A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Decellularization of Whole Human Heart Inside a Pressurized Pouch in an Inverted Orientation
In This Article
Summary
This method enables decellularization of a complex solid organ using a simple protocol based on osmotic shock and perfusion of ionic detergent with minimal organ matrix disruption. It comprises a novel decellularization technique for human hearts inside a pressurized pouch with real-time monitoring of flow dynamics and cellular debris outflow.
Abstract
The ultimate solution for patients with end-stage heart failure is organ transplant. But donor hearts are limited, immunosuppression is required, and ultimately rejection can occur. Creating a functional, autologous bio-artificial heart could solve these challenges. Biofabrication of a heart comprised of scaffold and cells is one option. A natural scaffold with tissue-specific composition as well as micro- and macro-architecture can be obtained by decellularizing hearts from humans or large animals such as pigs. Decellularization involves washing out cellular debris while preserving 3D extracellular matrix and vasculature and allowing "cellularization" at a later timepoint. Capitalizing on our novel finding that perfusion decellularization of complex organs is possible, we developed a more "physiological" method to decellularize non-transplantable human hearts by placing them inside a pressurized pouch, in an inverted orientation, under controlled pressure. The purpose of using a pressurized pouch is to create pressure gradients across the aortic valve to keep it closed and improve myocardial perfusion. Simultaneous assessment of flow dynamics and cellular debris removal during decellularization allowed us to monitor both fluid inflow and debris outflow, thereby generating a scaffold that can be used either for simple cardiac repair (e.g. as a patch or valve scaffold) or as a whole-organ scaffold.
Introduction
Heart failure leads to high mortality in patients. The ultimate treatment option for end-stage heart failure is allo-transplantation. However, there is a long wait-list for transplantation due to the shortage of donor organs, and patients face post-transplantation hurdles that range from life-long immunosuppression to chronic organ rejection1,2. Bioengineering functional hearts by repopulating decellularized human-sized hearts with a patient's own cells could circumvent these hurdles3.
A major step in "engineering" a heart is the creation of a scaffold with appropriate vascular and parenchymal structure, composition and function to guide the alignment and organization of delivered cells. In the presence of the appropriate framework, cells seeded on the scaffold should recognize the environment and perform the expected function as part of that organ. In our opinion, decellularized organ extracellular matrix (dECM) comprises the necessary characteristics of the ideal scaffold.
By utilizing intrinsic vasculature, complex whole-organ decellularization can be achieved via antegrade or retrograde perfusion4 to remove cellular components while preserving the delicate 3D extracellular matrix and vasculature2,5,6,7. A functional vasculature is important in bioengineering whole organs just as it is in vivo, for nutrient distribution and waste removal8. Coronary perfusion decellularization has been proven to be effective in creating decellularized hearts from rats4, or pigs4,7,9,10,11,12,13, and humans5,7,14,15,16. Yet, integrity of the valves, atria and other "thin" regions can suffer.
Human-size decellularized heart scaffolds can be obtained from pigs using pressure control7,9,10,11,12 or infusion flow rate control13,17 and from human donors using pressure control5,7,14,15. Decellularization of human donor hearts occurs over 4-8 days under pressure controlled at 80-100 mmHg in upright orientation5,15,16 or over 16 days under pressure controlled at 60 mmHg14. Under antegrade, pressure-controlled decellularization, the aortic valve competency plays a crucial role in maintaining coronary perfusion efficiency and stable pressure at the aortic root. Our previous work revealed that the orientation of the heart influences its coronary perfusion efficiency during the decellularization procedure and therefore the scaffold integrity in the end9.
As a continuation of our previous work9, we introduce a novel concept wherein a pericardium-like pouch is added to improve whole-heart decellularization. We describe the decellularization of human hearts placed inside pressurized pouches, inversely oriented, and under pressure controlled at 120 mmHg at the aortic root. This protocol includes monitoring the flow profile and collection of outflow media throughout the decellularization procedure to evaluate coronary perfusion efficiency and cell debris removal. Biochemical assays are then performed to test the effectiveness of the method.
Protocol
All experiments adhered to the ethics committee guidelines from the Texas Heart Institute.
1. Organ Preparation
NOTE: In collaboration with LifeGift, a nonprofit organ procurement organization in Texas (http://www.lifegift.org), donated human hearts not suitable for transplant were used for research with approved consent.
- To procure hearts, intravenously infuse 30,000 U heparin to the hearts. Securely suture cardioplegia cannula in the aorta and attach a clamped perfusion line. Perforate the inferior vena cava (IVC) to vent the right heart. Cut either the left superior pulmonary vein or the left atrial appendage to vent the left chambers of the heart.
- Infuse 1 L of cardioplegia or heparinized saline. Dissect aortic arch branches, superior vena cava (SVC) and other pulmonary veins to release the heart from any vascular or surrounding tissue attachment. Submerge the well-heparinized heart in iced saline solution.
- Inspect the donated human heart (both anteriorly and posteriorly, Figure 1). Place the heart on a dissecting tray and inspect for any structural damage or anatomical malformations. If liver and/or lungs were procured for transplantation, the heart may present with a short inferior vena cava and/or absence of left atrial posterior wall.
- Perform internal inspection for possible defects - atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), or valve (aortic, pulmonary, mitral, tricuspid) malformation.
- If a septal defect is present, correct it with appropriate sutures (Figure 2A, 2B). The correction of septal defects is needed to monitor decellularization progress via pulmonary artery (PA) outflow turbidity measurement. Correction of the septal defect removes left to right shunt, hence, the outflow from PA represents the outflow from the coronary circulation through the coronary sinus.
- Ligate superior and inferior vena cava with 2-0 silk suture (Figure 2C).
- Dissect the aorta (Ao) away from the main PA (Figure 2D) for subsequent cannulation.
- Insert connectors, based on the diameter of the vessel, (Figure 3) into Ao and PA and secure them with 2-0 silk sutures (Figure 4A).
- Insert a tubing line through the left atrium (Figure 4B) and toward the left ventricle (LV) (Figure 3), using one of the pulmonary vein orifices.
- Connect an infusion line to the connector placed in the Ao and the outflow line to the one in the PA (Figure 3).
- Place the prepared heart into a polyester pouch in inverted orientation (upside down).
- Place the pouch with heart into a perfusion container and close the lid (Figure 4C).
- Connect each of the lines to the respective ports in the rubber stopper (based on the diameter of container) and insert it to the lid of the perfusion container to seal the polyester pouch (Figure 4C and Figure 5B).
- Perfuse 1x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (136 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4 and 1.8 mM KH2PO4 in distilled water, pH 7.4) via the infusion port of the rubber stopper to verify outflow from the PA and from the line inserted into LV.
- Use this flow to clean the organ of any residual traces of blood in the vasculature. If flow is not observed, tighten the connection lines as they might be loose.
2. System Setup and Organ Decellularization Procedure
- Assemble the bioreactor and place in an upright orientation (Figure 5). The perfusion system includes a personal computer (PC), proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller, a peristaltic pump for Ao infusion, a perfusion bioreactor, a pressure head container for LV perfusate retention (2L aspirator bottle with bottom sidearm), and a peristaltic pump to drain excess fluid from the pressure head container and to collect the outflow from PA.
- In the rubber septum, connect the infusion line, pressure-head line, PA-outflow line and bioreactor draining line to the rubber cap surface ports placed on top of the perfusion bioreactor (Figure 5A).
- Decellularize hearts under constant pressure of 120 mmHg measured at the aortic root. Mean pressure of the LV should be within 14-18 mmHg throughout the whole decellularization process.
- Decellularize hearts as follows: 4 h of hypertonic solution (500 mM NaCl), 2 h of hypotonic solution (20 mM NaCl), 120 h of sodium dodecyl sulfate (1% SDS) solution, and a final wash with 120 L of 1X PBS (Figure 6A).
- Decellularize the hearts under constant pressure control (120 mmHg). Infusion flow rate into Ao is heart-dependent and is, on average, 98.06±16.22 mL/min for hypertonic solution, 76.14±7.90 mL/min for hypotonic solution, 151.50±5.76 mL/min for SDS, and 185.24±7.10 mL/min for PBS. The total consumed volume of each reagent averages 23.36±5.70 L for hypertonic solution and 9.13±1.26 L for hypotonic solution.
- Recirculate the final 60 L of 1% SDS (1 L per gram of heart weight) until the end of SDS perfusion. Figure 6A shows a timeline for the decellularization process, eliciting endpoints for data collection: flow rate monitoring (Ao and PA) and outflow collection (PA and non-PA) from pressure head during decellularization.
- Since the SVC and IVC are ligated, it is reasonable to assume that all fluid collected from the PA is the result of actual coronary perfusion (Figure 5B). Determine coronary perfusion efficiency by directly dividing the flow rate of perfusate out of the PA by the flow rate of infused solution into Ao:
Coronary perfusion efficiency =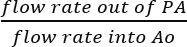 (%).
(%). - Perform comparative analysis of the perfusate obtained from the PA and the LV and the infused solutions in duplicate by loading 200 μL per well in a clear bottom 96-well plate and reading absorbance at 280 nm. The absorbance value, selected empirically after trying different values, was found to give the best normalized values.
- Use the turbidity of clean infused reagent as the control. The turbidity of the outflow perfusate represents washout of cell debris and can be quantified instantly during decellularization as a tracking tool of the process.
- During the final wash with 10 L of 1X PBS, add 500 mL of sterile neutralized 2.1% peracetic acid solution, neutralized with 10N NaOH, leading to a 0.1% peracetic acid solution (v/v) in PBS. Use this solution to sterilize the scaffold.
3. Evaluation of Decellularized Hearts
NOTE: After decellularization, representative hearts will be used for coronary angiogram imaging and biochemical assays.
- Perform coronary angiography of the representative decellularized human heart to examine the intactness of the coronary vasculature. Briefly, using a fluoroscope, image decellularized human heart after injection of contrast agent through coronary ostial cannula in the main right and left coronary arteries.
- Dissect the decellularized heart to get samples from 19 areas to evaluate the remaining deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), glycosaminoglycan (GAG) and SDS levels in decellularized tissues. Remove the base of the heart from ventricles and dissect the ventricles into 4 equal sections (Figure 6C). Divide each section into the anterior and posterior right ventricle (RV), the anterior and posterior LV, and the interventricular septum (IVS). The tissue containing the apex is dissected into the LV and RV for sampling.
- Cut tissue samples for DNA, GAG and SDS assays (~15 mg of wet weight).
- Extract double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) by digesting samples in 1 M NaOH for 3 h at 65 °C and adjust pH to 7 using 10x Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer and 1 M hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Quantify dsDNA using a dsDNA Assay kit with a calf thymus standard (see Table of Materials). Read samples in duplicate using a fluorescence microplate reader (excitation at 480 nm and emission at 520 nm). Calculate the percentage of residual dsDNA in the decellularized hearts by comparing dsDNA concentration in each tissue to that in cadaveric (% cadaveric).
- Obtain sulfated GAGs into solution by digesting tissue samples in a papain extraction solution (0.2 M sodium phosphate buffer with EDTA disodium salt, cysteine HCl, sodium acetate, and papain) at 65 °C for 3 hours. Measure GAG content (in duplicate) by using a Glycosaminoglycan Assay Kit.
- Lyophilize samples for SDS assay in a heated vacuum and measure dry weight. Add 200 µL of ultrapure water to each dried sample and homogenize to extract the residual SDS into solution. Mix this SDS solution to chloroform and a methylene blue solution (12 mg of methylene blue in 1 L of 0.01 M HCl). The SDS will separate in the organic layer by binding to the methylene blue dye.
- Using a fluorescence microplate reader, read the absorbance (655 nm) of the standards and samples in duplicate to calculate the residual SDS. Normalize this SDS value to tissue dry weight.
- Image samples from thick regions (i.e., LV, RV and septum) of human heart with nonlinear optical microscopy (NLOM) to confirm cellular removal after decellularization. The NLOM setup is detailed in our previous publications18,19,20. NLOM enables us to image cell, elastin, collagen and myosin fibers through its two-photon fluorescence (TPF) and second harmonic generation (SHG) channels without using any exogenous stain or dye21.
Results
After a 7-day decellularization with antegrade aortic perfusion under constant pressure of 120 mmHg, the human heart turned translucent (Figure 6B). The heart was grossly dissected into 19 sections for biochemical (DNA, GAG and SDS) analysis (Figure 6C) to evaluate the final decellularized product.
Throughout the decellularization process, infusion flow rate of differen...
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study to report inverted decellularization of human hearts inside a pressurized pouch with time-lapse monitoring of flow rate and cell debris removal. The pericardium-like pouch keeps the orientation of the heart stable throughout the decellularization procedure. Submerging and inverting the whole hearts inside a pouch prevents dehydration and minimizes excessive strain on the aorta (from heart weight) when compared to the conventional upright Langendorff perfusion decellularization me...
Disclosures
Dr. Taylor is the founder and shareholder in Miromatrix Medical, Inc. This relationship is managed in accordance with the conflict of interest policies by the University of Minnesota and Texas Heart Institute; the other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Houston Endowment grant and the Texas Emerging Technology Fund. The authors acknowledge the organ procurement agency LifeGift, Inc. and the donor's families for making this study possible.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 2-0 silk suture | Ethicon | SA85H | Suture used to ligate superior and inferior vena cava |
| 1/4" x 3/8" connector with luer | NovoSci | 332023-000 | Connect aorta and pulmonary artery |
| Masterflex platinum-cured silicone tubing | Cole-Parmer | HV-96410-16 | Tubing to connect heart chambers/veins |
| infusion and outflow line | Smiths Medical | MX452FL | For flowing solutions through the vasculature |
| Polyester pouch (Ampak 400 Series SealPAK Pouches) | Fisher scientific | 01-812-17 | Pericardium-like pouch for containing heart during decellularization |
| Snapware Square-Grip Canister | Snapware | 1022 | 1-liter Container used for perfusing heart |
| Black rubber stoppers | VWR | 59586-162 | To seal the perfusion container |
| Peristaltic pump | Harvard Apparatus | 881003 | To pump fluid through the inflow lines and to drain fluids |
| 2 L aspirator bottle with bottom sidearm | VWR | 89001-532 | For holding solutions/perfusate |
| Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay kit | Life Technologies | P7589 | For quantifying dsDNA |
| Calf thymus standard | Sigma | D4522 | DNA standard |
| Blyscan Glycosaminoglycan Assay Kit | Biocolor Ltd | Blyscan #B1000 | GAG assay kit |
| Plate reader | Tecan | Infinite M200 Pro | For analytical assays |
| GE fluoroscopy | General Electric | OEC 9900 Elite | Angiogram |
| Visipaque | GE | 13233575 | Contrast agent |
References
- Writing Group Members. Executive Summary: Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics--2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 133 (4), 447-454 (2016).
- Zia, S., et al. Hearts beating through decellularized scaffolds: whole-organ engineering for cardiac regeneration and transplantation. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 36 (4), 705-715 (2016).
- Zimmermann, W. H. Strip and Dress the Human Heart. Circulation Research. 118 (1), 12-13 (2016).
- Ott, H. C., et al. Perfusion-decellularized matrix: Using nature's platform to engineer a bioartificial heart. Nature Medicine. 14 (2), 213-221 (2008).
- Sanchez, P. L., et al. Acellular human heart matrix: A critical step toward whole heart grafts. Biomaterials. 61, 279-289 (2015).
- Peloso, A., et al. Current achievements and future perspectives in whole-organ bioengineering. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 6, 107 (2015).
- Guyette, J. P., et al. Perfusion decellularization of whole organs. Nature Protocols. 9 (6), 1451-1468 (2014).
- Momtahan, N., Sukavaneshvar, S., Roeder, B. L., Cook, A. D. Strategies and Processes to Decellularize and Cellularize Hearts to Generate Functional Organs and Reduce the Risk of Thrombosis. Tissue Engineering Part B-Reviews. 21 (1), 115-132 (2015).
- Lee, P. F., et al. Inverted orientation improves decellularization of whole porcine hearts. Acta Biomaterialia. , (2016).
- Momtahan, N., et al. Automation of Pressure Control Improves Whole Porcine Heart Decellularization. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. , (2015).
- Weymann, A., et al. Development and Evaluation of a Perfusion Decellularization Porcine Heart Model - Generation of 3-Dimensional Myocardial Neoscaffolds. Circulation Journal. 75 (4), 852-860 (2011).
- Weymann, A., et al. Bioartificial heart: A human-sized porcine model--the way ahead. PLoS One. 9 (11), e111591 (2014).
- Remlinger, N. T., Wearden, P. D., Gilbert, T. W. Procedure for decellularization of porcine heart by retrograde coronary perfusion. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (70), e50059 (2012).
- Guyette, J. P., et al. Bioengineering Human Myocardium on Native Extracellular Matrix. Circulation Research. 118 (1), 56-72 (2016).
- Sanchez, P. L., et al. Data from acellular human heart matrix. Data Brief. 8, 211-219 (2016).
- Garreta, E., et al. Myocardial commitment from human pluripotent stem cells: Rapid production of human heart grafts. Biomaterials. 98, 64-78 (2016).
- Wainwright, J. M., et al. Preparation of Cardiac Extracellular Matrix from an Intact Porcine Heart. Tissue Engineering Part C-Methods. 16 (3), 525-532 (2010).
- Larson, A. M., Yeh, A. T. Ex vivo characterization of sub-10-fs pulses. Optics Letters. 31 (11), 1681-1683 (2006).
- Lee, P. F., Yeh, A. T., Bayless, K. J. Nonlinear optical microscopy reveals invading endothelial cells anisotropically alter three-dimensional collagen matrices. Experimental Cell Research. 315 (3), 396-410 (2009).
- Lee, P. F., Bai, Y., Smith, R. L., Bayless, K. J., Yeh, A. T. Angiogenic responses are enhanced in mechanically and microscopically characterized, microbial transglutaminase crosslinked collagen matrices with increased stiffness. Acta Biomaterialia. 9 (7), 7178-7190 (2013).
- Wu, Z., et al. Multi-photon microscopy in cardiovascular research. Methods. 130, 79-89 (2017).
- Ramanathan, T., Skinner, H. Coronary blood flow. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 5 (2), 61-64 (2005).
- Murthy, V. L., et al. Clinical Quantification of Myocardial Blood Flow Using PET: Joint Position Paper of the SNMMI Cardiovascular Council and the ASNC. Journal of Nuclear Cardiology. 25 (1), 269-297 (2018).
- Molina, D. K., DiMaio, V. J. Normal organ weights in men: Part I-the heart. The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 33 (4), 362-367 (2012).
- Molina, D. K., DiMaio, V. J. Normal Organ Weights in Women: Part I-The Heart. The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 36 (3), 176-181 (2015).
- Robertson, M. J., Dries-Devlin, J. L., Kren, S. M., Burchfield, J. S., Taylor, D. A. Optimizing cellularization of whole decellularized heart extracellular matrix. PLoS One. 9 (2), e90406 (2014).
- Robertson, M. J., Soibam, B., O'Leary, J. G., Sampaio, L. C., Taylor, D. A. Cellularization of rat liver: An in vitro model for assessing human drug metabolism and liver biology. PLoS One. 13 (1), e0191892 (2018).
- Baghalishahi, M., et al. Cardiac extracellular matrix hydrogel together with or without inducer cocktail improves human adipose tissue-derived stem cells differentiation into cardiomyocyte-like cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. , (2018).
- Perea-Gil, I., et al. In vitro comparative study of two decellularization protocols in search of an optimal myocardial scaffold for recellularization. American Journal of Translational Research. 7 (3), 558-573 (2015).
- Freytes, D. O., O'Neill, J. D., Duan-Arnold, Y., Wrona, E. A., Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Natural cardiac extracellular matrix hydrogels for cultivation of human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Methods Molecular Biology. 1181, 69-81 (2014).
- Oberwallner, B., et al. Preparation of cardiac extracellular matrix scaffolds by decellularization of human myocardium. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A. 102 (9), 3263-3272 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved