A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Atomic Force Microscopy Measurements of Cartilage in Intact and Regenerating Axolotl Limbs
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
In this protocol, we show how to prepare axolotl tissue for atomic force microscopy (AFM) and perform indentation measurements in intact and regenerating limb cartilage.
Abstract
Mechanical forces provide important signals for normal cell function and pattern formation in developing tissues, and their role has been widely studied during embryogenesis and pathogenesis. Comparatively, little is known of these signals during animal regeneration.
The axolotl is an important model organism for the study of regeneration, given its ability to fully restore many organs and tissues after injury, including missing cartilage and bone. Due to its crucial role as the main supporting tissue in the vertebrate body, regaining skeletal function during regeneration requires both the restoration of the missing structures as well as their mechanical properties. This protocol describes a method for processing axolotl limb samples for atomic force microscopy (AFM), which is the gold standard for probing cell and tissue mechanical properties at high spatial resolution.
Taking advantage of the regenerative capabilities of the axolotl, this study measured the stiffness of limb cartilage during homeostasis and two stages of limb regeneration: tissue histolysis and cartilage condensation. We show that AFM is a valuable tool for gaining insights into dynamic tissue restructuring and the mechanical changes that occur during regeneration.
Introduction
The skeleton, especially cartilage and bones, provides the main mechanical support for soft tissues of the body in vertebrates. Therefore, any damage in the skeletal system is likely to greatly compromise functionality and even survival. In humans, bone fractures are one of the most common traumatic injuries1, most of which repair in a matter of weeks, but 5%-10% of these will have delays in healing or never fully recover2,3. Moreover, humans are not able to recuperate from extensive bone or cartilage loss4,5. Some salamanders, however, can regenerate a variety of body structures, including full limbs6, making them an ideal model for the study of skeletal regeneration.
The axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) is a type of salamander where limb regeneration has been extensively studied. This process occurs in four main sequential but overlapping phases: 1) wound healing, 2) inflammation/histolysis, 3) blastema formation, and 4) blastema outgrowth/differentiation (reviewed in7,8). Following amputation, keratinocytes bordering the injury site migrate rapidly, closing the wound and forming the wound epithelium (WE). During the ensuing inflammation and histolysis, pathogens are eliminated, debris and damaged cells are cleared, and the extracellular matrix (ECM) under the amputation surface is remodeled9. Tissue histolysis is essential for limb regeneration to take place10, where the secretion of proteolytic enzymes is crucial not only for overall ECM remodeling, but also to release the cells giving rise to the blastema and to free bioactive molecules sequestered in the ECM itself8. In fact, studies in many regenerative contexts and model organisms have shown that the unique material properties of the ECM during histolysis are capable of inducing dedifferentiation processes or directing the migration of cells toward the injury site (reviewed in11). Furthermore, resorption of calcified tissue during the late stages of histolysis has shown to be key for proper integration of newly-formed limb skeletal elements12. Following the histolysis stage, the blastema is formed under the wound epithelium (WE) as an accumulation of undifferentiated, multi-lineage progenitors resulting from de-differentiated mature tissue cells or resident stem cells. Blastema cells proliferate and differentiate into all missing cell types. Finally, limb morphogenesis takes place, where skeletal tissue is regenerated through the condensation of chondroprogenitors derived from periskeletal cells and transdifferentiated dermal fibroblasts13,14,15.
Although many of the biochemical cues regulating changes in cell identity and ECM composition have been identified10,13,14,16,17,18, tissue mechanical properties during the different phases of limb regeneration, as well as their influence in regeneration, have remained largely unexplored. Many studies have shown that cells sense and integrate mechanical cues that regulate their fate and behavior in several contexts (reviewed in19,20). Therefore, complementing our cellular and molecular knowledge of limb regeneration with tissue mechanical measurements will greatly improve our understanding of these processes.
Different techniques have been developed that allow for mechanical characterization and force manipulation of biological samples21. Among these techniques, atomic force microscopy (AFM) has become the gold standard in mechanobiology, in which the viscoelastic properties of biological samples are probed at high spatial resolution by indenting with an ultrasensitive force sensor, the AFM cantilever22. Since this technique requires direct contact with the sample, typically, tissue slices are generated, which can be challenging in some cases. Thus, preparation conditions need to be adapted and optimized for each particular sample so that it can remain as close to physiological conditions as possible and minimal artifacts are generated23. This protocol describes how to measure tissue stiffness in axolotl limbs using AFM, focusing on cartilaginous tissues in intact conditions, while undergoing histolysis, and in cartilage condensation stages (Figure 1 and Figure 2). This method may be expanded for the measurement of other tissue types as well.
Protocol
Axolotls (Ambystoma mexicanum) were grown in the Axolotl facility of the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden (CRTD) of the Dresden University of Technology (TUD). A full description of the husbandry conditions can be found in24. Briefly, rooms were kept at 20-22 °C with a 12/12 h day/night cycle. All handling and surgical procedures were carried out in accordance with local ethics committee guidelines and were approved by the Landesdirektion Sachsen, Germany.
This study used white (d/d) axolotls for all experiments, a naturally occurring mutant strain lacking body pigmentation (few to no melanophores and xanthophores), with iridophores only in the iris of the eyes. This study used axolotls measuring 8-15 cm from snout to tail (5-7 months old) without sex-specific bias.
1. Preparation
- Prepare a 10% (w/v) benzocaine stock solution that will be used for anesthesia and euthanasia of the axolotls (see below). For this, mix in a volumetric bottle 50 g of benzocaine with 100% ethanol until the 500 mL limit has been reached.
- Prepare a 0.03% (w/v) benzocaine stock solution.
- For 1 L, mix 50 mL of 10x Tris-buffered saline (TBS) with 30 mL of 10% (w/v) benzocaine and 5 mL of 4000% (w/v) Holtfreter's solutions with 915 mL of distilled water and mix overnight with a magnetic stir bar.
- For 1 L of 10x TBS solution, mix 24.2 g of Trizma base and 90 g of NaCl with 990 mL of deionized water. Mix well with a magnetic stir bar. Then, add approximately 10 mL of concentrated HCl (12 M or 37%) and adjust for pH 8.
- For 1 L of 4000% (w/v) Holtfreter's solution, mix 158.4 g of NaCl, 11.13 g of MgSO4·7H2O, 5.36 g of CaCl2·2H2O and 2.88 g of KCl with deionized water until 1 L.
- Prepare a 0.01% (w/v) working benzocaine dilution in holding tank water for anesthesia by diluting the 0.03% (w/v) stock solution 1:3.
- For 1 L of solution, use 333 mL of the benzocaine stock solution plus 666 mL of holding tank water.
- Prepare a 5 mg/mL butorphanol tartrate stock solution for analgesia. For this, mix 100 mg of butorphanol (+)-tartrate salt with 20 mL of ultrapure water. Store aliquots at 4 °C.
- On the day of the amputations, freshly prepare 0.5 mg/L butorphanol tartrate working solution to decrease animal pain following surgical procedures by diluting the stock solution 1:10.000 in holding tank water.
- For animals smaller than 8 cm long, mix 20 µL of stock solution into 200 mL holding tank water.
- For larger animals, mix 60 µL of stock solution into 600 mL holding tank water.
- Prepare sterile amphibian phosphate-buffered saline (APBS), an 80% (v/v) PBS solution, and keep it at room temperature (RT) by mixing 800 mL of DPBS with 200 mL of deionized water.
- Prepare 1 mg/mL insulin stock solution. For this, mix 250 mg of insulin powder with 25 mL of HCl 0.1 M and slowly agitate until dissolved. While agitating, add 225 mL of APBS until the solution is clear. Sterile filter, and store 4 mL aliquots at -20 °C.
- Prepare sterile culture medium (all % (v/v): 62.5% L15 medium, 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin, 1% Insulin, 1% L-Glutamine) and keep at 4 °C until the day of use. On the experimental day, equilibrate to RT prior to use.
- For 400 mL of culture medium, use 250 mL of L15 medium, 40 mL of heat-inactivated FBS, 4 mL of Penicillin/Streptomycin, 4 mL of Insulin solution (from Step 1.7), 4 mL of L-Glutamine, and 98 mL of deionized sterile water. Prepare under sterile conditions and a sterile filter after mixing all components. Prepare 15 mL aliquots.
- Prepare 2.5% and 3% (w/v) low melting point (lmp)-agarose in APBS solution and heat at 70 °C to dissolve agarose completely. Prepare aliquots in 1.5 mL tubes and store at 4 °C until the day of use.
- For 20 mL of 2.5% (w/v) lmp-agarose, mix 0.5 g of lmp-agarose with 20 mL of APBS in a 50 mL tube and heat in a water bath at 70 °C until agarose has fully melted. The solution has to become clear and transparent. Prepare aliquots while still warm.
- For 20 mL of 3% (w/v) lmp-agarose, mix 0.6 g of lmp-agarose with 20 mL of APBS and proceed as above.
- (Optional): For 20 mL of 1% (w/v) lmp-agarose, mix 0.2 g of lmp-agarose with 20 mL of APBS and proceed as above.
NOTE: Melting time depends on the concentration of the lmp-agarose and may range approximately from 15-40 min.
- For amputation and tissue mounting, use a brightfield stereoscope.
- Assemble 100 mm diameter plastic Petri dishes, forceps, scalpel, and surgical scissors for amputations and tissue collection.
- Prepare 35 mm diameter plastic Petri dishes for indentation measurements.
- Prepare ~1 cm long cylinders of ~1 cm diameter. For this, heat a cardboard cutter under a Bunsen burner flame and cut a 15 mL tube with the heated blade.
- Cut small 1 cm2 squares of parafilm and store.
- Prepare a metallic or cold block at -20 °C by leaving it in the freezer for at least 1 h.
- Prepare plastic Pasteur pipettes.
- (Optional): Prepare fixative MEMFa solution (3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid [MOPS] 0.1 M pH 7.4, Ethylene glycol-bis (2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid [EGTA] 2 mM, MgSO4·7H2O 1 mM, 3.7% formaldehyde). For this, add 10.465 g of MOPS, 0.123 g of MgSO4·7H2O, 2 mL of 0.5 M EDTA pH 8.0, and add water until 45 mL. Add 5 mL formaldehyde 37% (w/v) to a total volume of 50 mL.
2. Reagents
- Refer to the Table of Materials for the reagents used for this work, but other commercial providers may also be used.
3. Axolotl amputation and limb regeneration
- Prior to all experimental procedures, anesthetize the animal in 0.01% (w/v) benzocaine diluted in holding tank water (step 1.3) for 20 min, making sure that animals are deeply anesthetized and unresponsive to tactile stimuli.
- Remove axolotl from the anesthesia and lay it on top of a 100 mm Petri dish containing a paper tissue moistened with anesthesia-containing water. Orient the limb perpendicular to the body axis and place the plate under the stereoscope for better visualization.
NOTE: A stereoscope with a compact goose neck lamp was used here. - Amputate the limb with a sharp sterile scalpel immediately distal to the calcified area of the zeugopodial region (radius/ulna) (Figure 1A).
NOTE: Adhering to the 3R animal welfare principle, it is recommended to use the limbs that were initially removed by the amputation as intact controls. - Leave the animal on the dish and cover it with a humidified tissue paper soaked with benzocaine-containing water for 15 min to allow blood clotting and wound closure to occur.
- Return animals to a tank containing fresh holding water with analgesics (butorphanol tartrate, 0.5 mg/L, from step 1.5).
- Move the animals to their original tank containing fresh holding water 24 h after post-operative analgesic treatment.
- Allow animals to regenerate until the desired stage of interest.
NOTE: The analyzed limbs were collected on the amputation day for the intact phase and 5 days post-amputation (dpa) for the histolysis phase in 5-month-old animals. The cartilage condensation stage was measured at 21 dpa in 7-month-old animals.
4. Tissue mounting and processing for measurements
- Heat the 1.5 mL tubes containing 2.5% or 3% (w/v) lmp-agarose (from step 1.9) on a thermoblock at 70 °C until agarose has fully melted. Change the tubes to a different thermoblock at 37 °C and allow the temperature to equilibrate before using.
NOTE: Here, 2.5% lmp-agarose was used to measure regenerating tissues and 3% for intact tissues. - Cover one side of the 1 cm long cylinders (from step 1.13) with one of the parafilm pieces (step 1.14) so they are completely sealed at their bottom.
- Equilibrate 15 mL aliquots of culture medium to RT (from step 1.8)
- Anesthetize the animals by immersing them in anesthetic-containing water (0.01% (w/v) benzocaine diluted in holding tank water) for at least 20 min.
- Image the limbs under a stereoscope with software allowing quantitative measurements. Measure the length of the structure of interest and calculate how much tissue needs to be removed from the distal end of the limb until the section of interest is reached.
- For regenerating limbs, collect them by cutting with a scalpel and/or surgical scissors at the elbow level and dissecting excessive tissue out from the limb. Leave the tissue in APBS solution while preparing the next step. Ensure the cut is transversal (90°) to the lower arm axis to create an even surface. For the intact limbs, remove the hand by cutting through the carpal region.
- Euthanize the animals by exposing them to a lethal dose of anesthesia (0.1% benzocaine) for at least 20 min. For this, add the required volume of 10% (w/v) benzocaine solution to reach a 0.1% (w/v) concentration.
- If animals were anesthetized in 100 mL of 0.01% (w/v) benzocaine solution, add 900 µL of the 10% (w/v) benzocaine solution.
- Rinse limbs by submerging them in APBS solution.
- Ensure that the Pasteur pipettes and the thermoblock (stabilized at 37 °C with agarose aliquots) are close to the working station. Take the cold block out of the -20 °C freezer and place the cylinder with the parafilm-covered end facing down on top of it.
- Grab the dissected limb and gently remove the excess liquid with tissue paper. Place the limb on a clean plate, add the melted lmp-agarose on top, and briefly move the limb around in the agarose to displace any remaining APBS from the skin surface.
- Working quickly, place the limb inside the cylinder, ensuring it is oriented vertically, with the area of interest facing upwards.
- While gently holding the limb with forceps, add lmp-agarose inside the cylinder until the tissue is fully covered. Gently remove the forceps before the agarose solidifies.
- Remove the cylinder from the cold block and let the agarose solidify completely at RT for approximately 30 s.
- Take the tissue-containing agarose block immediately to the vibratome room, along with sterile culture medium aliquots and APBS, at RT.
- Remove the parafilm from the bottom of the cylinder and attach the agarose containing the tissue to the vibratome stage with cyanoacrylate glue. Make sure that both agarose and sample are glued to the stage.
- Submerge the stage in APBS for sectioning.
NOTE: Intact tissues include the stiffer bone/cartilage, whereas regenerating tissues are softer. Therefore, vibratome parameters have to be adjusted accordingly. This study used the following parameters: Intact tissues (amplitude 1.2 mm and speed 0.1 mm/s) and regenerating tissues (amplitude 0.9 mm and speed 0.4 mm/s). - Begin sectioning the agarose in short steps (e.g., in 100 µm steps) until the tissue tip is reached. Then, section the tissue block until the distal portion of tissue (calculated in step 4.5) is removed. This way, a transversal cross-section of the area of interest will be readily accessible.
NOTE: The removed tissue section will contain the immediately adjacent surface to the one probed with AFM and can serve as a reference for tissue structure. Therefore, it can be used for direct complementary analysis or fixed for subsequent staining (see section 6). - Carefully remove the tissue-containing block from the vibratome stage with a razor blade and remove all traces of glue. Immediately glue the block on a 35 mm plastic Petri dish with surgical tissue adhesive glue and add approximately 2 mL of culture medium at RT to ensure the tissue is fully covered.
NOTE: The exposed tissue surface in the agarose block is the surface to be probed.
5. Measurements with AFM
- At least 1 day prior to measurements, prepare the cantilever for measurements.
NOTE: For this work, tipless silicon cantilevers were functionalized with polystyrene beads (diameter 20 µm), and the bead-cantilever bond was left to strengthen for at least 1 day before being used for indentation measurements.- Attach beads to cantilevers using epoxy glue with a processing time of 5 min.
- Quickly lower the cantilever with minimal contact onto a glue-coated glass slide so that a small droplet of glue is formed at its end, and bring it immediately afterwards into contact with a suitable bead.
- Hold the cantilever-bead contact for ~10 min before lifting the cantilever with a bound bead off the surface.
- Calibrate the cantilever prior to measurements.
NOTE: The modified cantilever was calibrated before each set of experiments by the thermal noise method using build-in procedures of the AFM software. - Insert the Petri dish with the tissue block (from step 4.18) and culture medium into the petri dish holder of the AFM and acquire an overview image in brightfield microscopy (Figure 1B).
NOTE: For indentation tests, a setup equipped with a motorstage on top of an upright light microscope is used. Mount the AFM head and position the cantilever over the tissue and bring the cantilever in proximity to the surface. - Choose the specific region of interest and record an array of force-distance curves (Figure 2A).
NOTE: Relative force setpoints of 2-25 nN were used in order to reach comparable indentation depths of ~1-4 µm for tissues of differing stiffness, with an approach and retraction speed of 7.5 µm/s, z length of 50 µm, grid size 70 µm x 70 µm with 3 x 3 points. - For every probed region, acquire a brightfield microscopy image to associate the obtained values to each particular region in the limb section.
- For all samples, probe at least 3 different regions per tissue type.
NOTE: In all cases, this study measured 4 regions in the center of the cartilage and 3 regions in the periphery of the cartilage region and kept the tissue under the microscope for a maximum of 1 h. - Once indentation measurements have finished, discard or fix the tissue for further analysis.
NOTE: Samples were fixed after concluding measurements by placing them in 2 mL tubes containing MEMFa solution and fixed overnight at 4 °C. MEMFa (step 1.17) was used, but formaldehyde 4% (w/v) solution in PBS may also be used.
6. (Optional) Processing of adjacent tissue sections
- If the adjacent tissue sections are used for subsequent staining, place them immediately after sectioning in a small 2 mL tube containing fixative and fix overnight at 4 °C.
- To reveal tissue architecture through the labeling of actin cytoskeleton and nuclei, wash 3 times with PBS for 5 min each to remove the fixative and stain with a solution containing Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated Phalloidin (1:250) and Hoechst 33258 (1:10000) in PBS for 1 h at RT on a rocking platform.
- Next, immobilize the stained samples on top of glass-bottomed dishes using 1% (w/v) lmp-agarose in APBS stabilized at 37 °C (from step 1.9). Make sure that the surface of interest is facing the glass. Once agarose solidifies, cover the samples with PBS to prevent dehydration.
NOTE: The intact and histolysis samples are imaged with an inverted confocal microscope (10x magnification and 8 µm optical sections). Images in Figure 1C are maximum projections of 8 optical sections.
- If the adjacent tissue section is used for immediate downstream analysis requiring fresh tissue (like RNA extraction, incubation with live dyes, etc), make sure to work quickly and to use a cell culture medium (from step 1.8) to ensure the highest possible tissue integrity.
7. Data analysis and display
- To calculate the apparent Young's modulus, analyze the force-distance curves by using the Hertz/Sneddon model (Eq.1) for a spherical indenter using the JPK/Bruker data processing software, assuming a Poisson ratio of 0.5.
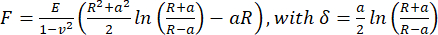 (Eq.1)
(Eq.1)
Where R: indenter radius, E: elastic modulus, ν: Poisson's ratio, a: radius of the circular contact area between the indenter and sample, δ: indentation depth. - For viscoelastic analysis, analyze the approach parts of the force-indentation curves in PyJibe 0.15.0 with the extension "Hertz model corrected for viscoelasticity using Kelvin-Voigt-Maxwell (KVM)" (written by Paul Müller, https://github.com/AFM-analysis/PyJibe)25. The fit function is based on a model described by Abuhattum et al.26, integrating Kelvin-Voigt-Maxwell model elements.
- Pre-process the force indentation curves to estimate the contact point using a piecewise fit with a line (baseline) and a polynomial fit function for the approach part.
- Fit the force-indentation curves to the "Hertz model corrected for viscoelasticity using Kelvin-Voigt-Maxwell (KVM) model". From the fit, obtain the unrelaxed Young's modulus, apparent Young's modulus, and apparent viscosity. The model also gives Maxwell relaxation and indentation times.
NOTE: In several analyzed force indentation curves (in particular the intact tissue), the Maxwell relaxation times were significantly larger or smaller than the indentation time, which indicates rather elastic behavior or Kelvin-Voigt mechanical behavior, respectively.
- Export all measurements to a spreadsheet and calculate the median apparent Young's moduli per tissue type and sample.
- Plot and statistically analyze the data with appropriate software.
NOTE: GraphPad Prism is used here, and when describing the results, the study refers to the mean ± SD of the median apparent Young's moduli per sample (displayed in Figure 2D-F). - Display optical slices from confocal images by projecting them with the Fiji maximum projection function. Adjust the brightness and contrast of each individual channel for optimal visualization of fluorescent stainings.
- Generate a figure panel with the appropriate software.
NOTE: Affinity Designer is used to generate the panels, and the model in Figure 1A is drawn using Affinity Designer.
Results
Using the protocol described above, we measured the apparent Young's modulus of cartilaginous axolotl limb tissues in homeostatic ("Intact") conditions, during early cartilage histolysis, and later cartilage condensation stages (Figure 1A). We also probed the mechanical properties of the skeletal elements in different regions, including their center and periphery, as shown in the images depicting the cantilever position (Figure 1B). To display tissue...
Discussion
Here, we demonstrate a technique for the measurement of cartilage stiffness in axolotl limbs with AFM. However, this method may be expanded for probing other tissue types as well. A key step for successful AFM measurements is sample preparation, which proved to be particularly challenging with axolotl samples. We found that probing the tissue surface that was still embedded in the agarose block was the best way to preserve tissue integrity. This is because the axolotl skin secretes high levels of mucous onto the surface ...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the Sandoval-Guzmán lab for continuous support and companionship during the development of this work. We are also grateful to Anja Wagner, Beate Gruhl, and Judith Konantz for their dedication to axolotl care. We also thank Paul Müller for providing codes for AFM data analysis. This work was supported by the Light Microscopy Facility of the CMCB Technology Platform at TU Dresden. AT is a fellow of the Mildred Scheel Early Career Center Dresden P2 funded by the German Cancer Aid (Deutsche Krebshilfe). RA is funded by a Temporary PI position (Eigene Stelle) from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) – AI 214/1-1.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Affinity Designer | Affinity | version 1.10.4 | For figure assembling |
| Agarose Low Melt | Roth | 6351.1 | For sample preparation |
| Alexa Fluor 488 Phalloidin | Invitrogen | A12379 | To stain tissue |
| Axiozoom | Zeiss | To image samplea under the AFM | |
| Benzocaine | Sigma-Aldrich | E1501 | To anesthetize the animals |
| Butorphanol (+)-tartrate salt | Sigma-Aldrich | B9156 | As analgesic |
| Cantilever | NanoWorld | Arrow TL1 | For AFM indentation measurements |
| Cellhesion 200 setup equipped with a motorstage | JPK/Bruker | For AFM indentation measurements | |
| CellSense Entry | For imaging in Stereoscope Olympus UC90 | ||
| Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (DPBS, 1x) | Gibco | 14190-144 | To clean samples and section under vibratome |
| FIJI (ImageJ2) | https://imagej.net/software/fiji | version 2.9.0/1.53t | For image processing |
| GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Software | (version 8.4.3) | To graph and statistically analyze the data |
| Heat-inactivated FBS | Gibco | 10270-106 | For cell culture medium |
| Histoacryl glue (2-Butyl-Cyanoacrylate) | Braun | To glue sample to petri dishes | |
| Hoechst 33258 | Abcam | ab228550 | To stain tissue |
| Insulin | Sigma-Aldrich | I5500 | For cell culture medium |
| Inverted confocal microscope | Zeiss | 780 LSM | To image tissue sections |
| Inverted confocal microscope | Zeiss | 980 LSM | To image tissue sections |
| JPK/Bruker data processing software | JPK/Bruker | SPM 6.4 | To analyze force-distance curves |
| L15 medium (Leibovitz) | Sigma | L1518 | For cell culture medium |
| L-Glutamine | Gibco | 25030-024 | For cell culture medium |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | For cell culture medium |
| polystyrene beads ( 20 µm diameter); ) | microParticles | For AFM indentation measurements | |
| Pyjibe | written by Paul Müller https://github.com/AFM-analysis/PyJibe | 0.15.0 | For viscoelastic analysis |
| Stereoscope Olympus SX10 | Olympus | SX10 | For limb amputations and tissue mounting |
| Stereoscope Olympus UC90 | Olympus | UC90 | For imaging |
| Vibratome Leica | Leica | VT 1200S | For tissue sectioning |
References
- Mills, L. A., Aitken, S. A., Simpson, A. H. R. W. The risk of non-union per fracture: current myths and revised figures from a population of over 4 million adults. Acta Orthop. 88 (4), 434-439 (2017).
- Calori, G. M., et al. Non-unions. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 14 (2), 186-188 (2017).
- Nandra, R., Grover, L., Porter, K. Fracture non-union epidemiology and treatment. Trauma. 18 (1), 3-11 (2016).
- Nauth, A., Schemitsch, E., Norris, B., Nollin, Z., Watson, J. T. Critical-size bone defects: Is there a consensus for diagnosis and treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 32 (3 Suppl), S7-S11 (2018).
- Schemitsch, E. H. Size matters: Defining critical in bone defect size. J Orthop Trauma. 31 (10), S20-S22 (2017).
- Joven, A., Elewa, A., Simon, A. Model systems for regeneration: Salamanders. Development (Cambridge). 146 (14), 0 (2019).
- Aires, R., Keeley, S. D., Sandoval-Guzmán, T. Basics of Self-Regeneration. Cell Engineering and Regeneration. , (2020).
- Stocum, D. L. Mechanisms of urodele limb regeneration. Regeneration. 4 (4), 159-200 (2017).
- Bassat, E., Tanaka, E. M. The cellular and signaling dynamics of salamander limb regeneration. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 73, 117-123 (2021).
- Vinarsky, V., Atkinson, D. L., Stevenson, T. J., Keating, M. T., Odelberg, S. J. Normal newt limb regeneration requires matrix metalloproteinase function. Dev Biol. 279 (1), 86-98 (2005).
- Godwin, J., Kuraitis, D., Rosenthal, N. Extracellular matrix considerations for scar-free repair and regeneration: Insights from regenerative diversity among vertebrates. International J Biochem Cell Biol. 56, 47-55 (2014).
- Riquelme-Guzmán, C., et al. Osteoclast-mediated resorption primes the skeleton for successful integration during axolotl limb regeneration. ELife. 11, e79966 (2022).
- Gerber, T., et al. Single-cell analysis uncovers convergence of cell identities during axolotl limb regeneration. Science. 362 (6413), aaq0681 (2018).
- Kragl, M., et al. Cells keep a memory of their tissue origin during axolotl limb regeneration. Nature. 460 (7251), 60-65 (2009).
- Currie, J. D., et al. Live Imaging of Axolotl Digit Regeneration Reveals Spatiotemporal Choreography of Diverse Connective Tissue Progenitor Pools. Dev Cell. 39 (4), 411-423 (2016).
- Qin, T., et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals novel mitochondria-related musculoskeletal cell populations during adult axolotl limb regeneration process. Cell Death Differ. 28 (3), 1110-1125 (2021).
- Sandoval-Guzman, T., et al. Fundamental differences in dedifferentiation and stem cell recruitment during skeletal muscle regeneration in two salamander species. Cell Stem Cell. 14, 174-187 (2014).
- Currie, J. D., et al. The Prrx1limb enhancer marks an adult subpopulation of injury-responsive dermal fibroblasts. Biol Open. 8, bio043711 (2019).
- Wagh, K., Ishikawa, M., Garcia, D. A., Stavreva, D. A., Upadhyaya, A., Hager, G. L. Mechanical regulation of transcription: Recent advances. Trends Cell Biol. 31 (6), 457-472 (2021).
- d'Angelo, M., et al. The role of stiffness in cell reprogramming: A potential role for biomaterials in inducing tissue regeneration. Cells. 8 (9), 1036 (2019).
- Akhtar, R., Sherratt, M. J., Cruickshank, J. K., Derby, B. Characterizing the elastic properties of tissues. Mater Today (Kidlington). 14 (3), 96-105 (2011).
- Krieg, M., et al. Atomic force microscopy-based mechanobiology. Nat Rev Phys. 1 (1), 41-57 (2019).
- El Kirat, K., Burton, I., Dupres, V., Dufrene, Y. F. Sample preparation procedures for biological atomic force microscopy. J Microsc. 218 (3), 199-207 (2005).
- Riquelme-Guzmán, C., et al. Postembryonic development and aging of the appendicular skeleton in Ambystoma mexicanum. Dev Dyn. 251 (6), 1015-1034 (2021).
- López-Alonso, J., Eroles, M., Janel, S., et al. PyFMLab: Open-source software for atomic force microscopy microrheology data analysis [version 2; peer review: 2 approved]. Open Res Europe 2024. 3 (187), (2024).
- Abuhattum, S., Mokbel, D., Müller, P., Soteriou, D., Guck, J., Aland, S. An explicit model to extract viscoelastic properties of cells from AFM force-indentation curves. iScience. 25 (4), 104016 (2022).
- Glorieux, L., et al. In-depth analysis of the pancreatic extracellular matrix during development for next-generation tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 24 (12), 10268 (2023).
- Hiratsuka, S., et al. Power-law stress and creep relaxations of single cells measured by colloidal probe atomic force microscopy. Jpn J Appl Phys. 48 (8 PART 3), 08JB17 (2009).
- Johnson, K. L., Kendall, K., Roberts, A. D. Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids. Proc R Soc Lond A. 324, 301-313 (1971).
- Kondiboyina, V., Duerr, T. J., Monaghan, J. R., Shefelbine, S. J. Material properties in regenerating axolotl limbs using inverse finite element analysis. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 150, 106341 (2024).
- Calve, S., Simon, H. Biochemical and mechanical environment cooperatively regulate skeletal muscle regeneration. FASEB J. 26 (6), 2538-2545 (2012).
- Calve, S., Simon, H. G. Extracellular control of limb regeneration. IUTAM Symposium on Cellular, Molecular and Tissue Mechanics. IUTAM Bookseries. 16, 257-266 (2010).
- Kaufmann, R. A., Kozin, S. H., Barnes, A., Kalluri, P. Changes in strain distribution along the radius and ulna with loading and interosseous membrane section. J Hand Surg Am. 27 (1), 93-97 (2002).
- Martin, A. R., et al. Measurement of distal forearm bone mineral density: Can different forearm segments be used interchangeably. J Clin Densitom. 2 (4), 381-387 (1999).
- Riquelme-Guzmán, C., et al. In vivo assessment of mechanical properties during axolotl development and regeneration using confocal Brillouin microscopy. Open Biol. 12 (6), 220078 (2022).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved