A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Fluorescence-Based Measurements of Phosphatidylserine/Phosphatidylinositol 4-Phosphate Exchange Between Membranes
In This Article
Summary
Here, we describe protocols using fluorescent lipid sensors and liposomes to determine whether a protein extracts and transports phosphatidylserine or phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in vitro.
Abstract
Several members of the evolutionarily conserved oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP)-related proteins(ORP)/OSBP homologs (Osh) family have recently been found to represent a novel lipid transfer protein (LTP) group in yeast and human cells. They transfer phosphatidylserine (PS) from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the plasma membrane (PM) via PS/phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI(4)P) exchange cycles. This finding allows a better understanding of how PS, which is critical for signaling processes, is distributed throughout the cell and the investigation of the link between this process and phosphoinositide (PIP) metabolism. The development of new fluorescence-based protocols has been instrumental in the discovery and characterization of this new cellular mechanism in vitro at the molecular level. This paper describes the production and the use of two fluorescently labelled lipid sensors, NBD-C2Lact and NBD-PHFAPP, to measure the ability of a protein to extract PS or PI(4)P and to transfer these lipids between artificial membranes. First, the protocol describes how to produce, label, and obtain high-purity samples of these two constructs. Secondly, this paper explains how to use these sensors with a fluorescence microplate reader to determine whether a protein can extract PS or PI(4)P from liposomes, using Osh6p as a case study. Finally, this protocol shows how to accurately measure the kinetics of PS/PI(4)P exchange between liposomes of defined lipid composition and to determine lipid transfer rates by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) using a standard fluorometer.
Introduction
The precise distribution of lipids between different membranes and within the membranes of eukaryotic cells1,2 has profound biological implications. Decrypting how LTPs function is an important issue in cell biology3,4,5,6, and in vitro approaches are of great value in addressing this issue7,8,9,10,11. Here, an in vitro, fluorescence-based strategy is presented that has been instrumental in establishing that several ORP/Osh proteins effect PS/PI(4)P exchange between cell membranes12 and thereby constitute a new class of LTPs. PS is an anionic glycerophospholipid that represents 2-10% of total membrane lipids in eukaryotic cells13,14,16. It is distributed along a gradient between the ER and the PM, where it represents 5-7% and up to 30% of glycerophospholipids, respectively17,18,19. Moreover, PS is essentially concentrated in the cytosolic leaflet of the PM. This build-up and the uneven partition of PS in the PM are critical for cellular signaling processes19. Owing to the negative charge of PS molecules, the cytosolic leaflet of the PM is much more anionic than the cytosolic leaflet of other organelles1,2,19,20. This enables the recruitment, via electrostatic forces, of signaling proteins such as myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS)21, sarcoma (Src)22, Kirsten-rat sarcoma viral oncogene (K-Ras)23, and Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1)24 that contain a stretch of positively charged amino acids and a lipidic tail.
PS is also recognized by conventional protein kinase C in a stereoselective manner via a C2 domain25. However, PS is synthesized in the ER26, indicating that it must be exported to the PM before it can play its role. It was not known how this was accomplished19 until the finding that, in yeast, Osh6p and Osh7p transfer PS from the ER to the PM27. These LTPs belong to an evolutionarily conserved family in eukaryotes whose founding member is OSBP and that contains proteins (ORPs in human, Osh proteins in yeast) integrating an OSBP-related domain (ORD) with a pocket to host a lipid molecule. Osh6p and Osh7p consist only of an ORD whose structural features are adapted to specifically bind PS and transfer it between membranes. Nevertheless, how these proteins directionally transferred PS from the ER to the PM was unclear. Osh6p and Osh7p can trap PI(4)P as an alternative lipid ligand12. In yeast, PI(4)P is synthesized from phosphatidylinositol (PI) in the Golgi and the PM by PI 4-kinases, Pik1p and Stt4p, respectively. In contrast, there is no PI(4)P in the ER membrane, as this lipid is hydrolyzed to PI by the Sac1p phosphatase. Hence, a PI(4)P gradient exists at both the ER/Golgi and ER/PM interfaces. Osh6p and Osh7p transfer PS from the ER to the PM via PS/PI(4)P exchange cycles using the PI(4)P gradient that exists between these two membranes12.
Within one cycle, Osh6p extracts PS from the ER, exchanges PS for PI(4)P at the PM and transfers PI(4)P back to the ER to extract another PS molecule. Osh6p/Osh7p interact with Ist2p28, one of the few proteins that connect and bring the ER membrane and the PM into close proximity with each other to create ER-PM contact sites in yeast29,30,31. In addition, the association of Osh6p with negatively charged membranes becomes weak as soon as the protein extracts one of its lipid ligands due to a conformational change that modifies its electrostatic features32. This aids Osh6p by shortening its membrane dwell time, thereby maintaining the efficiency of its lipid transfer activity. Combined with the binding to Ist2p, this mechanism could allow Osh6p/7p to both quickly and accurately execute lipid exchange at the ER/PM interface. In human cells, ORP5 and ORP8 proteins execute PS/PI(4)P exchange at ER-PM contact sites via distinct mechanisms33. They have a central ORD, akin to Osh6p, but are directly anchored to the ER via a C-terminal transmembrane segment33 and dock into the PM via an N-terminal Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain that recognizes PI(4)P and PI(4,5)P233,34,35. ORP5/8 use PI(4)P to transfer PS, and it has been shown that ORP5/8 additionally regulate PM PI(4,5)P2 levels and presumably modulate signaling pathways. In turn, a decrease in PI(4)P and PI(4,5)P2 levels lowers ORP5/ORP8 activity as these proteins associate with the PM in a PIP-dependent fashion. Abnormally high PS synthesis, which leads to Lenz-Majewski syndrome, impacts PI(4)P levels through ORP5/836. When the activity of both proteins is blocked, PS becomes less abundant at the PM, lowering the oncogenic capability of signaling proteins37.
Conversely, ORP5 overexpression seems to promote cancer cell invasion and metastatic processes38. Thus, alterations to ORP5/8 activity can severely modify cellular behavior through changes in lipid homeostasis. Further, ORP5 and ORP8 occupy ER-mitochondria contact sites and preserve some mitochondrial functions, possibly by supplying PS39. Additionally, ORP5 localizes to ER-lipid droplet contact sites to deliver PS to lipid droplets by PS/PI(4)P exchange40. The strategy described herein to measure (i) PS and PI(4)P extraction from liposomes and (ii) PS and PI(4)P transport between liposomes has been devised to establish and analyze the PS/PI(4)P exchange activity of Osh6p/Osh7p12,32 and used by other groups to analyze the activity of ORP5/ORP835 and other LTPs10,41. It is based on the use of a fluorescence plate reader, a standard L-format spectrofluorometer, and two fluorescent sensors, NBD-C2Lact and NBD-PHFAPP, that can detect PS and PI(4)P, respectively.
NBD-C2Lact corresponds to the C2 domain of the glycoprotein, lactadherin, that was reengineered to include a unique solvent-exposed cysteine near the presumed PS binding site; a polarity-sensitive NBD (7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol) fluorophore is covalently linked to this residue (Figure 1A)12. To be more precise, the C2 domain of lactadherin (Bos taurus, UniProt: Q95114,residues 270-427) was cloned into a pGEX-4T3 vector to be expressed in fusion with glutathione S-transferase (GST) in Escherichia coli. The C2Lact sequence was then mutated to substitute two solvent-accessible cysteine residues (C270, C427) with alanine residues and to introduce a cysteine residue into a region near the putative PS-binding site (H352C mutation) that can be subsequently labeled with N,N'-dimethyl-N-(iodoacetyl)-N'-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl) ethylene diamine (IANBD) 12. A cleavage site for thrombin is present between the GST protein and the N-terminus of the C2 domain. A major advantage is that this domain selectively recognizes PS in a Ca2+-independent manner contrary to other known C2 domains or Annexin A542. NBD-PHFAPP is derived from the PH domain of the human four-phosphate-adaptor protein 1 (FAPP1), which was reengineered to include a single solvent-exposed cysteine that can be labeled with an NBD group near the PI(4)P binding site (Figure 1A)43. The nucleotide sequence of the PH domain of the human FAPP protein (UniProt: Q9HB20, segment [1-100]) has been cloned into a pGEX-4T3 vector to be expressed in tandem with a GST tag. The PHFAPP sequence has been modified to insert a unique cysteine residue within the membrane-binding interface of the protein43. Moreover, a nine-residue linker has been introduced between the thrombin cleavage site and the N-terminus of the PH domain to ensure accessibility to the protease.
To measure PS extraction from liposomes, NBD-C2Lact is mixed with liposomes made of phosphatidylcholine (PC) containing trace amounts of PS. Owing to its affinity for PS, this construct binds to the liposomes, and the NBD fluorophore experiences a change in polarity as it comes into contact with the hydrophobic environment of the membrane, which elicits a blue-shift and an increase in fluorescence. If PS is extracted almost completely by a stoichiometric amount of LTP, the probe does not associate with liposomes, and the NBD signal is lower (Figure 1B)32. This difference in signal is used to determine whether an LTP (e.g., Osh6p) extracts PS. A similar strategy is used with NBD-PHFAPP to measure PI(4)P extraction (Figure 1B), as described previously12,32. Two FRET-based assays were designed to (i) measure PS transport from LA to LB liposomes, which mimic the ER membrane and the PM, respectively, and (ii) PI(4)P transport in the reverse direction. These assays are performed under the same conditions (i.e., same buffer, temperature, and lipid concentration) to measure PS/PI(4)P exchange. To measure PS transport, NBD-C2Lact is mixed with LA liposomes composed of PC and doped with 5 mol% PS and 2 mol% of a fluorescent rhodamine-labelled phosphatidylethanolamine (Rhod-PE)-and LB liposomes incorporating 5 mol% PI(4)P.
At time zero, FRET with Rhod-PE quenches the NBD fluorescence. If PS is transported from LA to LB liposomes (e.g., upon injecting Osh6p), a fast dequenching occurs due to the translocation of NBD-C2Lact molecules from LA to LB liposomes (Figure 1C). Given the amount of accessible PS, NBD-C2Lact remains essentially in a membrane-bound state over the course of the experiment12. Thus, the intensity of the NBD signal directly correlates with the distribution of NBD-C2Lact between LA and LB liposomes and can be easily normalized to determine how much PS is transferred. To measure the transfer of PI(4)P in the opposite direction, NBD-PHFAPP is mixed with LA and LB liposomes; given that it only binds to LB liposomes that contain PI(4)P, but not Rhod-PE, its fluorescence is high. If PI(4)P is transferred to LA liposomes, it translocates to these liposomes, and the signal decreases due to FRET with Rhod-PE (Figure 1C). The signal is normalized to determine how much PI(4)P is transferred43.
Protocol
1. Purification of NBD-C2Lact
NOTE: Although this protocol details the use of a cell disruptor to break bacteria, it can be modified to use other lysis strategies (e.g., a French press). At the beginning of the purification, it is mandatory to use buffer that is freshly degassed, filtered, and supplemented with 2 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) to prevent the oxidation of cysteine. However, for the protein labelling step, it is crucial to completely remove DTT. Many steps must be carried out on ice or in a cold room to avoid any protein degradation. Samples of 30 µL volume must be collected at different steps of the protocol to perform an analysis by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) using a 15% acrylamide gel to check the progress of the purification. Mix enough denaturing Laemmli sample buffer with each aliquot, and heat the mixture at 95 °C. Freeze and store the tubes at -20 °C until analysis.
- Expression of GST-C2Lact in Escherichia coli
- Mix 20 µL of BL21 Gold competent cells with 18 µL of sterilized water. Then, mix 2 µL of pGEX-C2Lact plasmid (at ~65 ng/µL) with the bacteria, and transform them by electroporation. Resuspend the bacteria with 150 µL of autoclaved Lennox Lysogeny-Broth (LB) medium (10 g/L tryptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, 5 g/L NaCl in deionized water, glucose-free). Let the bacteria grow at 37 °C for 1 h in a 2 mL snap-cap microcentrifuge tube.
- Inoculate 25 mL of LB medium, supplemented with 50 µg/mL ampicillin, with 150 µL of bacterial suspension in a 125 mL sterile Erlenmeyer flask. Place the flask in an orbital shaker at 37 °C, and let the bacteria grow overnight with agitation at 185 rpm.
- Fill two sterile 2 L Erlenmeyer flasks with 500 mL of LB medium supplemented with 50 µg/mL ampicillin, and add 5 mL of preculture suspension. Let the bacteria grow at 37 °C with agitation at 220 rpm.
- Periodically measure the optical density (OD) of the suspension at a wavelength (λ) of 600 nm. When the OD reaches a value of ~0.6-0.7, add 500 µL of a stock solution of 1 M isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) to each flask to initiate the expression of GST-C2Lact. Shake the flasks at 185 rpm for 4 h at 37 °C.
- Transfer the contents of each flask to a polypropylene centrifuge bottle. Centrifuge the two bottles for 30 min at 4600 × g at 4 °C to pellet the bacteria. Discard the supernatant, and resuspend each pellet in 50 mL of cold phosphate-buffered saline.
- Transfer the bacterial suspension contained in each bottle to a 50 mL conical centrifuge tube. Centrifuge the two tubes for 30 min at 2300 × g at 4 °C. Remove the supernatant, and store the tubes, each of which contains a bacterial pellet, at -20 °C.
- Purification of C2Lact
- On ice, fill two 50 mL conical centrifugal tubes with 50 mL of buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, and 150 mM NaCl (hereafter called TN buffer), previously filtered and degassed by membrane vacuum filtration.
- To prepare the lysis buffer in each tube, dissolve a tablet of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid-free protease inhibitor cocktail in the TN buffer by mild sonication or vortexing. Add other antiproteases, (10 µM bestatin, 1 µg/mL pepstatin A, and 10 µM phosphoramidon). Importantly, supplement the buffer with 2 mM DTT.
- Fill the two tubes that contain the bacterial pellets prepared in step 1.1.6, with lysis buffer to obtain a final volume of 30 mL in each tube, and slowly defrost the pellets on ice for 10 min. Crush each pellet with a stainless steel spatula, and resuspend them by vortexing the tubes and/or by pipetting the suspension back and forth with a pipette controller and a 25 mL pipette until a homogeneous suspension is obtained.
- Perform lysis using a precooled cell disruptor (see the Table of Materials) by loading 30 mL of the sample inside the reservoir and running a breaking cycle in continuous mode with a pressure of 1.6 bar. Collect the lysate in the same tube, keep the tube on ice, and immediately add 250 µL from a stock solution of 200 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) prepared in isopropanol.
- Lyse the other sample following the same procedure. Use the remainder of the lysis buffer to wash the cell disruptor, and collect the wash to adjust the volume of each lysate (~30 mL) to a final volume of 50 mL.
- Supplement each lysate with 5 mM MgCl2,and add 20 µg/mL of DNAse I to fragment the DNA and thus reduce the viscosity of the sample. Incubate on ice for 30 min. Collect a sample for gel analysis.
- Transfer each 50 mL lysate to a prechilled polycarbonate ultracentrifuge tube (two in total, see the Table of Materials). Centrifuge at 186,000 × g at 4 °C for at least 1 h using an ultracentrifuge.
- In parallel to the centrifugation step, dispense 1.4 mL of a slurry containing glutathione coupled to 4% agarose beads into two 50 mL conical centrifugal tubes, add 20 mL of TN buffer supplemented with 1 mM DTT (TND buffer) to each tube, centrifuge at 1200 × g for 5 min, and discard the supernatant. Repeat this washing step twice.
- After the centrifugation of the bacterial lysate, remove a 30 µL sample from the supernatant, and transfer the supernatant from each ultracentrifuge tube to a corresponding 50 mL conical centrifuge tube that contains clean beads. For gel analysis, resuspend the debris pellet in one of the ultracentrifuge tubes with 50 mL of TND buffer, and collect a 30 µL sample.
- Place the tubes on a rotator for 3-4 h at 4 °C to obtain a homogeneous bead suspension. Pool the bead suspensions in an empty 25 mL chromatography column. Let the beads decant, and remove the buffer and unbound proteins by gravity flow. Take a sample from the eluate for analysis.
- Resuspend the beads with 20 mL of TND buffer, and collect the eluate by gravity flow. Repeat this step twice to completely wash the beads. Pool the collected eluates, and retain a 30 µL sample for further analysis.
NOTE: After a short decantation, a volume of ~2 mL of bead suspension, to which GST-C2Lact is attached, sediments at the bottom of the column. - Add 1 mL of bead suspension to two 2 mL snap-cap microcentrifuge tubes. Fill each tube with TND buffer to a final volume of 1.970 mL. Take a 30 µL sample from one tube for further analysis (B1 sample). Add 10 µL of 10 mM CaCl2 solution and 25 µL from a stock solution of human thrombin protease solution at 0.02 U/µL.
- Place the two tubes on a rotator at 4 °C overnight to allow thrombin to cleave off the GST tag from the C2Lact domain. On the next day, in each tube, mix 10 µL of 200 mM PMSF solution with the bead suspension to inhibit the thrombin action.
- Centrifuge the tubes at 700 × g for 5 min, and collect the supernatant, which contains soluble C2Lact domain, from each tube, without taking the beads. Pool the supernatants into a 2 mL snap-cap microcentrifuge tube (E1 eluate) that is kept on ice.
- Add 1 mL of TND buffer to each tube to resuspend the beads, and wash them; repeat step 1.2.14. Perform this step thrice more to recover a maximum amount of protein. Each time, pool the collected supernatants into a new 2 mL tube (E2, E3, E4, and E5 eluates), and take an aliquot for further analysis. At the end of washing steps, take an aliquot from the bead suspension (aliquot B2).
- Analyze the 30 µL samples that were collected at the different steps of the purification protocol by SDS-PAGE separation on a 15% acrylamide gel.
- Remove potential contaminating beads by pooling all the supernatants (i.e., ~10 mL) collected during steps 1.2.14 and 1.2.15 into a 10 mL chromatography column. Collect the eluate by gravity flow, and retain the beads at the bottom of the column.
- Concentrate the C2Lact sample using a centrifugal filter unit with a molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) of 3 kDa and a centrifugation speed of 2300 × g. Stop the concentration procedure when the volume of the protein sample is ~1 mL.
- Preparation and purification of NBD-C2Lact
- Equilibrate a desalting column (see the Table of Materials) with TN buffer. Load the column with 1 mL of concentrated C2Lact sample. Allow the sample to enter the gel bed completely, add 1.5 mL of freshly degassed DTT-free TN buffer to the column, and collect the eluate by gravity flow into a 2 mL snap-cap microcentrifuge tube.
- Dilute 50 µL of eluate in a final volume of 300 µL TN buffer, and record an absorbance spectrum from 230 to 450 nm using pure TN buffer as a blank. Determine the C2Lact concentration based on the absorbance measured at 280 nm, considering an extinction coefficient ε equal to 44,920 M-1.cm-1.
- To label the C2Lact construct with a NBD fluorophore, mix the protein with a ten-fold molar excess of N,N'-dimethyl-N-(iodoacetyl)-N'-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)ethylenediamine (IANBD amide).
- Dissolve 1 mg of IANBD in anhydrous dimethylformamide (DMF), keeping in mind that the final volume of DMF used for labeling the C2Lact construct must not exceed 5% (v/v) of the protein sample volume.
- To determine the volume of DMF (VDMF) to dissolve IANBD, first calculate the required amount of IANBD (m, expressed in mg) to label the protein by using formula 1.
m = 10,000 × C × V × MWIANBD (1)
where C is the concentration of C2Lact measured in step 1.3.2, V is the volume of the C2Lact sample, and MWIANBD is the molecular weight of the fluorophore (420 g/mol). - Calculate VDMF by using formulae 2 (with m0=1) and 3.
VDMF= (m0/m) × VIANBD (2)
VIANBD=0.05 × V (3)
Where m0 is the quantity of IANBD powder in mg, and VIANBD is the volume of IANBD solution to be added to the C2Lact sample. - Add volume VIANBD of the freshly-prepared IANBD solution to the C2Lact sample, and shake the reaction mixture at 800-900 rpm for 30 min at 25 °C using a thermomixer protected from light. Let the reaction proceed for 90 min on ice. In the meantime, clean a centrifugal filter unit (MWCO= 3 kDa) with 10 mL of TN buffer.
- Add L-cysteine (in 10-fold molar excess to IANBD) to the reaction mixture to inactivate free IANBD.
- Add 15 mL of TN buffer to the NBD-C2Lact solution, and transfer the NBD-C2Lact solution to the centrifugal filter unit. Concentrate the sample to 2 mL to separate most of the free NBD from the protein by centrifugation at 2300 × g. Repeat this washing step two times. Centrifuge the sample in a 2 mL snap-cap centrifuge tube for 10 min at 19,000 × g at 4 °C to pellet potential aggregates, and collect the supernatant.
- Dilute 50 µL of eluate in a final volume of 300 µL of TN buffer. Record the absorbance spectrum from 230 to 650 nm using the eluate collected during the concentration procedure as a blank. Determine the NBD-C2Lact concentration using the maximal absorbance at λ=280 and 495 nm and extinction coefficients ε= 44,920 M-1.cm-1 (protein) and 25,000 M-1.cm-1 (NBD fluorophore).
NOTE: If the two concentration values are alike, this indicates that the C2Lact construct is labeled at a 1:1 ratio with the NBD group. - If the NBD-C2Lact concentration estimated from the measurement of NBD absorbance exceeds the concentration estimated from the absorbance of tryptophan (Trp) residues, repeat step 1.3.5 to further remove free NBD.
- Add glycerol to the sample to obtain a final concentration of 10% (v/v) to cryo-protect the NBD-C2Lact construct during flash-freezing. Measure the final protein concentration.
- Prepare 50 µL aliquots of protein in 0.5 mL snap-cap microcentrifuge tubes. Flash-freeze the tubes in liquid nitrogen, and store them at -80 °C.
2. Purification of NBD-PHFAPP
NOTE: The procedure to produce and label PHFAPP is identical to that of NBD-C2Lact until the transfer of NBD-C2Lact solution to a centrifugal filter unit in step 1.3.4. From this step onwards, follow the protocol that is described below.
- After the concentration step, keep 2 mL of NBD-PHFAPP at 4 °C in the dark for not more than 1 day before performing size-exclusion chromatography. Prior to size-exclusion chromatography, verify that there is no orange deposit (aggregation during concentration) at the bottom of the tube. If this is the case, centrifuge the sample at 540,000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C, and purify the supernatant by size-exclusion chromatography.
NOTE: Size-exclusion chromatography is performed on a column packed with crosslinked dextran-acrylamide copolymer (see the Table of Materials), previously equilibrated with TND buffer, using a fast protein liquid chromatography system (see the Table of Materials). The column must be protected from light. A flow rate of 1 mL/min was used, and the elution of the NBD-PHFAPP construct was followed by recording the absorbance at λ=280 (protein) and 480 nm (NBD) at the column exit.- Inject the NBD-PHFAPP sample loaded in a 2 mL injection loop onto the column, and immediately collect 2.5 mL fractions of eluate.
- Analyze all the fractions that correspond to the main peak detected at 280 and 480 nm on a 15% SDS-PAGE gel. Mix a 25 µL sample of each fraction with 15 µL of Laemmli sample buffer prior to heating and loading onto the gel.
NOTE: A main peak, which is simultaneously detected at λ= 280 and 480 nm, appears once a volume of ~150 mL buffer is passed through the column. - Pool the fractions that exclusively contain NBD-PHFAPP protein (~12.2 kDa), and add glycerol at a final concentration of 10% (v/v). Concentrate the sample using a centrifugal filter unit with a MWCO of 3 kDa to a final volume of 1 mL using a centrifugation speed of 2300 × g.
- Prepare aliquots, and record an absorbance spectrum as described for NBD-C2Lact. Use an extinction coefficient ε= 29,450 M-1.cm-1 to determine the concentration of the protein based on the absorbance measured at λ=280 nm.
3. Preparation of liposomes for PS and PI(4)P extraction or transfer assays
NOTE: Perform all the steps at room temperature unless otherwise specified. Handle organic solvents, rotavapor, and liquid nitrogen with caution.
- Prepare fresh, filtered, and degassed 50 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES)-potassium hydroxide (KOH), pH 7.4, 120 mM potassium acetate (HK) buffer.
- For each type of liposome, take precise amounts of different lipids from stock solutions, and mix them in a 25 mL pear-shaped glass flask (Table 1). Add pure chloroform to adjust the volume of each mixture to 1 mL. Label each flask with the liposome name. Wrap the flasks containing lipid mixture doped with Rhod-PE with aluminum foil.
- Place the flask on a rotary evaporator. Dry the lipids under vacuum and at 25 °C for at least 30 min at a rotation speed of 500 rpm. For lipid films that contain PI(4)P, prewarm the flask at 32-34 °C for 5 min, under gentle rotation, to properly mix PI(4)P with the other lipids before creating vacuum in the flask to remove the solvent, which will leave behind a film of dry lipids on the flask wall.
- Disconnect the flask from the evaporator, and place it in a vacuum chamber for 45 min to remove any remaining traces of solvent. Fill the flask with 2 mL of HK buffer, and add a few 4 mm-diameter glass beads to the solution. Gently vortex the flask for 2 min to resuspend the lipids and prepare multilamellar lipid vesicles (MLVs) with a lipid concentration of 4 mM. Prepare 0.5 mL aliquots of MLVs in 1.5 mL screw-cap microcentrifuge tubes.
- Freeze-thaw the tubes 5x (using liquid nitrogen and a water bath at 37 °C, respectively). Extrude the liposomes or store them at -20 °C.
- Use a mini extruder to prepare the liposomes (i.e., large unilamellar vesicles) from the MLVs according to the manufacturer's guidelines. Use a polycarbonate filter with uniform cylindrical pores of 200 nm diameter.
- To prepare each type of liposome, extrude at least 250 µL of the corresponding suspension of MLVs. Store the extruded liposomes at 4 °C and in the dark if they contain Rhod-PE. Use the liposomes within 2 days.
| Lipid composition (mol/mol) | Lipid | |||||
| Liposome name | DOPC (25 mg/mL) | POPS (10 mg/mL) | 16:0 Liss Rhod-PE (1 mg/mL) | C16:0/C16:0-PI(4)P (1 mg/mL) | ||
| Extraction assays | Liposome 2 mol% PS | PC/PS 98/2 | 247 µL | 12.5 µL | ||
| Liposome 2 mol% PI(4)P | PC/PI(4)P 98/2 | 247 µL | 153 µL | |||
| PC liposome | PC 100 | 252 µL | ||||
| Transport assays | LA | PC/PS/Rhod-PE 93/5/2 | 234 µL | 31.4 µL | 200 µL | |
| LA without PS | PC/Rhod-PE 98/2 | 247 µL | 200 µL | |||
| LB | PC/PI(4)P 95/5 | 237 µL | 383 µL | |||
| LB without PI(4)P | PC 100 | 252 µL | ||||
| LA-Eq | PC/PS/PI(4)P/Rhod-PE 93/2.5/2.5/2 | 234 µL | 15.7 µL | 200 µL | 191 µL | |
| LB-Eq | PC/PS/PI(4)P 95/2.5/2.5 | 239 µL | 15.7 µL | 191 µL | ||
Table 1: Volumes of lipid stock solutions to be mixed for liposome preparation. Abbreviations: PS= phosphatidylserine; PC = phosphatidylcholine; PI(4)P = phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate; Rhod-PE = rhodamine-labelled phosphatidylethanolamine; DOPC = dioleoylphosphatidylcholine; POPS= 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine; 16:0 Liss Rhod-PE = 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-(lissamine rhodamine B sulfonyl).
4. Measurement of PS or PI(4)P extraction
NOTE: Measurements must be conducted using a black 96-well plate and a fluorescence plate reader equipped with monochromators: one for fluorescence excitation and one for emission, with a variable bandwidth.
- Prepare fresh, filtered, and degassed HK buffer supplemented with 1 mM MgCl2 (HKM buffer). Prepare pure PC liposomes and PC liposomes doped with 2 mol% PS or 2 mol% PI(4)P (4 mM final lipid concentration, see Table 1).
NOTE: Keep the tubes filled with the suspension of extruded liposomes at room temperature throughout the experiment, and keep the proteins on ice. Additionally, protect the lipid sensors from light. - For the PS extraction assay, in one well, mix liposomes containing 2 mol% PS (80 µM final lipid concentration, 0.8 µM accessible PS concentration) with NBD-C2Lact (250 nM final concentration) in a final volume of 100 µL. Fill a second well with the same amount of liposome (80 µM, 2 mol% PS) and NBD-C2Lact (250 nM) mixed with 3 µM LTP (Osh6p as a positive control or a protein of interest).
NOTE: An incubation time of 5 min is sufficient for Osh6p to achieve lipid extraction. - Fill a third well with NBD-C2Lact (250 nM) mixed with pure PC liposomes (80 µM). Fill a fourth well only with pure PC liposomes (80 µM). Repeat steps 4.2-4.3 to prepare three additional series of four wells.
- For each well, record an NBD spectrum from 505 to 650 nm (bandwidth 5 nm) upon excitation at 490 nm (bandwidth 5 nm) at 25 °C. For each series, subtract the spectrum recorded with only liposomes from the other spectra.
NOTE: F and Fmax correspond to the intensity at 536 nm measured with PS-containing liposomes in the presence or absence of LTP, respectively, whereas F0 is the intensity at the same wavelength with pure PC liposomes. For each series, the percentage of accessible PS that is extracted by the protein is given by using the following formula.
100 × (1-((F-F0)/(Fmax-F0))) (4) - For the PI(4)P extraction assay, prepare liposomes doped with 2 mol% PI(4)P, and carry out measurements with the NBD-PHFAPP probe. Perform control experiments and determine the extraction percentage in the same way as described above.
NOTE: Liposome and protein concentration are identical to those used in the PS extraction assay.
5. Real-time measurement of PS transport
NOTE: A standard fluorimeter (90° format) equipped with a temperature-controlled cell holder and a magnetic stirrer is used to record lipid transfer kinetics. To accurately acquire data, it is key to permanently maintain the sample at the same temperature (set between 25 and 37 °C depending on the origin of the protein (e.g., yeast or human)) and to constantly stir it. The protocol described below is for the measurement of lipid transport in a 600 µL sample contained in a cylindrical quartz cell.
- Prepare freshly degassed and filtered HKM buffer. Keep the tubes containing extruded liposomes at room temperature. Wrap tubes containing liposomes with Rhod-PE in aluminum foil, and/or store them in an opaque box to prevent any photobleaching.
- Adjust the excitation and emission monochromators at λ = 460 nm (with a short bandwidth (1-3 nm)) and at λ = 530 nm (with a large bandwidth (≥ 10 nm)), respectively. Set the acquisition time at 25 min with a time resolution ≤ 1 s.
- In the quartz cuvette, dilute 30 µL of the LA liposome suspension and a volume of NBD-C2Lact stock solution in prewarmed HKM buffer to prepare a 570 µL sample that contains 200 µM total lipids and 250 nM NBD-C2Lact. Add a small magnetic stirring bar, and position the cuvette in the fluorometer holder.
- Once the sample is thermally equilibrated (after 3-5 min), trigger the measurement. After 1 min, add 30 µL of LB liposome suspension (final concentration of 200 µM total lipids) to the sample. After 3 min, inject LTP into the sample so that the final concentration of the LTP is 200 nM, and acquire the signal for the remaining 21 min.
- Carry out a parallel experiment to normalize the NBD signal. Mix 30 µL of LA-Eq liposome suspension with 250 nM NBD-C2Lact in HKM buffer (final volume of 570 µL). After 1 min, inject 30 µL of LB-Eq liposome suspension.
NOTE: The lipid composition of LA-Eq and LB-Eq liposomes are similar to that of LA and LB liposomes used in the transfer assay, except that each of them contains 2.5 mol% PS and 2.5 mol% PI(4)P. As a result, the NBD signal that is measured, referred to as FEq, corresponds to the signal that should be measured if PS was fully equilibrated between LA and LB liposomes by a transfer process. - Convert the kinetic curves measured with an LTP of interest to determine the amount of PS (in µM) transferred from LA to LB liposomes over time. Normalize each data point (F) of the curve by using the following formula.
FNorm = (F-F0)/(FEq-F0) (5)
in which F0 corresponds to the NBD signal just before the addition of an LTP, and FEq is the signal measured in step 5.5.
NOTE: The amount of PS (in µM) transferred from LA to LB liposomes corresponds to 2.5 × FNorm, considering that the equilibrium corresponds to a situation where one half of accessible PS molecules, contained in the outer leaflet of the LA liposomes, (i.e., corresponding to 5 mol% of 0.5 × 200 µM total lipids) has been transferred into LB liposomes.
6. Real-time measurement of PI(4)P transport
- Set the fluorimeter (excitation and emission wavelength, bandwidth, acquisition time, time resolution) as done for the PS transfer assay. Likewise, use the same buffer, cuvette, and liposomes to perform the experiments under constant stirring at the same temperature.
- In the cuvette, mix 30 µL of LB liposome suspension and NBD-PHFAPP with prewarmed HKM buffer to obtain a final volume of 570 µL (200 µM total lipids, 250 nM NBD- PHFAPP). Once the thermal equilibration of the sample is reached, start the measurement, and after 1 min, inject 30 µL of LA liposome suspension. After 3 min, inject the LTP of interest (final concentration of 200 nM), and record the signal.
- Perform a second experiment to normalize the NBD signal. Mix 30 µL of LB-Eq liposome suspension with 250 nM NBD-PHFAPP in 570 µL of HKM buffer. After 1 min, inject 30 µL of LA-Eq liposome suspension.
NOTE: Here, the NBD signal, referred to as FEq, corresponds to the one which should be measured if PI(4)P was fully equilibrated between LA and LB liposomes. - Convert the kinetic curves to determine the amount of PI(4)P (in µM) transferred from LB to LA liposomes over time. Each data point (F) is normalized by using formula 5 in which F0 corresponds to the NBD signal prior to the addition of an LTP, and FEq is the signal measured in step 6.3.
NOTE: The amount of PI(4)P (in µM) transferred from LB to LA liposomes corresponds to 2.5 × FNorm, considering that the equilibrium corresponds to a situation where one half of the PI(4)P contained in the outer leaflet of the LB liposomes (i.e., 0.5 × 5 µM) has been transferred in LA liposomes.
7. Analysis of kinetics curves
- Quantify the extent to which an LTP is efficient by determining the speed at which this LTP transfers lipids from one liposome population to the other one in the first few seconds following its injection to the cuvette.
- Perform a linear regression of the first data points of the transfer kinetics to obtain a slope. Divide the slope value by the LTP concentration in the reaction mixture to determine the number of lipid molecules transferred per protein per time unit (min or s).
Results
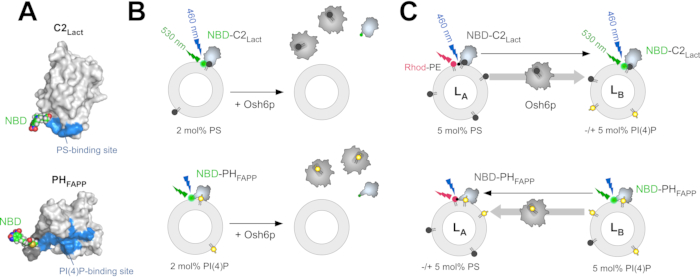
Figure 1: Description of the fluorescent lipid sensors and in vitro assays. (A) Three-dimensional models of NBD-C2Lact and NBD-PHFAPP based on the crystal structure of the C2 domain of bovine lactadherin (PDB ID: 3BN648) and the NMR structure of the PH domain of the human FAPP1 ...
Discussion
The outcomes of these assays directly rely on the signals of the fluorescent lipid sensors. Thus, the purification of these probes labelled at a 1:1 ratio with NBD and without free NBD fluorophore contamination is a critical step in this protocol. It is also mandatory to check whether the LTP under examination is properly folded and not aggregated. The amount of LTP tested in the extraction assays must be equal to or higher than that of accessible PS or PI(4)P molecules to properly measure whether this LTP efficiently ex...
Disclosures
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. A. Cuttriss for her careful proofreading of the manuscript. This work is funded by the French National Research Agency grant ExCHANGE (ANR-16-CE13-0006) and by the CNRS.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| L-cysteine ≥97 % (FG) | Sigma | W326305-100G | Prepare a 10 mM L-cysteine stock solution in water. Aliquots are stored at -20 °C |
| 2 mL Amber Vial, PTFE/Rub Lnr, for lipids storage in CHCL3 | Wheaton | W224681 | |
| 4 mm-diameter glass beads | Sigma | Z265934-1EA | |
| 50 mL conical centrifuge tube | Falcon | ||
| ÄKTA purifier | GE healthcare | FPLC | |
| Aluminium foil | |||
| Amicon Ultra-15 with a MWCO of 3 and 10 kDa | Merck | UFC900324, UFC901024 | |
| Amicon Ultra-4 with a MWCO of 3 and 10 kDa | Merck | UFC800324, UFC801024 | |
| Ampicillin | Prepare a 50 mg/mL stock solution with filtered and sterilized water and store it at -20 °C. | ||
| Bestatin | Sigma | B8385-10mg | |
| BL21 Gold Competent Cells | Agilent | ||
| C16:0 Liss (Rhod-PE) in CHCl3 (1 mg/mL) | Avanti Polar Lipids | 810158C-5MG | |
| C16:0/C16:0-PI(4)P | Echelon Lipids | P-4016-3 | Dissolve 1 mg of C16:0/C16:0-PI(4)P powder in 250 µL of MeOH and 250 µL of CHCl3. Then complete with CHCl3 to 1 mL. The solution must become clear. |
| C16:0/C18:1-PS (POPS) in CHCl3 (10 mg/mL) | Avanti Polar Lipids | 840034C-25mg | |
| C18:1/C18:1-PC (DOPC) in CHCl3 (25 mg/mL) | Avanti Polar Lipids | 850375C-500mg | |
| CaCl2 | Sigma | Prepare 10 mM CaCl2 stock solution in water. | |
| Cell Disruptor | Constant Dynamics | ||
| Chloroform (CHCl3) RPE-ISO | Carlo Erba | 438601 | |
| Complete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail | Roche | 5056489001 | |
| Deionized (Milli-Q) water | |||
| Dimethylformamide (DMF), anhydrous, >99% pure | |||
| DNAse I Recombinant, RNAse free, in powder | Roche | 10104159001 | |
| DTT | Euromedex | EU0006-B | Prepare 1 M DTT stock solution in Milli-Q water. Prepare 1 mL aliquots and store them at -20 °C. |
| Econo-Pac chromatography columns (1.5 × 12 cm). | Biorad | 7321010 | |
| Electroporation cuvette 2 mm | Ozyme | EP102 | |
| Electroporator Eppendorf 2510 | Eppendorf | ||
| Fixed-Angle Rotor Ti45 and Ti45 tubes | Beckman | Spinning the batcerial lysates | |
| Glass-syringes (10, 25, and 50 µL) for fluorescence experiment | Hamilton | ||
| Glass-syringes (25 , 100, 250, 500, and 1000 µL) to handle lipid stock solutions | Hamilton | 1702RNR, 1710RNR, 1725RNR, 1750RN type3, 1001RN | |
| Glutathione Sepharose 4B beads | GE Healthcare | 17-0756-05 | |
| Glycerol (99% pure) | Sigma | G5516-500ML | |
| Hemolysis tubes with a cap | |||
| HEPES , >99 % pure | Sigma | H3375-500G | |
| Illustra NAP 10 desalting column | GE healthcare | GE17-0854-02 | |
| Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) | Euromedex | EU0008-B | Prepare 1 M IPTG stock solution in Milli-Qwater. Prepare 1 mL aliquots and store them at -20 °C. |
| K-Acetate | Prolabo | 26664.293 | |
| Lennox LB Broth medium without glucose | Prepared with milli-Q water and autoclaved. | ||
| Liquid nitrogen | Linde | ||
| Methanol (MeOH) ≥99.8% | VWR | 20847.24 | |
| MgCl2 | Sigma | Prepare a 2 M MgCl2 solution. Filter the solution using a 0.45 µm filter. | |
| Microplate 96 Well PS F-Botom Black Non-Binding | Greiner Bio-one | 655900 | |
| Mini-Extruder with two 1 mL gas-tight Hamilton syringes | Avanti Polar Lipids | 610023 | |
| Monochromator-based fluorescence plate reader | TECAN | M1000 Pro | |
| N,N'-Dimethyl-N-(Iodoacetyl)-N'-(7-Nitrobenz-2-Oxa-1,3-Diazol-4-yl)Ethylenediamine) (IANBD Amide) | Molecular Probes | Dissolve 25 mg of IANBD in 2.5 mL of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and prepare 25 aliquot of 100 µL in 1.5 mL screw-cap tubes. Do not completely screw the cap. Then, remove DMSO in a freeze-dryer to obtain 1 mg of dry IANBD per tube. Tubes are closed and stored at -20 °C in the dark. | |
| NaCl | Sigma | S3014-1KG | |
| PBS | 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM NaH2PO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4, autoclaved and stored at 4 °C. | ||
| Pear-shaped glass flasks (25 mL, 14/23, Duran glass) | Duran Group | ||
| Pepstatin | Sigma | p5318-25mg | |
| pGEX-C2LACT plasmid | Available on request from our lab | ||
| pGEX-PHFAPP plasmid | Available on request from our lab | ||
| Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) ≥98.5% (GC) | Sigma | P7626-25g | Prepare a 200 mM PMSF stock solution in isopropanol |
| Phosphoramidon | Sigma | R7385-10mg | |
| Polycarbonate filters (19 mm in diameter) with pore size of 0.2 µm | Avanti Polar Lipids | 610006 | |
| Poly-Prep chromatography column (with a 0-2 mL bed volume and a 10 mL reservoir) | Biorad | 7311550 | |
| Prefilters (10 mm in diameter). | Avanti Polar Lipids | 610014 | |
| PyMOL | http://pymol.org/ | Construction of the 3D models of the proteins (Figure 1A) | |
| Quartz cuvette for UV/visible fluorescence (minimum volume of 600 µL) | Hellma | ||
| Quartz cuvettes | Hellma | ||
| Refrigerated centrifuge Eppendorf 5427R | Eppendorf | ||
| Rotary evaporator | Buchi | B-100 | |
| Screw-cap microcentriguge tubes (1.5 mL) | Sarsted | ||
| Small magnetic PFTE stirring bar (5 × 2 mm) | |||
| Snap-cap microcentriguge tubes (0.5, 1, and 2 mL) | Eppendorf | ||
| SYPRO orange | fluorescent stain to detect protein in SDS-PAGE gel | ||
| Thermomixer | Starlab | ||
| THROMBIN, FROM HUMAN PLASMA | Sigma | 10602400001 | Dissolve 20 units in 1 mL of milli-Q water and prepare 25 µL aliquots in 0.5 mL Eppendorf tubes. Then freeze and store at -80 °C. |
| Tris, ultra pure | MP | 819623 | |
| Ultracentrifuge L90K | Beckman | ||
| UV/Visible absorbance spectrophotometer | SAFAS | ||
| UV/visible spectrofluorometer with a temperature-controlled cell holder and stirring device | Jasco or Shimadzu | Jasco FP-8300 or Shimadzu RF-5301PC | |
| Vacuum chamber | |||
| Water bath | Julabo | ||
| XK 16/70 column packed with Sephacryl S200HR | GE healthcare |
References
- Drin, G. Topological regulation of lipid balance in cells. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 83, 51-77 (2014).
- Bigay, J., Antonny, B. Curvature, lipid packing, and electrostatics of membrane organelles: defining cellular territories in determining specificity. Developmental Cell. 23 (5), 886-895 (2012).
- Prinz, W. A. Lipid trafficking sans vesicles: where, why, how. Cell. 143 (6), 870-874 (2010).
- Holthuis, J. C., Menon, A. K. Lipid landscapes and pipelines in membrane homeostasis. Nature. 510 (7503), 48-57 (2014).
- Wong, L. H., Copic, A., Levine, T. P. Advances on the transfer of lipids by lipid transfer proteins. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 42 (7), 516-530 (2017).
- Wong, L. H., Gatta, A. T., Levine, T. P. Lipid transfer proteins: the lipid commute via shuttles, bridges and tubes. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 20 (2), 85-101 (2019).
- Iaea, D. B., Dikiy, I., Kiburu, I., Eliezer, D., Maxfield, F. R. STARD4 membrane interactions and sterol binding. Biochemistry. 54 (30), 4623-4636 (2015).
- Wilhelm, L. P., et al. STARD3 mediates endoplasmic reticulum-to-endosome cholesterol transport at membrane contact sites. The EMBO Journal. 36 (10), 1412-1433 (2017).
- Bian, X., Saheki, Y., De Camilli, P. Ca(2+) releases E-Syt1 autoinhibition to couple ER-plasma membrane tethering with lipid transport. The EMBO Journal. 37 (2), 219-234 (2018).
- Horenkamp, F. A., Valverde, D. P., Nunnari, J., Reinisch, K. M. Molecular basis for sterol transport by StART-like lipid transfer domains. The EMBO Journal. 37 (6), 98002 (2018).
- Jentsch, J. A., et al. Structural basis of sterol binding and transport by a yeast StARkin domain. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 293 (15), 5522-5531 (2018).
- Moser von Filseck, J., et al. INTRACELLULAR TRANSPORT. Phosphatidylserine transport by ORP/Osh proteins is driven by phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. Science. 349 (6246), 432-436 (2015).
- Daum, G., et al. Systematic analysis of yeast strains with possible defects in lipid metabolism. Yeast. 15 (7), 601-614 (1999).
- Ejsing, C. S., et al. Global analysis of the yeast lipidome by quantitative shotgun mass spectrometry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (7), 2136-2141 (2009).
- Leidl, K., Liebisch, G., Richter, D., Schmitz, G. Mass spectrometric analysis of lipid species of human circulating blood cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1781 (10), 655-664 (2008).
- Sampaio, J. L., et al. Membrane lipidome of an epithelial cell line. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (5), 1903-1907 (2011).
- Vance, J. E., Steenbergen, R. Metabolism and functions of phosphatidylserine. Progress in Lipid Research. 44 (4), 207-234 (2005).
- Zinser, E., et al. Phospholipid synthesis and lipid composition of subcellular membranes in the unicellular eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Bacteriology. 173 (6), 2026-2034 (1991).
- Leventis, P. A., Grinstein, S. The distribution and function of phosphatidylserine in cellular membranes. Annual Review of Biophysics. 39, 407-427 (2010).
- Yeung, T., et al. Membrane phosphatidylserine regulates surface charge and protein localization. Science. 319 (5860), 210-213 (2008).
- Kim, J., Shishido, T., Jiang, X., Aderem, A., McLaughlin, S. Phosphorylation, high ionic strength, and calmodulin reverse the binding of MARCKS to phospholipid vesicles. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 269 (45), 28214-28219 (1994).
- Sigal, C. T., Zhou, W., Buser, C. A., McLaughlin, S., Resh, M. D. Amino-terminal basic residues of Src mediate membrane binding through electrostatic interaction with acidic phospholipids. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 91 (25), 12253-12257 (1994).
- Gal Bivona, T., et al. PKC regulates a farnesyl-electrostatic switch on K-Ras that promotes its association with Bcl-XL on mitochondria and induces apoptosis. Molecular Cell. 21 (4), 481-493 (2006).
- Finkielstein, C. V., Overduin, M., Capelluto, D. G. Cell migration and signaling specificity is determined by the phosphatidylserine recognition motif of Rac1. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (37), 27317-27326 (2006).
- Bolsover, S. R., Gomez-Fernandez, J. C., Corbalan-Garcia, S. Role of the Ca2+/Phosphatidylserine Binding Region of the C2 Domain in the Translocation of Protein Kinase Cα to the Plasma Membrane. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (12), 10282-10290 (2003).
- Vance, J. E., Tasseva, G. Formation and function of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine in mammalian cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1831 (3), 543-554 (2013).
- Maeda, K., et al. Interactome map uncovers phosphatidylserine transport by oxysterol-binding proteins. Nature. 501 (7466), 257-261 (2013).
- D'Ambrosio, J. M., et al. Osh6 requires Ist2 for localization to ER-PM contacts and efficient phosphatidylserine transport in budding yeast. Journal of Cell Science. 133 (11), 243733 (2020).
- Manford, A. G., Stefan, C. J., Yuan, H. L., Macgurn, J. A., Emr, S. D. ER-to-plasma membrane tethering proteins regulate cell signaling and ER morphology. Developmental Cell. 23 (6), 1129-1140 (2012).
- Collado, J., et al. Tricalbin-mediated contact sites control ER curvature to maintain plasma membrane integrity. Developmental Cell. 51 (4), 476-487 (2019).
- Hoffmann, P. C., et al. Tricalbins contribute to cellular lipid flux and form curved ER-PM contacts that are bridged by rod-shaped structures. Developmental Cell. 51 (4), 488-502 (2019).
- Lipp, N. F., et al. An electrostatic switching mechanism to control the lipid transfer activity of Osh6p. Nature Communications. 10 (1), 3926 (2019).
- Chung, J., et al. INTRACELLULAR TRANSPORT. PI4P/phosphatidylserine countertransport at ORP5- and ORP8-mediated ER-plasma membrane contacts. Science. 349 (6246), 428-432 (2015).
- Sohn, M., et al. PI(4,5)P2 controls plasma membrane PI4P and PS levels via ORP5/8 recruitment to ER-PM contact sites. The Journal of Cell Biology. 217 (5), 1797-1813 (2018).
- Ghai, R., et al. ORP5 and ORP8 bind phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-biphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P 2) and regulate its level at the plasma membrane. Nature Communications. 8 (1), 757 (2017).
- Sohn, M., et al. Lenz-Majewski mutations in PTDSS1 affect phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate metabolism at ER-PM and ER-Golgi junctions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (16), 4314-4319 (2016).
- Kattan, W. E., et al. Targeting plasma membrane phosphatidylserine content to inhibit oncogenic KRAS function. Life Science Alliance. 2 (5), 00431 (2019).
- Du, X., Turner, N., Yang, H. The role of oxysterol-binding protein and its related proteins in cancer. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. 81, 149-153 (2018).
- Galmes, R., et al. ORP5/ORP8 localize to endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts and are involved in mitochondrial function. EMBO reports. 17 (6), 800-810 (2016).
- Du, X., et al. ORP5 localizes to ER-lipid droplet contacts and regulates the level of PI(4)P on lipid droplets. The Journal of Cell Biology. 219 (1), 201905162 (2020).
- Wang, H., et al. ORP2 delivers cholesterol to the plasma membrane in exchange for phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2). Molecular Cell. 73 (3), 458-473 (2019).
- Kay, J. G., Grinstein, S. Sensing phosphatidylserine in cellular membranes. Sensors (Basel). 11 (2), 1744-1755 (2011).
- Moser von Filseck, J., Vanni, S., Mesmin, B., Antonny, B., Drin, G. A phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate powered exchange mechanism to create a lipid gradient between membranes. Nature Communications. 6, 6671 (2015).
- Wills, R. C., Goulden, B. D., Hammond, G. R. V. Genetically encoded lipid biosensors. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 29 (13), 1526-1532 (2018).
- Raychaudhuri, S., Im, Y. J., Hurley, J. H., Prinz, W. A. Nonvesicular sterol movement from plasma membrane to ER requires oxysterol-binding protein-related proteins and phosphoinositides. The Journal of Cell Biology. 173 (1), 107-119 (2006).
- Lenoir, M., et al. Structural basis of wedging the Golgi membrane by FAPP pleckstrin homology domains. EMBO reports. 11 (4), 279-284 (2010).
- Liu, Y., Kahn, R. A., Prestegard, J. H. Interaction of Fapp1 with Arf1 and PI4P at a membrane surface: an example of coincidence detection. Structure. 22 (3), 421-430 (2014).
- Shao, C., Novakovic, V. A., Head, J. F., Seaton, B. A., Gilbert, G. E. Crystal structure of lactadherin C2 domain at 1.7A resolution with mutational and computational analyses of its membrane-binding motif. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 283 (11), 7230-7241 (2008).
- Lipp, N. F., Ikhlef, S., Milanini, J., Drin, G. Lipid exchangers: cellular functions and mechanistic links with phosphoinositide metabolism. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 8, 663 (2020).
- Venditti, R., et al. Molecular determinants of ER-Golgi contacts identified through a new FRET-FLIM system. The Journal of Cell Biology. 218 (3), 1055-1065 (2019).
- Pemberton, J. G., et al. Defining the subcellular distribution and metabolic channeling of phosphatidylinositol. The Journal of Cell Biology. 219 (3), (2020).
- Nakanishi, H., de los Santos, P., Neiman, A. M. Positive and negative regulation of a SNARE protein by control of intracellular localization. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 15 (4), 1802-1815 (2004).
- Maekawa, M., Yang, Y., Fairn, G. D. Perfringolysin O theta toxin as a tool to monitor the distribution and inhomogeneity of cholesterol in cellular membranes. Toxins. 8 (3), 67 (2016).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved