Un abonnement à JoVE est nécessaire pour voir ce contenu. Connectez-vous ou commencez votre essai gratuit.
Method Article
Stabilisation d’une ostéotomie fémurienne avec une fixation par plaque chez Ambystoma mexicanum
Dans cet article
Résumé
Un protocole pour la chirurgie de l’ostéotomie fémorale avec l’utilisation de la fixation de la plaque interne chez les axolotls matures est présenté. La procédure peut être utilisée pour effectuer des études comparatives sur la régénération des membres et la guérison des fractures chez les amphibiens aquatiques.
Résumé
L’axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) est un organisme modèle prometteur pour la médecine régénérative en raison de sa remarquable capacité à régénérer les organes perdus ou endommagés, y compris les membres, le cerveau, le cœur, la queue et autres. Des études sur l’axolotl ont mis en lumière les voies cellulaires et moléculaires régissant l’activation des progéniteurs et la restauration des tissus après une blessure. Ces connaissances peuvent être appliquées pour faciliter la guérison des blessures inaptes à la régénération, telles que la non-consolidation osseuse. Dans le protocole actuel, la stabilisation de l’ostéotomie du fémur à l’aide d’un système de fixation de plaque interne est décrite. La procédure a été adaptée pour être utilisée chez les animaux aquatiques (axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum). Des axolotls de ≥20 cm, du museau à l’extrémité de la queue, avec des fémurs comparables entièrement ossifiés, de la taille d’une souris, ont été utilisés, et une attention particulière a été accordée au positionnement et à la fixation de la plaque, ainsi qu’aux soins postopératoires. Cette technique chirurgicale permet une fixation osseuse standardisée et stabilisée et pourrait être utile pour une comparaison directe avec la régénération des membres axolotl et des études analogues de la cicatrisation osseuse chez les amphibiens et les mammifères.
Introduction
L’axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) est un modèle important pour la régénération des organes, y compris la queue, la moelle épinière, le cerveau, le cœur, les branchies et les membres 1,2,3,4,5. Des études détaillées de la régénération des membres de l’axolotl ont révélé des mécanismes de dédifférenciation cellulaire et de formation d’un pool de cellules souches, le blastème, au site d’amputation. En raison de la capacité des cellules de blastème à reconstruire toutes les parties manquantes des membres, y compris un squelette à motifs 6,7, l’axolotl semble être un organisme modèle attrayant pour les études de guérison osseuse. Récemment, plusieurs études se sont davantage concentrées sur la biologie osseuse chez les axolotls, décrivant la morphologie squelettique, la composition cellulaire et la dynamique de l’ossification.
Il a été constaté chez les mammifères que le processus de cicatrisation osseuse dans les os longs se produit via l’ossification endochondrale et se compose de plusieurs étapes : hématome, tissu de granulation et formation de callosités molles, ossification des callosités en callosités dures et en os tissés, et remodelage osseux8. Une étude récente a montré que des stades similaires peuvent être observés dans la cicatrisation osseusede l’axolotl 9.
Jusqu’à présent, les fractures de l’axolotl étaient étudiées dans un système non stabilisé, où l’os est simplement coupé avec des ciseaux d’iridectomie. Les grandes fractures ont été créées dans le zeugopod, où l’ostéotomie est effectuée sur l’un des os, tandis que l’autre sert de support10,11. En revanche, les fractures sont régulièrement étudiées chez les mammifères, y compris les rats et les souris, à l’aide de systèmes de fixation fiables, tels que la broche intramédullaire et les plaques d’alignement osseux, pour contrôler la taille de la fracture et assurer l’alignement osseux.
Ainsi, la méthode vise à assurer une fixation stabilisée et uniforme du fémur axolotl avant l’ostéotomie. Afin de rendre les études sur l’axolotl plus comparables à celles des mammifères, y compris les souris et les humains, la fixation de la broche intramédullaire12, du fixateur de plaque externe13,14 et de la plaque d’alignement osseux interne 15,16,17 a été envisagée. Il a été démontré que cette dernière assure une bonne fixation osseuse et permet de créer un espace d’une certaine taille en utilisant une ou deux coupes avec une scie Gigly d’un diamètre spécifique. Comme les axolotls représentent les larves aquatiques d’Ambystoma mexicanum, le fixateur externe pourrait avoir causé des complications post-chirurgicales en raison de la plaie ouverte et du contact avec l’eau. Comme les axolotls ne développent pas de centres d’ossification secondaires même très tard dans leur développement (20 ans18), et donc que le clou intramédullaire standard utilisé chez la souris pourrait ne pas être empêché de percer les épiphyses, il a été décidé d’appliquer une méthode de fixation de plaque interne aux grands axolotls. Chez les grands axolotls, la taille du fémur et le degré d’ossification ressemblent à ceux d’une souris adulte, permettant ainsi une ostéotomie mi-diaphysaire avec fixation de plaque de titane1.
La taille de l’espace de fracture détermine en grande partie la dynamique et le résultat de la guérison. Par exemple, chez une souris, les fractures stabilisées de 0,25 mm guérissent principalement par ossification intramembraneuse en raison de leur petite taille et de leur stabilisation rigide ; une fracture de 0,7 mm cicatrise par ossification endochondrale, avec formation d’un cal cartilagineux autour de la fracture ; Les défauts importants, tels que les défauts de taille critique de 3,5 mm, ne guérissent pas complètement et sont donc utilisés pour modéliser la fracture osseuse non consolidée16. Dans cette étude, le protocole de fixation de la plaque du fémur de l’axolotl avant l’ostéotomie à l’aide de l’exemple d’un espace de fracture de 0,7 mm a été établi dans le but ultime de comparer la cicatrisation de l’os de l’axolotl à celle de la souris9.
Après l’ostéotomie, les fractures ont subi un processus d’ossification endochondrale, bien que plus lent que chez la souris, peut-être en raison du mode de vie aquatique des axolotls et des taux de division cellulaire plus lents. Dans la méthode présentée ici, l’ostéotomie à espace de 0,7 mm avec fixation par plaque rigide est illustrée ; Cependant, d’autres tailles d’espace et des fixateurs semi-flexibles, ainsi que des plaques de différents matériaux, sont potentiellement possibles. Dans l’ensemble, la méthode présentée ici peut être utilisée pour la fixation osseuse standardisée et sera utile pour les études comparant la régénération des membres de l’axolotl à la cicatrisation osseuse ou l’étude de la cicatrisation osseuse chez les axolotls dans différentes conditions pour assurer la fixation standardisée des fractures.
Protocole
La procédure suivante a été réalisée avec l’approbation du magistrat de Vienne (GZ : MA 58-65248-2021-26). Âgés de 5 à 8 ans, ≥ axolotls longs (Ambystoma mexicanum) de 20 cm du museau à la queue (Ambystoma mexicanum) étaient utilisés pour la chirurgie des fractures et les amputations. Des hommes et des femmes ont été utilisés pour les chirurgies. Les axolotls ont été élevés dans les installations de l’Institut de recherche en pathologie moléculaire. La douleur et le risque d’infections ont été gérés à l’aide d’analgésiques et d’antibiotiques appropriés pour assurer le succès. Les réactifs et l’équipement utilisés pour l’étude sont énumérés dans la table des matériaux.
1. Préparation des animaux
- Baignez l’animal dans une solution de benzocaïne à 0,03 % pendant environ 15 à 20 minutes jusqu’à ce que la sédation complète soit atteinte et qu’il n’y ait plus de mouvement réflexe au contact du membre avec une pince à épiler.
- Placez l’animal avec le côté ventral vers le bas sur des serviettes en papier humides imbibées d’une solution de benzocaïne à 0,03 % et couvrez-le d’essuie-tout imbibé de benzocaïne. La peau des animaux aquatiques, tels que les axolotls, est sensible au dessèchement, et il est donc essentiel de couvrir la surface du corps pour prévenir la déshydratation et assurer une respiration cutanée (cutanée).
- Étirez la patte postérieure pour l’actionner à l’aide d’une pince annulaire. N’appliquez pas de réactifs de désinfection, tels que l’éthanol, car la peau de l’axolotl est sensible aux produits chimiques et facilement irritée. Au lieu de cela, utilisez du PBS 0,7x (A-PBS) avec 50 U/mL de pénicilline et 20 μg/mL de streptomycine pour nettoyer le membre et plus tard pour l’irrigation osseuse lors du sciage.
REMARQUE : L’infection n’est généralement pas un problème pour les chirurgies pratiquées sur les axolotls. Cependant, en raison de la nature aquatique de ces animaux et des sutures placées à la surface de la peau, nous recommandons l’utilisation d’antibiotiques pour éviter toute contamination du site chirurgical.
2. Chirurgie
REMARQUE : Stérilisez tous les outils chirurgicaux. Les méthodes de stérilisation courantes telles que la stérilisation thermique, l’autoclave et le lavage à l’éthanol à 70 %, suivi d’une élimination complète des restes d’alcool, conviennent à cet effet. Si vous opérez sur plusieurs animaux, stérilisez les outils entre les deux à l’aide d’un stérilisateur à billes chaudes ou d’éthanol à 70 %.
- Faites une incision longitudinale latérale (1,5-2 cm) avec un scalpel au-dessus de l’os du fémur couvrant toute la cuisse dans le membre postérieur supérieur. Pour ce faire, palpez l’os avant de couper la peau.
- Déplacez soigneusement les muscles et les nerfs du site de chirurgie sans couper. Utilisez une pince à courbure pour le faire efficacement.
- Placez doucement une pince arquée sous le fémur pour l’exposer à la chirurgie.
- Placez une plaque de fixation rigide à 4 trous de 7,75 mm avec la diaphyse du fémur, en évitant de toucher les articulations, et fixez-la en position alignée avec une pince.
- Utilisez quatre vis en titane de 2 mm pour fixer l’os à la plaque.
REMARQUE : Les vis utilisées dans ce protocole ont une conception complexe et se composent de 4 parties : la partie principale (sera vissée dans l’os), la tête de vis (permet de retirer les vis et la plaque à l’aide de la clé carrée), le col plus étroit (utilisé comme point de rupture une fois la vis serrée dans l’os) et une poignée de vis (utilisée pour la fixation au tournevis et au dispositif de guidage de la scie). - L’ordre de fixation des vis est important. Commencez par les vis intérieures, puis les deux vis extérieures pour vous assurer que la plaque est alignée avec l’axe de l’os. Utilisez une perceuse manuelle pour créer le premier trou dans l’os pour une insertion facile de la vis, suivi de la pose d’une1ère vis. Percez au milieu de la circonférence osseuse pour éviter un os plus mince d’un côté, ce qui pourrait entraîner une fracture osseuse spontanée. Utilisez l’irrigation avec 0,7x PBS + 1% Pen/Strep pendant le forage. Ne cassez pas la poignée de la ou des vis 1ère (facultatif : 1ère et 2èmes).
- Appliquez le dispositif de guidage de scie sur la ou les 1ère vis (en option : 1ère et 2ème ) et alignez-la avec l’os et la plaque.
REMARQUE : Dans ce protocole, une plaque, des vis, un dispositif de guidage de scie et une scie sont fournis par le même fabricant et optimisés pour s’adapter les uns aux autres. Le dispositif de guidage de scie peut être disponible en différentes tailles pour être compatible avec différentes plaques et tailles de scie. - Utilisez le dispositif de guidage de la scie pour percer et insérer le reste des vis. Assurez-vous de l’alignement de la plaque avec l’os. Cassez les poignées des vis.
- Placez un morceau de film plastique (6-7 mm sur 4-5 cm), stérilisé par essuyage avec de l’éthanol à 70 %, puis stérilisé à l’autoclave ou à la chaleur (140 °C pendant 4 heures), sous le fémur pour éviter d’endommager les tissus mous pendant le processus d’ostéotomie.
REMARQUE : À cet effet, un morceau de film plastique, coupé d’un sac pour la stérilisation à la chaleur peut être utilisé. - Placez la scie à fil Gigly entre l’os et le film de protection.
- Coupez l’os à l’aide de la scie à fil Gigly de 0,66 mm, en créant une seule coupe de 0,7 mm dans le fémur. Utilisez une irrigation constante avec 0,7x PBS + 1% Pen/Strep pendant le sciage pour minimiser les dommages aux tissus et la friction.
- Retirez la scie et le guide de scie et utilisez un tournevis pour casser les poignées de vis des vis.
- Retirez le film de protection et irriguez le site de chirurgie avec 0,7x PBS + 1% Pen/Strep.
- Couvrez le haut de la plaque et les vis avec de la cire d’abeille stérile pour protéger la peau et les muscles de l’irritation par les bords des vis.
- Placez les muscles et la peau sur la cire d’abeille en os.
- Fermez le site d’incision avec une suture synthétique 7.0 (polypropylène/polyéthylène) à l’aide de simples points de suture interrompus. La suture synthétique est utilisée pour minimiser la contamination par les bactéries et les champignons d’origine hydrique.
3. Prise en charge postopératoire
- Pour réveiller l’animal, placez-le dans un réservoir avec de l’eau douce artificielle de bassin, complétée par 50 U/mL de pénicilline, 20 μg/mL de streptomycine et un analgésique Butorphanol (0,5 mg/L d’eau).
- Observez l’animal pour commencer à bouger ses branchies, à faire des pas et à nager, généralement dans l’heure suivant la chirurgie.
- Gardez l’animal pendant 3 jours dans de l’eau d’étang artificiel avec 50 μg/ml de pénicilline et 20 μg/ml de streptomycine avant de le remettre dans le réservoir de rétention. Pour assurer l’analgésie, ajoutez du Butorphanol (0,5 mg/L d’eau).
- Assurez-vous que les sutures restent en place et que la cicatrisation des plaies est correcte.
Résultats
L’intervention chirurgicale décrite ici (Figure 1) dure entre 20 min et 30 min et nécessite la présence d’un chirurgien et d’un assistant. En option, utilisez un microscope à dissection binoculaire ou un système de loupe.
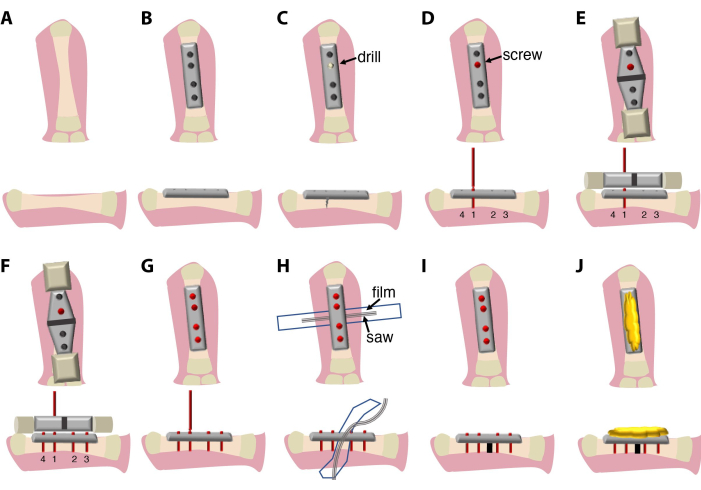
Figure 1 : Schémas de l’interven...
Discussion
La méthode actuellement décrite de fixation de la plaque du fémur et d’ostéotomie permet son application chez les animaux aquatiques, tels que Ambystoma mexicanum (axolotl). Cette méthode chirurgicale a récemment été utilisée pour comparer la cicatrisation des fractures et la régénération des membres chez les axolotls à la cicatrisation des fractures chez les souris9. Comme chez les souris, une plaque de fixation à 4 trous peut être fixé...
Déclarations de divulgation
Les auteurs ne déclarent aucun intérêt concurrent.
Remerciements
Les auteurs tiennent à remercier Sabine Stumpp pour l’excellent support technique et Lidia Grösser pour son aide dans les opérations. Cette recherche a été financée par le Fonds autrichien pour la science [bourse Hertha Firnberg numéro T-1219], ERC [Advanced Grant, 742046 RegGeneMems], DFG [CRC 1444].
matériels
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.66 mm Gigly wire saw | RISystem | RIS.590.120 | |
| 7.0 Optilene suture | Braun | C3090538 | |
| Benzocaine | Sigma-Aldrich | E1501 | dilute to 0.03% prior to using |
| Butorphanol (Butomidor 10 mg/mL) | Richter Pharma AG | - | dilute to 0.5 mg/L prior to using |
| Drill bit 0.30 mm | RISystem | RIS.590.200 | |
| Dumont #5 Forceps - Standard/Inox | Fine Science Tools | 11251-20 | |
| Hand drill | RISystem | RIS.390.130 | better to have at least 3 pieces |
| Micro CT data analyzer | Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA | SkyScan NRecon software | |
| Micro CT specimen scanner | Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA | SkyScan 1172 | |
| Moria MC31b Iris forceps - smooth, curved, 10 cm | Fine Science Tools | 11373-12FST | 2 pieces |
| MouseFix Drill-&Saw guide 1.75 mm, rigid | RISystem | RIS.301.102 | |
| MouseFix plate 4 hole, rigid | RISystem | RIS.401.110 | |
| MouseFix screw, L =2.00 mm | RISystem | RIS.401.100 | need 4 per bone |
| Narrow Pattern Forceps | VWR | FSCI11002-12 | |
| penicillin/streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | |
| Ring forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11103-09 | |
| scalpel #15 | B Braun, Thermo Fischer Scientific | 5518032 | |
| Square box wrench 0.50 mm | RISystem | RIS.590.111 | |
| Sterile bone wax, 2.5 g | Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson | W810 | |
| Student Fine Scissors - Straight/11.5cm | Fine Science Tools | 91460-11 |
Références
- Amamoto, R., et al. Adult axolotls can regenerate original neuronal diversity in response to brain injury. Elife. 5, 13998 (2016).
- Butler, E. G., Ward, M. B. Reconstitution of the spinal cord following ablation in urodele larvae. J Exp Zool. 160 (1), 47-65 (1965).
- Echeverri, K., Tanaka, E. M. Ectoderm to mesoderm lineage switching during axolotl tail regeneration. Science. 298 (5600), 1993-1996 (2002).
- Vargas-Gonzalez, A., Prado-Zayago, E., Leon-Olea, M., Guarner-Lans, V., Cano-Martinez, A. Myocardial regeneration in Ambystoma mexicanum after surgical injury. Arch Cardiol Mex. 75 (3), S321-S329 (2005).
- Vieira, W. A., Wells, K. M., McCusker, C. D. Advancements to the axolotl model for regeneration and aging. Gerontology. 66 (3), 212-222 (2020).
- Song, F., Li, B., Stocum, D. L. Amphibians as research models for regenerative medicine. Organogenesis. 6 (3), 141-150 (2010).
- McCusker, C., Bryant, S. V., Gardiner, D. M. The axolotl limb blastema: Cellular and molecular mechanisms driving blastema formation and limb regeneration in tetrapods. Regeneration (Oxf). 2 (2), 54-71 (2015).
- Einhorn, T. A., Gerstenfeld, L. C. Fracture healing: Mechanisms and interventions). Nat Rev Rheumatol. 11 (1), 45-54 (2015).
- Polikarpova, A., et al. The specialist in regeneration-the Axolotl-a suitable model to study bone healing. NPJ Regen Med. 7 (1), 35 (2022).
- Chen, X., et al. The axolotl fibula as a model for the induction of regeneration across large segment defects in long bones of the extremities. PLoS One. 10 (6), e0130819 (2015).
- Cosden-Decker, R. S., Bickett, M. M., Lattermann, C., MacLeod, J. N. Structural and functional analysis of intra-articular interzone tissue in axolotl salamanders. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20 (11), 1347-1356 (2012).
- Williams, J. N., Li, Y., Valiya Kambrath, A., Sankar, U. The generation of closed femoral fractures in mice: A model to study bone healing. J Vis Exp. (138), e58122 (2018).
- Cheung, K. M., et al. An externally fixed femoral fracture model for mice. J Orthop Res. 21 (4), 685-690 (2003).
- Jiang, S., Knapstein, P., Donat, A., Tsitsilonis, S., Keller, J. An optimized protocol for a standardized, femoral osteotomy model to study fracture healing in mice. STAR Protoc. 2 (3), 100798 (2021).
- Matthys, R., Perren, S. M. Internal fixator for use in the mouse. Injury. 40, S103-S109 (2009).
- Manassero, M., et al. Establishment of a segmental femoral critical-size defect model in mice stabilized by plate osteosynthesis. J Vis Exp. (116), e52940 (2016).
- Gunderson, Z. J., Campbell, Z. R., McKinley, T. O., Natoli, R. M., Kacena, M. A. A comprehensive review of mouse diaphyseal femur fracture models. Injury. 51 (7), 1439-1447 (2020).
- Riquelme-Guzman, C., et al. Postembryonic development and aging of the appendicular skeleton in Ambystoma mexicanum. Dev Dyn. 251 (6), 1015-1034 (2022).
- Gentz, E. J., et al. Medicine and surgery of amphibians. ILAR J. 48 (3), 255-259 (2007).
- Lang, A., et al. Collagen I-based scaffolds negatively impact fracture healing in a mouse-osteotomy-model although used routinely in research and clinical application. Acta Biomater. 86, 171-184 (2019).
Réimpressions et Autorisations
Demande d’autorisation pour utiliser le texte ou les figures de cet article JoVE
Demande d’autorisationThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon