A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
ELIME (Enzyme Linked Immuno Magnetic Electrochemical) Method for Mycotoxin Detection
In This Article
Summary
A protocol to detect trichothecenes (mycotoxins of concern for human health) using a newly developed screening method based on a competitive immunochemical method and a final electrochemical detection is demonstrated.
Abstract
Immunoassays are a valid alternative to the more expensive and time consuming quantitative HPLC or GC1, 2 methods for the screening detection of hazardous mycotoxins in food commodities. In this protocol we show how to fabricate and interrogate an electrochemical competitive Enzyme linked immunomagnetic assay based on the use of magnetic beads as solid support for the immunochemical chain3 and screen printed electrodes as sensing platform.
Our method aims to determine the total amount of HT-2 and T-2 toxins, mycotoxins belonging to the trichothecenes family and of great concern for human health4. The use of an antibody clone with a cross reactivity of 100% towards HT-2 and T-2 allows to simultaneously detect both toxins with similar sensitivity5.
The first step of our assay is the coating step where we immobilize HT2-KLH conjugate toxin on the surface of magnetic beads. After a blocking step, necessary to avoid non-specific absorptions, the addition of a monoclonal antibody allows the competition between immobilized HT-2 and free HT-2 or T-2 present in the sample or dissolved in a standard solution.
At the end of the competition step, the amount of monoclonal antibody linked to the immobilized HT-2 will be inversely proportional to the amount of toxin in the sample solution.
A secondary antibody labeled with alkaline phosphatase (AP) is used to reveal the binding between the specific antibody and the immobilized HT-2. The final measurement step is performed by dropping an aliquot of magnetic bead suspension, corresponding to a specific sample/standard solution, on the surface of a screen-printed working electrode; magnetic beads are immobilized and concentrated by means of a magnet placed precisely under the screen-printed electrode. After two minutes of incubation between magnetic beads and a substrate for AP, the enzymatic product is detected by Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) using a portable instrument (PalmSens) also able to initiate automatically eight measurements within an interval of few seconds.
Protocol
1) Blocking coated Magnetic Beads:
Proceed as follow to block Coated Magnetic beads:
- Prepare a set of 2 ml Eppendorf tubes;
- Homogenize (shaking but not vortexing) coated magnetic beads (see the appendix for preparation of coated magnetic beads) using the sample rotating mixer;
- Immediately after homogenization, pipette 10 μl of coated magnetic beads into each separate Eppendorf tubes;
- Add 1ml of skimmed milk blocking solution into each Eppendorf tube of the set;
- Let magnetic beads incubate for 30 min at room temperature on the rotating sample mixer;
- Remove blocking solution: to do so place the tube in magnetic particle concentrator with the magnetic part put on for 2 min (see magnetic beads sticking on the lateral wall of the tube); carefully pipette off the supernatant, leaving beads undisturbed;
- Add 1 ml of PBS buffer + NaN3 + BSA as storage solution for each tube;
- Store coated and blocked magnetic beads at 4°C (please note that coated magnetic beads are stable for at least 2 months at 4°C);
2) Immunological chain on magnetic beads for construction of the calibration curve and sample analysis
Proceed as follow to have magnetic beads ready for the measurement:
- Take one Eppendorf tube (2 ml) of coated and blocked solution for each sample extract you are going to analyze;
- Take an extra Eppendorf tube for each working calibrant solution;
- Homogenize magnetic beads for 2 min on the rotating sample mixer before use;
- Remove storage liquid using magnetic particle concentrator;
- Wash magnetic beads three times with PBS/BSA washing solution. Remove washing liquid;
- Competition step: Add for each tube containing the washed magnetic beads, 200μl of sample extract prepared; use one magnetic bead tube for each sample. Repeat the same procedure for each standard solution. Add 200 μl of monoclonal antibody solution to each magnetic bead tube. Let magnetic beads incubate for half an hour on the rotating sample mixer at room temperature;
- Remove from Eppendorf tubes the solution used for the competition-step;
- Labeling step: Add 400μl of labeled secondary antibody to each magnetic bead Eppendorf tube. Let magnetic beads incubate for half an hour on the rotating sample mixer at room temperature;
- Remove labeling solution from Eppendorf tubes;
- Wash magnetic beads three times with PBS/TWEEN® 20 washing solution. Remove the liquid;
- Resuspend with 100μl of DEA buffer each aliquot of magnetic beads. Now the magnetic beads are ready for electrochemical measurement step;
3) Assembly of PalmSens with Multiplexer (Mux) options
Please note: enzymatic product of substrate hydrolysis fouls the electrode surface; for this reason a new electrode is needed for each measurement.
- Connect a PC laptop to PalmSens through the serial cable;
- Connect the 9-DIN plug of CH8 Multiplexer with PalmSens.
- Connect serial cable of Eight channel Mux electric contact with CH8 Multiplexer;
- Place electrode strip on the eight magnet block. Pay attention to place each magnet under each working electrodes (of note, the need of a single magnet for each electrode is imperative otherwise the magnetic particle will not be concentrated on the working electrode area);
- Plug in electrodes strip into eight channel Mux electric contact;
For DPV measurement use the following parameters in the appropriate boxes:
E begin: 0 (V);E end: 0.6 (V); E step: 0.016 (V); E pulse: 0.0339 (V); E conditioning: 0 (V); E deposition: 0 (V); Scan rate: 0.1 (V/s); T pulse: 0.06 (s); T conditioning: 0 (s); T deposition: 0 (s); T equilibration: 8 (s).
4) Enzymatic reaction and Electrochemical Measurement
- Homogenize by gently shaking each Eppendorf tube containing magnetic beads ready for electrochemical measurement step in order to obtain a well dispersed suspension of magnetic beads;
- Pipette from each Eppendorf, immediately after homogenization, an aliquot of 20 μl of the magnetic bead dispersion onto the corresponding working electrode surface. For each electrode of one strip use 20 μl of magnetic beads taken from different Eppendorf tubes (e.g. for eight electrode use eight different Eppendorf);
- Add 80 μl of enzymatic substrate solution on the first electrode. Start 2 min count down. After 14 sec, add 80 μl of enzymatic substrate solution on the second electrode. After further 14 sec, add 80 μl of enzymatic substrate solution on the third electrode. Proceed at the same time interval (14 seconds) till the last electrode (that means: drop each aliquot of substrate with intervals of 14 sec). The interval time of 14 sec is calculated as the time required by the potentiostat to perform the measurement; of note, the 80 μl solution on each sensor should cover the working, reference and counter electrode. Moreover, the solutions for each sensor should not come into contact with solutions of neighboring electrodes.
- After the 2 min count down from the first addition of enzymatic substrate solution, start the electrochemical measurement;
- Use the PalmSens Lite software to obtain current peaks (μA) for each solution.
5) Calculation
Establish a calibration curve using a logistic 4 parameters equation and calculate the concentration of total HT-2/T-2 toxin amount in nanograms per millilitre for each Eppendorf tube containing unknown sample.
The experimental data, peak height (μA) against the concentration of the calibrants (ng/ml), have to be fitted using a non-linear four-parameter logistic (4-PL) equation plot (1) (using Sigma Plot 8.0 or Kaleidagraph). The nonlinear 4-PL model is usually adopted to describe ligand binding assays(LBAs) 6.
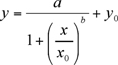 (1)
(1)
a, b, x0, y0 are logistic parameters as given by the Sigma Plot curve fit programme.
Use the explicated formula to calculate the content of HT-2/T-2 toxin total amount in the diluted sample extract solution
 (2)
(2)
x is the mass concentration of the total amount of HT-2/T-2 toxins in the diluted extract solution, calculated from the logistic 4 parameters equation in nanogram per milliltre (ng/ml)
y is the current value in μA obtained for the unknown sample
Appendix
6) Coated Magnetic Beads
Proceed as follow to have Coated Magnetic beads:
Washing procedure
- Homogenize tosylactivated Dynabeads® M-280 (stock solution 2 x 109 beads/ml) by shaking and vortexing (max speed) for 1 min (avoid foaming) (please note the concentration of magnetic beads needs to be always the same to ensure reproducibility in the measurement);
- Immediately pipette 1 ml of the above homogenized beads into a 2 ml Eppendorf tube;
- Place the tube in magnetic particle concentrator with the magnetic part put on for 2 min (see magnetic beads sticking on the lateral wall of the tube);
- Carefully pipette off the supernatant, leaving beads undisturbed;
- Remove the Eppendorf tube from the magnetic particle concentrator and resuspend the beads in 1 ml of 0.1 M borate buffer pH 9.5. Mix gently for 2 min in the rotating sample mixer for 2 min;
- Pipette off the supernatant;
- Pipette 1 ml of borate buffer solution into the Eppendorf tube. Magnetic beads are now ready for coating step;
Coating procedure
- Add 600 ml of HT-2 conjugated with KLH (Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin) stock solution to 1 ml of magnetic beads) (final HT-2-KLH concentration of 375 mg/ml); incubate magnetic beads and HT-2-KLH solution for 20h at 37°C* with slow tilt rotation on rotating sample mixer;
- After incubation place the tube in the magnetic particle concentrator and pipette off the supernatant;
Wash coated beads two times with 1 ml of PBS/BSA buffer solution. Between each washing remove PBS/BSA solution. All washing step were performed setting magnetic beads and PBS/BSA on rotating mixer for 5 min; - Wash magnetic beads once using 1 ml of TRIS/BSA buffer solution. Remove TRIS/BSA solution. Carry out this step by setting magnetic beads and TRIS/BSA buffer on rotating mixer for 4 h at 37°C*;
- Wash magnetic beads once using 1ml of refreshed (kept in the fridge at 4°C) PBS/BSA buffer solution. Remove PBS/BSA solution. Carry out this step setting magnetic beads and PBS/BSA buffer on rotating mixer for 5min at room temperature;
- After washing step remove all washing liquid and add 1 ml PBS buffer + NaN3 + BSA as storage liquid;
- Store coated magnetic beads at 4°C (please note that coated magnetic beads are stable for at least 2 months at 4°C);
*For this purpose the mixer is placed in oven equipped with a hole which allows the insertion of the cable for the power supply. Alternatively the mixer could be placed in a thermostated room at 37°C.
7) Sample preparation and extraction
25 g of finely ground sample (baby food or breakfast cereals) are weighed into a blender jar and extracted with 100 ml of acetonitrile/water solution (86/14) for 3 min in a high-speed blender. After centrifugation at 4000 rpm (3000 g) for 5 min, 8 ml of supernatant were taken and purified with Mycosep column, 4 ml of the cleaned extract were dried under nitrogen flow. Dried samples can be stored at -30 °C up to several months.
8) Sample reconstitution
Breakfast cereals
Reconstitute the dried breakfast cereal extract (cereal based food destined for adult consumption) with 40 ml of PBS pH 7.4. In this way a sample with a concentration of toxin equal to the supposed legal limit (200 ng/g) will give in the measurement step a signal falling in the middle of the working range.
Baby food
Reconstitute the dried baby food extract (cereal based food destined for infant consumption) with 4 ml of PBS. In this way a sample with a concentration of toxins equal to the supposed legal limit (20-25 ng/g) will give in the measurement step a signal falling in the middle of the working range.
Discussion
The use of antibodies as biomolecular recognition probe has seen a widespread use for sensing technologies; immunochemical detection methodologies, such as ELISAs and MEIAs, are, nowadays, among the most used and applied platforms in many laboratories7.
While these approaches achieve exceptional sensitivity and specificity, a primary objective of many research groups in the last years has been the improvement and optimization of their performances.
In t...
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Nancy Downer and all members from the laboratory of Analytical Chemistry, University of Rome "Tor Vergata" for their collaboration and logistic support. This work was supported by the EU project "BioCop".
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Potassium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | P9333 | |
| Potassium dihydrogen phosphate | Sigma-Aldrich | P9791 | |
| Disodium hydrogen phosphate | Sigma-Aldrich | S3264 | |
| Sodium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | S3014 | |
| MgCl2 anhydrous | Sigma-Aldrich | M8266 | |
| DEA (99.5%) | Sigma-Aldrich | 31589 | |
| HCl 37% | Sigma-Aldrich | 320331 | |
| H3BO3 | Sigma-Aldrich | B6768 | |
| Tris[hydroxymethyl]-aminomethane | Sigma-Aldrich | 252859 | |
| BSA (albumin bovine serum) | Sigma-Aldrich | A4503 | |
| NaOH | Sigma-Aldrich | S5881 | |
| TWEEN 20 | Sigma-Aldrich | P9416 | |
| NaN3 | Aldrich | 71290 | |
| 1-Naphthyl phosphate disodium salt | Fluka | N7255 | |
| Skimmed milk blocking solution - non fat dry milk | Bio-Rad | 170-6404 | |
| HT-2 conjugated with KLH (Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin), stock solution (1 mg/ml in PBS): | Biopure | 004050 | The HT-2-KLH conjugate was obtained by CDI-method where the free OH-groups on position 3 and 4 at the HT-2 toxin were activated by N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) and the activated HT-2 toxin was let to react with aminogroups of the protein (KLH) to generate a stable carbammate linkage. |
| Secondary labeled antibody: Anti-mouse IgG (H+L) from horse, conjugated with Alkaline Phosphatase, concentration 1 mg/ml. | Vector Laboratories | AP-2000 | |
| HT-2 toxin | Biopure | ||
| Magnetic beads: Dynabeads® | Invitrogen | M-280 Tosylactivated | Concentration 2 x 109 beads/ml. |
| Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4 | Dissolve 0.20 g of potassium chloride, 0.20 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.16 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate and 8.00 g of sodium chloride in 900 ml of water | ||
| Diethanolamine buffer, DEA, 0.97 M + 1 mM MgCl2 + 0.15 M KCl, pH 9.8 | Dissolve 0.0476g of MgCl2 anhydrous and 7.3.59 g of KCl in ~ 300 ml of water. After dissolution add 51 ml of DEA (99.5%). Adjust pH to 9.8 with HCl (6 M). Dilute to 500 ml with water. | ||
| Borate buffer, 0.1 M, pH 9.5 | Dissolve 3.09 g of H3BO3 in ~ 300 ml of distilled water; adjust pH to 9.5 with NaOH and/or HCl (6 M or lower concentrations). Dilute to 500 ml with distilled water. | ||
| TRIS buffer, 0.2 M, pH 8.5 | Dissolve 3.85 g of Tris[hydroxymethyl]-aminomethane in 100 ml of water. Adjust to pH 8.5 with NaOH and/or HCl (6 M or lower concentrations). Dilute to 200 ml with water. | ||
| TRIS buffer + BSA solution (0.1%), pH 8.4 | Dissolve 0.050 g of BSA in 50 ml of TRIS buffer pH 8.4. This solution must be freshly prepared on the day of use. | ||
| PBS buffer + TWEEN® 0.05% | Dissolve 0.250 g of TWEEN 20 in 500 ml of the previously prepared PBS buffer, pH 7.4 | ||
| PBS buffer + BSA solution 0.1% | Dissolve 0.050 g of BSA in 50 ml of PBS buffer, pH 7.3. This solution must be freshly prepared on the day of use. | ||
| PBS buffer + BSA 0.1% + NaN3 0.02% | Dissolve 0.050 g of BSA and 0.010 of NaN3 in 50 ml of PBS buffer, pH 7.3. Storage solution | ||
| Enzymatic substrate | Dissolve 0.010 g of 1-Naphthyl phosphate sodium salt in 100 ml of DEA buffer pH 9.8. Wrap the flask tightly in aluminium foil. This solution must be freshly prepared on the day of use. | ||
| Skimmed milk blocking solution | Add 0.20 g of Blotting Grade Blocker Non-Fat Dry Milk (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) to 200 ml of PBS buffer pH 7.3. This solution must be freshly prepared on the day of use. | ||
| HT-2 stock solution | Dissolve 10 mg of trichothecene HT-2 toxin vial, in 10 ml of acetonitrile to give a solution with a concentration of 1 mg/ml. Split up this solution into single-use aliquots of 30 ml and store them at less than -30 °C. | ||
| HT-2 Working standard solution | Pipette 20 ml of HT-2 toxin stock solution into a 2 ml calibrated volumetric flask and dilute with acetonitrile to obtain a HT-2 working solution containing 10 μg /ml of trichothecene toxin. This solution should be freshly prepared on the day of use. | ||
| HT-2 Working calibrant solutions | Dilute the HT-2 working standard solution (10 μg/ml) to prepare working calibrant solution 100 ng/ml. Dilute HT-2 working calibrant solution 100 ng/ml to prepare working calibrant solutions of the following concentrations 0 (blank), 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 10 ng/ml. These solutions must be prepared fresh on the day of use. | ||
| HT-2 conjugated with KLH | Split up HT-2 conjugated with KLH (Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin) stock solution (1 mg/ml in PBS) into single-use aliquots of 350 μl. Store aliquots at -30 °C. | ||
| Specific Monoclonal Antibody | Dilute 1:350 (v:v) the stock concentration (1.383 mg/ml) of monoclonal antibody in PBS to use in competition step. This solution must be prepared fresh at the moment of use. 10 ml antibody stock solution in PBS for a final volume of 3.5 ml, are enough to analyze 17 standards and /or samples. | ||
| Secondary Labeled Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG (H+L) conjugated with Alkaline Phosphatase is diluted 1:100 (v:v) in PBS to use in competition step. 100 μl antibody stock solution in PBS for a final volume of 10 ml, are enough to analyze 25 standards and /or samples. This solution must be prepared fresh at the moment of use. | ||
| Magnetic Particle Concentrator: MPC®-S | Invitrogen | ||
| PalmSens instrument | PalmSens | Provided with PalmSens Lite, Serial cable connecting PC laptop and Mux options software | |
| CH8 PalmSens Multiplexer | PalmSens | ||
| Eight channel Mux electric contact | hand made | ||
| Strip with eight screen printed electrodes (SPEs) | hand made | ||
| Specially designed support for electrodes strip | hand made. Includes 8 neodymium magnets each of which is placed below each working electrode surface of the SPE | ||
| Calibrated microliter pipettes | Gilson, Inc. | ||
| Magnetic stirrer and stir bars. | |||
| Glass beakers (100, 50, 20 ml). | |||
| Volumetric flasks (2ml). | |||
| 0.2 and 2ml Eppendorf tubes. | Eppendorf | ||
| Falcon tubes of 5ml and 15ml. | Falcon BD | ||
| Laboratory Vortex Mixer | Do not use vortex mixer to resuspend magnetic beads coated with HT2-KLH or linked with immunological chain to avoid denaturing of proteic parts | ||
| Laboratory oven or thermostated room | Choose a oven able to keep a temperature of 37±3 °C. |
References
- Koch, P. State of the art of trichothecenes analysis. Toxicol. Letters. 153, 109-112 (2004).
- Krska, R., Baumgartner, S., Josephs, R. State of the art in the analysis of type-A and-B trichothecene mycotoxins in cereals. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 371, 285-299 (2001).
- Morozova, T. Y., Morozov, V. N. Force differentiation in recognition of cross-reactive antigens by magnetic beads. Anal. Biochem. , 263-271 (2008).
- . FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 74. JOINT FAO/WHO EXPERT COMMITTEE ON FOOD ADDITIVES Fifty-sixth meeting. , 115 (2001).
- Piermarini, S., Volpe, G., Ricci, F., Micheli, L., Moscone, D., Palleschi, G., Fuhrer, M., Krska, R., Baumgartner, S. Rapid Screening Electrochemical Methods for Aflatoxin B1 and Type-A Trichothecenes: a preliminary study. Anal. Lett. 40, 1333-1346 (2007).
- Findlay, J. W. A., Dillard, R. F. Appropriate calibration curve fitting in ligand binding assays. AAPS J. 9 (2), E260-E267 (2007).
- Ricci, F., Volpe, G., Micheli, l., Palleschi, G. A review on novel developments and applications of immunosensors in food analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta. 605 (2), 111-129 (2007).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved