Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Spectral Karyotyping to Study Chromosome Abnormalities in Humans and Mice with Polycystic Kidney Disease
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
Spectral Karyotyping (SKY) is an advanced cytogenetics technique to identify genomic and chromosomal aberrations. This technique takes advantage of chromosome painting probes, which allow classification of all chromosomes. SKY can also identify complex chromosome aberrations and segregation defects in mice and humans with various diseases, including polycystic kidney disease.
Streszczenie
Conventional method to identify and classify individual chromosomes depends on the unique banding pattern of each chromosome in a specific species being analyzed 1, 2. This classical banding technique, however, is not reliable in identifying complex chromosomal aberrations such as those associated with cancer. To overcome the limitations of the banding technique, Spectral Karyotyping (SKY) is introduced to provide much reliable information on chromosome abnormalities.
SKY is a multicolor fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) technique to detect metaphase chromosomes with spectral microscope 3, 4. SKY has been proven to be a valuable tool for the cytogenetic analysis of a broad range of chromosome abnormalities associated with a large number of genetic diseases and malignancies 5, 6. SKY involves the use of multicolor fluorescently-labelled DNA probes prepared from the degenerate oligonucleotide primers by PCR. Thus, every chromosome has a unique spectral color after in-situ hybridization with probes, which are differentially labelled with a mixture of fluorescent dyes (Rhodamine, Texas Red, Cy5, FITC and Cy5.5). The probes used for SKY consist of up to 55 chromosome specific probes 7-10.
The procedure for SKY involves several steps (Figure 1). SKY requires the availability of cells with high mitotic index from normal or diseased tissue or blood. The chromosomes of a single cell from either a freshly isolated primary cell or a cell line are spread on a glass slide. This chromosome spread is labeled with a different combination of fluorescent dyes specific for each chromosome. For probe detection and image acquisition,the spectral imaging system consists of sagnac interferometer and a CCD camera. This allows measurement of the visible light spectrum emitted from the sample and to acquire a spectral image from individual chromosomes. HiSKY, the software used to analyze the results of the captured images, provides an easy identification of chromosome anomalies. The end result is a metaphase and a karyotype classification image, in which each pair of chromosomes has a distinct color (Figure 2). This allows easy identification of chromosome identities and translocations. For more details, please visit Applied Spectral Imaging website (http://www.spectral-imaging.com/).
SKY was recently used for an identification of chromosome segregation defects and chromosome abnormalities in humans and mice with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD), a genetic disease characterized by dysfunction in primary cilia 11-13. Using this technique, we demonstrated the presence of abnormal chromosome segregation and chromosomal defects in ADPKD patients and mouse models 14. Further analyses using SKY not only allowed us to identify chromosomal number and identity, but also to accurately detect very complex chromosomal aberrations such as chromosome deletions and translocations (Figure 2).
Protokół
1. Cell pretreatment and metaphase preparation
- The cells are grown in Dulbecco's Modification of Eagle's Medium (DMEM) containing 10-15% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C with 5% CO2 incubator, until they reach 70-80% confluency.
- Treat the cells with colcemid solution at 0.05 μg/ml for 30-60 min.
- Collect the medium containing any floating cells in 50-ml sterile falcon centrifuge tubes. Rinse the cells on the plate with sterile1X-PBS. After incubating with sterile trypsin for 1-2 min, harvest and collect the remaining cells into the same tube.
- Spin the tubes at 1000 r.p.m. for 5 min, aspirate the supernatant leaving 0.5 ml and loosen pellet by flicking with finger only.
- Depending on the pellet size, add 5-10 ml of hypotonic solution of 0.56% KCl in dH2O and incubate the suspension at 37°C for 30-45 min.
- Add one drop of methanol/acetic acid (3:1 vol/vol) per ml of hypotonic cell suspension and invert the tube gently for mixing.
- Centrifuge at 1200 r.p.m. for 5 min and collect pellet as step 1.4, then add 5 ml of fresh methanol/acetic acid (3:1 vol/vol) fixative solution dropwise while flicking the pellet continously. This procedure is critical so that the metaphase spreads will not be trapped in the cells' clumps which would compromise the experiment.
- Centrifuge again at 1200 r.p.m. for 5 min and add 5-10 ml of ice-cold methanol/acetic acid fixative along the wall of the tube. At this stage, if needed, the cells can be stored in fixative solution in a tightened and sealed tube at -20°C for short term or -80°C for long term (years) for future use.
- Clean slides in absolute ethanol, then dip the slide in dH2O for approximately10X in order to form a sheath of water on the surface of the slide. Place the slide on a glass plate and drop 15-20μl of cell suspension (from step 1.8) from 10" above the slide. Place the slide in a water bath set at 65-70°C for 1-2 min and allow to dry.
- Check the slide under a light microscope using 10X and 40X dry objectives making sure there is metaphase chromosomes and the spreads are evenly spaced. Check for cytoplasm presence surrounding the chromosomes. If cytoplasm is present proceed with slide pretreatment (pepsin digestion), if no cytoplasm is present and the chromosomes have good morphology, then there is no need for slide pretreatment.
2. Slide pretreatment (pepsin treatment)
- Apply 120 μl of 1:200 RNase solution (20 mg/ml) dissolved in 2X-SSC onto a 24 mm x 60 mm microscope coverglass and invert the metaphase slide face down on the coverglass then gently invert the metaphase slide face up and incubate at 37°C for 45 min.
- Carefully remove the coverglass without scratching the slide and wash in 2X-SSC buffer in a coplin jar every 5 min for 15 min with shaking.
- Add 5-15 μl of pepsin stock solution (100 mg/ml in dH2O) into a clean beaker and then add 100 ml of prewarmed (37°C) 0.01M HCl. It is important that the pepsin is added into a clean beaker first and not directly into the HCl solution, otherwise it wouldn't dissolve in solution. Incubate the slide in a coplin jar containing the HCl/pepsin solution at 37°C for 3-5 min. This step is very critical as too much digestion will cause the chromosomes to be overdigested and too little digestion will leave the cytoplasm undigested which might lead to non-specific binding of the probe and interfere with the hybridization signal.
- Wash the slide in a coplin jar containing 100 ml 1X-PBS for 5 min twice at room temperature.
- Wash the slide in a coplin jar containing 100 ml 1X-PBS/MgCl2 for 5 min at room temperature (50 ml of 1M MgCl2 in 950 ml of 1X-PBS).
- Place the slide in a coplin jar containing 100 ml 1% formaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature (1.7 ml of 37% formaldehyde in 100 ml of 1X-PBS/MgCl2).
- Wash the slide in a coplin jar containing 100 ml 1X-PBS for 5 min.
- Observe the slide under a light microscope using 40X dry lens to ensure that the slides are digested properly and no cytoplasm is present and the chromosome morphology is preserved. Select an area for hybridization using a diamond pen.
3. Chromosome and probe denaturation and hybridization
- Prepare fresh denaturing solution (70% formamide/2X SSC, pH 7.0) and prewarm to 70-80°C in a coplin jar placed in a water bath Place the slide in the coplin jar containing the denaturing solution in a water bath at 70°C for mouse chromosomes and 80°C for human chromosomes for 30s-1.5 min.
- Immediately place the slide in ice-cold 70% ethanol for 3 min followed by 80% and 100% ethanol for 3 min each and air dry. Examine the slide for chromosome morphology. Good chromosome morphology is denoted by dark chromosomes and not "phase-light" or halo chromosomes.
- Warm the SkyPaint probe (SKY paint kit; vial#1) at 37°C with shaking for 20 min, vortex and centrifuge briefly at 1000 r.p.m. for a few seconds.
- Denature the probe in a thermocycler programmed for a two-step cycle at 85°C for 5 min cycle followed by 37°C for 60 min to allow labeled-probe DNA for preannealing.
- Apply 10μl of the denatured probe onto the area of hybridization and cover with a 22 mm x 40 mm coverglass making sure not to trap air bubbles. Seal the edges of the coverglass with rubber cement and incubate in a humidified chamber at 37°C for 48-72 hrs.
4. Fluorescent probe detection
- Remove the coverglass carefully and place the slide in a coplin jar containing prewarmed (45°C) washing solution I (freshly prepared 50% formamide in 2X SSC). Wash for 5 min three times at 45°C in a shaking water bath at 45 r.p.m.
- Wash the slide in washing solution II (1X SSC) at 45°C for 5 min twice with shaking.
- Wash the slide in washing solution III (4X SSC/0.1% Tween 20) for 5 min at 45°C with shaking.
- Apply 80 μl of blocking reagent (SKY paint kit; vial#2), place a coverslip and incubate at 37°C for 30 min.
- Remove the slide and allow the fluid to drain. Apply 80 μl of Cy5 staining reagent (Concentrated Antibody Detection CAD kit; vial#3), apply a coverglass and incubate at 37°C for 40 min.
- Wash the slide with washing solution III at 45°C for 5 min three times with shaking.
- Apply 80 μl of Cy5.5 staining reagent (Concentrated Antibody Detection CAD kit; vial#4), place a coverglass and incubate at 37°C for 40 min.
- Wash the slide with washing solution III at 45°C for 5 min three times with shaking.
- Tilt the slide and allow the fluid to drain. Apply 20 μl of the anti-fade DAPI reagent (SKY paint kit; vial#5) and place a 24 mm x 60 mm microscope coverglass. Carefully remove air bubbles that might have formed. Slides can be imaged immediately or stored at 4°C in the dark for no longer than 1 week.
5. Image acquisition and analysis
- Image acquisition is accomplished by viewing metaphase slides using an Olympus microscope equipped with a 60X oil immersion lens, a Spectral cube (custom designed triple band pass filter), a DAPI filter and a sagnac interferometer module with a CCD camera.
- Spectral-Karyotypes were carried out using SKY View software (Applied spectral imaging Version 1.62) following the user's manual.
- After analyzing the images, the chromosomes can be viewed as color images (with specific fluorescent colors), pseudo color images (with colors for classification) and inverted DAPI images (specific banding pattern).
6. Representative Results
A complete SKY procedure usually takes about one week time (Figure 1). This includes image acquisition and analysis provided that the metaphase cells are in adequate supply. Karyotyping analysis reveals normal mouse karyotype (40,XY) of cells from wild type mice (Figure 2a). In contrast, cells from Pkd1-/- mouse (PKD mouse model) shows a significant increase in chromosome number and structural abnormalities, such as chromosome deletions (Chromosome # 8) and translocations (chromosomes # 11 and 19) (Figure 2b). We also analyzed vascular tissues from the ADPKD patients. A simple study by counting the chromosomal numbers indicated that non-ADPKD and some ADPKD vascular samples had normal chromosomal numbers of 23 pairs (Figure 2c). In general, however, we observed failure of chromosomal segregation, resulting in 46 pairs of chromosomes in ADPKD samples instead of 23 pairs (Figure 2d).
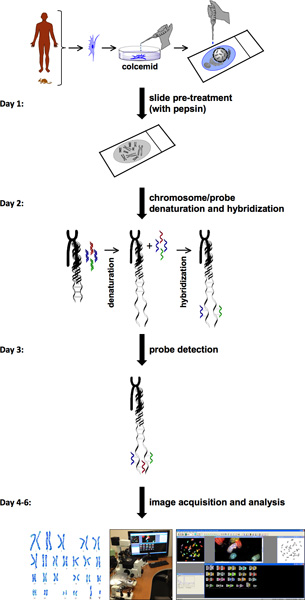
Figure 1. SKY protocol flowchart. Flow chart of the SKY protocol illustrates steps to complete an experiment starting from cell pretreatment and metaphase preparations to image acquisition and analysis. An approximate one-week timeline is presented on the left with step-by-step procedures for each day.

Figure 2. Spectral karyotyping on immortalized mouse cell lines and freshly isolated human primary cells. Color and inverted DAPI images of individual chromosomes are shown before the chromosomal sorting. After sorting, chromosomes are presented in the "classification" table. a) SKY image of a metaphase spread from wild type mouse contains normal karyotype (40, XY). b) SKY image of a metaphase spread from Pkd1-/- mouse shows abnormal chromosome number (68 instead of 40) and chromosome abnormalities such as chromosome deletions (chromosome #8) and chromosome translocations (chromosomes #11 and 19). c) SKY image of a metaphase spread from the vascular tissue of a non-ADPKD patient has normal karyotype (46, XX). d) SKY image of a metaphase spread from the vascular tissue of an ADPKD patient contains abnormal karyotype (92, XXXX). Parts of the data have been previously reported and reused with permission 14.
Dyskusje
Spectral Karyotyping (SKY) is a cytogenetics technique used in studying genomic and chromosomal compositions. This technique takes advantage of chromosome painting probes, and the detection of these probes are acquired through a sagnac interferometer. The complete SKY process usually takes about one week, and it involves several key steps (Figure 1). The SKY uses a standard protocol, which was first described by Padilla-Nash et al 3. The protocol has since been adapted by various cyto...
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
Authors would like to thank Brian Muntean, Shao Lo, Maki Takahashi and Blair Mell for their technical assistance. This work was supported by awards from the NIH (DK080640) and The University of Toledo & ProMedica Translational Research Stimulation Award to Dr. Surya Nauli.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| DMEM | Cellgro | 10-013-CV | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Hyclone | SH30088-03 | |
| Penecillin/Streptomycin | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | SV30010 | |
| Colcemid | Roche Group | 10 295 892 001 | 10 μg/ml |
| HCl | Fisher Scientific | A144-500 | |
| KCl | Fisher Scientific | S77375-1 | |
| Phosphate buffered saline | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | SH30256-01 | |
| SKY paint probe kit (Human) | Applied Spectral Imaging | SKY000028 | |
| SKY paint probe kit (Mouse) | Applied Spectral Imaging | SKY000030 | |
| Concentrated antibody detection kit | Applied Spectral Imaging | SKY000033 | |
| Trypsin | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | SH30236.01 | |
| Methanol | Fisher Scientific | A433P-4 | |
| Acetic acid | Fisher Scientific | A38-212 | |
| RNase A | Roche Group | 10 109 169 001 | |
| Pepsin | Sigma-Aldrich | P6887-5G | |
| MgCl2 | Fluka | 63069-500ML | |
| 37% Formaldehyde | Mallinckrodt Baker Inc. | 2106-02 | |
| 20X SSC | Promega Corp. | V4261 | |
| Formamide | Fluka | 47671 | prepare just before use |
| Tween-20 | Fisher Scientific | BP337-500 | |
| Microscope glass slides | Fisher Scientific | 12-549 | |
| Microscope cover glass 24x60mm | VWR international | 16004-312 | |
| Rubber cement | Elmer’s | ||
| Hybridization/ humidifiedchamber/Tray | Simport | M920-2 | put wet paper towels at the bottom |
| Thermocycler | Eppendorf | Epgradient S | |
| Shaking platform/Orbital shaker | Bellco Glass | ||
| Shaking/water bath | Precision Scientific | ||
| DAPI filter cube | Chroma Technology Corp. | ||
| SKY filter cube | Chroma Technology Corp. | ||
| SpectraCube | Applied Spectral Imaging | ||
| Inverted cell culture microscope | Nikon Instruments | Nikon Eclipse TS100 | |
| Fluorescence microscope | Olympus Corporation | IX70 | 60X oil |
Odniesienia
- Caspersson, T., Farber, S., Foley, G. E., Kudynowski, J., Modest, E. J., Simonsson, E., Wagh, U., Zech, L. Chemical differentiation along metaphase chromosomes. Experimental Cell Research. 49, 219-222 (1968).
- Seabright, M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 2, 971-972 (1971).
- Padilla-Nash, H. M., Barenboim-Stapleton, L., Difilippantonio, M. J., Ried, T. Spectral karyotyping analysis of human and mouse chromosomes. Nature Protocols. 1, 3129-3142 (2006).
- Schrock, E., Zschieschang, P., O'Brien, P., Helmrich, A., Hardt, T., Matthaei, A., Stout-Weider, K. Spectral karyotyping of human, mouse, rat and ape chromosomes--applications for genetic diagnostics and research. Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 114, 199-221 (2006).
- Padilla-Nash, H. M., Heselmeyer-Haddad, K., Wangsa, D., Zhang, H., Ghadimi, B. M., Macville, M., Augustus, M., Schrock, E., Hilgenfeld, E., Ried, T. Jumping translocations are common in solid tumor cell lines and result in recurrent fusions of whole chromosome arms. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer. 30, 349-363 (2001).
- Veldman, T., Vignon, C., Schrock, E., Rowley, J. D., Ried, T. Hidden chromosome abnormalities in haematological malignancies detected by multicolour spectral karyotyping. Nature Genetics. 15, 406-410 (1997).
- Karpf, A. R., Matsui, S. Genetic disruption of cytosine DNA methyltransferase enzymes induces chromosomal instability in human cancer cells. Cancer Research. 65, 8635-8639 (2005).
- Matsui, S., Faitar, S. L., Rossi, M. R., Cowell, J. K. Application of spectral karyotyping to the analysis of the human chromosome complement of interspecies somatic cell hybrids. Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics. 142, 30-35 (2003).
- Nestor, A. L., Hollopeter, S. L., Matsui, S. I., Allison, D. A model for genetic complementation controlling the chromosomal abnormalities and loss of heterozygosity formation in cancer. Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 116, 235-247 (2007).
- Ried, T., Liyanage, M., du Manoir, S., Heselmeyer, K., Auer, K., Macville, M., Schrock, E. Tumor cytogenetics revisited: comparative genomic hybridization and spectral karyotyping. Journal of Molecular Medicine (Berlin, Germany). 75, 801-814 (1997).
- AbouAlaiwi, W. A., Takahashi, M., Mell, B. R., Jones, T. J., Ratnam, S., Kolb, R. J., Nauli, S. M. Ciliary polycystin-2 is a mechanosensitive calcium channel involved in nitric oxide signaling cascades. Circulation Research. 104, 860-869 (2009).
- Nauli, S. M., Alenghat, F. J., Luo, Y., Williams, E., Vassilev, P., Li, X., Elia, A. E., Lu, W., Brown, E. M., Quinn, S. J., Ingber, D. E., Zhou, J. Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells. Nature Genetics. 33, 129-137 (2003).
- Nauli, S. M., Kawanabe, Y., Kaminski, J. J., Pearce, W. J., Ingber, D. E., Zhou, J. Endothelial cilia are fluid shear sensors that regulate calcium signaling and nitric oxide production through polycystin-1. Circulation. 117, 1161-1171 (2008).
- AbouAlaiwi, W. A., Ratnam, S., Booth, R. L., Shah, J. V., Nauli, S. M. Endothelial cells from humans and mice with polycystic kidney disease are characterized by polyploidy and chromosome segregation defects through survivin down-regulation. Human Molecular Genetics. 20, 354-367 (2011).
- Padilla-Nash, H. M., Nash, W. G., Padilla, G. M., Roberson, K. M., Robertson, C. N., Macville, M., Schrock, E., Ried, T. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of the bladder carcinoma cell line BK-10 by spectral karyotyping. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer. 25, 53-59 (1999).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone