Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Method Article
Un ensayo químico de acetil-clic para medir la acetilación de la acetil 1 de la histona acetiltransferasa 1
En este artículo
Resumen
Los ensayos químicos rápidos y precisos para detectar inhibidores específicos son una herramienta importante en el arsenal de desarrollo de fármacos. Aquí, presentamos un ensayo químico escalable de acetil-clic para medir la inhibición de la actividad de acetilación de HAT1.
Resumen
HAT1, también conocida como histona acetiltransferasa 1, desempeña un papel crucial en la síntesis de cromatina al estabilizar y acetilar el H4 naciente antes del ensamblaje de nucleosomas. Es necesario para el crecimiento tumoral en varios sistemas, lo que lo convierte en un objetivo potencial para el tratamiento del cáncer. Para facilitar la identificación de compuestos que pueden inhibir la actividad enzimática de HAT1, hemos ideado un ensayo de clic acetil para un cribado rápido. En este sencillo ensayo, empleamos HAT1/Rbap46 recombinante, que se purifica a partir de células humanas activadas. El método utiliza el análogo de acetil-CoA 4-pentinoil-CoA (4P) en un enfoque de química de clic. Esto implica la transferencia enzimática de un mango alquino a través de una reacción de acilación dependiente de HAT1 a un péptido N-terminal H4 biotinilado. A continuación, el péptido capturado se inmoviliza en placas de neutravidina, seguido de una funcionalización química con biotina-azida. Posteriormente, se emplea el reclutamiento de estreptavidina-peroxidasa para oxidar el rojo amplex, lo que da como resultado una salida fluorescente cuantitativa. Mediante la introducción de inhibidores químicos durante la reacción de acilación, podemos cuantificar la inhibición enzimática en función de una reducción de la señal de fluorescencia. Es importante destacar que esta reacción es escalable, lo que permite un cribado de alto rendimiento de posibles inhibidores de la actividad enzimática de HAT1.
Introducción
Entre las numerosas acetiltransferasas eucariotas, HAT1 fue la histona acetiltransferasa inicial que se aisló 1,2,3. Investigaciones posteriores han establecido firmemente su papel fundamental en la replicación de la cromatina, particularmente en la síntesis de nuevos nucleosomas durante la faseS 4. Nuestros esfuerzos de investigación condujeron al reconocimiento de que HAT1 está altamente estimulado por el tratamiento con factor de crecimiento epidérmico (EGF) en células mamarias5. Además, ha salido a la luz que HAT1 es necesaria para la rápida proliferación celular y la formación de tumores in vivo 6,7,8,9. Los datos indican que HAT1 es fundamental en la coordinación de los procesos anabólicos y epigenéticos para la división celular, impulsando el crecimiento tumoral.
HAT1 diacetila la cola aminoterminal de la histona H4 en las lisinas 5 y 12 en complejo con la proteína chaperona Rbap46, que se une a la histona y presenta el aminoterminal a HAT1. Los tetrámeros de histonas o disomas10, junto con HAT1/Rbap46 y otras chaperonas de histonas11, se importan al núcleo. A continuación, se liberan histonas para depositarlas en la horquilla de replicación u otros sitios para apoyar la activación o represión de genes. La función de la marca de diacetilación HAT1 en la histona H4 no se comprende completamente. Es probable que se elimine rápidamente en un lapso de 15 a 30 minutos por la acción de las histonas desacetilasas 12,13,14,15 después de que H4 se inserta en la cromatina. Por lo tanto, la marca de diacetilación HAT1 no se propaga en la cromatina y puede no cumplir un verdadero papel epigenético, aunque se ha postulado un papel en el reclutamiento de enzimas modificadoras de la cromatina a la cromatinanaciente 12. Además, HAT1 no acetilla directamente la cromatina; Su actividad se restringe a las histonas solubles.
El desarrollo de inhibidores de la acetiltransferasa de histonas de moléculas pequeñas se ha visto obstaculizado por ensayos inespecíficos y de bajo rendimiento, lo que a menudo resulta en la generación de compuestos biológicamente reactivos16,17. El ensayo de referencia para medir las actividades de la acetiltransferasa requiere el uso de 3-H-acetil-coA, lo que limita el rendimiento y requiere radiación. No obstante, recientemente, se han descrito y confirmado inhibidores de la acetiltransferasa de moléculas pequeñas específicos y muy potentes dirigidos a CBP/p30018 y KAT6A/B19,20 mediante el uso de 3-H-acetil-CoA. De cara al futuro, se están diseñando ensayos mejorados para lograr un mejor rendimiento y evitar riesgos de laboratorio.
Los avances recientes en el monitoreo de la acetilación21 han utilizado la química de clic para permitir el monitoreo de reacciones enzimáticas. Hay una variedad de precursores habilitados para clics a los que se puede acceder por rutas sintéticas simples o disponibles para su compra que se pueden incorporar en reacciones enzimáticas. Estas reacciones se llevan a cabo típicamente en sistemas recombinantes, aunque los ensayos basados en células también son factibles22. La ventaja de los cofactores y sustratos habilitados para clic es que el cribado puede medir directamente la actividad enzimática sin necesidad de sistemas de lectura acoplados que a menudo se ven perturbados por los compuestos de cribado y requieren pasos de manipulación adicionales. Esto permite tratamientos con inhibidores solo durante la etapa enzimática, mientras que todas las etapas posteriores de funcionalización y detección se llevan a cabo después de un lavado extenso para eliminar los compuestos, lo que limita la posibilidad de que se produzcan interferencias en el ensayo. Estas ventajas hacen que el diseño de los ensayos habilitados para clic sea preferible a los ensayos acoplados que comúnmente se basan en la detección de coenzima A libre.
Una consideración importante es la aceptación de los cofactores habilitados para hacer clic en el sitio activo de la enzima. Es posible que los cofactores habilitados para clics existentes no sean totalmente compatibles con el sitio activo optimizado para el cofactor nativo. La información estructural y el modelado se pueden utilizar para diseñar sustituciones de aminoácidos para ampliar el sitio activo e incorporar sustratos alterados23. Esto puede permitir un cribado con una cinética enzimática mejorada y niveles más bajos de sustrato y enzimas. El inconveniente de este enfoque es que las bolsas catalíticas alteradas pueden no identificar los inhibidores que interactúan fuertemente con la enzima nativa. En última instancia, se requiere una combinación de enfoques para identificar y validar posibles inhibidores enzimáticos.
Aquí, describimos un método desarrollado para purificar y ensayar la actividad de la enzima HAT1 utilizando el cofactor clic 4-pentinoil-CoA24. Este ensayo (Figura 1) utiliza la secuencia de la enzima nativa en complejo con su proteína asociada requerida Rbap46, que se ha demostrado que aumenta la actividad enzimática. La purificación de la enzima a partir de células humanas permite la activación enzimática en el celulo, lo que puede preservar modificaciones postraduccionales estimulantes importantes para la actividad enzimática completa. El diseño y la optimización de ensayos enzimáticos recombinantes para cribados químicos de alto rendimiento se han utilizado con éxito para identificar y caracterizar inhibidores de moléculas pequeñas HAT1.
Protocolo
1. Método 1: Producción y purificación del complejo recombinante HAT1/Rbap46
- Descongelación, recuperación y expansión de células HEK293f
- Descongele 1-10 millones de células de mamíferos HEK293f26 en 30 ml de medios de expresión freestyle 293 en un matraz de 100 ml. Incubar en 8% de CO2 a 37 °C mientras gira a 60 rpm.
- Al día siguiente, cuente y verifique la viabilidad de la celda, luego ajuste la velocidad de rotación a 120 rpm. Expandir a 300 mL de cultivo en un matraz de 1 L, manteniendo la densidad de siembra en 500.000 células/mL y dividiendo las células antes de que la densidad supere 3 x 106 células/mL.
- Transfección HEK293f
- Siembre 5 x 105 células/mL en un cultivo de 300 mL en un matraz de 1 L y cultive durante 24 h. Al día siguiente, cuente las células para asegurarse de que estén entre 7,5 x 105 y 1,2 x 106 células/ml.
- Preparar una mezcla de 300 μg de pHEK-FLAG-HAT1 y 300 μg de ADN plasmídico pHEK-Rbap46 en 30 mL de PBS. Agregue 1.2 mL de polietilenimina (PEI) al ADN/PBS y mezcle. Incubar durante 20 min a RT. Añadir la mezcla de DNA/PBS/PEI al cultivo de 300 mL e incubar a 37 °C durante 48 h a 120 rpm.
- Recolección de células
- Cuente las células para asegurarse de que estén entre 1,7 x 106 y 2,5 x 106 células/ml. A esta densidad celular, añadir forskolina a una concentración final de 12,5 μM para activar HAT1 e incubar las células durante 30 min, 37 °C, 120 rpm.
- Pulverizar las células a 300 x g durante 5 min, lavar una vez con 30 ml de PBS y congelar rápidamente en N2 líquido. Almacenar a -80 °C hasta la purificación de la proteína o proceder directamente a la purificación.
- Purificación de perlas FLAG complejas HAT1/Rbap46
- Lisar las células y preparar el extracto de proteína.
- Prepare el tampón de lisis añadiendo un comprimido de cóctel inhibidor de la proteasa (PIC) a 50 ml de RSB-500 (20 mM de Tris-HCl pH 7,5, 500 mM de NaCl, 25 mM de MgCl2).
- Descongele el gránulo celular de 300 ml de cultivo en hielo y lise con 40 ml de tampón de lisis helado con Triton X-100 al 0,1%. Sonicar en hielo, luego centrifugar a 10.000 x g durante 10 min a 4°C. Recoja todo el sobrenadante en un tubo de 50 ml con hielo, que ahora es el extracto de proteína.
- Prepara las cuentas de FLAG.
- Divida las perlas FLAG en cuatro tubos cónicos de 15 ml añadiendo 400 μl de suspensión de perlas de agarosa M2-FLAG en cada tubo que contenga 5 ml de glicina 0,1 M pH 3,5, Triton X-100 al 0,01 %. Agite vigorosamente cada tubo durante 5 s con la mano.
- Centrífuga de impulsos durante 30 s a 1000 x g a 4 °C, aspirar sobrenadante, lavar dos veces con 5 mL de RSB-500 + 0,1% Triton X-100 (Tx-100; sin inhibidor de la proteasa) e incubar en hielo.
- Realizar inmunoprecipitación con FLAG.
- Agregue 10 ml de extracto de proteína a cada tubo cónico de 15 ml que contenga perlas lavadas. Incubar los tubos a 4 °C con rotación invertida durante al menos 90 min o toda la noche.
- Lavar las cuentas encuadernadas 5 veces en 10 mL de RSB-500 + 0,1% Tx-100. Para cada lavado, invierta el tubo 2x-5x para resuspender las perlas, luego gránulos a 1000 x g durante 1 min a 4 °C. Por último, lavar 1 vez en RSB-100 (20 mM de Tris-HCl pH 7,5, 100 mM de NaCl, 25 mM de MgCl2) + 0,1% de Tx-100.
- Elución del péptido FLAG: Eluir el complejo HAT1 en 1,5 ml de tampón de elución (EB) que contiene 0,5 mg/ml de péptido FLAG. Incubar a 4 °C durante al menos 1 h o toda la noche. Centrifugar por pulsos las perlas eluidas a 1000 x g durante 30 s a 4 °C y recoger el sobrenadante, que contiene el complejo HAT1/Rbap46 purificado.
- Concentra la proteína y elimina el péptido FLAG.
- Agregue eluido a un tubo de filtro de corte de 20 ml y 10,000 Dalton. Aumente el volumen a 15 ml con EB. Centrifugar a 2500 x g durante 15 min a 4 °C, repitiendo dos veces con 15 mL adicionales de EB cada vez.
- Recupere el eluido final del tubo del filtro y verifique la concentración de proteínas por A260. Espere una concentración de 1 mg de proteína total en 6 ml de EB (por cultivo inicial de 300 ml). Compruebe la pureza de la proteína mediante SDS-PAGE, Coomassie e inmunotransferencia, y almacene las alícuotas a -80 °C.
- Lisar las células y preparar el extracto de proteína.
2. Método 2: curva estándar de acetil-clic HAT1
- Preparación de la curva estándar
- Sintetizar un péptido H4 N-terminal de control positivo con la secuencia: SCRG[Pra]GGKGLG[Pra]GGAKRHRKVLRGG[Lys(Biotina)], donde [Pra] denota Propargilglicina.
- Resuspender el péptido Pra a 0,1 mg/mL en DMSO. Mezcle el péptido Pra con el péptido de histona H4 biotinilado (1-23-GGK-biotina) para crear una curva estándar (Figura 2; volúmenes encontrados en la Tabla 1). Las curvas patrón pueden hacerse frescas antes del atado de la placa o, si se hacen de antemano, mezclarse con 20 μl de urea 8 M y almacenarse a -20 °C hasta la etapa 3.3.
3. Método 3: Ensayo de acetil-clic HAT1
- Ensamblaje de reacciones de acetilación con inhibidores de prueba
- Ensamble reacciones de acetilación por duplicado en tubos de PCR de 0,2 ml o placas de PCR de 96 pocillos a partir de los siguientes componentes: péptido H4 de histona biotinilado (1-23-GGK-biotina) resuspendido en DMSO a 0,1 mg/ml (34,8 μM), enzima HAT1 prediluida en EB, tampón 20x (1M Tris pH 8,5, 0,1% NP40), DTT de 2 mM, 4-pentinoil-CoA disuelto en agua a 1 mg/ml (1 mM). Una reacción de 20 μL comprende 10 μL de enzima, 1 μL de péptido H4, 1 μL de tampón 20x, 1 μL de DTT premezclado y alícuota a pocillos de una placa de PCR de 96 pocillos en hielo.
- Añadir 1 μL de DMSO (control negativo) o compuesto de prueba disuelto a 1-10 μM, o H4K12CoA25 (o inhibidor de control positivo adecuado), por pocillo. Mezclar mediante un pipeteo suave e incubar durante 10 minutos en hielo para permitir que se formen complejos enzima-inhibidores.
- Continuación de la reacción de acetilación
- Combine 2 μL de 4-pentinoil-CoA con 4 μL de agua, luego agréguelos a los pocillos. Mezclar suavemente mediante pipeteo, centrifugar a 300 x g durante 30 s a RT para recoger el contenido e incubar a 37 °C durante 1 h en tubos o placas tapados con lámina resellable.
- Procesar el contenido directamente para los productos de reacción o enfriar con 20 μL de urea 8 M y almacenar a -20 °C hasta el procesamiento.
- Unión peptídica a la placa de neutravidina
- Agregue el contenido de la reacción con o sin urea a las placas de 96 pocillos recubiertas de neutravidina negra prebloqueada con albúmina sérica bovina (BSA) que contienen 80 μL de PBST (PBS + 0,1% Tween-20) por pocillo.
- Agregue péptidos de curva estándar por duplicado a sus propios pocillos que contengan 80 μL de PBST. Unir los péptidos con una suave agitación orbital durante 1 h a temperatura ambiente (RT).
- Lavado: Una vez finalizada la unión, aspire el líquido de los pocillos y lave los pocillos con 200 μL de PBST 3x 15 pasadas (volumen de carrera de 180 μL) utilizando una arandela de placas.
- Reacción química de clic
- Prepare los reactivos para la reacción de clic de la siguiente manera: 100 mM de ligando Tris(3-hidroxipropiltriazolymetil)amina (THPTA) en agua y 20 mM de CuSO4 en agua. THPTA previene la hidrólisis catalizada por Cu (II) y apaga los radicales y peróxidos generados a partir de O2 / Cu / ascorbato.
- Añadir la mezcla THPTA/Cu a 300 mM de ascorbato de sodio en agua y 2,5 mM de azida de biotina en DMSO. La reacción de un clic contiene 140 μL de PBS, 10 μL de THPTA, 10 μL de CuSO4, 10 μL de ascorbato de sodio, 20 μL de biotina-azida. Mezcle siempre los reactivos de clic frescos, luego dispense 190 μL a cada pocillo, selle la placa e incube a 37 ° C durante 1 h.
- Lavado: Aspirar el líquido de los pocillos y lavar la placa 3 veces con PBST (180 μL de volumen sistólico, 15 pasadas por cada lavado).
- Unión estreptavidina-rábano picante peroxidasa: Diluir estreptavidina-HRP (0,224 mg/ml) 1:10 en estreptavidina (0,224 mg/ml), luego diluir aún más 1:1000 en PBST. Añadir Steptavidin-HRP: mezcla de estreptavidina (100 μL por pocillo) e incubar a RT durante 1 h con una suave agitación orbital.
- Lavar 3 veces con PBST como en los pasos anteriores.
- Oxidación roja Amplex
- Combine los reactivos de detección de rojo Amplex de la siguiente manera: 4,45 ml de tampón NaHPO4 (1x = 50 mM de concentración final), 50 μL de rojo amplex (20 mM diluidos en DMSO), 500 μl deH2O2 diluido.
- Diluir H2O2 del 30% de stock al 3% en 1x tampón NaHPO4 , luego añadir 22,7 μL de 3% H2O2 en 977 μL de 1x tampón NaHPO4 (este es el H2O2 utilizado para la reacción amplex). Añadir 100 μL de la mezcla de reacción de rojo amplex por pocillo, incubar a RT durante 30 min protegido de la luz, y luego detectar la excitación/emisión de fluorescencia 571/585 nm utilizando un lector de placas de fluorescencia estándar.
- Cálculo de la inhibición enzimática: Calcule el porcentaje de inhibición (Figura 3) de acuerdo con la siguiente fórmula:
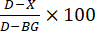 , donde D es el valor de fluorescencia de las reacciones de control tratadas solo con DMSO, X es el valor de las reacciones tratadas con compuestos de prueba y BG es el valor de los pocillos de fondo (control del péptido H4, sin enzima añadida).
, donde D es el valor de fluorescencia de las reacciones de control tratadas solo con DMSO, X es el valor de las reacciones tratadas con compuestos de prueba y BG es el valor de los pocillos de fondo (control del péptido H4, sin enzima añadida). - Curva de dosis: Seleccione los compuestos de prueba que inhiben la actividad de la enzima HAT1 para repetir los ensayos, con el compuesto diluido en serie. Determinar empíricamente las diluciones de los compuestos. Por ejemplo, comience con una concentración de stock de 2 mM y, a continuación, diluya en serie 1:3 durante ocho diluciones. A continuación, diluir 1:20 en ensayos enzimáticos que producen una dosis máxima de 100 μM.
- Representación gráfica de la curva: Utilice la regresión de mínimos cuadrados para ajustar las curvas de inhibición dosis-respuesta (utilizando los valores de inhibición porcentual del paso 3.10) en el software de análisis de datos (GraphPad Prism) y derive los valores de IC50 para cada compuesto (Figura 4).
- Reacción de acetilación con acetil-CoA:
- Utilícelo para confirmar la actividad enzimática con el cofactor nativo acetil-CoA en lugar de 4-pentinoil-CoA. Llevar a cabo ensayos de acetilación de HAT1 como se describe en los pasos 3.1-3.2 con acetil-CoA en lugar de 4-pentinoil-CoA.
- Localice los productos de la reacción en membranas de nitrocelulosa (1-2 μL), déjelos secar, luego séquelos con anticuerpos anti-H4-lisina-12-acetilo o anti-H4-lisina-5-acetil. Cuantificar la señal de inmunotransferencia mediante densitometría.
Resultados
Se deben incluir curvas estándar duplicadas (16 pocillos) en cada placa para garantizar el rendimiento adecuado del ensayo. Los datos de la curva estándar deben configurarse en forma de tabla, con un rango de 100% a 0% de acuerdo con la proporción de péptido que contiene Pra y péptido H4 nativo en solución (Tabla 1). La señal roja Amplex será la más alta en los pocillos peptídicos H4 nativos al 100 % y la más baja en los pocillos peptídicos H4 nativos al 0 % pra/100 % H4 nativos. Una vez que ...
Discusión
En la última década, la química de clic se volvió prominente20, permitiendo el diseño preciso de estructuras químicas que interactúan. En este contexto, diversas conexiones covalentes bioortogonales21 han surgido como opciones prometedoras para la formación de complejos en su entorno natural. La química de clic emplea pares de grupos funcionales que exhiben reacciones rápidas y selectivas, comúnmente conocidas como "reacciones de clic". Estas reacciones se produc...
Divulgaciones
Hemos presentado patentes que describen el ensayo de acetil clic HAT1 (PCT/US20/29395). J.J.G. informa de acuerdos de consultoría con Sharma Therapeutics, LLC y Guidepoint y apoyo a la investigación (a su institución) de Hummingbird Biosciences.
Agradecimientos
Agradecemos a George Zheng por proporcionar H4K12CoA. Agradecemos a los miembros de Gruber Lab por sus útiles discusiones y comentarios. Agradecemos el apoyo de los NIH/NCI (1K08CA245024), CPRIT (RR200090) y la Fundación V (V2022-022).
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 4P CoA | Cayman Chemical | 10547 | Click chemistry co-factor |
| Amplex Red | Fisher Sci | A12222 | Fluorescence substrate |
| Biotin-PEG-Azide | Alfa Aesar | J64996MC | Click chemistry |
| Copper Sulfate | Sigma-aldrich | 7758-98-7 | Click chemistry |
| DMSO | Fisher Scientific | 67-68-5 | diluent |
| DTT | Acros Organics | 03-12-3483 | reducting agent |
| Forskolin | VWR | 102987-310 | Protein expression |
| Freestyle 293 Expression Medium | Thermo Fisher | 12338018 | Media |
| Freestyle 293-F cells | Thermo Fisher | R790-07 | Protein expression |
| H4-peptide/1-23-GGK-biotin | Anaspec | AS65097 | peptide substrate |
| HEPES | Sigma-aldrich | 7365-45-9 | EB buffer |
| Hydrogen peroxide 30% solution | Sigma-aldrich | Z00183-99-0 | initiator |
| M2 FLAG antibody slurry | Millipore-Sigma | A2220 | Protein purification |
| Macrosep 10K Filter (Pall Lab) | VWR | 89131-980 | Protein purification |
| Neutravidin Plate | Thermo Sci | 15127 | BSA-pre-blocked |
| NP40 (IGEPAL) | MP Biomedical | 198596 | 20x buffer |
| pHEK-293 plasmid | Takara Bio | 3390 | Protein expression |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline 10x | Alfa Aesar | Z00082-33-6 | wash buffer |
| Pra peptide | Genscript | Custom synthesis | biotinylated |
| Sodium Ascorbate | Sigma-aldrich | 134-03-2 | Click chemistry |
| Sodium chloride | Sigma-aldrich | 7647-14-5 | EB buffer |
| Sodium phosphate | VWR International | 7558-80-7 | buffer |
| Streptavidin | EMD Millipore | 189730 | competitor |
| Streptavidin-HRP | Cell Signaling | 3999S | enzyme |
| THPTA ligand | Fisher Sci | 1010-500 | Click chemistry |
| Tris base | Sigma-aldrich | 77-86-1 | 20x buffer |
| Triton-X 100 | VWR International | 9002-93-1 | EB buffer |
| Tween-20 | Sigma-aldrich | 9005-64-5 | Wash buffer |
| Urea | Sigma-Aldrich | 57-13-6 | quencher |
Referencias
- Kleff, S., et al. Identification of a gene encoding a yeast histone H4 acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 270 (42), 24674-24677 (1995).
- Parthun, M. R., Widom, J., Gottschling, D. E. The major cytoplasmic histone acetyltransferase in yeast: links to chromatin replication and histone metabolism. Cell. 87 (1), 85-94 (1996).
- Verreault, A., et al. Nucleosomal DNA regulates the core-histone-binding subunit of the human Hat1 acetyltransferase. Curr Biol. 8 (2), 96-108 (1998).
- Parthun, M. R. Histone acetyltransferase 1: more than just an enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1819 (3-4), 256-263 (2013).
- Gruber, J. J., et al. HAT1 coordinates histone production and acetylation via H4 promoter binding. Mol Cell. 75 (4), 711-724 e5 (2019).
- Fan, P., et al. Overexpressed histone acetyltransferase 1 regulates cancer immunity by increasing programmed death-ligand 1 expression in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38 (1), 47 (2019).
- Xia, P., et al. MicroRNA-377 exerts a potent suppressive role in osteosarcoma through the involvement of the histone acetyltransferase 1-mediated Wnt axis. J Cell Physiol. 234 (12), 22787-22798 (2019).
- Yang, G., et al. Histone acetyltransferase 1 is a succinyltransferase for histones and non-histones and promotes tumorigenesis. EMBO Rep. 22 (2), e50967 (2021).
- Xue, L., et al. RNAi screening identifies HAT1 as a potential drug target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7 (7), 3898-3907 (2014).
- Zhang, W., et al. Structural plasticity of histones H3-H4 facilitates their allosteric exchange between RbAp48 and ASF1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20 (1), 29-35 (2013).
- Campos, E. I., et al. The program for processing newly synthesized histones H3.1 and H4. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 17 (11), 1343-1351 (2010).
- Agudelo Garcia, P. A., et al. Identification of multiple roles for histone acetyltransferase 1 in replication-coupled chromatin assembly. Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (16), 9319-9335 (2017).
- Nagarajan, P., et al. Histone acetyl transferase 1 is essential for mammalian development, genome stability, and the processing of newly synthesized histones H3 and H4. PLoS Genet. 9 (6), e1003518 (2013).
- Annunziato, A. T. Assembling chromatin: the long and winding road. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1819 (3-4), 196-210 (2013).
- Annunziato, A. T., Seale, R. L. Histone deacetylation is required for the maturation of newly replicated chromatin. J Biol Chem. 258 (20), 12675-12684 (1983).
- Dahlin, J. L., et al. Assay interference and off-target liabilities of reported histone acetyltransferase inhibitors. Nat Commun. 8 (1), 1527 (2017).
- Baell, J. B., Miao, W. Histone acetyltransferase inhibitors: where art thou. Future Med Chem. 8 (13), 1525-1528 (2016).
- Lasko, L. M., et al. Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours. Nature. 550 (7674), 128-132 (2017).
- Baell, J. B., et al. Inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases KAT6A/B induce senescence and arrest tumour growth. Nature. 560 (7717), 253-257 (2018).
- Falk, H., et al. An efficient high-throughput screening method for MYST family acetyltransferases, a new class of epigenetic drug targets. J Biomol Screen. 16 (10), 1196-1205 (2011).
- He, M., et al. Chemical biology approaches for investigating the functions of lysine acetyltransferases. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 57 (5), 1162-1184 (2018).
- Lipchik, A. M., et al. A peptide-based biosensor assay to detect intracellular Syk kinase activation and inhibition. Biochemistry. 51 (38), 7515-7524 (2012).
- Song, J., et al. Chemoproteomic profiling of protein substrates of a major lysine acetyltransferase in the native cellular context. ACS Chem Biol. 17 (5), 1092-1102 (2022).
- Gaddameedi, J. D., et al. Acetyl-click screening platform identifies small-molecule inhibitors of histone acetyltransferase 1 (HAT1). J Med Chem. 66 (8), 5774-5801 (2023).
- Ngo, L., Brown, T., Zheng, Y. G. Bisubstrate inhibitors to target histone acetyltransferase 1 (HAT1). Chem Biol Drug Des. 93 (5), 865-873 (2019).
- Parker, C. G., Pratt, M. R. Click chemistry in proteomic investigations. Cell. 180 (4), 605-632 (2020).
- Islam, K. The bump-and-hole tactic: Expanding the scope of chemical genetics. Cell Chem Biol. 25 (10), 1171-1184 (2018).
- Radziwon, K., Weeks, A. M. Protein engineering for selective proteomics. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 60, 10-19 (2021).
- Rich, R. L., Myszka, D. G. Survey of the year 2007 commercial optical biosensor literature. J Mol Recognit. 21 (6), 355-400 (2008).
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoExplorar más artículos
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados