A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Exploring Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism of Single 3D Microtissue Spheroids Using Extracellular Flux Analysis
In This Article
Erratum Notice
Summary
These protocols will help users probe mitochondrial energy metabolism in 3D cancer cell-line-derived spheroids using Seahorse extracellular flux analysis.
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) cellular aggregates, termed spheroids, have become the forefront of in vitro cell culture in recent years. In contrast to culturing cells as two-dimensional, single-cell monolayers (2D culture), spheroid cell culture promotes, regulates, and supports physiological cellular architecture and characteristics that exist in vivo, including the expression of extracellular matrix proteins, cell signaling, gene expression, protein production, differentiation, and proliferation. The importance of 3D culture has been recognized in many research fields, including oncology, diabetes, stem cell biology, and tissue engineering. Over the last decade, improved methods have been developed to produce spheroids and assess their metabolic function and fate.
Extracellular flux (XF) analyzers have been used to explore mitochondrial function in 3D microtissues such as spheroids using either an XF24 islet capture plate or an XFe96 spheroid microplate. However, distinct protocols and the optimization of probing mitochondrial energy metabolism in spheroids using XF technology have not been described in detail. This paper provides detailed protocols for probing mitochondrial energy metabolism in single 3D spheroids using spheroid microplates with the XFe96 XF analyzer. Using different cancer cell lines, XF technology is demonstrated to be capable of distinguishing between cellular respiration in 3D spheroids of not only different sizes but also different volumes, cell numbers, DNA content and type.
The optimal mitochondrial effector compound concentrations of oligomycin, BAM15, rotenone, and antimycin A are used to probe specific parameters of mitochondrial energy metabolism in 3D spheroids. This paper also discusses methods to normalize data obtained from spheroids and addresses many considerations that should be considered when exploring spheroid metabolism using XF technology. This protocol will help drive research in advanced in vitro spheroid models.
Introduction
Advances in in vitro models in biological research have rapidly progressed over the last 20 years. Such models now include organ-on-a-chip modalities, organoids, and 3D microtissue spheroids, all of which have become a common focus to improve the translation between in vitro and in vivo studies. The use of advanced in vitro models, particularly spheroids, spans several research fields, including tissue engineering, stem cell research, cancer, and disease biology1,2,3,4,5,6,7, and safety testing, including genetic toxicology8,9,10, nanomaterials toxicology11,12,13,14, and drug safety and efficacy testing8,15,16,17,18,19.
Normal cell morphology is critical to biological phenotype and activity. Culturing cells into 3D microtissue spheroids allows cells to adopt a morphology, phenotypic function, and architecture, more akin to that observed in vivo but difficult to capture with classical monolayer cell culture techniques. Both in vivo and in vitro, cellular function is directly impacted by the cellular microenvironment, which is not limited to cellular communication and programming (e.g., cell-cell junction formations, opportunities to form cell niches); cell exposure to hormones and growth factors in the immediate environments (e.g., cellular cytokine exposure as part of an inflammatory response); composition of physical and chemical matrices (e.g., whether cells are grown in stiff tissue culture plastic or an elastic tissue environment); and most importantly, how cellular metabolism is impacted by nutrition and access to oxygen as well as the processing of metabolic waste products such as lactic acid.
Metabolic flux analysis is a powerful way to examine cellular metabolism within defined in vitro systems. Specifically, XF technology allows for the analysis of live, real-time changes in cellular bioenergetics of intact cells and tissues. Given that many intracellular metabolic events occur within the order of seconds to minutes, real-time functional approaches are paramount for understanding real-time changes in cellular metabolic flux in intact cells and tissues in vitro.
This paper provides protocols for cultivating cancer-derived cell lines A549 (lung adenocarcinoma), HepG2/C3A (hepatocellular carcinoma), MCF-7 (breast adenocarcinoma), and SK-OV-3 (ovarian adenocarcinoma) as in vitro 3D spheroid models using forced-aggregation approaches (Figure 1). It also (i) describes in detail how to probe mitochondrial energy metabolism of single 3D spheroids using the Agilent XFe96 XF analyzer, (ii) highlights ways to optimize XF assays using single 3D spheroids, and (iii) discusses important considerations and limitations of probing 3D spheroid metabolism using this approach. Most importantly, this paper describes how datasets are collected that allow the calculation of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) to determine oxidative phosphorylation and thus mitochondrial function in cellular spheroids. Though not analyzed for this protocol, extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) is another parameter that is measured alongside OCR data in XF experiments. However, ECAR is often poorly or incorrectly interpreted from XF datasets. We provide a commentary as to the limitations of calculating ECAR following basic approaches from the technology manufacturer.
Protocol
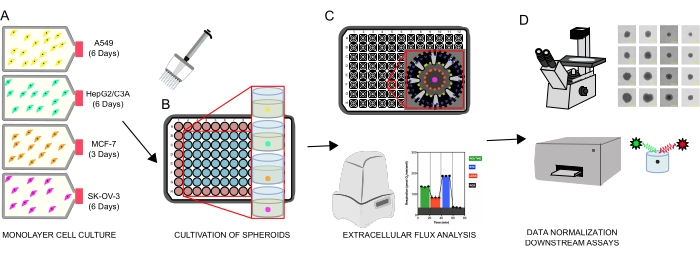
Figure 1: Graphical workflow for the generation of cellular spheroids, extracellular flux analysis and downstream assays. Four cancer cell lines were selectively cultured as monolayers (A), detached from tissue culture flasks, and seeded into ultralow attachment 96-well microplates to form spheroids (B). A549 lung carcinoma, HepG2/C3A liver carcinoma, SK-OV-3 ovarian adenocarcinoma, and MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells were seeded at 1 × 103-8 × 103 cells/well and grown up to 7 days to form single spheroids and optimize spheroid seeding density and cultivation time by continuous observation and planimetric measurements. Once formed, single spheroids were washed into a serum-free XF medium and carefully seeded into spheroid assay microplates, precoated with poly-D-lysine (C). Spheroids were subjected to extracellular flux analysis using the XFe96 analyzer using several protocols to address: (1) optimal spheroid size for basal mitochondrial respiration response; (2) optimized titration of mitochondrial respiratory inhibitors; (3) optimization of spheroid placement within microplate wells. (D) Post XF analyses, phase contrast microscopy, and spheroid DNA quantification were used for data normalization and other downstream in vitro assays. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
1. Cultivation of cancer cell lines as 3D in vitro spheroids
| Cell line | Description | Culture medium | Source |
| A549 | Lung carcinoma cell line | RPMI 1640 | European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures (ECACC) |
| Sodium pyruvate (1 mM) | |||
| Penicillin- Streptomycin - (100 U/mL – 100 mg/mL) | |||
| 10 % (v/v) FBS | |||
| HepG2/C3A | Hepatic carcinoma cell line, a clonal derivative of the parent HepG2 cell line | DMEM | American Tissue Culture Collection (ATCC) |
| Penicillin- Streptomycin - (100 U/mL – 100 mg/mL) | |||
| 10 % (v/v) FBS | |||
| MCF7 | Breast adenocarcinoma cell line | RPMI 1640 | European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures (ECACC) |
| Sodium pyruvate (1 mM) | |||
| Penicillin- Streptomycin - (100 U/mL – 100 mg/mL) | |||
| 10 % (v/v) FBS | |||
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian adenocarcinoma cell line | RPMI 1640 | European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures (ECACC) |
| Sodium pyruvate (1 mM) | |||
| Penicillin- Streptomycin - (100 U/mL – 100 mg/mL) | |||
| 10 % (v/v) FBS | |||
| Component | RPMI assay medium (50 mL final volume) | ||
| Base Medium | Agilent Seahorse XF RPMI, pH 7.4 | ||
| Glucose (1 M sterile stock) | 11 mM (0.55 mL stock solution) | ||
| L-glutamine (200 mM sterile stock) | 2 mM (0.5 mL of stock solution) | ||
| Sodium pyruvate (100 mM sterile stock) | 1 mM (0.5 mL of stock solution) |
Table 1: Cancer cell line media and XF media compositions.
- Culture all cell lines using standard aseptic tissue culture technique and confirm that they are free of mycoplasma using a suitable assay kit.
- Culture the cell lines in T75 tissue culture flasks or equivalent, using the recommended medium (Table 1). Culture the cell lines to 65-80% confluency and passage them regularly up to a maximum of 25 passages.
- Rinse the cell culture flasks twice in Dulbecco's modified phosphate-buffered saline (DBPS).
- Detach the cells from the flasks with 3 mL of the cell dissociation reagent (see the Table of Materials) for 5 min at 37 °C and confirm the detachment by microscopy.
- Aspirate the detached cell suspension gently to ensure a single-cell suspension and deactivate the cell dissociation reagent with 7 mL of complete tissue culture medium.
- Collect the cells by centrifugation at 300 × g for 5 min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the cells in complete medium.
- Count the cells using a hemocytometer or an automated cell counter and titrate to the desired cell density required for seeding.
NOTE: To seed an entire 96-well plate at 100 µL/well at 4 × 103 cells/well, cells should be titrated to 4 × 104 cells/mL in a recommended volume of 12 mL. - Decant the cell suspension into a sterile reservoir and dispense 100 µL of the cell suspension into each well of a cell-repellent microplate using a multichannel pipettor.
NOTE: Only the inner 60 wells of a microplate should be seeded and the remainder filled with DPBS. This will form an evaporation barrier, ensure spheroid homogeneity across the plate, and minimize plate edge effects. - Centrifuge spheroid microplates at 300 × g for 15 min to force the cells into loose aggregates.
- Incubate the plates at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for a minimum of 3 days to ensure spheroid formation.
- Perform phase-contrast microscopy using standardized laboratory practices to monitor the growth of spheroids. Replenish the cell culture medium every 3 days or twice weekly by performing a half-volume medium exchange.
2. Probing mitochondrial energy metabolism of single spheroids using Extracellular Flux (XF) Technology
- Assay preparation (one day prior)
- Check spheroid viability using an inverted light microscope with phase contrast at 4x magnification to ensure intact spheroid structure, morphology, and overall uniformity between samples.
- Hydrate the sensor cartridge.
- Aliquot ~20 mL of the calibrant into a conical tube.
- Place the conical tube containing the calibrant in a non-CO2 37 °C incubator overnight.
- Remove the contents from the assay kit.
- Remove the sensor cartridge from the utility plate and place it upside down on the worktop next to the utility plate.
- Pipette 200 µL of sterile ddH2O into each well of the sensor cartridge utility plate using a multichannel P300 pipette.
- Place the sensor cartridge on top of the utility plate.
- Check that the water level in each well is high enough to submerge the sensor probes.
- Transfer the assembled sensor cartridge to a non-CO2 37 °C incubator and leave it overnight.
NOTE: This step can be performed 12-72 h prior to assay commencement.
- Coat spheroid assay microplate
- Using aseptic techniques, add 30 µL/well of sterile Poly-D-Lysine (0.1 mg/mL) solution to the spheroid microplate and incubate it for 30 min at room temperature.
- Aspirate the solution from each well of the spheroid microplate, invert the plate, and tap it firmly onto tissue paper to remove any residual solution.
- Wash the plate twice with 200 µL/well of sterile ddH2O.
- After the final wash, invert the microplate and tap it firmly onto tissue paper to remove any residual water.
- Allow the plate to air-dry for 30 min before using or storing it at 4 °C for future use.
NOTE: The spheroid assay microplate should be coated with a molecular adhesive to ensure that the spheroids are fixed at the bottom of the microplate. Without a molecular adhesive, spheroids can become dislodged and interfere with assay results. Other molecular adhesives can also be used as an alternative to Poly-D-Lysine for precoating plates. Precoated plates can be stored at 4 °C but should be left to equilibrate to room temperature before assay commencement.
- Prepare XF Assay medium
- Prepare XF RPMI medium, as detailed in Table 1, and sterile-filter with a 0.22 μm syringe filter
- Assay preparation (1 h prior to assay)
- Prewarm the supplemented XF RPMI assay medium to 37 °C.
- Prewarm the coated spheroid assay microplate in a non-CO2 37 °C incubator or dry bath.
- Prepare the sensor cartridge.
- Take out the conical tube containing the calibrant and the sensor cartridge from the air incubator.
- Remove the sensor cartridge from the utility plate and place it upside down on the work surface.
- Using a P300 multichannel pipette, aspirate the water from the utility plate and discard it.
- Pour the calibrant solution into a sterile reagent reservoir and add 200 µL/well of the prewarmed calibrant to the utility plate using a P300 multichannel pipette.
- Pick up the sensor cartridge and place it back on top of the utility plate, ensuring the sensors are well submerged in the calibrant.
- Transfer the assembled sensor cartridge back into the non-CO2 37 °C incubator until ready to load the port injection solutions.
- Wash the spheroids with the assay medium.
- Remove the spheroid culture plate from the 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator and observe the spheroids under the microscope to ensure their integrity prior to the spheroid transfer steps.
- Load all wells of the spheroid plate with 180 µL/well of prewarmed assay medium, including any background correction wells.
- Partially fill a 7 cm Petri dish with 3 mL of the assay medium.
- Using a multichannel pipette loaded with wide orifice pipette tips, transfer the spheroids from the 96-well culture plate into 7 cm Petri dishes by setting the pipettor at an aspiration volume of 10-50 µL.
- Seed spheroids into the pre-coated spheroid assay microplate.
- Using a dissection microscope and a lightbox apparatus, transfer the spheroids from the Petri dish to the spheroid assay microplate as detailed below.
- Set the volume of a single-channel pipettor fitted with a wide orifice pipette tip to 20 µL and carefully aspirate a single spheroid. Place the tip directly in the center of each well of the spheroid assay microplate and allow gravity to elute a single spheroid into the center of each well, i.e., do not expel any medium from the pipette tip and allow capillary action to withdraw the spheroid from the pipette tip. To confirm elution, the contents of the pipettor can be pipetted back into the 7 cm Petri dish under the microscope.
NOTE: Gravity elution of a single spheroid typically takes 15-30 s depending on spheroid size/density. During this time, the pipettor should not be removed. Any background correction wells should be free of spheroids and only contain assay medium. Under the microscope, confirm the position of each spheroid. Each spheroid should ideally be positioned within the center of each well. - Once all the spheroids have been transferred to the spheroid assay microplate, transfer the plate to a non-CO2 incubator at 37 °C for a minimum of 1 h prior to the assay.
- Set the volume of a single-channel pipettor fitted with a wide orifice pipette tip to 20 µL and carefully aspirate a single spheroid. Place the tip directly in the center of each well of the spheroid assay microplate and allow gravity to elute a single spheroid into the center of each well, i.e., do not expel any medium from the pipette tip and allow capillary action to withdraw the spheroid from the pipette tip. To confirm elution, the contents of the pipettor can be pipetted back into the 7 cm Petri dish under the microscope.
- Using a dissection microscope and a lightbox apparatus, transfer the spheroids from the Petri dish to the spheroid assay microplate as detailed below.
3. Preparation and loading of compounds into the sensor cartridge for XF assays
| Injection Strategy | Compound (Port) | XFe96 microwell starting volume (µL) | Desired final well concentration | Port Volume (µL) | Final XFe96 microwell volume post injection (µL) | Working stock concentration |
| 1 | Oligomycin (A) | 180 | 3 ug/mL | 20 | 200 | 30 µg/mL |
| Rotenone (B) | 200 | 2 µM | 20 | 220 | 22 µM | |
| Antimycin A (B) | 200 | 2 µM | 20 | 220 | 22 µM | |
| 2 | BAM15 (A) | 180 | 5 µM | 20 | 200 | 50 µM |
| Rotenone (B) | 200 | 2 µM | 20 | 220 | 22 µM | |
| Antimycin A (B) | 200 | 2 µM | 20 | 220 | 22 µM |
Table 2: Mitochondrial compound concentrations for probing mitochondrial energy metabolism of single 3D spheroids using the XFe96 Analyzer.
- Prepare working stock concentrations of each compound as noted in Table 2 using fully supplemented, prewarmed XF RPMI assay medium.
- Orient the cartridge plate (coupled to the utility plate) column-wise, 1-12 from left to right.
- If using a loading guide, place it atop the cartridge plate according to the well-loading procedure, e.g., if port A is be loaded first, ensure that A is visible in the upper-left corner of the guide.
- Transfer the working solution of each compound into a suitable reservoir and, using a calibrated P100 multichannel pipette, dispense 20 µL into all corresponding ports. Repeat for each compound into the remaining ports.
NOTE: If any ports are not used on the sensor cartridge plate, these can be left empty or filled with assay medium. If only a selection of a specific port letter is being used, ensure that the other ports corresponding to that letter are loaded with assay medium; otherwise, air will be injected into the well, compromising the results in those wells. - After port loading, remove the plate-loading guides (if used) and prepare the analyzer for loading the sensor cartridge.
NOTE: If the assay is not being run immediately after loading the ports, place the lid back on the sensor cartridge and put the plate back in the 37 °C air incubator until ready to load into the machine.
4. Assay design, injection strategies, and data acquisition
- Running the assay
- Power on the analyzer and connect to controller (computer).
NOTE: This can be verified by the instrument connection status in the widget panel of the Wave Controller software. - Navigate to the templates page in the WAVE software, find the assay template file for the experiment and double-click to open it.
NOTE: If the assay template does not appear on the Templates view, import the template file into the template folder from a shared network drive or USB flash drive. - To start the assay, click the Run Assay tab.
NOTE: If the group definitions have been correctly allocated within the plate map, the assay will be ready to run as indicated by the green tick on the right-hand side of the page. At this stage, any additional information can be input on the assay summary page or the page left blank; proceed to the next step. Due to the delayed penetration of mitochondrial modulators in 3D microtissue spheroids (Figure 2), use the measurement protocol information described in Table 3.
- Power on the analyzer and connect to controller (computer).
| Measurement Period | Injection Number and Port | Measurement Details | Period Duration (h:min:s) |
| Calibration | Not applicable | XF analysers always perform this calibration to make sure measurements are accurate | 00:20:00 (this is an average and can vary between machines) |
| Equillibration | Not applicable | Equilibration occurs after Calibration and it is recommended. | 00:10:00 |
| Basal | Not applicable | Cycles = 5 | 00:30:00 |
| Mix = 3:00 | |||
| Wait = 0:00 | |||
| Measure = 3:00 | |||
| Oligomycin / BAM15 | Injection 1 (Port A) | Cycles = 10 | 01:00:00 |
| Mix = 3:00 | |||
| Wait = 0:00 | |||
| Measure = 3:00 | |||
| Rotenone + antimycin A | Injection 2 (Port B) | Cycles = 10 | 01:00:00 |
| Mix = 3:00 | |||
| Wait = 0:00 | |||
| Measure = 3:00 | |||
| Total Time: | 03:00:00 | ||
Table 3: Protocol setup for probing mitochondrial energy metabolism of single 3D spheroids using the XFe96 Analyzer.
- Click start run to bring up the save location dialog box.
- Enter the save location for the result file, and place the assembled sensor cartridge onto the thermal tray that appears from the door on the side of the analyzer. Wait for the thermal tray to open automatically and the screen to display the Load Calibrant Utility Plate message. Before following the on-screen prompts, ensure i) proper fit of the sensor cartridge on the Utility plate, ii) the lid is removed from the sensor cartridge, and iii) correct orientation of the sensor cartridge on the utility plate.
- Follow the on-screen commands to initiate sensor cartridge calibration.
NOTE: The time taken to complete calibration is approximately 10-20 min (for assays at 37 °C). - After sensor cartridge calibration, load the spheroid microplate into the analyzer by following the on-screen instructions on the Wave Controller to initiate the 12 min equilibration step.
NOTE: Green boxes with white ticks indicate a 'good' calibration for that well. If any wells fail to provide a 'good' calibration, they will be indicated with a red box and white cross. Such wells should be noted and excluded from any analysis after the assay is completed using the modification assay tab. - Wait for the analyzer to automatically begin acquiring baseline measurements after the machine has completed the equilibration step (as outlined in the instrument protocol).
- To complete the experiment, follow the on-screen commands on the WAVE controller.
NOTE: Once the spheroid microplate has been removed from the analyzer, discard the sensor cartridge and set aside the spheroid plate for further analysis if necessary (e.g., double-stranded (ds) DNA quantification). If the microplate is not required for further analysis, it can be discarded along with the sensor cartridge. - Wait for the assay dialog to appear and view the results or return to the templates view.
5. Data normalization and analysis strategies - post assay normalization and downstream assays (optional steps)
- Data normalization
- To normalize spheroid data, refer to the series of protocols pertinent to data normalization strategies for calculating spheroid size and volume and quantifying dsDNA in spheroid assays. These have been included as supplemental files; see Supplemental file 1 and Supplemental file 2.
- Data analysis
- To export data into one of the automated analysis generators, follow the data export commands on the WAVE controller and select the export generator that matches the assay type. Alternatively, export the data file and upload it into Seahorse analytics.
NOTE: The downside of report generators and Seahorse analytics is that data analysis is limited to how the XF assay is designed and does not allow for averages to be taken across measurement cycles. Manual export of datasets from the instrument software allows for user preference in this regard. Given that the injection strategy for assessing mitochondrial respiration of 3D spheroids will likely differ from that of a typical 'MitoStress' test, a series of spreadsheet templates have been developed to help analyze these datasets, specific to 3D cell cultures and will be provided upon request. These data template files will provide data on the key mitochondrial respiratory parameters detailed and explained in Figure 2. - To analyze the data, export the data as a spreadsheet report from the WAVE controller software and use an independent spreadsheet template for analysis.
- To export data into one of the automated analysis generators, follow the data export commands on the WAVE controller and select the export generator that matches the assay type. Alternatively, export the data file and upload it into Seahorse analytics.
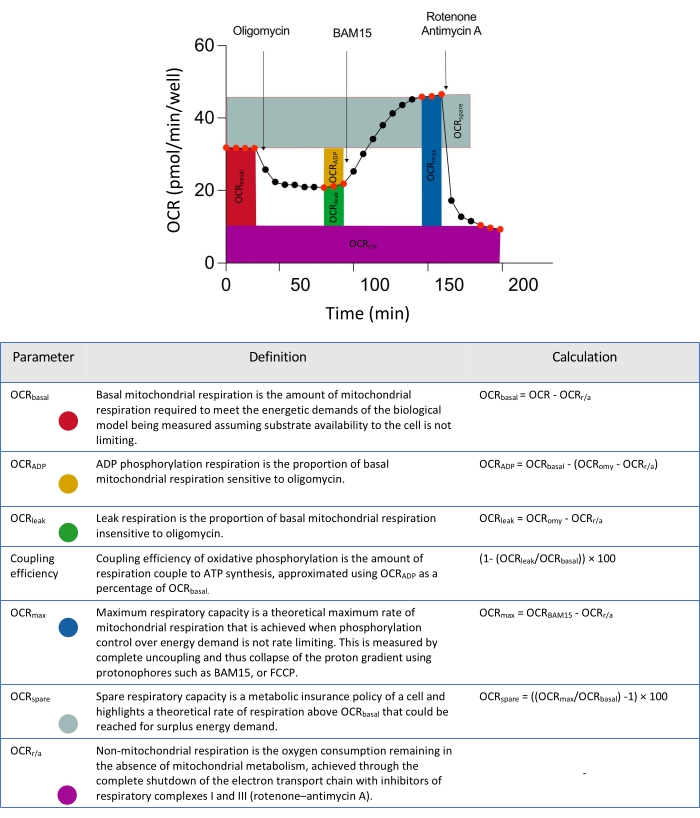
Figure 2: Schematic descriptors for parameters derived from extracellular flux data analyses. Abbreviation: OCR = oxygen consumption rate. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
To obtain well-formed, compact spheroids, each cell line was optimized individually for seeding density and duration of cultivation (Figure 3). A549, HepG2/C3A, and SK-OV-3 cell lines initially formed loose aggregates that did not progress to round spheroids with clearly defined perimeters until after 7 days in culture. Conversely, MCF-7 cells could form spheroids within 3 days. There was a clear correlation between the initial cell seeding density and spheroid volume after the culture perio...
Discussion
Main findings and outputs
This paper provides a detailed protocol to probe mitochondrial energy metabolism of single 3D spheroids using a series of cancer-derived cell lines with the XFe96 XF Analyzer. A method is developed and described for the rapid cultivation of A549, HepG2/C3A, MCF7, and SK-OV-3 cellular spheroids using cell-repellent technologies for forced aggregation. This protocol addresses many considerations of probing spheroid metabolism with XF technology, including (1) optimizati...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
N.J.C was supported by a BBSRC MIBTP CASE Award with Sygnature Discovery Ltd (BB/M01116X/1, 1940003)
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| A549 | ECACC | #86012804 | Lung carcinoma cell line |
| Agilent Seahorse XF RPMI Medium, pH 7.4 | Agilent Technologies Inc. | 103576-100 | XF assay medium with 1 mM HEPES, without phenol red, sodium bicarbonate, glucose, L-glutamine, and sodium pyruvate |
| Agilent Seahorse XFe96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer | Agilent Technologies Inc. | - | Instrument for measuring rates of spheroid oxygen uptake in single spheroids |
| Antimycin A | Merck Life Science | A8674 | Mitochondrial respiratory complex III inhibitor |
| BAM15 | TOCRIS bio-techne | 5737 | Mitochondrial protnophore uncoupler |
| Black-walled microplate | Greiner Bio-One | 655076 | For fluorescence-based assays |
| CELLSTAR cell-repellent surface 96 U well microplates | Greiner Bio-One | 650970 | Microplates for generating spheroids |
| CellTiter-Glo 3D Cell Viability Assay | Promega | G9681 | Assay for the determination of cell viability in 3D microtissue spheroids |
| Cultrex Poly-D-Lysine | R&D Systems a biotechne brand | 3439-100-01 | Molecular cell adhesive for coating XFe96 spheroid microplates to facillitate attachment of spheroids |
| D-(+)-Glucose | Merck Life Sciences | G8270 | Supplement for cell culture growth and XF assay medium |
| Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) | Gibco | 11885084 | Culture medium for HepG2/C3A spheroids |
| EVOS XL Core Imaging System | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AMEX1000 | Phase-contrast imaging microscope |
| EZ-PCR Mycoplasma test kit | Biological Industries | 20-700-20 | Mycoplasma screening in cell cultures |
| FIJI Is Just Image J | Analysis of collated images | ||
| Foetal bovine serum | Merck Life Science | F7524 | Supplement for cell culture medium |
| HepG2/C3A | ATCC | #CRL-10741 | Hepatic carcinoma cell line, a clonal derivative of the parent HepG2 cell line |
| Lactate-Glo | Promega | J5021 | Assay for measurement of lactate within spheorid culture medium |
| L-glutamine (200 mM solution) | Merk Life Sciences | G7513 | Supplement for cell culture growth and XF assay medium |
| M50 Stereo microscope | Leica Microsytems | LEICAM50 | Stereo dissection micrscope; used for spheorid handling |
| MCF-7 | ECACC | #86012803 | Breast adenocarcinoma cell line |
| Oligomycin from Streptomyces diastatochromogenes | Merck Life Science | O4876 | ATP Synthase Inhibitor |
| Penicilin-Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140122 | Antibiotics added to cell culture medium |
| Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit | Initrogen | P7589 | Analysis of dsDNA in spehroids |
| Rotenone | Merck Life Science | R8875 | Mitochondrial Respiratory Complex I Inhibitor |
| RPMI 1640 | Gibco | 21875091 | Culture medium for A549, MCF7, and SK-OV-3 spheroids |
| Seahorse Analytics | Agilent Technologies Inc. | Build 421 | https://seahorseanalytics.agilent.com |
| Seahorse XFe96 Spheroid FluxPak | Agilent Technologies Inc. | 102905-100 | Each Seahorse XFe96 Spheroid FluxPak contains: 6 Seahorse XFe96 Spheroid Microplates (102978-100), 6 XFe96 sensor cartridges, and 1 bottle of Seahorse XF Calibrant Solution 500 mL (100840-000) |
| Serological pipette: 5, 10, and 25 mL | Greiner Bio-One | 606107; 607107; 760107 | Consumables for cell culture |
| SK-OV-3 | ECACC | #HTB-77 | Ovarian adenocarcinoma cell line |
| Sodium pyruvate (100 mM solution) | Merck Life Science | S8636 | Supplement for cell culture growth and XF assay medium |
| T75 cm2 cell culture flask | Greiner Bio-One | 658175 | Tissue culture treated flasks for maintaining cell cultures |
| TrypLExpress | Gibco | 12604-021 | Cell dissociation reagent |
| Wave controller software | Agilent Technologies Inc. | - | |
| Wide orifice tip | STARLAB International GmbH | E1011-8400 | Pipette tips with wide opening for spheroid handling |
References
- Correa de Sampaio, P., et al. A heterogeneous in vitro three dimensional model of tumour-stroma interactions regulating sprouting angiogenesis. PLoS One. 7 (2), 30753 (2012).
- Amann, A., et al. Development of an innovative 3D cell culture system to study tumour-stroma interactions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 9 (3), 92511 (2014).
- Russell, S., Wojtkowiak, J., Neilson, A., Gillies, R. J. Metabolic profiling of healthy and cancerous tissues in 2D and 3D. Scientific Reports. 7 (1), 15285 (2017).
- Zanoni, M., et al. 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: a systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Scientific Reports. 6, 19103 (2016).
- Song, Y., et al. Patient-derived multicellular tumor spheroids towards optimized treatment for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Experimental and Clinica Cancer Research. 37 (1), 109 (2018).
- Courau, T., et al. Cocultures of human colorectal tumor spheroids with immune cells reveal the therapeutic potential of MICA/B and NKG2A targeting for cancer treatment. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer. 7 (1), 74 (2019).
- Ivanova, E., et al. Use of ex vivo patient-derived tumor organotypic spheroids to identify combination therapies for HER2 mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 26 (10), 2393-2403 (2020).
- Mandon, M., Huet, S., Dubreil, E., Fessard, V., Le Hegarat, L. Three-dimensional HepaRG spheroids as a liver model to study human genotoxicity in vitro with the single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 10548 (2019).
- Stampar, M., et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2/C3A) cell-based 3D model for genotoxicity testing of chemicals. Science of the Total Environment. 755, 143255 (2020).
- Coltman, N. J., et al. Application of HepG2/C3A liver spheroids as a model system for genotoxicity studies. Toxicology Letters. 345, 34-45 (2021).
- Tchoryk, A., et al. Penetration and uptake of nanoparticles in 3D tumor spheroids. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 30 (5), 1371-1384 (2019).
- Leite, P. E. C., et al. Suitability of 3D human brain spheroid models to distinguish toxic effects of gold and poly-lactic acid nanoparticles to assess biocompatibility for brain drug delivery. Partical Fibre Toxicology. 16 (1), 22 (2019).
- Elje, E., et al. Hepato(Geno)toxicity assessment of nanoparticles in a HepG2 liver spheroid model. Nanomaterials. 10 (3), 545 (2020).
- Conway, G. E., et al. Adaptation of the in vitro micronucleus assay for genotoxicity testing using 3D liver models supporting longer-term exposure durations. Mutagenesis. 35 (4), 319-330 (2020).
- Wang, Z., et al. HepaRG culture in tethered spheroids as an in vitro three-dimensional model for drug safety screening. Journal of Applied Toxicology. 35 (8), 909-917 (2015).
- Proctor, W. R., et al. Utility of spherical human liver microtissues for prediction of clinical drug-induced liver injury. Archives of Toxicology. 91 (8), 2849-2863 (2017).
- Basharat, A., Rollison, H. E., Williams, D. P., Ivanov, D. P. HepG2 (C3A) spheroids show higher sensitivity compared to HepaRG spheroids for drug-induced liver injury (DILI). Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 408, 115279 (2020).
- Benning, L., Peintner, A., Finkenzeller, G., Peintner, L. Automated spheroid generation, drug application and efficacy screening using a deep learning classification: a feasibility study. Scientific Reports. 10 (1), 11071 (2020).
- Mittler, F., et al. High-content monitoring of drug effects in a 3D spheroid model. Frontiers in Oncology. 7, 293 (2017).
- Brand, M. D., Nicholls, D. G. Assessing mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. The Biochemical Journal. 435 (2), 297-312 (2011).
- Benz, R., McLaughlin, S. The molecular mechanism of action of the proton ionophore FCCP (carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone). Biophysical Journal. 41 (3), 381-398 (1983).
- Kasianowicz, J., Benz, R., McLaughlin, S. The kinetic mechanism by which CCCP (carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone) transports protons across membranes. The Journal of Membrane Biology. 82 (2), 179-190 (1984).
- Kenwood, B. M., et al. Identification of a novel mitochondrial uncoupler that does not depolarize the plasma membrane. Molecular Metabolism. 3 (2), 114-123 (2013).
- Mitchell, P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 191, 144-148 (1961).
- Alexopoulos, S. J., et al. Mitochondrial uncoupler BAM15 reverses diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Nature Communications. 11 (1), 2397 (2020).
- Chen, S. -. Y., et al. Mitochondrial uncoupler SHC517 reverses obesity in mice without affecting food intake. Metabolism - Clinical and Experimental. 117, 154724 (2021).
- Goedeke, L., Shulman, G. I. Therapeutic potential of mitochondrial uncouplers for the treatment of metabolic associated fatty liver disease and NASH. Molecular Metabolism. 46, 101178 (2021).
- Hill, B. G., et al. Integration of cellular bioenergetics with mitochondrial quality control and autophagy. Biological chemistry. 393 (12), 1485-1512 (2012).
- Demine, S., Renard, P., Arnould, T. Mitochondrial uncoupling: a key controller of biological processes in physiology and diseases. Cells. 8 (8), 795 (2019).
- Wang, J., et al. Uncoupling effect of F16 is responsible for its mitochondrial toxicity and anticancer activity. Toxicological Sciences. 161 (2), 431-442 (2018).
- Tretter, L., Chinopoulos, C., Adam-Vizi, V. Plasma membrane depolarization and disturbed Na+ homeostasis induced by the protonophore carbonyl cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-hydrazon in isolated nerve terminals. Molecular Pharmacology. 53 (4), 734-741 (1998).
- Connop, B. P., Thies, R. L., Beyreuther, K., Ida, N., Reiner, P. B. Novel effects of FCCP [carbonyl cyanide p-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone] on amyloid precursor protein processing. Journal of neurochemistry. 72 (4), 1457-1465 (1999).
- Stöckl, P., et al. Partial uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation induces premature senescence in human fibroblasts and yeast mother cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 43 (6), 947-958 (2007).
- Firsov, A. M., et al. Protonophoric action of BAM15 on planar bilayers, liposomes, mitochondria, bacteria and neurons. Bioelectrochemistry. 137, 107673 (2021).
- Dranka, B. P., Hill, B. G., Darley-Usmar, V. M. Mitochondrial reserve capacity in endothelial cells: The impact of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 48 (7), 905-914 (2010).
- Eilenberger, C., Rothbauer, M., Ehmoser, E. K., Ertl, P., Kupcu, S. Effect of spheroidal age on sorafenib diffusivity and toxicity in a 3D HepG2 spheroid model. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 4863 (2019).
- vanden Brand, D., Veelken, C., Massuger, L., Brock, R. Penetration in 3D tumor spheroids and explants: Adding a further dimension to the structure-activity relationship of cell-penetrating peptides. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1860 (6), 1342-1349 (2018).
- Niora, M., et al. Head-to-head comparison of the penetration efficiency of lipid-based nanoparticles into tumor spheroids. ACS Omega. 5 (33), 21162-21171 (2020).
- Millard, M., et al. Drug delivery to solid tumors: the predictive value of the multicellular tumor spheroid model for nanomedicine screening. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 12, 7993-8007 (2017).
- Ruas, J. S., et al. Underestimation of the maximal capacity of the mitochondrial electron transport system in oligomycin-treated cells. PLoS One. 11 (3), 0150967 (2016).
- Benton, G., DeGray, G., Kleinman, H. K., George, J., Arnaoutova, I. In vitro microtumors provide a physiologically predictive tool for breast cancer therapeutic screening. PLoS One. 10 (4), 0123312 (2015).
- Hirpara, J., et al. Metabolic reprogramming of oncogene-addicted cancer cells to OXPHOS as a mechanism of drug resistance. Redox Biology. 25, 101076 (2019).
- Ware, M. J., et al. Generation of homogenous three-dimensional pancreatic cancer cell spheroids using an improved hanging drop technique. Tissue Engineering. Part C, Methods. 22 (4), 312-321 (2016).
- Song, Y., et al. TGF-β-independent CTGF induction regulates cell adhesion mediated drug resistance by increasing collagen I in HCC. Oncotarget. 8 (13), 21650-21662 (2017).
- Wrzesinski, K., et al. HepG2/C3A 3D spheroids exhibit stable physiological functionality for at least 24 days after recovering from trypsinisation. Toxicology Research. 2 (3), 163-172 (2013).
- Gaskell, H., et al. Characterization of a functional C3A liver spheroid model. Toxicology Research. 5 (4), 1053-1065 (2016).
- Takahashi, Y., et al. 3D spheroid cultures improve the metabolic gene expression profiles of HepaRG cells. Bioscience Reports. 35 (3), 00208 (2015).
- Hendriks, D. F. G., Puigvert, L. F., Messner, S., Mortiz, W., Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Hepatic 3D spheroid models for the detection and study of compounds with cholestatic liability. Scientific Reports. 6, 35434 (2016).
- Leung, B. M., Lesher-Perez, S. C., Matsuoka, T., Moraes, C., Takayama, S. Media additives to promote spheroid circularity and compactness in hanging drop platform. Biomaterials Science. 3 (2), 336-344 (2015).
- Cavo, M., et al. A synergic approach to enhance long-term culture and manipulation of MiaPaCa-2 pancreatic cancer spheroids. Scientific Reports. 10 (1), 10192 (2020).
- Carlsson, J., Yuhas, J. M. Liquid-overlay culture of cellular spheroids. Recent Results in Cancer Research. 95, 1-23 (1984).
- Costa, E. C., Gaspar, V. M., Coutinho, P., Correia, I. J. Optimization of liquid overlay technique to formulate heterogenic 3D co-cultures models. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 111 (8), 1672-1685 (2014).
- Lundholt, B. K., Scudder, K. M., Pagliaro, L. A simple technique for reducing edge effect in cell-based assays. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 8 (5), 566-570 (2003).
- Zhang, X. D., et al. The use of strictly standardized mean difference for hit selection in primary RNA interference high-throughput screening experiments. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 12 (4), 497-509 (2007).
- Yepez, V. A., et al. OCR-Stats: Robust estimation and statistical testing of mitochondrial respiration activities using Seahorse XF Analyzer. PLoS One. 13 (7), 0199938 (2018).
- Silva, L. P., et al. Measurement of DNA concentration as a normalization strategy for metabolomic data from adherent cell lines. Analytical Chemistry. 85 (20), 9536-9542 (2013).
Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: Exploring Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism of Single 3D Microtissue Spheroids using Extracellular Flux Analysis
Posted by JoVE Editors on 3/11/2022. Citeable Link.
An erratum was issued for: Exploring Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism of Single 3D Microtissue Spheroids using Extracellular Flux Analysis. The Representative Results section was updated.
Figure 5 was updated from:
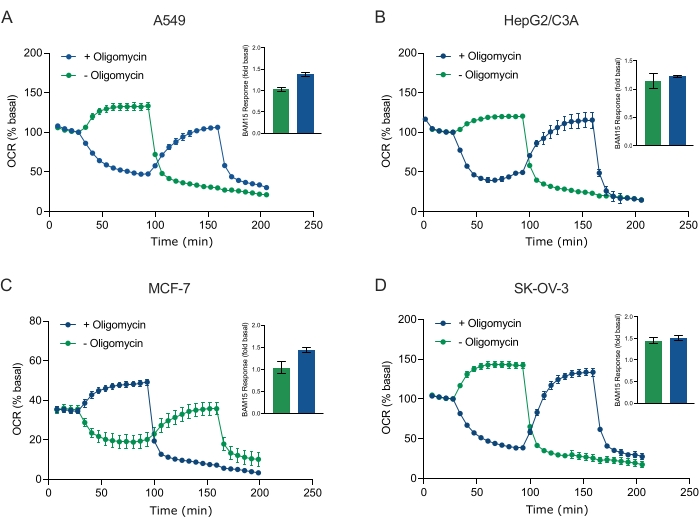
Figure 5: Single or sequential injection of mitochondrial respiratory compounds. Cancer-cell-derived spheroids of MCF-7, HEPG2/C3A, SK-OV-3, and A549 were placed into wells of an XFe96 spheroid microplate in XF RPMI and probed for OCR using the Agilent Seahorse XFe96 analyzer. OCR was measured 5x, after which 2 µg/mL oligomycin (injection Port A: green trace) or 5 µM BAM15 (injection Port A: blue trace or injection port B: green trace) to inhibit the mitochondrial ATP synthase and determine maximal respiratory capacity, respectively. Kinetic OCR data are expressed as % basal (A-D). Maximal respiratory capacity (OCRmax) was calculated as a factor of basal OCR by the equation: OCRmax = OCRBAM15 / OCRbasal. OCRmax was obtained from OCR averages across measurement cycles 8-10 post BAM15 injection with (green bars) and without (blue bars) oligomycin. Data are averages ± SEM from 3-8 individual well replicates across the spheroid assay microplate. Abbreviations: OCR = oxygen consumption rate. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
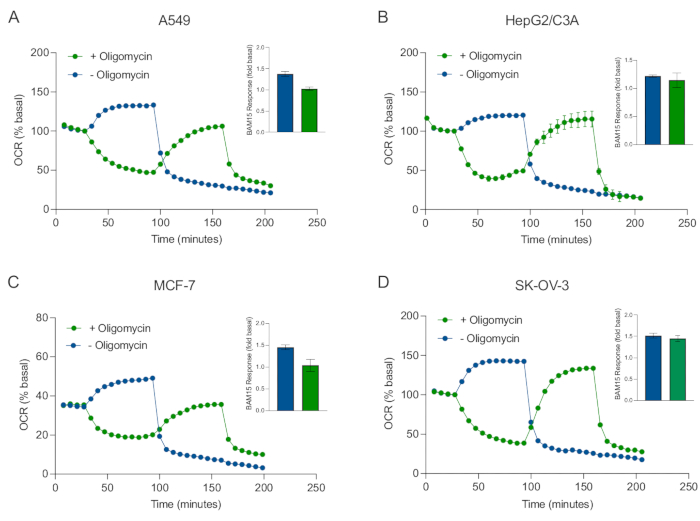
Figure 5: Single or sequential injection of mitochondrial respiratory compounds. Cancer-cell-derived spheroids of MCF-7, HEPG2/C3A, SK-OV-3, and A549 were placed into wells of an XFe96 spheroid microplate in XF RPMI and probed for OCR using the Agilent Seahorse XFe96 analyzer. OCR was measured 5x, after which 2 µg/mL oligomycin (injection Port A: green trace) or 5 µM BAM15 (injection Port A: blue trace or injection port B: green trace) to inhibit the mitochondrial ATP synthase and determine maximal respiratory capacity, respectively. Kinetic OCR data are expressed as % basal (A-D). Maximal respiratory capacity (OCRmax) was calculated as a factor of basal OCR by the equation: OCRmax = OCRBAM15 / OCRbasal. OCRmax was obtained from OCR averages across measurement cycles 8-10 post BAM15 injection with (green bars) and without (blue bars) oligomycin. Data are averages ± SEM from 3-8 individual well replicates across the spheroid assay microplate. Abbreviations: OCR = oxygen consumption rate. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved