Usando um medidor de pH
Visão Geral
Fonte: Laboratório do Dr. Zhongqi He - Departamento de Agricultura dos Estados Unidos
Ácidos e bases são substâncias capazes de doar prótons (H+) e íons hidróxido (OH- ),respectivamente. São dois extremos que descrevem produtos químicos. Misturar ácidos e bases pode cancelar ou neutralizar seus efeitos extremos. Uma substância que não é ácida nem básica é neutra. Os valores de concentração de prótons ([H+]) para a maioria das soluções são inconvenientemente pequenos e difíceis de comparar para que uma quantidade mais prática, pH, tenha sido introduzida. pH foi originalmente definido como o logaritmo decimal da recíproca da concentração molar de prótons, 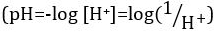 mas foi atualizado para o logaritmo decimal do recíproco da atividade de íons de
mas foi atualizado para o logaritmo decimal do recíproco da atividade de íons de 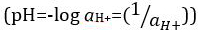 hidrogênio. A primeira definição é agora ocasionalmente expressa como p[H]. A diferença entre p[H] e pH é bastante pequena. Foi declarado que pH = p[H] + 0,04. É prática comum usar o termo 'pH' para ambos os tipos de medições.
hidrogênio. A primeira definição é agora ocasionalmente expressa como p[H]. A diferença entre p[H] e pH é bastante pequena. Foi declarado que pH = p[H] + 0,04. É prática comum usar o termo 'pH' para ambos os tipos de medições.
A escala de pH normalmente varia de 0 a 14. Para uma solução de 1 M de ácido forte, pH=0 e para uma solução de 1 M de base forte, pH=14. Assim, os valores de pH medidos estarão principalmente na faixa de 0 a 14, embora valores fora dessa faixa sejam inteiramente possíveis. A água pura é neutra com pH=7. Um pH menor que 7 é ácido, e um pH maior que 7 é básico. Como a escala de pH é logarítmica, o pH é uma quantidade inafundada. Cada valor de pH inteiro abaixo de 7 é 10x mais ácido do que o próximo inteiro. Por exemplo, um pH de 4 é 10x mais ácido do que um pH de 5 e 100x (10 x 10) mais ácido do que um pH de 6. O mesmo vale para valores de pH acima de 7, cada um dos quais é 10x mais básico (ou alcalino) do que o próximo valor total mais baixo. Por exemplo, um pH de 10 é 10x mais básico que um pH de 9.
Procedimento
1. pH Calibração
- Ligue a energia do medidor pressionando o botão "power".
- Conecte a sonda de compensação automática de temperatura (ATC) se estiver disponível e/ou não estiver com o eletrodo.
- Verifique se o modo de medição é pH. Caso não, pressione o botão "MODE" até que o modo "pH" apareça no visor LCD.
- Consulte o guia de referência rápido na parte inferior do medidor ou nas proximidades para obter ajuda, se necessário.
- Use sempre tampões pH frescos, não utilizados e não
Resultados
A Figura 1 mostra o pH dos solos agrícolas impactados pelo manejo do cultivo e irrigação das águas subterrâneas. Estas amostras de solo foram coletadas de 5 campos de batata sob diferentes práticas de rotação de cultivo com ou sem irrigação de águas subterrâneas. O pH mais baixo é observado em solos do Campo 4 em séries irrigadas por chuvas e águas subterrâneas. A irrigação de águas subterrâneas aumentou consistentemente o pH do solo em todos os 5 campos. As informações de pH são essenciais para a reco...
Aplicação e Resumo
pH é um dos parâmetros químicos mais medidos de soluções aquosas. É um parâmetro crítico no tratamento de água e esgoto para aplicações municipais e industriais, produção química, pesquisa agrícola e produção. Também é fundamental no monitoramento ambiental, pesquisa química e de ciências da vida, pesquisa bioquímica e farmacêutica, produção eletrônica e muitas outras aplicações. A Figura 2 lista valores de pH de algumas substâncias comuns.
A água...
Pular para...
Vídeos desta coleção:

Now Playing
Usando um medidor de pH
General Chemistry
345.9K Visualizações

Vidraria de laboratório comuns e seus usos
General Chemistry
656.1K Visualizações

Soluções e Concentrações
General Chemistry
274.2K Visualizações

Determinando a densidade de um sólido e um líquido
General Chemistry
556.1K Visualizações

Determinação de composição percentual em massa em uma solução aquosa
General Chemistry
383.5K Visualizações

Determinação da Fórmula Empírica
General Chemistry
181.9K Visualizações

Determinação das Regras de Solubilidade de Compostos Iônicos
General Chemistry
141.4K Visualizações

Introdução à Titulação
General Chemistry
424.5K Visualizações

Lei dos gases ideais
General Chemistry
78.5K Visualizações

Determinação espectrofotométrica de uma constante de equilíbrio
General Chemistry
158.5K Visualizações

Princípio de Le Châtelier
General Chemistry
265.2K Visualizações

Depressão do ponto de congelamento para determinar um composto desconhecido
General Chemistry
160.7K Visualizações

Determinação das Leis de Velocidade e da Ordem de Reação
General Chemistry
196.1K Visualizações

Uso de Calorimetria de Varredura Diferencial para Medir Mudanças na Entalpia
General Chemistry
44.5K Visualizações

Complexos de Química de Coordenação
General Chemistry
91.5K Visualizações
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos os direitos reservados