A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Intracameral Injection in Rats with Low Risk of Adverse Effects
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes a technique for intracameral injection in rats using a central corneal incision and a long tunnel into the anterior chamber. This injection method minimizes the risk of inducing inadvertent tissue damage and thereby improves precision and reproducibility.
Abstract
Intracameral injection is a standard administration routine in ophthalmology. The application of intracameral injection in rodents for research is challenging due to the limiting dimensions and anatomy of the eye, including the small aqueous humor volume, the lens curvature, and lens thickness. Potential damage during intracameral injections introduces adverse effects and experimental variability. This protocol describes a procedure for intracameral injection in rats, allowing precision and reproducibility.
Sprague-Dawley rats were used as experimental models. Since the lens position in rats protrudes into the anterior chamber, injecting from the periphery, as done in humans, is unfavorable. Therefore, an incision is created in the central corneal region using a 31 gauge 0.8 mm stiletto blade to form a self-sealing tunnel into the anterior chamber. An incision at an angle close to the flat allows to create a long tunnel, which minimizes the loss of aqueous humor and shallowing of the anterior chamber. A 34 gauge nanoneedle is inserted into the tunnel for injection. This enables penetration with minimal friction resistance and avoids touching the lens. Injection of trypan-blue allows visualization by slit microscopy the presence of the dye in the anterior chamber and exclude leakage. Bioavailability to the corneal endothelial layer is demonstrated by injection of Hoechst dye, which stained the nuclei of corneal endothelial cells after injection.
In conclusion, this protocol implements a procedure for accurate intracameral injection in rats. This procedure may be used for intracameral delivery of various drugs and compounds in experimental rat models, increasing the efficiency and reproducibility of ophthalmic research.
Introduction
The bioavailability of compounds delivered by topical administration to the surface of the eye is greatly limited, typically <5%1. Compounds administered by eye drops are mainly eliminated by drainage, induced lacrimation, tear fluid turnover, and conjunctival absorption. In addition, the permeation of compounds through the ocular surface is highly restricted by the cornea-conjunctiva barrier1,2,3. The cornea is composed of three main layers: the outermost epithelium, the intermediate stroma, and the innermost endothelium. The superficial corneal epithelium is interconnected by strong tight junctions and creates high paracellular resistance, which is the main barrier to substance permeability. Multiple epithelium layers further limit the permeation of hydrophilic and large molecules through the intercellular spaces of the cornea epithelium. Succeeding the epithelium, the stroma is composed of collagen fibers and contains aqueous pores. In contrast to the corneal epithelium, the stroma allows the movement of hydrophilic drugs; however, it is greatly impermeable to lipophilic compounds1,2,3. Together, the corneal epithelium and stromal layers present major tissue barriers that limit drug absorption. The corneal endothelium is not considered to restrict drug transport.
Alternative to the corneal delivery route is the conjunctival route. The conjunctiva is a multi-epithelium layer that covers the inner side of the eyelids and the anterior part of the sclera. The conjunctiva is characterized by fewer tight junctions than the corneal epithelium, allowing better permeability of hydrophilic drugs. However, vascularization of the conjunctiva results in systemic absorption of a large fraction of the administered molecules, again greatly limiting the bioavailability of delivered compounds to the anterior chamber1,2. An efficient way to bypass the outer ocular permeability barriers is to deliver the drug directly into the region of interest. For example, intravitreal injection is common for delivery into the vitreous humor4. Likewise, intracameral injection is utilized for delivery into the anterior chamber5. Establishing an efficient concentration at the anterior chamber is critical to various clinical situations, such as the treatment of infection by intracameral injection of antibiotics and postoperative anti-inflammatory treatments in cataract surgeries. Despite the advantage of improved substance bioavailability granted by intracameral injection, there are major safety concerns that should be considered. For example, intracameral drug injection may induce increased intraocular pressure, toxic anterior segment syndrome, and toxic endothelial cell destruction syndrome5,6. It is, therefore, essential to carefully assess in pre-clinical studies the efficacy and safety of drugs delivered by intracameral injections to maximize treatment efficiency and minimize potential adverse effects in patients.
Experimental animal models are indispensable in pre-clinical studies to investigate new treatments. Small rodents, such as mice and rats, are the most commonly utilized laboratory animals for such purposes. These animals exhibit numerous similarities to human anatomy and physiology, providing valuable insights. Moreover, their use is economically advantageous due to their small size, ease of maintenance, fast gestation, and ability to produce large numbers of offspring7.
Despite the widespread use of small rodents in eye disease models, their unique eye dimensions and anatomy pose significant challenges during experimental manipulations. For instance, procedures like intracameral injections, which are relatively straightforward in humans, become technically demanding in mice and rats. The challenges stem from factors such as the small volume of aqueous humor, the relatively large and inflexible lens, and the obstructive positioning and curvature of the lens within the rodents' eyes (Figure 1)8. These challenges increase the risk of damage during intracameral injections in rodents, leading to potential adverse effects and introducing experimental variability that can impact the validity of study conclusions. In our research, we have successfully developed a procedure for safe intracameral injection in rats. The technique involves creating a long, flat, self-sealing tunnel in the cornea into the anterior chamber. This method not only ensures precision but also enhances experimental reproducibility, addressing the issues associated with injection techniques in small rodents.
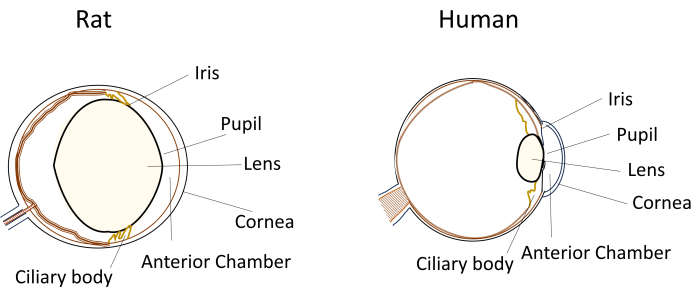
Figure 1: Schematic representation of the anatomical anterior segment features of rat and human eyes. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
The experiments in the protocol were approved by the National Permit Committee - for animal science and comply with the ARVO Statement the use of animals in ophthalmic and vision research. Female Sprague-Dawley rats, aged 8-10 weeks, were used for the present study and were exposed to 12/12 h light-dark cycles. The animals were obtained from a commercial source (see Table of Materials).
1. Animal preparation
- Prepare an anesthetic mixture of ketamine (80 mg/kg body weight in 0.8 mL) and xylazine (4 mg/kg body weight in 0.2 mL) and inject it intraperitoneally in a single injection to anesthetize the rats.
- Inject analgesic buprenorphine (0.03 mg/kg) intraperitoneally in a single injection.
- Apply topical ophthalmic anesthetic 0.4% oxybuprocaine to both eyes.
2. Creating a self-sealing corneal tunnel
- Stabilize the eye by holding the superior sclera at the vertical midline next to the corneoscleral junction with surgical ophthalmic forceps.
- Under a surgical microscope, place a sterile 0.8 mm, 31 G stiletto blade in the paracentral corneal region in the vertical midline (above the center of the pupil) in a flat position at an angle as close as possible to horizontal (Figure 2).
- In this position, puncture the cornea to make an incision and create a long tunnel (2-3 mm) until it penetrates into the central area of the anterior chamber. Avoid touching the lens (Figure 2).
NOTE: A successful tunnel will not induce leakage of the aqueous humor and shallowing of the anterior chamber. - Apply topical 0.3% ofloxacin and 0.1% dexamethasone to the injected eye.
- Examine under slit microscopy as follows.
- Observe the depth of the anterior chamber of the injected eye compared to the non-injected eye.
NOTE: The depth should be similar. - Observe the lens of the injected eye compared to the non-injected eye.
NOTE: The lens should be clear. Opacity may reflect lens damage during the surgical procedure.
- Observe the depth of the anterior chamber of the injected eye compared to the non-injected eye.
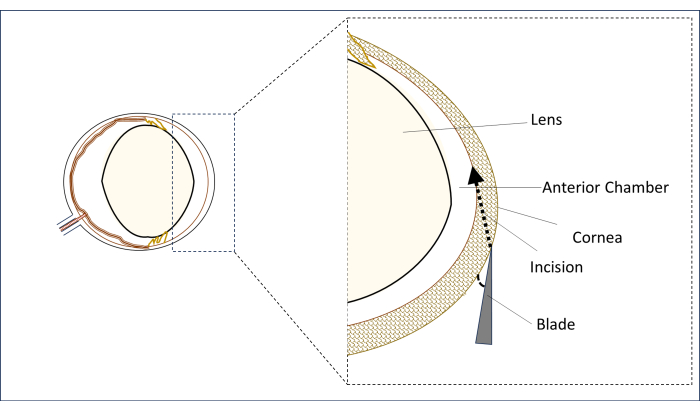
Figure 2: Schematic representation of the blade and incision angle and position. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Option 1: Intracameral injection of trypan blue for assessing the successful injection into the anterior chamber
- Load 5 µL of trypan blue into a sterile 10 µL glass Hamilton syringe with a 34 G blunt needle.
NOTE: Injection of trypan blue is described as a means to evaluate the success of injection during the model calibration or setup stages. In the experimental settings, the syringe may be loaded with a solution of the compound of choice. - Insert the loaded syringe needle through the tunnel created in section 2 into the anterior chamber.
- Inject and hold the needle in place after injection for 2-3 seconds until all fluid clears.
- Remove the needle by pulling it out gently and slowly to avoid leakage from the corneal tunnel.
- Examine under slit microscopy. Evaluate the depth of the anterior chamber to exclude shallowing and verify the presence of trypan blue in the anterior chamber.
- Repeat slit examination after 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h.
4. Option 2: Intracameral injection of Hoechst for assessing the bioavailability of injected material to the endothelial cell layer
- Load 5 µL of Hoechst into a sterile 10 µL glass Hamilton syringe with a 34 G blunt needle.
NOTE: Injection of Hoechst is described as a means to evaluate the bioavailability of injected material by uptake into the endothelial cell layer and is useful during the model calibration or setup stages. In the experimental settings, the syringe may be loaded with a solution of the compound of choice. - Insert the loaded syringe needle through the tunnel created in section 2 into the anterior chamber.
- Inject and hold the needle in place after injection for 2-3 seconds until all fluid clears.
- Remove the needle by pulling it out gently and slowly to avoid leakage from the corneal tunnel incision.
- Approximately 15-20 min post-injection, euthanize the rats by intraperitoneal injection of 500 mg/kg sodium pentobarbitone.
- Enucleate both eyes and isolate corneas. Collect the non-injected cornea as a control.
- Stain both corneas with 0.5% Alizarin Red S according to manufacturer instructions to identify endothelial cells.
- Examine under a light microscope to image the alizarin-red staining of endothelial cells and under a fluorescent microscope to observe Hoechst staining, compared to the non-injected cornea as control.
Results
Sprague Dawley rats were intracamerally injected with 5 µL of trypan blue according to the protocol described above. Slit lamp examination immediately after injection demonstrated that the chamber was stained with trypan blue, indicating that the injected material reached the anterior chamber (Figure 3). Furthermore, the anterior chamber depth was intact, suggesting that the injection did not cause leakage of aqueous humor and shallowing of the chamber.
Discussion
Pre-clinical research models should provide a controlled and reproducible environment to ensure the reliability and applicability of findings. In ophthalmology research, eye injection models are commonly used in diverse research aspects ranging from establishing disease models, testing new treatments, and assessing tissue reactions and potential adverse effects.
Intracameral injections serve as a common technique in experimental ophthalmology, facilitating the direct delivery of compounds to t...
Disclosures
Marcovich A. L. holds patents in Steba Biotech, Yeda Weizmann, EyeYon Medical, and Mor Isum and is a consultant for EyeYon Medical and Johnson & Johnson. All other authors have no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Israel Science Foundation grants 2670/23 and 1304/20.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Alizarin Red | Alpha Aesar | 042040.5 | |
| Buprenorphine | Richter pharma | 102047 | |
| Dexamethasone 0.1% | Fisher Pharmaceutical | 393102-0413 | |
| Hamilton glass syringe 10 μL | Hamilton Co. | 721711 | |
| Hoeschst | Merck | B2261 | |
| Ketamine | Bremer pharma GMBH (medimarket) | 17889 | |
| Ofloxacin 0.3% eye drops | Allergan | E92170 | |
| Oxybuprocaine Hydrochloride 0.4% | Fisher Pharmaceutical | N/A | |
| Pentobarbital sodium 200 mg/mL | CTS | N/A | |
| Slit microscope | Haag-streit bern | b-90019115 | |
| Sprague-Dawley Rats | Envigo | N/A | |
| Stiletto blade 31 G 0.8 mm | Tecfen medical (skymed) | QKN2808 | |
| Surgical microscope | Zeiss | OPMI-6 CFC | |
| Trypan Blue | Sartorius | 03-102-1B | |
| Xylazine | Eurovet Animal Health | 615648 |
References
- Ramsay, E., et al. Corneal and conjunctival drug permeability: Systematic comparison and pharmacokinetic impact in the eye. Eur J Pharm Sci. 119, 83-89 (2018).
- Cholkar, K., Dasari, S. R., Pal, D., Mitra, A. K. . Eye: Anatomy, Physiology and Barriers to Drug Delivery. Ocular Transporters and Receptors. , (2013).
- Prausnitz, M. R. Permeability of cornea, sclera, and conjunctiva: A literature analysis for drug delivery to the eye. J Pharm Sci. 87 (12), 1479-1488 (1998).
- Varela-Fernández, R., et al. Drug delivery to the posterior segment of the Eye: Biopharmaceutic and pharmacokinetic considerations. Pharmaceutics. 12 (3), 269 (2020).
- Gautam, M., et al. Intracameral drug delivery: A Review of agents, indications, and outcomes. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 39 (2), 102-116 (2023).
- Shah, T. J., Conway, M. D., Peyman, G. A. Intracameral dexamethasone injection in the treatment of cataract surgery induced inflammation: design, development, and place in therapy. Clin Ophthalmol. 12, 2223-2235 (2018).
- Perlman, R. L. Mouse models of human disease: An evolutionary perspective. Evol Med Public Health. 2016 (1), 170-176 (2016).
- Chawla, S., Jena, S. . The Anatomy and Physiology of Laboratory Rat.Essentials of Laboratory Animal Science: Principles and Practices. , (2021).
- Lundström, M., Wejde, G., Stenevi, U., Thorburn, W., Montan, P. Endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: a nationwide prospective study evaluating incidence in relation to incision type and location. Ophthalmology. 114 (5), 866-870 (2007).
- Fine, I. H. Clear corneal incisions. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 34 (2), 59-72 (1994).
- Herretes, S., Stark, W. J., Pirouzmanesh, A., Reyes, J. M. G., McDonnell, P. J., Behrens, A. Inflow of ocular surface fluid into the anterior chamber after phacoemulsification through sutureless corneal cataract wounds. Am J Ophthalmol. 140 (4), 737-740 (2005).
- Masket, S., Belani, S. Proper wound construction to prevent short-term ocular hypotony after clear corneal incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 33 (3), 383-386 (2007).
- Taban, M., Rao, B., Reznik, J., Zhang, J., Chen, Z., McDonnell, P. J. Dynamic morphology of sutureless cataract wounds - Effect of incision angle and location. Surv Ophthalmol. 49, S62-S72 (2004).
- Belforte, N., Sande, P. H., de Zavalía, N., Dorfman, D., Rosenstein, R. E. Therapeutic benefit of radial optic neurotomy in a rat model of glaucoma. PLoS One. 7 (3), e34574 (2012).
- Moreno, M. C., et al. A new experimental model of glaucoma in rats through intracameral injections of hyaluronic acid. Exp Eye Res. 81 (1), 71-80 (2005).
- Belforte, N., Sande, P., de Zavalía, N., Knepper, P., Rosenstein, R. Effect of chondroitin sulfate on intraocular pressure in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51 (11), 5768-5775 (2010).
- Matsumoto, Y., Kanamori, A., Nakamura, M., Negi, A. Rat chronic glaucoma model induced by intracameral injection of microbeads suspended in sodium sulfate-sodium hyaluronate. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 58 (3), 290-297 (2014).
- Liu, Y., et al. A novel rat model of ocular hypertension by a single intracameral injection of cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogel (Healaflow® ). Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 127 (5), 361-370 (2020).
- Bowen, R. C., et al. Comparative analysis of the safety and efficacy of intracameral cefuroxime, moxifloxacin and vancomycin at the end of cataract surgery: a meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 102 (9), 1268-1276 (2018).
- Kato, A., et al. Prophylactic antibiotics for postcataract surgery endophthalmitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of 6.8 million eyes. Sci Rep. 12 (1), 17416 (2022).
- Wang, M., Liu, Y., Dong, H. Effect of cefuroxime intracameral injection antibiotic prophylactic on postoperative endophthalmitis wound post-cataract: A meta-analysis. Int Wound J. 20 (5), 1376-1383 (2023).
- Katz, G., et al. Intracameral cefuroxime and the incidence of post-cataract endophthalmitis: an Israeli experience. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 253 (10), 1729-1733 (2015).
- Lipnitzki, I., Ben Eliahu, S., Marcovitz, A. L., Ezov, N., Kleinmann, G. Intraocular concentration of moxifloxacin after intracameral injection combined with presoaked intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 40 (4), 639-643 (2014).
- Colleaux, K. M., Hamilton, W. K., Morgan, R. A. Effect of prophylactic antibiotics and incision type on the incidence of endophthalmitis after cataract surgery. Can J Ophthalmol. 35 (7), 373-378 (2000).
- Libre, P. E., Della-Latta, P., Chin, N. X. Intracameral antibiotic agents for endophthalmitis prophylaxis: A pharmacokinetic model. J Cataract Refract Surg. 29 (9), 1791-1794 (2003).
- Carino, N. S., Slomovic, A. R., Chung, F., Marcovich, A. L. Topical tetracaine versus topical tetracaine plus intracameral lidocaine for cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 24 (12), 1602-1608 (1998).
- Minakaran, N., Ezra, D. G., Allan, B. D. Topical anaesthesia plus intracameral lidocaine versus topical anaesthesia alone for phacoemulsification cataract surgery in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 7 (7), (2020).
- Dan-Ni, W., Li-Dian, H., Zhi-Guo, P., Qiang, W., Lei, S. Intracameral anti-VEGF injection for advanced neovascular glaucoma after vitrectomy with silicone oil tamponade. Int J Ophthalmol. 14 (3), 129-135 (2021).
- Bhagat, P. R., Agrawal, K. U., Tandel, D. Study of the effect of injection bevacizumab through various routes in neovascular glaucoma. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 10 (2), 39-48 (2016).
- Al-Qaysi, Z. K., Beadham, I. G., Schwikkard, S. L., Bear, J. C., Al-Kinani, A. A., Alany, R. G. Sustained release ocular drug delivery systems for glaucoma therapy. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 20 (7), 905-919 (2023).
- Eghrari, A. O., Gottsch, J. D. Fuchs' corneal dystrophy. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 5 (2), 147-159 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved