A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Identifying the Binding Proteins of Small Ligands with the Differential Radial Capillary Action of Ligand Assay (DRaCALA)
In This Article
Summary
The Differential Radial Capillary Action of Ligand Assay (DRaCALA) can be used to identify small ligand binding proteins of an organism by using an ORFeome library.
Abstract
The past decade has seen tremendous progress in the understanding of small signaling molecules in bacterial physiology. In particular, the target proteins of several nucleotide-derived secondary messengers (NSMs) have been systematically identified and studied in model organisms. These achievements are mainly due to the development of several new techniques including the capture compound technique and the differential radial capillary action of ligand assay (DRaCALA), which were used to systematically identify target proteins of these small molecules. This paper describes the use of the NSMs, guanosine penta- and tetraphosphates (p)ppGpp, as an example and video demonstration of the DRaCALA technique. Using DRaCALA, 9 out of 20 known and 12 new target proteins of (p)ppGpp were identified in the model organism, Escherichia coli K-12, demonstrating the power of this assay. In principle, DRaCALA could be used for studying small ligands that can be labeled by radioactive isotopes or fluorescent dyes. The critical steps, pros, and cons of DRaCALA are discussed here for further application of this technique.
Introduction
Bacteria use several small signaling molecules to adapt to constantly changing environments1,2. For example, the autoinducers, N-acylhomoserine lactones and their modified oligopeptides, mediate the intercellular communication among bacteria to coordinate population behavior, a phenomenon known as quorum sensing2. Another group of small signaling molecules is the NSMs, including the widely studied cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), cyclic di-AMP, cyclic di-guanosine monophosphate (cyclic di-GMP), and guanosine penta- and tetra phosphates (p)ppGpp1. Bacteria produce these NSMs as a response to a variety of different stress conditions. Once produced, these molecules bind to their target proteins and regulate several different physiological and metabolic pathways to cope with the encountered stresses and enhance bacterial survival. Therefore, identification of the target proteins is an unavoidable prerequisite for deciphering the molecular functions of these small molecules.
The past decade has witnessed a boom of knowledge of these small signaling molecules, mainly due to several technical innovations that unveiled the target proteins of these small molecules. These include the capture compound technique3,4,5, and the differential radial capillary action of ligand assay (DRaCALA)6 to be discussed in this paper.
Invented by Vincent Lee and co-workers in 20116, DRaCALA deploys the ability of a nitrocellulose membrane to differentially sequester free and protein-bound ligands. Molecules such as proteins cannot diffuse on a nitrocellulose membrane, while small ligands, such as the NSMs, are able to. By mixing the NSM (e.g., ppGpp) with the protein to be tested and spotting them on the membrane, two scenarios can be expected (Figure 1): If (p)ppGpp binds to the protein, the radiolabeled (p)ppGpp will be retained in the center of the spot by the protein and will not diffuse outward, giving an intense small dot (i.e., strong radioactive signal) under a phosphorimager. However, if (p)ppGpp does not bind to the protein, it will diffuse freely outward to produce a large spot with uniform background radioactive signal.
Furthermore, DRaCALA can detect the interaction between a small molecule and an unpurified protein in a whole cell lysate if the protein is present in a sufficient amount. This simplicity allows the use of DRaCALA in rapidly identifying protein targets by using an ORFeome expression library. Indeed, target proteins of cAMP7, cyclic di-AMP8, cyclic di-GMP9,10, and (p)ppGpp11,12,13 have been systematically identified by using DRaCALA. This video article uses (p)ppGpp as an example to demonstrate and describe the critical steps and considerations in performing a successful DRaCALA screening. Of note, a more thorough description of DRaCALA14 is highly recommended to read in combination with this article before performing DRaCALA.
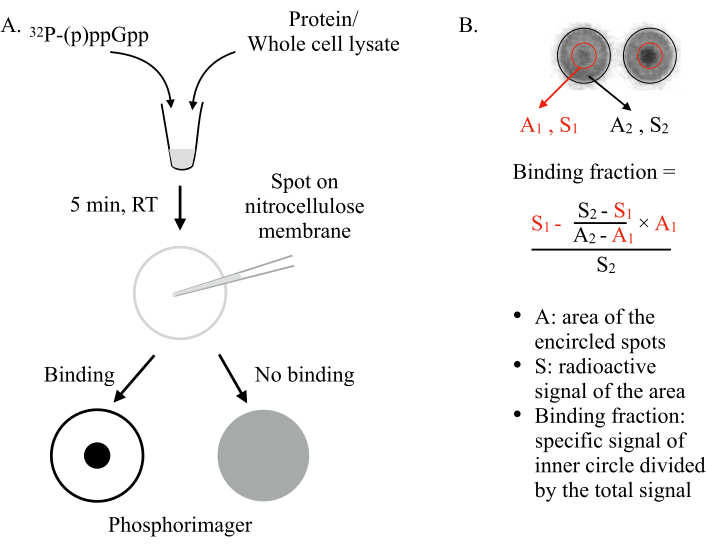
Figure 1: The principle of DRaCALA. (A) Schematic of the DRaCALA assay. See the text for details. (B) Quantification and calculation of the binding fraction. See the text for details. Briefly, the DRaCALA spots will be analyzed by drawing two circles that circumscribe the whole spot and the inner dark dot (i.e., the retained (p)ppGpp due to the binding of the tested protein). The specific binding signal is the radioactive signal of the inner circle (S1) after subtracting the non-specific background signal (calculated by A1 × ((S2-S1)/(A2-A1))). The binding fraction is the specific binding signal divided by the total radioactive signal (S2). Abbreviations: DRaCALA = Differential Radial Capillary Action of Ligand Assay; (p)ppGpp = guanosine penta- and tetraphosphates; RT = room temperature. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
1. Preparation of whole cell lysates
- Inoculate the E. coli K-12 ASKA ORFeome collection strains15 into 1.5 mL Lysogeny broth (LB) containing 25 µg/mL chloramphenicol in 96-well deep well plates. Grow overnight (O/N) for 18 h at 30 °C with shaking at 160 rpm. On the next day, add isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (final 0.5 mM) to the O/N cultures to induce protein expression at 30 °C for 6 h.
- Pellet cells at 500 x g for 10 min. Freeze the pellets at -80 °C until use. To lyse the cells, add 150 µL of lysis buffer L1 (40 mM Tris pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, supplemented with 2 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 40 µg/mL DNase 1, and 0.5 mg/mL lysozyme) to resuspend the pellet.
- Freeze the cells at -80 °C for 30 min, and then thaw at 37 °C for 20 min. Repeat this cycle three times to lyse the cells. Store the lysates at -80 °C before use.
2. Purification of Relseq and GppA
NOTE: The recombinant proteins Relseq from Streptococcus equisimilis and GppA from E. coli K-12 are used to synthesize the radiolabeled pppGpp and ppGpp, respectively.
- Grow and collect cells overexpressing each protein.
- Grow the E. coli BL21 DE3 strain up to exponential phase (optical density (OD) ~0.3-0.4) in LB broth, and spin down 1 mL of culture at 6000 x g for 5 min. Decant the supernatant, and resuspend the cells with 100 µL of ice-cold TSB broth (LB broth supplemented with 0.1 g/mL PEG3350, 0.05 mL/mL dimethylsulfoxide, 20 mM MgCl2).
- Mix the plasmids bearing the histidine-tagged relseq and gppA, each 100 ng, with the above cell suspensions in TSB, and incubate on ice for 30 min. Heat-shock the cells at 42 °C for 40 s. Place the mixture on ice for 2 min, and add 1 mL of LB broth at room temperature to allow the cells to recover for 1 h at 37 °C with agitation at 160 rpm.
- Plate the recovered cells on LB agar plates supplemented with the corresponding antibiotics (Relseq:100 µg/mL ampicillin; GppA: 30 µg/mL kanamycin).On the next day, inoculate the colonies in LB broth to start O/N precultures of both strains at 37 °C.
- After 18 h, inoculate 500 mL of LB medium with 10 mL of the O/N cultures and the corresponding antibiotics. Grow the cultures by shaking at 160 rpm at 37 °C. When the OD600nm reaches 0.5-0.7, induce protein expression by adding 0.5 mM IPTG and growing for 3 h at 30 °C with shaking at 160 rpm.
- Collect the cells by spinning at 6084 x g for 10 min at 4 °C. Resuspend the pellet in 20 mL of ice-cold 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and re-centrifuge at 1912 x g for 20 min at 4 °C. Decant the supernatant, and freeze the pellets at -20 °C before use.
- Nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) affinity purification
NOTE: From this point onwards, ensure that the samples are cold.- Add 40 mL of ice-cold lysis buffer L2 (50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 10 mM imidazole, 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol supplemented with protease inhibitors (EDTA-free tablet; see the Table of Materials) to resuspend the pellet. Lyse the cells via sonication (60% amplitude, 2 s ON/ 4 s OFF for 8 min ON). Clear the lysate by spinning at 23,426 x g for 40 min at 4 °C, and continue with the supernatant for the purification.
- During the above centrifugation, prepare the Ni-NTA resin.
- Transfer 500 µL of homogenized Ni-NTA resin into a standing polypropylene chromatography column, and let it settle for 15 min and the storage solution drain through. Wash the resin with 15 mL of ultrapure water twice, and then wash the column with 15 mL of the lysis buffer L2.
- Load the cleared supernatant of cell lysate from step 1 onto the column, and let it flow through. Wash the column with 30 mL of washing buffer (50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 20 mM imidazole).
- Elute the proteins with 400 µL of the elution buffer (50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 500 mM imidazole) three times. Then, repeat elution with another 300 µL of the elution buffer. Combine the eluted proteins to a final volume of 700 µL.
- Gel filtration
- Prepare gel filtration buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.5; 200 mM NaCl; 5% glycerol). Wash the size exclusion column with one column volume (25 mL) of the gel filtration buffer.
- Load the above 700 µL sample by using a 500 µL loop, run at 0.5 mL/min, and collect 2-3 fractions, each of 0.5 mL volume, containing the respective proteins.
- Combine and concentrate the fractions containing each of the proteins using a spin column, and measure the protein concentration using the Bradford assay.
3. Synthesis of 32P-labeled pppGpp and ppGpp
- Assemble a small-scale Relseq reaction in a screw cap tube (see Table 1).
NOTE: Work with radioactive reagents only in a licensed place and with personal protective equipment.
| Volume (μL) | ||
| Small scale | Large scale | |
| Ultrapure water | ||
| 10x Relseq buffer* | 2 | 50 |
| ATP (8 mM final) | ||
| Relseq (4 μM final) | ||
| 32P-α-Guanosine triphosphate (GTP) (final 120 nM) (CAUTION) | 0.2 | 5 |
| total | 20 | 500 |
Table 1: Assembling information for the small- and large-scale synthesis reactions of 32P-labeled pppGpp. *10x Relseq buffer contains 250 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.6; 1M NaCl; 80 mM MgCl2. Abbreviation: pppGpp = guanosine pentaphosphate.
- Incubate the tube at 37 °C in a thermomixer for 1 h, then at 95 °C for 5 min, and place on ice for 5 min. Spin down the precipitated protein at 15,700 x g for 5 min, and transfer the supernatant (synthesized 32P-pppGpp) to a new screw cap tube.
- To synthesize 32P-ppGpp from 32P-pppGpp, transfer half of the 32p-pppGpp product to a new screw cap tube, and add 1 µM GppA. Incubate the tube at 37 °C for 10 min, at 95 °C for 5 min, and then place on ice for 5 min.
- Spin down the precipitated protein at 15,700 x g for 5 min, and transfer the supernatant (synthesized 32P-ppGpp) to a new screw cap tube.
- Analyze the 32P-pppGpp and 32P-ppGpp by running 1 µL of the samples on a thin layer chromatography (TLC) plate (polyethyleneimine-modified cellulose TLC plates) using the 1.5 M KH2PO4, pH 3.4, as mobile phase.
NOTE: Use the α-32P-labeled guanosine 5'-triphosphate (32P-α-GTP) as control. - Dry the TLC plate completely, place it between a transparent plastic folder, and expose it to a storage phosphor screen for 5 min. Visualize and quantify the signals by using a phosphorimager.
NOTE: When the ratios of 32P-pppGpp and 32P-ppGpp are higher than 85%, a large-scale reaction (500 µL, sufficient for screening 20 96-well plates) could be assembled and synthesized by using Table 1.
4. DRaCALA screening of the target proteins of (p)ppGpp
- Thaw and transfer 20 µL of whole cell lysates to a 96-well V-bottom microtiter plate. Add 2.5 U/well of endonuclease from Serratia marcescens, and incubate at 37 °C for 15 min to reduce lysate viscosity. Place the lysates on ice for 20 min.
- Mix the 32P-pppGpp and 32P-ppGpp in a 1:1 ratio, and add 1x lysis buffer L1 to make the final concentration of (p)ppGpp equal to 4 nM.
NOTE: Given the chemical similarity between pppGpp and ppGpp, a mix of both chemicals will simplify the screening process. - Use a multichannel pipette and filtered pipette tips to add and mix 10 µL of the (p)ppGpp mixture with the cell lysate. Incubate at room temperature (RT) for 5 min.
- Wash the 96 x pin tool by placing in 0.01% solution of non-ionic detergent for 30 s, and dry on a tissue paper for 30 s. Repeat the washing of the pin tool 3x.
- Place the pin tool in the above 96-well sample plates, and wait for 30 s. Lift the pin tool straight up, and place it straight down on a nitrocellulose membrane for 30 s.
NOTE: If a spot is missing, spot 2 µL of the corresponding samples with a pipette and filtered tips. It is advisable to make a duplicate spot of the same sample as indicated below. - Dry the membrane for 5 min at RT. Place the membrane between a transparent plastic folder, and expose it to a storage phosphor screen for 5 min. Visualize by using a phosphorimager.
5. Quantification and identification of potential target proteins
- Use the analysis software associated with the phosphorimager to open the .gel file of the visualized plates. Use the Array analysis function to define the 96 spots by setting up a grid of 12 columns x 8 rows.
- Define big circles to circumscribe the outer edge of the whole spots (see Figure 1B). Export the Volumn+Background and Area of the defined big circles, and save in a spreadsheet.
NOTE: If required, reposition each individual circle to perfectly overlap with the spots, and resize each individual circle to make it slightly bigger than the actual spot. - Size down the defined circles to circumscribe the small inner dots. Export the Volumn+Background, and Area of the defined small circles, and save in a spreadsheet.
- Calculate the binding fractions in the spreadsheet by using the equation in Figure 1B, and plot the data. Identify the potential binding proteins in the wells that show high binding fractions in comparison to the majority of other wells.

Figure 2: Overall workflow of the DRaCALA screening process. Protein production from an Escherichia coli ASKA collection is induced, and the cells are lysed. Meanwhile, the recombinant proteins Relseq-His and GppA-His are purified and used to synthesize 32P-labeled pppGpp and ppGpp from 32P-α-GTP. The radioactively labeled (p)ppGpp molecules are then mixed with the lysates, and a 96 pin-tool is used to spot the mixtures onto a nitrocellulose membrane for subsequent exposure to a phosphor storage screen, imaging, and quantification of the radioactive signals. Abbreviations: DRaCALA = Differential Radial Capillary Action of Ligand Assay; (p)ppGpp = guanosine penta- and tetraphosphates; RT = room temperature; IPTG = isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside; GTP = guanosine 5'-triphosphate; SDS-PAGE = sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis ; TLC = thin layer chromatography. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
Following the above-described protocol will typically yield two types of results (Figure 3).
Figure 3A shows a plate with relatively low background binding signals (binding fractions < 0.025) from the majority of wells. The positive binding signal from the well H3 gives a binding fraction of ~0.35 that is much higher than that observed for the other wells. Even without quantification, well H3 is remarkable, suggesting that a targe...
Discussion
One of the critical steps in performing DRaCALA screening is to obtain good whole cell lysates. First, the tested proteins should be produced in large amounts and in soluble forms. Second, the lysis of cells should be complete, and the viscosity of the lysate must be minimal. The inclusion of lysozyme and the use of three cycles of freeze-thaw are often enough to lyse cells completely. However, the released chromosomal DNA makes the lysate viscous and generates high background binding signal, resulting in false positives...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by an NNF Project Grant (NNF19OC0058331) to YEZ, and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement (Nº 801199) to MLS.

Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 32P-α-GTP | Perkinelmer | BLU006X250UC | |
| 96 x pin tool | V&P Scientific | VP 404 | 96 Bolt Replicator, on 9 mm centers, 4.2 mm Bolt Diameter, 24 mm long |
| 96-well V-bottom microtiter plate | Sterilin | MIC9004 | Sterilin Microplate V Well 611V96 |
| Agar | OXOID - Thermo Fisher | LP0011 | Agar no. 1 |
| ASKA collection strain | NBRP, SHIGEN, JAPAN | Ref: DNA Research, Volume 12, Issue 5, 2005, Pages 291–299. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsi012 | |
| Benzonase | SIGMA | E1014-25KU | genetically engineered endonuclease from Serratia marcescens |
| Bradford Protein Assay Dye | Bio-Rad | 5000006 | Reagent Concentrate |
| DMSO | SIGMA | D8418 | ≥99.9% |
| DNase 1 | SIGMA | DN25-1G | |
| gel filtration10x300 column | GE Healthcare | 28990944 | contains 20% ethanol as preservative |
| Glycerol | PanReac AppliChem | 122329.1214 | Glycerol 87% for analysis |
| Hypercassette | Amersham | RPN 11647 | 20 x 40 cm |
| Imidazole | SIGMA | 56750 | puriss. p.a., ≥ 99.5% (GC) |
| IP Storage Phosphor Screen | FUJIFILM | 28956474 | BAS-MS 2040 20x 40 cm |
| Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) | SIGMA | I6758 | Isopropyl β-D-thiogalactoside |
| Lysogeny Broth (LB) | Invitrogen - Thermo Fisher | 12795027 | Miller's LB Broth Base |
| Lysozyme | SIGMA | L4949 | from chicken egg white; BioUltra, lyophilized powder, ≥98% |
| MgCl2 (Magnesium chloride) | SIGMA | 208337 | |
| MilliQ water | ultrapure water | ||
| multichannel pipette | Thermo Scientific | 4661110 | F1 - Clip Tip; 1-10 ul, 8 x channels |
| NaCl | VWR Chemicals | 27810 | AnalaR NORMAPUR, ACS, Reag. Ph. Eur. |
| Ni-NTA Agarose | Qiagen | 30230 | |
| Nitrocellulose Blotting Membrane | Amersham Protran | 10600003 | Premium 0.45 um 300 mm x 4 m |
| PBS | OXOID - Thermo Fisher | BR0014G | Phosphate buffered saline (Dulbecco A), Tablets |
| PEG3350 (Polyethylene glycol 3350) | SIGMA | 202444 | |
| phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) | SIGMA | 93482 | Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride solution - 0.1 M in ethanol (T) |
| Phosphor-imager | GE Healthcare | 28955809 | Typhoon FLA-7000 Phosphor-imager |
| Pipette Tips, filtered | Thermo Scientific | 94410040 | ClipTip 12.5 μl nonsterile |
| Poly-Prep Chromatography column | Bio-Rad | 7311550 | polypropylene chromatography column |
| Protease inhibitor Mini | Pierce | A32955 | Tablets, EDTA-free |
| screw cap tube | Thermo Scientific | 3488 | Microcentifuge Tubes, 2.0 ml with screw cap, nonsterile |
| SLS 96-deep Well plates | Greiner | 780285 | MASTERBLOCK, 2 ML, PP, V-Bottom, Natural |
| spin column | Millipore | UFC500396 | Amicon Ultra -0.5 ml Centrifugal Filters |
| Thermomixer | Eppendorf | 5382000015 | Thermomixer C |
| TLC plate (PEI-cellulose F TLC plates) | Merck Millipore | 105579 | DC PEI-cellulose F (20 x 20 cm) |
| Tris | SIGMA | BP152 | Tris Base for Molecular Biology |
| Tween 20 | SIGMA | P1379 | viscous non-ionic detergent |
| β-mercaptoethanol | SIGMA | M3148 | 99% (GC/titration) |
References
- Kalia, D., et al. Nucleotide, c-di-GMP, c-di-AMP, cGMP, cAMP, (p)ppGpp signaling in bacteria and implications in pathogenesis. Chemical Society Reviews. 42 (1), 305-341 (2013).
- Camilli, A., Bassler, B. L. Bacterial small-molecule signaling pathways. Science. 311 (5764), 1113-1116 (2006).
- Luo, Y., et al. The cAMP capture compound mass spectrometry as a novel tool for targeting cAMP-binding proteins: from protein kinase A to potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 8 (12), 2843-2856 (2009).
- Nesper, J., Reinders, A., Glatter, T., Schmidt, A., Jenal, U. A novel capture compound for the identification and analysis of cyclic di-GMP binding proteins. Journal of Proteomics. 75 (15), 4874-4878 (2012).
- Laventie, B. J., et al. Capture compound mass spectrometry--a powerful tool to identify novel c-di-GMP effector proteins. Journal of Visual Experiments. (97), e51404 (2015).
- Roelofs, K. G., Wang, J., Sintim, H. O., Lee, V. T. Differential radial capillary action of ligand assay for high-throughput detection of protein-metabolite interactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (37), 15528-15533 (2011).
- Zhang, Y., et al. Evolutionary adaptation of the essential tRNA methyltransferase TrmD to the signaling molecule 3 ',5 '-cAMP in bacteria. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 292 (1), 313-327 (2017).
- Corrigan, R. M., et al. Systematic identification of conserved bacterial c-di-AMP receptor proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (22), 9084-9089 (2013).
- Roelofs, K. G., et al. Systematic identification of cyclic-di-GMP binding proteins in Vibrio cholerae reveals a novel class of cyclic-di-GMP-binding ATPases associated with type II secretion systems. PLoS Pathogen. 11 (10), 1005232 (2015).
- Fang, X., et al. GIL, a new c-di-GMP-binding protein domain involved in regulation of cellulose synthesis in enterobacteria. Molecular Microbiology. 93 (3), 439-452 (2014).
- Corrigan, R. M., Bellows, L. E., Wood, A., Grundling, A. ppGpp negatively impacts ribosome assembly affecting growth and antimicrobial tolerance in Gram-positive bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (12), 1710-1719 (2016).
- Zhang, Y., Zbornikova, E., Rejman, D., Gerdes, K. Novel (p)ppGpp binding and metabolizing proteins of Escherichia coli. Mbio. 9 (2), 02188 (2018).
- Yang, J., et al. The nucleotide pGpp acts as a third alarmone in Bacillus, with functions distinct from those of (p) ppGpp. Nature Communications. 11 (1), 5388 (2020).
- Orr, M. W., Lee, V. T. Differential radial capillary action of ligand assay (DRaCALA) for high-throughput detection of protein-metabolite interactions in bacteria. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1535, 25-41 (2017).
- Kitagawa, M., et al. Complete set of ORF clones of Escherichia coli ASKA library (A complete Set of E. coli K-12 ORF archive): Unique resources for biological research. DNA Research. 12 (5), 291-299 (2005).
- Hochstadt-Ozer, J., Cashel, M. The regulation of purine utilization in bacteria. V. Inhibition of purine phosphoribosyltransferase activities and purine uptake in isolated membrane vesicles by guanosine tetraphosphate. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 247 (21), 7067-7072 (1972).
- Zhang, Y. E., et al. p)ppGpp regulates a bacterial nucleosidase by an allosteric two-domain switch. Molecular Cell. 74 (6), 1239-1249 (2019).
- Wang, B., et al. Affinity-based capture and identification of protein effectors of the growth regulator ppGpp. Nature Chemical Biology. 15 (2), 141-150 (2019).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved