A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Using Low-Cost Dyes to Visualize Glycogen Accumulation and Gut Integrity in Caenorhabditis elegans
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Teaching biological sciences can be made more stimulating for students through the use of experimentation. This manuscript presents two different yet complementary protocols that can be utilized in the classroom to encourage students to formulate and test hypotheses related to high-calorie diets, starvation, and aging.
Abstract
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is a transparent, non-parasitic nematode with a simple biology, which makes it a great tool for biological sciences teaching through the staining of the cells or their molecular content. Lugol dye (iodine-potassium iodide solution) has been widely used in biochemistry to stain glycogen stores. In this context, it is possible to observe differences between fed and starved animals, besides the effects of different conditions, such as different diets and oxygen levels. Erioglaucine is a blue dye that indicates the loss of the intestinal barrier. When the intestinal barrier is intact, the blue dye stains inside the lumen; however, when this integrity is disrupted, the dye leaks into the body cavity. Using a stereomicroscope or a microscope, teachers can demonstrate physiological and biochemical alterations, or they can instigate students to ask a scientific question and hypothesize and test their hypothesis using these assays. The present protocol describes two staining techniques in C. elegans that can be easily carried out by students.
Introduction
Biological sciences teaching in high school is a continuous challenge. Notably, the access and use of technology have brought important advances in the teaching-learning process, however, tools such as artificial intelligence chatbots make rationalizing and seeking evidence more difficult due to easy (and sometimes incorrect) responses obtained1. Because of that, the use of a scientific method with practical experimentation in an inquiry-based approach in the classroom is an important strategy to develop or stimulate critical thinking, creativity, and technical skills in the students2.
In this context, the free living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has been successfully used in experimentation for teaching purposes3 because of its particular advantages: It is not a parasite and the Escherichia coli used for feeding is biosafety level-1, therefore reducing near to zero the biological hazard; it has an elegant and quantifiable locomotion movement, which is interesting for students to observe; and it is transparent, which allows organ observation, but also staining with pigments that can indicate the presence of biomolecules or the occurrence of physiological alterations4. Therefore, it is possible to hypothesize and test in the classroom simple postulations related to biochemistry and physiological changes such as aging.
Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate, formed by a long and branched chain of glucose molecules formed by glucosyl residues with (1→4)-α glycosidic linear linkages and (1→6)-α glycosidic bonds at branch points and is particularly important for muscle contraction, cell differentiation and glycemia maintenance5. Glycogen is synthesized after feeding due to insulin activation of the enzyme glycogen-synthase. During exercise or fasting, epinephrine or glucagon, respectively, activate glycogen phosphorylase and, therefore, break down the polysaccharide to provide glucose-6-phosphate to the muscle cells or release free glucose to circumvent hypoglycemia6,7. Alterations in glycogen levels impacts cell differentiation, signaling, redox regulation, and stemness under various physiological and pathophysiological conditions, including cancer8. In C. elegans, glycogen is mainly found in esophageal muscle, hypodermis, intestine, neurons and mainly in body wall muscles9. The glycogen content can be measured by using Lugol's Iodine solution, since iodine binds into the helical coils forming an iodine-glycogen complex, giving a visible sharp blue-black or brown-black color, which has been successfully used to demonstrate glycogen content in C. elegans10. It has been demonstrated that glycogen accumulation caused by high glucose feeding can reduce worm's lifespan, therefore accelerating the aging process11,12. In addition, metabolic disturbances, other hormones, and exposure to xenobiotics can alter glycogen metabolism as well13,14. Therefore, experimentation on glycogen content in C. elegans is quite interesting, since diverse factors may disturb its metabolism and can stimulate an in-class discussion on basic biochemistry associated with transversal themes such as exercise, diets, diseases, and aging.
Aging is a time-dependent functional decline caused by cellular damage. This damage can be associated with oxidative stress, telomere attrition, loss of proteostasis, inflammation and even by accumulation of insoluble polyglucosan bodies15, just to name a few. One of the hallmarks of aging is the reduction of intestinal integrity, associated with several chronic conditions that occur during the life of an organism16. Maintenance of intestinal homeostasis depends on the integrity of the intestinal epithelium, which is supported by junctional proteins forming a physical barrier and connecting adjacent epithelial cells. When there is damage to this epithelium, leakage of luminal content into the interstitium occurs17. Based on this mechanism, the smurf test has been used to verify intestinal integrity in several animal models, since this blue dye Erioglaucine disodium salt does not cross the intestinal membrane, remaining in the lumen18. When worms are infected with a pathogen, contaminated with some toxicants or age, altering the interstitial integrity, the dye crosses the barrier and spreads all over the worm, which becomes all blue. This assay allows discussion on the physiology of aging and experimenting on factors that can accelerate or delay this process by exposing worms to different conditions. The protocols here will describe in detail these two, dye-based methods that can be easily done in class to instigate and stimulate students to formulate and test hypotheses related to biochemistry and physiology.
The first part of protocol shows its applicability to analyze qualitatively and quantitatively the glycogen content in C. elegans model10. The purpose of second part of the protocol is to assess the integrity of the C. elegans intestine. This technique allows for the monitoring of C. elegans aging by evaluating the integrity of the intestinal membranes. Furthermore, it allows evaluating whether a substance accelerates or delays aging and whether any substances have toxic potential on the intestinal barrier19.
The C. elegans strain used for the present study was Bristol N2 wild type. However, the procedure can be replicated using strains that exhibit comparable growth rates, or the method must be adjusted based on need of equipment replacement, considering they have the same or similar function, or depending on the strain used, as certain strains have specific maintenance and/or sensitivity requirements; this information can be obtained from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) or WormBase website. These changes should not impact the reproducibility of the method.
Protocol
NOTE: Escherichia coli OP50 (E. coli OP50) bacteria and Bristol N2 wild type strains can be obtained from the CGC, University of Minnesota, USA or from donation from a C. elegans laboratory. For researchers' safety, it is imperative to use Personal Protective Equipment. Although the concentrations of reagents like hypochlorite and sodium hydroxide are low, it is essential to wear the recommended PPE, as highlighted in the manuscript, to minimize any potential risks associated with these chemicals.
1. Glycogen content
- Preparation of test plates
- Prepare six, 60 mm x 15 mm NGM agar plates20 (10 mL of nematode growth media agar, NGM, as described in Supplementary Table 1) per worm strain and allow them to dry for 1 day at room temperature. Keep the plates closed to prevent contamination.
- Add 200 µL of E. coli OP50 liquid culture (with an optical density = 0.600, approximately at a wavelength of 600 nm) per plate to inoculate a total of four, 60 mm x 15 mm NGM plates per strain in the flow hood. Allow the closed plates to incubate at 37 °C for 1 day before use.
NOTE: Prepare six plates (step 1.1) but inoculate only 4 with E. coli OP50 bacteria. Reserve the remaining two plates at 4 °C for later use when placing the worms under starvation conditions. This analysis may be performed in duplicate. - On the test day, add 200 µL of 0.025 M D-Glucose to two (6 mm x 15 mm) NGM agar plates per strain that were previously seeded with E. coli OP50 bacteria. Allow the plates to dry at room temperature in the flow hood.
NOTE: The NGM agar plates seeded with E. coli OP50 bacteria can also be dried near to alcohol lamps as an alternative to using a flow hood.
- Synchronization
- Approximately 3 days before the synchronization, transfer 3-4 chunks (3 cm x 3cm) from a maintenance NGM agar with C. elegans Bristol N2 (wild type) at different stages (around 500 worms per chunk) to a new plate (150 mm x 90 mm) that has been previously seeded with E. coli OP50 bacteria.
- Place the new plate with worms in a controlled environment at 20 °C and maintain humidity >95% for 3 days (72 h allow most of the worms to reach the gravid adult stage).
NOTE: The growth temperature may need to be adjusted depending on the C. elegans strain(s) being used. - Using a Pasteur pipette, collect the worms from the prepared plate with distilled H2O and transfer them to a 50 mL centrifuge tube.
- Wait for the sedimentation of the worms by gravity (approximately 15 min) and then remove the supernatant. Repeat this process 3x to eliminate the bacteria. After the last wash, reduce the volume to 5 mL.
- Add 10 mL of bleaching solution (Supplementary Table 1) and vigorously shake using the hands for approximately 6 min.
- Immediately after the shaking is complete, fill the tubes to 50 mL capacity with M9 buffer.
- Centrifuge at 1400 x g for 3 min, remove the supernatant up to 5 mL and then add 45 mL of M9 buffer again. Repeat this process 4x.
- After the last wash, reduce the volume to 15 mL and maintain it at a controlled temperature (20 °C) and humidity (>95%) for approximately 14 h.
NOTE: The synchronization process can be replaced by obtaining eggs through oviposition: Transfer approximately 20 adult pregnant worms to an NGM plate (6 mm x 15 mm) previously seeded with 200 µL of E. coli OP50. Allow the worms to lay eggs for 1 day. After that, remove the pregnant worms and wait for the eggs to hatch.
- Preparation of worms
- Using an automatic pipette add 10 µL of the synchronized worms (step 1.2.8) to a microscope slide and count the number of worms. Calculate how much volume must be pipetted to obtain 500-1000 worms/µL.
- Transfer 500-1000 L1 synchronized worms (step 1.2.8) to NGM agar plates (150 mm x 90 mm, Supplementary Table 1) seeded with E. coli OP50 bacteria as a food source, until they reach the larvae stage 4 (L4) at 20 °C.
NOTE: Worms can be transferred using an automatic pipette. If an automatic pipette is not available, use a glass Pasteur pipette, and volumes can be controlled using microtube labels or glass graduated pipettes. - After 48 h of synchronization20: collect the L4 larvae from the plates with M9 buffer (Supplementary Table 1), with the aid of a plastic Pasteur pipette to a clean conical tube 50 mL and wash them 3x with fresh M9 buffer or repeat the washes until all remaining E. coli OP50 bacteria are completely removed (at room temperature).
NOTE: The washing step is important because some worms will experience starvation during the procedure.
- Running the assay
- Transfer 500-1000 L4 worms (step 1.3.1) from each of the new NGM agar plates (60mm x 15mm) previously prepared (steps 1.1.2 and 1.1.3). Keep them at 20 °C for 48 h until the test day. This schedule will result in three experimental groups as following, in duplicate (Figure 1):
A- (starvation): worms will grow on regular NGM agar plates without E. coli OP50 bacteria;
B- (regular): worms will grow on regular NGM agar plates seeded with E. coli OP50 bacteria;
C- (high glucose): worms will grow on NGM agar plates seeded with E. coli OP50 bacteria and containing 0.025 M D-glucose. - On the test day (after 48 h): collect the worms and give them three brief washes in the M9 buffer (steps 1.2.2 and 1.2.3)
NOTE: Here, prepare NGM agar plates with the addition of D-glucose (step 1.3) and set them aside until it is time to add the worms.- Iodine staining: prepare a 5% (v/v) Lugol's Iodine solution (iodine/potassium iodide solution) using fresh M9 buffer.
NOTE: Lugol's Iodine solution can be obtained from local reagent suppliers or pharmacies, therefore the initial concentration may vary. If necessary, calculate to obtain a 5% (v/v) solution.
- Iodine staining: prepare a 5% (v/v) Lugol's Iodine solution (iodine/potassium iodide solution) using fresh M9 buffer.
- Transfer approximately 100 µL of washed worms (step 4.2) from each group to the 1.5 mL microtube containing diluted Lugol solution (5% v/v). Using an automatic pipette in a 1:5 proportion transfer 100 µL of worms to 400 µL of Lugol solution, followed by gentle agitation in a mixer for 5 min.
NOTE: If a mixer is unavailable, it is possible to shake the microtubes carefully by hands. - Right after these 5 min, centrifuge the 1.5 mL microtube (worms + Lugol solution) at 1400 x g for 3 min.
NOTE: If this assay is performed on worms from the L4 stage or beyond, it is possible to achieve gravity sedimentation instead of using a centrifuge. Leave the microtubes open in racks on the benchtop for 10 min until all the worms have settled at the bottom of the microtube. - Remove the supernatant and wash the worms with 1.0 mL of fresh M9 buffer. Repeat the wash until all remaining iodine is removed from the solution (minimum 3x).
- After the last washing step, remove the supernatant except for a residual of approximately 100 µL. Use this to gently resuspend the worms and for microscopic analysis.
- Transfer approximately 50 µL of the resuspended worm solution to microscopy slides and cover them with cover slips. Observe the bright field images using a stereomicroscope (at 1.5x).
NOTE: If a stereomicroscope is unavailable, a regular microscope can be used, and images can be captured with a cell phone camera (at 3.4x) using an adapter. To prevent errors from light/brightness/exposure, it is crucial that all cell phone camera settings remain consistent for all pictures.
- Transfer 500-1000 L4 worms (step 1.3.1) from each of the new NGM agar plates (60mm x 15mm) previously prepared (steps 1.1.2 and 1.1.3). Keep them at 20 °C for 48 h until the test day. This schedule will result in three experimental groups as following, in duplicate (Figure 1):
- Data inspection
- Quantitative data: Calculate the glycogen content based on the iodine staining of worms.
- Save images from stereomicroscope containing a minimum of 10 worms per group as a .jpeg file for further processing. Download the free ImageJ software to do this. Details are provided in Supplementary File 1, Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Figure 2.
- Open the .jpeg image using ImageJ software (which can be downloaded for free at https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/download.html). Click on Segmented line and outline the worm (one worm at a time). Click on Analyze, and then select Measure to obtain the stain quantification. The data will be displayed as the Mean in the table. Mean indicates the data calculated from staining density per worm area.
- Qualitative data: Obtain images from the stereomicroscope of each group and visually compare the staining of the worms. Create a scoring system, if needed, to analyze the staining: 0 colorless; 1 lightly stained; 2 stained and 3 heavily stained. Using the stereomicroscope, manually count approximately 10 worms per group (minimum) with a hand counter.
- Quantitative data: Calculate the glycogen content based on the iodine staining of worms.
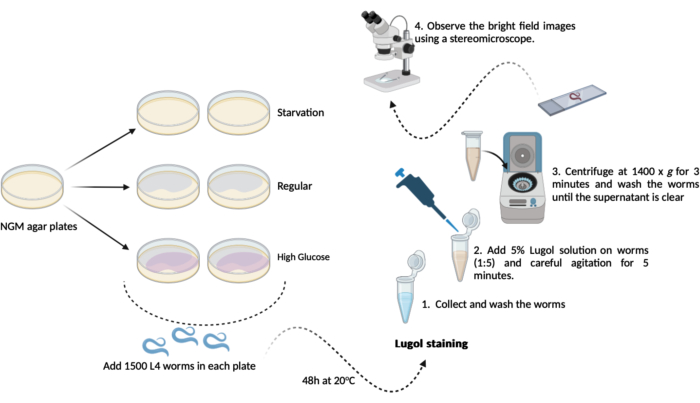
Figure 1: Overall glycogen content assay schematic in C. elegans. A schematic of the experimental performed here to carry out the glycogen content assay. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Evaluation of intestinal permeability
- Preparation of worms
- Approximately 14 h after synchronization (step 1.2.8), transfer 500-1000 worms (step 1.3.1 and NOTE) at the first larval stage (L1) to each new NGM agar plate (60 mm x 15 mm) previously prepared and keep them at 20 °C until the day of the test. This schedule will lead to two experimental groups as follows (Figure 2):
A- (young): worms will grow on NGM agar plates seeded with the bacteria E. coli OP50 until larval stage 4 (L4);
B- (old): the worms will grow on NGM agar plates seeded with the bacteria E. coli OP50 until the 7th day of adulthood.
NOTE: The worms maintained until the 7th day of adulthood must be washed with M9 buffer every day and transferred to new NGM agar plates (60 mm x 15mm) with 200 µL of E. coli OP50 bacteria previously seeded for food replacement and removal of the progeny. Younger worms float during decantation and can be separated by removing supernatant. The proportion of smurf worms increases with age. However, the evaluation of intestinal permeability can be performed at any stage and age, depending on the purpose of the study.
- Approximately 14 h after synchronization (step 1.2.8), transfer 500-1000 worms (step 1.3.1 and NOTE) at the first larval stage (L1) to each new NGM agar plate (60 mm x 15 mm) previously prepared and keep them at 20 °C until the day of the test. This schedule will lead to two experimental groups as follows (Figure 2):
- Running the assay
- On the test day, collect L4 worms (2 days after step 2.1.1) and adulthood worms on 7th day (now in their 9th day) with M9 buffer (Supplementary Table 1) and transfer to labeled 1.5 mL microtubes.
- Centrifuge at 1400 x g for 3 min, remove the supernatant, add 1.0 mL of M9, and mix gently. Repeat this process 3x to remove the bacteria. After the last wash, reduce the volume to 500 µL.
- Using an automatic pipette, add 10 µL of the worm sediment to a microscope slide and count the number of worms. Calculate the volume to be pipetted to obtain 100 worms/µL.
- Smurf staining: prepare a 25% Erioglaucine disodium salt (Supplementary Table 1) solution using distilled water. If necessary, use the vortex for better solubilization.
- In new previously identified microtubes, using an automatic pipette, add the volume containing 100 worms, 100 µL of 25% Erioglaucine disodium salt solution, 200 µL of E. coli OP50 and complete with M9 buffer for a final volume of 500 µL.
NOTE: The volumes of Erioglaucine disodium, E. coli and number of worms are fixed. The volume of the M9 buffer is variable and can be used to bring the final volume to 500 µL. - Incubate for 3 h with agitation in a mixer, protected from light, at room temperature.
NOTE: If a mixer is unavailable, shake the microtubes carefully with your hands every 15 min. - After 3 h, centrifuge the 1.5 mL microtube at 1400 x g for 3 min. Remove 1.0 mL of supernatant and wash the worms with 1.0 mL of M9 buffer.
- Repeat washes until the remaining Erioglaucine disodium salt solution is removed from the solution. After the last washing step, remove the supernatant except for a residual of approximately 250 µL. Use this to carefully resuspend worms and process them for microscopic analysis.
- Transfer approximately 50 worms of resuspended worm solution to microscopy slides and cover them with cover slips. Incubate the microscopy slides in the refrigerator at -20 °C for 10 min to paralyze the worms.
NOTE: Another alternative to paralyze the worms is to add 10 µL of Levamisole hydrochloride solution (10 mM ; Supplementary Table 1) and cover them with cover slips. - Observe and count the total number of worms and the totally dyed worms using the bright field in a stereomicroscope (at 1.5x). Images can be obtained from a cell phone camera (at 3.4x) coupled with an adapter. To prevent errors from light/brightness/exposure, it is crucial that all cell phone camera settings remain consistent for all pictures.
- Data inspection
- Qualitative data: Obtain images from stereomicroscope of each group (L4 and 7th day of adulthood) and visually compare the staining of the worms.
- Count the total number of worms and the number of smurf worms (blue worms) using a stereomicroscope.
- Express results as the percentage of smurf worms by comparing the young worms (L4, as a control group) and old worms (7th day of adulthood):
A x X = 100 (%) x B
X = 100 x B / A
Where, A = total number of worms
B= number of smurf worms

Figure 2: Overall intestinal permeability assay schematic in C. elegans. (A) C. elegans preparation. (B) Staining with Erioglaucine disodium salt. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
The glycogen content assay provides a robust and rapid method for screening various testing conditions, such as comparative studies of different strains that may influence glycogen synthesis or degradation. In this study, L4 worms were subjected to three distinct test conditions: fasting, feeding, and glucose-enriched groups. The assay was performed three times, with each condition replicated twice in each assay; a representative image is displayed in Figure 3. Following each assay, worms st...
Discussion
In summary, this protocol provides a qualitative evaluation of glycogen content in individual C. elegans worms using Lugol staining: a straightforward, robust, and swift assay. Lugol staining is a label-free and non-invasive approach that facilitates the acquisition of molecular data at subcellular resolutions, allowing for the monitoring of glycogen content fluctuations within single worms10. Furthermore, the assay offers the advantage of cost-effectiveness due to its minimal equipment r...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
D.S.A acknowledges funding from Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento (CNPq/Brazil), grant number #301808/2018-0, #313117/2019-5, Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS/Brazil), grant number, 21/2551-0001963-8, Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, Finance Code 001 for N.S.J and A.C.S)
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1.5 mL microtubes | Local suppliers | - | |
| 37-degree incubator | KS 4000i | 97014-816 | |
| 50 mL conical tube | Local suppliers | - | |
| 6 cm Petri plates | Local suppliers | - | |
| Agar bacteriological | Dinâmica Química Contemporânea Ltda. | 9002-18-0 | |
| C. elegans Bristol N2 (wild type) | Caenorhabditis elegans Genetic Center (CGC, Minnesota, USA) | - | |
| CaCL2 | Dinâmica Química Contemporânea Ltda. | 10035-04-8 | |
| Cholesterol | Sigma-Aldrich Brasil Ltda | 57-88-5 | |
| D-(+)-Glucose anhydrous | Neon | 50-99-7 | |
| Distilled H2O | Local suppliers | - | |
| Erioglaucine disodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich Brasil Ltda | 3844-45-9 | |
| Escherichia coli OP50 | Caenorhabditis elegans Genetic Center (CGC, Minnesota, USA) | - | |
| Flow hood | Mylabor | ||
| Incubator | Panasonic Healthcare company of North America, MIR-254-PA. | - | |
| KH2PO4 | Dinâmica Química Contemporânea Ltda. | 7778-77-0 | |
| Levamisole hydrochloride | RIPERCOL L 150F | - | |
| Lugol solution | Sigma-Aldrich Brasil Ltda | L6146 | |
| MgSO4 | Synth | S1063-01-AH | |
| Microcentrifuge | Centrifuge 5425R Eppendorf SE, Germany | ||
| Na2HPO4 | Dinâmica Química Contemporânea Ltda. | 7558-79-4 | |
| NaCl | Dinâmica Química Contemporânea Ltda. | 7647-14-5 | |
| Nystatin | Sigma-Aldrich Brasil Ltda | N6261 | |
| Peptone bacteriological | êxodo científica | 91079-38-8 | |
| Stereomicroscope | Leica S8 Apo Stereomicroscope (São Paulo, Brazil) | ||
| Streptomycin Sulfate | Estreptomax | - |
References
- Thorp, H. H. ChatGPT is fun, but not an author. Science. 379 (6630), 313 (2023).
- Lemons, M. L. An inquiry-based approach to study the synapse: Student-driven experiments using C. elegans. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 15 (1), A44-A55 (2016).
- Andersen, J., Krichevsky, A., Leheste, J. R., Moloney, D. J. Caenorhabditis elegans as an undergraduate educational tool for teaching RNAi. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 36 (6), 417-427 (2008).
- Martins, R. R., McCracken, A. W., Simons, M. J. P., Henriques, C. M., Rera, M. How to catch a smurf? - Ageing and beyond... In vivo assessment of intestinal permeability in multiple model organisms. Bio Protoc. 8 (3), e2722 (2018).
- Ellingwood, S. S., Cheng, A. Biochemical and clinical aspects of glycogen storage diseases. J Endocrinol. 238 (3), R131-R141 (2018).
- Cori, C. F., Cori, G. T. Glycogen formation in the liver from d-and l-lactic acid. J Bio Chem. 81 (2), 389-403 (1929).
- Wosilait, W. D., Sutherland, E. W. The relationship of epinephrine and glucagon to liver phosphorylase. II. Enzymatic inactivation of liver phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 218 (1), 469-481 (1956).
- Zhang, H., Ma, J., Tang, K., Huang, B. Beyond energy storage: roles of glycogen metabolism in health and disease. FEBS J. 288 (12), 3772-3783 (2021).
- Liu, Q., et al. Characterization of glycogen molecular structure in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans. Carbohydr Polym. 237, 116181 (2020).
- Cherkas, A., et al. Label-free molecular mapping and assessment of glycogen in C. elegans.Analyst. 144 (7), 2367-2374 (2019).
- Gusarov, I., et al. Glycogen controls Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan and resistance to oxidative stress. Nat Commun. 8, 15868 (2017).
- Seo, Y., Kingsley, S., Walker, G., Mondoux, M. A., Tissenbaum, H. A. Metabolic shift from glycogen to trehalose promotes lifespan and healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 115 (12), E2791-E2800 (2018).
- Frazier, H. N., Roth, M. B. Adaptive sugar provisioning controls survival of C. elegans embryos in adverse environments. Curr Biol. 19 (10), 859-863 (2009).
- da Silva, F. N., Zimath, P. L., do Amaral, T. A., Martins, J. R. N., Rafacho, A. Coadministration of olanzapine causes minor impacts on the diabetogenic outcomes induced by dexamethasone treatment in rats. Life Sci. 322, 121660 (2023).
- Gusarov, I., Nudler, E. Glycogen at the crossroad of stress resistance, energy maintenance, and pathophysiology of aging. Bioessays. 40 (9), e1800033 (2018).
- Untersmayr, E., Brandt, A., Koidl, L., Bergheim, I. The intestinal barrier dysfunction as driving factor of inflammaging. Nutrients. 14 (5), 949 (2022).
- Lin, P. Y., Stern, A., Peng, H. H., Chen, J. H., Yang, H. C. Redox and metabolic regulation of intestinal barrier function and associated disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 23 (22), 14463 (2022).
- Dambroise, E., et al. Two phases of aging separated by the Smurf transition as a public path to death. Sci Rep. 6, 23523 (2016).
- Laranjeiro, R., et al. Swim exercise in Caenorhabditis elegans extends neuromuscular and gut healthspan, enhances learning ability, and protects against neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 116 (47), 23829-23839 (2019).
- Stiernagle, T. Maintenance of C. elegans.WormBook. , 1-11 (2006).
- McGhee, J. D. The C. elegans intestine. WormBook: The Online Review of C. elegans Biology. , (2007).
- McGee, M. D., et al. Loss of intestinal nuclei and intestinal integrity in aging C. elegans. Aging Cell. 10 (4), 699-710 (2011).
- Gelino, S., et al. Intestinal autophagy improves healthspan and longevity in C. elegans during dietary restriction. PLoS genetics. 12 (7), e1006135 (2016).
- Rera, M., Clark, R. I., Walker, D. W. Intestinal barrier dysfunction links metabolic and inflammatory markers of aging to death in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109 (52), 21528-21533 (2012).
- Zhang, G., Gu, Y., Dai, X. Protective effect of bilberry anthocyanin extracts on dextran sulfate sodium-induced intestinal damage in Drosophila melanogaster. Nutrients. 14 (14), 2875 (2022).
- Gelino, S., et al. Intestinal autophagy improves healthspan and longevity in C. elegans during dietary restriction. PLoS Genet. 12 (7), e1006135 (2016).
- Qu, M., Xu, K., Li, Y., Wong, G., Wang, D. Using acs-22 mutant Caenorhabditis elegans to detect the toxicity of nanopolystyrene particles. Sci Total Environ. 643, 119-126 (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved