A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
An In Vitro Protocol for Evaluating MicroRNA Levels, Functions, and Associated Target Genes in Tumor Cells
In This Article
Summary
This protocol uses a probe-based real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay, 3’ untranslated regions (3’ UTR) cloning, and a luciferase assay to verify the target genes of a miRNA of interest and to understand the functions of miRNAs.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory RNAs which are recognized to modulate numerous intracellular signaling pathways in several diseases including cancers. These small regulatory RNAs mainly interact with the 3’ untranslated regions (3’ UTR) of their target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) ultimately resulting in the inhibition of decoding processes of mRNAs and the augmentation of target mRNA degradations. Based on the expression levels and intracellular functions, miRNAs are able to serve as regulatory factors of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive mRNAs. Identification of bona fide target genes of a miRNA among hundreds or even thousands of computationally predicted targets is a crucial step to discern the roles and basic molecular mechanisms of a miRNA of interest. Various miRNA target prediction programs are available to search possible miRNA-mRNA interactions. However, the most challenging question is how to validate direct target genes of a miRNA of interest. This protocol describes a reproducible strategy of key methods on how to identify miRNA targets related to the function of a miRNA. This protocol presents a practical guide on step-by-step procedures to uncover miRNA levels, functions, and related target mRNAs using the probe-based real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay following a miRNA mimic transfection, dose-response curve generation, and luciferase assay along with the cloning of 3’ UTR of a gene, which is necessary for proper understanding of the roles of individual miRNAs.
Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are the small regulatory RNAs that mainly modulate the process of translation and degradation of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) by reacting to the 3’ untranslated regions (3’ UTR) in bona fide target genes1. Expression of miRNAs can be regulated by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. The imbalance of such regulatory mechanisms brings uncontrolled and distinctive miRNAs expression levels in numerous diseases including cancers2. A single miRNA can have multiple interactions with diverse mRNAs. Correspondingly, an individual mRNA can be controlled by various miRNAs. Therefore, intracellular signaling networks are intricately influenced by distinctively expressed miRNAs by which physiological disorders and diseases can be initiated and deteriorated2,3,4,5,6. Although the altered expression of miRNAs has been observed in various types of cancers, the molecular mechanisms that modulate the manners of cancer cells in conjunction with miRNAs are still largely unknown.
Accumulating evidence has been showing that the oncogenic or tumor-suppressive roles of miRNAs depend on the types of cancers. For example, by targeting forkhead box o3 (FOXO3), miR-155 promotes the cell proliferation, metastasis, and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer7,8. In contrast, the restriction of glioma cell invasion is induced by miR-107 via the regulation of neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 (NOTCH2) expression9. The assessment of miRNA-target interactions in connection with miRNA functions is an indispensable part to better understand how miRNAs regulate various biological processes in both healthy and diseased states10. In addition, the discovery of bona fide target(s) of miRNAs can further provide a fine-tuned strategy for a miRNA-based therapy with various anti-cancer drugs. However, the main challenge in the field of miRNAs is the identification of direct targets of miRNAs. Here, detailed methods are presented as reproducible experimental approaches for the miRNA target gene determination. Successful experimental design for the miRNA target identification involves various steps and considerations (Figure 1). Comparison of mature miRNA levels in tumor cells and normal cells can be one of the common procedures to select a miRNA of interest (Figure 1A). The functional study of a selected miRNA to detect the effects of a miRNA on cell proliferation is important to narrow down the list of best potential candidate targets of a miRNA of interest (Figure 1B). Based on the experimentally validated functions of miRNAs, a systematic review of literature and database in company with a miRNA target prediction program is required to search the most relevant information on gene functions (Figure 1C). The identification of real target genes of a miRNA of interest can be achieved by implementing experiments such as the luciferase assay along with the cloning of 3’ UTR of a gene, real-time PCR, and western blotting (Figure 1D). The goal of the current protocol is to provide comprehensive methods of key experiments, the probe-based real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay following a miRNA mimic transfection, dose-response curve generation, and luciferase assay along with the cloning of 3’ UTR of a gene. The current protocol can be useful for a better understanding of the functions of individual miRNAs and the implication of a miRNA in cancer therapy.
Protocol
1. Mature MicroRNA (miRNA) Expression Analysis
- Mature miRNA complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis
- Add 254 ng of total RNA and 4.5 µL of deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) mixtures, and then add ultrapure water into PCR strip-tubes to make up to 18 µL (Figure 2A). Prepare the reaction for each total RNA sample purified from several cell lines using enough amount of DNase I mixtures based on the total number of reactions.
NOTE: DNase I mixtures are composed of DNase I (1.8 µL), ribonuclease inhibitor (0.3 µL), and 25 mM MgCl2 (2.4 µL). To reproducibly procure total RNA, a column-based extraction method was applicated instead of using a phenol-chloroform based extraction method. It was reported that the extraction yield of some miRNAs can be varied depending on the number of cells when using a phenol-chloroform based extraction method11,12. - Incubate the tubes in a thermal cycler. Run the tubes for 10 min at 37 °C, and heat-inactivate DNase I by 5 min incubation at 90 °C. Immediately place the tubes on ice after incubation.
- Transfer 7.1 µL of DNase I treated total RNA into 2 sets of new tubes and then add 1.5 µL of antisense primers for the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene (Figure 2B).
NOTE: The amount of total RNA for cDNA synthesis becomes 100 ng at this step. The stock concentration of GAPDH antisense primers is 10 µM. Adding GAPDH antisense primers is for the generation of GAPDH cDNAs using a gene-specific primer method. - Incubate the tubes using a thermal cycler. Start at 80 °C for 5 min followed by the reaction at 60 °C for 5 min. Immediately place the tubes on ice after incubation.
- Add 3.4 µL of reverse transcription (RT) enzyme mixtures in each reaction (Figure 2B). RT enzyme mixtures are composed of 100 mM deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (0.15 µL), 10x RT buffer (1.5 µL), ribonuclease inhibitor (0.75 µL), and reverse transcription enzyme (1 µL). Prepare enough amount of mixtures based on the total number of reactions.
- Add 3 µL of 5x RT primers for a specific miRNA in each reaction (Figure 2B).
NOTE: Total volume is 15 µL for each reaction. - Run the tubes using a thermal cycler. Start at 16 °C for 30 min followed by the reaction at 42 °C for 30 min, and finally at 85 °C for 5 min. Hold at 4 °C for any remaining time (Figure 2B). Single-stranded cDNAs are generated in this step for both a specific miRNA and GAPDH gene in the same tube.
- Add 254 ng of total RNA and 4.5 µL of deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) mixtures, and then add ultrapure water into PCR strip-tubes to make up to 18 µL (Figure 2A). Prepare the reaction for each total RNA sample purified from several cell lines using enough amount of DNase I mixtures based on the total number of reactions.
- Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and data analysis
- Dilute each cDNA with ultrapure water at 1:49 ratio.
- Prepare the reaction mixtures for a specific miRNA and GAPDH (Table 1). For the detection of a specific miRNA and GAPDH, set up triplicate reactions for each cDNA sample.
- Perform the real-time PCR and data analysis (Figure 2C). Analyze data using the comparative CT method13,14.
2. MicroRNA (miRNA) MimicTransfection
NOTE: miRNA-107 is selected from step 1. Since miRNA-107 is down-regulated in tumor cells compared with normal cells, it can be speculated that miRNA-107 is a tumor suppressive miRNA. In the case of a miRNA which is up-regulated in tumor cells compared with normal cells (e.g., miRNA-301), antisense oligonucleotides against miRNA-301 can be applied for steps 2, 3, and 4.
- Count the cells with a counting-chamber device and plate the cells in a 96-well plate. Cell density is 2 x 103 cells/100 µL for each well. Do not use cell culture media containing penicillin-streptomycin (P/S) because P/S can reduce the transfection efficiency.
- Prepare a set of transfection mixtures to transfect the cells at several final concentrations of miRNA control mimic and miRNA-107 mimic on the next day (Figure 3).
- From the stock (25 μM concentration) of miRNA control mimic or miRNA-107 mimic, dilute and add corresponding amount of control mimic or miRNA-107 mimic in the reduced-serum media along with a transfection reagent using microcentrifuge tubes (Figure 3A). Gently mix the oligo containing mixtures using a micropipette. The total amount of oligos (miRNA mimic control + miRNA-107 mimic) should be same in each well. Blank wells include 100 µL of cell culture media and reduced-serum media containing a transfection reagent without cells.
- After a 10 min incubation in a cell culture hood, gently mix the oligo containing mixtures again and then add 50 μL of the mixtures into each well. Keep the transfected cells in a cell culture incubator. Replace the transfection reagent containing media with the fresh cell culture media containing both fetal bovine serum (FBS) and P/S after 6-12 h incubation. Further incubate the cells for 72 h. The total treatment duration of miRNA mimic is 96 h.
3. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
- Cell fixation
- Remove the cell culture media in each well of the plate and promptly fill 100 μL of 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) into each well. Carefully aspirate the cell culture media from each well to avoid any cell damage and detachment from the bottom.
NOTE: Prepare 40% TCA by adding 20 g of TCA powder into 50 mL of distilled water. From 40% TCA, make 10% TCA by diluting 40% TCA with distilled water at a 1:3 dilution ratio. - Keep the plate containing 10% TCA in a refrigerator (4 °C) for 1 h.
- Wash the plate several times by submerging into the water tub and dry it. Remove excess water from inside of wells by tapping the plate until there is no water left in wells. Leave the plate on a laboratory bench to dry it before going to the next step.
- Remove the cell culture media in each well of the plate and promptly fill 100 μL of 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) into each well. Carefully aspirate the cell culture media from each well to avoid any cell damage and detachment from the bottom.
- Cell staining
- Pipette 50 μL of 0.4% SRB solution into each well including blank wells. Gently shake the plate until 0.4% SRB solution consistently covers the bottom of wells.
NOTE: Prepare and use 0.4% SRB solution by adding 0.4 g of SRB powder into 100 mL of 1% acetic acid. Shake the solution carefully to mix it. Wrap the bottle of 0.4% SRB solution in a light protective material such as aluminum foil. Store 0.4% SRB solution in a refrigerator. - After incubation for 40 min to 60 min, wash the plate by rinsing it with 1% acetic acid. Wash the plate until the unbound dye is totally washed away (Figure 3B).
- Leave the plate on a laboratory bench to dry it before going to the next step.
NOTE: The plate should be entirely dried before going to step 3.3.
- Pipette 50 μL of 0.4% SRB solution into each well including blank wells. Gently shake the plate until 0.4% SRB solution consistently covers the bottom of wells.
- Absorbance measurement
- Pipette 100 μL of Tris base solution (10 mM) into the corresponding wells including blank wells. Keep the plate on a shaker for 10 min. Measure the absorbance at 492 nm.
4. Generation of a Dose-response Curve
- Analyze the SRB assay data in a spreadsheet. Subtract the blank absorbance from the absorbance values of each group and calculate the average (AVE) and standard deviation (STD) of absorbance values of each group.
- Calculate the percentage of average absorbance (AVE%) and that of standard deviation (STD%) of each group using absorbance values of the SRB assay.
NOTE: The AVE% of miRNA control mimic treated group is 100%. Calculate the STD% using the following formula: STD% = (STD of each group / AVE absorbance of control mimic treated group) x 100. - Import the raw data including treatment concentrations, AVE%, and STD% into the software by vertically aligning those data. Since Log 0 is not defined, set the first concentration of X axis to a value that is close to 0 (e.g., 0.01).
- Click Create graph tab and choose Simple scatter-error bars. Select Worksheet columns as symbol values and click Next. In the data format panel, select XY pairs and click Next. Select corresponding data columns in the select data panel. Click Finish button to create the plot.
NOTE: The X axis represents the concentrations, the Y axis indicates the percentage of average absorbance of each concentration (AVE%), and the error bars point out the percentage of standard deviation of each concentration (STD%). - Double-click on the X axis to modify the type of scale and the scaling of axis. Change the type of scale from linear to log. Modify the start and end range number to 0.01 and 200, respectively.
- Right-click on any scatter plot, choose Curve fit, and go to the sub-category User- defined. Select Dose-response curve, click Next buttons, and then click Finish button. The dose-response curve is now generated along with a report tab (Figure 4A).
- To input Equation 1 in the software for the generation of a dose-response curve, click the Analysis tab and select Regression wizard. Go to User-defined in the equation category and then click the New button. Insert Equation 1, variables, initial parameters, and constraints into the corresponding blank boxes (Figure 4B, C). Click Add as button and set the name of the equation as Dose-response curve. The equation name is now generated in the sub-category User-defined in the equation category. f indicates the percentage of cell viability (% cell viability) in Equation 1.
Equation 1
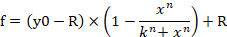
- Go to the report tab and then check the n, k, and R values.
NOTE: y0 indicates 100% cell viability of miRNA control mimic treated group, n indicates the Hill-type coefficient (the slope of a plot), k indicates the concentration of miRNA-107 mimic that produces a 50% of the miRNA-107 mimic’s maximum effect (the half maximal inhibitory concentration, IC50), and R indicates the residual unaffected fraction (the resistance fraction)15. The equation used to generate a dose-response curve recognizes the range from y0 to R value (if any) as 100% (Figure 4A). Therefore, it is necessary to acquire the adjusted k (IC50) value that is calculated based on the range from y0 to a value of zero (Figure 4A). Adjusted k (IC50) along with other ICx values (e.g., IC10 through IC90) can be obtained using Equation 2, which is derived from Equation 1. The derivation of Equation 2 from Equation 1 is indicated in Supplementary Figure 1.
Equation 2
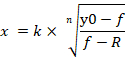
- Double-click the left mouse button on the cell in which Equation 2 is applied. Using Equation 2 and parameters from the generated dose-response curve, it is available to calculate the adjusted values of ICx, ranging from IC10 to IC90 (Figure 4D).
- Input the equal sign followed by the formula beginning with a bracket in the cell. When entering the formula, fix the value of n, k, and R as the absolute cell references by adding the dollar sign to the corresponding column and row, so that these fixed values will not be changed when auto-filling the formula down to the rows (Figure 4D). Alternatively, adjusted values can be manually calculated using Equation 2.
NOTE: IC90 value is not determined because the R value is greater than 10. In addition, if R value is above 20, the value of IC80 is also not determined (Figure 4D).
5. Verification of the Direct Target Gene of a MicroRNA of Interest
NOTE: After performing the functional experiment such as the SRB assay, miRNA-107 is confirmed as a tumor suppressive miRNA and it is highly feasible that miRNA-107 directly targets oncogenes. Check the list of all predicted target genes using a miRNA target prediction program such as TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/vert_71/), and then narrow down to potential candidate targets based on the function of a gene in databases including PubMed and GeneCards.
- Primer design for the cloning of 3’ untranslated region (UTR)
- Put the name of a gene in GeneCards (https://www.genecards.org/) and click Symbol of a gene. Assess to Ensembl genome browser by clicking Ensembl ID of a gene and then click Transcripts ID in the transcript table. After that, click Exons existed in the Transcript-based displays list on the left.
- Copy the nucleotide sequences of the 3’ UTR and paste it into the primer design program. Copy the sequences again from this program and paste it into a word processor. Check the presence of miRNA binding sequences as well as the presence of restriction enzymes sites used for the cloning.
NOTE: If there are no restriction enzyme recognition sites within the 3’ UTR, the restriction enzymes selected for the cloning can be used for the next step. - In the primer design program, accept the 3’ UTR sequences and start to design the forward and reverse primers with the following condition. Length: 20-30 nucleotides, Tm: 45-58 °C, GC%: 40-60%. The difference between the Tm values of the two primers should be less than 5 °C. The primer sequences used in this study are provided in Supplementary Figure 2. Add restriction enzyme recognition sequences as well as 4 random nucleotides to the designed primers.
- Gradient PCR
- Prepare 25 µL of PCR reaction mixtures including designed primers per one annealing temperature (Table 2). Prepare enough amount of mixtures based on the total number of reactions. Mix the solution by pipetting and add 25 µL of reaction mixtures into each tube. Centrifuge the tubes for few seconds.
- Perform 35-40 PCR cycles from denaturation step to extension step. Set up the PCR cycle as the following steps: 98 °C for 1 min (1 cycle, polymerase activation step), 95 °C for 10 s (denaturation step), 45 °C-68 °C for 30 s (annealing step), 68 °C (extension step, 10 s-1 min per 1000 bp), 68 °C for 3 min (termination step), and finally cool down to 4 °C.
- Run the PCR products and check bands on a 1% agarose gel with DNA ladders. Find the best annealing temperature (Figure 5A). Amplify 3’ UTR of a gene again using the best annealing temperature for the next step.
- Double digestion
- Make the reaction mixtures including two restriction enzymes, XhoI (or AsiSI) and NotI, in a tube (Table 3). Incubate the mixtures for 3-4 h using a water bath (37 °C).
- Run the double digested products on a 1% agarose gel and then cut the bands under UV light. In the case of luciferase vectors, before running on a gel, react double digested vectors with 10 U of alkaline phosphatases for another 1 h to prevent a recircularization during the ligation step.
- Purify the double digested PCR products and luciferase vectors from the excised bands.
- Ligation of PCR products into the luciferase vectors
- Make 20 μL of ligation reaction mixtures including the DNA ligase (Table 4).
NOTE: The molar ratio of PCR product (insert) to luciferase vector can be 3:1. 1:1 or 2:1. - Briefly centrifuge the tube for 10-15 s and incubate at 16 °C overnight using a thermal cycler.
NOTE: Alternatively, the tube can be incubated at 4 °C for 2-3 days for the ligation. In this step, the PCR insert will be cloned into the region positioned downstream of a renilla reporter gene (Figure 5B). Binding of miRNAs into the cloned 3’ UTR of a gene can decrease in the renilla activity. Firefly luciferase is for the normalization of renilla expression levels.
- Make 20 μL of ligation reaction mixtures including the DNA ligase (Table 4).
- Transformation and colony PCR
- Add the ligation mixtures (3-5 μL) into the tube containing competent cells. Gently tap the tube and keep it on ice (20 min).
NOTE: Unfreeze competent cells on ice before adding the ligation mixtures. - Quickly and gently transfer the tube to a heat block. Following a heat-shock (42 °C for 30 s-1 min), place the tube on ice for 20 min.
- Spread competent cells on the Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plate. Grow competent cells in an incubator (37 °C) overnight.
NOTE: Ampicillin (50-100 µg/mL) is contained in the agar plate. - Pick an individual colony and resuspend E. coli in one of the 8-strip tubes containing ultrapure water. Repeat this step to resuspend E. coli from randomly selected 4-8 colonies (Figure 5C).
- Transfer 25 μL of E. coli suspension into another set of 8-strip tubes. Now, there are 2 sets of tubes of E. coli suspension.
NOTE: One tube is for colony PCR and another one is for inoculation. E. coli suspension for inoculation can be temporarily stored at 4 °C (Figure 5C). - Perform the colony PCR using E. coli suspension. This step is to determine if the colonies contain an insert. Select the best colonies to inoculate and isolate luciferase vectors harboring 3’ UTR of a gene (Figure 5C).
NOTE: Repeat step 5.1-5.5 for each 3’ UTR of selected genes. Follow the condition of PCR reaction shown in Table 2 by replacing the genomic DNA with E. coli suspension.
- Add the ligation mixtures (3-5 μL) into the tube containing competent cells. Gently tap the tube and keep it on ice (20 min).
- Luciferase assay
- Prepare a 24-well plate. Use 1-2 x 104 cells in 500 μL cell culture media for each well. Do not use cell culture media containing P/S for the transfection because using P/S can reduce the transfection efficiency.
- Transfect 50 ng of luciferase vectors into the cells with control mimic or a specific miRNA mimic using a transfection reagent (Figure 5D). If screening the effects of a specific miRNA mimic at more than one concentration, keep the total amount of oligos same in each well (see step 2).
- Wash the inside of wells twice using phosphate buffered saline (PBS) on the next day.
- Apply 200 μL of lysis reagent into the wells and sufficiently carry out cell lysis before measuring the luciferase activity.
NOTE: Keep the plate on a shaking plate at least 15 min. - Transfer 5-10 μL of cell lysate into the new tube and add 100 μL of reagent I. Immediately mix the solution by pipetting and read the firefly luciferase activity using a luminometer.
NOTE: Read the firefly luciferase activity for 10-15 s. - Add 100 μL of reagent II in the same tube, and then mix by pipetting twice. Read the renilla luciferase activity for 10-15 s using a luminometer. Repeat step 5.6.5 and 5.6.6 for each sample.
- Calculate the ratio of renilla to firefly (Figure 5E).
NOTE: The activity of firefly represents the transfection efficiency of luciferase constructs into the cells.
Results
Successful and accurate confirmation of miRNA levels is important for the interpretation of data by which the classification of miRNAs is possible based on the anticipated roles of miRNAs in the development and progression of a disease. The levels of miRNA-107 and miRNA-301 were measured in three pancreas cell lines using the probe-based quantitative PCR. The synthesis of cDNAs of both a specific miRNA and a reference gene in the same reaction can increase the reproducibility of data. PANC-1 and CAPAN-1 are human pancrea...
Discussion
Strategies for the determination of bona fide miRNA targets with the functions of a miRNA of interest are indispensable for the understanding of multiple roles of miRNAs. Identification of miRNA target genes can be a guideline for interpreting the cell signaling events modulated by miRNAs in a cell. An unveiling of functionally important target genes of miRNAs can provide the fundamental knowledge to develop a miRNA-based therapy in cancer.
Several methods such as microarrays, small RNA librar...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1D1A3B03035662); and Hallym University Research Fund, 2017 (HRF-201703-003).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 15 mL conical tube | SPL Life Sciences | 50015 | |
| 24-well plate | Thermo Scientific | 142475 | |
| 50 mL conical tube | SPL Life Sciences | 50050 | |
| 6-well plate | Falcon | 353046 | |
| 6X DNA loading dye | Real Biotech Corporation | RD006 | 1 mL |
| 8-cap strip | Applied Biosystems | N8010535 | For cDNA synthesis |
| 8-tube strip | Applied Biosystems | N8010580 | For cDNA synthesis |
| 96-well plate | Falcon | 353072 | |
| Acetic acid | Sigma | A6283-1L | 1 L |
| Agarose A | Bio Basic | D0012 | 500 g |
| Alkaline phosphatase | New England Biolabs | M0290S | 10,000 U/mL |
| Ampicillin | Bio basic Canada Inc | AB0028 | 25 g |
| AriaMx 96 tube strips | Agilent Technologies | 401493 | For real time PCR |
| AriaMx real-time PCR system | Agilent Technologies | G8830A | qPCR amplification, detection, and data analysis |
| AsiSI | New England Biolabs | R0630 | 10,000 units/mL |
| CAPAN-1 cells | ATCC | HTB-79 | |
| Cell culture hood | Labtech | Model: LCB-1203B-A2 | |
| Counting chambers with V-slash | Paul Marienfeld | 650010 | Cells counter |
| CutSmart buffer | New England Biolabs | B7204S | 10X concentration |
| DMEM | Gibco | 11965-092 | 500 mL |
| DNA gel extraction kit | Bionics | DN30200 | 200 prep |
| DNA ladder | NIPPON Genetics EUROPE | MWD1 | 1 Kb ladder |
| DNase I | Invitrogen | 18068015 | 100 units |
| Dual-luciferase reporter assay system | Promega | E1910 | 100 assays |
| Fetal bovine serum | Gibco | 26140-079 | 500 mL |
| HIT competent cells | Real Biotech Corporation(RBC) | RH617 | Competent cells |
| HPNE cells | ATCC | CRL-4023 | |
| LB agar broth | Bio Basic | SD7003 | 250 g |
| Lipofectamine 2000 | Invitrogen | 11668-027 | 0.75 mL |
| Lipofectamine RNAiMax | Invitrogen | 13778-075 | 0.75 mL |
| Luminometer | Promega | Model: E5311 | |
| Microcentrifuge tube | Eppendorf | 22431021 | |
| Microplate reader | TECAN | Infinite F50 | |
| miRNA control mimic | Ambion | 4464058 | 5 nmole |
| miRNA-107 mimic | Ambion | 4464066 | 5 nmole |
| miRNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | 217004 | 50 prep |
| Mupid-2plus (electrophoresis system) | TaKaRa | Model: AD110 | |
| NotI | New England Biolabs | R3189 | 20,000 units/mL |
| Oligo explorer program | GeneLink | For primer design | |
| Optical tube strip caps (8X Strip) | Agilent Technologies | 401425 | For real time PCR |
| Opti-MEM | Gibco | 31985-070 | 500 Ml |
| PANC-1 cells | ATCC | CRL-1469 | |
| Penicillin/streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | 100 mL |
| Phosphate buffer saline | Gibco | 14040117 | 1000 mL |
| Plasmid DNA miniprep S& V kit | Bionics | DN10200 | 200 prep |
| PrimeSTAR GXL DNA polymerase | TaKaRa | R050A | 250 units |
| Shaker | TECAN | Shaking platform | |
| Shaking incubator | Labtech | Model: LSI-3016A | |
| Sigmaplot 14 software | Systat Software Inc | For dose-response curve generation | |
| Sulforhodamine B powder | Sigma | S1402-5G | 5 g |
| SYBR green master mix | Smobio | TQ12001805401-3 | Binding fluorescent dye for dsDNA |
| T4 DNA ligase | TaKaRa | 2011A | 25,000 U |
| TaqMan master mix | Applied Biosystems | 4324018 | 200 reactions, no AmpErase UNG |
| TaqMan microRNA assay (hsa-miR-107) | Applied Biosystems | 4427975 | Assay ID: 000443 (50RT, 150 PCR rxns) |
| TaqMan microRNA assay (hsa-miR-301) | Applied Biosystems | 4427975 | Assay ID: 000528 (50RT, 150 PCR rxns) |
| TaqMan miR RT kit | Applied Biosystems | 4366597 | 1000 reactions |
| Thermo CO2 incubator (BB15) | ThermoFisher Scientific | 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubation | |
| Trichloroacetic acid | Sigma | 91228-100G | 100 g |
| Trizma base | Sigma | T4661-100G | 100 g |
| Ultrapure water | Invitrogen | 10977-015 | 500 mL |
| Veriti 96 well thermal cycler | Applied Biosystems | For amplification of DNA (or cDNA) | |
| XhoI | New England Biolabs | R0146 | 20,000 units/mL |
References
- He, L., Hannon, G. J. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nature Reviews Genetics. 5 (7), 522-531 (2004).
- Park, J. K., Doseff, A. I., Schmittgen, T. D. MicroRNAs Targeting Caspase-3 and -7 in PANC-1 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (4), (2018).
- Park, J. K., et al. MicroRNAs-103/107 coordinately regulate macropinocytosis and autophagy. Journal of Cell Biology. 215 (5), 667-685 (2016).
- Henry, J. C., et al. miR-199a-3p targets CD44 and reduces proliferation of CD44 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 403 (1), 120-125 (2010).
- Hoefert, J. E., Bjerke, G. A., Wang, D., Yi, R. The microRNA-200 family coordinately regulates cell adhesion and proliferation in hair morphogenesis. Journal of Cell Biology. 217 (6), 2185-2204 (2018).
- Anfossi, S., Fu, X., Nagvekar, R., Calin, G. A. MicroRNAs, Regulatory Messengers Inside and Outside Cancer Cells. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 1056, 87-108 (2018).
- Khoshinani, H. M., et al. Involvement of miR-155/FOXO3a and miR-222/PTEN in acquired radioresistance of colorectal cancer cell line. Japanese Journal of Radiology. 35 (11), 664-672 (2017).
- Gao, Y., et al. MicroRNA-155 increases colon cancer chemoresistance to cisplatin by targeting forkhead box O3. Oncology Letters. 15 (4), 4781-4788 (2018).
- Catanzaro, G., et al. Loss of miR-107, miR-181c and miR-29a-3p Promote Activation of Notch2 Signaling in Pediatric High-Grade Gliomas (pHGGs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 18 (12), (2017).
- Akbari Moqadam, F., Pieters, R., den Boer, M. L. The hunting of targets: challenge in miRNA research. Leukemia. 27 (1), 16-23 (2013).
- Brown, R. A. M., et al. Total RNA extraction from tissues for microRNA and target gene expression analysis: not all kits are created equal. BMC Biotechnology. 18 (1), (2018).
- Kim, Y. K., Yeo, J., Kim, B., Ha, M., Kim, V. N. Short structured RNAs with low GC content are selectively lost during extraction from a small number of cells. Molecular Cell. 46 (6), 893-895 (2012).
- Schmittgen, T. D., Livak, K. J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nature Protocols. 3 (6), 1101-1108 (2008).
- Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25 (4), 402-408 (2001).
- Park, J. K., Seo, J. S., Lee, S. K., Chan, K. K., Kuh, H. J. Combinatorial Antitumor Activity of Oxaliplatin with Epigenetic Modifying Agents, 5-Aza-CdR and FK228, in Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Biomolecules & Therapeutics. 26 (6), 591-598 (2018).
- Xia, X., et al. Downregulation of miR-301a-3p sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine treatment via PTEN. American Journal of Translational Research. 9 (4), 1886-1895 (2017).
- Lee, K. H., et al. Epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA miR-107 regulates cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 9 (3), 293-301 (2009).
- van Tonder, A., Joubert, A. M., Cromarty, A. D. Limitations of the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay when compared to three commonly used cell enumeration assays. BMC Research Notes. 8, 47 (2015).
- Wang, P., Henning, S. M., Heber, D. Limitations of MTT and MTS-based assays for measurement of antiproliferative activity of green tea polyphenols. PloS One. 5 (4), e10202 (2010).
- Wu, L., Belasco, J. G. Let me count the ways: mechanisms of gene regulation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Molecular Cell. 29 (1), 1-7 (2008).
- Jin, Y., Chen, Z., Liu, X., Zhou, X. Evaluating the microRNA targeting sites by luciferase reporter gene assay. Methods in Molecular Biology. , 117-127 (2013).
- Ma, Z., et al. Gamma-synuclein binds to AKT and promotes cancer cell survival and proliferation. Tumour Biology. 37 (11), 14999-15005 (2016).
- Pan, Z. Z., Bruening, W., Giasson, B. I., Lee, V. M., Godwin, A. K. Gamma-synuclein promotes cancer cell survival and inhibits stress- and chemotherapy drug-induced apoptosis by modulating MAPK pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (38), 35050-35060 (2002).
- Martinez-Sanchez, A., Murphy, C. L. MicroRNA Target Identification-Experimental Approaches. Biology (Basel). 2 (1), 189-205 (2013).
- Lee, E. J., et al. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. International Journal of Cancer. 120 (5), 1046-1054 (2007).
- Nuovo, G. J., et al. A methodology for the combined in situ analyses of the precursor and mature forms of microRNAs and correlation with their putative targets. Nature Protocols. 4 (1), 107-115 (2009).
- Schmittgen, T. D., et al. Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA. Methods. 44 (1), 31-38 (2008).
- Diederichs, S., Haber, D. A. Dual role for argonautes in microRNA processing and posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA expression. Cell. 131 (6), 1097-1108 (2007).
- Orellana, E. A., Kasinski, A. L. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay in Cell Culture to Investigate Cell Proliferation. Bio Protocol. 6 (21), (2016).
- Lawrie, C. H. MicroRNAs in hematological malignancies. Blood Reviews. 27 (3), 143-154 (2013).
- Quah, B. J., Warren, H. S., Parish, C. R. Monitoring lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo with the intracellular fluorescent dye carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester. Nature Protocols. 2 (9), 2049-2056 (2007).
- Xing, Z., Li, D., Yang, L., Xi, Y., Su, X. MicroRNAs and anticancer drugs. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica. 46 (3), 233-239 (2014).
- Moeng, S., et al. MicroRNA-107 Targets IKBKG and Sensitizes A549 Cells to Parthenolide. Anticancer Research. 38 (11), 6309-6316 (2018).
- Chou, T. C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Research. 70 (2), 440-446 (2010).
- Flamand, M. N., Gan, H. H., Mayya, V. K., Gunsalus, K. C., Duchaine, T. F. A non-canonical site reveals the cooperative mechanisms of microRNA-mediated silencing. Nucleic Acids Research. 45 (12), 7212-7225 (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved