (1997).
- Formal, S. B., Hale, T. L., Sansonetti, P. J. Invasive enteric pathogens. Rev Infect Dis. 5, S702-S707 (1983).
- Pál, T., Hale, T. L. Plasmid-associated adherence of Shigella flexneri in a HeLa cell model. Infect Immun. 57 (8), 2580-2582 (1989).
- Noben, M., et al. Human intestinal epithelium in a dish: Current models for research into gastrointestinal pathophysiology. United European Gastroenterol J. 5 (8), 1073-1081 (2017).
- Liévin-Le Moal, V., Servin, A. L. Pathogenesis of human enterovirulent bacteria: lessons from cultured, fully differentiated human colon cancer cell lines. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev R. 77 (3), 380-439 (2013).
- Mitchell, D. M., Ball, J. M. Characterization of a spontaneously polarizing HT-29 cell line, HT-29/cl.f8. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Anim. 40 (10), 297-302 (2004).
- Gagnon, M., Zihler Berner, A., Chervet, N., Chassard, C., Lacroix, C. Comparison of the Caco-2, HT-29 and the mucus-secreting HT29-MTX intestinal cell models to investigate Salmonella adhesion and invasion. J Microbiol Methods. 94 (3), 274-279 (2013).
- Koestler, B. J., et al. Human intestinal enteroids as a model system of Shigella pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 87 (4), 00733 (2019).
- Ranganathan, S., et al. Evaluating Shigella flexneri pathogenesis in the human enteroid model. Infect Immun. 87 (4), (2019).
- Nickerson, K. P., et al. A versatile human intestinal organoid-derived epithelial monolayer model for the study of enteric pathogens. Microbiol Spectr. 9 (1), 1-17 (2021).
- Perlman, M., Senger, S., Verma, S., Carey, J., Faherty, C. S. A foundational approach to culture and analyze malnourished organoids. Gut Microbes. 15 (2), 2248713 (2023).
- Pope, L. M., Reed, K. E., Payne, S. M. Increased protein secretion and adherence to HeLa cells by Shigella spp. following growth in the presence of bile salts. Infect Immun. 63 (9), 3642-3648 (1995).
- Faherty, C. S., et al. The synthesis of OspD3 (ShET2) in Shigella flexneri is independent of OspC1. Gut Microbes. 7 (6), 486-502 (2016).
- Ridlon, J. M., Kang, D. -. J., Hylemon, P. B. Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria. J Lipid Res. 47 (2), 241-259 (2006).
- Köseoğlu, V. K., Hall, C. P., Rodríguez-López, E. M., Agaisse, H. The Autotransporter IcsA promotes Shigella flexneri biofilm formation in the presence of bile salts. Infect Immun. 87 (7), 1-14 (2019).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。