A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism and Function of Pore-Forming Toxins Using Leishmania major
In This Article
Summary
Presented here is a protocol using Leishmania major promastigotes to determine the binding, cytotoxicity, and signaling induced by pore-forming toxins. A proof-of-concept with streptolysin O is provided. Other toxins can also be used to leverage the genetic mutants available in L. major to define new mechanisms of toxin resistance.
Abstract
Understanding the function and mechanism of pore-forming toxins (PFTs) is challenging because cells resist the membrane damage caused by PFTs. While biophysical approaches help understand pore formation, they often rely on reductionist approaches lacking the full complement of membrane lipids and proteins. Cultured human cells provide an alternative system, but their complexity and redundancies in repair mechanisms make identifying specific mechanisms difficult. In contrast, the human protozoan pathogen responsible for cutaneous leishmaniasis, Leishmania major, offers an optimal balance between complexity and physiologic relevance. L. major is genetically tractable and can be cultured to high density in vitro, and any impact of perturbations on infection can be measured in established murine models. In addition, L. major synthesizes lipids distinct from their mammalian counterparts, which could alter membrane dynamics. These alterations in membrane dynamics can be probed with PFTs from the best-characterized toxin family, cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs). CDCs bind to ergosterol in the Leishmania membrane and can kill L. major promastigotes, indicating that L. major is a suitable model system for determining the cellular and molecular mechanisms of PFT function. This work describes methods for testing PFT function in L. major promastigotes, including parasite culture, genetic tools for assessing lipid susceptibility, membrane binding assays, and cell death assays. These assays will enable the rapid use of L. major as a powerful model system for understanding PFT function across a range of evolutionarily diverse organisms and commonalities in lipid organization.
Introduction
Pore-forming toxins (PFTs) are the largest family of bacterial toxins1, but the mechanisms by which they perforate and destroy cells are poorly understood. The best-studied family of pore-forming toxins is that of cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs). CDCs are primarily synthesized by gram-positive bacteria, including the causative agent of necrotizing fasciitis, Streptococcus pyogenes2. S. pyogenes secretes the CDC streptolysin O (SLO), which binds to sterols in the plasma membrane of host cells as monomers, oligomerizes, and inserts ~20-30 nm pores into the membrane1. The role that lipids play in this process remains poorly determined.
One approach to studying lipid-CDC interactions is the use of chemically defined liposomes. While defined liposomes provide information on the necessary thresholds of lipids to sustain toxin binding and pore formation3,4, they do not fully recapitulate cellular functions. For example, reconstituted liposomes lack the lipid asymmetry of mammalian hosts and lipid modifications in response to toxins5. One alternative to liposomes is to use mammalian cell lines. While these cell lines are more physiologically relevant, there is a large degree of redundancy in toxin sensing and resistance mechanisms2. As a consequence, the repair pathways used to resist CDCs remain poorly determined. Notably, Ca2+ influx is the primary activator of membrane repair1. Downstream of Ca2+ influx, multiple pathways are engaged, including a ceramide-dependent repair6,7 and a MEK-dependent repair pathway6. These pathways interact with other protein effectors, including the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT)8, and annexins6,9,10. Dissecting these pathways in mammalian cells is challenging due to the redundancy, which muddles data interpretation.
One way to balance complexity with simplicity for dissecting repair pathways is the use of simpler organisms, such as protozoan pathogens in the genus Leishmania. Leishmania sp. cause leishmaniasis in humans and other animals. Leishmaniasis ranges from cutaneous leishmaniasis (self-limited skin lesions) to the fatal visceral leishmaniasis (hepatosplenomegaly), depending on the species and other factors11. Leishmania major, the causative agent of cutaneous leishmaniasis, is transmitted to humans via a sandfly vector and is used to understand Leishmania function and infection12. In addition, Leishmania sp. are digenic12. They exist as intracellular mammalian macrophage parasites termed amastigotes and as free-swimming, flagellated promastigotes in the sandfly12. L. major promastigotes can be cultured in serum-supplemented media such as M199 to high density13. Promastigotes are also genetically tractable; many gene knockouts exist, including those targeting lipid biosynthesis pathways13. These knockouts can be evaluated for growth and differences in infectivity and lesion development via infection of Balb/c mice13.
In addition to the relative ease of Leishmania culture and the range of lipid biosynthesis knockouts, the parasite has a simpler genome than mammals. The best-characterized species of Leishmania is L. major, which has many existing genetic tools, such as mutants with defective lipid metabolism14. Notably, many repair proteins are absent. L. major has no homologs identified to date for key mammalian repair proteins such as annexins. This enables the characterization of evolutionarily conserved repair pathways without the complexity of mammalian systems. However, repair pathways have not been characterized in Leishmania to date. At the same time, key signaling pathways involved in repair, such as the MEK pathway6, are conserved in Leishmania sp.15,16, though homologs need to be validated. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is well-studied in L. mexicana, where it contributes to intracellular survival and thermostability in mammalian cells and controls metacyclogenesis16. In Leishmania sp., 10 of the 15 MAPKs have been characterized17. LmMAPK9 and LmMAPK13 are predicted to be the most similar to mammalian ERK1/2 based on identity in the conserved phosphorylation lip sequence. The phosphorylation lip sequence is TEY for both mammalian ERK1/2 and LmMAPK9 and LmMAPK13. However, eight of the Leishmania MAPKs have a TDY phosphorylation motif15. At least two homologs of MEK have been identified in Leishmania sp., LmxMKK18 and MEKK-related kinase (MRK1)19. This suggests that insights identified in Leishmania could translate to mammalian systems. Where they do not translate to mammalian systems, they represent therapeutic targets for treating leishmaniasis.
In order to use L. major promastigotes to study membrane repair and interactions with toxins, medium-throughput techniques are needed. While high-resolution live cell imaging enables the visualization of labeled proteins and membranes in real time, it is low throughput and may not measure cellular survival. Medium-throughput viability assays include dye uptake measured by flow cytometry, the measurement of mitochondrial activity, or the release of cellular proteins like lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). In mammalian cells, LDH assays do not quantitatively measure cell death20. Furthermore, population-based assays like LDH release or mitochondrial activity do not allow robust single-cell or multiparametric analysis20. In contrast, flow cytometry-based assays enable multiparametric single-cell analysis20. However, these assays have not been applied to understanding toxin biology or responses to toxins in L. major promastigotes.
In this study, SLO is used as a tool to understand the plasma membrane perturbation of the sphingolipid null mutant of L. major in two different buffers-the M199 media routinely used to culture L. major promastigotes and the simpler Tyrode's buffer. A medium-throughput flow cytometry assay is described and used to generate toxin dose-response curves. Data from the flow cytometric assay are modeled to a logistic curve to determine the LC50 values. With this information, a sublytic dose of SLO can be determined so that MAPK antibodies can be validated using western blotting.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All appropriate guidelines and standard microbiological, safety, and cell culture practices were employed for the use and handling of the RG2 pathogen Leishmania major and recombinant DNA. All experiments with live L. major were performed in a biosafety cabinet in a BSL-2 certified laboratory. The work was overseen by the Texas Tech University Institutional Biosafety Committee.
NOTE: From a safety perspective, live L. major promastigotes are Risk Group 2 pathogens. Handle using appropriate containment, precautions, and oversight from the Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC). Handle toxic substances and chemicals in accordance with institutional procedures for toxic substances. If recombinant toxins are used, IBC approval and oversight may be needed for recombinant DNA work.
1. Cultivation and preparation of L. major promastigotes
- Obtain, or make and validate, L. major genetic mutants as previously described using either homologous recombination or CRISPR-based methods13,21. Use knockouts complemented with the gene added back on a plasmid to ensure specificity of the knockout.
- Culture wild type L. major and spt2- promastigotes at 27 °C in complete M199 medium. Culture the episomal addback cells (spt2-/+SPT2) in complete M199 plus 10 µg/mL G418 (see Table 1 and Table of Materials).
NOTE: The entire experimental setup involving experiments with L. major cells must be performed in a BSL2-certified biosafety cabinet. - Cultivate the promastigotes in complete M199 medium22 until they reach log phase (2-8 x 106 cells/mL), as determined by L. major growth curve assays done previously23. Plan 1 x 105 cells for each well for cytotoxicity, plus 5 x 105 cells for staining control. For western blot, plan 2 x 107 cells per well.
NOTE: Perform cytotoxicity assay with two technical replicates. - To verify the proper cell density, mix an aliquot (10-40 µL) of promastigotes with an equal volume of fixative (3.7% paraformaldehyde in 1x PBS). Load 10 µL of the fixed sample onto each side of the hemacytometer.
CAUTION: Formaldehyde is a toxic chemical. Handle in accordance with institutional policies for hazardous chemicals. - Perform cell counting using a microscope at 20x magnification. Count all the cells in the 25 small squares in the center of the hemacytometer. Repeat for the squares on both sides and average the counts.
NOTE: If the variation between counts is >10, recount and average. If the average count is <10 or >100, alter the dilution and recount, and then calculate the culture density using the following formula:
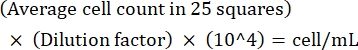 (Eq 1)
(Eq 1)
For example, if there are on an average 250 Leishmania in 25 squares, the culture density is 5 x 106 cells/mL. - After counting, transfer 5 x 106 cells to a 15 mL conical tube and centrifuge at 1,500 x g for 8 min at room temperature to pellet the cells.
- Discard the supernatant using a 10 mL pipette and briefly vortex the cell pellet. Add 5 mL of 1x PBS to the same tube and wash the cells by gently inverting 3-6x. Centrifuge at 1,500 x g for 8 min at room temperature to pellet the cells.
- Discard the supernatant using a 10 mL pipette and resuspend the 5 x 106 cell pellet in 5 mL of medium (e.g., M199 or 1x Tyrode's buffer) used for the experiments with a 5 mL pipette to give a final concentration of 1 x 106 cells/mL.
2. Cytotoxicity assay
- Experimental preparation
- Purify the toxin as previously described24, or purchase the toxin from a vendor. Aliquot into single-use aliquots and store −80 °C for up to 1 year. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
- Determine the hemolytic activity for each toxin using human red blood cells (see Table of Materials)24.
NOTE: Hemolytic activity is used because it controls for differences in activity due to purification, mutations, etc. The species choice of erythrocytes may alter the hemolytic activity (e.g., intermedilysin requires human red blood cells). - Plan two technical replicates for each condition, seven dilutions for the dose-response curve, and a no-toxin control.
NOTE: With wild-type (WT), spt2-, and spt2-/+SPT2 promastigotes, two treatments may be tested in one V-bottom 96-well plate. For example, sensitivity to media could be compared (Figure 1). Instead of a V-bottom plate, 1.2 mL microtiter tubes (see Table of Materials) may be used. Due to the acquisition times on the cytometer, running more than one plate at a time is not recommended. - Determine which assay buffer to use based on the test conditions needed and the purpose of the experiment.
NOTE: In this example, two assay buffers are compared: M199 and Tyrode's buffer supplemented with the viability dye propidium iodide (PI). Cholesterol in serum will interfere with CDC activity24. - Calculate the amount of toxin needed based on the conditions and number of genotypes treated. Ensure that 50% specific lysis occurs halfway down the dilution curve.
NOTE: For CDCs, a two-fold serial dilution will give a good range for later logistic modeling. For spt2- promastigotes, 4,000 HU/mL SLO is the recommended starting dilution. Where inactive toxins are used, a mass equivalent to the highest dose may be used instead. - Plan a 200 µL final volume per well, and add a small volume extra (50-100 µL) to account for pipette error.
NOTE: With three genotypes, each done in duplicate, there will be six samples for the serial dilution. - Determine the total amount of toxin needed using the following formula:
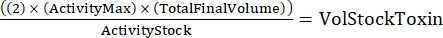 (Eq 2)
(Eq 2)
where ActivityMax is the highest concentration used (HU/mL); TotalFinalVolume is the total volume (for six samples, 200 x 6 + 100 = 1,300 µL); ActivityStock is the activity of the toxin stock (HU/mL); and VolStockToxin is the volume of toxin stock needed. - Prepare sufficient assay buffer needed for the experiment. Supplement the basal medium with a viability dye and any Ca2+ or EGTA needed to control Ca2+ levels. Vortex to mix.
NOTE: For example, for every 10 mL Tyrode's buffer, add 50 µL of 2 mg/mL PI and 200 µL of 100 mM CaCl2, giving final concentrations of 10 µg/mL and 2 mM, respectively. - Ensure the viability dye PI does not conflict with any other probes used, such as for fluorescent binding assays using Cy5 or AlexaFluor647-conjugated toxins20,25.
- Plan toxin dilutions to make a 2x solution of toxin. Add assay buffer to 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes and chill on ice. Only add the toxin immediately prior to starting the assay.
NOTE: In this example, 1.3 mL of assay buffer would be added for the top dilution, and 650 µL would be added for serial dilutions to prepare the 2x toxin solution.
- Experiment
- Reserve 0.5 mL of processed promastigotes from step 1.8 in a separate tube as "Unstained control".
NOTE: This sample will be used to set up gating on the flow cytometer. - Add 2 mg/mL PI to a final concentration of 10 µg/mL to the remaining promastigotes. Vortex for 3 s.
NOTE: After the addition of PI to the processed promastigotes, these cells can only be used for a time period of 2.5 h. After 2.5 h, the cells start to die, and the results become erroneous. - Add 1 x 105 (in 100 µL/well) processed promastigotes to each well of a V-bottom 96-well plate or 1.2 mL microtiter tubes (Figure 1). Place the plate or tube rack on ice at an approximately 45° angle from viewing. Perform the work in a biosafety cabinet when handling Leishmania promastigotes.
- Add 100 µL of assay buffer with PI to each no-toxin control (last row). Verify that the control was correctly added by visually identifying tubes with a total volume of 200 µL that appear darker in color.
- Remove the toxin aliquots from −80°C, thaw on ice, and pool as needed. Add the volume of toxin calculated in step 2.1.5 to the highest dilution (prepared in step 2.1.10). Then, serially dilute the toxin (Figure 1). Pipette up and down at least 8x to ensure mixing.
NOTE: Perform on ice because CDCs rapidly inactivate at room temperature. - Starting from the lowest toxin concentration, quickly add 100 µL of toxin to the correct row (Figure 1 and Figure 2) and continue until all the toxin has been added to the cells.
- Seal the plate with sealing tape. Incubate at 37 °C for 30 min. After the incubation period, package and transport the plate to the flow cytometer.
- Reserve 0.5 mL of processed promastigotes from step 1.8 in a separate tube as "Unstained control".
- Data acquisition
- Set up the flow cytometer (see Table of Materials) and acquisition software according to the manufacturer's instructions and per facility policy. Do not perform the flow cytometry procedure without prior training on the cytometer.
NOTE: In this example, a 4-laser Attune NxT was used. PI was collected on the YL-1 channel (excited by a 561 nm laser, passed through a 577 LP, reflected from 600 DLP, and filtered through 585/16 bandpass), though the wide spectrum of PI allows collection on other channels. - Using the unstained L. major promastigote sample, set the gates for forward and side scatter and the initial fluorescent parameters based on the dyes chosen.
- Include one extra parameter if desired for dot plots to check autofluorescence (e.g., "no stain") (Figure 3).
NOTE: In this example, the BL-1 channel (excited by a 488 nm laser, passed through 495 DLP and 503 LP, reflected from 555 DLP, and filtered via 530/30 bandpass) was used. - Using single stained controls, set the gates for the viability dye (PI in this study) and any fluorescently labeled toxins. Monitor forward scatter versus time for micro-clogs.
NOTE: PI will dimly stain all the cells above unstained controls. Dead cells will be readily separable, with transiently permeabilized cells in between populations. - Acquire >10,000 gated events for each sample on the cytometer.
NOTE: It is recommended to read from most sensitive to least sensitive, but the order of acquisition can be reversed to determine any impact of read order on sample results. - Save the data and export as needed for analysis.
- Set up the flow cytometer (see Table of Materials) and acquisition software according to the manufacturer's instructions and per facility policy. Do not perform the flow cytometry procedure without prior training on the cytometer.
- Data analysis
NOTE: In this study, Excel with Solver plug-in (see Table of Materials) was used for data analysis (see Supplemental File 1).- Gate total, single cell L. major promastigotes by gating on forward and side scatter and time as needed (Figure 3). Use height or area as recommended for the flow cytometer.
NOTE: For the flow cytometer used here, height is the recommended parameter instead of area. - Identify and gate dead cells as "PI high". Gate intermediate cells as "PI low". PI high cells are dead cells, while PI low cells are transiently permeabilized26.
NOTE: PI high cells typically show a 2-3 log shift from negative cells. - Export the data to Excel. Obtain the sample name/ID and %PI high to determine killing.
NOTE: If fluorescent toxins were used, the median fluorescent intensity (MFI) of live, transiently permeabilized, and negative populations will be needed. %PI low may be exported for transient permeabilization. - Determine the average %PI high for each condition between the two technical replicates.
NOTE: If average MFI is needed for fluorescent toxins, calculate this as well. - Calculate %Specific Lysis from the %PI high using the following formula24,25:
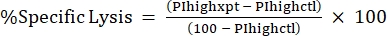 (Eq 3)
(Eq 3)
where PIhighxpt is the %PI high for the experimental condition; and PIhighctl is the %PI high for the no-toxin control. - Plot %Specific Lysis against toxin concentration for the dose-response curve (Figure 4).
- Organize the dose-response curve in Excel for logistic modeling. Include toxin concentration and average %Specific Lysis along with experimental details and/or raw %PI high calculations (Table 2).
- Verify that the Solver add-in is enabled.
NOTE: To enable the Solver in the desktop version of Excel, go to File > Options > Add-ins, and check the Solver box. Restart Excel. - Label four more columns as "modeled", "residuals", "parameters", and "parameter values". Verify that the first columns correspond to the experimental parameters, the toxin concentration, and %Specific Lysis (Table 2).
- Add the following parameters in the "parameters" column: L, k, c, SUM, and LC50. Initialize the parameters L, k, and c by entering the following values in the "parameter values" column: 100, 0.05, 1,000.
- In the "modeled" column, create the logistic model using the following formula:
 (Eq 4)
(Eq 4)
Set L, k, and c to the cells containing those parameters in the "parameter values" column.
Set x to the cell containing the toxin concentration.
NOTE: For Table 2, cell G4, the formula is as follows: =$J$3/(1+EXP(-$J$4*(D4-$J$5))) - Apply this equation to all the %Specific Lysis values except the no-toxin control.
- In the "residuals" column, calculate the square of the difference between the modeled number and the actual specific lysis using the following equation:
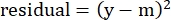 (Eq. 5)
(Eq. 5)
where y is the experimental %Specific Lysis; and m is the corresponding value in the "modeled" column calculated in steps 2.4.10-2.4.11. - In the "parameter values" column next to "SUM", sum all the values in the residuals column.
- In the "parameter values" column next to "LC50", initialize the equation to calculate the LC50 from the determined values. This is solving Eq 4 for x when m = 50.
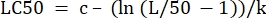 (Eq 6)
(Eq 6)
For Table 2, the Excel formula is as follows: =J5-(LN(J3/(50)-1))/J4 - Open the Solver from the Data Tab. Select the Set Objective to be the cell containing the sum of the residuals calculated. Set it to Min.
- Change the variable cells for the parameter values of L, k, and c.
NOTE: The solver may behave better if "Make Unconstrained Variables Non-negative" is left checked. - For negative k values, modify Eq 4 and Eq 6 by factoring out −1 from k to change k to positive. Use the GRG Nonlinear solving method. Click Solve.
- Check the curve and that the LC50 is automatically calculated using Eq 6 (Table 2). Verify the fit by graphically plotting both %Specific lysis and modeling against toxin concentration.
NOTE: It may also be checked by calculating the R2 for the curve.
- Gate total, single cell L. major promastigotes by gating on forward and side scatter and time as needed (Figure 3). Use height or area as recommended for the flow cytometer.
3. Protein analysis of toxin-challenged L. major promastigotes
- Prepare L. major promastigotes as described in section 1.
- Resuspend 2 x 107 WT, spt2-, and spt2-/+SPT2 L. major promastigotes in 2 mL of the desired assay buffer using a 5 mL pipette (e.g., serum-free M199). Add toxin to a final sublytic concentration and incubate at 37 °C for 30 min.
NOTE: For example, a sublytic dose of SLO for spt2- promastigotes is 500 HU/mL. - Include other genotypes and no-toxin controls.
- Centrifuge the promastigotes at 1,500 x g for 10 min to pellet the cells. Discard the supernatant using a 10 mL pipette. Run the closed tube containing the cell pellet rapidly three times across an irregular surface, such as the grill of the biosafety cabinet, to break up the cell pellet.
NOTE: The cell pellet is almost invisible to the naked eye. - Reconstitute 1x SDS-PAGE sample buffer with 2-mercaptoethanol immediately before use and heat to 95 °C for 10 min before addition to the cell pellet. Resuspend the cell pellet in hot 1x SDS-PAGE sample buffer, and mix well by pipetting up and down. Heat the resuspended cell pellet in 1x sample buffer at 95 °C for 10 min.
NOTE: After solubilization in sample buffer, store the samples long-term at −20 °C if required. - Prepare the resolving gel. Degas all the components except ammonium persulfate (APS) and TEMED for 15 min.
- Add APS and TEMED immediately before casting the gel. Carefully overlay the resolving gel with water. Allow the resolving gel to polymerize, ~30-45 min.
- Decant the water and prepare the stacking gel. Add the stacking gel, taking care to avoid bubbles. Insert a comb with the relevant number of wells, and allow to polymerize for 5 min. Monitor polymerization using any leftover stacking gel.
- Assemble the gel for running SDS-PAGE and add reservoir buffer to the chamber.
- Load 10 µL of each sample per well, or 8 µL of the protein ladder. Run at 180 V until the samples enter the resolving gel, and then reduce voltage to ~160 V and run until the dye front is ~0.5 cm from the edge of the plate.
NOTE: The time it takes for the samples to reach the bottom may vary between 1-1.5 h. The time may be lengthened by reducing the voltage. Never reduce the voltage to zero. Higher voltages may increase gel "smiling" and crack the plates. - Transfer the gel either to Coomassie stain (for protein staining) or to 1x transfer buffer (for western blotting). For Coomassie staining, stain overnight, and then destain, image, and dry.
- For western blot, prepare the transfer system according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- For a wet transfer, use cold 1x transfer buffer and pre-wet pads, filter paper, and nitrocellulose. For the Bio-rad Protean III system (see Table of Materials) used here, the filter paper may be cut to 10 cm x 7.5 cm. Cut the nitrocellulose to 9 cm x 6.75 cm.
NOTE: Nitrocellulose is highly flammable. Avoid open flames and other potential sources of ignition. - Lay out the transfer cassette with pads, filter paper, and nitrocellulose. Roll out air bubbles. Add the gel carefully.
- Add the filter paper and roll out air bubbles. Add the pad, close the cassette, and insert into the holder in the correct orientation (ensure nitrocellulose faces the red terminal). Add a stir bar and an ice pack to the side, and top off the reservoir with cold 1x transfer buffer. Transfer at 110 V for 90 min.
NOTE: The heat generated during the transfer may adversely affect the transfer. To ensure a good transfer, always use cold 1x transfer buffer. - Remove the nitrocellulose and stain with Ponceau solution for ~5 min. Rinse with ultrapure water. Mark the protein ladder in pencil and trim the blot as needed. Destain the blot using leftover transfer buffer.
NOTE: Ponceau may be reused many times. - Block the nitrocellulose in 25 mL of 5% BSA in 1x TBST at 4 °C, with shaking, overnight. Then, discard the blocking solution and add primary antibody (1:1,000) in 1% BSA in 1x TBST. Shake at 4 °C overnight.
NOTE: The primary antibody may be saved at −20 °C and reused several times. - Wash the nitrocellulose 3x for 10 min each in 1x TBST with shaking. Discard the wash and add 10 mL of HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (1:10,000) in 1% BSA in 1x TBST. Shake at room temperature for 1 h. Wash the nitrocellulose 3x for 10 min each in 1x TBST with shaking.
- Prepare ECL reagent immediately before imaging the nitrocellulose. Immediately before imaging, decant the TBST and add the ECL reagent to the nitrocellulose. Shake for 1 min. Image the gel.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Increased promastigote sensitivity to SLO in Tyrode's buffer compared to M199
The SLO sensitivity of L. major promastigotes was compared between different assay buffers. Wild-type, spt2-, and spt2-/+SPT2 promastigotes were challenged with SLO in serum-free M199 or Tyrode's buffer supplemented with 2 mM CaCl2 for 30 min prior to analysis on a flow cytometer. Suitable parasites for analysis were single cells identified by forwar...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
In this study, methods to study the molecular mechanisms and functions of PFTs were described, using the human pathogen Leishmania major as a model system. A medium-throughput flow cytometry-based cytotoxicity assay to measure single-cell viability was developed. Viability is quantitative at the population level because LC50 values can be calculated from the dose-response curve using logistic modeling. As a proof-of-principle, a flow cytometric assay was used to illustrate that the choice of media can...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
This work was supported by the National Institute Of Allergy And Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health grant R21AI156225 to PAK and KZ (co-I) and R01AI139198 to KZ (co-I). CH would like to acknowledge the Department of Biological Sciences for the Teaching Assistantship provided during the time of this study.
The funding agencies had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; nor in the decision to publish the results. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies. The authors declare they have no competing conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank members of the Keyel and Zhang labs for their critical review of the manuscript. The authors thank the College of Arts and Sciences Microscopy for the use of facilities.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1.2 mL microtiter (Marsh) tubes | Fisher | 02-681-376 | Cytotoxicity assay |
| 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube | Fisher | 05-408-129 | Toxin dilutions |
| 15 mL centrifuge tube | Avantor VWR (Radnor, PA) | 89039-666 | To hold cells and media |
| 1x Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | Fisher | BP399 | For cell processing |
| 3% H2O2 | Walmart (Fayetteville, AR) | N/A | For ECL |
| 5x M199 | Cell-gro | 11150067 | Basal growth media for L. major promastigotes |
| Biosafety cabinet | Baker | To culture cells in sterile conditions | |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Fisher | BP1605-100 | Fraction V acceptable purity |
| CaCl2 | Fisher | BP510-100 | Stock concentration 100 mM |
| Centrifuge | Thermo Fisher | Heraeus Megafuge 40R | To pellet the cells from culture |
| Cy5 Mono-reactive dye pack | Cytiva (Marlborough, MA) | PA25031 | Fluorophore label for toxins |
| Digital dry bath | Benchmark | BSH1002 | To denature protein samples |
| EGTA | Amresco | 0732-100G | Stock concentration 0.5 M |
| Excel | Microsoft (Redmond, VA) | Data analysis software | |
| Flow cytometer (4-laser Attune NxT) | Fisher | Cytometer for data acquisition | |
| FlowJo | BD (Ashland, OR) | Software | |
| Formaldehyde | Fisher | BP531-500 | Fixative for counting cells |
| G418 | Fisher | BP673-1 | Selection agent for cells |
| Hellmanex III | Sigma | Z805939 | Dilute 1:4 for cleaning cytometer |
| Hemacytometer | Fisher | 0267151B | For counting cells |
| Human red blood cells | Zen-bio (Durham, NC) | SER-10MLRBC | To validate toxin activity |
| Ice bucket | |||
| Light microscope | Nikon | Eclipse 55i | To visualize cells |
| Nitrocellulose | Fisher | 88018 | For probing proteins via antibodies |
| Pipettors and tips | Avantor VWR | To dispense reagents | |
| Power supply | Bio-Rad | To run SDS-PAGE and transfers | |
| Propidium iodide | Biotium | 40016 | Stock concentration 2 mg/mL in water |
| Protein ladder | Bio-Rad | 161-0373 | To determine molecular weight of proteins |
| SDS-PAGE Running Apparatus (Mini Protean III) | Bio-Rad | 165-3302 | To separate proteins based on their size |
| Sealing tape | R&D | DY992 | To seal plates with cells |
| Streptolysin O C530A plasmid insert | Cloned into pBAD-gIII vector (Reference: 7) | ||
| Streptolysin O C530A toxin | Lab purified | Specific activity 4.34 x 105 HU/mg | |
| Swinging bucket rotor | Thermo Fisher | 75003607 | To centrifuge cells |
| V-bottom plate | Greiner Bio-one | 651206 | For cytotoxicity assay |
| Vortex | Benchmark | BV1000 | To mix cells |
| Western blot imaging system (Chemi-doc) | Bio-Rad | To visualize proteins by western blot | |
| Western Blot Transfer Apparatus (Mini Protean III) | Bio-Rad | 170-3930 | Transfer proteins to nitrocellulose |
| Whatman Filter paper | GE Healthcare Life Sciences | 3030-700 | Used in transfer of proteins to nitrocellulose |
| Antibody | |||
| Anti-ERK antibody | Cell Signaling Technologies | Cat# 9102S | Rabbit (1:1000 dilution) |
| Anti-lipophosphoglycan (LPG) antibody | CreativeBioLabs | Cat# WIC79.3 | Mouse (1: 1000) |
| Anti-MEK antibody | Cell Signaling Technologies | Cat# 9122L | Rabbit (1:1000) |
| Anti-mouse IgG, HRP conjugate | Jackson Immunoresearch | Cat#715-035-151 | Donkey (1:10000) |
| Anti-phosphoERK antibody | Cell Signaling Technologies | Cat# 9101S | Rabbit (1:1000) |
| Anti-pMEK antibody | Cell Signaling Technologies | Cat# 9121S | Rabbit (1:1000) |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP conjugate | Jackson Immunoresearch | Cat#711-035-152 | Donkey (1:10000) |
| Anti-tubulin antibody | Sigma | Cat# T5168 | Mouse (1: 2000) |
| Leishmania major Genotypes | Reference: 13 | ||
| Episomal addback (spt2-/+SPT2) | Δspt2::HYG/Δspt2:PAC/+pXG-SPT2 | ||
| Serine palmitoyltransferase subunit 2 knockout (spt2-) | Δspt2::HYG/Δspt2::PAC | ||
| Wild type (WT) | LV39 clone 5 (Rho/SU/59/P) |
References
- Thapa, R., Ray, S., Keyel, P. A. Interaction of macrophages and cholesterol-dependent cytolysins: The impact on immune response and cellular survival. Toxins. 12 (9), 531(2020).
- Limbago, B., Penumalli, V., Weinrick, B., Scott, J. R. Role of streptolysin O in a mouse model of invasive group A streptococcal disease. Infection & Immunity. 68 (11), 6384-6390 (2000).
- Farrand, A. J., et al. The cholesterol-dependent cytolysin membrane-binding interface discriminates lipid environments of cholesterol to support beta-barrel pore insertion. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 290 (29), 17733-17744 (2015).
- Soltani, C. E., Hotze, E. M., Johnson, A. E., Tweten, R. K. Structural elements of the cholesterol-dependent cytolysins that are responsible for their cholesterol-sensitive membrane interactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (51), 20226-20231 (2007).
- Schoenauer, R., et al. Down-regulation of acid sphingomyelinase and neutral sphingomyelinase-2 inversely determines the cellular resistance to plasmalemmal injury by pore-forming toxins. FASEB Journal. 33 (1), 275-285 (2019).
- Ray, S., Roth, R., Keyel, P. A. Membrane repair triggered by cholesterol-dependent cytolysins is activated by mixed lineage kinases and MEK. Science Advances. 8 (11), (2022).
- Babiychuk, E. B., Monastyrskaya, K., Draeger, A. Fluorescent annexin A1 reveals dynamics of ceramide platforms in living cells. Traffic. 9 (10), 1757-1775 (2008).
- Jimenez, A. J., et al. ESCRT machinery is required for plasma membrane repair. Science. 343 (6174), 1247136(2014).
- Demonbreun, A. R., et al. An actin-dependent annexin complex mediates plasma membrane repair in muscle. Journal of Cell Biology. 213 (6), 705-718 (2016).
- Wolfmeier, H., et al. Ca(2)(+)-dependent repair of pneumolysin pores: A new paradigm for host cellular defense against bacterial pore-forming toxins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1853 (2), 2045-2054 (2015).
- Bravo, F., Sanchez, M. R. New and re-emerging cutaneous infectious diseases in Latin America and other geographic areas. Dermatologic Clinics. 21 (4), 655-668 (2003).
- Manfredi, M., Iuliano, S. Cutaneous leishmaniasis with long duration and bleeding ulcer. Clinical Microbiology Open Access. 05, 2-6 (2016).
- Zhang, K., et al. Sphingolipids are essential for differentiation but not growth in Leishmania. EMBO Journal. 22 (22), 6016-6026 (2003).
- Zhang, K. Balancing de novo synthesis and salvage of lipids by Leishmania amastigotes. Current Opinions in Microbiology. 63, 98-103 (2021).
- Kaur, P., Goyal, N. Pathogenic role of mitogen activated protein kinases in protozoan parasites. Biochimie. 193, 78-89 (2022).
- Wiese, M. Leishmania MAP kinases--Familiar proteins in an unusual context. International Journal of Parasitology. 37 (10), 1053-1062 (2007).
- Brumlik, M. J., Pandeswara, S., Ludwig, S. M., Murthy, K., Curiel, T. J. Parasite mitogen-activated protein kinases as drug discovery targets to treat human protozoan pathogens. Journal of Signal Transduction. 2011, 971968(2011).
- Wiese, M., Kuhn, D., Grunfelder, C. G. Protein kinase involved in flagellar-length control. Eukaryotic Cell. 2 (4), 769-777 (2003).
- Agron, P. G., Reed, S. L., Engel, J. N. An essential, putative MEK kinase of Leishmania major. Molecular Biochemistry of Parasitology. 142 (1), 121-125 (2005).
- Ray, S., Thapa, R., Keyel, P. A. Multiple parameters beyond lipid binding affinity drive cytotoxicity of cholesterol-dependent cytolysins. Toxins. 11 (1), (2018).
- Beneke, T., et al. A CRISPR Cas9 high-throughput genome editing toolkit for kinetoplastids. Royal Society Open Science. 4 (5), 170095(2017).
- Kapler, G. M., Coburn, C. M., Beverley, S. M. Stable transfection of the human parasite Leishmania major delineates a 30-kilobase region sufficient for extrachromosomal replication and expression. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 10 (3), 1084-1094 (1990).
- Moitra, S., Pawlowic, M. C., Hsu, F. F., Zhang, K. Phosphatidylcholine synthesis through cholinephosphate cytidylyltransferase is dispensable in Leishmania major. Scientific Reports. 9, 7602(2019).
- Keyel, P. A., Heid, M. E., Watkins, S. C., Salter, R. D. Visualization of bacterial toxin induced responses using live cell fluorescence microscopy. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (68), 4227(2012).
- Romero, M., et al. Intrinsic repair protects cells from pore-forming toxins by microvesicle shedding. Cell Death & Differentiation. 24 (5), 798-808 (2017).
- Keyel, P. A., et al. Streptolysin O clearance through sequestration into blebs that bud passively from the plasma membrane. Journal of Cell Science. 124, 2414-2423 (2011).
- Dong, Z., Patel, Y., Saikumar, P., Weinberg, J. M., Venkatachalam, M. A. Development of porous defects in plasma membranes of adenosine triphosphate-depleted Madin-Darby canine kidney cells and its inhibition by glycine. Laboratory Investigations. 78 (6), 657-668 (1998).
- Loomis, W. P., den Hartigh, A. B., Cookson, B. T., Fink, S. L. Diverse small molecules prevent macrophage lysis during pyroptosis. Cell Death & Disease. 10 (4), 326(2019).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved