A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Flow-sorting and Exome Sequencing of the Reed-Sternberg Cells of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma
In This Article
Summary
Here, we describe a combined flow cytometric cell sorting and low-input, next-generation library construction protocol designed to produce high-quality, whole-exome data from the Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL).
Abstract
The Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma are sparsely distributed within a background of inflammatory lymphocytes and typically comprise less than 1% of the tumor mass. Material derived from bulk tumor contains tumor content at a concentration insufficient for characterization. Therefore, fluorescence activated cell sorting using eight antibodies, as well as side- and forward-scatter, is described here as a method of rapidly separating and concentrating with high purity thousands of HRS cells from the tumor for subsequent study. At the same time, because standard protocols for exome sequencing typically require 100-1,000 ng of input DNA, which is often too high, even with flow sorting, we also provide an optimized, low-input library construction protocol capable of producing high-quality data from as little as 10 ng of input DNA. This combination is capable of producing next-generation libraries suitable for hybridization capture of whole-exome baits or more focused targeted panels, as desired. Exome sequencing of the HRS cells, when compared against healthy intratumor T or B cells, can identify somatic alterations, including mutations, insertions and deletions, and copy number alterations. These findings elucidate the molecular biology of HRS cells and may reveal avenues for targeted drug treatments.
Introduction
Advancements in cancer genomics as a result of next-generation sequencing have led to significant breakthroughs in the identification of therapeutic targets and in prognostication for many hematologic and non-hematologic neoplasms. New individualized treatment strategies based on specific genomic alterations are rapidly being introduced in many tumor types (reviewed in references1,2). Despite significant progress in lymphoma genomics, the genome of the neoplastic HRS cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) had been underexplored. The investigations have been hampered by the scarcity of neoplastic HRS cells within a reactive microenvironment, making it difficult to isolate purified HRS cell populations3.
The method for isolating viable HRS cells from primary tumors was developed by Fromm et al.4,5,6. The method uses an eight-antibody cocktail, consisting of CD30, CD15, CD40, CD95, CD45 CD20, CD5, and CD64, to unequivocally identify HRS cells from a CHL tumor suspension. Using this methodology, we are able to isolate at least 1,000 viable HRS cells from fresh or frozen cell suspensions from tumor biopsies consisting of at least 107 cells (approximately 10 mg of tissue). The purity is greater than 90% by flow cytometric analysis and is estimated to be least 80% by exome genomic analysis of ten consecutive cases.
We have refined a flow cytometric cell isolation technique that has greatly eased the process, allowing for the rapid isolation of thousands of viable HRS cells from primary CHL tumors7. We have utilized the technique to produce what is believed to be the first whole-exome sequence of the tumor cells in primary cases of Hodgkin lymphoma. Our studies demonstrate the feasibility of high-throughput, genome-wide studies of individual CHL cases and have already led to the identification of novel genomic alterations with the potential to explain aspects of CHL pathogenesis.
We further developed a pipeline to utilize the extracted DNA for high-throughput genomic studies. In order to achieve reliable results from as few as 1,000 sorted HRS cells (thhe minimum obtained from sequential cases), we further developed a modified next-generation DNA library construction procedure8 that allowed us to increase adaptor ligation efficiency and to generate DNA fragment libraries without excessive amplification. This method allows for the analysis of routine clinical samples and the detection of recurrent mutations and chromosomal alterations7.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
1. Tissue Processing and Freezing
- Collect lymph node tissue in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium (RPMI) and process within 24 h of collection. Transfer excised lymph node tissue9 to a Petri dish containing 10 mL of RPMI with 2% fetal calf serum (FCS) and finely mince it with a fresh scalpel blade. Use the back of a 10-mL syringe plunger to further grind/dissociate the tissue.
- Transfer the liquid to a 50-mL conical tube through a 100 µm cell strainer. Rinse the Petri dish and the filter with an additional 10 mL of RPMI 2% FCS.
- Obtain a cell count using either an automated cell counter or a hemocytometer.
NOTE: Generally, at least 2 x 107 cells would be expected from approximately 5 mm3 of CHL lymph node tissue. A viability of over 80% is expected, but it may vary by sample. - Spin down the cells at 400 x g for 10 min and aspirate the supernatant. Place the tube containing cell pellet on ice.
- Pre-chill freezing medium on ice. Resuspend the cells in cold freezing medium at a concentration of 2 x 107/mL and resuspend it by pipetting. Do not vortex. Incubate the suspension on ice for 10 min.
- Aliquot the sample 1 mL/cryo vial (pre-chilled on ice). Transfer the vials to a -80 °C freezer for 1-2 days and transfer them again to liquid nitrogen.
2. Preparing Cell Suspensions for Cell Sorting
NOTE: Each lot of antibody must be properly titered using 10 million cells in a 300- µΛ staining volume. Peripheral blood may be used for all antibodies except CD30, for which the KMH2 cell line spiked into peripheral blood may be used for titration10. We generally begin with the manufacturer-recommended volume of antibody and perform two two-fold dilutions and one two-fold increase (four data points) for each lot of antibody titration. For example, if the manufacturer recommends a 10-µL volume, we perform the titration using 2, 5, 10, and 20 µL volumes.
- Set a water bath to 37 °C. Premix the titered amount of antibodies in a dark glass vial and add PBS + 2% BSA for a total cocktail volume of 100 µL.
NOTE: Although we recommend titering the antibodies, the following volumes may be used as a starting point: CD64, 20 µL; CD95, 5 µL; CD30, 20 µL; CD5, 10 µL; CD20, 10 µL; CD15, 20 µL; CD40, 5 µL; and CD45, 10 µL. - Transfer the vial from liquid nitrogen into an ice bucket containing dry ice to prevent thawing. Pre-warm 50 mL of thawing medium containing RPMI/20% FCS/DNase (100 µg/mL) in a 50-mL conical tube in a 37 °C water bath.
- Transfer 45 mL of thawing medium to a fresh tube and keep it at 37 °C. Rapidly thaw the cells by holding a cryogenic vial in a 37 °C water bath until only a very small frozen portion remains.
- Pour the vial contents into the tube containing 45 mL of thawing medium. Rinse the empty cryogenic vial 2 times with 1 mL of thawing medium and combine the rinses.
- Incubate the cells at room temperature for 15 min to allow for DNase digestion and cell re-equilibration. Spin down the cells at 500 x g for 10 min and aspirate the supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells in approximately 200 µL of the thawing medium held back (5 mL) and let it equilibrate to room temperature for 2-3 min. Recovery of >70% of frozen viable cells is expected.
NOTE: Optionally, for greater purity of sorted HRS cells that may be rosetted by attached T cells, a cocktail of unlabeled antibodies may be added at this step (see the optional protocol). - Add 100 µL of an antibody cocktail and incubate for 15 min at room temperature (RT), protected from light. Add 3 mL of sorting medium, spin down the cells at 500 x g for 10 min, and aspirate the supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells in 1 mL of sorting medium and transfer them to a 5 mL flow tube top strainer.
- Rinse both the 50 mL conical tube and the cell strainer with an additional 1 mL of sorting medium and place cells on ice.
3. (Optional Protocol) T Cell Rosette Blocking
NOTE: HRS cells are rosetted by T cells in tissue sections and cell suspension, and these T cells may potentially contaminate the sorted HRS fraction. These interactions are mediated by CD54 and CD58 on the HRS cell binding to LFA-1 and CD2 on the T cells4,11. These interactions can be blocked with unlabeled antibodies to these adhesion molecules.
- Aliquot 100,000 to 500,000 cells in 100 µL of RPMI.
- Incubate the cell suspension with unlabeled antibodies to CD2, CD54, CD58, and LFA-1 (10 µL each) on ice for 1 h. The cell suspension can now be labeled with fluorescent antibodies.
4. HRS-, B-, and T-cell Isolation Using Cell Sorting
NOTE: Although we used a special research order instrument using 5 lasers (see the Materials spreadsheet), any sorter with the capability of detecting the fluorochromes used in the antibody panel should be sufficient. The execution of the steps below requires a familiarity with software12 function and a basic knowledge of cell sorter operations. Please refer to the online software manual for detailed instructions.
- Cytometer setup:
- Turn on the computer and login. Power on the BSC (and BSC outlets), and then power on the cytometer. Wait at least 90 s for the internal CPU of the cytometer to start, and then open the laser control software and verify that all lasers are powered on. Launch the cytometer software13 and login.
- Within the cytometer software, click on "Cytometer → View Configurations." When the dialog box for the configuration sub-program opens, highlight the 130-µm custom configuration and click "set configuration" and "OK." Exit the configuration sub-program.
- Observe the dialog box in the cytometer software and click "use CS&T settings." Install a 130-µm nozzle into the instrument and turn the stream on by clicking the red "X" button in the stream window. Allow the instrument to warm up for at least 30 min.
- Run a performance check on the instrument using the desired method (a performance-tracking software module is included with the sorter described here, see the software manual (pp. 117 - 122) and reference standard (refer to the Materials for the standard used in this setup).
- Click "Cytometer → CST," ensure that the "Characterize" field is set to "Check Performance" on the pull-down menu, and click "Run." When prompted by software, load a tube of reference particles onto the sample stage and click "OK."
- After the run completes, click "Finish" and close the software module. After the cytometer software has finished reconnecting to the cytometer, click "use CS&T settings" in the dialog box that appears.
- Determine the correct drop delay using the automatic drop delay feature of the cytometer software (see pp. 154 - 161 of the software manual).
- Open the "Drop Delay" experiment in the "Browser" window of the cytometer software, install a tube of calibration particles on the sample stage, and click "Load" in the "Acquisition Dashboard" window. Turn on the automatic stream monitoring feature by clicking the "Sweet Spot" button in the "Stream" window. Leave this feature on at all times for all following steps.
- Turn on the deflection plate voltage by clicking the "Voltage" button in the side-stream window, and then turn on test sorting by clicking the "Test Sort" button immediately adjacent to the "Voltage" button.
- Adjust all side-stream settings to zero except for the left side stream. Adjust the left side stream setting such that two stream-spots are visible in the side-stream window. Click the "Optical Filter" button and verify that the left side-stream spot will fall within the left box that appears in the black area of the side-stream window.
- Adjust the left side-stream setting if needed. Turn off test sorting by clicking on the "Test Sort" button again. In the "Browser" window, expand the "Global Worksheets" element of the "Drop Delay" experiment by clicking on the "+."
- Double-click on "Sort Layout_001" to open the sort layout, verify by visual inspection that the left sort population has "P1" assigned to it, and click "Sort" in the "Sort Layout" window. In the "Sort Layout" window, click "Auto Delay" and then "Run."
- When the run completes, click "Exit." Install a tube of sterile deionized water on the sample stage and click "Load" in the "Acquisition Dashboard" window. Run the tube of water for at least 5 min to clear residual test particles from the instrument before proceeding.
- Run compensation controls (using compensation beads from the Materials spreadsheet or equivalent) using a built-in compensation setup in the sorter software (see pp. 131 - 137 of the software manual for additional details).
- Create a new experiment by clicking "Experiment New Experiment." In the "Parameters" tab of the "Instrument Status" window, delete unused parameters, if any. Click "Experiment Compensation Setup Create Compensation Controls."
- In the "Browser" window, expand the "Compensation Controls" specimen by clicking the "+" sign. Run compensation control tubes without recording the data, and if necessary, adjust the detector voltages (in the "Parameters" tab of the "Instrument Status" window) so that positively-stained bead populations for each fluorochrome are between channel 10,000 and 100,000 and are the brightest in their primary detection channel.
- Write down the voltages needed for each parameter for each tube. Highlight the "Unstained Control" tube under the "Compensation Controls" specimen by single left-clicking it. Load the unstained control tube onto the sample stage and click "Load" in the "Acquisition Control" window.
- Manually enter the determined voltages by running individual compensation controls into the detector voltage fields for all parameters, and then click "Record" in the "Acquisition Control" window. Run all remaining compensation controls, recording the data without changing any detector settings. Install a tube of sterile, deionized water for 5 min to clear any residual material from the instrument before proceeding.
- HRS-cell gating:
- Acquire and record at least 100,000 events for initial gating while adjusting the flow rate to acquire 3,000-4,000 events/s (see step 4.1).
NOTE: It may be necessary to add additional sorting medium to dilute the cells if the cell concentration is too high. Stop the acquisition. - Gate HRS cells using the steps outlined in Figure 1
NOTE: In most CHL cases, between 0.01% and 0.1% of cells will be HRS cells.
- Acquire and record at least 100,000 events for initial gating while adjusting the flow rate to acquire 3,000-4,000 events/s (see step 4.1).
- B- and T-cell gating:
- Identify somatic controls (B and T cells) by the gating of CD20 and CD5, respectively (gating lymphocytes by CD45/SSH), followed by CD20 versus CD5 (see Figure 1).
- Target collection streams to collection tubes in a pre-chilled two-way or four-way collection rack. Fill either flow tubes or 15-mL centrifuge-style tubes at least halfway with collection medium.
- Assign HRS and control populations to proper collection tubes in the sort setup following vendor instructions. Restart the cell acquisition and start the sort.
- Collect all HRS cells and up to 1 million B and T cells. Target the collection streams to collection tubes in a pre-chilled four-way (or two-way) collection rack.
5. DNA Extraction
- Pellet collected cells by centrifugation in 1.5 mL conical tubes at 3,000 x g for 10 min and resuspend once with 1 mL of PBS to wash the cells.
- Pellet once more at 3,000 x g for 10 min and remove the supernatant; be very careful not to disturb the tiny pellet.
- Add 150 µL of lysis buffer (or an appropriate volume for the kit used) to the washed cells and mix by pipetting up and down.
NOTE: One may store cell lysate at -70 °C at this point, if needed. - Construct a column assembly by placing the filter column inside the tube and add the lysate from step 5.5 to the column. Spin the assembly at 13,000 x g for 3 min.
- Remove the minicolumn from the assembly and discard the liquid in the collection tube. Replace the minicolumn in the collection tube.
- Add 650 µL of column wash solution to each assembly. Centrifuge for 1 min at 13,000 x g. Discard the liquid from the collection tube. Repeat this step for a total of 4 washes.
- Discard the liquid from the collection tube and reassemble the minicolumn assembly. Centrifuge for 2 min at 13,000 x g to dry the binding matrix.
- Transfer the minicolumn to a new 1.5 mL tube and add 25 µL of 10 mM Tris-Cl, which is preferred for subsequent sonication step, or Nuclease-Free Water heated to 65 °C. Incubate for 2 min at room temperature and centrifuge the assembly at 13,000 x g for 1 min. Repeat once more with 25 µL for a total of 50 µL.
- Mix the DNA elution by pipetting up and down and quantify using fluorimetry14.
6. Library Construction
- Preparation before beginning:
- Set up the sonicator at water level 12, Intensity 5, Cycles/burst 200, and Temp 7.
- Based on the available DNA quantity determined by fluorimetry and on the experimental design, determine the amount of DNA to use for library construction.
NOTE: Keep in mind that if too little DNA is used and library quality is compromised, there may be little application for material that is left behind for validation purposes. For substandard input quantities, the greater the input mass, the higher the complexity of the resulting sequencing library. Some guidelines for this protocol are as follows: 10 ng should yield good results, and 50 ng may be considered a rough maximum. - Decide upon the adapter:insert molar ratio based loosely on the values in Table 1.
- Calculate the amount of adapter to use in the following fashion:
NOTE: Number of moles of DNA input, n
i. n = 1.54e-12-12 * input mass (in ng) / (mean fragment size)
ii. when the mean fragment size is 200 bp, this simplifies to:
n = 7.7e-15 * input mass (in ng)
Number of moles of adapter to include, a
i. a = n * r
Volume of adapter stock to use in adapter ligation step, v
i. v (in µL ) = a /[10-12 * adapter stock concentration (in µM )]
NOTE: If the adapter concentration is low, to ensure that the necessary amount of adapter is included, adapter solution may be used to dilute the end-repair reagents in lieu of water.
Example: For 100 ng of input DNA with a mean fragment size of 200 bp, for a desired molar adapter:insert ratio of 15:1 and an adapter stock concentration of 2 µM, the recommended volume of adapter to use is 5.8 µL. - Assign indexed barcodes to the samples.
NOTE: Libraries that will be pooled together into a hybridization reaction or a lane on a sequencer's flow cell must not contain any redundant indices.
- Library construction – DNA shearing:
- Add the full amount of DNA to be used to a sonication tube. If the volume of sample containing the input DNA alone is less than 50 µL, add Buffer EB up to a 50 µL total volume and mix.
- Sonicate for 30 s.
- Remove the tube and perform a quick-spin in a mini centrifuge just enough to collect any spray from the upper portion of the walls of the microtube.
- Repeat steps 6.2.2-6.2.3 for a total of seven 30-s sonication sessions for a total of 210 s of sonication.
NOTE: Feel free to experiment with dividing the 210 s into fewer sessions.
- Library construction - End repair, A-tailing, and adapter ligation:
NOTE: Avoid doing any size selection before the library PCR amplification step.- Follow the manufacturer's instructions19 for end-repair and A-tailing after the sonication of the sample DNA.
- After A-tailing, use the appropriate number of moles of adapter (calculated in step 6.1.3) in the reaction. Combine the adapter, A-tailed DNA fragments, enzyme, and buffer and incubate overnight at 20 °C for approximately 16 h.
- Library construction - Library amplification:
- Perform a bead cleanup of the adapter ligation reaction. After adding beads to the PCR product, wait 5 min at room temperature. Place it against a magnetic stand and remove the liquids, wash twice in 200 µL of 80% ethanol, dry the beads long enough to remove most of the liquid without over-drying, and elute the DNA off of the beads by pipetting 25 µL of nuclease-free water, as suggested, onto the beads while the tube remains against a magnetic stand.
NOTE: it may be possible to experiment with preserving the beads in polyethylene glycol
(PEG) until after the amplification instead of discarding them, but this has not been tested. - Include 0.6 µL of a 1:1,000 dilution of Green dye per 50 µL of PCR master mix. Alternatively, use a real-time PCR-compatible intercolating dye of choice in the appropriate volume for the equipment.
- Program the PCR reaction at 98 °C for 45 s for the initial denaturation, followed by a cycle of denaturation, annealing, and extension at 98 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, or choose the appropriate program if using an alternative polymerase enzyme.
- Set the machine to take fluorescence data at 72 °C for each cycle. Program a final extension at 72 °C for 1 min followed by a hold at 4 °C for an indefinite amount of time. The PCR primers for the amplification of the adapter-ligated library using reagents in the supplementary table are: Oligo 1, AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGA and Oligo 2, CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAG
- Amplify the library using the PCR conditions described above while observing the fluorescence intensity values in real-time with the qPCR software, stopping just before the end of the exponential growth phase.
- After amplification, do a standard bead cleanup (see step 6.4.1) using 0.8x the volume of the amplification reaction recovered, typically 0.8 x 50 = 40 µL of beads. Add the beads to the PCR product and wait 5 min at room temperature.
- Place it against a magnetic stand and remove the liquids, wash twice in 200 µL of 80% ethanol, dry the beads long enough to remove most of the liquid without over-drying, and elute by adding nuclease-free water to the dry beads.
- Quantify the resulting DNA using fluorimetry. Visualize the library fragments for size; see the section on Data QC expectations for more details.
- Perform a bead cleanup of the adapter ligation reaction. After adding beads to the PCR product, wait 5 min at room temperature. Place it against a magnetic stand and remove the liquids, wash twice in 200 µL of 80% ethanol, dry the beads long enough to remove most of the liquid without over-drying, and elute the DNA off of the beads by pipetting 25 µL of nuclease-free water, as suggested, onto the beads while the tube remains against a magnetic stand.
7. Exome Hybridization
- Combine four libraries with distinct adapter bar codes.
NOTE: Mass by fluorimetry and size by gel are used to calculate the molarity, and then libraries are combined in equimolar amounts for a total of a 1,000-ng mass of pooled library. It is best to keep all tumor-normal pairs together rather than separating them into separate pools. - Apply the exome capture protocol15 and do 8 PCR cycles after the capture cleanup. Other choices of capture targets may be possible.
8. Multiplexed Sequencing
- Sequence a single hybridization capture containing four multiplexed libraries in a single lane on the sequencing platform referenced in the Materials spreadsheet16.
NOTE: Alternative configurations are possible for advanced users who wish to further plan and optimize their target read depth of coverage.
9. Analysis (Can be Substituted with Alternative Pipeline(s) if Desired)
- Snps and small indels:
- Map raw data to the human reference genome, UCSC hg19, using Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA)17 or an alternative algorithm of choice. Filter or mark reads with a mapping quality score below 20 and PCR duplicates using Samtools18 or Picard19.
- Detect somatic nucleotide variants and small indels in HRS samples compared to the T-cell somatic controls using Strelka20 or a variant caller of choice. Apply snpEff21 to annotate the Strelka output. If desired, systematically inspect variant loci for artifacts using the Integrated Genome Viewer (IGV)22,23.
- Copy number alterations:
- Calculate the log-transformed ratio "ltr" for every exome target interval "i" of intra-library normalized read counts in the tumor against those of the normal in the following manner:
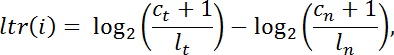
NOTE: c is the number of reads mapping to a given capture interval, l is the total library size, t denotes tumor, and n denotes normal. - Filter out intervals with insufficient coverage (Ct+Cn < 100 reads) for further analysis. Conduct pan-interval segmentation using DNAcopy v.1.024 from Bioconductor in R.
NOTE: Consider segments where the absolute value of the mean ltr is below 0.5 to be copy-neutral. Remaining segments may be designated as copy number gains, if the sign of the mean ltr is positive (in other words, there are significantly more reads in the tumor sample than in the normal sample after normalization), or copy number losses, if the sign of the mean ltr is negative.
- Calculate the log-transformed ratio "ltr" for every exome target interval "i" of intra-library normalized read counts in the tumor against those of the normal in the following manner:
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
A bioanalyzer plot should be taken after library amplification and 0.8x bead cleanup. One should see a "normal-like" distribution of fragment sizes in the desired range (Figure 2a). Deviations from this shape, such as a visible "shoulder" in the curve, indicate the presence of a high or low molecular weight artifact. For example, Figure 2b-2d shows examples of libraries containing visible artifact...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Future applications or directions after mastering this technique
This work allows for exome sequencing from samples containing at least 10 ng of DNA. In the clinical context, this limit excludes most fine-needle aspiration samples due to insufficient material, but it includes adequate core biopsies and excisional biopsy samples. This will enable the acquisition of data from a larger set of possible samples.
Critical steps within the protocol...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The development of this project method was funded by the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine of Weill Cornell Medical College. We acknowledge the Tri-Institutional Training Program in Computational Biology and Medicine for partial funding. We would like to thank the scientists who shared their time and knowledge with us, especially Maryke Appel; Dan Burgess; Iwanka Kozarewa; Chad Locklear; and everyone from the Weill Cornell Medical College Genomics Core Facility, including Jenny Zhang, Xiaobo (Shawn) Liang, Dong Xu, Wei Zhang, Huimin Shang, Tatiana Batson, and Tuo Zhang.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Petri or Cell Culture Dish (sterile) | |||
| RPMI-1640 Media | Roswell Park Memorial Institute | ||
| Fetal Calf Serum (FCS), (heat inactivated) | |||
| Freezing Media (RPMI, 20% FCS, 10% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO))-make fresh and keep sterile | |||
| RPMI with 2% FCS (make fresh or store for up to 1 month) | |||
| scalpel with fresh blade | |||
| 10 mL syringe (no needle) | |||
| Cryogenic vials | |||
| 50 mL conical centrifuge tubes, force | |||
| Centrifuge | capable of handling 50 mL conical centrifuge tubes and providing 400g | ||
| Hepes buffer(1 M, cell culture grade) | |||
| phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | |||
| Pluoronic-F68 | Thermo-Fisher | 24040-032 | |
| DNAase-I | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO | D4527-10KU | store as 5 mg/mL in RPMI in -200 °C |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | |||
| Sort Media (PBS + 2% BSA + 25 mM HEPES + Pluoronic –F68 (1x)) | |||
| CD64-FITC (22) | Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL | 20 μL suggested starting volume; Titering is suggested | |
| CD30-PE (BerH83) | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | 20 μL suggested starting volume; Titering is suggested | |
| CD5-ECD (BL1a) | Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL | 10 μL suggested starting volume; Titering is suggested | |
| CD40-PerCP-eFluor 710 (1C10) | Ebiosciences, San Diego, CA | 5 μL suggested starting volume; Titering is suggested | |
| CD20-PC7 (B9E9) | Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL | 10 μL suggested starting volume; Titering is suggested | |
| CD15-APC (HI98) | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | 20 μL suggested starting volume; Titering is suggested | |
| CD45 APC-H7 (2D1) | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | Can be substituted with 10 μL suggested volume of CD45-Krome Orange (J.33, Beckman Coulter); Titering is suggested | |
| CD95-Pacific Blue (DX2) | Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY | 5 μL suggested starting volume; Titering is suggested | |
| CD2 (5 μg; clone RPA-2.10) | Biolegend, San Diego, CA | For optional protocol; Titering is suggested | |
| CD54 (10 μg; clone 84H10) | Serotec, Oxford, United Kingdom | For optional protocol; Titering is suggested | |
| CD58 (10 μg; clone TS2/9) | eBioscience, San Diego, CA | For optional protocol; Titering is suggested | |
| LFA-1 (12 μg; clone MHM23) | Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO | For optional protocol; Titering is suggested | |
| BD CS&T Beads | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | ||
| BD Accudrop Beads | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | ||
| BC Versa Comp antibody capture beads | Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL | Compensation Beads | |
| BD-FACS ARIA special research order instrument using 5 lasers | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | any BD-FACS aria with capabilities to detect the fluorochromes in the antibody panel should be sufficient | |
| Wizard | Promega | A2360 | |
| 10 mM Tris-Cl buffer | NA | ||
| Qubit dsDNA HS Assay kit | Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA | ||
| S2 Sonicator | Covaris, Woburn, MA | Alternatives may be substituted | |
| microTUBE | Covaris, Woburn, MA | ||
| Low-Throughput Library Preparation Kit | Kapa Biosystems, Wilmington, MA | KK8221 | |
| Sybr Green | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO | S9430 | |
| Agencourt AMPure XP Beads | Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL | ||
| Bioanalyzer | Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA | ||
| SeqCap EZ Exome v.3.0 | Roche Nimblegen | 6465684001 | |
| HiSeq | Illumina | ||
| TruSeq-style Universal adapter | Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), Coralville, Iowa | HPLC purification; AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGAT*C*T | |
| TruSeq-style index adapter | Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), Coralville, Iowa | HPLC purification; /5Phos/GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCTGAACTCCAGTCACNNNNNNATCTCGTATGCCGTCTTCTGCTTG | |
| TruSeq-style PCR primer 1 | Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), Coralville, Iowa | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGA | |
| TruSeq-style PCR primer 2 | Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), Coralville, Iowa | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAG | |
| Nuclease Free Duplex Buffer | Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), Coralville, Iowa | ||
| BD FACSDIVA software | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | ||
| BD Falcon Tubes | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA | ||
| BD Flow Tubes | BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA |
References
- Abrams, J. National Cancer Institute's Precision Medicine Initiatives for the new National Clinical Trials Network. American Society of Clinical Oncology educational book / ASCO. American Society of Clinical Oncology. Meeting. , 71-76 (2014).
- Gagan, J., Van Allen, E. M. Next-generation sequencing to guide cancer therapy. Genome medicine. 7, 80(2015).
- Matsuki, E., Younes, A. Lymphomagenesis in Hodgkin lymphoma. Seminars in cancer biology. 34, 14-21 (2015).
- Fromm, J. R., Kussick, S. J., Wood, B. L. Identification and purification of classical Hodgkin cells from lymph nodes by flow cytometry and flow cytometric cell sorting. Am J Clin Pathol. 126 (5), 764-780 (2006).
- Fromm, J. R., Thomas, A., Wood, B. L. Flow cytometry can diagnose classical hodgkin lymphoma in lymph nodes with high sensitivity and specificity. Am J Clin Pathol. 131 (3), 322-332 (2009).
- Roshal, M., Wood, B. L., Fromm, J. R. Flow cytometric detection of the classical hodgkin lymphoma: clinical and research applications. Advances in hematology. 2011, 387034(2011).
- Reichel, J., et al. Flow sorting and exome sequencing reveal the oncogenome of primary Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood. 125 (7), 1061-1072 (2015).
- Kozarewa, I. A Modified Method for Whole Exome Resequencing from Minimal Amounts of Starting DNA. PLoS ONE. 7 (3), e32617(2012).
- Brunicardi, F. C. Schwartz's Principles of Surgery. , 10th ed, McGraw-Hill Education / Medical. (2014).
- Kantor, A. B., Roederer, M. FACS analysis of leukocytes. Handbook of Experimental Immunology. 2, Blackwell Scientific. (1996).
- Sanders, M. E. Molecular pathways of adhesion in spontaneous rosetting of T-lymphocytes to the Hodgkin's cell line L428. Cancer Res. 48 (1), 37-40 (1988).
- Biosciences. FACSDiva Software v6.0. , Available from: http://www.bdbiosciences.com/in/instruments/software/facsdiva/resources/overview.jsp (2007).
- Biosciences. FACSAria II User's Guide. Part No. 644832, Revision A. , (2009).
- Life Technologies. Qubit 3.0 Fluorometer, Catalog Number Q33216. , Available from: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/Q33216 (2017).
- Roche Nimblegen. SeqCap EZ Library SR User's Guide ver. 4.1. , (2013).
- Illumina. HiSeq High-Throughput Sequencing System. , Available from: http://www.illumina.com/systems/hiseq_2500_1500.html (2016).
- Li, H., Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 25 (14), 1754-1760 (2009).
- Li, H. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25 (16), 2078-2079 (2009).
- The Broad Institute. Picard Tools. , Available from: http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/ (2016).
- Saunders, C. T. Strelka: accurate somatic small-variant calling from sequenced tumor-normal sample pairs. Bioinformatics. 28 (14), 1811-1817 (2012).
- Cingolani, P., et al. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly (Austin). 6 (2), 80-92 (2012).
- Dobin, A. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 29 (1), 15-21 (2013).
- Thorvaldsdottir, H., Robinson, J. T., Mesirov, J. P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Briefings in bioinformatics. 14 (2), 178-192 (2013).
- DNA copy number data analysis. v.R package version 1.34.0. , Available from: https://omictools.com/dnacopy-tool (2013).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved