A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Isolation and Characterization of the Murine Uterosacral Ligaments and Pelvic Floor Organs
In This Article
Summary
This article presents a detailed protocol for dissecting uterosacral ligaments and other pelvic floor tissues, including the cervix, rectum, and bladder in mice, to expand the study of female reproductive tissues.
Abstract
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is a condition that affects the integrity, structure, and mechanical support of the pelvic floor. The organs in the pelvic floor are supported by different anatomical structures, including muscles, ligaments, and pelvic fascia. The uterosacral ligament (USL) is a critical load-bearing structure, and injury to the USL results in a higher risk of developing POP. The present protocol describes the dissection of murine USLs and the pelvic floor organs alongside the acquisition of unique data on the USL biochemical composition and function using Raman spectroscopy and the evaluation of mechanical behavior. Mice are an invaluable model for preclinical research, but dissecting the murine USL is a difficult and intricate process. This procedure presents an approach to guide the dissection of murine pelvic floor tissues, including the USL, to enable multiple assessments and characterization. This work aims to aid the dissection of pelvic floor tissues by basic scientists and engineers, thus expanding the accessibility of research on the USL and pelvic floor conditions and the preclinical study of women's health using mouse models.
Introduction
Approximately 50% of women are affected by pelvic organ prolapse (POP)1,2. About 11% of these women fit the criteria for undergoing surgical repair, which has a poor success rate (~30%)3,4. POP is characterized by the descent of any or all of the pelvic organs (i.e., bladder, uterus, cervix, and rectum) from their natural position due to the failure of the USL and the pelvic floor muscles to provide adequate support5. This condition involves anatomical dysfunction and disruption of the connective tissue, as well as neuromuscular injury, in addition to predisposing factors3,6. POP is associated with multiple factors such as age, weight, parity, and delivery type (i.e., vaginal or caesarian births). These factors are thought to affect the mechanical integrity of all the pelvic floor tissues, with pregnancy and parity thought to be the main drivers of POP5,7,8.
The uterosacral ligaments (USLs) are important supportive structures for the uterus, cervix, and vagina and tether the cervix to the sacrum4. Damage to the USLs puts women at increased risk of developing POP. It is believed that pregnancy and childbirth impose additional strain on the USL, which potentially induces injury and increases the chances of POP. The USL is a complex tissue composed of smooth muscle cells, blood vessels, and lymphatics distributed heterogeneously along the ligament, which can be divided into three distinct sections: cervical, intermediate, and sacral region9. The mechanical integrity of the USL is derived from extracellular matrix (ECM) components like collagens, elastin, and proteoglycans5,9,10. Type I collagen fibers are known to be a major load-bearing tensile component of ligamentous tissues and are, therefore, likely involved in USL failure and POP11.
There is a lack of knowledge regarding the causes, prevalence, and effects of POP in women. The development of an appropriate animal model of POP is necessary to advance our understanding of the female pelvic floor. Mice and humans have similar anatomical landmarks within the pelvis, such as the ureters, rectum, bladder, ovaries, and round ligaments9, as well as similar intersection points of the USL with the uterus, cervix, and sacrum. Further, mice offer ease of genetic manipulation and have the potential to be an easily accessible, cost-effective model for the study of POP9.
This study developed a method to access and isolate the USL and the different pelvic floor tissues from nulliparous (i.e., never pregnant) mice. The extracted USLs were subjected to enzymatic digestion (i.e., to remove collagens and glycosaminoglycans), tested to determine the mechanical response under tensile loading, and evaluated for biochemical composition in a proof-of-concept study. The ability to isolate intact tissues will facilitate further mechanical and biochemical characterizations of the pelvic floor components, which is a crucial first step toward improving our understanding of the injury risks related to childbirth, pregnancy, and POP.
Protocol
All animal experiments and procedures were performed according to protocol #2705, approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Colorado Boulder. Six week old female C57BL/6J mice were used for the present study. The animals were obtained from a commercial source (see Table of Materials).
1. Animal preparation
- Euthanize the animal following the institutionally approved method.
NOTE: The present study used CO2 inhalation in alignment with the American Veterinary Medical Association's guidelines (a displacement rate of 30% to 70% of the chamber volume with CO2 per minute), followed by cervical dislocation, to ensure successful euthanization.- Work under a hood, if possible, to minimize the spread of mice allergens. Once the mouse stops moving and breathing, allow 2 min or more to verify the lack of response.
NOTE: If the mouse is pregnant or post-partum, the pups must be individually euthanized. Pups E15.5 and older must be decapitated during the dissection.
- Work under a hood, if possible, to minimize the spread of mice allergens. Once the mouse stops moving and breathing, allow 2 min or more to verify the lack of response.
- Prepare the dissection setup with a dissection pad, an 11-blade scalpel, curved thin sharp scissors, two pairs of forceps, curved forceps, 5-0 polyglactin suture, a dissecting microscope, and six pins (Figure 1, see Table of Materials).
- Place the mouse on the pad, and pin the forelimbs down (Figure 2A). Make an incision of approximately 1-1.5 cm in the abdomen with scissors (Figure 2B). Gently use the scissors to separate the skin at the cranial, caudal, and lateral sides of the incision (Figure 2C, D).
- Flip the mouse to its dorsal side, and gently peel back the skin toward the hindlimbs to remove the skin away from the dissection site (Figure 2E-H).
- Pin the mouse at the limbs (Figure 2I), and make an incision of approximately 1 cm into the abdomen from the thorax to the pelvis (Figure 2J).
NOTE: Ensure not to damage the underlying organs. - Gently push the organs toward the thorax to clear the field of view (Figure 2K).
NOTE: Irrigate the tissues with 1x PBS to maintain hydration. - Clear all of the fat tissue from the pelvic floor (Figure 2L-N).
NOTE: Use forceps to gently pull and clear fat off the organs and tissues of interest.

Figure 1: A clean workspace with all the tools needed to perform the dissections. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
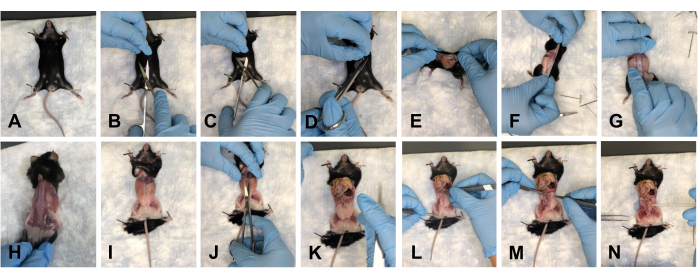
Figure 2: Removal of the skin and opening of the pelvic and thoracic cavities of the mouse. (A) Pinning down all the limbs. (B) Initial incision. (C) Separating the skin from underlying fascia using scissors. (D) Cutting of the skin and preparing for removal. (E-G) Pulling the skin off by going around the mouse. (H) Completely removing the skin from the dorsal side. (I) Complete removal of the skin from the torso, and re-pinning of the mouse limbs. (J) Opening of the abdomen. (K) View of the open abdomen. (L) Moving the organs out of the field of view. (M) Removing the fat. (N) View of the cleared pelvic floor. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. USL harvesting
- Cut the uterine horns from the ovaries (Figure 3B), pull away from the field of view, and cut off at the cervical connection (Figure 3C).
NOTE: The uterine horns can be identified following the schematic in Figure 3A. Irrigate the tissues with 1x PBS to maintain hydration. - Cut the ureters away from the bladder connection (Figure 3D).
NOTE: This is to avoid confusion with the USL. - Cut the colon as close to the cervix as possible (Figure 3E,F).
NOTE: Irrigate the tissues with 1x PBS to maintain hydration. - Place the mouse along with the dissection pad under the dissecting scope to visualize the USLs (Figure 3G).
- Gently use the forceps to clean the surrounding fat from the USLs.
NOTE: Use a second pair of forceps to hold the cervix up at a small angle to enhance the visualization of where the USL intersects with the cervix. Irrigate the tissues with 1x PBS to maintain hydration. - Tie a 5-0 polyglactin suture around the cervical end of both USLs (Figure 4B, C).
NOTE: The USLs can be identified using the schematic and magnification images (Figure 4I-K) - In this study, one USL is used for morphological or biochemical analyses (i.e., Raman microscopy, immunohistochemistry, histology). Cut the cervical end of the USL, leaving a piece of the cervix attached, and cut a piece of muscle from the bottom of the USL (Figure 4D). Place the dissected tissue in a bath with 1x PBS to keep the tissue hydrated (Figure 4G, H).
- Use the remaining USL for mechanical testing and imaging. Cut the cervical end of the USL, leaving a piece of cervix attached, to facilitate the mechanical setup (Figure 4D).
NOTE: The cervical tissue will act as an anchor to secure the USL during the mechanical test. - Once all the tissues of interest are harvested (steps 3-5), dislocate the femurs from the pelvis (Figure 4E).
NOTE: One should hear a faint clicking sound when the femoral head is disarticulated from the acetabular cup. - Cut the pelvic bone from the distal and proximal ends of the pelvic bone, leaving about 10 mm of total tissue (Figure 4F). Place the dissected tissue in 1x PBS.

Figure 3: Cleared pelvic floor for USL dissection. (A) Schematic of the anatomy. (B) Cutting the uterine horns at the ovarian connection. (C) Cutting off uterine horns. (D) Cutting of the ureters. (E) Cutting of the colon. (F) A clear view of the rectum and USLs. (G) Placing the mouse and dissection pad under the dissecting scope. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 4: View of the USL and surrounding tissues and dissection of the USLs. (A) Schematic of anatomical landmarks surrounding the USL. (B) Tying a suture around the cervical ends. (C) Slicing off the cervical ends of the USL. (D) Slicing off the USL to be used for the biochemical analyses at the sacral connection. (E) Cutting of the femurs from the pelvic bone. (F) Cutting off the proximal end of the pelvis. (G) Dissecting the USL in a 35 mm Petri dish. (H) The USL with the attached pelvis in a 35 mm petri dish. (I) The USL and rectum at 0.75x magnification. (J) Removing fat from the USL. (K) Cleaning of the USLs at 1.0x magnification. Scale bar = 2 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Bladder harvesting
- After the fat is cleared, hold the bladder with the forceps, and gently lift it at an angle of approximately 40° (Figure 5A).
- With the scissors, slice off the bladder from the distal side, right above the cervix (Figure 5B).
- Place the tissue in a bath with 1x PBS to keep the tissue hydrated (Figure 5H).
4. Rectum harvesting
- Once the USLs are disconnected from the cervix and the bladder is dissected, lift the cervix at an angle of approximately 40° with the forceps. There is the rectovaginal fascia that connects the rectum and the cervix. With the scalpel, gently cut this connection (Figure 5C, D).
- Cut the pubic bone at the pubic symphysis using scissors. Gently widen the workspace to increase visual access to the tissue insertions.
- With the forceps, gently pull the rectum toward the thorax, and use the scissors to follow the rectum from its posterior side to the anus. Cut the rectum at the anus (Figure 5E).
- Place the tissue in 1x PBS to keep the tissue hydrated (Figure 5I).
5. Cervix-vagina complex harvesting
- After the USLs are removed from the cervix, use the forceps to hold the cervix. Cut the cervix as close to the vulva as possible using scissors (Figure 5F, G).
NOTE: Ensure to cut the pubic symphysis to see the distal end of the vagina visually. - Place the tissue in 1x PBS to keep the tissue hydrated (Figure 5J).
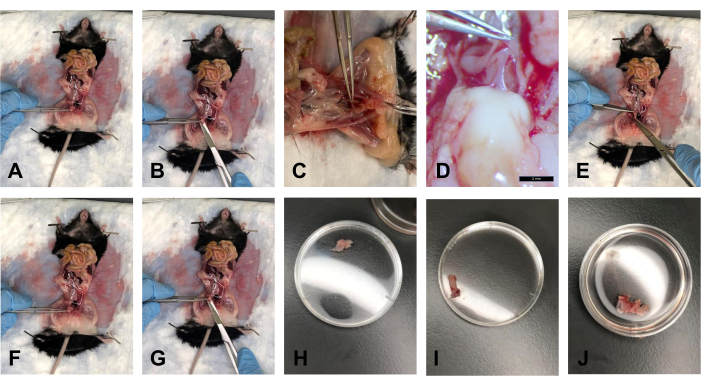
Figure 5: Bladder, rectum, and cervix/vagina dissections. (A) Holding the bladder at an angle. (B) Cutting off the bladder. (C) Cutting the tendon connecting the cervix and rectum. (D) The tendon at 1.0x magnification. (E) Cutting the rectum. (F) Holding onto the cervix with forceps. (G) Cutting at the distal end of the vagina. (H) The bladder in a 35 mm Petri dish. (I) The rectum in a 35 mm Petri dish. (J) The cervix-vagina tissue complex in a 35 mm Petri dish. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
6. Sample preparation for tissue characterization
- Mechanical and visual analyses of the USL
- Place the USL with the pelvic attachment over a T-shaped wall within a custom staining well to ensure full immersion in the staining solution (CAD drawings of the well can be found in Supplementary Coding File 1 and Supplementary Coding File 2).
NOTE: Use suture and forceps to help with the placement. - Dilute a commercially available dye that stains free amine groups (5 µL, see Table of Materials) in 2.5 mL of 1x PBS, add the solution to the custom staining well, and stain the tissue for 2 h on a rocker at 4 °C.
NOTE: Vortex the solution before adding it to the staining well. - During the last 15 min of staining, add 2.5 µL of a commercially available dead cell nuclei stain (see Table of Materials) to the solution.
NOTE: Vortex the solution prior to adding to the staining well.
- Place the USL with the pelvic attachment over a T-shaped wall within a custom staining well to ensure full immersion in the staining solution (CAD drawings of the well can be found in Supplementary Coding File 1 and Supplementary Coding File 2).
- Raman analysis of the USLs
- Pin the USL in a straight line on a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) block that is contained in a custom well.
NOTE: The PDMS is used as a soft substrate to enable the pinning of the sample in the desired configuration. Blocks of varying dimensions can be made by mixing the two components following the manufacturer's instructions (see Table of Materials), casting in a Petri dish, and, after polymerization, cutting the PDMS into the required geometry with a scalpel blade. - Pin with insect pins at the suture loop and at the pelvic muscle. Hydrate the tissue with 1x PBS.
- Pin the USL in a straight line on a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) block that is contained in a custom well.
- Remaining tissues
- Snap-freeze the remaining tissues with liquid nitrogen or in an appropriate embedding compound, depending on the desired analyses.
- Save the tissues at −80 °C until subsequent analyses (e.g., immunohistochemical or biochemical assays).
Results
Each step of the dissection of a wild-type mouse is detailed in the associated video and figures related to the protocol. For this study, 6 week old female C57BL/6J mice were used (Supplementary Table 1). Three sample groups with USLs treated with different enzymes were analyzed: control (no treatment), collagenase-treated, and chondroitinase-treated groups. The smooth muscle, nerves, and lymphatics in the USL are surrounded by an ECM rich in fibrillar collagens and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Discussion
The effect of structural damage on female reproductive tissues is understudied, and an easily accessible animal model for POP research is needed. The mouse is a cost-effective model that can mimic human reproductive studies16. Due to the growing interest in the study of the female reproductive system, there is a need for methods that aid the study of these tissues. To address this need, in this work, a method is established to dissect and prepare murine pelvic floor tissues for structural and func...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the CU Boulder Summer Underground Research Opportunities Program (UROP) grant (C.B.), the NSF Graduate Research Fellowship (L.S.), the Schmidt Science Fellowship (C.L.), the University of Colorado Research & Innovation Seed Grant Program (2020 award to V.F., S.C., and K.C.), and the Anschutz Boulder Nexus Seed Grant at the University of Colorado (to V.F. and K.C.). Special acknowledgment goes to Dr. Tyler Tuttle for help with the loading chamber design as well as the Calve lab members for helpful discussions.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 11 Blade | Fisher | 3120030 | Removable blade |
| 1x PBS | Fisher | BP399-1 | Diluted from 10x concentration |
| Chondroitinase ABC | Sigma | C3667-10UN | Enzyme |
| Collagenase Type I | Worthington Biochemical | LS004194 | Enzyme |
| Confocal Microscope | Leica | STELLARIS 5 | Upright configuration |
| Dissection Microscope | Leica | S9E | With camera |
| Dumont #5 Forceps | Fisher | NC9626652 | Thin tip |
| Female C57BL/6J mice | Jackson Laboratory | strain #: 000664 | |
| FemtoTools Micromanipulator | FemtoTools | FT-RS1002 | 100 mN load cell |
| FST Curved Forceps | Fisher | NC9639443 | Curved tip |
| FST Sharp 9 mm Scissors | Fisher | NC9639443 | Dissection scissors |
| Ghost Dye 780 | Tonbo | 13-0865-T500 | Free amine stain |
| Kimwipes | Fisher | 06-666 | Box of 50 wipes |
| OCT | Tissue Tek | 4583 | Used for tissue preservation |
| PDMS | Thermo Fisher | 044764.AK | Follow manufacturer's instructions |
| Petri Dishes 35 mm | Fisher | FB0875711A | Used for dissected tissue |
| Polyglactin 5-0 Suture | Veter.Sut | VS385VL | With needle |
| Renishaw InVia Raman Microscope | Renishaw | PN192(EN)-02-A | With confocal objectives |
| Rocking Platform | VWR | 10127-876 | 2 tier platform |
| Surgical Gloves | Fisher | 52818 | For dissection |
| Sytox | Thermo Fisher | S11381 | Nuclear stain |
| T-pins | Fisher | S99385 | For dissection |
| Transfer Pipets | Fisher | 13-711-7M | For dissection |
| Underpads | Fisher | 22037950 | To cover dissection pad |
References
- Maldonado, P. A., Wai, C. Y. Pelvic organ prolapse. Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America. 43 (1), 15-26 (2016).
- Drewes, P. G., et al. Pelvic organ prolapse in fibulin-5 knockout mice: Pregnancy-induced changes in elastic fiber homeostasis in mouse vagina. American Journal of Pathology. 170 (2), 578-589 (2007).
- Barber, M. D., Maher, C. Epidemiology and outcome assessment of pelvic organ prolapse. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction. 24 (11), 1783-1790 (2013).
- Becker, W. R., De Vita, R. Biaxial mechanical properties of swine uterosacral and cardinal ligaments. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology. 14 (3), 549-560 (2015).
- Donaldson, K., Huntington, A., De Vita, R. Mechanics of uterosacral ligaments: Current knowledge, existing gaps, and future directions. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 49 (8), 1788-1804 (2021).
- Amundsen, C. L., Flynn, B. J., Webster, G. D. Anatomical correction of vaginal vault prolapse by uterosacral ligament fixation in women who also require a pubovaginal sling. Journal of Urology. 169 (5), 1770-1774 (2003).
- Jelovsek, J. E., Maher, C., Barber, M. D. Pelvic organ prolapse. The Lancet. 396 (9566), 1027-1038 (2007).
- Blomquist, J. L., Muñoz, A., Carroll, M., Handa, V. L. Association of delivery mode with pelvic floor disorders after childbirth. Journal of the American Medical Association. 320 (23), 2438-2447 (2018).
- Iwanaga, R., et al. Comparative histology of mouse, rat, and human pelvic ligaments. International Urogynecology Journal. 27 (11), 1697-1704 (2016).
- Zhu, Y. P., et al. Evaluation of extracellular matrix protein expression and apoptosis in the uterosacral ligaments of patients with or without pelvic organ prolapse. International Urogynecology Journal. 32 (8), 2273-2281 (2021).
- Jimenez, J. M., et al. Multiscale mechanical characterization and computational modeling of fibrin gels. bioRxiv. , (2022).
- Fischenich, K. M., et al. Human articular cartilage is orthotropic where microstructure, micromechanics, and chemistry vary with depth and split-line orientation. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 28 (10), 1362-1372 (2020).
- Luetkemeyer, C. M., Neu, C. P., Calve, S. A method for defining tissue injury criteria reveals ligament deformation thresholds are multimodal. bioRxiv. , (2023).
- O'Brien, C. M., et al. In vivo Raman spectroscopy for biochemical monitoring of the human cervix throughout pregnancy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 218 (5), 1-18 (2018).
- Louwagie, E. M., et al. et al. ultrasonic dimensions and parametric solid models of the gravid uterus and cervix. PLoS One. 16 (1), 0242118 (2021).
- Drewes, P. G., et al. Pelvic organ prolapse in fibulin-5 knockout mice. The American Journal of Pathology. 170 (2), 578-589 (2007).
- Rahn, D. D., Ruff, M. D., Brown, S. A., Tibbals, H. F., Word, R. A. Biomechanical properties of the vaginal wall: Effect of pregnancy, elastic fiber deficiency, and pelvic organ prolapse. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 198 (5), 1-6 (2008).
- Roman, S., et al. Evaluating alternative materials for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse: A comparison of the in vivo response to meshes implanted in rabbits. Journal of Urology. 196 (1), 261-269 (2016).
- Couri, B. M., Lenis, A. T., Borazjani, A., Paraiso, M. F., Damaser, M. S. Animal models of female pelvic organ prolapse: Lessons learned. Expert Review of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 7 (3), 49 (2012).
- Abramowitch, S. D., Feola, A., Jallah, Z., Moalli, P. A. Tissue mechanics, animal models, and pelvic organ prolapse: A review. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecologyand Reproductive Biology. 144, S146-S158 (2009).
- Tan, T., Cholewa, N. M., Case, S. W., De Vita, R. Micro-structural and biaxial creep properties of the swine uterosacral-cardinal ligament complex. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 44 (11), 3225-3237 (2016).
- Tan, T., et al. Histo-mechanical properties of the swine cardinal and uterosacral ligaments. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 42, 129-137 (2015).
- Baah-Dwomoh, A., Alperin, M., Cook, M., De Vita, R. Mechanical analysis of the uterosacral ligament: Swine vs. human. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 46 (12), 2036-2047 (2018).
- Vardy, M. D., et al. The effects of hormone replacement on the biomechanical properties of the uterosacral and round ligaments in the monkey model. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 192 (5), 1741-1751 (2005).
- Shahryarinejad, A., Vardy, M. D. Comparison of human to macaque uterosacral-cardinal ligament complex and its relationship to pelvic organ prolapse. Toxicological Pathology. 36 (7), 101 (2008).
- Smith, T. M., Luo, J., Hsu, Y., Ashton-Miller, J., DeLancey, O. L. A novel technique to measure in vivo uterine suspensory ligament stiffness. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 209 (5), 1-7 (2013).
- Vandamme, T. F. Use of rodents as models for human diseases. Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences. 6 (1), 2-9 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved